|
Agorophiidae
''Agorophius'' is an extinct genus of toothed whale that lived during the Oligocene period, approximately , in the waters off what is now South Carolina. Taxonomy The holotype of ''Agorophius pygmaeus'', MCZ 8761, was first mentioned in an 1848 report on the geology of South Carolina by Michael Tuomey. It was eventually described as ''Zeuglodon pygmaeus'' by Johannes Peter Müller in 1849. Louis Agassiz coined the name ''Phocodon holmesii'' for the same specimen, classifying it as an odontocete. Later authors considered ''Zeuglodon pygmaeus'' a species of either ''Dorudon'' or '' Squalodon'', and in 1895 Edward Drinker Cope eventually recognized it as being a distinct genus, which he named ''Agorophius''. Although the skull is lost and the tooth is the only extant part of MCZ 8761, Fordyce (1981) was able to diagnose ''Agorophius'' based on existing descriptions of the skull by Muller, Cope, and Agassiz.R. E. Fordyce. 1981. Systematics of the odontocete whale Agorophius pygmaeus ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Xenorophus
''Xenorophus'' is a genus of primitive odontocete from late Oligocene (Chattian) marine deposits in South Carolina. It belongs to the Xenorophidae. Classification ''Xenorophus'' was originally described on the basis of a skull from the Chandler Bridge Formation of South Carolina in the collections of the USNM. Later authors, but also Remington Kellogg who described the genus, classified it in the family Agorophiidae, which eventually became a repository for primitive odontocetes. Whitmore and Sanders (1977) and Fordyce (1981), however, preferred to treat ''Xenorophus'' as Odontoceti ''incertae sedis''. A cladistic analysis by Mark Uhen published in 2008 recognized ''Xenorophus'' as belonging with '' Archaeodelphis'' and '' Albertodelphis'' in an odontocete clade more primitive than '' Agorophius'' or '' Simocetus'', and named it Xenorophidae Xenorophidae is an extinct family of odontocetes, currently known from the Oligocene of the Southeastern United States The Southeaste ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Toothed Whale
The toothed whales (also called odontocetes, systematic name Odontoceti) are a parvorder of cetaceans that includes dolphins, porpoises, and all other whales with teeth, such as beaked whales and the sperm whales. 73 species of toothed whales are described. They are one of two living groups of cetaceans, the other being the baleen whales (Mysticeti), which have baleen instead of teeth. The two groups are thought to have diverged around 34 million years ago (mya). Toothed whales range in size from the and vaquita to the and sperm whale. Several species of odontocetes exhibit sexual dimorphism, in that there are size or other morphological differences between females and males. They have streamlined bodies and two limbs that are modified into flippers. Some can travel at up to 30 knots. Odontocetes have conical teeth designed for catching fish or squid. They have well-developed hearing that is well adapted for both air and water, so much so that some can survive even i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ashley Formation
The Ashley Formation is a Formation (geology), geologic formation in South Carolina. It preserves fossils dating back to the Paleogene Period (geology), period. Vertebrate fauna Mammals Reptiles Fish Cartilaginous fish Bony fish See also * List of fossiliferous stratigraphic units in South Carolina * Paleontology in South Carolina References Further reading * {{cite web, title= Fossilworks: Gateway to the Paleobiology Database, author= ((Various Contributors to the Paleobiology Database)), url= https://www.fossilworks.org, access-date= 17 December 2021 Paleogene geology of South Carolina ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chandler Bridge Formation
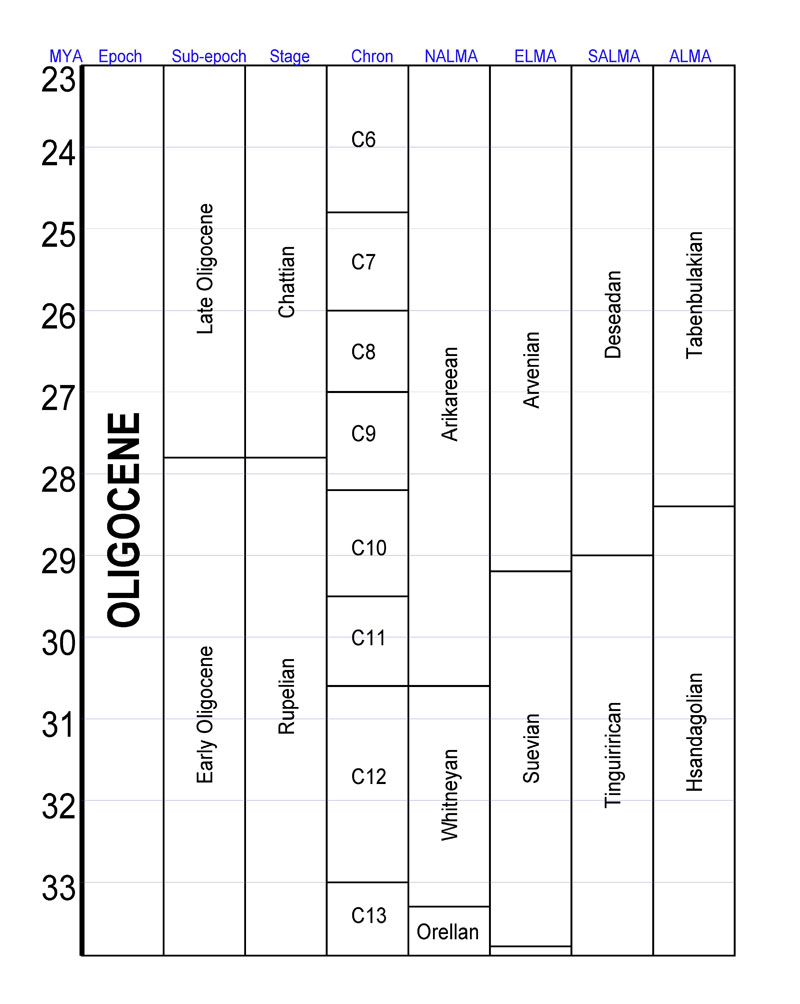
The Chandler Bridge Formation is a Formation (geology), geologic formation in South Carolina. It preserves fossils dating back to the Chattian (Late Oligocene) of the Paleogene Period (geology), period, corresponding to the Arikareean in the North American land mammal age, NALMA classification.Chandler Bridge Formation at Fossilworks.org The formation overlies the Ashley Formation and is overlain by the Edisto Formation.Albright et al., 2019, p.84 Vertebrate paleofauna Mammals Carnivorans Cetaceans Sirenians Reptiles Birds Crocodilian ...
|
Oligocene
The Oligocene ( ) is a geologic epoch (geology), epoch of the Paleogene Geologic time scale, Period that extends from about 33.9 million to 23 million years before the present ( to ). As with other older geologic periods, the rock beds that define the epoch are well identified but the exact dates of the start and end of the epoch are slightly uncertain. The name Oligocene was coined in 1854 by the German paleontologist Heinrich Ernst Beyrich from his studies of marine beds in Belgium and Germany. The name comes from Ancient Greek (''olígos'') 'few' and (''kainós'') 'new', and refers to the sparsity of Neontology, extant forms of Mollusca, molluscs. The Oligocene is preceded by the Eocene Epoch and is followed by the Miocene Epoch. The Oligocene is the third and final epoch of the Paleogene Period. The Oligocene is often considered an important time of transition, a link between the archaic world of the tropical Eocene and the more modern ecosystems of the Miocene. Major chang ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Monotypic Prehistoric Cetacean Genera
In biology, a monotypic taxon is a taxonomic group (taxon) that contains only one immediately subordinate taxon. A monotypic species is one that does not include subspecies or smaller, infraspecific taxa. In the case of genera, the term "unispecific" or "monospecific" is sometimes preferred. In botanical nomenclature, a monotypic genus is a genus in the special case where a genus and a single species are simultaneously described. Theoretical implications Monotypic taxa present several important theoretical challenges in biological classification. One key issue is known as "Gregg's Paradox": if a single species is the only member of multiple hierarchical levels (for example, being the only species in its genus, which is the only genus in its family), then each level needs a distinct definition to maintain logical structure. Otherwise, the different taxonomic ranks become effectively identical, which creates problems for organizing biological diversity in a hierarchical system. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Prehistoric Mammals Of North America
Prehistory, also called pre-literary history, is the period of human history between the first known use of stone tools by hominins million years ago and the beginning of recorded history with the invention of writing systems. The use of symbols, marks, and images appears very early among humans, but the earliest known writing systems appeared years ago. It took thousands of years for writing systems to be widely adopted, with writing having spread to almost all cultures by the 19th century. The end of prehistory therefore came at different times in different places, and the term is less often used in discussing societies where prehistory ended relatively recently. It is based on an old conception of history that without written records there could be no history. The most common conception today is that history is based on evidence, however the concept of prehistory hasn't been completely discarded. In the early Bronze Age, Sumer in Mesopotamia, the Indus Valley Civilis ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oligocene Cetaceans
The Oligocene ( ) is a geologic epoch of the Paleogene Period that extends from about 33.9 million to 23 million years before the present ( to ). As with other older geologic periods, the rock beds that define the epoch are well identified but the exact dates of the start and end of the epoch are slightly uncertain. The name Oligocene was coined in 1854 by the German paleontologist Heinrich Ernst Beyrich from his studies of marine beds in Belgium and Germany. The name comes from Ancient Greek (''olígos'') 'few' and (''kainós'') 'new', and refers to the sparsity of extant forms of molluscs. The Oligocene is preceded by the Eocene Epoch and is followed by the Miocene Epoch. The Oligocene is the third and final epoch of the Paleogene Period. The Oligocene is often considered an important time of transition, a link between the archaic world of the tropical Eocene and the more modern ecosystems of the Miocene. Major changes during the Oligocene included a global expansion of gras ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Prehistoric Toothed Whales
Prehistory, also called pre-literary history, is the period of human history between the first known use of stone tools by hominins million years ago and the beginning of recorded history with the invention of writing systems. The use of symbols, marks, and images appears very early among humans, but the earliest known writing systems appeared years ago. It took thousands of years for writing systems to be widely adopted, with writing having spread to almost all cultures by the 19th century. The end of prehistory therefore came at different times in different places, and the term is less often used in discussing societies where prehistory ended relatively recently. It is based on an old conception of history that without written records there could be no history. The most common conception today is that history is based on evidence, however the concept of prehistory hasn't been completely discarded. In the early Bronze Age, Sumer in Mesopotamia, the Indus Valley Civilis ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Xenorophidae
Xenorophidae is an extinct family of odontocetes, currently known from the Oligocene of the Southeastern United States The Southeastern United States, also known as the American Southeast or simply the Southeast, is a geographical List of regions in the United States, region of the United States located in the eastern portion of the Southern United States and t .... Known genera of xenorophids include '' Albertocetus'', '' Archaeodelphis'', '' Xenorophus'', '' Cotylocara'', '' Echovenator'', and '' Inermorostrum''.. References Prehistoric toothed whales Prehistoric mammal families Oligocene cetaceans Fauna of the Southeastern United States {{paleo-whale-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Archaeodelphis
''Archaeodelphis'' is an extinct genus of primitive odontocete cetacean from late Oligocene (Chattian) marine deposits in South Carolina, and belonging to the family Xenorophidae Xenorophidae is an extinct family of odontocetes, currently known from the Oligocene of the Southeastern United States The Southeastern United States, also known as the American Southeast or simply the Southeast, is a geographical List of re .... Description ''Archaeodelphis'' has polydont teeth, like other xenorophids.G. M. Allen. 1921. A new fossil cetacean. Bulletin of the Museum of Comparative Zoology 65(1):1-14. References Xenorophidae Oligocene cetaceans Fossil taxa described in 1921 {{paleo-whale-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |