|
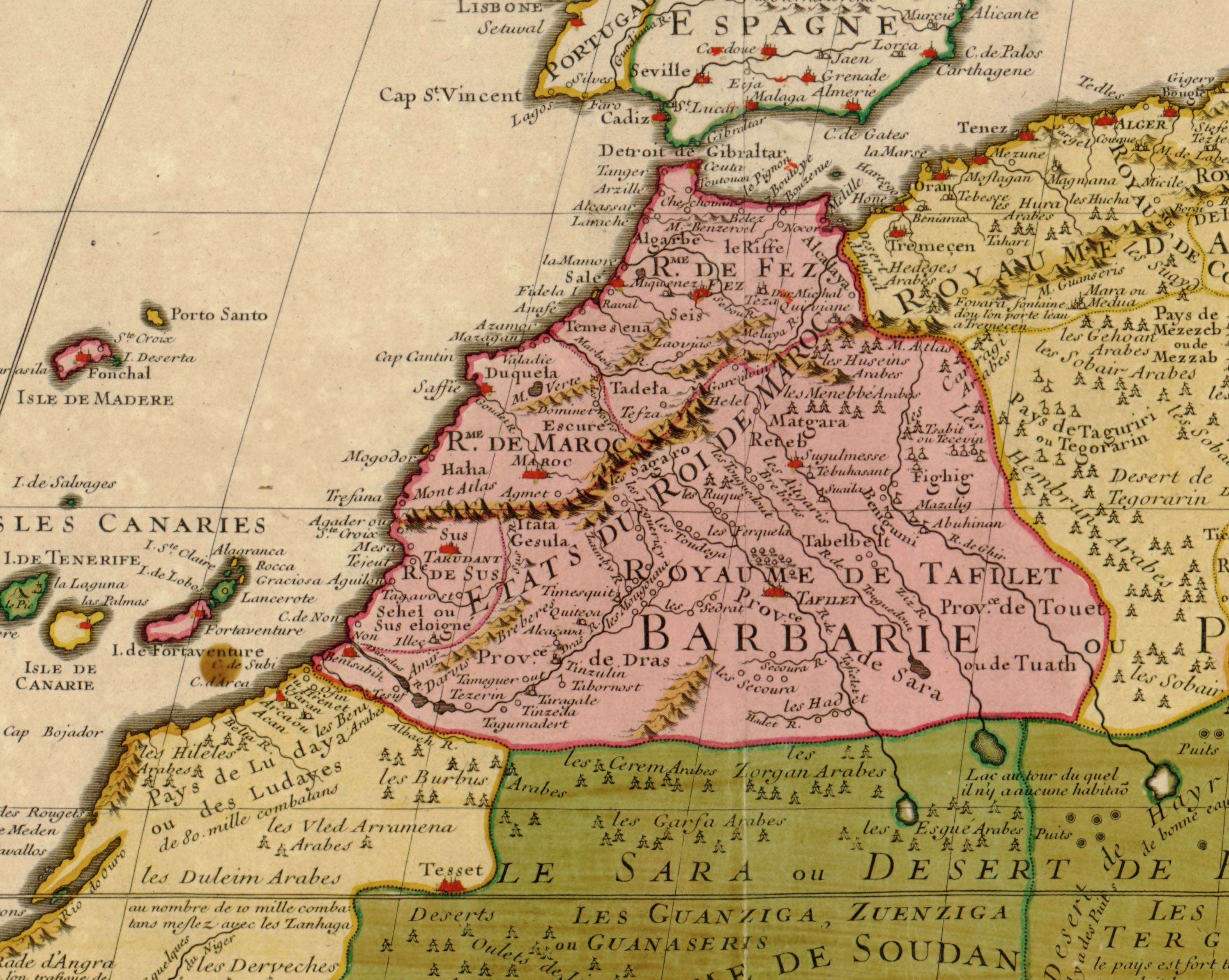
Bab Oudaia
Bab Oudaya (also spelled Bab Oudaia or Bab Udaya; ), also known as Bab Lakbir or Bab al-Kabir (), is the monumental gate of the Kasbah of the Udayas in Rabat, Morocco. The gate, built in the late 12th century, is located at the northwest corner of the Kasbah, uphill from the Medina quarter, medina of Rabat. It is often cited as one of the most beautiful gates of Almohad Caliphate, Almohad and Moroccan architecture. Historical background In 1150 or 1151, the Almohad ruler Abd al-Mu'min built a new kasbah (citadel) over the site of a former Almoravid dynasty, Almoravid ribat on the southwest shore of the Bou Regreg, Bou Regreg River, within which he included a palace and a mosque. His successor, Abu Yusuf Yaqub al-Mansur, Abu Yusuf Ya'qub al-Mansur (ruled 1184–1199), embarked on a huge project to construct a new fortified imperial capital, called ''al-Mahdiyya'' or ''Ribat al-Fath'', on the site of what is now the old city of Rabat, with new walls extending over a vast area b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
City Gate
A city gate is a gate which is, or was, set within a city wall. It is a type of fortified gateway. Uses City gates were traditionally built to provide a point of controlled access to and departure from a walled city for people, vehicles, goods and animals. Depending on their historical context they filled functions relating to defense, security, health, trade, taxation, and representation, and were correspondingly staffed by military or municipal authorities. The city gate was also commonly used to display diverse kinds of public information such as announcements, tax and toll schedules, standards of local measures, and legal texts. It could be heavily fortified, ornamented with Escutcheon (heraldry), heraldic shields, sculpture or inscriptions, or used as a location for warning or intimidation, for example by displaying the heads of Capital punishment, beheaded criminals or public enemies. Notably in Denmark, many market towns used to have at least one city gate mostly as part ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hassan Tower
Hassan Tower or Tour Hassan (; is the minaret of an incomplete mosque in Rabat, Morocco. It was commissioned by Abu Yusuf Yaqub al-Mansur, the third caliph of the Almohad Caliphate, near the end of the 12th century. The tower was intended to be the largest minaret in the world, and the mosque, if completed, would have been the largest in the western Muslim world. When al-Mansur died in 1199, construction on the mosque stopped. The minaret was left standing at a height of 44 meters. The rest of the mosque was also left incomplete, with only the beginnings of several walls and 348 columns being constructed. The tower, along with the remains of the mosque and the modern Mausoleum of Mohammed V, forms an important historical and tourist complex in Rabat. Name Although the tower and the mosque were commissioned by Abu Yusuf Yaqub al-Mansur, the monument is known as the "Hassan" Tower or the al-Hassan Mosque. It is called Hassan Tower, because the settlementin which it was built was ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Quran
The Quran, also Romanization, romanized Qur'an or Koran, is the central religious text of Islam, believed by Muslims to be a Waḥy, revelation directly from God in Islam, God (''Allah, Allāh''). It is organized in 114 chapters (, ) which consist of individual verses ('). Besides its religious significance, it is widely regarded as the finest work in Arabic literature, and has significantly influenced the Arabic, Arabic language. It is the object of a modern field of academic research known as Quranic studies. Muslims believe the Quran was orally revealed by God to the final Islamic Prophets and messengers in Islam, prophet Muhammad in Islam, Muhammad through the Angel#Islam, angel Gabriel#Islam, Gabriel incrementally over a period of some 23 years, beginning on the Night of Power, Laylat al-Qadr, when Muhammad was 40, and concluding in 632, the year of his death. Muslims regard the Quran as Muhammad's most important Islamic view of miracles, miracle, a proof of his prophet ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sebka
''Sebka'' () refers to a type of decorative motif used in western Islamic ("Moorish") architecture and Mudéjar architecture. History and description Various types of interlacing rhombus-like motifs are heavily featured on the surfaces of minarets and other architectural elements in Morocco and al-Andalus during the Almohad period (12th–13th centuries). They continued to spread to other decorative mediums such as carved stucco over the walls of various buildings in Marinid and Nasrid architecture, eventually becoming a standard feature in the western Islamic ornamental repertoire, often in combination with arabesque elements. George Marçais, a 20th-century scholar on the architecture of the region, said that this motif originated with the complex interlacing arches in the 10th-century extension of the Great Mosque of Cordoba by Caliph al-Hakam II. It was then miniaturized and widened into a repeating net-like pattern that can cover surfaces. This motif, in turn, had m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Horseshoe Arch
The horseshoe arch (; ), also called the Moorish arch and the keyhole arch, is a type of arch in which the circular curve is continued below the horizontal line of its diameter, so that the opening at the bottom of the arch is narrower than the arch's full span. Evidence for the earliest uses of this form are found in Late antique, Late Antique and Sasanian architecture, and it was then used in Spain by the Visigoths. But in the 19th century, perhaps when these earlier uses had not been realized, it became emblematic of Islamic architecture, especially Moorish architecture and Mozarabic art in Iberia. It also made later appearances in Moorish Revival architecture, Moorish Revival and Art Nouveau styles. Horseshoe arches can take rounded, pointed or Multifoil arch, lobed form. History Origins and early uses The origins of the horseshoe arch are complicated. It appeared in pre-Islamic Sasanian architecture such as the Taq Kasra, Taq-i Kasra in present-day Iraq and the Palace ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bab Oudaya Floor Plan Cropped And Labeled (from Les Monuments Mauresques Du Maroc 1921 (147185285)
Bab or BAB can refer to: *Bab (toponymy), a component of Arabic toponyms literally meaning "gate" * Set (mythology) (also known as Bab, Baba, or Seth) ancient Egyptian god * Bab (Shia Islam), a term designating deputies of the Imams in Shia Islam * Báb (Sayyid `Alí Muḥammad Shírází, 1819–1850), founder of Bábism and a central figure in the Bahá'í Faith * Bab-ı Âli, the gate to the palace of the Grand vizier of the Ottoman Empire * Báb, Nitra District, a village and municipality in the Nitra District in western central Slovakia * Bab Ballads, cartoons published by W. S. Gilbert under the childhood nickname, ''Bab'' * Back-arc basin, a geologic feature: a submarine basin associated with island arcs and subduction zones * "Base Attack Bonus", a term used in d20 System RPG games * Beale Air Force Base (IATA airport code: BAB), in California * ''Biotechnology and Applied Biochemistry'', an academic journal * Boris Berezovsky (businessman) (1946–2013), Boris Abramovich B ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Maurice Tranchant De Lunel
Maurice Tranchant de Lunel (25 November 1869, in La Ferté-sous-Jouarre – 1944, in La Seyne-sur-Mer), was a 20th-century French architect and writer. Biography An architect of historical monuments in Morocco, de Lunel was the designer of the Grand Mosque of Paris.Théliol MylèneLe Service des beaux-arts, antiquités et monuments historiques, clef de voûte de la politique patrimoniale française au Maroc sous la résidence de Lyautey (1912–1925) ''Outre-mers'', tome 98, n°370-371, 1er semestre 2011. Le contact colonial dans l'empire français : XIXe–XXe siècles, sous la direction de Maria Romo-Navarrete et Sarah Mohamed-Gaillard, pp. 185-193 (DOI : 10.3406/outre.2011.4545) In 1912 he was appointed director of the Department of Antiquities, fine art and historic monuments of the French protectorate in Morocco by Lyautey. His mission was to preserve Moroccan monuments and establish a ranking list of historical monuments in Morocco.Nadège Theilborie,La patrimonialisation ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
French Protectorate In Morocco
The French protectorate in Morocco, also known as French Morocco, was the period of French colonial rule in Morocco that lasted from 1912 to 1956. The protectorate was officially established 30 March 1912, when List of rulers of Morocco, Sultan Abd al-Hafid of Morocco, Abd al-Hafid signed the Treaty of Fez, though the French French conquest of Morocco, military occupation of Morocco had begun with the invasion of Oujda and the Bombardment of Casablanca (1907), bombardment of Casablanca in 1907. The French protectorate lasted until the dissolution of the Treaty of Fez on 2 March 1956, with the Franco-Moroccan Joint Declaration. Morocco's independence movement, described in Moroccan historiography as the Revolution of the King and the People, restored the exiled Mohammed V of Morocco, Mohammed V but it did not end the French presence in Morocco. France preserved its influence in the country, including a right to station French troops and to have a say in Morocco's foreign policy. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Abd Al-Rahman Of Morocco
''Moulay'' Abd al-Rahman bin Hisham (; 19 February 1778 – 28 August 1859) was List of rulers of Morocco, Sultan of Morocco from 30 November 1822 to 28 August 1859, as a ruler of the 'Alawi dynasty. He was a son of Hisham bin Mohammed, Moulay Hisham. He was proclaimed sultan in Fez, Morocco, Fes after the death of Sulayman of Morocco, Moulay Sulayman. During his long reign he proved himself competent in an age where Africa was being Scramble for Africa, colonized by stronger European nations, such as neighbouring Ottoman Algeria which was Invasion of Algiers in 1830, invaded by France. He was able to preserve Moroccan independence and maintain Moroccan borders without ceding any land, while also supporting Emirate of Abdelkader, Emir Abd al-Qadir's resistance in Algeria against France. He also signed the necessary treaties to enforce his beliefs, and fought numerous conflicts with European nations, especially July Monarchy, France. Biography Abd al-Rahman bin Hisham was born i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fez, Morocco
Fez () or Fes (; ) is a city in northern inland Morocco and the capital of the Fez-Meknes, Fez-Meknes administrative region. It is one of the List of cities in Morocco, largest cities in Morocco, with a population of 1.256 million, according to the 2024 Moroccan census, census. Located to the northwest of the Atlas Mountains, it is surrounded by hills and the old city is centered around the Oued Fes, Fez River (''Oued Fes'') flowing from west to east. Fez has been called the "Mecca of the West" and the "Athens of Africa". It is also considered the spiritual and cultural capital of Morocco. Founded under Idrisid dynasty, Idrisid rule during the 8th century Common Era, CE, Fez initially consisted of two autonomous and competing settlements. Successive waves of mainly Arab immigrants from Ifriqiya (Tunisia) and al-Andalus (Spain/Portugal) in the early 9th century gave the nascent city its Arab character. After the downfall of the Idrisid dynasty, other empires came and went until t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Guich
''Guich'' tribes, ''Gish'' tribes, or ''Jaysh'' tribes ( or ), or sometimes ''Makhzen'' tribes, were tribes of usually Arab origin organized by the sultans of Moroccan dynasties under the pre-colonial Makhzen regime to serve as troops and military garrisons, as well as to protect the outskirts of the capital and suppress rebellions. They were usually cantoned in their own lands and maintained a state of perpetual military mobilization. The contingents were formed in order to be loyal to the sultan only instead of to other local interests, but they often maintained a coherent group identity long after the death of the sultan and were sometimes the source of political instability. The historical ''guich'' system took shape primarily under the reign of the 'Alawid sultan Mawlay Isma'il, although variations of similar military organisations were used by prior rulers and dynasties. The major historical ''guich'' tribes were the Cheraga, the Udayas, the Cherarda, and the Bwakher. The ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oudaya
The Oudaya () also written as Udaya, Oudaia and sometimes referred to as Wadaya () is an Arabs, Arab tribe in Morocco of Maqil origin. They are situated around Fez, Morocco, Fez and Meknes, Marrakesh and in Rabat. They were recruited by Ismail Ibn Sharif as one of the guich tribes that formed an integral component of the pre-colonial Moroccan military. The Mghafra (), a sub-tribe of the Oudaya, founded several emirates in Mauritania, for example the Emirate of Trarza, as a result of the Char Bouba war, Char Bouba War. Etymology The name Oudaya is the plural of the Arabic word Wadi, oued () which means river as well as the words ''awdāʾ'' (اوداء), ''awdiya'' (أودية) and ''awdāh'' (أوداه; in the dialect of Tayy). This was corrupted into ''awādiya'' (أوادية). Ibn Sidah said the correct form is ''awdāya'' (الاوداية) and said: History Origins According to historical authors Leo Africanus and Luis del Mármol Carvajal, Marmol Carvajal, the Ouda ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |