|
British Rail Class 21 (NBL)
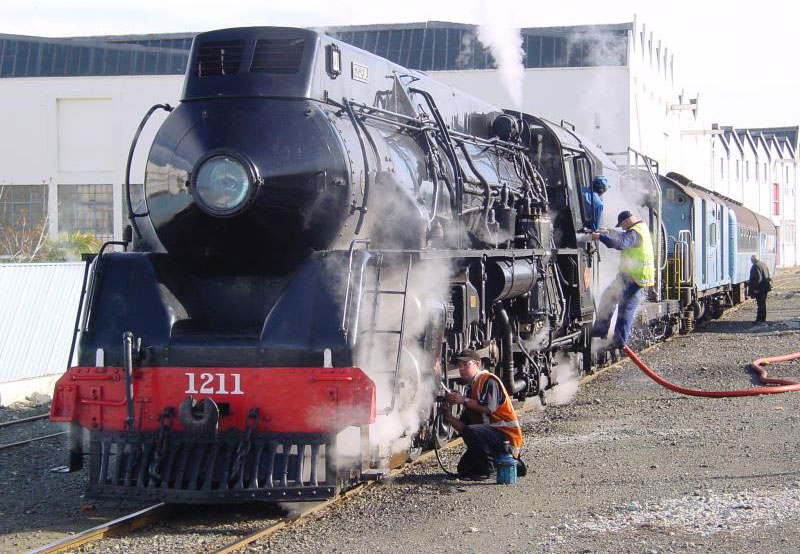
The British Rail Class 21 was a type of Type 2 diesel-electric locomotive built by the North British Locomotive Company in Glasgow for British Rail in 1958–1960. They were numbered D6100-D6157. Thirty-eight of the locomotives were withdrawn by August 1968; the rest were rebuilt with bigger engines to become Class 29, although those locos only lasted until 1971. Description Under the British Railways Modernisation Plan, a batch of ten diesel-electric locomotives were ordered from the North British Locomotive Co. for evaluation under BR's dieselisation pilot scheme. At the same time, six externally similar locomotives with hydraulic transmission were ordered for comparison, these becoming Class 22. Repeat orders resulted in a total of 58 of the diesel-electric locomotives being built (numbered D6100–6157). They were delivered between December 1958 and November 1960. Operation Eastern Region The first 38 locomotives entered service in 1958-59 from the Eastern Region de ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
North British Locomotive Co
The North British Locomotive Company (NBL, NB Loco or North British) was created in 1903 through the merger of three Glasgow locomotive manufacturing companies; Sharp, Stewart and Company (Atlas Works), Neilson, Reid and Company (Hyde Park Works) and Dübs and Company (Queens Park Works), creating the largest locomotive manufacturing company in Europe and the British Empire and the second largest in the world after the Baldwin Locomotive Works in the United States. Its main factories were located at the neighbouring Atlas and Hyde Park Works in central Springburn, as well as the Queens Park Works in Polmadie. A new central Administration and Drawing Office for the combined company was completed across the road from the Hyde Park Works on Flemington Street by James Miller in 1909, later sold to Glasgow Corporation in 1961 to become the main campus of North Glasgow College (now Glasgow Kelvin College). The two other Railway works in Springburn were St. Rollox railway wor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
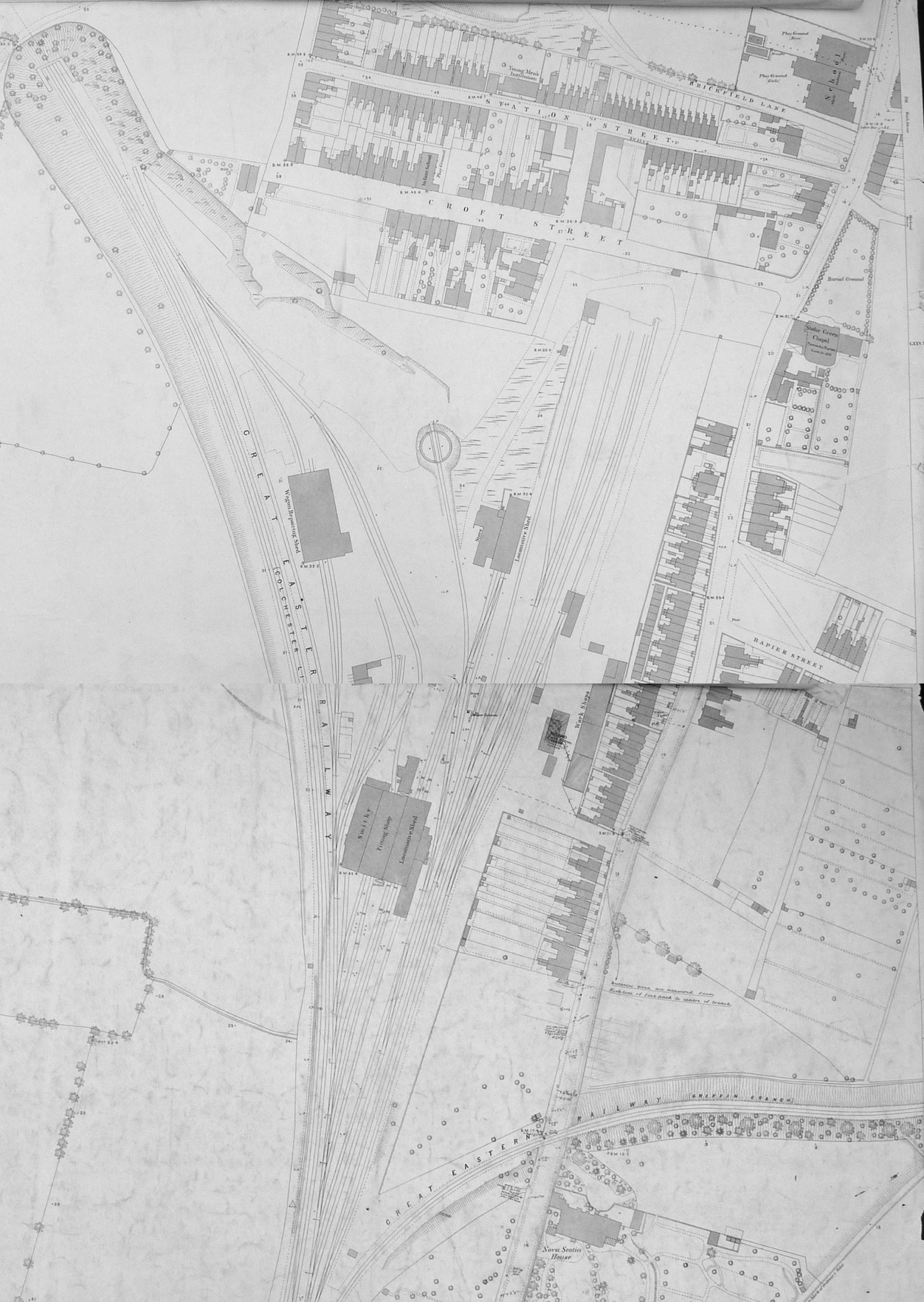
Ipswich Engine Shed
Ipswich engine shed was an Motive power depot, engine shed located in Ipswich, Suffolk on the Great Eastern Main Line. It was located just south of Stoke Tunnel (Ipswich), Stoke tunnel and the current Ipswich railway station. Locomotives accessed the site from Halifax, Ipswich, Halifax Junction which was also the junction for the Griffin Wharf branch of Ipswich docks. The depot opened in 1846 and closed in 1968 although the site remained in railway use for a further thirty years. In British Railways days it was allocated the code 32B. History Opening and early years Locomotive activity started on the depot site with the opening of the Ipswich Stoke Hill railway station, original Ipswich station located at Croft Street and (presumably the newly named) Station St in June 1846 by the Eastern Union Railway. Locomotives belonging to sister company the Ipswich and Bury Railway would also have used the facilities when their line opened in November 1846 although the two railway companies ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
MAN B&W Diesel
MAN Diesel SE was a German manufacturer of large-bore diesel engines for marine propulsion systems and power plant applications. In 2010 it was merged with MAN Turbo to form MAN Diesel & Turbo. History In 1980 MAN acquired the Burmeister & Wain Danish shipyard and diesel engine producer. Though engine production at Christianshavn was discontinued in 1987, successful engine programs were rolled out. At Teglholmen in 1988 a spare parts and key components production factory was established, as was an R&D centre at the same site in 1992. Though all Copenhagen operations were consolidated at Teglholmen in 1994 and the last volume production unit at the B&W Shipyard was delivered in 1996, in 2000 MAN B&W Diesel two-stroke diesel engines had over 70% market share, with a substantial number of MC-line engines on order. The electronically controlled line of ME diesel two-stroke engines was added in 2002 with a maximum cylinder bore of 108 cm. MAN B&W Diesel, Denmark, employed appro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
North British Locomotive Works
The North British Locomotive Company (NBL, NB Loco or North British) was created in 1903 through the merger of three Glasgow locomotive manufacturing companies; Sharp, Stewart and Company (Atlas Works), Neilson, Reid and Company (Hyde Park Works) and Dübs and Company (Queens Park Works), creating the largest locomotive manufacturing company in Europe and the British Empire and the second largest in the world after the Baldwin Locomotive Works in the United States. Its main factories were located at the neighbouring Atlas and Hyde Park Works in central Springburn, as well as the Queens Park Works in Polmadie. A new central Administration and Drawing Office for the combined company was completed across the road from the Hyde Park Works on Flemington Street by James Miller in 1909, later sold to Glasgow Corporation in 1961 to become the main campus of North Glasgow College (now Glasgow Kelvin College). The two other Railway works in Springburn were St. Rollox railway works, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Warranty
In law, a warranty is an expressed or implied promise or assurance of some kind. The term's meaning varies across legal subjects. In property law, it refers to a covenant by the grantor of a deed. In insurance law, it refers to a promise by the purchaser of an insurance about the thing or person to be insured. In contract law, a warranty is a contractual assurance given, typically, by a seller to a buyer, for example confirming that the seller is the owner of the property being sold. A warranty is a term of a contract, but not usually a condition of the contract or an innominate term, meaning that it is a term "not going to the root of the contract",Hogg M. (2011). ''Promises and Contract Law: Comparative Perspectives''p. 48 Cambridge University Press. and therefore only entitles the innocent party to damages if it is breached, i.e. if the warranty is not true or the defaulting party does not perform the contract in accordance with the terms of the warranty. A warranty is not ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eastfield TMD
Eastfield TMD was a railway traction maintenance depot situated in Glasgow, Scotland. Eastfield was a steam shed under British Railways with the depot code 65A; the diesel depot was coded as ED under the TOPS scheme from 1973. History In 1987, the allocation of the depot included Classes 20, 26, 27, 37 and 47, and DMU Classes 101 and 104. Meanwhile, Class 08 shunters were also stabled. At that time, the depot had a wheel lathe and two snowploughs. The depot's logo is commonly noted as having been a Scottie dog, however it was more closely reflective of a West Highland White Terrier. The depot was closed in the early 1990s and the buildings demolished. All locomotives were reallocated to other depots. In the early 2000s a new depot was built by First ScotRail, but on a smaller scale to service Classes 158 and 170 Year 170 ( CLXX) was a common year starting on Sunday of the Julian calendar. At the time, it was known as the Year of the Consulship of Clarus and Cor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aberdeen Ferryhill TMD
Aberdeen Ferryhill TMD was a railway traction maintenance depot in Aberdeen, Scotland. The depot was approximately south of Aberdeen railway station Aberdeen railway station is the main railway station in Aberdeen, Scotland. It is the busiest railway station in Scotland north of the major cities of Edinburgh and Glasgow. It is located on Guild Street in the city centre, next to Union Squa .... The depot code originally assigned by British Railways was 61B, but it was given the code AB latterly. Ferryhill Depot closed on 6th December 1987. The adjacent turntable and associated former engine shed form part of the Ferryhill Railway Heritage Centre now preserving the site's heritage. History In 1987 the depot had an allocation of Class 08 shunters. The depot also had two snowploughs. Other locomotives usually stabled at the depot included Classes 26, 27, 37 and 47. References Sources * * Railway depots in Scotland {{Scotland-rail-transport-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ian Allan Publishing
Ian Allan Publishing was an English publisher, established in 1942, which specialised in transport books. It was founded by Ian Allan. In 1942, Ian Allan, then working in the public relations department for the Southern Railway at Waterloo station, decided he could deal with many of the requests he received about rolling stock by collecting the information into a book. The result was his first book, ''ABC of Southern Locomotives''. This proved to be a success, contributing to the emergence of trainspotting as a popular hobby in the UK, and leading to the formation of the company.Ian Allan…the man who launched a million locospotters '' The Railway Magazine'' issue 1174 February 1999 pages 20-27 The company grew from a small producer of books for train enthusiasts and spotters to a large transport publisher. Each year it published books covering subjects such as military and civil aviation, naval and maritime topics, buses, trams, trolleybuses and steam railways, includi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Scottish Region Of British Railways
The Scottish Region (ScR) was one of the six regions created on British Railways (BR) and consisted of ex-London, Midland and Scottish Railway (LMS) and ex-London and North Eastern Railway (LNER) lines in Scotland. It existed from the creation of BR in 1948, and was renamed to ScotRail (British Rail), ScotRail in the mid-1980s (see separate entity for details). History World War II had seriously disrupted Scotland's railways due to the LMS and LNER rolling stock in Scotland being transferred to the major cities in Northern England in order to replace what had been destroyed by Germany, German air-raids. At the time, the Government believed that only state intervention could provide the necessary re-supplying of rolling stock and save several unprofitable routes from closure. Following the election of the Labour Party (UK), Labour government in 1945, the railways were nationalised on 1 January 1948 under the terms of the Transport Act 1947. Through the creation of the Scottish ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
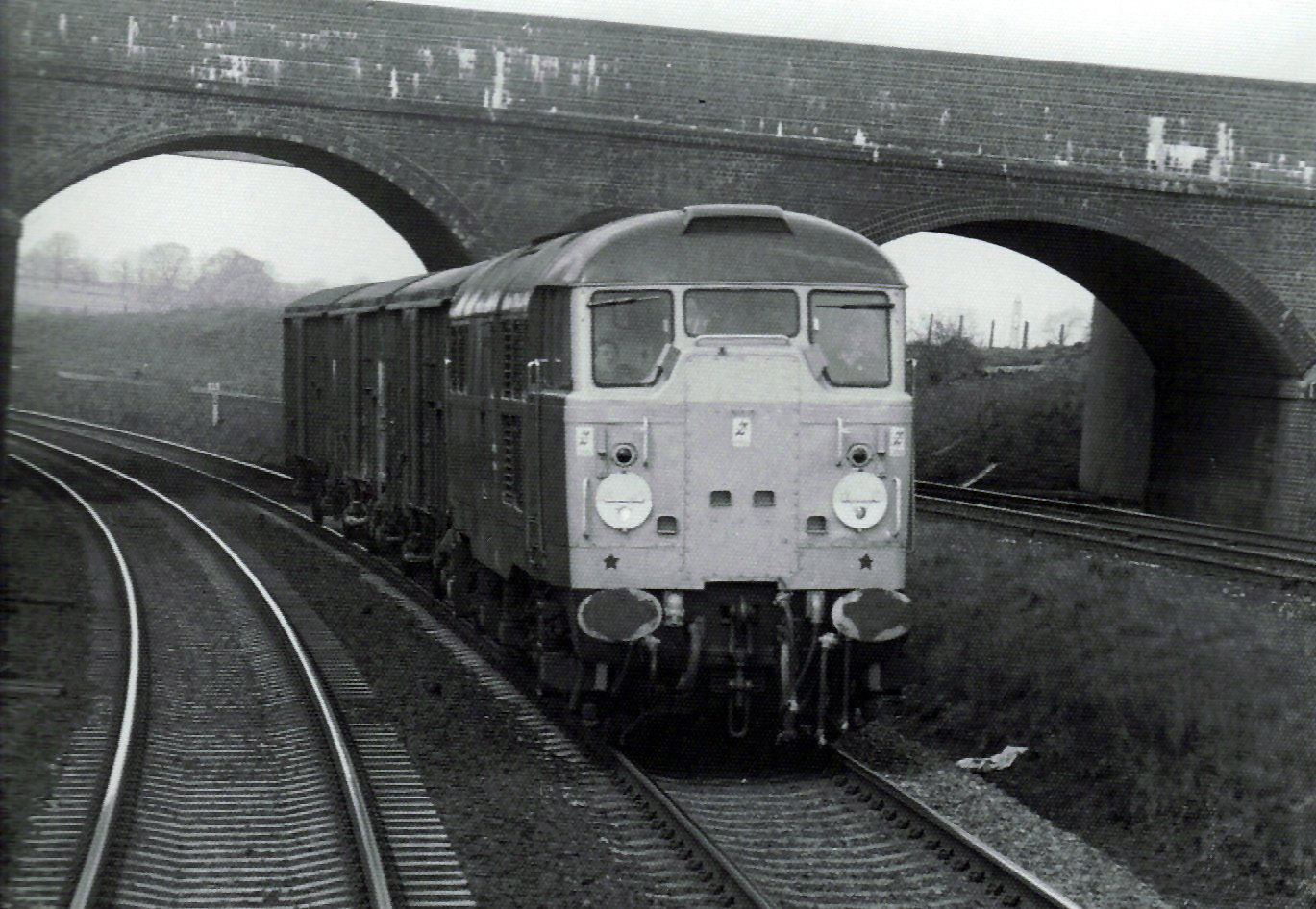
British Rail Class 31
The British Rail Class 31 diesel locomotives, also known as the Brush Type 2 and previously as Class 30, were built by Brush Traction from 1957 to 1962. They were numbered in two series, D5500-D5699 and D5800-D5862. Construction of the first locomotive was completed in the final week of September 1957, and the handing-over took place on 31 October. The first Class 31 entered service in November 1957, after the launch of the British Rail Class 20, Class 20 locomotive and was one of the Pilot Scheme locomotives ordered by British Railways to replace steam traction. Engines They were originally built with Mirrlees Blackstone, Mirrlees JVS12T (D5500–D5519) and engines and Brush electrical equipment, but the engines were not successful and in 1964 D5677 was fitted with an English Electric 12SVT engine (similar to the 12CSVT used in the British Rail Class 37, Class 37 but without an intercooler) rated at . The trial proved successful, and between 1965 and 1969 the entire class was ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
British Rail Class 26
The British Rail Class 26 diesel locomotives, also known as the BRCW Type 2, were built by the Birmingham Railway Carriage and Wagon Company (BRCW) at Smethwick in 1958–59. Forty seven examples were built and the last were withdrawn from service in 1994. Like their higher-powered sisters, the BRCW Classes British Rail Class 27, 27 and British Rail Class 33, 33, they had all-steel bodies and cab ends with fibreglass cab roofs. They were numbered D5300-D5346. Origins The History of rail transport in Great Britain 1948–1994#The Modernisation Plan, British Rail Modernisation Plan contained a large requirement for small diesel locomotives in the - range and under BR's 'Pilot Scheme', small batches of locomotives were ordered from numerous different manufacturers for evaluation. BRCW obtained an order for 20 Mixed-traffic locomotive, mixed traffic diesel-electric locomotives powered by Sulzer 6LDA28 engines. The Birmingham Railway Carriage and Wagon Company (BRCW) was a ro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |