|
Anthedon (Palestine)
Anthedon (), also referred to as Al-Balakhiyya, was a Hellenistic city near Gaza. It was first mentioned by Josephus as a city conquered by Alexander Jannaeus alongside Raphia. Pompey removed it from Jewish rule during his conquest of Judaea. Gabinius re-founded and repopulated the city, and later, Augustus incorporated Anthedon into Herod's realm, along with other coastal cities. Herod renamed it ''Agrippias'' or ''Agrippeion'' in honor of Agrippa, but the name did not endure. Anthedon's status between Herod's death and the First Jewish–Roman War is uncertain, but it may have become imperial property, such as Iamnia. During the war, Jewish forces destroyed Anthedon along with Gaza and pillaged nearby villages, although it is possible that the city was not totally destroyed. Anthedon minted coins under Elagabalus and Severus Alexander, possibly also under Caracalla. Some suggest the city may have attained polis status during this period, but this remains speculative. In ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hellenistic Palestine
Hellenistic Palestine (320 BCE- 63 BCE) is the term for Palestine (region), historic Palestine during the Hellenistic period, when Achaemenid Syria was conquered by Alexander the Great in 333 BCE and subsumed into his growing Macedonian empire. After his death in 323 BCE, Alexander's empire was divided among his generals, the Diadochi, marking the beginning of Macedonian rule over various territories, including Coele-Syria. The region came under Ptolemaic dynasty, Ptolemaic rule beginning when Ptolemy I Soter took control of Egypt in 322 BCE and subsequently Yehud Medinata in 320 BCE due to its strategic significance. This period saw numerous conflicts as former generals vied for control, leading to ongoing power struggles and territorial exchanges. Ptolemaic rule brought initial stability and economic prosperity to the region. Ptolemy I and his successor, Ptolemy II Philadelphus, maintained control over Yehud Medinata, with the latter bringing the Ptolemaic dynasty to its zenith by ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sozomen
Salamanes Hermias Sozomenos (; ; c. 400 – c. 450 AD), also known as Sozomen, was a Roman lawyer and historian of the Christian Church. Family and home Sozoman was born around 400 in Bethelia, a small town near Gaza, into a wealthy Christian family of Palestine. He told the history of Southern Palestine derived from oral tradition. He appeared to be familiar with the region around Gaza, and mentioned having seen Bishop Zeno of Majuma, at the seaport of Gaza. Sozomen wrote that his grandfather lived at Bethelia, near Gaza, and became a Christian together with his household, probably under Constantius II. A neighbor named Alaphrion was miraculously healed by Saint Hilarion, who cast out a demon from Alaphrion, and, as eyewitnesses to the miracle, his family converted, along with Alaphrion's. The conversion marked a turning-point in the Christianization of southern Palestine, according to his account. The grandfather became within his own circle a highly esteemed interpret ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hellenistic Period
In classical antiquity, the Hellenistic period covers the time in Greek history after Classical Greece, between the death of Alexander the Great in 323 BC and the death of Cleopatra VII in 30 BC, which was followed by the ascendancy of the Roman Empire, as signified by the Battle of Actium in 31 BC and the Roman conquest of Ptolemaic Egypt the following year, which eliminated the last major Hellenistic kingdom. Its name stems from the Ancient Greek word ''Hellas'' (, ''Hellás''), which was gradually recognized as the name for Greece, from which the modern historiographical term ''Hellenistic'' was derived. The term "Hellenistic" is to be distinguished from "Hellenic" in that the latter refers to Greece itself, while the former encompasses all the ancient territories of the period that had come under significant Greek influence, particularly the Hellenized Middle East, after the conquests of Alexander the Great. After the Macedonian conquest of the Achaemenid Empire in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Byzantine Empire
The Byzantine Empire, also known as the Eastern Roman Empire, was the continuation of the Roman Empire centred on Constantinople during late antiquity and the Middle Ages. Having survived History of the Roman Empire, the events that caused the fall of the Western Roman Empire in the 5th centuryAD, it endured until the fall of Constantinople to the Ottoman Empire in 1453. The term 'Byzantine Empire' was coined only after its demise; its citizens used the term 'Roman Empire' and called themselves 'Romans'. During the early centuries of the Roman Empire, the western provinces were Romanization (cultural), Latinised, but the eastern parts kept their Hellenistic culture. Constantine the Great, Constantine I () legalised Christianity and moved the capital to Constantinople. Theodosius I, Theodosius I () made Christianity the state religion and Greek gradually replaced Latin for official use. The empire adopted a defensive strategy and, throughout its remaining history, expe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Iron Age
The Iron Age () is the final epoch of the three historical Metal Ages, after the Chalcolithic and Bronze Age. It has also been considered as the final age of the three-age division starting with prehistory (before recorded history) and progressing to protohistory (before written history). In this usage, it is preceded by the Stone Age (subdivided into the Paleolithic, Mesolithic and Neolithic) and Bronze Age. These concepts originated for describing Iron Age Europe and the ancient Near East. In the archaeology of the Americas, a five-period system is conventionally used instead; indigenous cultures there did not develop an iron economy in the pre-Columbian era, though some did work copper and bronze. Indigenous metalworking arrived in Australia with European contact. Although meteoric iron has been used for millennia in many regions, the beginning of the Iron Age is defined locally around the world by archaeological convention when the production of Smelting, smelted iron (espe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gaza Strip
The Gaza Strip, also known simply as Gaza, is a small territory located on the eastern coast of the Mediterranean Sea; it is the smaller of the two Palestinian territories, the other being the West Bank, that make up the State of Palestine. Inhabited by mostly Palestinian refugees and their descendants, Gaza is one of the List of countries and dependencies by population density, most densely populated territories in the world. An end of 2024 estimate puts the population of the Strip at 2.1 million, which was a 6% decline from the previous year due to the Gaza war. Gaza is bordered by Egypt on the southwest and Israel on the east and north. Its capital and largest city is Gaza City. The territorial boundaries were established while Gaza Administration of the Gaza Strip by Egypt, was controlled by the Kingdom of Egypt at the conclusion of the 1948 Arab–Israeli war. During that period the All-Palestine Protectorate, also known as All-Palestine, was established with limited reco ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
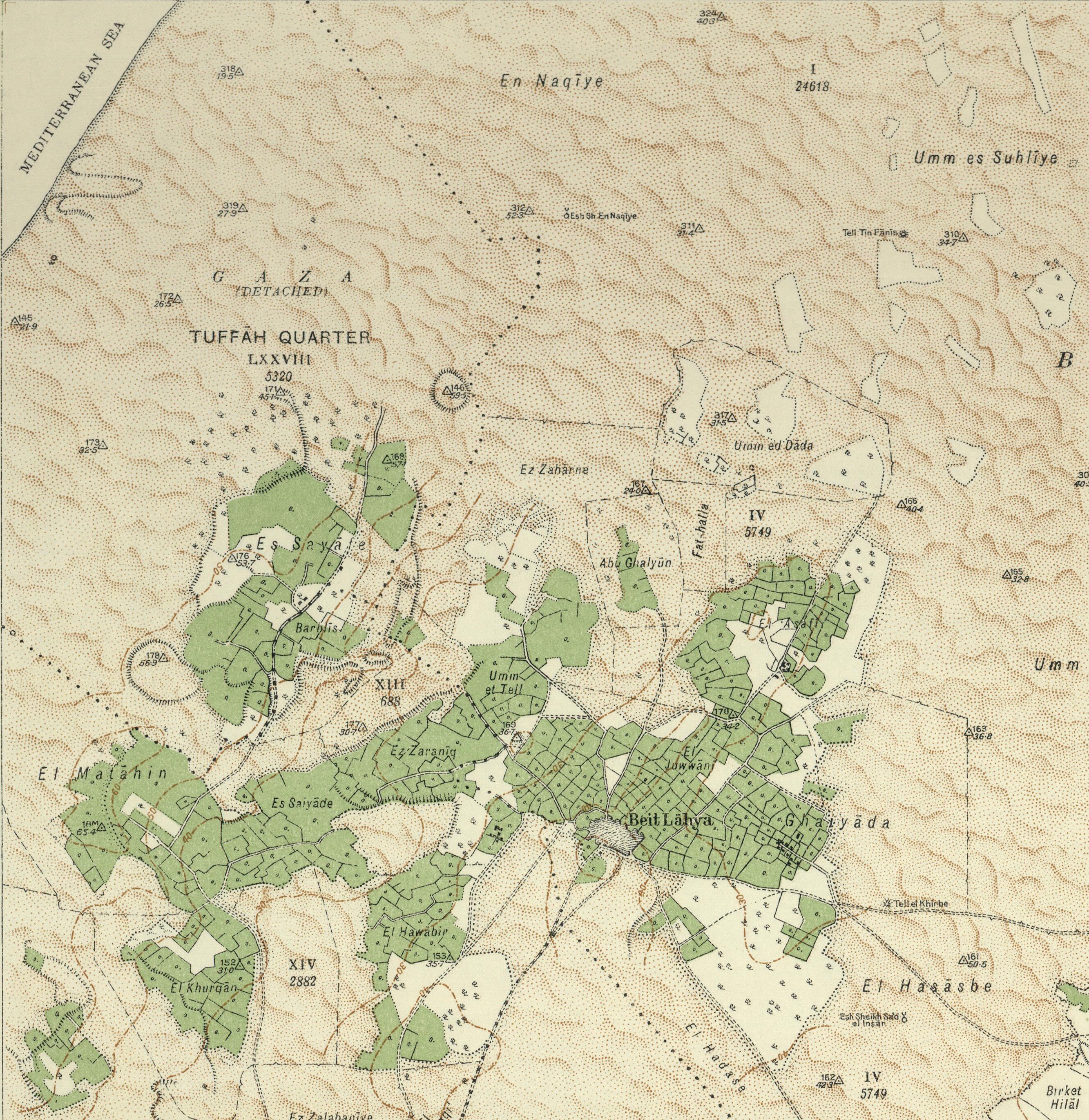
Beit Lahia
Beit Lahia or Beit Lahiya () is a city in the Gaza Strip, north of Jabalia, in the North Gaza Governorate of the State of Palestine. It sits next to Beit Hanoun and close to the border with Israel. According to the Palestinian Central Bureau of Statistics, the city had a population of 89,838 in 2017. Geography Beit Lahia is surrounded by dunes, some of which rise to above sea level. The area is renowned for its many large sycamore fig trees. The city is known for its fresh, sweet water, berries and citrus trees. According to Edward Henry Palmer, "Lahia" was from "Lahi", a personal name. History Roman period Beit Lahia has an ancient hill and nearby lay abandoned village ruins. The town has been identified as the ''Bethelia'' and had originally a pagan temple. According to the 5th century historian Sozomen, whose family had lived in the town for several generations, the townspeople started converting to Christianity due to the hermit Hilarion who is attributed to have hea ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Archaeological Site
An archaeological site is a place (or group of physical sites) in which evidence of past activity is preserved (either prehistoric or recorded history, historic or contemporary), and which has been, or may be, investigated using the discipline of archaeology and represents a part of the archaeological record. Sites may range from those with few or no remains visible above ground, to buildings and other structures still in use. Beyond this, the definition and geographical extent of a "site" can vary widely, depending on the period studied and the theoretical approach of the archaeologist. Geographical extent It is almost invariably difficult to delimit a site. It is sometimes taken to indicate a settlement of some sort, although the archaeologist must also define the limits of human activity around the settlement. Any episode of deposition, such as a hoard or burial, can form a site as well. Development-led archaeology undertaken as cultural resources management has the disad ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Council Of Jerusalem (536)
The Council of Jerusalem of 536 was a meeting of Chalcedonian representatives of the church of the Three Palestines (Palaestina Prima, Prima, Palaestina Secunda, Secunda, Palaestina Tertia, Tertia) to condemn certain persons accused of the Monophysite heresy. It was convoked at the initiative the Roman emperor Justinian I following the forced resignation of the Patriarch Anthimus I of Constantinople in February or March, an event in which Pope Agapetus I had played the main role. Following the Council of Constantinople (536), Council of Constantinople in May–June 536, Patriarch Menas of Constantinople wrote to Patriarch Peter of Jerusalem urging him to hold a council of the Three Palestines to condemn the same heretics as had Constantinople: Anthimus, Severus of Antioch, Zoora, Zaʿūra the Stylite and Peter of Apamea. The emperor also sent a letter. These letters were delivered by the monks of the Judaean Desert who had traveled to Constantinople to take part in the council there ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Council Of Chalcedon
The Council of Chalcedon (; ) was the fourth ecumenical council of the Christian Church. It was convoked by the Roman emperor Marcian. The council convened in the city of Chalcedon, Bithynia (modern-day Kadıköy, Istanbul, Turkey) from 8 October to 1 November 451. The council was attended by over 520 bishops or their representatives, making it the largest and best-documented of the first seven ecumenical councils. The principal purpose of the council was to re-assert the teachings of the ecumenical Council of Ephesus against the teachings of Eutyches and Nestorius. Such doctrines viewed Christ's divine and human natures as separate (Nestorianism) or viewed Christ as solely divine ( monophysitism). Agenda The ruling of the council stated: Whilst this judgment marked a significant turning point in the Christological debates, it also generated heated disagreements between the council and the Oriental Orthodox Church, who did not agree with such conduct or proceedings. Th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Council Of Ephesus
The Council of Ephesus was a council of Christian bishops convened in Ephesus (near present-day Selçuk in Turkey) in AD 431 by the Roman Emperor Theodosius II. This third ecumenical council, an effort to attain consensus in the church through an assembly representing all of Christendom, Richard Kieckhefer (1989). "Papacy". '' Dictionary of the Middle Ages''. . confirmed the original Nicene Creed, * * * and condemned the teachings of Nestorius, Patriarch of Constantinople, who preferred that the Virgin Mary be called '' Christotokos'', "Christ-bearer", over '' Theotokos'', "God-bearer"; in contrast to Cyril of Alexandria who deemed ''Theotokos'' to be enough on its own. It met from 22 June to 31 July 431 at the Church of Mary in Ephesus in Anatolia. Background Nestorius' doctrine, Nestorianism, which emphasized the distinction between Christ's human and divine natures and argued that Mary should preferably be called ''Christotokos'' (Christ-bearer) over ''Theotokos'' (G ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Synod
A synod () is a council of a Christian denomination, usually convened to decide an issue of doctrine, administration or application. The word '' synod'' comes from the Ancient Greek () ; the term is analogous with the Latin word . Originally, synods were meetings of bishops, and the word is still used in that sense in Catholicism, Oriental Orthodoxy and Eastern Orthodoxy. In modern usage, the word often refers to the governing body of a particular church, whether its members are meeting or not. It is also sometimes used to refer to a church that is governed by a synod. Sometimes the phrase "general synod" or "general council" refers to an ecumenical council. The word ''synod'' also refers to the standing council of high-ranking bishops governing some of the autocephalous Eastern Orthodox and Oriental Orthodox churches. Similarly, the day-to-day governance of patriarchal and major archiepiscopal Eastern Catholic Churches is entrusted to a permanent synod. Usages in diffe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |