|
AMULET (processor)
AMULET is a series of microprocessors implementing the ARM processor architecture. Developed by the ''Advanced Processor Technologies'' group at the Department of Computer Science at the University of Manchester (formerly the AMULET and PAL groups based at the same institution), AMULET is unique amongst ARM implementations in being an asynchronous microprocessor, not making use of a square wave clock signal for data synchronization and movement. List of AMULET microprocessors *AMULET1 — Designed in 1990 and first fabricated in 1993. Its estimated performance is approximately 70% of that of a comparably-sized synchronous ARM6 running at 20 MHz. *AMULET2 — A re-implementation of AMULET1 first fabricated in 1996. Features on-chip memory that can be used either as processor cache or mapped RAM. The APT group estimates AMULET2 to have a similar power dissipation/performance ratio as ARM8. One very notable feature due to the asynchronous design is the drop of power dis ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
ARM Architecture
ARM (stylised in lowercase as arm, formerly an acronym for Advanced RISC Machines and originally Acorn RISC Machine) is a family of reduced instruction set computer, RISC instruction set architectures (ISAs) for central processing unit, computer processors. Arm Holdings develops the ISAs and licenses them to other companies, who build the physical devices that use the instruction set. It also designs and licenses semiconductor intellectual property core, cores that implement these ISAs. Due to their low costs, low power consumption, and low heat generation, ARM processors are useful for light, portable, battery-powered devices, including smartphones, laptops, and tablet computers, as well as embedded systems. However, ARM processors are also used for desktop computer, desktops and server (computing), servers, including Fugaku (supercomputer), Fugaku, the world's fastest supercomputer from 2020 to 2022. With over 230 billion ARM chips produced, , ARM is the most widely used ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
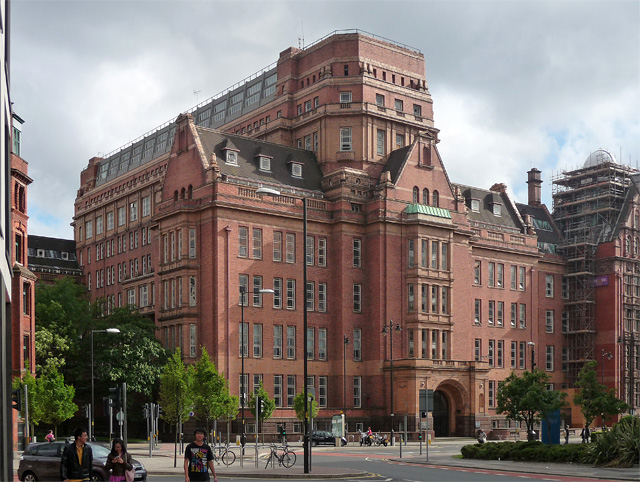
Department Of Computer Science, University Of Manchester
The Department of Computer Science at the University of Manchester is the longest established department of Computer Science in the United Kingdom and one of the largest. It is located in the Kilburn Building on the Wilmslow Road#Oxford Road, Oxford Road and currently has over 800 students taking a wide range of undergraduate and postgraduate courses and 60 Full-time equivalent, full-time academic staff. Teaching and study Undergraduate The Department currently offers a wide range of undergraduate courses from Bachelor of Science, Bachelor of Science (BSc), Bachelor of Engineering, Bachelor of Engineering (BEng) and Master of Engineering, Master of Engineering (MEng). These are available as Bachelor's degree, single honours or as joint honours degrees within the themes of Artificial Intelligence, Computer Science, Computer engineering, Computer systems engineering, Software engineering, Mathematics, Internet, Internet Computing, Business software, Business applications and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
University Of Manchester
The University of Manchester is a public university, public research university in Manchester, England. The main campus is south of Manchester city centre, Manchester City Centre on Wilmslow Road, Oxford Road. The University of Manchester is considered a red brick university, a product of the civic university movement of the late 19th century. The current University of Manchester was formed in 2004 following the merger of the University of Manchester Institute of Science and Technology (UMIST) and the Victoria University of Manchester. This followed a century of the two institutions working closely with one another. Additionally, the university owns and operates major cultural assets such as the Manchester Museum, The Whitworth art gallery, the John Rylands Library, the Tabley House, Tabley House Collection and the Jodrell Bank Observatory – a UNESCO World Heritage Site. The University of Manchester Institute of Science and Technology had its origins in the Manchester Mechan ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Asynchronous CPU
Asynchronous circuit (clockless or self-timed circuit) is a sequential digital logic circuit that does not use a global clock circuit or signal generator to synchronize its components. Instead, the components are driven by a handshaking circuit which indicates a completion of a set of instructions. Handshaking works by simple data transfer protocols. Many synchronous circuits were developed in early 1950s as part of bigger asynchronous systems (e.g. ORDVAC). Asynchronous circuits and theory surrounding is a part of several steps in integrated circuit design, a field of digital electronics engineering. Asynchronous circuits are contrasted with synchronous circuits, in which changes to the signal values in the circuit are triggered by repetitive pulses called a clock signal. Most digital devices today use synchronous circuits. However asynchronous circuits have a potential to be much faster, have a lower level of power consumption, electromagnetic interference, and bette ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Square Wave (waveform)
A square wave is a non-sinusoidal waveform, non-sinusoidal periodic waveform in which the amplitude alternates at a steady frequency between fixed minimum and maximum values, with the same duration at minimum and maximum. In an ideal square wave, the transitions between minimum and maximum are instantaneous. The square wave is a special case of a pulse wave which allows arbitrary durations at minimum and maximum amplitudes. The ratio of the high period to the total period of a pulse wave is called the duty cycle. A true square wave has a 50% duty cycle (equal high and low periods). Square waves are often encountered in electronics and signal processing, particularly digital electronics and digital signal processing. Its stochastic counterpart is a two-state trajectory. Origin and uses Square waves are universally encountered in digital switching circuits and are naturally generated by binary (two-level) logic devices. They are used as timing references or "clock signa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
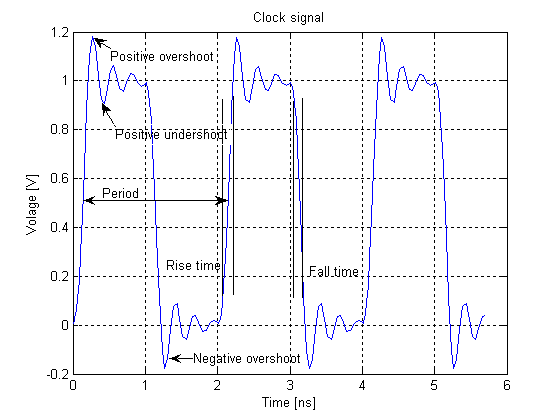
Clock Signal
In electronics and especially synchronous digital circuits, a clock signal (historically also known as ''logic beat'') is an electronic logic signal (voltage or current) which oscillates between a high and a low state at a constant frequency and is used like a metronome to synchronize actions of digital circuits. In a synchronous logic circuit, the most common type of digital circuit, the clock signal is applied to all storage devices, flip-flops and latches, and causes them all to change state simultaneously, preventing race conditions. A clock signal is produced by an electronic oscillator called a clock generator. The most common clock signal is in the form of a square wave with a 50% duty cycle. Circuits using the clock signal for synchronization may become active at either the rising edge, falling edge, or, in the case of double data rate, both in the rising and in the falling edges of the clock cycle. Digital circuits Most integrated circuits (ICs) of suffi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Digital Enhanced Cordless Telecommunications
Digital Enhanced Cordless Telecommunications (DECT) is a cordless telephone, cordless telephony standard maintained by ETSI. It originated in Europe, where it is the common standard, replacing earlier standards, such as CT1 and CT2. Since the DECT-2020 standard onwards, it also includes Internet of things, IoT communication. Beyond Europe, it has been adopted by Australia and most countries in Asia and South America. North American adoption was delayed by United States radio-frequency regulations. This forced development of a variation of DECT called DECT 6.0, using a slightly different frequency range, which makes these units incompatible with systems intended for use in other areas, even from the same manufacturer. DECT has almost completely replaced other standards in most countries where it is used, with the exception of North America. DECT was originally intended for fast roaming between networked base stations, and the first DECT product was Net3, Net3 wireless LAN. H ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
ARM Processors
In human anatomy, the arm refers to the upper limb in common usage, although academically the term specifically means the upper arm between the glenohumeral joint (shoulder joint) and the elbow joint. The distal part of the upper limb between the elbow and the radiocarpal joint ( wrist joint) is known as the forearm or "lower" arm, and the extremity beyond the wrist is the hand. By anatomical definitions, the bones, ligaments and skeletal muscles of the shoulder girdle, as well as the axilla between them, are considered parts of the upper limb, and thus also components of the arm. The Latin term ''brachium'', which serves as a root word for naming many anatomical structures, may refer to either the upper limb as a whole or to the upper arm on its own. Structure Bones The humerus is one of the three long bones of the arm. It joins with the scapula at the shoulder joint and with the other long bones of the arm, the ulna and radius at the elbow joint. The elbow is a compl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |