|
Arthropoda
Arthropods ( ) are invertebrates in the phylum Arthropoda. They possess an exoskeleton with a cuticle made of chitin, often mineralised with calcium carbonate, a body with differentiated ( metameric) segments, and paired jointed appendages. In order to keep growing, they must go through stages of moulting, a process by which they shed their exoskeleton to reveal a new one. They form an extremely diverse group of up to ten million species. Haemolymph is the analogue of blood for most arthropods. An arthropod has an open circulatory system, with a body cavity called a haemocoel through which haemolymph circulates to the interior organs. Like their exteriors, the internal organs of arthropods are generally built of repeated segments. They have ladder-like nervous systems, with paired ventral nerve cords running through all segments and forming paired ganglia in each segment. Their heads are formed by fusion of varying numbers of segments, and their brains are formed by fu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Arthropod
Arthropods ( ) are invertebrates in the phylum Arthropoda. They possess an arthropod exoskeleton, exoskeleton with a cuticle made of chitin, often Mineralization (biology), mineralised with calcium carbonate, a body with differentiated (Metamerism (biology), metameric) Segmentation (biology), segments, and paired jointed appendages. In order to keep growing, they must go through stages of moulting, a process by which they shed their exoskeleton to reveal a new one. They form an extremely diverse group of up to ten million species. Haemolymph is the analogue of blood for most arthropods. An arthropod has an open circulatory system, with a body cavity called a haemocoel through which haemolymph circulates to the interior Organ (anatomy), organs. Like their exteriors, the internal organs of arthropods are generally built of repeated segments. They have ladder-like nervous systems, with paired Anatomical terms of location#Dorsal and ventral, ventral Ventral nerve cord, nerve cord ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
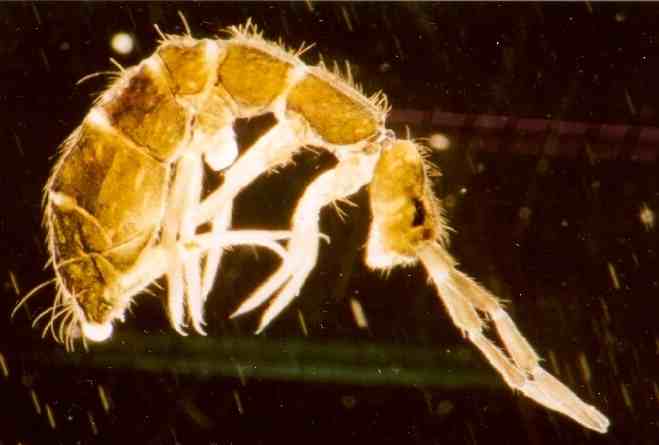
Trilobite
Trilobites (; meaning "three-lobed entities") are extinction, extinct marine arthropods that form the class (biology), class Trilobita. One of the earliest groups of arthropods to appear in the fossil record, trilobites were among the most successful of all early animals, existing in oceans for almost 270million years, with over 22,000 species having been described. Because trilobites had wide diversity and an easily fossilized mineralised exoskeleton made of calcite, they left an extensive fossil record. The study of their fossils has facilitated important contributions to biostratigraphy, paleontology, evolution, evolutionary biology, and plate tectonics. Trilobites are placed within the clade Artiopoda, which includes many organisms that are morphologically similar to trilobites, but are largely unmineralised. The relationship of Artiopoda to other arthropods is uncertain. Trilobites evolved into many ecological niches; some moved over the seabed as predators, scavengers, or ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Invertebrate
Invertebrates are animals that neither develop nor retain a vertebral column (commonly known as a ''spine'' or ''backbone''), which evolved from the notochord. It is a paraphyletic grouping including all animals excluding the chordata, chordate subphylum Vertebrata, i.e. vertebrates. Well-known Phylum, phyla of invertebrates include arthropods, molluscs, annelids, echinoderms, flatworms, cnidarians, and sponges. The majority of animal species are invertebrates; one estimate puts the figure at 97%. Many invertebrate taxon, taxa have a greater number and diversity of species than the entire subphylum of Vertebrata. Invertebrates vary widely in size, from 10 Micrometre, μm (0.0004 in) myxozoans to the 9–10 m (30–33 ft) colossal squid. Some so-called invertebrates, such as the Tunicata and Cephalochordata, are actually sister chordate subphyla to Vertebrata, being more closely related to vertebrates than to other invertebrates. This makes the "invertebrates" para ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chelicerata
The subphylum Chelicerata (from Neo-Latin, , ) constitutes one of the major subdivisions of the phylum Arthropoda. Chelicerates include the sea spiders, horseshoe crabs, and arachnids (including harvestmen, scorpions, spiders, solifuges, ticks, and mites, among many others), as well as a number of extinct lineages, such as the eurypterids (sea scorpions) and chasmataspidids. Chelicerata split from Mandibulata by the mid-Cambrian, as evidenced by stem-group chelicerates like Habeliida and '' Mollisonia'' present by this time. The surviving marine species include the four species of xiphosurans (horseshoe crabs), and possibly the 1,300 species of pycnogonids (sea spiders), if the latter are indeed chelicerates. On the other hand, there are over 77,000 well-identified species of air-breathing chelicerates, and there may be about 500,000 unidentified species. Like all arthropods, chelicerates have segmented bodies with jointed limbs, all covered in a cuti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Centipede
Centipedes (from Neo-Latin , "hundred", and Latin , "foot") are predatory arthropods belonging to the class Chilopoda (Ancient Greek , ''kheilos'', "lip", and Neo-Latin suffix , "foot", describing the forcipules) of the subphylum Myriapoda, an arthropod group which includes millipedes and other multi-legged animals. Centipedes are elongated segmented ( metameric) animals with one pair of legs per body segment. All centipedes are venomous and can inflict painful stings, injecting their venom through pincer-like appendages known as forcipules or toxicognaths, which are actually modified legs instead of fangs. Despite the name, no species of centipede has exactly 100 legs; the number of pairs of legs is an odd number that ranges from 15 pairs to 191 pairs. Centipedes are predominantly generalist carnivorous, hunting for a variety of prey items that can be overpowered. They have a wide geographical range, which can be found in terrestrial habitats from tropical rainforests ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Millipede
Millipedes (originating from the Latin , "thousand", and , "foot") are a group of arthropods that are characterised by having two pairs of jointed legs on most body segments; they are known scientifically as the class Diplopoda, the name derived from this feature. Each double-legged segment is a result of two single segments fused together. Most millipedes have very elongated cylindrical or flattened bodies with more than 20 segments, while pill millipedes are shorter and can roll into a tight ball. Although the name "millipede" derives from Latin for "thousand feet", no species was known to have 1,000 or more until the discovery in 2020 of '' Eumillipes persephone'', which can have over 1,300 legs. There are approximately 12,000 named species classified into 16 orders and around 140 families, making Diplopoda the largest class of myriapods, an arthropod group which also includes centipedes and other multi-legged creatures. Most millipedes are slow-moving detritivores, eat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Springtail
Springtails (class Collembola) form the largest of the three lineages of modern Hexapoda, hexapods that are no longer considered insects. Although the three lineages are sometimes grouped together in a class called Entognatha because they have internal Arthropod mouthparts, mouthparts, they do not appear to be any more closely related to one another than they are to insects, which have external mouthparts. Springtails are omnivorous, free-living organisms that prefer moist conditions. They do not directly engage in the decomposition of organic matter, but contribute to it indirectly through the fragmentation of organic matter and the control of soil microbial communities. The word ''Collembola'' is from Ancient Greek 'glue' and 'peg'; this name was given due to the existence of the collophore, which was previously thought to stick to surfaces to stabilize the creature. Early DNA sequence studies suggested that Collembola represent a separate Lineage (evolution), evolutionary ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
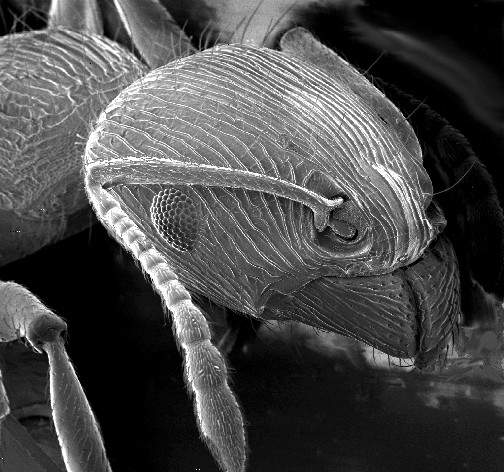
Arthropod Exoskeleton
Arthropods are covered with a tough, resilient integument, cuticle or exoskeleton of chitin. Generally the exoskeleton will have thickened areas in which the chitin is reinforced or stiffened by materials such as minerals or hardened proteins. This happens in parts of the body where there is a need for rigidity or elasticity. Typically the mineral crystals, mainly calcium carbonate, are deposited among the chitin and protein molecules in a process called biomineralization. The crystals and fibres interpenetrate and reinforce each other, the minerals supplying the hardness and resistance to compression, while the chitin supplies the tensile strength. Biomineralization occurs mainly in crustaceans. In insects and arachnids, the main reinforcing materials are various proteins hardened by linking the fibres in processes called sclerotisation and the hardened proteins are called sclerotin. The dorsal tergum, ventral sternum, and the lateral pleura form the hardened plates or sclerit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
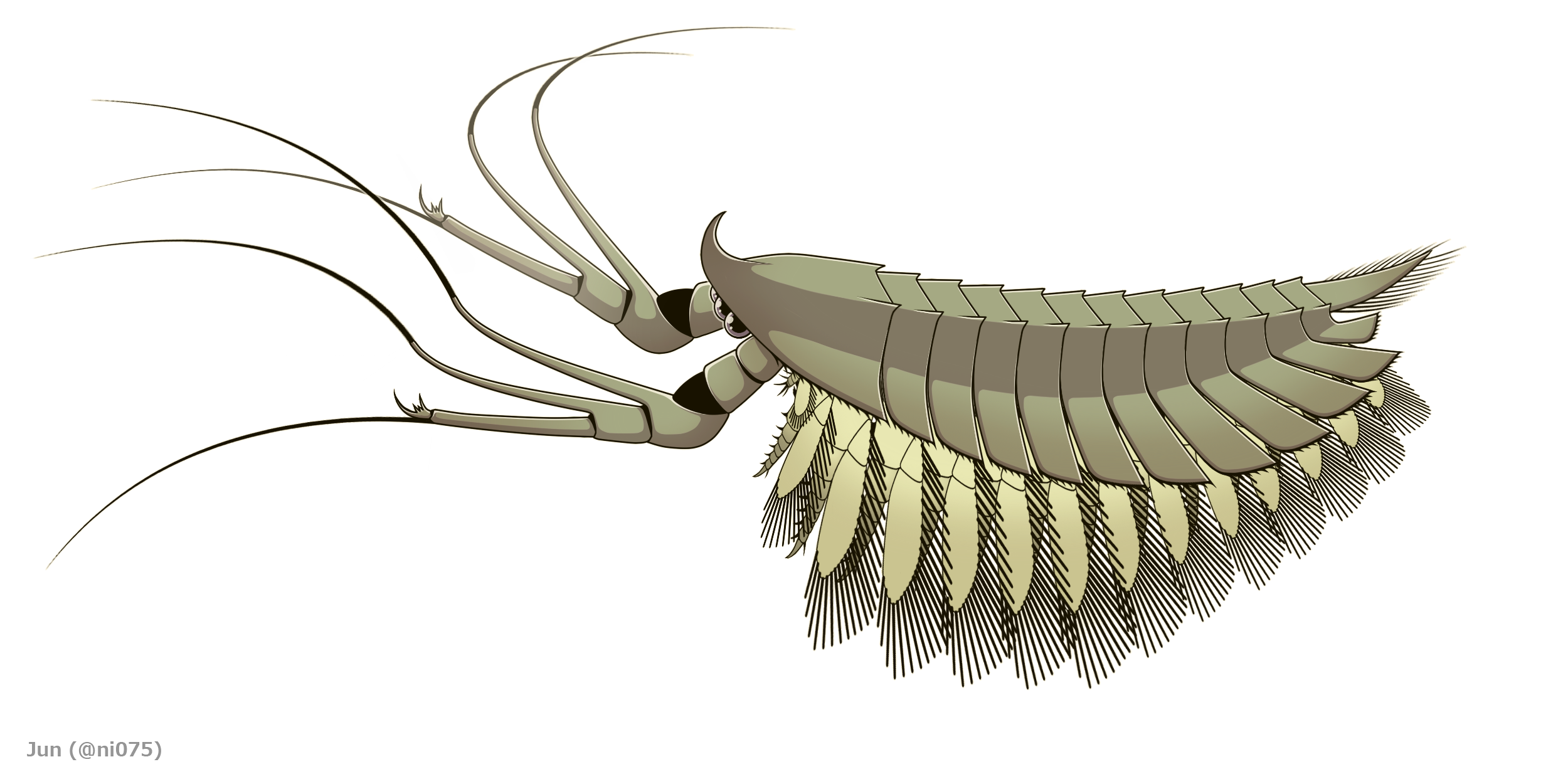
Leanchoilia
''Leanchoilia'' is a megacheiran marine arthropod known from Cambrian deposits of the Burgess Shale in Canada and the Chengjiang biota of China. Description ''L. superlata'' was about long and had long, whip-like flagellae extending from its great appendages. Its internal organs are occasionally preserved within the substrate in three dimensions. Their two pairs of eyes are protected and covered by their exterior head shields, with two eyes being located on each side. Species Seven species are tentatively accepted today: ''L. superlata'' (the type species), ''L. persephone'' and ''L. protogonia'' from the Burgess Shale, ''L. illecebrosa'' and ''L. obesa'' from the Chengjiang biota, 'L. robisoni'' from Kaili, and ''L.''? ''hanceyi'' from the Spence Shale. ''L. superlata'' and ''L. persephone'' may however be examples of sexual dimorphism. Distribution 55 specimens of ''Leanchoilia'' are known from the Greater Phyllopod bed, where they comprise 0.1% of the community. S ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Arachnid
Arachnids are arthropods in the Class (biology), class Arachnida () of the subphylum Chelicerata. Arachnida includes, among others, spiders, scorpions, ticks, mites, pseudoscorpions, opiliones, harvestmen, Solifugae, camel spiders, Amblypygi, whip spiders and Uropygi, vinegaroons. Adult arachnids have eight Arthropod leg, legs attached to the cephalothorax. In some species the frontmost pair of legs has converted to a sensory function, while in others, different appendages can grow large enough to take on the appearance of extra pairs of legs. Almost all Extant taxon, extant arachnids are terrestrial animal, terrestrial, living mainly on land. However, some inhabit freshwater environments and, with the exception of the pelagic zone, marine environments as well. They comprise over 110,000 named species, of which 51,000 are species of spiders. The term is derived from the Ancient Greek, Greek word (''aráchnē'', 'spider'), from the myth of the hubristic human weaver Arachne, w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Isoxys
''Isoxys'' (meaning "equal surfaces") is a genus of extinct bivalved Cambrian arthropod; the various species of which are thought to have been freely swimming predators. It had a pair of large spherical eyes (which are the most commonly preserved feature of the soft-bodied anatomy), and two large frontal appendages used to grasp prey. Description Species of ''Isoxys'' have roughly semicircular bivalved carapaces, which vary in morphology between species. The front and rear edges of the carapaces bear forward and posterior facing spines, respectively which in some species are greatly elongated''.'' The carapaces of ''Isoxys'' are typically in length (with the juveniles of some species being as small as ), excluding the spines, though some species are known to reach over . In long-spined species when including spine length, some specimens exceed . The opening angle of the carapace was close to vertical, giving it a narrow profile when viewed from above.'''' The head had a pair ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Johann Ludwig Christian Gravenhorst
Johann Ludwig Christian Carl Gravenhorst (14 November 1777 – 14 January 1857), sometimes Jean Louis Charles or Carl, was a German entomologist, herpetologist, and zoologist. Life Gravenhorst was born in Braunschweig. His early interest in insects was encouraged by two of his professors, both amateur entomologists. He entered the University of Helmstedt to study law in 1797. However, the death of his father two years later left him a great fortune; so he was able to change his direction. He enrolled at the University of Göttingen where he followed the courses of Johann Friedrich Blumenbach. He returned to present his thesis to Helmstädt on a subject of entomology. He went to Paris in 1802 and there met Georges Cuvier, Pierre André Latreille, and Alexandre Brongniart. Parallel to his studies, he assembled, thanks to his financial means, a very important natural history collection. In 1805, he obtained a professorial chair in Göttingen and published the following y ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |