|
Sebka
''Sebka'' () refers to a type of decorative motif used in western Islamic ("Moorish") architecture and Mudéjar architecture. History and description Various types of interlacing rhombus-like motifs are heavily featured on the surfaces of minarets and other architectural elements in Morocco and al-Andalus during the Almohad period (12th–13th centuries). They continued to spread to other decorative mediums such as carved stucco over the walls of various buildings in Marinid and Nasrid architecture, eventually becoming a standard feature in the western Islamic ornamental repertoire, often in combination with arabesque elements. George Marçais, a 20th-century scholar on the architecture of the region, said that this motif originated with the complex interlacing arches in the 10th-century extension of the Great Mosque of Cordoba by Caliph al-Hakam II. It was then miniaturized and widened into a repeating net-like pattern that can cover surfaces. This motif, in turn, had m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Moorish Architecture
Moorish architecture is a style within Islamic architecture that developed in the western Islamic world, including al-Andalus (the Iberian Peninsula) and what is now Morocco, Algeria, and Tunisia (part of the Maghreb). Scholarly references on Islamic architecture often refer to this architectural tradition in terms such as architecture of the Islamic West or architecture of the Western Islamic lands. This architectural tradition integrated influences from pre-Islamic Roman, Byzantine, and Visigothic architectures, from ongoing artistic currents in the Islamic Middle East, and from North African Berber traditions. Major centers of artistic development included the main capitals of the empires and Muslim states in the region's history, such as Córdoba, Kairouan, Fes, Marrakesh, Seville, Granada and Tlemcen. While Kairouan and Córdoba were some of the most important centers during the 8th to 10th centuries, a wider regional style was later synthesized and shared across the Ma ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
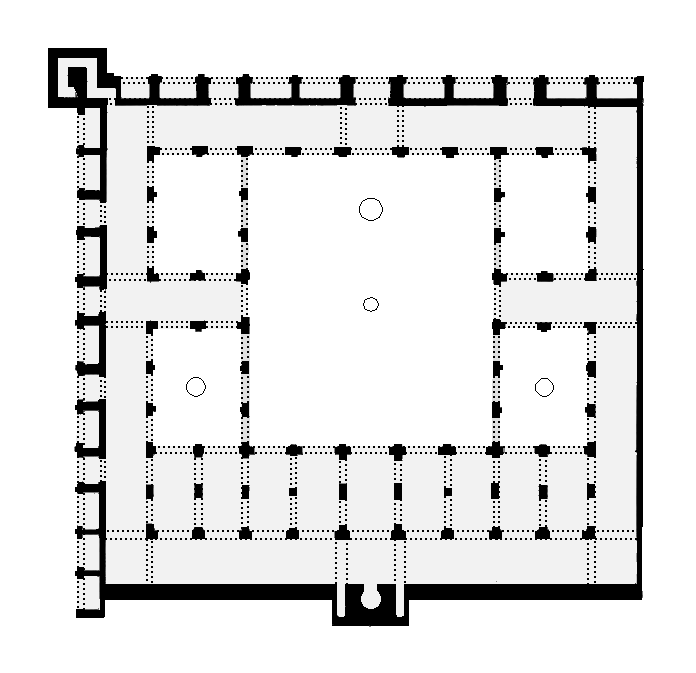
Kasbah Mosque (Marrakech)
The Kasbah Mosque (), also known as the Moulay al-Yazid Mosque, is a historic mosque in Marrakesh, Morocco. It was originally built by the Almohad ruler Yaqub al-Mansur in 1185–1190 CE. It is located in the Kasbah district, the city's former citadel, near the site of its historic royal palaces. Along with the Kutubiyya Mosque, it is one of the most important historic mosques in Marrakesh. History Construction of the mosque was probably begun around 1185 and finished by 1190 (CE), at the apogee of the Almohad Empire. It was commissioned by the Almohad caliph Yaqub al-Mansur (ruled 1184–1199) as part of the newly created imperial kasbah (citadel) district which was to be the residence of the Almohad Caliph and the seat of government. This followed with a long tradition of rulers in the Islamic world (and beyond) who built palace-cities or separate royal districts. The Kasbah Mosque was built to be the congregational mosque for the caliph and for this royal district, wh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alcázar Of Seville
The Alcázar of Seville, officially called Royal Alcázar of Seville (), is a historic royal palace in Seville, Spain. It was formerly the site of the Al-Andalus, Islamic-era citadel of the city, begun in the 10th century and then developed into a larger palace complex by the Abbadid dynasty (11th century) and the Almohad Caliphate, Almohads (12th to early 13th centuries). After the Crown of Castile, Castilian conquest of the city in 1248, the site was progressively rebuilt and replaced by new palaces and gardens. Among the most important of these is a richly decorated Mudéjar art, Mudéjar-style palace built by Peter of Castile, Pedro I during the 1360s. The palace is a preeminent example of Mudéjar style in the Iberian Peninsula and also includes sections with Gothic architecture, Gothic and Renaissance architecture, Renaissance elements. The upper stories of the Alcázar are still occupied by the Spanish royal family, royal family when they visit Seville and are administered ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Giralda
The Giralda ( ) is the bell tower of Seville Cathedral in Seville, Spain. It was built as the minaret for the Great Mosque of Seville in al-Andalus, during the reign of the Almohad dynasty, with a Renaissance-style belfry added by the Catholics after the expulsion of the Muslims from the area. The cathedral, including the Giralda, was registered in 1987 as a World Heritage Site by UNESCO, along with the Alcázar and the General Archive of the Indies. It remains one of the most important symbols of the city, as it has been since the Middle Ages. The tower is one of the most famous monuments of Moorish architecture in Spain and one of the most refined examples of Almohad architecture. Origin Initial construction The mosque was built to replace the older Mosque of Ibn 'Addabas, built in the 9th century under Umayyad rule, since the congregation had grown larger than that modest mosque could accommodate. It was commissioned in 1171 by caliph Abu Ya'qub Yusuf. Sevillian archite ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Multifoil Arch
A multifoil arch (or polyfoil arch), also known as a cusped arch, polylobed arch, or scalloped arch, is an arch characterized by multiple circular arcs or leaf shapes (called foils, lobes, or cusps) that are cut into its interior profile or intrados. The term ''foil'' comes from the old French word for "leaf." A specific number of foils is indicated by a prefix: trefoil (three), quatrefoil (four), cinquefoil (five), sexfoil (six), octofoil (eight). The term multifoil or scalloped is specifically used for arches with more than five foils. The multifoil arch is characteristic of Islamic art and architecture; particularly in the Moorish architecture of al-Andalus (Iberian Peninsula) and North Africa and in Mughal architecture of the Indian subcontinent. Variants of the multifoil arch, such as the trefoil arch, are also common in other architectural traditions such as Gothic architecture. Origins The first multifoil arches were developed by the Umayyads and can be found in a s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mosque–Cathedral Of Córdoba
The Mosque–Cathedral of Córdoba ( ), officially known by its ecclesiastical name of Cathedral of Our Lady of the Assumption (), is the cathedral of the Roman Catholic Diocese of Córdoba, Diocese of Córdoba dedicated to the Assumption of Mary and located in the Spanish region of Andalusia. Due to its status as a former mosque, it is also known in Spanish as the and in a historical sense as the Great Mosque of Córdoba. According to traditional accounts a Visigothic Kingdom, Visigothic church, the Catholic Church, Catholic Christian Basilica of Vincent of Saragossa, originally stood on the site of the current Mosque-Cathedral, although this has been a matter of scholarly debate. The Great Mosque was constructed in 785 on the orders of Abd al-Rahman I, founder of the Islamic Emirate of Córdoba. It was expanded multiple times afterwards under Abd al-Rahman's successors up to the late 10th century. Among the most notable additions, Abd al-Rahman III added a minaret (finished i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Al-Andalus
Al-Andalus () was the Muslim-ruled area of the Iberian Peninsula. The name refers to the different Muslim states that controlled these territories at various times between 711 and 1492. At its greatest geographical extent, it occupied most of the peninsula as well as Septimania under Umayyad rule. These boundaries changed through a series of conquests Western historiography has traditionally characterized as the ''Reconquista'',"Para los autores árabes medievales, el término Al-Andalus designa la totalidad de las zonas conquistadas – siquiera temporalmente – por tropas arabo-musulmanas en territorios actualmente pertenecientes a Portugal, España y Francia" ("For medieval Arab authors, Al-Andalus designated all the conquered areas – even temporarily – by Arab-Muslim troops in territories now belonging to Spain, Portugal and France"), García de Cortázar, José Ángel. ''V Semana de Estudios Medievales: Nájera, 1 al 5 de agosto de 1994'', Gobie ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Interlacing Arches
Interlaced arches is a scheme of decoration employed in Romanesque and Gothic architecture, where arches spring from alternate piers, interlacing or intersecting one another. In the former case, the first arch archivolt is carried alternately over and under the second, in the latter the archivolts actually intersect and stop one another. An example of the former exists in St Peter-in-the-East in Oxford and of the latter in St. Joseph’s chapel in Glastonbury, and in the Bristol Cathedral. The arches in the interlacing arcade can be either semicircular or pointed, and usually form purely decorative blind arcades. The interlaced arches are most likely an invention of Islamic architecture (cf. Bab al-Mardum Mosque, 999-1000 AD and Mosque–Cathedral of Córdoba, 833-988). This decoration was especially popular in England, with the most famous example at Lincoln Cathedral (St Hugh's choir). File:Mezquita del Cristo de la Luz 01, Toledo.jpg, Bab al-Mardum Mosque File:Double Ar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Spain
Spain, or the Kingdom of Spain, is a country in Southern Europe, Southern and Western Europe with territories in North Africa. Featuring the Punta de Tarifa, southernmost point of continental Europe, it is the largest country in Southern Europe and the fourth-most populous European Union member state. Spanning across the majority of the Iberian Peninsula, its territory also includes the Canary Islands, in the Eastern Atlantic Ocean, the Balearic Islands, in the Western Mediterranean Sea, and the Autonomous communities of Spain#Autonomous cities, autonomous cities of Ceuta and Melilla, in mainland Africa. Peninsular Spain is bordered to the north by France, Andorra, and the Bay of Biscay; to the east and south by the Mediterranean Sea and Gibraltar; and to the west by Portugal and the Atlantic Ocean. Spain's capital and List of largest cities in Spain, largest city is Madrid, and other major List of metropolitan areas in Spain, urban areas include Barcelona, Valencia, Seville, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
La Tour Hassan - Photo De Abdellatif AMAJGAG (cropped For Sebka Pattern)
LA most frequently refers to Los Angeles, the second most populous city in the United States of America. La, LA, or L.A. may also refer to: Arts and entertainment Music *La (musical note), or A, the sixth note *"L.A.", a song by Elliott Smith on ''Figure 8'' (album) * ''L.A.'' (EP), by Teddy Thompson *''L.A. (Light Album)'', a Beach Boys album * "L.A." (Neil Young song), 1973 *The La's, an English rock band *L.A. Reid, a prominent music producer *Yung L.A., a rapper *Lady A, an American country music trio * "L.A." (Amy Macdonald song), 2007 *"La", a song by Australian-Israeli singer-songwriter Old Man River *''La'', a Les Gordon album Other media * l(a, a poem by E. E. Cummings * La (Tarzan), fictional queen of the lost city of Opar (Tarzan) *''Lá'', later known as Lá Nua, an Irish language newspaper * La7, an Italian television channel *LucasArts, an American video game developer and publisher * Liber Annuus, academic journal Business, organizations, and government age ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Seville
Seville ( ; , ) is the capital and largest city of the Spain, Spanish autonomous communities of Spain, autonomous community of Andalusia and the province of Seville. It is situated on the lower reaches of the Guadalquivir, River Guadalquivir, in the southwest of the Iberian Peninsula. Seville has a municipal population of about 701,000 , and a Seville metropolitan area, metropolitan population of about 1.5 million, making it the largest city in Andalusia and the List of metropolitan areas in Spain, fourth-largest city in Spain. Its old town, with an area of , contains a UNESCO World Heritage Site comprising three buildings: the Alcázar of Seville, Alcázar palace complex, the Seville Cathedral, Cathedral and the General Archive of the Indies. The Seville harbour, located about from the Atlantic Ocean, is the only river port in Spain. The capital of Andalusia features hot temperatures in the summer, with daily maximums routinely above in July and August. Seville was founded ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Palmette
The palmette is a motif in decorative art which, in its most characteristic expression, resembles the fan-shaped leaves of a palm tree. It has a far-reaching history, originating in ancient Egypt with a subsequent development through the art of most of Eurasia, often in forms that bear relatively little resemblance to the original. In ancient Greek and Roman uses it is also known as the anthemion (from the Greek ανθέμιον, a flower). It is found in most artistic media, but especially as an architectural ornament, whether carved or painted, and painted on ceramics. It is very often a component of the design of a frieze or border. The complex evolution of the palmette was first traced by Alois Riegl in his '' Stilfragen'' of 1893. The half-palmette, bisected vertically, is also a very common motif, found in many mutated and vestigial forms, and especially important in the development of plant-based scroll ornament. Description The essence of the palmette is a symmetrical ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |