Ipswich Engine Shed on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
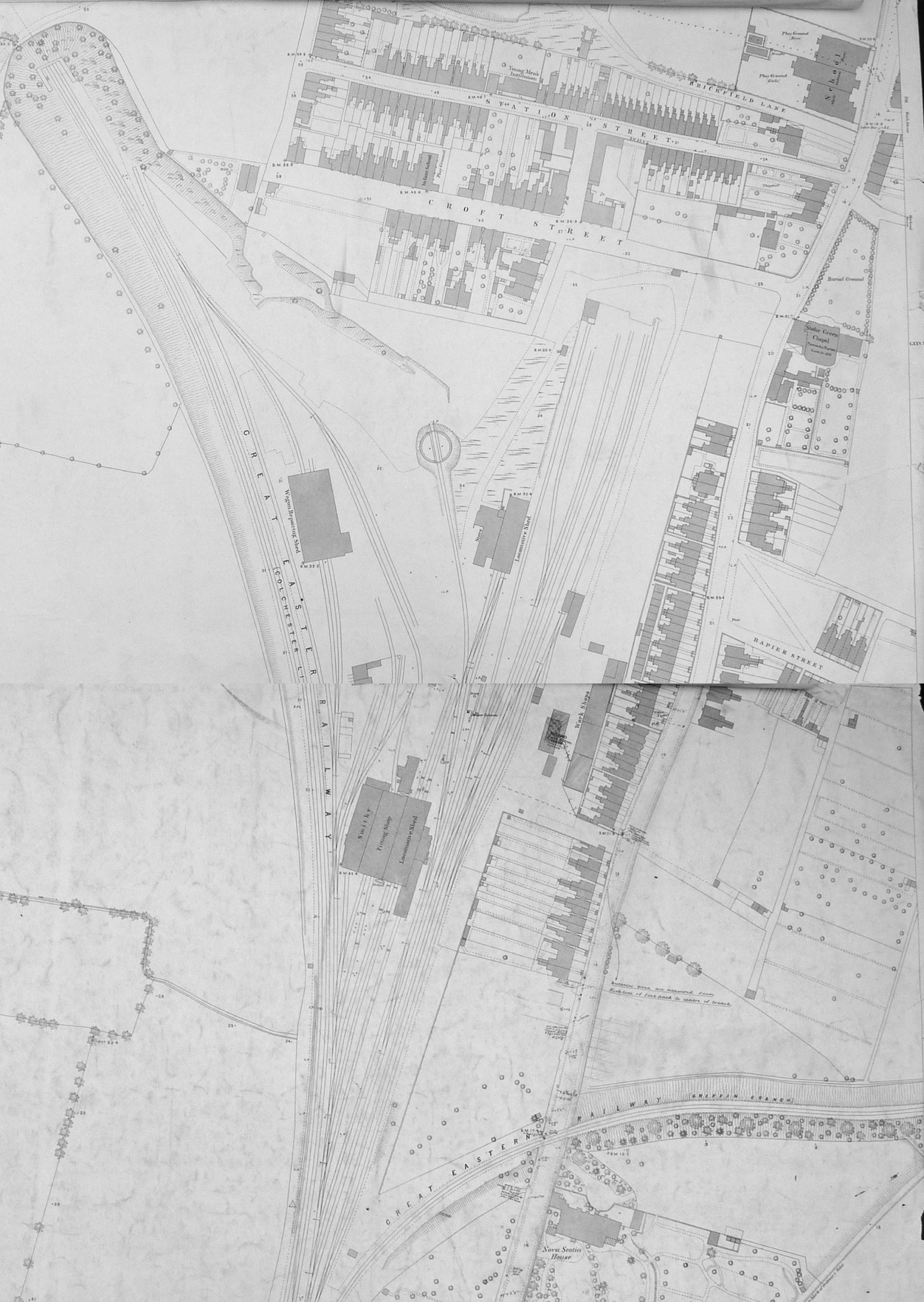 Ipswich engine shed was an engine shed located in
Ipswich engine shed was an engine shed located in
 Ipswich engine shed was an engine shed located in
Ipswich engine shed was an engine shed located in Ipswich
Ipswich () is a port town and borough in Suffolk, England, of which it is the county town. The town is located in East Anglia about away from the mouth of the River Orwell and the North Sea. Ipswich is both on the Great Eastern Main Line r ...
, Suffolk
Suffolk () is a ceremonial county of England in East Anglia. It borders Norfolk to the north, Cambridgeshire to the west and Essex to the south; the North Sea lies to the east. The county town is Ipswich; other important towns include L ...
on the Great Eastern Main Line
The Great Eastern Main Line (GEML, sometimes referred to as the East Anglia Main Line) is a major railway line on the British railway system which connects Liverpool Street station in central London with destinations in east London and th ...
. It was located just south of Stoke tunnel and the current Ipswich railway station. Locomotives accessed the site from Halifax Junction which was also the junction for the Griffin Wharf branch of Ipswich docks. The depot opened in 1846 and closed in 1968 although the site remained in railway use for a further thirty years.
In British Railways days it was allocated the code 32B.
History
Opening and early years
Locomotive activity started on the depot site with the opening of the original Ipswich station located at Croft Street and (presumably the newly named) Station St in June 1846 by the Eastern Union Railway. Locomotives belonging to sister company the Ipswich and Bury Railway would also have used the facilities when their line opened in November 1846 although the two railway companies were worked as one from January the following year. In June 1851 the EUR had 31 locomotives breaking down thus: All locomotives carried a green livery. In 1854 the EUR was taken over by theEastern Counties Railway
The Eastern Counties Railway (ECR) was an English railway company incorporated in 1836 intended to link London with Ipswich via Colchester, and then extend to Norwich and Yarmouth.
Construction began in 1837 on the first nine miles at the Lond ...
and in 1860 the new Ipswich railway station opened after the tunnel was completed.Jill Freestone and Richard W Smith "Ipswich Engines and Ipswich Men" (1998) It was at this time a carriage and wagon works was established on the site of the old station.
The initial engine shed was a two road shed with associated sidings and a small (befitting the size of engine of the time) turntable. The history of the shed for the next 90 or so years was a case of poor facilities being provided for what was a busy engine shed, and head of a significantly sized organisational district including major sub-sheds at Colchester and Parkeston as well as a host of smaller sheds.
The site was always cramped and poorly equipped with every day servicing of engines taking place in the open.
Great Eastern
TheGreat Eastern Railway
The Great Eastern Railway (GER) was a pre-grouping British railway company, whose main line linked London Liverpool Street to Norwich and which had other lines through East Anglia. The company was grouped into the London and North Eastern R ...
was formed in 1862 by the amalgamation of several East Anglian Railways.
In August 1878 there was a fire in the four road engine shed which resulted in a number of workmen losing their tools. The company replaced these with a grant and the shed was repaired.
At the end of 1922 the shed at Ipswich had an allocation of 131 locomotives being the third biggest shed on the Great Eastern behind Stratford (555) and Cambridge (178) sheds. The allocation consisted of:
London North Eastern years
TheLondon and North Eastern Railway
The London and North Eastern Railway (LNER) was the second largest (after LMS) of the "Big Four" railway companies created by the Railways Act 1921 in Britain. It operated from 1 January 1923 until nationalisation on 1 January 1948. At tha ...
came into existence in 1923.
Whilst Great Eastern types provided the majority of the types allocated to Ipswich shed, newer LNE types and engines from other LNER constituent companies were allocated.
* B1 4-6-0
* B17 4-6-0
* C12 4-4-2T Ivatt Great Northern locomotive some of which were used on Felixstowe Branch LineH.I. Quayle & G.T. Bradbury ''The Felixstowe Railway'' The Oakwood Press (1977)
* C14 4-4-2T Robinson/GC - From 1936. Three of which allocated to Felixstowe shed the other two to Ipswich. Included 6123, 6128 & 6130
* L1 2-6-4T
* N5 0-6-2T Parker/M,S & L - 5913 allocated to Ipswich in 1938
* N7 0-6-2T
During the Second World War a US Army Class S160 ( USATC S160 Class) 2-8-0 was allocated to the shed for a few weeks in 1943. Most of the class were allocated to Stratford and March and other members of the class visited Ipswich during this time.
BR years
In the early years ofBritish Rail
British Railways (BR), which from 1965 traded as British Rail, was a state-owned company that operated most of the overground rail transport in Great Britain from 1948 to 1997. It was formed from the nationalisation of the Big Four (British ra ...
, Ipswich shed was host to visiting Southern Railway Battle of Britain class 4-6-2 locomotives before the introduction of the Britannia class in the early 1950s.
Working conditions in the shed were extremely poor and the Shed Foreman later wrote "The conditions in which the boiler washers and tube cleaners worked in winter beggared description with boilers being emptied and blown down, others being washed out and steam and water everywhere" This state of affairs led to the preparation of plans to modernize the depot.
The shed was completely rebuilt in 1954 into a concrete 6 track straight through road shed. In 1955 the locomotive allocation totalling 79 locomotives was as follows:
The 0-6-0T engines were generally used for shunting and local trip work. J15, J39 and J17 were freight locomotives. All other locomotives were primarily passenger but it was not unknown for some of them to work freight trains as well. The Ivatt designed 2MT 2-6-2T no 41200 was allocated to the shed for tests on local branches including the Aldeburgh Branch Line. Later that year the first Diesel Multiple Unit
A diesel multiple unit or DMU is a multiple-unit train powered by on-board diesel engines. A DMU requires no separate locomotive, as the engines are incorporated into one or more of the carriages. Diesel-powered single-unit railcars are als ...
s worked in the area and no other members of this class were allocated.
In 1959 Ipswich received its first allocation of mainline diesels.
On 11 June 1959 class J19 0-6-0 locomotive number 64641 was the last steam locomotive to be repaired at the depot.
On 5 March 1960 the last steam working from Ipswich shed was headed by J15 0-6-0 no 65389 which worked the last freight train to Snape.
However a pair of B1 4-6-0s (61059 numbered departmental 17 and 61252 numbered 22) were retained as a carriage heating units. No. 17 operated between 1964 and succeeding No. 22 which had undertaken the role since December 1963.
In November 1963 Class 15 No. 8221 crashed through the buffer stops and into Croft Street.
The following diesel classes were allocated to Ipswich engine shed.
* British Rail Class D1/1
British Rail Class D1/1 (formerly DY1) was a class of shunting locomotives commissioned by British Rail in England. It was a diesel locomotive in the pre-TOPS period built by the Hunslet Engine Company with a Gardner 6L3 engine.
History
The ...
* British Rail Class 03
* British Rail Class 04
* British Rail Class 05
* British Rail Class 15
* British Rail Class 21
* British Rail Class 24
* British Rail Class 31
* British Rail Class 37
The British Rail Class 37 is a diesel-electric locomotive. Also known as the English Electric Type 3, the class was ordered as part of the British Rail modernisation plan. They were numbered in two series, D6600–D6608 and D6700–D6999.
...
* British Rail Class 40
The British Rail Class 40 is a type of British railway diesel electric locomotive. A total of 200 were built by English Electric between 1958 and 1962. They were numbered D200-D399. They were, for a time, the pride of British Rail's early d ...
* British Rail Class 47
In 1963 the diesel allocation at Ipswich consisted of 55 locomotives which broke down thus:
The Class 03, 04, 05 and DY1/1 locomotives were all shunting engines. The Class 15 engines were generally employed on local freight workings whilst Class 24 and Class 31s were employed on mixed traffic (i.e. both freight and passenger workings).
Closure
The depot was closed on 6 May 1968 with fuelling facilities for locomotives being provided at Ipswich railway station. The last diesel locomotive - a Class 15 - underwent maintenance at the depot on 5 May 1968. Maintenance of the remaining shunter fleet was undertaken at Colchester. The depot remained empty for about a week before a number of engineers maintenance trains were stabled there. A number of withdrawn British Rail Class 15 locomotives were stored on site during the 1970s. During the early 1980s the site was used as the electrification depot for the extension of the overhead wiring from Colchester to Harwich. Ipswich (May 1985) and Norwich. The site was used for the celebration of 150 years of the Eastern Union Railway in 1996. After closure of the depot the Carriage and Wagon Works continued for many years closing in 1994. The site was used to store some locomotives between 2000 and 2001 before demolition c 2003. Wagon repairs were carried out in Ipswich Lower Yard after this date. Class 37 locomotive 37379 was named 'Ipswich WRD, Quality Approved' in recognition of the work the depot undertook. The site today is occupied by a housing estate.Operations
During BR days Ipswich shed was in the Norwich division and was allocated the code 32B. It had a number of sub-sheds including Felixstowe, Framlingham, Aldeburgh and Laxfield.Staffing
After signing on and before signing off engine crew would often have to walk to or from Ipswich station before commencing duty or finishing their duties. This must have meant some shifts must have not been very productive in terms of time worked. In the 1950s shed staff numbered 440-450 although by 1959 this had reduced to just under 200. Details and stories of Ipswich enginemen can be found in the 1998 book "Ipswich Engines and Ipswich Men" published by the local Over Stoke History Group.Routes worked
The following routes were worked by Ipswich men. These may have varied from year to year and are not specific to any one era.Main Lines
* London to Norwich on theGreat Eastern Main Line
The Great Eastern Main Line (GEML, sometimes referred to as the East Anglia Main Line) is a major railway line on the British railway system which connects Liverpool Street station in central London with destinations in east London and th ...
* London to Great Yarmouth and Lowestoft on the East Suffolk Line
* Mayflower Line to Harwich
* Ipswich to Ely Line to Cambridge
* Ipswich - Doncaster (Parkeston boat train which started running in 1885 to Doncaster and in 1892 to York).
* Ipswich - Manchester (later route of Parkeston Boat train named North Country Continental
North is one of the four compass points or cardinal directions. It is the opposite of south and is perpendicular to east and west. ''North'' is a noun, adjective, or adverb indicating direction or geography.
Etymology
The word ''no ...
)
In 1929 the Manchester working was one of the most prestigious workings starting at 06:30 on a Monday morning. The train departed at 08:30 calling at Bury St Edmunds, Ely, March (where two carriages for Birmingham were detached), Spalding, Sleaford (water stop), Lincoln (where carriages for York were detached), Worksop, Sheffield Victoria to Wooley Bridge (where Manchester drivers took over). The Ipswich drivers overnighted at the dormitory at Gorton then after working a local train returned to Ipswich later that day. This train was worked by a LNER B17 4-6-0 locomotive.
Branch Lines
* Felixstowe Branch Line * Aldeburgh Branch Line *Hadleigh Railway
The Hadleigh Railway was a long single track branch railway line in Suffolk, England, that connected Hadleigh to the main line railway network at Bentley Junction. It was built by the nominally independent Eastern Union and Hadleigh Junction Rai ...
* Mid-Suffolk Light Railway
* Framlingham Branch
* Eye Branch
* Snape Branch Line
Shunt turns
A shunt turn is where a shunting locomotive is allocated to shunting a yard or set of sidings. Some shunt turns required 'trip' working between yards or sidings.1943
* Ipswich Upper Yard (2 turns) * Ipswich Lower Yard * Ipswich Grffin Wharf/Upper Yard * Ipswich Docks (4 turns) - all allocated to tram engines (J70 class) * Stowmarket1968 (shortly after closure)
* Ipswich Upper Yard (2 turns) * Ipswich Lower Yard * Ipswich Cliff Quay (Docks) * Ipswich Wagon Shops (former depot) * StowmarketEngineering Facilities
The shed was capable of carrying out repairs to steam locomotives and the following facilities were located on site. * Tube shop * Smith shop (containing 8 forges and a steam hammer) - forgings produced/repaired, motions straightened, springs forged * Coppersmith shop (also white metal work carried out in here) * Lathe shopIncidents
Ipswich men John Barnard (driver) and William Macdonald (fireman) were killed in the 'Westerfield Junction boiler explosion' on 25 September 1900. Further information on that accident can be found on the Westerfield railway station page. John Barnard's son William Barnard (driver) and Stanley Keeble (fireman) were killed in a collision at Colchester in 1913. On 1 January 1927 there was a train crash at Woodbridge station. A wagon coupling had broken at Bealings station and when the engine stopped at Woodbridge, the rear portion running downhill smashed into the back of the stationary train. Only one minor injury was recorded. Fireman L Rayner of Ipswich was recorded as being knocked off his feet - the driver's name is unknown, but it is almost certain he came from Ipswich as well. The Ipswich-based driver of B1 4-6-0 61057 locomotive was involved in a rear-end collision in foggy conditions in Witham on 7 March 1950. The driver was seriously injured and the fireman W 'spot' Haggar was killed. Class 15 locomotive D8221 overran the buffer stops and ended up in Croft Street in 1963. It was rescued by one of Ipswich's B1 departmental steam locomotives No. 22.Great Eastern Railway Society Journal No 82 page 29 The Ipswich Breakdown Train by Percy Wilby(April 1995)See also
*Ipswich TMD
Ipswich TMD is a traction maintenance depot located in Ipswich, Suffolk, England. The depot is situated on the Great Eastern Main Line and is near Ipswich station
Ipswich railway station is on the Great Eastern Main Line in the East of En ...
References
{{coord, 52.0451, N, 1.1524, E, display=title, region:GB_type:landmark Transport in Ipswich Railway depots in England Great Eastern Railway London and North Eastern Railway Rail transport in Suffolk