|
Batch Queue
In system software, a job queue ( batch queue, input queue), is a data structure maintained by job scheduler software containing jobs to run. Users submit their programs that they want executed, "jobs", to the queue for batch processing. The scheduler software maintains the queue as the pool of jobs available for it to run. Multiple batch queues might be used by the scheduler to differentiate types of jobs depending on parameters such as: * job priority * estimated Run time (program lifecycle phase), execution time * resource requirements The use of a batch queue gives these benefits: * sharing of computer resources among many users * time-shifts job processing to when the computer is less busy * avoids idling the compute resources without minute-by-minute human supervision * allows around-the-clock high utilization of expensive computing resources Any process that comes to the CPU should wait in a queue. See also *Command pattern *Command queue *Job scheduler *Priority ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
|
System Software
System software is software designed to provide a platform for other software. An example of system software is an operating system (OS) (like macOS, Linux, Android, and Microsoft Windows). Application software is software that allows users to do user-oriented tasks such as creating text documents, playing or developing games, creating presentations, listening to music, drawing pictures, or browsing the web. Examples of such software are computational science software, game engines, search engines, industrial automation, and software as a service applications. In the late 1940s, application software was custom-written by computer users to fit their specific hardware and requirements. System software was usually supplied by the manufacturer of the computer hardware and was intended to be used by most or all users of that system. Many operating systems come pre-packaged with basic application software. Such software is not considered system software when it can be uninstalled with ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
|
Job Scheduler
A job scheduler is a computer application for controlling unattended background program execution of jobs. This is commonly called batch scheduling, as execution of non-interactive jobs is often called batch processing, though traditional ''job'' and ''batch'' are distinguished and contrasted; see that page for details. Other synonyms include batch system, distributed resource management system (DRMS), distributed resource manager (DRM), and, commonly today, workload automation (WLA). The data structure of jobs to run is known as the job queue. Modern job schedulers typically provide a graphical user interface and a single point of control for definition and monitoring of background executions in a distributed network of computers. Increasingly, job schedulers are required to orchestrate the integration of real-time business activities with traditional background IT processing across different operating system platforms and business application environments. ''Job scheduling'' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
 |
Batch Processing
Computerized batch processing is a method of running software programs called jobs in batches automatically. While users are required to submit the jobs, no other interaction by the user is required to process the batch. Batches may automatically be run at scheduled times as well as being run contingent on the availability of computer resources. History The term "batch processing" originates in the traditional classification of methods of production as job production (one-off production), batch production (production of a "batch" of multiple items at once, one stage at a time), and flow production (mass production, all stages in process at once). Early history Early computers were capable of running only one program at a time. Each user had sole control of the machine for a scheduled period of time. They would arrive at the computer with program and data, often on punched paper cards and magnetic or paper tape, and would load their program, run and debug it, and carry off thei ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
 |
Run Time (program Lifecycle Phase)
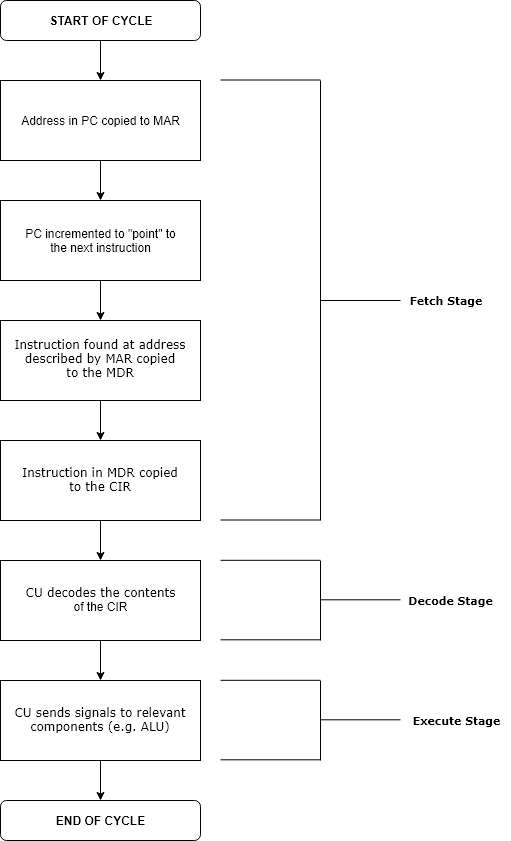
Execution in computer and software engineering is the process by which a computer or virtual machine interprets and acts on the instructions of a computer program. Each instruction of a program is a description of a particular action which must be carried out, in order for a specific problem to be solved. Execution involves repeatedly following a " fetch–decode–execute" cycle for each instruction done by the control unit. As the executing machine follows the instructions, specific effects are produced in accordance with the semantics of those instructions. Programs for a computer may be executed in a batch process without human interaction or a user may type commands in an interactive session of an interpreter. In this case, the "commands" are simply program instructions, whose execution is chained together. The term run is used almost synonymously. A related meaning of both "to run" and "to execute" refers to the specific action of a user starting (or ''launching'' o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
Command Pattern
In object-oriented programming, the command pattern is a Behavioral pattern, behavioral Design pattern (computer science), design pattern in which an object is used to Information hiding, encapsulate all information needed to perform an action or trigger an event at a later time. This information includes the method name, the object that owns the method and values for the method parameters. Four terms always associated with the command pattern are ''command'', ''receiver'', ''invoker'' and ''client''. A ''command'' object knows about ''receiver'' and invokes a method of the receiver. Values for parameters of the receiver method are stored in the command. The receiver object to execute these methods is also stored in the command object by Object composition#Aggregation, aggregation. The ''receiver'' then does the work when the execute() method in ''command'' is called. An ''invoker'' object knows how to execute a command, and optionally does bookkeeping about the command execution. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
|
Command Queue
In computer science, a command queue is a queue that determines when a command is executed, usually by order of priority or on a first-in first-out basis. Instead of waiting for each command to be executed before sending the next one, a program will put all its commands in the command queue, freeing it to perform other functions while the queue is processed by the operating system. This delegation not only frees the program from handling the queue but can also help optimize execution. For instance, when handling multiple requests from several users, a network server's hard drive can reorder the requests in its queue using the elevator algorithm, which minimizes mechanical movement. Examples * Native Command Queuing (NCQ) in Serial ATA (SATA) * Tagged Command Queuing (TCQ) in Parallel ATA and SCSI See also *Batch processing *Burst mode (computing) *Command pattern *Job queue *Job scheduler A job scheduler is a computer application for controlling unattended background prog ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
|
Job Scheduler
A job scheduler is a computer application for controlling unattended background program execution of jobs. This is commonly called batch scheduling, as execution of non-interactive jobs is often called batch processing, though traditional ''job'' and ''batch'' are distinguished and contrasted; see that page for details. Other synonyms include batch system, distributed resource management system (DRMS), distributed resource manager (DRM), and, commonly today, workload automation (WLA). The data structure of jobs to run is known as the job queue. Modern job schedulers typically provide a graphical user interface and a single point of control for definition and monitoring of background executions in a distributed network of computers. Increasingly, job schedulers are required to orchestrate the integration of real-time business activities with traditional background IT processing across different operating system platforms and business application environments. ''Job scheduling'' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
|
Priority Queue
In computer science, a priority queue is an abstract data type similar to a regular queue (abstract data type), queue or stack (abstract data type), stack abstract data type. In a priority queue, each element has an associated ''priority'', which determines its order of service. Priority queue serves highest priority items first. Priority values have to be instances of an ordered data type, and higher priority can be given either to the lesser or to the greater values with respect to the given order relation. For example, in Java (programming language), Java standard library, ''PriorityQueues the least elements with respect to the order have the highest priority. This implementation detail is without much practical significance, since passing to the converse relation, opposite order relation turns the least values into the greatest, and vice versa. While priority queues are often implemented using Heap (data structure) , heaps, they are conceptually distinct. A priority queue can ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
|
Task Queue
In computing, scheduling is the action of assigning resources to perform tasks. The resources may be processors, network links or expansion cards. The tasks may be threads, processes or data flows. The scheduling activity is carried out by a mechanism called a scheduler. Schedulers are often designed so as to keep all computer resources busy (as in load balancing), allow multiple users to share system resources effectively, or to achieve a target quality-of-service. Scheduling is fundamental to computation itself, and an intrinsic part of the execution model of a computer system; the concept of scheduling makes it possible to have computer multitasking with a single central processing unit (CPU). Goals A scheduler may aim at one or more goals, for example: * maximizing ''throughput'' (the total amount of work completed per time unit); * minimizing ''wait time'' (time from work becoming ready until the first point it begins execution); * minimizing '' latency'' or '' re ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |