Command pattern on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
In
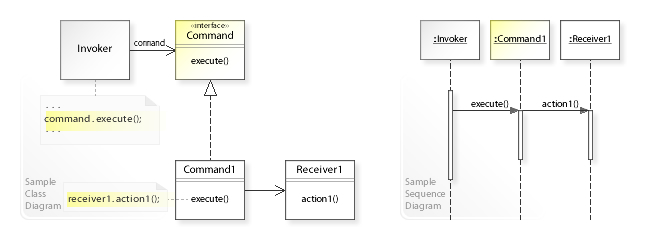 In the above
In the above

Windows Presentation Foundation
(WPF), introduces routed commands, which combine the command pattern with event processing. As a result, the command object no longer contains a reference to the target object nor a reference to the application code. Instead, invoking the command object's ''execute'' command results in a so-called ''Executed Routed Event'' that during the event's tunneling or bubbling may encounter a so-called ''binding'' object that identifies the target and the application code, which is executed at that point.
using System;
namespace CommandPattern;
public interface ICommand
/* The Invoker class */
public class Switch
/* An interface that defines actions that the receiver can perform */
public interface ISwitchable
/* The Receiver class */
public class Light : ISwitchable
/* The Command for turning off the device - ConcreteCommand #1 */
public class CloseSwitchCommand : ICommand
/* The Command for turning on the device - ConcreteCommand #2 */
public class OpenSwitchCommand : ICommand
/* The test class or client */
internal class Program
Command Pattern
{{DEFAULTSORT:Command Pattern Software design patterns Articles with example C Sharp code Articles with example Java code Articles with example JavaScript code Articles with example Python (programming language) code Articles with example Ruby code Articles with example Scala code
object-oriented programming
Object-oriented programming (OOP) is a programming paradigm based on the concept of " objects", which can contain data and code. The data is in the form of fields (often known as attributes or ''properties''), and the code is in the form of ...
, the command pattern is a behavioral
Behavior (American English) or behaviour (British English) is the range of actions and mannerisms made by individuals, organisms, systems or artificial entities in some environment. These systems can include other systems or organisms as we ...
design pattern
A design pattern is the re-usable form of a solution to a design problem. The idea was introduced by the architect Christopher Alexander and has been adapted for various other disciplines, particularly software engineering. The " Gang of Four" b ...
in which an object is used to encapsulate all information needed to perform an action or trigger an event at a later time. This information includes the method name, the object that owns the method and values for the method parameters.
Four terms always associated with the command pattern are ''command'', ''receiver'', ''invoker'' and ''client''. A ''command'' object knows about ''receiver'' and invokes a method of the receiver. Values for parameters of the receiver method are stored in the command. The receiver object to execute these methods is also stored in the command object by aggregation
Aggregation may refer to:
Business and economics
* Aggregation problem (economics)
* Purchasing aggregation, the joining of multiple purchasers in a group purchasing organization to increase their buying power
* Community Choice Aggregation, the ...
. The ''receiver'' then does the work when the execute() method in ''command'' is called. An ''invoker'' object knows how to execute a command, and optionally does bookkeeping about the command execution. The invoker does not know anything about a concrete command, it knows only about the command ''interface''. Invoker object(s), command objects and receiver objects are held by a ''client'' object, the ''client'' decides which receiver objects it assigns to the command objects, and which commands it assigns to the invoker. The client decides which commands to execute at which points. To execute a command, it passes the command object to the invoker object.
Using command objects makes it easier to construct general components that need to delegate, sequence or execute method calls at a time of their choosing without the need to know the class of the method or the method parameters. Using an invoker object allows bookkeeping about command executions to be conveniently performed, as well as implementing different modes for commands, which are managed by the invoker object, without the need for the client to be aware of the existence of bookkeeping or modes.
The central ideas of this design pattern closely mirror the semantics of first-class function
In computer science, a programming language is said to have first-class functions if it treats functions as first-class citizens. This means the language supports passing functions as arguments to other functions, returning them as the values from ...
s and higher-order function
In mathematics and computer science, a higher-order function (HOF) is a function that does at least one of the following:
* takes one or more functions as arguments (i.e. a procedural parameter, which is a parameter of a procedure that is itse ...
s in functional programming language
In computer science, functional programming is a programming paradigm where programs are constructed by applying and composing functions. It is a declarative programming paradigm in which function definitions are trees of expressions that ...
s. Specifically, the invoker object is a higher-order function of which the command object is a first-class argument.
Overview
The command design pattern is one of the twenty-three well-known '' GoF design patterns'' that describe how to solve recurring design problems to design flexible and reusable object-oriented software, that is, objects that are easier to implement, change, test, and reuse. Using the command design pattern can solve these problems: * Coupling the invoker of a request to a particular request should be avoided. That is, hard-wired requests should be avoided. * It should be possible to configure an object (that invokes a request) with a request. Implementing (hard-wiring) a request directly into a class is inflexible because it couples the class to a particular request at compile-time, which makes it impossible to specify a request at run-time. Using the command design pattern describes the following solution: * Define separate (command) objects that encapsulate a request. * A class delegates a request to a command object instead of implementing a particular request directly. This enables one to configure a class with a command object that is used to perform a request. The class is no longer coupled to a particular request and has no knowledge (is independent) of how the request is carried out. See also the UML class and sequence diagram below.Structure
UML class and sequence diagram
 In the above
In the above UML
The Unified Modeling Language (UML) is a general-purpose, developmental modeling language in the field of software engineering that is intended to provide a standard way to visualize the design of a system.
The creation of UML was originally ...
class diagram
In software engineering, a class diagram in the Unified Modeling Language (UML) is a type of static structure diagram that describes the structure of a system by showing the system's classes, their attributes, operations (or methods), and the r ...
, the Invoker class doesn't implement a request directly.
Instead, Invoker refers to the Command interface to perform a request (command.execute()), which makes the Invoker independent of how the request is performed.
The Command1 class implements the Command interface by performing an action on a receiver (receiver1.action1()).
The UML
The Unified Modeling Language (UML) is a general-purpose, developmental modeling language in the field of software engineering that is intended to provide a standard way to visualize the design of a system.
The creation of UML was originally ...
sequence diagram
shows the run-time interactions: The Invoker object calls execute() on a Command1 object.
Command1 calls action1() on a Receiver1 object,
which performs the request.
UML class diagram
Uses
; GUI buttons and menu items : InSwing
Swing or swinging may refer to:
Apparatus
* Swing (seat), a hanging seat that swings back and forth
* Pendulum, an object that swings
* Russian swing, a swing-like circus apparatus
* Sex swing, a type of harness for sexual intercourse
* Swing rid ...
and Borland Delphi programming, an is a command object. In addition to the ability to perform the desired command, an may have an associated icon, keyboard shortcut, tooltip text, and so on. A toolbar button or menu item component may be completely initialized using only the object.
; Macro
Macro (or MACRO) may refer to:
Science and technology
* Macroscopic, subjects visible to the eye
* Macro photography, a type of close-up photography
* Image macro, a picture with text superimposed
* Monopole, Astrophysics and Cosmic Ray Observat ...
recording : If all user actions are represented by command objects, a program can record a sequence of actions simply by keeping a list of the command objects as they are executed. It can then "play back" the same actions by executing the same command objects again in sequence. If the program embeds a scripting engine, each command object can implement a method, and user actions can then be easily recorded as scripts.
; Mobile code: Using languages such as Java where code can be streamed/slurped from one location to another via URLClassloaders and Codebases the commands can enable new behavior to be delivered to remote locations (EJB Command, Master Worker).
; Multi-level undo
Undo is an interaction technique which is implemented in many computer programs. It erases the last change done to the document, reverting it to an older state. In some more advanced programs, such as graphic processing, undo will negate the las ...
: If all user actions in a program are implemented as command objects, the program can keep a stack of the most recently executed commands. When the user wants to undo a command, the program simply pops the most recent command object and executes its method.
; Networking : It is possible to send whole command objects across the network to be executed on the other machines, for example player actions in computer games.
; Parallel processing: Where the commands are written as tasks to a shared resource and executed by many threads in parallel (possibly on remote machines; this variant is often referred to as the Master/Worker pattern)
; Progress bars : Suppose a program has a sequence of commands that it executes in order. If each command object has a method, the program can easily estimate the total duration. It can show a progress bar that meaningfully reflects how close the program is to completing all the tasks.
; Thread pool
In computer programming, a thread pool is a software design pattern for achieving concurrency of execution in a computer program. Often also called a replicated workers or worker-crew model, a thread pool maintains multiple threads waiting for ...
s : A typical, general-purpose thread pool class might have a public method that adds a work item to an internal queue of tasks waiting to be done. It maintains a pool of threads that execute commands from the queue. The items in the queue are command objects. Typically these objects implement a common interface such as that allows the thread pool to execute the command even though the thread pool class itself was written without any knowledge of the specific tasks for which it would be used.
; Transactional behavior : Similar to undo, a database engine or software installer may keep a list of operations that have been or will be performed. Should one of them fail, all others can be reversed or discarded (usually called ''rollback''). For example, if two database tables that refer to each other must be updated, and the second update fails, the transaction can be rolled back, so that the first table does not now contain an invalid reference.
; Wizards : Often a wizard presents several pages of configuration for a single action that happens only when the user clicks the "Finish" button on the last page. In these cases, a natural way to separate user interface code from application code is to implement the wizard using a command object. The command object is created when the wizard is first displayed. Each wizard page stores its GUI changes in the command object, so the object is populated as the user progresses. "Finish" simply triggers a call to . This way, the command class will work.
Terminology
The terminology used to describe command pattern implementations is not consistent and can therefore be confusing. This is the result ofambiguity
Ambiguity is the type of meaning in which a phrase, statement or resolution is not explicitly defined, making several interpretations plausible. A common aspect of ambiguity is uncertainty. It is thus an attribute of any idea or statement w ...
, the use of synonyms
A synonym is a word, morpheme, or phrase that means exactly or nearly the same as another word, morpheme, or phrase in a given language. For example, in the English language, the words ''begin'', ''start'', ''commence'', and ''initiate'' are ...
, and implementations that may obscure the original pattern by going well beyond it.
# Ambiguity.
## The term command is ambiguous. For example, ''move up, move up'' may refer to a single (move up) command that should be executed twice, or it may refer to two commands, each of which happens to do the same thing (move up). If the former command is added twice to an undo stack, both items on the stack refer to the same command instance. This may be appropriate when a command can always be undone the same way (e.g. move down). Both the Gang of Four
The Gang of Four () was a Maoist political faction composed of four Chinese Communist Party (CCP) officials. They came to prominence during the Cultural Revolution (1966–1976) and were later charged with a series of treasonous crimes. The ...
and the Java example below use this interpretation of the term ''command''. On the other hand, if the latter commands are added to an undo stack, the stack refers to two separate objects. This may be appropriate when each object on the stack must contain information that allows the command to be undone. For example, to undo a ''delete selection'' command, the object may contain a copy of the deleted text so that it can be re-inserted, if the ''delete selection'' command must be undone. Note that using a separate object for each invocation of a command is also an example of the chain of responsibility pattern.
## The term execute is also ambiguous. It may refer to running the code identified by the command object's ''execute'' method. However, in Microsoft's Windows Presentation Foundation
Windows Presentation Foundation (WPF) is a free and open-source graphical subsystem (similar to WinForms) originally developed by Microsoft for rendering user interfaces in Windows-based applications. WPF, previously known as "Avalon", was init ...
a command is considered to have been executed when the command's ''execute'' method has been invoked, but that does not necessarily mean that the application code has run. That occurs only after some further event processing.
# Synonyms and homonyms.
## Client, Source, Invoker: the button, toolbar button, or menu item clicked, the shortcut key pressed by the user.
## Command Object, Routed Command Object, Action Object: a singleton object (e.g. there is only one CopyCommand object), which knows about shortcut keys, button images, command text, etc. related to the command. A source/invoker object calls the Command/Action object's execute/performAction method. The Command/Action object notifies the appropriate source/invoker objects when the availability of a command/action has changed. This allows buttons and menu items to become inactive (grayed out) when a command/action cannot be executed/performed.
## Receiver, Target Object: the object that is about to be copied, pasted, moved, etc. The receiver object owns the method that is called by the command's ''execute'' method. The receiver is typically also the target object. For example, if the receiver object is a ''cursor'' and the method is called ''moveUp'', then one would expect that the cursor is the target of the moveUp action. On the other hand, if the code is defined by the command object itself, the target object will be a different object entirely.
## Command Object, routed event arguments, event object: the object that is passed from the source to the Command/Action object, to the Target object to the code that does the work. Each button click or shortcut key results in a new command/event object. Some implementations add more information to the command/event object as it is being passed from one object (e.g. CopyCommand) to another (e.g. document section). Other implementations put command/event objects in other event objects (like a box inside a bigger box) as they move along the line, to avoid naming conflicts. (See also chain of responsibility pattern.)
## Handler, ExecutedRoutedEventHandler, method, function: the actual code that does the copying, pasting, moving, etc. In some implementations the handler code is part of the command/action object. In other implementations the code is part of the Receiver/Target Object, and in yet other implementations the handler code is kept separate from the other objects.
## Command Manager, Undo Manager, Scheduler, Queue, Dispatcher, Invoker: an object that puts command/event objects on an undo stack or redo stack, or that holds on to command/event objects until other objects are ready to act on them, or that routes the command/event objects to the appropriate receiver/target object or handler code.
# Implementations that go well beyond the original command pattern.
## Microsoft'Windows Presentation Foundation
(WPF), introduces routed commands, which combine the command pattern with event processing. As a result, the command object no longer contains a reference to the target object nor a reference to the application code. Instead, invoking the command object's ''execute'' command results in a so-called ''Executed Routed Event'' that during the event's tunneling or bubbling may encounter a so-called ''binding'' object that identifies the target and the application code, which is executed at that point.
Example
Consider a "simple" switch. In this example we configure the Switch with two commands: to turn the light on and to turn the light off. A benefit of this particular implementation of the command pattern is that the switch can be used with any device, not just a light. The Switch in the following C# implementation turns a light on and off, but the Switch's constructor is able to accept any subclasses of Command for its two parameters. For example, you could configure the Switch to start an engine.See also
* Batch queue * Closure * Command queue *Function object
In computer programming, a function object is a construct allowing an object to be invoked or called as if it were an ordinary function, usually with the same syntax (a function parameter that can also be a function). Function objects are often ...
* Job scheduler
A job scheduler is a computer application for controlling unattended background program execution of jobs. This is commonly called batch scheduling, as execution of non-interactive jobs is often called batch processing, though traditional ''job' ...
* Model–view–controller
Model–view–controller (MVC) is a software architectural pattern commonly used for developing user interfaces that divide the related program logic into three interconnected elements. This is done to separate internal representations of infor ...
* Priority queue
In computer science, a priority queue is an abstract data-type similar to a regular queue or stack data structure in which each element additionally has a ''priority'' associated with it. In a priority queue, an element with high priority is se ...
* Software design pattern
In software engineering, a software design pattern is a general, reusable solution to a commonly occurring problem within a given context in software design. It is not a finished design that can be transformed directly into source or machine c ...
* GoF – Design Patterns
History
The first published mention of using a Command class to implement interactive systems seems to be a 1985 article by Henry Lieberman. The first published description of a (multiple-level) undo-redo mechanism, using a Command class with ''execute'' and ''undo'' methods, and a history list, appears to be the first (1988) edition ofBertrand Meyer
Bertrand Meyer (; ; born 21 November 1950) is a French academic, author, and consultant in the field of computer languages. He created the Eiffel programming language and the idea of design by contract.
Education and academic career
Meyer rece ...
's book Object-oriented Software Construction, section 12.2.
References
External links
Command Pattern
{{DEFAULTSORT:Command Pattern Software design patterns Articles with example C Sharp code Articles with example Java code Articles with example JavaScript code Articles with example Python (programming language) code Articles with example Ruby code Articles with example Scala code