|
Badangi
Badangi is a village in Vizianagaram district of the Indian state of Andhra Pradesh. It is located in Badangi mandal. Demography Badangi mandal has a population of 49,384 in 2011. Males consists of 24,881 and females 24,503 of the population. According to 2001 census average literacy rate is 49%, below the national average of 59.5%. Male literacy rate is 60% and that of females 38%. Badangi Airstrip There is a historic airstrip near Badangi village. It was used as command base for Royal Air Force in British India. The construction was started in 1942 and completed in 1943. It was constructed by Mackenzie company and was the second biggest RAF base after the one at Lahore. It was built on of land and consisted of two runways in a cross formation. It had control-tower overlooking both the runways, a separate underground armament depot that housed the 250-pound torpedo bombs, many underground bunkers, hangars, staff quarters and a natural pond for the fire-fighting. The RAF squa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Badangi Mandal
Badangi mandal is one of the 34 mandals in Vizianagaram district of Andhra Pradesh, India. Badangi is the headquarters of the mandal. The mandal is bounded by Bobbili, Therlam, Merakamudidam and Ramabhadrapuram mandals. Demographics census, the mandal had a population of 48,219. The total population constitute, 24,357 males and 23,862 females. The entire population is rural in nature. Government and politics Badangi mandal is one of the four mandals in Bobbili (Assembly constituency), which in turn is a part of Vizianagaram (Lok Sabha constituency), one of the 25 Lok Sabha constituencies representing Andhra Pradesh. The present MLA is Sambangi Venkata China Appala Naidu, who won the Andhra Pradesh Legislative Assembly election, 2019 representing Yuvajana Sramika Rythu Congress Party The Yuvajana Sramika Rythu Congress Party (, YSRCP or YCP), often shortened to simply the YSR Congress Party, is an Indian regional political party based in the state of Andhra Pra ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
INS Dega
INS ''Dega'' , is a naval air station of the Indian Navy. It is located in Visakhapatnam, Andhra Pradesh on the east coast of India. History The Indian Navy started aviation operations in Visakhapatnam in when the 321 Helicopter Flight was based at INS Circars in Visakhapatnam on 23 December 1972. In 1976, four helipads along with hangars were set up adjacent to the civil airfield. On 12 March 1986, the civilian Visakhapatnam Airport was transferred from the National Airport Authority of India (now, Airports Authority of India) to the Indian Navy. The air station was then designated as Naval Air Station, Visakhapatnam. The 321 Chetak Flight was initially based in the Air Base along with other shipborne flights. Additional hangars, maintenance facilities and an operations complex were constructed soon after. On 21 October 1991, the air station was renamed and formally commissioned as INS ''Dega'' by then Vice Admiral Laxminarayan Ramdas. It is named for the Telugu language ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vizianagaram District
Vizianagaram district is one of the six districts in the Uttarandhra region of the States and union territories of India, Indian state of Andhra Pradesh with its headquarters located at Vizianagaram. The district was once the part of ancient Kalinga (historical region), Kalinga.Saripilli Dibbilingeswara temple, Jayathi Mallikarjuna Temple are the finest examples of ancient Eastern Ganga Dynasty built monuments in the district. The district is bounded on the east by the district of Srikakulam district, Srikakulam, north by Parvathipuram Manyam district, Parvathipuram Manyam south by Visakhapatnam district, Visakhapatnam, Anakapalli district, Anakapalli, southeast by the Bay of Bengal, and west by Alluri Sitharama Raju district. It was formed on 1 June 1979, with some parts carved from the neighbouring districts of Srikakulam and Visakhapatnam. The district is named after the princely state of Vizianagaram (''Vijaya'' means victory and ''Nagaram'' means city in Telugu). In 2011, it ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
India
India, officially the Republic of India, is a country in South Asia. It is the List of countries and dependencies by area, seventh-largest country by area; the List of countries by population (United Nations), most populous country since 2023; and, since its independence in 1947, the world's most populous democracy. Bounded by the Indian Ocean on the south, the Arabian Sea on the southwest, and the Bay of Bengal on the southeast, it shares land borders with Pakistan to the west; China, Nepal, and Bhutan to the north; and Bangladesh and Myanmar to the east. In the Indian Ocean, India is near Sri Lanka and the Maldives; its Andaman and Nicobar Islands share a maritime border with Thailand, Myanmar, and Indonesia. Modern humans arrived on the Indian subcontinent from Africa no later than 55,000 years ago., "Y-Chromosome and Mt-DNA data support the colonization of South Asia by modern humans originating in Africa. ... Coalescence dates for most non-European populations averag ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
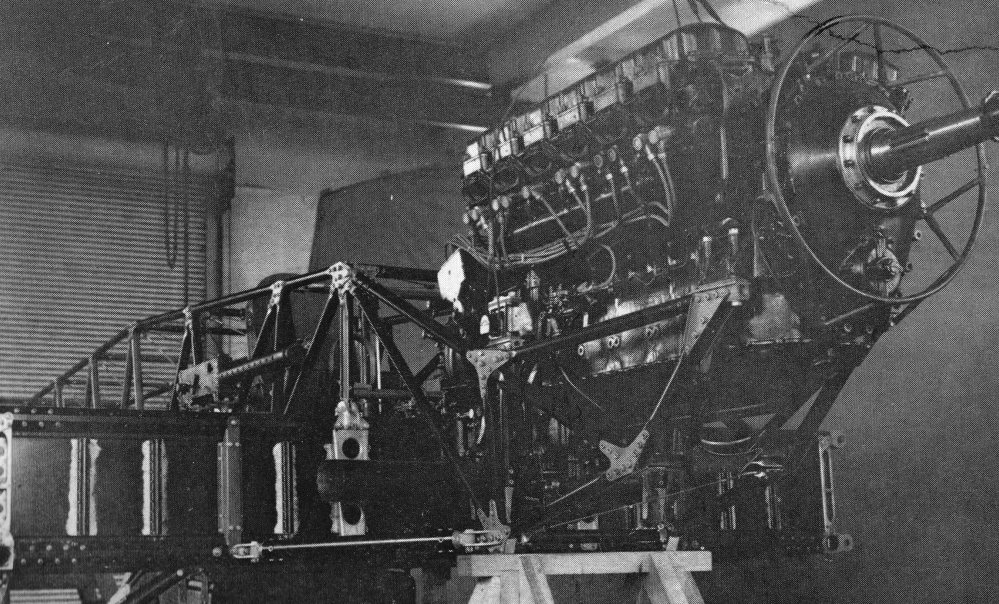
Vickers Wellington
The Vickers Wellington (nicknamed the Wimpy) is a British twin-engined, long-range medium bomber. It was designed during the mid-1930s at Brooklands in Weybridge, Surrey. Led by Vickers-Armstrongs' chief designer Rex Pierson, a key feature of the aircraft is its geodetic airframe fuselage structure, which was principally designed by Barnes Wallis. Development had been started in response to Air Ministry List Of Air Ministry Specifications, Specification B.9/32, issued in the middle of 1932, for a bomber for the Royal Air Force. This specification called for a twin-engined day bomber capable of delivering higher performance than any previous design. Other aircraft developed to the same specification include the Armstrong Whitworth Whitley and the Handley Page Hampden. During the development process, performance requirements such as for the tare weight changed substantially, and the engine used was not the one originally intended. Despite the original specification, the Wellingto ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Supermarine Spitfire
The Supermarine Spitfire is a British single-seat fighter aircraft that was used by the Royal Air Force and other Allies of World War II, Allied countries before, during, and after World War II. It was the only British fighter produced continuously throughout the war. The Spitfire remains popular among enthusiasts. Around List of surviving Supermarine Spitfires, 70 remain airworthy, and many more are static exhibits in aviation museums throughout the world. The Spitfire was a short-range, high-performance interceptor aircraft designed by R. J. Mitchell, chief designer at Supermarine Aviation Works, which operated as a subsidiary of Vickers-Armstrong from 1928. Mitchell modified the Spitfire's distinctive elliptical wing (designed by Beverley Shenstone) with innovative sunken rivets to have the thinnest possible cross-section, achieving a potential top speed greater than that of several contemporary fighter aircraft, including the Hawker Hurricane. Mitchell continued to refine ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hawker Hurricane
The Hawker Hurricane is a British single-seat fighter aircraft of the 1930s–40s which was designed and predominantly built by Hawker Aircraft Ltd. for service with the Royal Air Force (RAF). It was overshadowed in the public consciousness by the Supermarine Spitfire during the Battle of Britain in 1940, but the Hurricane inflicted 60% of the losses sustained by the ''Luftwaffe'' in the campaign, and fought in all the major theatres of the Second World War. The Hurricane originated from discussions between RAF officials and aircraft designer Sir Sydney Camm about a proposed monoplane derivative of the Hawker Fury biplane in the early 1930s. Despite an institutional preference for biplanes and lack of interest by the Air Ministry, Hawker refined its monoplane proposal, incorporating several innovations which became critical to wartime fighter aircraft, including retractable landing gear and the more powerful Rolls-Royce Merlin engine. The Air Ministry ordered Hawker's ''Interce ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
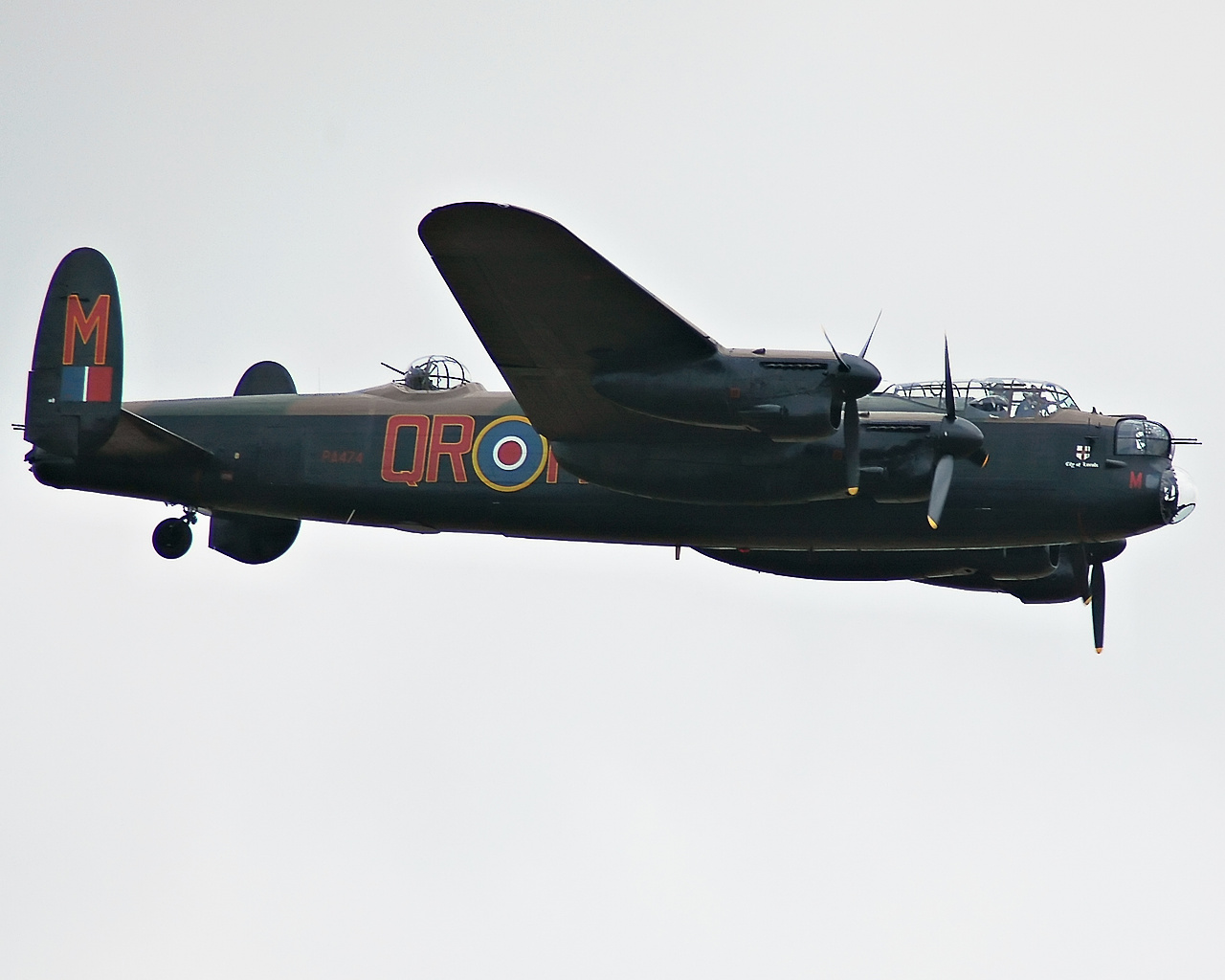
Avro Lancaster
The Avro Lancaster, commonly known as the Lancaster Bomber, is a British World War II, Second World War heavy bomber. It was designed and manufactured by Avro as a contemporary of the Handley Page Halifax, both bombers having been developed to the same specification, as well as the Short Stirling, all three aircraft being four-engined heavy bombers adopted by the Royal Air Force (RAF) during the same era. The Lancaster has its origins in the twin-engine Avro Manchester which had been developed during the late 1930s in response to the Air Ministry List of Air Ministry specifications, Specification P.13/36 for a medium bomber for "world-wide use" which could carry a torpedo internally, and make shallow dive-bombing attacks. Originally developed as an evolution of the Manchester (which had proved troublesome in service and was retired in 1942), the Lancaster was designed by Roy Chadwick and powered by four Rolls-Royce Merlins and in one of the versions, Bristol Hercules engines. I ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Douglas C-47 Skytrain
The Douglas C-47 Skytrain or Dakota ( RAF designation) is a military transport aircraft developed from the civilian Douglas DC-3 airliner. It was used extensively by the Allies during World War II. During the war the C-47 was used for troop transport, cargo, paratrooper, for towing gliders and military cargo parachute drops. The C-47 remained in front-line service with various military operators for many years.Parker 2013, pp. 13, 35, 37, 39, 45–47. It was produced in approximately triple the numbers as the larger, much heavier payload Curtiss C-46 Commando, which filled a similar role for the U.S. military. Approximately 100 countries' armed forces have operated the C-47 with over 60 variants of the aircraft produced. As with the civilian DC-3, the C-47 remains in service, over 80 years after the type's introduction. Design and development The C-47 differed from the civilian DC-3 by way of numerous modifications, including being fitted with a cargo door, hoist attac ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
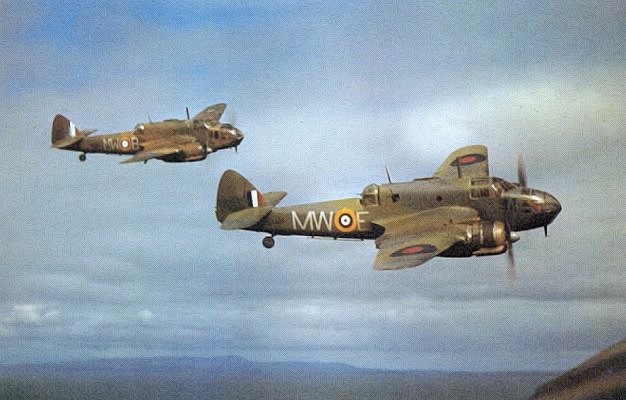
Bristol Beaufighter
The Bristol Type 156 Beaufighter (often called the Beau) is a British multi-role aircraft developed during the Second World War by the Bristol Aeroplane Company. It was originally conceived as a heavy fighter variant of the Bristol Beaufort torpedo bomber. The Beaufighter proved to be an effective night fighter, which came into service with the Royal Air Force (RAF) during the Battle of Britain, its large size allowing it to carry heavy armament and early aircraft interception radar without major performance penalties. The Beaufighter was used in many roles; receiving the nicknames ''Rockbeau'' for its use as a rocket-armed ground attack aircraft and ''Torbeau'' as a torpedo bomber against Axis shipping, in which it replaced the Beaufort. In later operations, it served mainly as a maritime strike/ground attack aircraft, RAF Coastal Command having operated the largest number of Beaufighters amongst all other commands at one point. The Royal Australian Air Force (RAAF) al ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bunker
A bunker is a defensive military fortification designed to protect people and valued materials from falling bombs, artillery, or other attacks. Bunkers are almost always underground, in contrast to blockhouses which are mostly above ground. They were used extensively in World War I, World War II, and the Cold War for weapons facilities, command and control centers, and storage facilities. Bunkers can also be used as protection from tornadoes. Trench bunkers are small concrete structures, partly dug into the ground. Many artillery installations, especially for coastal artillery, have historically been protected by extensive bunker systems. Typical industrial bunkers include mining sites, food storage areas, dumps for materials, data storage, and sometimes living quarters. When a house is purpose-built with a bunker, the normal location is a reinforced below-ground bathroom with fiber-reinforced plastic shells. Bunkers deflect the blast wave from nearby explosions to prevent ear ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |