|
Baindari
Baindari (Manchu: ; ) (?-1607) was a Jurchen ''beile'' (chieftain) of the Hoifa tribal confederation. He was a member of the Nara clan although his ancestors were originally members of the Ikderi clan and belonged originally to the Nimaca tribe on the banks of the Amur river. Migrating southward, they put themselves under the protection of some Nara clansmen. Then, after slaying seven oxen in a sacrifice to Heaven, they exchanged their own name for that of their protectors. Six generations later, his grandfather Wangginu, consolidated his position by establishing a settlement at Mount Hūrki on the Huifa river, where the natural advantages of his location enabled him to withstand repeated attacks from the Mongols. On the death of his grandfather Wangginu, who was beile of the Hoifa, Baindari murdered seven uncles who might have stood in his way and proclaimed himself beile of the Hoifa. In 1593, he joined the Hoifa with the tribes of Yehe, Hada, Ula, Khorchin, Sibe, Guwalca, Ju� ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Clan Nara
Nara (Manchu: , Wade-Giles: nara hala, Chinese: , or ) is a clan name shared by a number of royal Manchu clans. The four tribes of the Hūlun confederation () – Hada (), Ula (), Hoifa () and Yehe () – were all ruled by clans bearing this name. The head of each clan held the princely title of "beile" (; Manchu: "chief, lord, or Prince of the Third Rank"). During the Jin Dynasty, Nara was listed as one of the noble "white clans" (). ''Nara'' is the Mongolic word for 'sun'. In Mongolia, the sun is associated to Genghis Khan as the nara tamga is the main tamga attributed to him. History The Naras lived in the Haixi area, which encompasses parts of modern-day Jilin, Heilongjiang, Liaoning and Inner Mongolia. The Hada Naras and Ula Naras are native to Manchuria and shared an ancestor. The Yehe Naras were founded by a Tümed Mongol prince Singgen Darhan who conquered the local Nara tribe and assumed their name, establishing his rule over the banks of the Yehe river. Th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
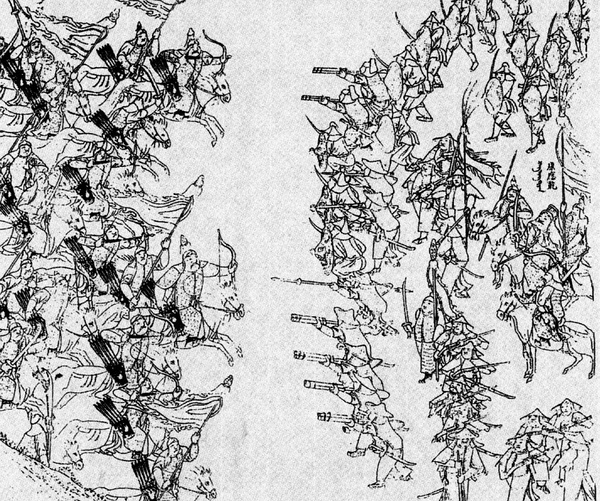
Nurhaci
Nurhaci (14 May 1559 – 30 September 1626), also known by his temple name as the Emperor Taizu of Qing (), was a Jurchen chieftain who rose to prominence in the late 16th century in Manchuria. A member of the House of Aisin-Gioro, he reigned as the founding khan of the Later Jin dynasty of China from 1616 to 1626. Nurhaci reorganized and united various Jurchen tribes (the later "Manchu"), consolidated the Eight Banners military system, and eventually launched attacks on both the Ming and Joseon dynasties. His conquest of Ming dynasty's northeastern Liaodong region laid the groundwork for the Qing conquest of the Ming by his descendants, who founded the Qing dynasty in 1636. He is also generally credited with ordering the creation of a new written script for the Manchu language based on the Mongolian vertical script. Name and titles Nurhaci is written as in Manchu language. Some suggest that the meaning of the name in the Manchu language is "the skin of a wild boar", ot ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Chieftains Of The Jurchens
The Jurchens were a Tungusic people who inhabited the region of Manchuria (present-day Northeast China) until the 17th century, when they adopted the name ''Manchu''. List of Jurchen chieftains during the Liao dynasty (926–1115) "Tamed" Jurchens or Shu Jurchen (熟女眞) "Wild" Jurchens or Sheng Jurchen (生女眞) * Wanyan Hanpu 完顏函普 (金始祖) (941–960) * Wanyan Wulu 完顏烏魯 (金德帝) (960–962) * Wanyan Bahai 完顏跋海 (金安帝) (962–983). * Wanyan Suike 完顏綏可 (金獻祖) (983–1005): In 1003, under his leadership the Wanyan tribe united five tribes in a federation called the "Five Nations" (wuguobu 五國部: Punuli (蒲努里/蒲奴里/蒲聶), Tieli 鐵驪, Yuelidu (越裡篤國), Aolimi (奧里米國), and Puali 剖阿里國). * Wanyan Shilu 完顏石魯 (金昭祖) (1005–1021) * Wanyan Wugunai 完顏烏古迺 (金景祖) (1021–1074): Meanwhile, King Hyung ordered to continue and finish the work of building a wall ( Cheolli ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Manchu Name
Manchu names are the names of the Manchu people in their own language. In addition to such names, most modern Manchus live in China and possess Chinese names. Traditionally, Manchus were called only by their given names in daily life although each belonged to a clan with its own clan name (Manchu: ''hala''). Each clan would be divided into several sub-clans (''mukūn''), but these did not have separate names. Given names Manchus given names are distinctive. Generally, there are several forms, such as bearing suffixes "-ngga", "-ngge" or "-nggo", meaning "having the quality of"; bearing the suffixes "-tai" or "-tu", meaning "having"; bearing the suffix, "-ju", "-boo"; numerals or animal names. Manchu given names were used solely or with titles but not with clan names. For example, Fiyanggū, who was from the Donggo clan, belonged to the Manchu Plain White Banner and distinguished himself in the campaigns against the Dzungars, was usually called "Fiyanggū be" (Lord Fiyanggū ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Manchu Language
Manchu (Manchu:, ) is a critically endangered East Asian Tungusic language native to the historical region of Manchuria in Northeast China. As the traditional native language of the Manchus, it was one of the official languages of the Qing dynasty (1636–1912) of China, although today the vast majority of Manchus speak only Mandarin Chinese. Several thousand can speak Manchu as a second language through governmental primary education or free classes for adults in classrooms or online. The Manchu language enjoys high historical value for historians of China, especially for the Qing dynasty. Manchu-language texts supply information that is unavailable in Chinese, and when both Manchu and Chinese versions of a given text exist they provide controls for understanding the Chinese. Like most Siberian languages, Manchu is an agglutinative language that demonstrates limited vowel harmony. It has been demonstrated that it is derived mainly from the Jurchen language though there ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jurchen People
Jurchen (Manchu language, Manchu: ''Jušen'', ; zh, 女真, ''Nǚzhēn'', ) is a term used to collectively describe a number of East Asian people, East Asian Tungusic languages, Tungusic-speaking peoples, descended from the Donghu people. They lived in the northeast of China, later known as Manchuria, before the 18th century. The Jurchens were renamed Manchu people, Manchus in 1635 by Hong Taiji. Different Jurchen groups lived as hunter-gatherers, pastoralist semi-nomads, or sedentary agriculturists. Generally lacking a central authority, and having little communication with each other, many Jurchen groups fell under the influence of neighbouring dynasties, their chiefs paying tribute and holding nominal posts as effectively hereditary commanders of border guards. Chinese officials of the Ming dynasty (1368-1644) classified them into three groups, reflecting relative proximity to China: #Jianzhou Jurchens, Jianzhou (Chinese: 建州) Jurchens, some of whom were mixed with Korea ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Amur River
The Amur (russian: река́ Аму́р, ), or Heilong Jiang (, "Black Dragon River", ), is the world's tenth longest river, forming the border between the Russian Far East and Northeastern China ( Inner Manchuria). The Amur proper is long, and has a drainage basin of . ''mizu'' ("water") in Japanese. The name "Amur" may have evolved from a root word for water, coupled with a size modifier for "Big Water". Its ancient Chinese names were ''Yushui'', ''Wanshui'' and ''Heishui'', formed from variants to ''shui'', meaning "water".The fishes of the Amur River:updated check-list and zoogeography'' The modern Chinese name for the river, ''Heilong Jiang'' means "Black Dragon River", while the Manchurian name ''Sahaliyan Ula'', the Mongolian names " Amar mörön " (Cyrillic: Амар мөрөн) originates from the name " Amar " meaning to rest and ''Khar mörön'' (Cyrillic: Хар мөрөн) mean Black River. Course The river rises in the hills in the western part of Northea ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Huifa River
The Huifa River () is a 267.7-km-long tributary of the Second Songhua River in center Northeast China. The source of river is located in Qingyuan Manchu Autonomous County of Liaoning Province and flows generally from west to east across Meihekou、 Huinan、 Huadian of Jilin Province and joins Second Songhua River at Toudaogou of Huadian City. History Large numbers of dolmens are distributed along the Huifa River's upper reaches. They date to the fifth century BCE and are related to similar megalithic tombs located on the Korean Peninsula and in the Liao River The Liao River () is the principal river in southern Northeast China, and one of the seven main river systems in China. Its name derived from the Liao region, a historical name for southern Manchuria, from which the Liaoning province, Liaodong P ... basin and Notes {{coord, 43.124167, 126.959056, type:river_region:CN, format=dms, display=title Rivers of Jilin Songhua River ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hulun (alliance)
Hūlun () was a powerful alliance of Jurchen tribes in the late 16th century, based primarily in modern Jilin province of China. The Hūlun alliance was formed by Wan (d. 1582), the leader of the Hada tribal federation, which had drawn its importance from the control of commerce between the late- Ming Liaodong and Jurchen tribes to the east via Guangshun Pass (east of Kaiyuan, which is located near the northern tip of today's Liaoning Province). Besides the Hada themselves, the Hūlun included three other tribal federations, known as Ula, Yehe, and Hoifa. While the Hūlun people were mostly of Jurchen origin, they had been heavily influenced by the Mongol language and culture, and intermarried with the neighboring Khorchin and Kharchin Mongols. Therefore, were viewed by their southern neighbors – Jianzhou Jurchens, which were in the late 16th century led by Nurhaci – as ''Monggo'' ("Mongols"). The Hūlun khan Wan aspired to paramount leadership in the region, e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |