springtail on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Springtails (Collembola) form the largest of the three lineages of modern hexapods that are no longer considered
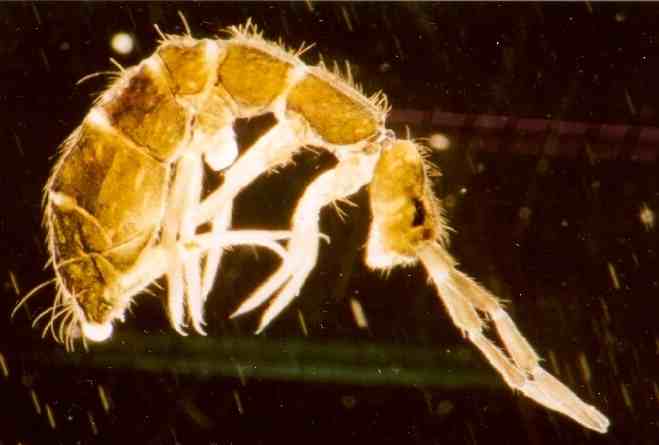 Members of the Collembola are normally less than long, have six or fewer abdominal segments, and possess a tubular
Members of the Collembola are normally less than long, have six or fewer abdominal segments, and possess a tubular

 In sheer numbers, they are reputed to be one of the most abundant of all macroscopic animals, with estimates of 100,000 individuals per square meter of ground, essentially everywhere on Earth where soil and related habitats (
In sheer numbers, they are reputed to be one of the most abundant of all macroscopic animals, with estimates of 100,000 individuals per square meter of ground, essentially everywhere on Earth where soil and related habitats (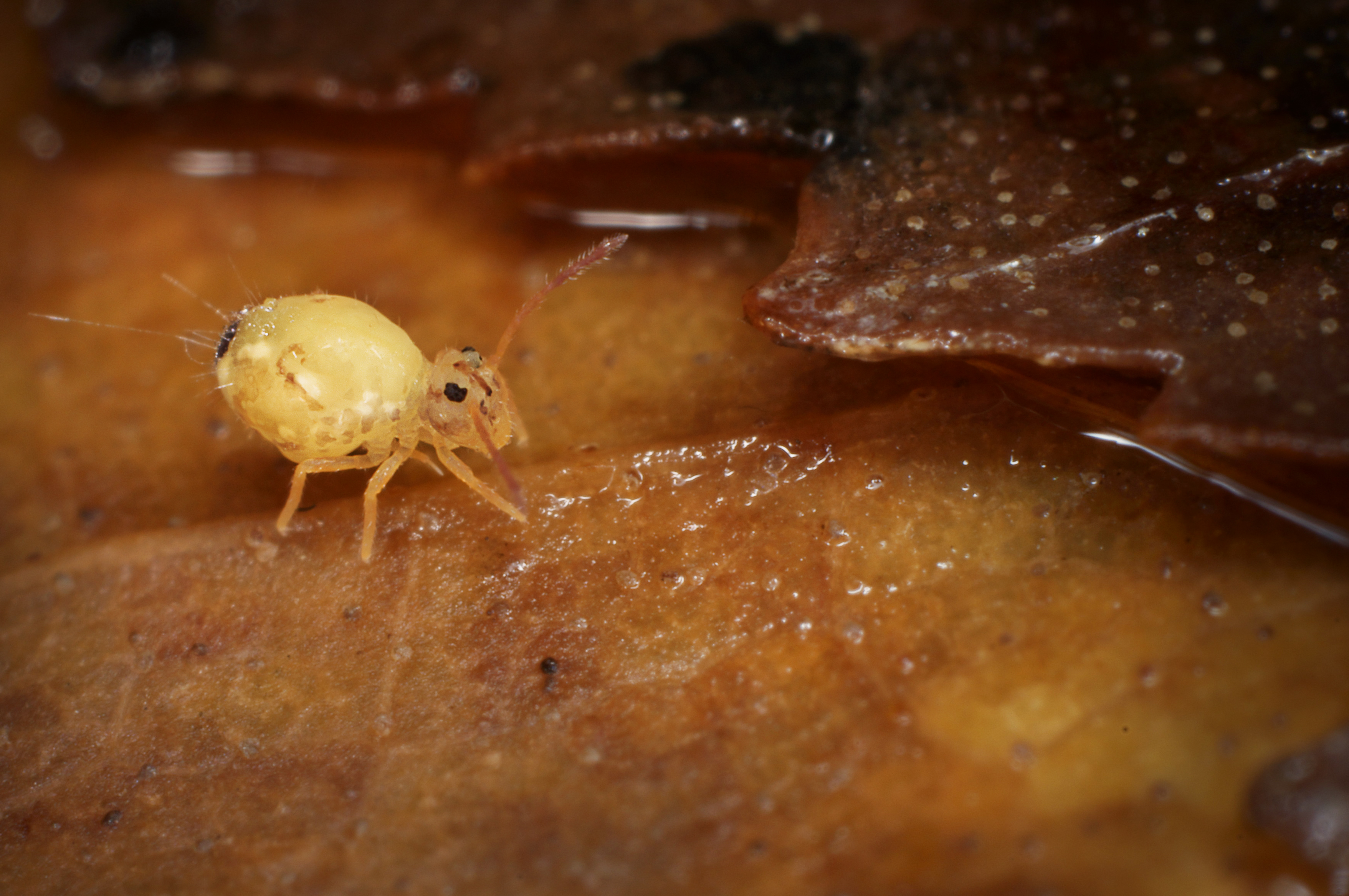 As a group, springtails are highly sensitive to
As a group, springtails are highly sensitive to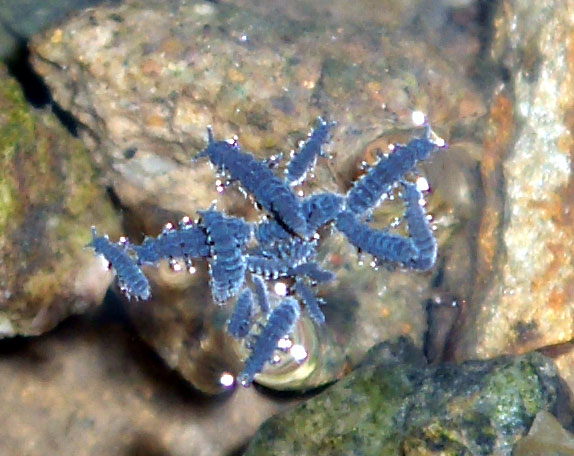  The horizontal distribution of springtail species is affected by environmental factors which act at the landscape scale, such as soil
The horizontal distribution of springtail species is affected by environmental factors which act at the landscape scale, such as soil
 Springtails are well known as
Springtails are well known as
Checklist of the Collembola of the World
Summary information about the distribution and ecology of Collembola (springtails) in the UK and Ireland
A small lecture from Steve Hopkin
* ttp://collembola.co.za/ Collembola species currently recorded from South Africa {{Authority control Articles containing video clips Extant Early Devonian first appearances Taxa named by John Lubbock, 1st Baron Avebury
insect
Insects (from Latin ') are pancrustacean hexapod invertebrates of the class Insecta. They are the largest group within the arthropod phylum. Insects have a chitinous exoskeleton, a three-part body (head, thorax and abdomen), three pairs ...
s (the other two are the Protura and Diplura). Although the three orders are sometimes grouped together in a class called Entognatha
The Entognatha are a class of wingless and ametabolous arthropods, which, together with the insects, makes up the subphylum Hexapoda. Their mouthparts are entognathous, meaning that they are retracted within the head, unlike the insects. Entog ...
because they have internal mouthparts
Mouthparts may refer to:
* The parts of a mouth
** Arthropod mouthparts
*** Insect mouthparts
{{disambig ...
, they do not appear to be any more closely related to one another than they are to all insects, which have external mouthparts.
Collembolans are omnivorous
An omnivore () is an animal that has the ability to eat and survive on both plant and animal matter. Obtaining energy and nutrients from plant and animal matter, omnivores digest carbohydrates, protein, fat, and fiber, and metabolize the nut ...
, free-living organisms that prefer moist conditions. They do not directly engage in the decomposition of organic matter, but contribute to it indirectly through the fragmentation of organic matter and the control of soil microbial communities. The word ''Collembola'' is from the ancient Greek "glue" and "peg"; this name was given due to the existence of the collophore, which was previously thought to stick to surfaces to stabilize the creature.
Some DNA sequence studies suggest that Collembola represent a separate evolutionary line from the other Hexapoda
The subphylum Hexapoda (from Greek for 'six legs') comprises most species of arthropods and includes the insects as well as three much smaller groups of wingless arthropods: Collembola, Protura, and Diplura (all of these were once considered in ...
, but others disagree; this seems to be caused by widely divergent patterns of molecular evolution
Molecular evolution is the process of change in the sequence composition of cell (biology), cellular molecules such as DNA, RNA, and proteins across generations. The field of molecular evolution uses principles of evolutionary biology and popula ...
among the arthropod
Arthropods (, (gen. ποδός)) are invertebrate animals with an exoskeleton, a Segmentation (biology), segmented body, and paired jointed appendages. Arthropods form the phylum Arthropoda. They are distinguished by their jointed limbs and Arth ...
s. The adjustments of traditional taxonomic rank
In biological classification, taxonomic rank is the relative level of a group of organisms (a taxon) in an ancestral or hereditary hierarchy. A common system consists of species, genus, family, order, class, phylum, kingdom, domain. While ol ...
for springtails reflects the occasional incompatibility of traditional groupings with modern cladistics
Cladistics (; ) is an approach to biological classification in which organisms are categorized in groups (" clades") based on hypotheses of most recent common ancestry. The evidence for hypothesized relationships is typically shared derived ch ...
: when they were included with the insects, they were ranked as an order
Order, ORDER or Orders may refer to:
* Categorization, the process in which ideas and objects are recognized, differentiated, and understood
* Heterarchy, a system of organization wherein the elements have the potential to be ranked a number of d ...
; as part of the Entognatha, they are ranked as a subclass. If they are considered a basal
Basal or basilar is a term meaning ''base'', ''bottom'', or ''minimum''.
Science
* Basal (anatomy), an anatomical term of location for features associated with the base of an organism or structure
* Basal (medicine), a minimal level that is nec ...
lineage of Hexapoda, they are elevated to full class status.
Morphology
 Members of the Collembola are normally less than long, have six or fewer abdominal segments, and possess a tubular
Members of the Collembola are normally less than long, have six or fewer abdominal segments, and possess a tubular appendage
An appendage (or outgrowth) is an external body part, or natural prolongation, that protrudes from an organism's body.
In arthropods, an appendage refers to any of the homologous body parts that may extend from a body segment, including ant ...
(the collophore or ventral tube) with reversible, sticky vesicles, projecting ventrally from the first abdominal segment. It is believed to be associated with fluid uptake and balance, excretion, and orientation of the organism itself. Most species have an abdominal, tail-like appendage known as a furcula
The (Latin for "little fork") or wishbone is a forked bone found in most birds and some species of non-avian dinosaurs, and is formed by the fusion of the two pink
clavicles. In birds, its primary function is in the strengthening of the Thorax, ...
. It is located on the fourth abdominal segment of collembolans and is folded beneath the body, held under tension by a small structure called the retinaculum (or tenaculum). When released, it snaps against the substrate, flinging the springtail into the air and allowing for rapid evasion and travel. All of this takes place in as little as 18 milliseconds.
Springtails also possess the ability to reduce their body size by as much as 30% through subsequent ecdyses
Ecdysis is the moulting of the cuticle in many invertebrates of the clade Ecdysozoa. Since the cuticle of these animals typically forms a largely inelastic exoskeleton, it is shed during growth and a new, larger covering is formed. The remnants ...
(molting) if temperatures rise high enough. The shrinkage is genetically controlled. Since warmer conditions increase metabolic rates and energy requirements in organisms, the reduction in body size is advantageous to their survival.
The Poduromorpha and Entomobryomorpha
The Entomobryomorpha are one of the three main groups (order) of springtails (Collembola), tiny hexapods related to insects. This group was formerly treated as a superfamily, the Entomobryoidea.
They can be best distinguished from the other ...
have an elongated body, while the Symphypleona and Neelipleona have a globular body. Collembola lack a tracheal respiration system, which forces them to respire through a porous cuticle, except for the two families Sminthuridae and Actaletidae, which exhibit a single pair of spiracles between the head and the thorax
The thorax or chest is a part of the anatomy of humans, mammals, and other tetrapod animals located between the neck and the abdomen. In insects, crustaceans, and the extinct trilobites, the thorax is one of the three main divisions of the ...
, leading to a rudimentary, although fully functional, tracheal system. The anatomical variance present between different species partially depends on soil morphology and composition. Surface-dwellers are generally larger, have darker pigments, have longer antennae and functioning furcula. Sub-surface-dwellers are usually unpigmented, have elongated bodies, and reduced furcula. They can be categorized into four main forms according to soil composition and depth: atmobiotic, epedaphic, hemiedaphic, and euedaphic. Atmobiotic species inhabit macrophytes and litter surfaces. They are generally 8-10 millimeters in length, pigmented, have long limbs, and a full set of ocelli (photoreceptors). Epedaphic species inhabit upper litter layers and fallen logs. They are slightly smaller and have less pronounced pigments, as well as less developed limbs and ocelli than the atmobiotic species. Hemiedaphic species inhabit the lower litter layers of decomposing organic material. They are 1-2 millimeters in length, have dispersed pigmentation, shortened limbs, and a reduced number of ocelli. Euedaphic species inhabit upper mineral layers known as the humus horizon. They are smaller than hemiedaphic species; have soft, elongated bodies; lack pigmentation and ocelli; and have reduced or absent furca.
Poduromorphs inhabit the epedaphic, hemiedaphic, and euedaphic layers and are characterized by their elongated bodies and conspicuous segmentation – three thoracic segments, six abdominal segments, and a prothorax.
The digestive tract of collembolan species consists of three main components: the foregut, midgut, and hindgut. The midgut is surrounded by a network of muscles and lined with a monolayer of columnar or cuboidal cells. Its function is to mix and transport food from the lumen into the hindgut through contraction. Many species of syntrophic bacteria, archaea, and fungi are present in the lumen. These different digestive regions have varying pH to support specific enzymatic activities and microbial populations. The anterior portion of the midgut and hindgut is slightly acidic (with a pH of approximately 6.0) while the posterior midgut portion is slightly alkaline (with a pH of approximately 8.0). Between the midgut and hindgut is an alimentary canal called the pyloric region, which is a muscular sphincter.
Systematics and evolution
Traditionally, the springtails were divided into theorders
Order, ORDER or Orders may refer to:
* Categorization, the process in which ideas and objects are recognized, differentiated, and understood
* Heterarchy, a system of organization wherein the elements have the potential to be ranked a number of ...
Arthropleona, Symphypleona, and occasionally also Neelipleona. The Arthropleona were divided into two superfamilies, the Entomobryoidea and the Poduroidea
Poduridae is a small family of stout-bodied springtails containing only the single genus ''Podura'', and making up the monotypic superfamily Poduroidea. The genus contains four species:
*'' Podura aquatica'' Linnaeus, 1758
*''Podura infernalis'' ...
. However, recent phylogenetic studies show Arthropleona is paraphyletic
In taxonomy (general), taxonomy, a group is paraphyletic if it consists of the group's most recent common ancestor, last common ancestor and most of its descendants, excluding a few Monophyly, monophyletic subgroups. The group is said to be pa ...
. Thus, the Arthropleona are abolished in modern classifications, and their superfamilies are raised in rank accordingly, being now orders Entomobryomorpha
The Entomobryomorpha are one of the three main groups (order) of springtails (Collembola), tiny hexapods related to insects. This group was formerly treated as a superfamily, the Entomobryoidea.
They can be best distinguished from the other ...
and the Poduromorpha. Technically, the Arthropleona are thus a partial junior synonym of the Collembola.
The term "Neopleona" is essentially synonymous with Symphypleona + Neelipleona. The Neelipleona was originally seen as a particularly advanced lineage of Symphypleona, based on the shared global body shape, but the global body of the Neelipleona is realized in a completely different way than in Symphypleona. Subsequently, the Neelipleona were considered as being derived from the Entomobryomorpha. Analysis of 18S and 28S rRNA
Ribosomal ribonucleic acid (rRNA) is a type of non-coding RNA which is the primary component of ribosomes, essential to all cells. rRNA is a ribozyme which carries out protein synthesis in ribosomes. Ribosomal RNA is transcribed from riboso ...
sequence
In mathematics, a sequence is an enumerated collection of objects in which repetitions are allowed and order matters. Like a set, it contains members (also called ''elements'', or ''terms''). The number of elements (possibly infinite) is called ...
data, though, suggests that they form the most ancient lineage of springtails, which would explain their peculiar apomorphies. This phylogenetic relationship was also confirmed using a phylogeny based on mtDNA
Mitochondrial DNA (mtDNA or mDNA) is the DNA located in mitochondrion, mitochondria, cellular organelles within eukaryotic cells that convert chemical energy from food into a form that cells can use, such as adenosine triphosphate (ATP). Mit ...
and whole-genome data.
The latest whole-genome phylogeny supporting four orders of collembola:
Springtails are attested to since the Early Devonian. The fossil from , '' Rhyniella praecursor'', is the oldest terrestrial arthropod, and was found in the famous Rhynie chert of Scotland
Scotland (, ) is a country that is part of the United Kingdom. Covering the northern third of the island of Great Britain, mainland Scotland has a border with England to the southeast and is otherwise surrounded by the Atlantic Ocean to th ...
. Given its morphology resembles extant species quite closely, the radiation of the Hexapoda
The subphylum Hexapoda (from Greek for 'six legs') comprises most species of arthropods and includes the insects as well as three much smaller groups of wingless arthropods: Collembola, Protura, and Diplura (all of these were once considered in ...
can be situated in the Silurian
The Silurian ( ) is a geologic period and system spanning 24.6 million years from the end of the Ordovician Period, at million years ago (Mya), to the beginning of the Devonian Period, Mya. The Silurian is the shortest period of the Paleozoi ...
, or more. Additional research concerning the coprolites (fossilized feces) of ancient collembolans allowed researchers to track their lineages back some 412 million years.
Fossil Collembola are rare. Instead, most are found in amber. Even these are rare and many amber deposits carry few or no collembola. The best deposits are from the early Eocene of Canada and Europe, Miocene of Central America, and the mid-Cretaceous of Burma and Canada. They display some unexplained characteristics: first, all but one of the fossils from the Cretaceous belong to extinct genera, whereas none of the specimens from the Eocene or the Miocene are of extinct genera; second, the species from Burma are more similar to the modern fauna of Canada than are the Canadian Cretaceous specimens.
There are about 3,600 different species.
Ecology
Eating behavior
Specific feeding strategies and mechanisms are employed to match specific niches. Herbivorous and detritivorous species fragment biological material present in soil and leaf litter, supporting decomposition and increasing the availability of nutrients for various species of microbes and fungi. Carnivorous species maintain populations of small invertebrates such as nematodes, rotifers, and other collembolan species. Springtails commonly consume fungal hyphae and spores, but also have been found to consume plant material and pollen, animal remains, colloidal materials, minerals and bacteria.Predators
Springtails are consumed by mesostigmatan mites in various families, includingAscidae
Ascidae is a family of mites in the order Mesostigmata.
Description
Ascidae are mites characterised by: seta ''st4'' usually on unsclerotised cuticle, peritrematic shield broadly connected to exopodal shield beside coxa IV, fixed chelicera ...
, Laelapidae
The Laelapidae are a family (biology), family of mites in the order Mesostigmata. The family is also referred to in the literature as Laelaptidae, which may be the correct spelling.
Description
Laelapidae have a shield covering all or most of ...
, Parasitidae, Rhodacaridae
Rhodacaridae is a family of mites in the order Mesostigmata.Walter, David Evans, edRhodacaridae Species Listing Biology Catalog. Texas A&M University. Retrieved on August 27, 2010.
Genera
* '' Afrodacarellus'' Hulbutt, 1974
* '' Afrogamasellus ...
and Veigaiidae.
Cave-dwelling springtails are a food source for spiders
Spiders (order Araneae) are air-breathing arthropods that have eight legs, chelicerae with fangs generally able to inject venom, and spinnerets that extrude silk. They are the largest order of arachnids and rank seventh in total species di ...
and harvestmen
The Opiliones (formerly Phalangida) are an Order (biology), order of arachnids Common name, colloquially known as harvestmen, harvesters, harvest spiders, or daddy longlegs. , over 6,650 species of harvestmen have been discovered worldwide, alth ...
in the same environment, such as the endangered harvestman '' Texella reyesi''.
Distribution
Springtails are cryptozoa frequently found inleaf litter
Plant litter (also leaf litter, tree litter, soil litter, litterfall or duff) is dead plant material (such as leaves, bark, needles, twigs, and cladodes) that have fallen to the ground. This detritus or dead organic material and its constituent ...
and other decaying material, where they are primarily detritivores and microbivores, and one of the main biological agents responsible for the control and the dissemination of soil microorganism
A microorganism, or microbe,, ''mikros'', "small") and ''organism'' from the el, ὀργανισμός, ''organismós'', "organism"). It is usually written as a single word but is sometimes hyphenated (''micro-organism''), especially in olde ...
s. In a mature deciduous woodland in temperate climate, leaf litter and vegetation typically support 30 to 40 species of springtails, and in the tropics the number may be over 100.
 In sheer numbers, they are reputed to be one of the most abundant of all macroscopic animals, with estimates of 100,000 individuals per square meter of ground, essentially everywhere on Earth where soil and related habitats (
In sheer numbers, they are reputed to be one of the most abundant of all macroscopic animals, with estimates of 100,000 individuals per square meter of ground, essentially everywhere on Earth where soil and related habitats (moss
Mosses are small, non-vascular flowerless plants in the taxonomic division Bryophyta (, ) '' sensu stricto''. Bryophyta ('' sensu lato'', Schimp. 1879) may also refer to the parent group bryophytes, which comprise liverworts, mosses, and ...
cushions, fallen wood
Wood is a porous and fibrous structural tissue found in the stems and roots of trees and other woody plants. It is an organic materiala natural composite of cellulose fibers that are strong in tension and embedded in a matrix of ligni ...
, grass
Poaceae () or Gramineae () is a large and nearly ubiquitous family of monocotyledonous flowering plants commonly known as grasses. It includes the cereal grasses, bamboos and the grasses of natural grassland and species cultivated in law ...
tufts, ant and termite
Termites are small insects that live in colonies and have distinct castes ( eusocial) and feed on wood or other dead plant matter. Termites comprise the infraorder Isoptera, or alternatively the epifamily Termitoidae, within the order Blat ...
nests) occur. Only nematodes, crustacean
Crustaceans (Crustacea, ) form a large, diverse arthropod taxon which includes such animals as decapods, seed shrimp, branchiopods, fish lice, krill, remipedes, isopods, barnacles, copepods, amphipods and mantis shrimp. The crustacean gro ...
s, and mite
Mites are small arachnids (eight-legged arthropods). Mites span two large orders of arachnids, the Acariformes and the Parasitiformes, which were historically grouped together in the subclass Acari, but genetic analysis does not show clear evid ...
s are likely to have global populations of similar magnitude, and each of those groups except mites is more inclusive: though taxonomic rank cannot be used for absolute comparisons, it is notable that nematodes are a phylum
In biology, a phylum (; plural: phyla) is a level of classification or taxonomic rank below kingdom and above class. Traditionally, in botany the term division has been used instead of phylum, although the International Code of Nomenclatu ...
and crustaceans a subphylum
In zoological nomenclature, a subphylum is a taxonomic rank below the rank of phylum.
The taxonomic rank of " subdivision" in fungi and plant taxonomy is equivalent to "subphylum" in zoological taxonomy. Some plant taxonomists have also used t ...
. Most springtails are small and difficult to see by casual observation, but one springtail, the so-called snow flea ('' Hypogastrura nivicola''), is readily observed on warm winter days when it is active and its dark color contrasts sharply with a background of snow.
In addition, a few species routinely climb trees and form a dominant component of canopy faunas, where they may be collected by beating or insecticide fogging. These tend to be the larger (>2 mm) species, mainly in the genera ''Entomobrya
''Entomobrya'' is a genus of slender springtails in the family Entomobryidae
Entomobryidae, sometimes called "slender springtails", is a family of springtails characterised by having an enlarged fourth abdominal segmentation (biology), segme ...
'' and ''Orchesella
''Orchesella'' is a genus of springtails belonging to the family Entomobryidae. This genus includes springtails with subdivided basal antennal segments.
Species
These 96 species belong to the genus ''Orchesella'':
* '' Orchesella adriatica'' S ...
'', though the densities on a per square meter basis are typically 1–2 orders of magnitude lower than soil populations of the same species. In temperate regions, a few species (e.g. ''Anurophorus
''Anurophorus'' is a genus of Collembola belonging to the family Isotomidae
Isotomidae is a family of elongate-bodied springtails in the order Entomobryomorpha.
Genera
These 109 genera belong to the family Isotomidae:
* '' Aackia'' Yosii, 19 ...
'' spp., ''Entomobrya albocincta'', ''Xenylla xavieri
''Xenylla littoralis'', northeast coast of Tasmania
''Xenylla'' is a genus of springtails and allies in the family Hypogastruridae
Hypogastruridae is a family of springtails. Members of the family are common and widespread with a cosmopolitan ...
'', ''Hypogastrura arborea
''Hypogastrura'' is a genus of springtails and allies in the family Hypogastruridae. There are at least 150 described species in the genus. Their name means ‘lack of a stomach tail’.
See also
* List of Hypogastrura species
References
...
'') are almost exclusively arboreal. In tropical regions a single square meter of canopy habitat can support many species of Collembola.
The main ecological factor driving the local distribution of species is the vertical stratification of the environment: in woodland
A woodland () is, in the broad sense, land covered with trees, or in a narrow sense, synonymous with wood (or in the U.S., the '' plurale tantum'' woods), a low-density forest forming open habitats with plenty of sunlight and limited shade (see ...
a continuous change in species assemblages can be observed from tree canopies to ground vegetation
Vegetation is an assemblage of plant species and the ground cover they provide. It is a general term, without specific reference to particular taxa, life forms, structure, spatial extent, or any other specific botanical or geographic charact ...
then to plant litter
Plant litter (also leaf litter, tree litter, soil litter, litterfall or duff) is dead plant material (such as leaves, bark, needles, twigs, and cladodes) that have fallen to the ground. This detritus or dead organic material and its constitue ...
down to deeper soil horizon
A soil horizon is a layer parallel to the soil surface whose physical, chemical and biological characteristics differ from the layers above and beneath. Horizons are defined in many cases by obvious physical features, mainly colour and texture. ...
s. This is a complex factor embracing both nutritional
Nutrition is the biochemical and physiological process by which an organism uses food to support its life. It provides organisms with nutrients, which can be metabolized to create energy and chemical structures. Failure to obtain sufficient ...
and physiological
Physiology (; ) is the scientific study of functions and mechanisms in a living system. As a sub-discipline of biology, physiology focuses on how organisms, organ systems, individual organs, cells, and biomolecules carry out the chemica ...
requirements, together with behavioural trends, dispersal limitation and probable species interactions. Some species have been shown to exhibit negative or positive gravitropism
Gravitropism (also known as geotropism) is a coordinated process of differential growth by a plant in response to gravity pulling on it. It also occurs in fungi. Gravity can be either "artificial gravity" or natural gravity. It is a general feat ...
, which adds a behavioural dimension to this still poorly understood vertical segregation. Experiments with peat samples turned upside down showed two types of responses to disturbance of this vertical gradient, called "stayers" and "movers".
 As a group, springtails are highly sensitive to
As a group, springtails are highly sensitive to desiccation
Desiccation () is the state of extreme dryness, or the process of extreme drying. A desiccant is a hygroscopic (attracts and holds water) substance that induces or sustains such a state in its local vicinity in a moderately sealed container. ...
, because of their tegumentary respiration, although some species with thin, permeable cuticles have been shown to resist severe drought by regulating the osmotic pressure of their body fluid. The gregarious behaviour of Collembola, mostly driven by the attractive power of pheromones
A pheromone () is a secreted or excreted chemical factor that triggers a social response in members of the same species. Pheromones are chemicals capable of acting like hormones outside the body of the secreting individual, to affect the behavi ...
excreted by adults, gives more chance to every juvenile or adult individual to find suitable, better protected places, where desiccation could be avoided and reproduction
Reproduction (or procreation or breeding) is the biological process by which new individual organisms – " offspring" – are produced from their "parent" or parents. Reproduction is a fundamental feature of all known life; each individual o ...
and survival rates (thereby fitness) could be kept at an optimum. Sensitivity to drought varies from species to species and increases during ecdysis
Ecdysis is the moulting of the cuticle in many invertebrates of the clade Ecdysozoa. Since the cuticle of these animals typically forms a largely inelastic exoskeleton, it is shed during growth and a new, larger covering is formed. The remnan ...
. Given that springtails moult
In biology, moulting (British English), or molting (American English), also known as sloughing, shedding, or in many invertebrates, ecdysis, is the manner in which an animal routinely casts off a part of its body (often, but not always, an outer ...
repeatedly during their entire life (an ancestral
An ancestor, also known as a forefather, fore-elder or a forebear, is a parent or ( recursively) the parent of an antecedent (i.e., a grandparent, great-grandparent, great-great-grandparent and so forth). ''Ancestor'' is "any person from w ...
character in Hexapoda
The subphylum Hexapoda (from Greek for 'six legs') comprises most species of arthropods and includes the insects as well as three much smaller groups of wingless arthropods: Collembola, Protura, and Diplura (all of these were once considered in ...
) they spend much time in concealed micro-sites where they can find protection against desiccation
Desiccation () is the state of extreme dryness, or the process of extreme drying. A desiccant is a hygroscopic (attracts and holds water) substance that induces or sustains such a state in its local vicinity in a moderately sealed container. ...
and predation
Predation is a biological interaction
In ecology, a biological interaction is the effect that a pair of organisms living together in a community have on each other. They can be either of the same species (intraspecific interactions), or o ...
during ecdysis, an advantage reinforced by synchronized moulting. The high humidity environment of many caves also favours springtails and there are numerous cave adapted species, including one, '' Plutomurus ortobalaganensis'' living down the Krubera Cave.
 The horizontal distribution of springtail species is affected by environmental factors which act at the landscape scale, such as soil
The horizontal distribution of springtail species is affected by environmental factors which act at the landscape scale, such as soil acidity
In computer science, ACID ( atomicity, consistency, isolation, durability) is a set of properties of database transactions intended to guarantee data validity despite errors, power failures, and other mishaps. In the context of databases, a sequ ...
, moisture
Moisture is the presence of a liquid, especially water, often in trace amounts. Small amounts of water may be found, for example, in the air (humidity), in foods, and in some commercial products. Moisture also refers to the amount of water vapo ...
and light
Light or visible light is electromagnetic radiation that can be perceived by the human eye. Visible light is usually defined as having wavelengths in the range of 400–700 nanometres (nm), corresponding to frequencies of 750–420 te ...
. Requirements for pH can be reconstructed experimentally. Altitudinal changes in species distribution can be at least partly explained by increased acidity at higher elevation. Moisture requirements, among other ecological and behavioural factors, explain why some species cannot live aboveground, or retreat in the soil during dry seasons, but also why some epigeal
Epigeal, epigean, epigeic and epigeous are biological terms describing an organism's activity above the soil surface.
In botany, a seed is described as showing epigeal germination when the cotyledons of the germinating seed expand, throw off th ...
springtails are always found in the vicinity of ponds and lakes, such as the hygrophilous ''Isotomurus palustris
''Isotomurus palustris'', the marsh springtail, is a species of elongate-bodied springtail in the family Isotomidae
Isotomidae is a family of elongate-bodied springtails in the order Entomobryomorpha.
Genera
These 109 genera belong to the fam ...
''. Adaptive features, such as the presence of a fan-like wettable mucro, allow some species to move at the surface of water ('' Sminthurides aquaticus'', ''Sminthurides malmgreni
''Sminthurides'' is a genus of globular springtails in the family Sminthurididae. There are more than 30 described species in ''Sminthurides''.
Species
These 32 species belong to the genus ''Sminthurides'':
* '' Sminthurides annulicornis'' Axe ...
''). ''Podura aquatica
''Podura aquatica'', the water springtail, is a species of springtail, one of only four described species in the family Poduridae. It is an abundant species with a Holarctic distribution.
As its common and scientific names suggest, this is an ex ...
'', a unique representative of the family Poduridae (and one of the first springtails to have been described by Carl Linnaeus
Carl Linnaeus (; 23 May 1707 – 10 January 1778), also known after his ennoblement in 1761 as Carl von Linné Blunt (2004), p. 171. (), was a Swedish botanist, zoologist, taxonomist, and physician who formalised binomial nomenclature, ...
), spends its entire life at the surface of water, its wettable eggs dropping in water until the non-wettable first instar hatches then surfaces.
In a variegated landscape, made of a patchwork of closed (woodland
A woodland () is, in the broad sense, land covered with trees, or in a narrow sense, synonymous with wood (or in the U.S., the '' plurale tantum'' woods), a low-density forest forming open habitats with plenty of sunlight and limited shade (see ...
) and open (meadow
A meadow ( ) is an open habitat, or field, vegetated by grasses, herbs, and other non- woody plants. Trees or shrubs may sparsely populate meadows, as long as these areas maintain an open character. Meadows may be naturally occurring or artif ...
s, cereal crops) environments, most soil
Soil, also commonly referred to as earth or dirt, is a mixture of organic matter, minerals, gases, liquids, and organisms that together support life. Some scientific definitions distinguish ''dirt'' from ''soil'' by restricting the former ...
-dwelling species are not specialized and can be found everywhere, but most epigeal
Epigeal, epigean, epigeic and epigeous are biological terms describing an organism's activity above the soil surface.
In botany, a seed is described as showing epigeal germination when the cotyledons of the germinating seed expand, throw off th ...
and litter
Litter consists of waste products that have been discarded incorrectly, without consent, at an unsuitable location. Litter can also be used as a verb; to litter means to drop and leave objects, often man-made, such as aluminum cans, paper cups ...
-dwelling species are attracted to a particular environment, either forested or not. As a consequence of dispersal limitation, landuse change, when too rapid, may cause the local disappearance of slow-moving, specialist species
A generalist species is able to thrive in a wide variety of environmental conditions and can make use of a variety of different resources (for example, a heterotroph with a varied diet). A specialist species can thrive only in a narrow range of env ...
, a phenomenon the measure of which has been called colonisation credit.
Relationship with humans
 Springtails are well known as
Springtails are well known as pests
PESTS was an anonymous American activist group formed in 1986 to critique racism, tokenism, and exclusion in the art world. PESTS produced newsletters, posters, and other print material highlighting examples of discrimination in gallery represent ...
of some agricultural crops. '' Sminthurus viridis'', the lucerne flea, has been shown to cause severe damage to agricultural crops, and is considered as a pest in Australia. Onychiuridae are also known to feed on tubers and to damage them to some extent. However, by their capacity to carry spores of mycorrhizal fungi and mycorrhiza helper bacteria
Mycorrhiza helper bacteria (MHB) are a group of organisms that form symbiotic associations with both ectomycorrhiza and arbuscular mycorrhiza. MHBs are diverse and belong to a wide variety of bacterial phyla including both Gram-negative and Gram ...
on their tegument, soil springtails play a positive role in the establishment of plant-fungal symbioses
Symbiosis (from Greek , , "living together", from , , "together", and , bíōsis, "living") is any type of a close and long-term biological interaction between two different biological organisms, be it mutualistic, commensalistic, or parasit ...
and thus are beneficial to agriculture. They also contribute to controlling plant fungal diseases through their active consumption of mycelia and spores
In biology, a spore is a unit of sexual or asexual reproduction that may be adapted for dispersal and for survival, often for extended periods of time, in unfavourable conditions. Spores form part of the life cycles of many plants, algae, ...
of damping-off and pathogenic fungi. It has been suggested that they could be reared to be used for the control of pathogenic fungi in greenhouses and other indoor cultures.
Various sources and publications have suggested that some springtails may parasitize
Parasitism is a close relationship between species, where one organism, the parasite, lives on or inside another organism, the host, causing it some harm, and is adapted structurally to this way of life. The entomologist E. O. Wilson has c ...
humans, but this is entirely inconsistent with their biology, and no such phenomenon has ever been scientifically confirmed, though it has been documented that the scales or hairs from collembolans can cause irritation when rubbed onto the skin. They may sometimes be abundant indoors in damp places such as bathrooms and basements, and incidentally found on one's person. More often, claims of persistent human skin infection by springtails may indicate a neurological problem, such as delusional parasitosis, a psychological rather than entomological problem. Researchers themselves may be subject to psychological phenomena. For example, a publication in 2004 claiming that springtails had been found in skin samples was later determined to be a case of pareidolia
Pareidolia (; ) is the tendency for perception to impose a meaningful interpretation on a nebulous stimulus, usually visual, so that one sees an object, pattern, or meaning where there is none.
Common examples are perceived images of animals, ...
; that is, no springtail specimens were actually recovered, but the researchers had digitally enhanced photos of sample debris to create images resembling small arthropod heads, which then were claimed to be springtail remnants. However, Steve Hopkin reports one instance of an entomologist aspirating an '' Isotoma'' species and in the process accidentally inhaling some of their eggs, which hatched in his nasal cavity and made him quite ill until they were flushed out.
In 1952, China accused the United States
The United States of America (U.S.A. or USA), commonly known as the United States (U.S. or US) or America, is a country primarily located in North America. It consists of 50 U.S. state, states, a Washington, D.C., federal district, five ma ...
military of spreading bacteria-laden insects and other objects during the Korean War
{{Infobox military conflict
, conflict = Korean War
, partof = the Cold War and the Korean conflict
, image = Korean War Montage 2.png
, image_size = 300px
, caption = Clockwise from top: ...
by dropping them from P-51 fighters above rebel villages over North Korea
North Korea, officially the Democratic People's Republic of Korea (DPRK), is a country in East Asia. It constitutes the northern half of the Korean Peninsula and shares borders with China and Russia to the north, at the Yalu (Amnok) and ...
. In all, the U.S. was accused of dropping ants, beetles, crickets, fleas, flies, grasshoppers, lice, springtails, and stoneflies as part of a biological warfare
Biological warfare, also known as germ warfare, is the use of biological toxins or infectious agents such as bacteria, viruses, insects, and fungi with the intent to kill, harm or incapacitate humans, animals or plants as an act of war. ...
effort. The alleged associated diseases included anthrax
Anthrax is an infection caused by the bacterium '' Bacillus anthracis''. It can occur in four forms: skin, lungs, intestinal, and injection. Symptom onset occurs between one day and more than two months after the infection is contracted. The s ...
, cholera, dysentery
Dysentery (UK pronunciation: , US: ), historically known as the bloody flux, is a type of gastroenteritis that results in bloody diarrhea. Other symptoms may include fever, abdominal pain, and a feeling of incomplete defecation. Complication ...
, fowl septicemia, paratyphoid, plague, scrub typhus, small pox
Smallpox was an infectious disease caused by variola virus (often called smallpox virus) which belongs to the genus Orthopoxvirus. The last naturally occurring case was diagnosed in October 1977, and the World Health Organization (WHO) ce ...
, and typhoid
Typhoid fever, also known as typhoid, is a disease caused by '' Salmonella'' serotype Typhi bacteria. Symptoms vary from mild to severe, and usually begin six to 30 days after exposure. Often there is a gradual onset of a high fever over several ...
. China created an international scientific commission for investigating possible bacterial warfare, eventually ruling that the United States probably did engage in limited biological warfare in Korea. The US government
The federal government of the United States (U.S. federal government or U.S. government) is the national government of the United States, a federal republic located primarily in North America, composed of 50 states, a city within a feder ...
denied all the allegations, and instead proposed that the United Nations send a formal inquiry committee to China and Korea, but China and Korea refused to cooperate. U.S. and Canadian entomologists further claimed that the accusations were ridiculous and argued that anomalous appearances of insects could be explained through natural phenomena. Springtail species cited in allegations of biological warfare in the Korean War were ''Isotoma (Desoria) negishina'' (a local species) and the "white rat springtail" '' Folsomia candida''.
Captive springtails are often kept in a terrarium as part of a clean-up crew.
Ecotoxicology laboratory animals
Springtails are currently used in laboratory tests for the early detection of soil pollution. Acute and chronic toxicity tests have been performed by researchers, mostly using theparthenogenetic
Parthenogenesis (; from the Greek grc, παρθένος, translit=parthénos, lit=virgin, label=none + grc, γένεσις, translit=génesis, lit=creation, label=none) is a natural form of asexual reproduction in which growth and developmen ...
isotomid
Isotomidae is a family of elongate-bodied springtails in the order Entomobryomorpha.
Genera
These 109 genera belong to the family Isotomidae:
* '' Aackia'' Yosii, 1966
* '' Acanthomurus'' Womersley, 1934
* '' Aggressopygus'' Potapov & Babenko, ...
''Folsomia candida''. These tests have been standardized. Details on a ringtest {{unreferenced, date=October 2010
A ringtest for quality management is part of an external quality assurance programme for a measuring method. Ringtest is also called proficiency test or interlaboratory test. Usually a reference institute sends ide ...
, on the biology and ecotoxicology of ''Folsomia candida'' and comparison with the sexual nearby species ''Folsomia fimetaria'' (sometimes preferred to ''Folsomia candida'') are given in a document written by Paul Henning Krogh. Care should be taken that different strains of the same species may be conducive to different results. Avoidance tests have been also performed. They have been standardized, too. Avoidance tests are complementary to toxicity tests, but they also offer several advantages: they are more rapid (thus cheaper), more sensitive and they are environmentally more reliable, because in the real world Collembola move actively far from pollution spots. It may be hypothesized that the soil could become locally depauperated in animals (and thus improper to normal use) while below thresholds of toxicity. Contrary to earthworm
An earthworm is a terrestrial invertebrate that belongs to the phylum Annelida. They exhibit a tube-within-a-tube body plan; they are externally segmented with corresponding internal segmentation; and they usually have setae on all segments. ...
s, and like many insects and molluscs, Collembola are very sensitive to herbicides and thus are threatened in no-tillage agriculture, which makes a more intense use of herbicides than conventional agriculture.
The springtail '' Folsomia candida'' is also becoming a genomic model organism for soil toxicology. With microarray
A microarray is a multiplex lab-on-a-chip. Its purpose is to simultaneously detect the expression of thousands of genes from a sample (e.g. from a tissue). It is a two-dimensional array on a solid substrate—usually a glass slide or silic ...
technology the expression of thousands of genes can be measured in parallel. The gene expression profiles of ''Folsomia candida'' exposed to environmental toxicants allow fast and sensitive detection of pollution, and additionally clarifies molecular mechanisms causing toxicology.
Collembola have been found to be useful as bio-indicators of soil quality. Laboratory studies have been conducted that validated that the jumping ability of springtails can be used to evaluate the soil quality of Cu- and Ni-polluted sites.
Climate warming impact
In polar regions that are expected to experience among the most rapid impact from climate warming, springtails have shown contrasting responses to warming in experimental warming studies. There are negative, positive and neutral responses reported. Neutral responses to experimental warming have also been reported in studies of non-polar regions. The importance of soil moisture has been demonstrated in experiments using infrared heating in an alpine meadow, which had a negative effect on mesofauna biomass and diversity in drier parts and a positive effect in moist sub-areas. Furthermore, a study with 20 years of experimental warming in three contrasting plant communities found that small scale heterogeneity may buffer springtails to potential climate warming.Reproduction
Sexual reproduction
Sexual reproduction is a type of reproduction that involves a complex life cycle in which a gamete ( haploid reproductive cells, such as a sperm or egg cell) with a single set of chromosomes combines with another gamete to produce a zygote th ...
occurs through the clustered or scattered deposition of spermatophores by male
Male (Mars symbol, symbol: ♂) is the sex of an organism that produces the gamete (sex cell) known as sperm, which fuses with the larger female gamete, or ovum, in the process of fertilization.
A male organism cannot sexual reproduction, repro ...
adults. Stimulation of spermatophore deposition by female pheromones
A pheromone () is a secreted or excreted chemical factor that triggers a social response in members of the same species. Pheromones are chemicals capable of acting like hormones outside the body of the secreting individual, to affect the behavi ...
has been demonstrated in ''Sinella curviseta
''Sinella curviseta'' is a species of slender springtail in the family Entomobryidae
Entomobryidae, sometimes called "slender springtails", is a family of springtails characterised by having an enlarged fourth abdominal segmentation (biolog ...
''. Mating behavior can be observed in Symphypleona. Among Symphypleona, males of some Sminthuridae use a clasping organ located on their antenna. Many collembolan species, mostly those living in deeper soil horizons, are parthenogenetic, which favors reproduction
Reproduction (or procreation or breeding) is the biological process by which new individual organisms – " offspring" – are produced from their "parent" or parents. Reproduction is a fundamental feature of all known life; each individual o ...
to the detriment of genetic diversity
Genetic diversity is the total number of Genetics, genetic characteristics in the genetic makeup of a species, it ranges widely from the number of species to differences within species and can be attributed to the span of survival for a species. ...
and thereby to population
Population typically refers to the number of people in a single area, whether it be a city or town, region, country, continent, or the world. Governments typically quantify the size of the resident population within their jurisdiction using ...
tolerance of environmental hazards. Parthenogenesis
Parthenogenesis (; from the Greek grc, παρθένος, translit=parthénos, lit=virgin, label=none + grc, γένεσις, translit=génesis, lit=creation, label=none) is a natural form of asexual reproduction in which growth and developmen ...
(also called thelytoky) is under the control of symbiotic bacteria
Bacteria (; singular: bacterium) are ubiquitous, mostly free-living organisms often consisting of one biological cell. They constitute a large domain of prokaryotic microorganisms. Typically a few micrometres in length, bacteria were am ...
of the genus ''Wolbachia
''Wolbachia'' is a genus of intracellular bacteria that infects mainly arthropod species, including a high proportion of insects, and also some nematodes. It is one of the most common parasitic microbes, and is possibly the most common repro ...
'', which live, reproduce and are carried in female reproductive organs and eggs of Collembola. Feminizing ''Wolbachia
''Wolbachia'' is a genus of intracellular bacteria that infects mainly arthropod species, including a high proportion of insects, and also some nematodes. It is one of the most common parasitic microbes, and is possibly the most common repro ...
'' species are widespread in arthropod
Arthropods (, (gen. ποδός)) are invertebrate animals with an exoskeleton, a Segmentation (biology), segmented body, and paired jointed appendages. Arthropods form the phylum Arthropoda. They are distinguished by their jointed limbs and Arth ...
s and nematodes, where they co-evolved with most of their lineages.
See also
*Hexapoda
The subphylum Hexapoda (from Greek for 'six legs') comprises most species of arthropods and includes the insects as well as three much smaller groups of wingless arthropods: Collembola, Protura, and Diplura (all of these were once considered in ...
References
External links
*Checklist of the Collembola of the World
Summary information about the distribution and ecology of Collembola (springtails) in the UK and Ireland
A small lecture from Steve Hopkin
* ttp://collembola.co.za/ Collembola species currently recorded from South Africa {{Authority control Articles containing video clips Extant Early Devonian first appearances Taxa named by John Lubbock, 1st Baron Avebury