The Golden Temple on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The Golden Temple is a
 Guru Ram Das acquired the land for the site. Two versions of stories exist on how he acquired this land. In one, based on a Gazetteer record, the land was purchased with Sikh donations of 700 rupees from the people and owners of the village of Tung. In another version, Emperor
Guru Ram Das acquired the land for the site. Two versions of stories exist on how he acquired this land. In one, based on a Gazetteer record, the land was purchased with Sikh donations of 700 rupees from the people and owners of the village of Tung. In another version, Emperor  In 1581, Guru Arjan initiated the construction of the gurdwara. During the construction the pool was kept empty and dry. It took 8 years to complete the first version of the Harmandir Sahib. Arjan planned a gurdwara at a level lower than the city to emphasise humility and the need to efface one's ego before entering the premises to meet the Guru. He also demanded that the gurdwara compound be open on all sides to emphasise that it was open to all. The sanctum inside the pool where his Guru seat was, had only one bridge to emphasise that the end goal was one, states Arvind-Pal Singh Mandair. In 1589, the gurdwara made with bricks was complete. Arjan is believed by some later sources to have invited the Sufi saint
In 1581, Guru Arjan initiated the construction of the gurdwara. During the construction the pool was kept empty and dry. It took 8 years to complete the first version of the Harmandir Sahib. Arjan planned a gurdwara at a level lower than the city to emphasise humility and the need to efface one's ego before entering the premises to meet the Guru. He also demanded that the gurdwara compound be open on all sides to emphasise that it was open to all. The sanctum inside the pool where his Guru seat was, had only one bridge to emphasise that the end goal was one, states Arvind-Pal Singh Mandair. In 1589, the gurdwara made with bricks was complete. Arjan is believed by some later sources to have invited the Sufi saint
 The Golden Temple's architecture reflects different architectural practices prevalent in the
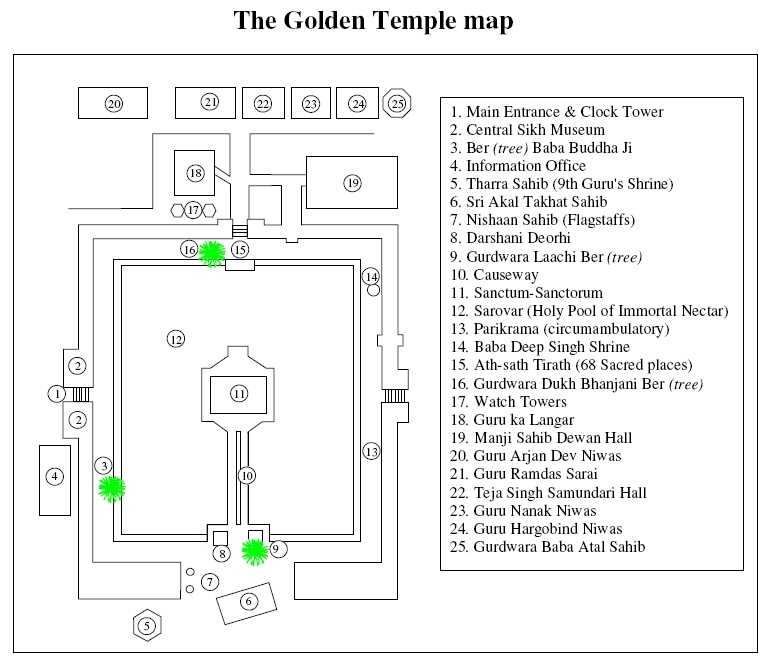
The Golden Temple's architecture reflects different architectural practices prevalent in the  The Darshani Deorhi is a two-storey structure that houses the temple management offices and treasury. At the exit of the path leading away from the sanctum is the ''Prasada'' facility, where volunteers serve a flour-based sweet offering called ''Karah prasad''. Typically, the pilgrims to the Golden Temple enter and make a clockwise circumambulation around the pool before entering the sanctum. There are four entrances to the gurdwara complex signifying the openness to all sides, but a single entrance to the sanctum of the temple through a causeway.
The Darshani Deorhi is a two-storey structure that houses the temple management offices and treasury. At the exit of the path leading away from the sanctum is the ''Prasada'' facility, where volunteers serve a flour-based sweet offering called ''Karah prasad''. Typically, the pilgrims to the Golden Temple enter and make a clockwise circumambulation around the pool before entering the sanctum. There are four entrances to the gurdwara complex signifying the openness to all sides, but a single entrance to the sanctum of the temple through a causeway.
 The Golden Temple complex originally was open and had numerous trees around the pool. It is now a walled, two-storey courtyard with four entrances, that preserve three Ber trees (
The Golden Temple complex originally was open and had numerous trees around the pool. It is now a walled, two-storey courtyard with four entrances, that preserve three Ber trees (

 The Golden Temple and Akal Takht were occupied by various militant groups in the early 1980s. These included the
The Golden Temple and Akal Takht were occupied by various militant groups in the early 1980s. These included the
gurdwara
A gurdwara or gurudwara () is a place of assembly and place of worship, worship in Sikhism, but its normal meaning is "place of guru" or "home of guru". Sikhism, Sikhs also refer to gurdwaras as ''Gurdwara Sahib''. People from all faiths and rel ...
located in Amritsar
Amritsar, also known as Ambarsar, is the second-List of cities in Punjab, India by population, largest city in the India, Indian state of Punjab, India, Punjab, after Ludhiana. Located in the Majha region, it is a major cultural, transportatio ...
, Punjab, India
Punjab () is a States and union territories of India, state in northwestern India. Forming part of the larger Punjab, Punjab region of the Indian subcontinent, the state is bordered by the States and union territories of India, Indian states ...
. It is the pre-eminent spiritual site of Sikhism
Sikhism is an Indian religion and Indian philosophy, philosophy that originated in the Punjab region of the Indian subcontinent around the end of the 15th century CE. It is one of the most recently founded major religious groups, major religio ...
. It is one of the holiest sites in Sikhism, alongside the Gurdwara Darbar Sahib Kartarpur
Gurdwara Darbar Sahib Kartarpur, also called Kartarpur Sahib, is a gurdwara (Sikh temple) in Kartarpur, Pakistan, Kartarpur, Shakargarh Tehsil, Narowal District, in the Punjab province of Pakistan. It is built on the very historic site where the f ...
in Kartarpur, and Gurdwara Janam Asthan
Gurdwara Janam Asthan ( Punjabi , Urdu: ; Punjabi : ਗੁਰਦੁਆਰਾ ਜਨਮ ਅਸਥਾਨ), also referred to as Gurdwara Nankana Sahib, is a highly revered gurdwara that is situated at the site where the founder of Sikhism, Guru Nanak ...
in Nankana Sahib
Nankana Sahib (; ) is a city and capital of Nankana Sahib District in the Punjab province of Pakistan. It is named after the first Guru of the Sikhs, Guru Nanak, who was born in the city and first began preaching here. Nankana Sahib is among ...
.
The ''sarovar'' (holy pool) on the site of the gurdwara was completed by the fourth Sikh Guru, Guru Ram Das
Guru Ram Das (Gurmukhi: ਗੁਰੂ ਰਾਮ ਦਾਸ, pronunciation: ; 24 September 1534 – 1 September 1581), sometimes spelled as Guru Ramdas, was the fourth of the ten Sikh gurus. He was born to a family based in Lahore, who ...
, in 1577. In 1604, Guru Arjan
Guru Arjan (Gurmukhi: ਗੁਰੂ ਅਰਜਨ, pronunciation: ; 15 April 1563 – 30 May 1606) was the fifth of the ten total Sikh Gurus. He compiled the first official edition of the Sikh scripture called the Adi Granth, which later expande ...
, the fifth Sikh Guru, placed a copy of the Adi Granth
The Guru Granth Sahib (, ) is the central holy religious scripture of Sikhism, regarded by Sikhs as the final, sovereign and eternal Guru following the lineage of the ten human gurus of the religion. The Adi Granth (), its first rendition, w ...
in the Golden Temple and was a prominent figure in its development. The gurdwara was repeatedly rebuilt by the Sikhs after it became a target of persecution
Persecution is the systematic mistreatment of an individual or group by another individual or group. The most common forms are religious persecution, racism, and political persecution, though there is naturally some overlap between these term ...
and was destroyed several times by the Mughal
Mughal or Moghul may refer to:
Related to the Mughal Empire
* Mughal Empire of South Asia between the 16th and 19th centuries
* Mughal dynasty
* Mughal emperors
* Mughal people, a social group of Central and South Asia
* Mughal architecture
* Mug ...
and invading Afghan
Afghan or Afgan may refer to:
Related to Afghanistan
*Afghans, historically refers to the Pashtun people. It is both an ethnicity and nationality. Ethnicity wise, it refers to the Pashtuns. In modern terms, it means both the citizens of Afghanist ...
armies. Maharaja Ranjit Singh
Ranjit Singh (13 November 1780 – 27 June 1839) was the founder and first maharaja of the Sikh Empire, in the northwest Indian subcontinent, ruling from 1801 until his death in 1839.
Born to Maha Singh, the leader of the Sukerchakia M ...
, after founding the Sikh Empire
The Sikh Empire was a regional power based in the Punjab, Punjab region of the Indian subcontinent. It existed from 1799, when Maharaja Ranjit Singh captured Lahore, to 1849, when it was defeated and conquered by the East India Company, Br ...
, rebuilt it in marble
Marble is a metamorphic rock consisting of carbonate minerals (most commonly calcite (CaCO3) or Dolomite (mineral), dolomite (CaMg(CO3)2) that have recrystallized under the influence of heat and pressure. It has a crystalline texture, and is ty ...
and copper
Copper is a chemical element; it has symbol Cu (from Latin ) and atomic number 29. It is a soft, malleable, and ductile metal with very high thermal and electrical conductivity. A freshly exposed surface of pure copper has a pinkish-orang ...
in 1809, and overlaid the sanctum with gold leaf
upA gold nugget of 5 mm (0.2 in) in diameter (bottom) can be expanded through hammering into a gold foil of about 0.5 m2 (5.4 sq ft). The Japan.html" ;"title="Toi gold mine museum, Japan">Toi gold mine museum, Japan.
Gold leaf is gold that has ...
in 1830. This has led to the name the Golden Temple.
The Golden Temple is spiritually the most significant shrine in Sikhism. It became a centre of the Singh Sabha Movement
The Singh Sabhā Movement, also known as the Singh Sabhā Lehar, was a Sikh movement that began in Punjab in the 1870s in reaction to the proselytising activities of Christians, Hindu reform movements (Brahmo Samaj, Arya Samaj) and Muslims ( Ali ...
between 1883 and the 1920s, and the Punjabi Suba movement
The Punjabi Suba movement was a political movement led by Punjabi-speakers (mainly Sikhs) from 1947 to 1966, demanding the creation of an autonomous ''Punjabi Suba'', or Punjabi-speaking state, in the post-independence Indian state of East Pu ...
between 1947 and 1966. In the early 1980s, the gurdwara became a centre of conflict between the Indian government and a radical movement led by Jarnail Singh Bhindranwale
Jarnail Singh Bhindranwale (; born Jarnail Singh Brar; 2 June 1947– 6 June 1984) was a Sikh militant. After Operation Bluestar, he posthumously became the leading figure for the Khalistan movement, although he did not personally advocate for ...
. In 1984, Prime Minister
A prime minister or chief of cabinet is the head of the cabinet and the leader of the ministers in the executive branch of government, often in a parliamentary or semi-presidential system. A prime minister is not the head of state, but r ...
Indira Gandhi
Indira Priyadarshini Gandhi (Given name, ''née'' Nehru; 19 November 1917 – 31 October 1984) was an Indian politician and stateswoman who served as the Prime Minister of India, prime minister of India from 1966 to 1977 and again from 1980 un ...
sent in the Indian Army
The Indian Army (IA) (ISO 15919, ISO: ) is the Land warfare, land-based branch and largest component of the Indian Armed Forces. The President of India is the Commander-in-Chief, Supreme Commander of the Indian Army, and its professional head ...
as part of Operation Blue Star
Operation Blue Star was a military operation by the Indian Armed Forces conducted between 1 and 10 June 1984 to remove Jarnail Singh Bhindranwale and other Sikh militants from the Golden Temple (Harmandir Sahib), a holy site of Sikhism, and i ...
, leading to the deaths of thousands of soldiers, militants and civilians, as well as causing significant damage to the gurdwara and the destruction of the nearby Akal Takht
The Akal Takht (; ), also spelt as Akal Takhat and historically known as Akal Bunga, is the most prominent of the Takht (Sikhism), five takhts (Seat (legal entity), seats of authority) of the Sikhs. Located within the Golden Temple, Darbar Sah ...
. The gurdwara complex was rebuilt again after the 1984 attack on it.
The Golden Temple is an open house of worship for all people, from all walks of life and faiths. It has a square plan with four entrances, and a circumambulation path around the pool. The four entrances of the gurudwara symbolise the Sikh belief in equality & the Sikh view that people from all groups, castes & ethnicities are welcome at their holy place. The complex is a collection of buildings around the sanctum and the pool. One of these is Akal Takht
The Akal Takht (; ), also spelt as Akal Takhat and historically known as Akal Bunga, is the most prominent of the Takht (Sikhism), five takhts (Seat (legal entity), seats of authority) of the Sikhs. Located within the Golden Temple, Darbar Sah ...
, the chief centre of religious authority of Sikhism
Sikhism is an Indian religion and Indian philosophy, philosophy that originated in the Punjab region of the Indian subcontinent around the end of the 15th century CE. It is one of the most recently founded major religious groups, major religio ...
. Additional buildings include a clock tower, the offices of the Gurdwara Committee, a Museum and a langar
Langar may refer to:
Community eating
*Langar (Sikhism)
*Langar (Sufism)
Places
Afghanistan
*Langar, Badakhshan, Afghanistan
*Langar, Bamyan, Afghanistan
*Langar, Faryab, Afghanistan
*Langar, Herat, Afghanistan
*Langar, Wardak, Afghanistan
...
– a free Sikh community-run kitchen that offers a vegetarian meal to all visitors without discrimination. Over 150,000 people visit the shrine every day for worship. The gurdwara complex has been nominated as a UNESCO World Heritage Site
World Heritage Sites are landmarks and areas with legal protection under an treaty, international treaty administered by UNESCO for having cultural, historical, or scientific significance. The sites are judged to contain "cultural and natural ...
, and its application is pending on the tentative list of UNESCO.
Nomenclature
The Harmandir Sahib is also spelled as Harimandar or Harimandir Sahib. It is also called the '' Durbār Sahib'', which means "sacred audience", as well as the Golden Temple for its gold leaf-covered sanctum centre. The word "Harmandir" is composed of two words: "Hari
Hari () is among the primary epithets of the Hindu preserver deity Vishnu, meaning 'the one who takes away' (sins). It refers to the one who removes darkness and illusion, the one who removes all obstacles to spiritual progress.
The name Ha ...
", which scholars translate as "God ", and "mandir
A Hindu temple, also known as Mandir, Devasthanam, Pura, or Kovil, is a sacred place where Hindus worship and show their devotion to deities through worship, sacrifice, and prayers. It is considered the house of the god to whom it is dedica ...
", which means "house". "Sahib
Sahib or Saheb () is a term of address originating from Arabic (). As a loanword, ''Sahib'' has passed into several languages, including Persian, Kurdish, Turkish, Azerbaijani, Kazakh, Uzbek, Turkmen, Tajik, Crimean Tatar, Urdu, Hi ...
" is further appended to the shrine's name, the term often used within Sikh tradition to denote respect for places of religious significance. The Sikh tradition has several gurdwaras named "Harmandir Sahib", such as those in Kiratpur and Patna
Patna (; , ISO 15919, ISO: ''Paṭanā''), historically known as Pataliputra, Pāṭaliputra, is the List of state and union territory capitals in India, capital and largest city of the state of Bihar in India. According to the United Nations, ...
. Of these, the one in Amritsar is most revered.
History
According to the Sikh historical records, the land that became Amritsar and houses the Harimandir Sahib was chosen byGuru Amar Das
Guru Amar Das (Gurmukhi: ਗੁਰੂ ਅਮਰ ਦਾਸ, pronunciation: ; 5 May 1479 – 1 September 1574), sometimes spelled as Guru Amardas, was the third of the Ten Gurus of Sikhism and became Sikh Guru on 26 March 1552 at age 73.
Befor ...
, the third Guru of the Sikh tradition. It was then called ''Guru Da Chakk'', after he had asked his disciple Ram Das to find land to start a new town with a man-made pool as its central point. After Guru Ram Das
Guru Ram Das (Gurmukhi: ਗੁਰੂ ਰਾਮ ਦਾਸ, pronunciation: ; 24 September 1534 – 1 September 1581), sometimes spelled as Guru Ramdas, was the fourth of the ten Sikh gurus. He was born to a family based in Lahore, who ...
succeeded Guru Amar Das in 1574, and in the face of hostile opposition from the sons of Amar Das, Ram Das founded the town that came to be known as "Ramdaspur". He started by completing the pool with the help of Baba Buddha
Baba Buddha (Gurmukhi: ਬਾਬਾ ਬੁੱਢਾ; ''bābā buḍhā''; lit. meaning "wise old man"; 6 October 1506 – 8 September 1631) was a prime figure in early Sikhism.
Early life
He was born to a Jat family in 1506 in the village of ...
(not to be confused with the Buddha of Buddhism). Ram Das built his new official centre and home next to it. He invited merchants and artisans from other parts of India to settle in the new town with him.
Ramdaspur town expanded during the time of Guru Arjan
Guru Arjan (Gurmukhi: ਗੁਰੂ ਅਰਜਨ, pronunciation: ; 15 April 1563 – 30 May 1606) was the fifth of the ten total Sikh Gurus. He compiled the first official edition of the Sikh scripture called the Adi Granth, which later expande ...
financed by donations and constructed by voluntary work. The town grew to become the city of Amritsar, and the area grew into the temple complex). The construction activity between 1574 and 1604 is described in ''Mahima Prakash Vartak'', a semi-historical Sikh hagiography
A hagiography (; ) is a biography of a saint or an ecclesiastical leader, as well as, by extension, an adulatory and idealized biography of a preacher, priest, founder, saint, monk, nun or icon in any of the world's religions. Early Christian ...
text likely composed in 1741, and the earliest known document dealing with the lives of all the ten Gurus. Arjan installed the scripture of Sikhism inside the new gurdwara in 1604. Continuing the efforts of Ram Das, Arjan established Amritsar as a primary Sikh pilgrimage destination. He wrote a voluminous amount of Sikh scripture including the popular Sukhmani Sahib
Sukhmani Sahib (), known under the title of Gauri Sukhmani in the scripture (named after the Gauri (raga), Gauri raga musical measure it belongs to), is usually translated to mean ''Prayer of Peace'' is a set of 192 ''Pada (foot), padas'' (stanz ...
.
Construction
 Guru Ram Das acquired the land for the site. Two versions of stories exist on how he acquired this land. In one, based on a Gazetteer record, the land was purchased with Sikh donations of 700 rupees from the people and owners of the village of Tung. In another version, Emperor
Guru Ram Das acquired the land for the site. Two versions of stories exist on how he acquired this land. In one, based on a Gazetteer record, the land was purchased with Sikh donations of 700 rupees from the people and owners of the village of Tung. In another version, Emperor Akbar
Akbar (Jalal-ud-din Muhammad Akbar, – ), popularly known as Akbar the Great, was the third Mughal emperor, who reigned from 1556 to 1605. Akbar succeeded his father, Humayun, under a regent, Bairam Khan, who helped the young emperor expa ...
is stated to have donated the land to the wife of Ram Das.
 In 1581, Guru Arjan initiated the construction of the gurdwara. During the construction the pool was kept empty and dry. It took 8 years to complete the first version of the Harmandir Sahib. Arjan planned a gurdwara at a level lower than the city to emphasise humility and the need to efface one's ego before entering the premises to meet the Guru. He also demanded that the gurdwara compound be open on all sides to emphasise that it was open to all. The sanctum inside the pool where his Guru seat was, had only one bridge to emphasise that the end goal was one, states Arvind-Pal Singh Mandair. In 1589, the gurdwara made with bricks was complete. Arjan is believed by some later sources to have invited the Sufi saint
In 1581, Guru Arjan initiated the construction of the gurdwara. During the construction the pool was kept empty and dry. It took 8 years to complete the first version of the Harmandir Sahib. Arjan planned a gurdwara at a level lower than the city to emphasise humility and the need to efface one's ego before entering the premises to meet the Guru. He also demanded that the gurdwara compound be open on all sides to emphasise that it was open to all. The sanctum inside the pool where his Guru seat was, had only one bridge to emphasise that the end goal was one, states Arvind-Pal Singh Mandair. In 1589, the gurdwara made with bricks was complete. Arjan is believed by some later sources to have invited the Sufi saint Mian Mir
Mian Mir or Miyan Mir (c. 1550 – 22 August 1635), was a famous Sufi Muslim saint who resided in Lahore, in the neighborhood now known as Dharampura.
He was a direct descendant of Caliph Umar ibn al-Khattab and belonged to the Qadiri order ...
of Lahore
Lahore ( ; ; ) is the capital and largest city of the Administrative units of Pakistan, Pakistani province of Punjab, Pakistan, Punjab. It is the List of cities in Pakistan by population, second-largest city in Pakistan, after Karachi, and ...
to lay its foundation stone, signalling pluralism and that the Sikh tradition welcomed all. This belief is however unsubstantiated. According to Sikh traditional sources such as Sri Gur Suraj Parkash Granth it was laid by Guru Arjan himself. After the inauguration, the pool was filled with water. On 16 August 1604, Arjan completed expanding and compiling the first version of the Sikh scripture and placed a copy of the Adi Granth
The Guru Granth Sahib (, ) is the central holy religious scripture of Sikhism, regarded by Sikhs as the final, sovereign and eternal Guru following the lineage of the ten human gurus of the religion. The Adi Granth (), its first rendition, w ...
in the gurdwara. He appointed Baba Buddha
Baba Buddha (Gurmukhi: ਬਾਬਾ ਬੁੱਢਾ; ''bābā buḍhā''; lit. meaning "wise old man"; 6 October 1506 – 8 September 1631) was a prime figure in early Sikhism.
Early life
He was born to a Jat family in 1506 in the village of ...
as the first Granthi
A Granthi (, ) is a person, female or male, of the Sikh religion who is a ceremonial reader of the Guru Granth Sahib, which is the holy book in Sikhism, often read to worshipers at Sikh temples called a Gurdwara.
The name Granthi comes from the ...
.
''Ath Sath Tirath'', which means "shrine of 68 pilgrimages", is a raised canopy on the ''parkarma'' (circumambulation marble path around the pool). The name, as stated by W. Owen Cole and other scholars, reflects the belief that visiting this temple is equivalent to 68 Hindu pilgrimage sites in the Indian subcontinent, or that a Tirath to the Golden Temple has the efficacy of all 68 Tiraths combined. The completion of the first version of the Golden Temple was a major milestone for Sikhism, states Arvind-Pal Singh Mandair, because it provided a central pilgrimage place and a rallying point for the Sikh community, set within a hub of trade and activity.
Mughal Empire era destruction and rebuilding
The growing influence and success of Guru Arjan drew the attention of theMughal Empire
The Mughal Empire was an Early modern period, early modern empire in South Asia. At its peak, the empire stretched from the outer fringes of the Indus River Basin in the west, northern Afghanistan in the northwest, and Kashmir in the north, to ...
. Arjan was arrested under the orders of the Mughal Emperor Jahangir
Nur-ud-din Muhammad Salim (31 August 1569 – 28 October 1627), known by his imperial name Jahangir (; ), was List of emperors of the Mughal Empire, Emperor of Hindustan from 1605 until his death in 1627, and the fourth Mughal emperors, Mughal ...
and asked to convert to Islam. He refused, was tortured and executed in 1606. Arjan's son and successor Guru Hargobind
Guru Hargobind (Gurmukhi: ਗੁਰੂ ਹਰਿਗੋਬਿੰਦ, pronunciation: l 19 June 1595 – 28 February 1644) was the sixth of ten Gurus of the Sikh religion. He had become Guru at the young age of eleven, after the execution of his ...
fought a Battle at Amritsar and later left Amritsar and its surrounding areas in 1635 for Kiratpur. For about a century after the Golden Temple was occupied by the Minas
Minas or MINAS may refer to:
People with the given name Minas
* Menas of Ethiopia (died 1563)
* Saint Menas (Minas, 285–309)
* Minias of Florence (Minas, Miniato, died 250)
* Minas Alozidis (born 1984), Greek hurdler
* Minas Avetisyan (192 ...
. In the 18th century, Guru Gobind Singh
Guru Gobind Singh (; born Gobind Das; 22 December 1666 – 7 October 1708) was the tenth and last human Sikh gurus, Sikh Guru. He was a warrior, poet, and philosopher. In 1675, at the age of nine he was formally installed as the leader of the ...
after creating the Khalsa
The term ''Khalsa'' refers to both a community that follows Sikhism as its religion,Khalsa: Sikhism< ...
sent Bhai Mani Singh
Bhai Mani Singh (7 April 1644 – 14 June 1738) was an 18th-century Sikh scholar and martyr. He was a childhood companion of Guru Gobind Singh and took the vows of Sikhism when the Guru inaugurated the Khalsa in March 1699. Soon after that, t ...
to take back the temple. The Golden Temple was viewed by the Mughal rulers and Afghan Sultans as the centre of Sikh faith and it remained the main target of persecution., Quote: "Ahmad Durrani was forced to return to India and edeclared a jihad, known as an Islamic holy war, against the Marathas. A multitude of tribes heralded the call of the holy war, which included the various Pashtun tribes, the Balochs, the Tajiks, and also the Muslim population residing in India. Led by Ahmad Durrani, the tribes joined the religious quest and returned to India (...) The domination and control of the fghanempire began to loosen in 1762 when Ahmad Shah Durrani crossed Afghanistan to subdue the Sikhs, followers of an indigenous monotheistic religion of India found in the 16th century by Guru Nanak. (...) Ahmad Shah greatly desired to subdue the Sikhs, and his army attacked and gained control of the Sikh's holy city of Amritsar, where he brutally massacred thousands of Sikh followers. Not only did he viciously demolish the sacred temples and buildings, but he ordered these holy places to be covered with cow's blood as an insult and desecration of their religion (...)" After the original temple was destroyed by hostile forces, the shrine was reconstructed in 1764 (a date which H.H. Cole affirms in his monograph on the temple), however most of the elaborate decorations and additions were added to the shrine in the early 19th century. However, according to Giani Gian Singh
Giani Gian Singh (15 April 1822 – 24 September 1921) was a 19th-century Sikh historian, literatus, hagiographer, martial artist, theologian, and scholar. He wrote the works ''Naveen'' ''Panth Prakash'' and ''Twarikh Guru Khalsa''.
Biography
...
's ''Tawarikh Sri Amritsar'' (1889), a slightly later date of 1776 is given for the construction of the temple tank (sarovar), the temple edifice proper, the causeway, and the entry gateway or archway (''Darshani Deori'').
The Golden Temple was the centre of historic events in Sikh history:
* In 1709, the governor of Lahore sent in his army to suppress and prevent the Sikhs from gathering for their festivals of Vaisakhi
Vaisakhi, also known as Baisakhi or Mesadi, marks the first day of the month of Vaisakh and is traditionally celebrated annually on 13 April or sometimes 14 April.
It is seen as a spring harvest celebration primarily in Punjab and Northern In ...
and Diwali
Diwali (), also called Deepavali (IAST: ''Dīpāvalī'') or Deepawali (IAST: ''Dīpāwalī''), is the Hindu festival of lights, with variations celebrated in other Indian religions such as Jainism and Sikhism. It symbolises the spiritual v ...
. The Sikhs defied by gathering in the Golden Temple. In 1716, Banda Singh and numerous Sikhs were arrested and executed.
* In 1737, the Mughal governor ordered the capture of the custodian of the Golden Temple named Mani Singh and executed him. He appointed Masse Khan as the police commissioner who then occupied the Temple and converted it into his entertainment centre with dancing girls. He befouled the pool. Sikhs avenged the sacrilege of the Golden Temple by assassinating Masse Khan inside the Temple in August 1740.
* In 1746, another Lahore official Diwan Lakhpat Rai working for Yahiya Khan, and seeking revenge for the death of his brother, filled the pool with sand. In 1749, Sikhs restored the pool when Muin ul-Mulk slackened Mughal operations against Sikhs and sought their help during his operations in Multan.
* In 1757, the Afghan ruler Ahmad Shah Durrani
Ahmad Shāh Durrānī (; ; – 4 June 1772), also known as Ahmad Shāh Abdālī (), was the first ruler and founder of the Durrani Empire. He is often regarded as the founder of modern Afghanistan.
Throughout his reign, Ahmad Shah fought ov ...
, also known as Ahmad Shah Abdali, attacked Amritsar and desecrated the Golden Temple. He had waste poured into the pool along with entrails of slaughtered cows, before departing for Afghanistan. The Sikhs restored it again.
* In 1762, Ahmad Shah Durrani returned and had the Golden Temple blown up with gunpowder. Sikhs returned and celebrated Diwali
Diwali (), also called Deepavali (IAST: ''Dīpāvalī'') or Deepawali (IAST: ''Dīpāwalī''), is the Hindu festival of lights, with variations celebrated in other Indian religions such as Jainism and Sikhism. It symbolises the spiritual v ...
in its premises. In 1764, Jassa Singh Ahluwalia
Jassa Singh Ahluwalia (3 May 1718 – 23 October 1783) was a Sikh leader during the period of the Sikh Confederacy, being the supreme leader of the Dal Khalsa (Sikh Army), Dal Khalsa. He was also Misldar of the Ahluwalia (misl), Ahluwalia Mi ...
collected donations to rebuild the Golden Temple. A new main gateway (Darshan Deorhi), causeway and sanctum were completed in 1776, while the floor around the pool was completed in 1784. The Sikhs also completed a canal to bring in fresh water from Ravi River
The Ravi River is a transboundary river in South Asia, flowing through northwestern India and eastern Pakistan, and is one of five major rivers of the Punjab region.
Under the Indus Waters Treaty of 1960, the waters of the Ravi and two oth ...
for the pool.
* The Golden Temple was attacked by the Afghan forces under Ahmed Shah Durrani on 1 December 1764. Baba Gurbaksh Singh along with 29 other Sikhs lead a last stand against the much larger Afghan forces and were killed in the skirmish. Abdali then destroyed the Golden Temple for the 3rd time.
Ranjit Singh era reconstruction
Ranjit Singh
Ranjit Singh (13 November 1780 – 27 June 1839) was the founder and first maharaja of the Sikh Empire, in the northwest Indian subcontinent, ruling from 1801 until his death in 1839.
Born to Maha Singh, the leader of the Sukerchakia M ...
founded the nucleus of the Sikh Empire at the age of 36 with help of Sukerchakia Misl
The Sukerchakia Misl was one of twelve Sikh Sikh Confederacy, misls in Punjab region, Punjab during the 18th century, concentrated in Gujranwala and Hafizabad districts in western Punjab region, Punjab (in modern-Pakistan) and ruled from (1752 ...
forces he inherited and those of his mother-in-law Rani Sada Kaur. In 1802, at age 22, he took Amritsar from the ''Bhangi misl'', paid homage at the Golden Temple and announced that he would renovate and rebuild it with marble and gold. The Sikh ruler donated the gilded copper panels for the roof, which was worth 500,000 rupees in the erstwhile currency. He entrusted ''Mistri
Mistri, or Mistry, is a term for a master-craftsman, foreman or supervisor of manual workers in India. Mistri is being replaced with terms "supervisor" and master craftsman with "Senior Technician" by the Indian Railway who replaced the designati ...
'' Yar Muhammad Khan to carry-out the roofing work, who himself was supervised by Bhai Sand Singh. The first gilded copper panel was placed on the shrine in 1803.
Various personalities helped decorate and embellish the ceiling of the first floor, with names of some contributors to the cause being Tara Singh Gheba, Partap Singh, Jodh Singh, and Ganda Singh Peshawari. Ganda Singh Peshawari sent his donation in the year 1823. For the decoration and gilding with copper of the main entryway and archway to the causeway leading to the temple proper, known as the ''Darshani Deori'', the prime personality who helped assist with this work was Raja Sangat Singh of Jind State. Due to the central and paramount importance of the shrine in Sikhism, essentially every Sikh ''sardar
Sardar, also spelled as Sardaar (, , 'commander', literally 'headmaster'), is a title of royal family, royalty and nobility that was originally used to denote princes, noblemen, chiefs, kings and other Aristocracy (class), aristocrats. It ha ...
'' of the era had contributed or donated in some manner to assist with the architectural and artistic renovations of the shrine. Owing to the large number of people helping with the renovation work back then, it is difficult to account for when certain parts of the temple were constructed or decorated and by whom (aside from instances where the work has a date inscribed to it) and a chronological record of how the temple evolved over time (in-regards to its murals, decorations, and other aspects) is near-impossible to complete.
The Temple was renovated in marble and copper in 1809, and in 1830 Ranjit Singh donated gold to overlay the sanctum with gold leaf. There is an inscription on embossed metal located at the entrance to the temple proper which commemorates the renovations of the temple undertaken by Ranjit Singh and done through Giani Sant Singh, of the Giani Samparda.
After learning of the gurdwara through Ranjit Singh, the 7th Nizam
Nizam of Hyderabad was the title of the ruler of Hyderabad State ( part of the Indian state of Telangana, and the Kalyana-Karnataka region of Karnataka). ''Nizam'' is a shortened form of (; ), and was the title bestowed upon Asaf Jah I ...
of Hyderabad
Hyderabad is the capital and largest city of the Indian state of Telangana. It occupies on the Deccan Plateau along the banks of the Musi River (India), Musi River, in the northern part of Southern India. With an average altitude of , much ...
, Mir Osman Ali Khan
Mir Osman Ali Khan, Asaf Jah VII (5 or 6 April 1886 – 24 February 1967) was the last Nizam (ruler) of Hyderabad State, the largest state in the erstwhile Indian Empire. He ascended the throne on 29 August 1911, at the age of 25 and rule ...
started giving yearly grants towards it. The management and operation of Durbar Sahib – a term that refers to the entire Golden Temple complex of buildings, was taken over by Ranjit Singh. He appointed Sardar Desa Singh Majithia (1768–1832) to manage it and made land grants whose collected revenue was assigned to pay for the Temple's maintenance and operation.
Ranjit Singh also made the position of Temple officials hereditary. The Giani family was the only family allowed to do Katha in the Golden Temple, they served the Sikh community till 1921, when the Shiromani Gurdwara Parbandhak Committee
The Shiromani Gurdwara Parbandhak Committee ( SGPC; Supreme Gurdwara Management Committee) is an organization in India responsible for the management of ''gurdwaras'', Sikh places of worship, in the states of Punjab and Himachal Pradesh and ...
came into power, they were the only family allowed to do Katha since 1788 and were also he heads of the Giani Samparda, they had built all the Bungas around the Golden Temple and helped in construction work including overlaying the temple with Gold and Marble. One of the main Bungas that was destroyed in 1988 was the Burj Gianian
Burj Gianian (lit. ''Tower of the Knowledgeable'', also known as the Gianian Bunga) was a structure next to the Akal Takht built by Giani Soorat Singh, a priest in the Sikh Empire, Sikh Raj who was the head of the Giani Samparda. It was built i ...
. The other family were the Kapurs, who were made as the Head Granthis, this included the ancestors of Bhai Jawahir Singh Kapur who also did try to become the Head Granthi in the late 1800s, but was not allowed (his father Bhai Atma Singh, grandfather Bhai Mohar Singh and their ancestors were also Head Granthis).
Destruction and reconstruction after Indian independence
The destruction of the temple complex occurred during theOperation Blue Star
Operation Blue Star was a military operation by the Indian Armed Forces conducted between 1 and 10 June 1984 to remove Jarnail Singh Bhindranwale and other Sikh militants from the Golden Temple (Harmandir Sahib), a holy site of Sikhism, and i ...
. It was the codename of an Indian military action carried out between 1 and 8 June 1984 to remove militant Sikh Jarnail Singh Bhindranwale
Jarnail Singh Bhindranwale (; born Jarnail Singh Brar; 2 June 1947– 6 June 1984) was a Sikh militant. After Operation Bluestar, he posthumously became the leading figure for the Khalistan movement, although he did not personally advocate for ...
and his followers from the buildings of the Harmandir Sahib (Golden Temple) complex in Amritsar
Amritsar, also known as Ambarsar, is the second-List of cities in Punjab, India by population, largest city in the India, Indian state of Punjab, India, Punjab, after Ludhiana. Located in the Majha region, it is a major cultural, transportatio ...
, Punjab
Punjab (; ; also romanised as Panjāb or Panj-Āb) is a geopolitical, cultural, and historical region in South Asia. It is located in the northwestern part of the Indian subcontinent, comprising areas of modern-day eastern Pakistan and no ...
. The decision to launch the attack rested with Prime Minister
A prime minister or chief of cabinet is the head of the cabinet and the leader of the ministers in the executive branch of government, often in a parliamentary or semi-presidential system. A prime minister is not the head of state, but r ...
Indira Gandhi
Indira Priyadarshini Gandhi (Given name, ''née'' Nehru; 19 November 1917 – 31 October 1984) was an Indian politician and stateswoman who served as the Prime Minister of India, prime minister of India from 1966 to 1977 and again from 1980 un ...
. In July 1982, Harchand Singh Longowal
Harchand Singh Longowal (2 January 1932 – 20 August 1985) was the President of the Akali Dal political party during the Punjab insurgency of the 1980s. He had signed the Punjab accord, also known as the Rajiv-Longowal Accord with Rajiv Gandhi ...
, the President of the Sikh political party Akali Dal
The Shiromani Akali Dal (SAD) (translation: ''Supreme Eternal Party'') is a Centre-right politics, centre-right Sikhism, Sikh-centric state political party in Punjab, India, Punjab, India. The party is the second-oldest in India, after Indian ...
, had invited Bhindranwale to take up residence in the Golden Temple Complex to evade arrest. The government claimed Bhindranwale later made the sacred temple complex an armoury
An arsenal is a place where arms and ammunition are made, maintained and repaired, stored, or issued, in any combination, whether privately or publicly owned. Arsenal and armoury (British English) or armory (American English) are mostly ...
and headquarters.
On 1 June 1984, after negotiations with the militants failed, Indira Gandhi ordered the army to launch Operation Blue Star, simultaneously attacking scores of Gurudwaras across Punjab. A variety of army units and paramilitary forces surrounded the Golden Temple complex on 3 June 1984. The fighting started on 5 June with skirmishes and the battle went on for three days, ending on 8 June. A clean-up operation codenamed Operation Woodrose
Operation Woodrose was a military operation carried out by the Indira Gandhi-led Indian government in the months after Operation Blue Star to "prevent the outbreak of widespread public protest" in the state of Punjab. The government arrested al ...
was also initiated throughout Punjab.
The army had underestimated the firepower possessed by the militants, whose armament included Chinese-made rocket-propelled grenade launchers
A rocket-propelled grenade (RPG), also known colloquially as a rocket launcher, is a shoulder-fired anti-tank weapon that launches rockets equipped with a shaped-charge explosive warhead. Most RPGs can be carried by an individual soldier, ...
with armour piercing capabilities. Tank
A tank is an armoured fighting vehicle intended as a primary offensive weapon in front-line ground combat. Tank designs are a balance of heavy firepower, strong armour, and battlefield mobility provided by tracks and a powerful engine; ...
s and heavy artillery
The formal definition of large-calibre artillery used by the United Nations Register of Conventional Arms (UNROCA) is "guns, howitzers, artillery pieces, combining the characteristics of a gun, howitzer, mortar, or rocket, capable of engaging ...
were used to attack the militants, who responded with anti-tank and machine-gun fire from the heavily fortified Akal Takht. After a 24-hour firefight, the army gained control of the temple complex. Casualty figures for the army were 83 dead and 249 injured. According to the official estimates, 1,592 militants were apprehended and there were 493 combined militant and civilian casualties. According to the government claims, high civilian casualties were attributed to militants using pilgrim
The asterisk ( ), from Late Latin , from Ancient Greek , , "little star", is a typographical symbol. It is so called because it resembles a conventional image of a heraldic star.
Computer scientists and mathematicians often vocalize it as ...
s trapped inside the temple as human shields.
Brahma Chellaney
Brahma Chellaney (born 18 January 1962) is an Indian geostrategist and columnist.
He is a professor of strategic studies at the Centre for Policy Research in New Delhi; a Richard von Weizsäcker Fellow of the Robert Bosch Academy in Berlin ...
, the Associated Press
The Associated Press (AP) is an American not-for-profit organization, not-for-profit news agency headquartered in New York City.
Founded in 1846, it operates as a cooperative, unincorporated association, and produces news reports that are dist ...
's South Asia correspondent, was the only foreign reporter who managed to stay on in Amritsar
Amritsar, also known as Ambarsar, is the second-List of cities in Punjab, India by population, largest city in the India, Indian state of Punjab, India, Punjab, after Ludhiana. Located in the Majha region, it is a major cultural, transportatio ...
despite the media blackout. His dispatches, filed by telex
Telex is a telecommunication
Telecommunication, often used in its plural form or abbreviated as telecom, is the transmission of information over a distance using electronic means, typically through cables, radio waves, or other communica ...
, provided the first non-governmental news reports on the bloody operation in Amritsar. His first dispatch, front-paged by ''The New York Times
''The New York Times'' (''NYT'') is an American daily newspaper based in New York City. ''The New York Times'' covers domestic, national, and international news, and publishes opinion pieces, investigative reports, and reviews. As one of ...
'', ''The Times
''The Times'' is a British Newspaper#Daily, daily Newspaper#National, national newspaper based in London. It began in 1785 under the title ''The Daily Universal Register'', adopting its modern name on 1 January 1788. ''The Times'' and its si ...
of London'' and ''The Guardian
''The Guardian'' is a British daily newspaper. It was founded in Manchester in 1821 as ''The Manchester Guardian'' and changed its name in 1959, followed by a move to London. Along with its sister paper, ''The Guardian Weekly'', ''The Guardi ...
'', reported a death toll about twice of what authorities had admitted. According to the dispatch, about 780 militants and civilians and 400 troops had perished in fierce gun-battles. Chellaney reported that about "eight to ten" men suspected of being Sikh militants had been shot with their hands tied. In that dispatch, Chellaney interviewed a doctor who said he had been picked up by the army and forced to conduct postmortems despite the fact he had never done any postmortem examination before. In reaction to the dispatch, the Indian government charged Chellaney with violating Punjab press censorship, two counts of fanning sectarian hatred and trouble, and later with sedition, calling his report baseless and disputing his casualty figures.
The military action in the temple complex was criticised by Sikhs worldwide, who interpreted it as an assault on the Sikh religion. Many Sikh soldiers in the army deserted their units; several Sikhs resigned from civil administrative office and returned awards received from the Indian government
The Government of India (ISO: Bhārata Sarakāra, legally the Union Government or Union of India or the Central Government) is the national authority of the Republic of India, located in South Asia, consisting of 36 states and union territor ...
. Five months after the operation, on 31 October 1984, Indira Gandhi was assassinated
Assassination is the willful killing, by a sudden, secret, or planned attack, of a personespecially if prominent or important. It may be prompted by political, ideological, religious, financial, or military motives.
Assassinations are orde ...
in an act of revenge by her two Sikh bodyguards, Satwant Singh
Satwant Singh (1962 – 6 January 1989) was one of the bodyguards, along with Beant Singh (assassin), Beant Singh, who Assassination of Indira Gandhi, assassinated the Prime Minister of India, Indira Gandhi, at her New Delhi residence on 31 Oct ...
and Beant Singh. Public outcry over Gandhi's death led to the killings of more than 3,000 Sikhs in Delhi alone, in the ensuing 1984 anti-Sikh riots
The 1984 anti-Sikh riots, also known as the 1984 Sikh massacre, was a series of organised pogroms against Sikhs in India following the assassination of Indira Gandhi by her Sikh bodyguards. Government estimates project that about 2,800 Sikhs w ...
. A few months after the government operation of 1984, major '' kar seva'' renovations were undertaken at the shrine complex, including a complete draining and then cleaning of the temple tank (''sarovar'') by volunteers.
Following the operation the central government
A central government is the government that is a controlling power over a unitary state. Another distinct but sovereign political entity is a federal government, which may have distinct powers at various levels of government, authorized or deleg ...
demolished hundreds of houses and created a corridor around the compound called "Galliara" (also spelled Galiara or Galyara) for security reasons. This was made into a public park and opened in June 1988.
In December 2021, a young man was allegedly beaten to death after disrupting the Rehras Sahib (evening prayer) at the sanctum of the temple. He reportedly jumped over a railing and picked up the sword lying before the temple's copy of the Guru Granth Sahib
The Guru Granth Sahib (, ) is the central holy religious scripture of Sikhism, regarded by Sikhs as the final, sovereign and eternal Guru following the lineage of the ten human gurus of the religion. The Adi Granth (), its first rendition, w ...
, before attempting to touch the Guru Granth Sahib itself. He was subsequently overpowered by the pilgrims and received fatal injuries to the head.
The 2023 Golden Temple blasts
The Golden Temple in Amritsar, India, was damaged by the first blast that happened on 7 May 2023, and by the second blast that happened on 8 May 2023. At midnight on 10 May 2023 a third blast occurred. The explosions were triggered by low-grade ...
occurred on 7 May and on 9 May 2023.
Architecture

Indian subcontinent
The Indian subcontinent is a physiographic region of Asia below the Himalayas which projects into the Indian Ocean between the Bay of Bengal to the east and the Arabian Sea to the west. It is now divided between Bangladesh, India, and Pakista ...
, as various iterations of temple were rebuilt and restored.
The first structure of the Harmandir Sahib constructed under the purview of Guru Arjan combined the concepts of '' dharamsaals'' and the holy water tanks (''sarovar
Temple tanks are wells or reservoirs built as part of the temple complex near Indian temples. They are called pushkarini, kalyani, kunda, sarovara, tirtha, talab, pukhuri, ambalakkuḷam, etc. in different languages and regions of India. Some ...
''). Rather than copying the traditional method of Hindu temple construction by building the shrine on a high plinth, Guru Arjan rather decided to build the shrine lower than the surroundings so that devotees would have to walk downwards to reach it. The four entrances represented that the Sikh faith was equally open to all four of the traditional Indian caste classifications ('' varnas''). No surviving account, depiction, or record is extant or known of the proto-type, pre-1764 Harmandir Sahib that was built by the Sikh gurus themselves. However, Kanwarjit Singh Kang believes the original, Guru-constructed structure was mostly comparable and similar to the present-day structure said to have been constructed in 1764.
James Fergusson considered the Golden Temple as a specimen of one of the forms that the architecture of Hindu temples developed into in the 19th century. When a list of structures of interest was prepared and published by the colonial government of Punjab in 1875, it was claimed that the architectural design of the Golden Temple, in the form it was constructed as by Ranjit Singh, was based ultimately on the shrine
A shrine ( "case or chest for books or papers"; Old French: ''escrin'' "box or case") is a sacred space">-4; we might wonder whether there's a point at which it's appropriate to talk of the beginnings of French, that is, when it wa ...: ''escri ...
of the Sufi saint Mian Mir
Mian Mir or Miyan Mir (c. 1550 – 22 August 1635), was a famous Sufi Muslim saint who resided in Lahore, in the neighborhood now known as Dharampura.
He was a direct descendant of Caliph Umar ibn al-Khattab and belonged to the Qadiri order ...
. Louis Rousselet
Louis-Théophile Marie Rousselet (1845–1929) was a French traveller, writer, photographer and pioneer of the darkroom. His photographic work now commands high prices. Many of his drawings and photographs were made into engravings by others.
...
stated in 1882 that the shrine was a "handsome style of Jat
The Jat people (, ), also spelt Jaat and Jatt, are a traditionally agricultural community in Northern India and Pakistan. Originally pastoralists in the lower Indus river-valley of Sindh, many Jats migrated north into the Punjab region in l ...
architecture." Major Henry Hardy Cole described the architecture of the edifice as being primarily drawn from Islamic sources with a significant input from Hindu styles. Percy Brown also classified the temple as being a synthesis of Islamic and Hindu architectural styles, but also observed that the structure has its own unique characteristics and inventions. Hermann Goetz
Hermann Gustav Goetz (7 December 1840 – 3 December 1876) was a German composer who spent much of his career in Switzerland. He is best known for his 1872 opera ''Der Widerspänstigen Zähmung'', based on Shakespeare's ''The Taming of the Shrew' ...
believed that the temple's architecture was a " Kangra transformation of Oudh
The Kingdom of Awadh (, , also Oudh State, Kingdom of Oudh, Awadh Subah, or Awadh State) was a Mughal subah, then an independent kingdom, and lastly a British protectorate in the Awadh region of North India until its annexation by the Br ...
architecture" that the Sikhs adopted for their own constructions, which he praises, however he also critiqued the temple for having "gaudy" elements commonly found in Indian gurdwaras, an example being the rococo-styled art. The Temple is described by Ian Kerr, and other scholars, as a mixture of the Indo-Islamic Mughal and the Hindu Rajput architecture.
The sanctum is a 12.25 x 12.25 metre square with two storeys and a gold leaf dome. This sanctum has a marble platform that is a 19.7 x 19.7 metre square. It sits inside an almost square (154.5 x 148.5 m2) pool called ''amritsar'' or ''amritsarovar'' (''amrit'' means nectar, ''sar'' is short form of ''sarovar'' and means pool). The pool is 5.1 metres deep and is surrounded by a 3.7 metre wide circumambulatory marble passage that is circled clockwise. The sanctum is connected to the platform by a causeway and the gateway into the causeway is called the Darshani Ḍeorhi (from ''Darshana Dvara''). For those who wish to take a dip in the pool, the Temple provides a half hexagonal shelter and holy steps to Har ki Pauri. Bathing in the pool is believed by many Sikhs to have restorative powers, purifying one's ''karma
Karma (, from , ; ) is an ancient Indian concept that refers to an action, work, or deed, and its effect or consequences. In Indian religions, the term more specifically refers to a principle of cause and effect, often descriptively called ...
''. Some carry bottles of the pool water home particularly for sick friends and relatives. The pool is maintained by volunteers who perform ''kar seva'' (community service) by draining and desilting it periodically.
There is a section of the shrine known as the ''Har-Ki-Pauri'', located on the backside of the temple proper, where pilgrims and worshippers can take a sip of the water from the holy temple tank. The water used for the daily ritual cleaning of the temple premises is also sourced from this section. The water is mixed with milk to dilute the milk content, with the combined solution used to clean the temple's surfaces on a daily basis.
The sanctum has two floors. The Sikh Scripture ''Guru Granth Sahib
The Guru Granth Sahib (, ) is the central holy religious scripture of Sikhism, regarded by Sikhs as the final, sovereign and eternal Guru following the lineage of the ten human gurus of the religion. The Adi Granth (), its first rendition, w ...
'' is seated on the lower square floor for about 20 hours every day, and for 4 hours it is taken to its bedroom inside Akal Takht with elaborate ceremonies in a palki, for ''sukhasana'' and ''Prakash''. The floor with the seated scripture is raised a few steps above the entrance causeway level. The upper floor in the sanctum is a gallery and connected by stairs. The ground floor is lined with white marble, as is the path surrounding the sanctum. The sanctum's exterior has gilded copper plates. The doors are gold leaf-covered copper sheets with nature motifs such as birds and flowers. The ceiling of the upper floor is gilded, embossed and decorated with jewels. The sanctum dome is semi-spherical with a pinnacle ornament. The sides are embellished with arched copings and small solid domes, the corners adorning cupolas, all of which are covered with gold leaf-covered gilded copper. There is a pavilion located on the second-floor called the ''Shish Mahal'' (mirror room).
The floral designs on the marble panels of the walls around the sanctum are Arabesque
The arabesque is a form of artistic decoration consisting of "surface decorations based on rhythmic linear patterns of scrolling and interlacing foliage, tendrils" or plain lines, often combined with other elements. Another definition is "Foliate ...
. The arches include verses from the Sikh scripture in gold letters. The frescoes follow the Indian tradition and include animal, bird and nature motifs rather than being purely geometrical. The stair walls have murals of Sikh Gurus such as the falcon carrying Guru Gobind Singh riding a horse.
 The Darshani Deorhi is a two-storey structure that houses the temple management offices and treasury. At the exit of the path leading away from the sanctum is the ''Prasada'' facility, where volunteers serve a flour-based sweet offering called ''Karah prasad''. Typically, the pilgrims to the Golden Temple enter and make a clockwise circumambulation around the pool before entering the sanctum. There are four entrances to the gurdwara complex signifying the openness to all sides, but a single entrance to the sanctum of the temple through a causeway.
The Darshani Deorhi is a two-storey structure that houses the temple management offices and treasury. At the exit of the path leading away from the sanctum is the ''Prasada'' facility, where volunteers serve a flour-based sweet offering called ''Karah prasad''. Typically, the pilgrims to the Golden Temple enter and make a clockwise circumambulation around the pool before entering the sanctum. There are four entrances to the gurdwara complex signifying the openness to all sides, but a single entrance to the sanctum of the temple through a causeway.
Akal Takht and Teja Singh Samundri Hall
In front of the sanctum and the causeway is the Akal Takht building. It is the chief ''Takht'', a centre of authority in Sikhism. Its name ''Akal Takht'' means "throne of the Timeless (God)". The institution was established byGuru Hargobind
Guru Hargobind (Gurmukhi: ਗੁਰੂ ਹਰਿਗੋਬਿੰਦ, pronunciation: l 19 June 1595 – 28 February 1644) was the sixth of ten Gurus of the Sikh religion. He had become Guru at the young age of eleven, after the execution of his ...
after the martyrdom of his father Guru Arjan, as a place to conduct ceremonial, spiritual and secular affairs, issuing binding writs on Sikh gurdwaras far from his own location. A building was later constructed over the Takht founded by Guru Hargobind, and this came to be known as Akal Bunga. The Akal Takht is also known as Takht Sri Akal Bunga. The Sikh tradition has five Takhts, all of which are major pilgrimage sites in Sikhism. These are in Anandpur, Patna, Nanded, Talwandi Sabo and Amritsar. The Akal Takht in the Golden Temple complex is the primary seat and chief. It is also the headquarters of the main political party of the Indian state of Punjab, Shiromani Akali Dal (Supreme Akali Party). The Akal Takht issues edicts or writs (''hukam'') on matters related to Sikhism and the solidarity of the Sikh community.
The Teja Singh Samundri Hall is the office of the Shiromani Gurdwara Parbandhak Committee
The Shiromani Gurdwara Parbandhak Committee ( SGPC; Supreme Gurdwara Management Committee) is an organization in India responsible for the management of ''gurdwaras'', Sikh places of worship, in the states of Punjab and Himachal Pradesh and ...
(Supreme Committee of Temple Management). It is located in a building near the Langar-kitchen and Assembly Hall. This office coordinates and oversees the operations of major Sikh temples.
Ramgarhia Bunga and Clock Tower
TheRamgarhia Bunga
Ramgarhia Bunga or Burj is the three-storeyed red stone watchtowers complex located near southeastern edge of the Golden Temple, Amritsar. The two minaret-style Ramgarhia Bunga high towers are visible from the ''parikrama'' (circumambulation) wa ...
– the two high towers visible from the ''parikrama'' (circumambulation) walkway around the tank, is named after a Sikh subgroup. The red sandstone minaret-style ''Bunga'' (buêgā) towers were built in the 18th century, a period of Afghan attacks and temple demolitions. It is named after the Sikh
Sikhs (singular Sikh: or ; , ) are an ethnoreligious group who adhere to Sikhism, a religion that originated in the late 15th century in the Punjab region of the Indian subcontinent, based on the revelation of Guru Nanak. The term ''Si ...
warrior and Ramgarhia
The Ramgarhia are a community of Sikhs from the Punjab region of northwestern India, encompassing members of the Lohar (blacksmiths) and Tarkhan (carpenters) subgroups.
Etymology
Originally called Thoka, meaning ''carpenter'', the Ramgarhia ...
misl
Major Indoor Soccer League has been the name of three different American professional indoor soccer leagues:
*Major Indoor Soccer League (1978–1992), known in its final two seasons as the Major Soccer League
*Major Indoor Soccer League (2001–2 ...
chief Jassa Singh Ramgarhia
Jassa Singh Ramgarhia (1723–1803) was a prominent Sikh leader during the period of the Sikh Confederacy. He was the founder of the Ramgarhia Misl.
Early life
Jassa Singh Ramgarhia was born into a Sikh family in 1723. According to W. H. McLe ...
. It was constructed as the temple watchtower
A watchtower or guardtower (also spelt watch tower, guard tower) is a type of military/paramilitary or policiary tower used for guarding an area. Sometimes fortified, and armed with heavy weaponry, especially historically, the structures are ...
s for sentinels to watch for any military raid approaching the temple and the surrounding area, help rapidly gather a defence to protect the Golden Temple complex. According to Fenech and McLeod, during the 18th century, Sikh misl chiefs and rich communities built over 70 such ''Bungas'' of different shapes and forms around the temple to watch the area, house soldiers and defend the temple. These served defensive purposes, provided accommodation for Sikh pilgrims and served as centres of learning in the 19th century. Most of the Bungas were demolished during the British colonial era. The Ramgarhia Bunga remains a symbol of the Ramgarhia
The Ramgarhia are a community of Sikhs from the Punjab region of northwestern India, encompassing members of the Lohar (blacksmiths) and Tarkhan (carpenters) subgroups.
Etymology
Originally called Thoka, meaning ''carpenter'', the Ramgarhia ...
Sikh community's identity, their historic sacrifices and contribution to defending the Golden Temple over the centuries.
The Clock Tower did not exist in the original version of the temple. In its location was a building, now called the "lost palace". The officials of the British India
The provinces of India, earlier presidencies of British India and still earlier, presidency towns, were the administrative divisions of British governance in South Asia. Collectively, they have been called British India. In one form or another ...
wanted to demolish the building after the Second Anglo-Sikh war and once they had annexed the Sikh Empire. The Sikhs opposed the demolition, but this opposition was ignored. In its place, the clock tower was added. The clock tower was designed by John Gordon in a Gothic cathedral style with red bricks. The clock tower construction started in 1862 and was completed in 1874. The tower was demolished by the Sikh community about 70 years later. In its place, a new entrance was constructed with a design more harmonious with the Temple. This entrance on the north side has a clock, houses a museum on its upper floor, and it continues to be called ''ghanta ghar deori''.
Ber trees
 The Golden Temple complex originally was open and had numerous trees around the pool. It is now a walled, two-storey courtyard with four entrances, that preserve three Ber trees (
The Golden Temple complex originally was open and had numerous trees around the pool. It is now a walled, two-storey courtyard with four entrances, that preserve three Ber trees (jujube
Jujube (UK ; US or ), sometimes jujuba, scientific name ''Ziziphus jujuba'', and also called red date, Chinese date, and Chinese jujube, is a species in the genus '' Ziziphus'' in the buckthorn family Rhamnaceae. It is often confused wit ...
). One of them is to the right of the main ''ghanta ghar deori'' entrance with the clock, and it is called the ''Ber Baba Buddha''. It is believed in the Sikh tradition to be the tree where Baba Buddha sat to supervise the construction of the pool and first temple.
A second tree is called ''Laachi Ber'', believed to the one under which Guru Arjan rested while the temple was being built. The third one is called ''Dukh Bhanjani Ber'', located on the other side of the sanctum, across the pool. It is believed in the Sikh tradition that this tree was the location where a Sikh was cured of his leprosy after taking a dip in the pool, giving the tree the epithet of "suffering remover". There is a small gurdwara underneath the tree. The ''Ath Sath Tirath'', or the spot equivalent to 68 pilgrimages, is in the shade underneath the ''Dukh Bhanjani Ber'' tree. Sikh devotees, states Charles Townsend, believe that bathing in the pool near this spot delivers the same fruits as a visit to 68 pilgrimage places in India.
Sikh history museums
The main ''ghanta ghari deori'' north entrance has a Sikh history museum on the first floor, according to the Sikh tradition. The display shows various paintings, of gurus and martyrs, many narrating the persecution of Sikhs over their history, as well as historical items such as swords, ''kartar'', comb, ''chakkars''. A new underground museum near the clock tower, but outside the temple courtyard also shows Sikh history. According to Louis E. Fenech, the display does not present the parallel traditions of Sikhism and is partly ahistorical such as a headless body continuing to fight, but a significant artwork and reflects the general trend in Sikhism of presenting their history to be one of persecution, martyrdoms and bravery in wars. The main entrance to the gurdwara has many memorial plaques that commemorate past Sikh historical events, saints and martyrs, contributions of Ranjit Singh, as well as commemorative inscriptions of all the Sikh soldiers who died fighting in the two World Wars and the various Indo-Pakistan wars.Daily ceremonies
There are several rites performed every day in the Golden Temple as per the historic Sikh tradition. These rites treat the scripture as a living person, a Guru out of respect. They include: * Closing rite called ''sukhasan'' (''sukh'' means "comfort or rest", ''asan'' means "position"). At night, after a series of devotionalkirtan
Sikh ''kirta''n with Indian harmoniums and '' Kenya.html" ;"title="tabla'' drums (a common and popular pairing), in Kenya">tabla'' drums (a common and popular pairing), in Kenya (1960s)
''Kirtana'' (; ), also rendered as ''Kiirtan'', ''Kirt ...
s and three part ardās
The Ardās (, pronunciation: ) is a set prayer in Sikhism. It is a part of worship service in a Gurdwara (Sikh temple), daily rituals such as the opening the ''Guru Granth Sahib'' for ''prakash'' (morning light) or closing it for ''sukhasan'' (n ...
, the ''Guru Granth Sahib'' is closed, carried on the head, placed into and then carried in a flower decorated, pillow-bed palki (palanquin), with chanting. Its bedroom is in the Akal Takht, on the first floor. Once it arrives there, the scripture is tucked into a bed.
* Opening rite called ''prakash'' which means "light". At about dawn every day, the ''Guru Granth Sahib'' is taken out its bedroom, carried on the head, placed and carried in a flower-decorated palki with chanting and bugle
The bugle is a simple signaling brass instrument with a wide conical bore. It normally has no valves or other pitch-altering devices, and is thus limited to its natural harmonic notes, and pitch is controlled entirely by varying the air a ...
sounding across the causeway. It is brought to the sanctum. Then after ritual singing of a series of Var Asa kirtans and ''ardas'', a random page is opened. This is the ''mukhwak'' of the day, it is read out loud, and then written out for the pilgrims to read over that day.
Guru Ram Das Langar
Harmandir Sahib complex has alangar
Langar may refer to:
Community eating
*Langar (Sikhism)
*Langar (Sufism)
Places
Afghanistan
*Langar, Badakhshan, Afghanistan
*Langar, Bamyan, Afghanistan
*Langar, Faryab, Afghanistan
*Langar, Herat, Afghanistan
*Langar, Wardak, Afghanistan
...
, a community-run free kitchen and dining hall. It is attached to the east side of the courtyard near the ''Dukh Bhanjani Ber'', outside of the entrance. Food is served here to all visitors who want it, regardless of faith, gender or economic background. Vegetarian food is served and all people eat together as equals. Everyone sits on the floor in rows, which is called ''sangat''. The meal is served by volunteers as part of their ''kar seva'' ethos. Over 100,000 meals are served at the langar every day.
Art
The art of the Golden Temple has rarely been analysed or studied in a serious manner. Within the Shish Mahal on the second-story of the building, there are mirror-work art designs which consist of small pieces of mirror which are inlaid into the walls and ceilings, highlighed with decorations of floral designs. The ceilings, walls and arches of the structure are embellished by intricate mural artwork. The ''pietra dura
''Pietra dura'' (), ''pietre dure'' () or intarsia lapidary ( see below), called ''parchin kari'' or ''parchinkari'' () in the Indian subcontinent, is a term for the inlay technique of using cut and fitted, highly polished colored stones to c ...
'' (inlaid stone design) artwork of the shrine, which features avian and other animalistic designs using semi-precious stones, was mostly inspired by the Mughal tradition. The temple premises is also decorated with embossed copper, ''gach'', ''tukri'', ''jaratkari'', and ivory inlay artwork. The external portions of the upper story's walls of the temple have been affixed with beaten copper plates that feature raised designs depicting usually florals and abstracts but there are some depictions of human figures as well. An example of embossed metal designs depicting humans are two raised copper panels located on the front-side of the temple prior, the first which depicts Guru Nanak
Gurū Nānak (15 April 1469 – 22 September 1539; Gurmukhi: ਗੁਰੂ ਨਾਨਕ; pronunciation: , ), also known as ('Father Nanak'), was an Indian spiritual teacher, mystic and poet, who is regarded as the founder of Sikhism and is t ...
surrounded by his companions, Bhai Mardana
Bhai Mardana (; 1459 — 1534) was one of the first Sikhs and longtime companion of Guru Nanak Dev, first in the line of gurus noted in Sikhism. Bhai Mardana was a Muslim by-birth who would accompany Guru Nanak Dev on his journeys and became on ...
and Bhai Bala
Bhai Bala (; 1466–1544) was a companion of Guru Nanak. Born in Talwandi into a Sandhu Jat family, Bala was also a close associate of Bhai Mardana.
Biography
According to the , he traveled with Guru Nanak and Bhai Mardana on all of their ...
, on each side. The second embossed panel features an equestrian portrayal of Guru Gobind Singh
Guru Gobind Singh (; born Gobind Das; 22 December 1666 – 7 October 1708) was the tenth and last human Sikh gurus, Sikh Guru. He was a warrior, poet, and philosopher. In 1675, at the age of nine he was formally installed as the leader of the ...
.
''Gach'' can be described as a kind of stone or gypsum. Gach was transformed into a paste and used on the walls, similar in nature to lime-plaster. Once applied to the wall, it was decorated into shape with steel cutters and other tools. Sometimes the gach had coloured glass pieces placed on it, which is known as ''tukri''. The Shish Mahal features a lot of examples of tukri work. On the other hand, ''jaratkari'' was an art form and method which involved placing inlaid and cut stones of varying colours and types into marble. Surviving exemplars of jaratkari art from the temple can be found on the bottom-section of the exterior walls which are encased with marble panels featuring jaratkari artwork. The jaratkari marble panels in this lower exterior section is classified as pietra dura and semi-precious stones, like lapis lazuli and onyx, were utilised. While the Mughals also decorated their edifices using jaratkari and pietra dura art, what sets apart the Sikh form of the art technique from the Mughal one is that the Sikh jaratkari art form also depicts human and animal figuratives with it, something that is not found in Mughal jaratkari art.
Inlaid ivory work can be witnessed on the doors of the Darshani Deori structure of the complex. The structure of the Darshani Deori was made out of ''shisham
''Dalbergia sissoo'', known commonly as North Indian rosewood or shisham, is a fast-growing, hardy, deciduous rosewood tree native to the Indian subcontinent and southern Iran. ''D. sissoo'' is a large, crooked tree with long, leathery leaves a ...
'' wood, the front of the edifice is overlaid with silverwork, including ornamated silver panels. The back of the structure is decorated with panels consisting of floral and geometric designs but also animal figuratives, such as deer, tigers, lions, and birds. Portions of the inlaid ivory had been coloured red or green, an aspect of the artwork that was praised by H.H. Cole for its harmoniousness.
The oldest extant mural
A mural is any piece of Graphic arts, graphic artwork that is painted or applied directly to a wall, ceiling or other permanent substrate. Mural techniques include fresco, mosaic, graffiti and marouflage.
Word mural in art
The word ''mural'' ...
s in the complex date back to the 1830s. Most of the vast array of murals that once coated the walls of the complex were destroyed in subsequent renovation works conducted under the guise of '' kar seva'', such as by being covered by marble slabs affixed to the walls. A prominent artist who painted many of the murals in the complex was Gian Singh Naqqash. The mural artwork of the temple consists primarily of floral designs with scattered examples of animal designs and themes. There are over 300 different design patterns dispersed all over the walls of the edifice. These wall paintings were created by ''Naqqashi'' artists, who had developed their own lingo to differentiate their various themes and designs. The most prominent design category was referred to as ''Dehin,'' which is described as "a medium of expression of the imaginative study of the artist's own creation of idealized forms". The base of dehin is known as ''Gharwanjh''. Gharwanjh is a "decorative device involving knotted grapples between animals". The gharwanjh designs of the Golden Temple features cobras, lions, and elephants holding one another or carrying floral vases which feature fruit and fairies as decoration. The decorative border of the dehin is known as ''Patta'', usually utilising creepers for its design. Furthermore, some dehin feature designs incorporating aquatic creatures.
The only mural depicting human figures within the temple proper is located on the wall behind the northern narrow staircase leading to the top of the shrine, and it is a depiction of Guru Gobind Singh on horseback alongside his retinue leaving the fort of Anandpur, ultimately a mural adaptation of what was originally a Kangra miniature painting. When H.H. Cole wrote about the murals of the Golden Temple, he witnessed many murals depicting Indic mythological scenes but these murals have since been seemingly lost to time and are no longer extant.
While W. Wakefield had recorded that he observed murals depicting erotic scenes painted on the Golden Temple's walls in a work published in 1875, Kanwarjit Singh Kang finds this to be a spurious account which is likely false because there is no corroborative accounts to support this.
The various artists and craftsmen who worked on creating the mural artwork and other accessory art of the temple are mostly unknown and it is nearly impossible to link any particular art piece with a specific name, aside from a very few. A traditional Sikh artist who had worked at the Golden Temple, named Hari Singh, had prepared a list of all the names of the artists, painters (''naqqashis''), and craftsmen he could recount that had also worked at some point in time at the Golden Temple, the names are as follows: Kishan Singh, Bishan Singh, Kapur Singh, Kehar Singh, ''Mahant
Mahant () is a religious superior, in particular the chief of a temple or the head of a monastery in Indian religions.
James Mallinson, one of the few westerners to be named as a mahant, describes the position of a mahant as a combination of an ...
'' Ishar Singh, Sardul Singh, Jawahar Singh, Mehtab Singh, ''Mistri
Mistri, or Mistry, is a term for a master-craftsman, foreman or supervisor of manual workers in India. Mistri is being replaced with terms "supervisor" and master craftsman with "Senior Technician" by the Indian Railway who replaced the designati ...
'' Jaimal Singh, Harnam Singh, Ishar Singh (not to be confused with Mahant Ishar Singh), Gian Singh, Lal Singh Tarn Taran, Mangal Singh, Mistri Narain Singh, Mistri Jit Singh, Atma Singh, Darja Mal, and Vir Singh.
Most of the artwork lost over the years, throughout the various changes and renovations to the temple, were murals. Murals started being lost in the temple around the last years of the 19th century, when devotees were allowed to start donating inlaid marble panels to affix to the walls of the shrine. The walls that were covered by these marble panels usually were painted with murals and thus the murals were either hidden under the marble panels or destroyed. The Golden Temple used to have many traditional buildings, known as ''bungas'', surrounding it. These bungas were a great source and collection of murals and thus their artwork was lost when the vast majority of the bungas were demolished over the years under the guise of modernising the religious site and expanding its ''parikrama
Parikrama or Pradakshina is clockwise circumambulation of sacred entities, and the path along which this is performed, as practiced in the Indian religions, Indic religions – Hinduism, Buddhism, Sikhism and Jainism. In Buddhism, it refers only ...
''. When the Darshani Deori was covered with marble panels, many wall paintings that had been executed by Mahant Ishar Singh were covered up and lost due to them.
Influence on contemporary era Sikhism
Singh Sabha movement
TheSingh Sabha movement
The Singh Sabhā Movement, also known as the Singh Sabhā Lehar, was a Sikh movement that began in Punjab in the 1870s in reaction to the proselytising activities of Christians, Hindu reform movements (Brahmo Samaj, Arya Samaj) and Muslims ( Ali ...
was a late-19th century movement within the Sikh community to rejuvenate and reform Sikhism at a time when Christian, Hindu and Muslim proselytizers were actively campaigning to convert Sikhs to their religion. The movement was triggered by the conversion of Ranjit Singh's son Duleep Singh and other well-known people to Christianity. Started in 1870s, the Singh Sabha movement's aims were to propagate the true Sikh religion, restore and reform Sikhism to bring back into the Sikh fold the apostates who had left Sikhism. There were three main groups with different viewpoints and approaches, of which the Tat Khalsa group had become dominant by the early 1880s. Before 1905, the Golden Temple had Brahmin priests, idols and images for at least a century, attracting pious Sikhs and Hindus., Quote: "Brahmin priests and their idols had been associated with the Golden Temple for at least a century and had over these years received the patronage of pious Hindus and Sikhs. In the 1890s these practices came under increasing attack by reformist Sikhs." In 1890s, these idols and practices came under attack from reformist Sikhs. In 1905, with the campaign of the Tat Khalsa, these idols and images were removed from the Golden Temple. The Singh Sabha movement brought the Khalsa back to the fore of gurdwara administration over the ''mahants'' (priests) class, who had taken over control of the main gurdwaras and other institutions vacated by the Khalsa
The term ''Khalsa'' refers to both a community that follows Sikhism as its religion,Khalsa: Sikhism< ...
in their fight for survival against the Mughals
The Mughal Empire was an early modern empire in South Asia. At its peak, the empire stretched from the outer fringes of the Indus River Basin in the west, northern Afghanistan in the northwest, and Kashmir in the north, to the highlands of pre ...
during the 18th century and had been most prominent during the 19th century.
Jallianwala Bagh massacre
As per tradition, the Sikhs gathered in the Golden Temple to celebrate the festival of Baisakhi in 1919. After their visit, many walked over to theJallianwala Bagh
Jallianwala Bagh () is a historic garden and memorial of national importance close to the Golden Temple complex in Amritsar, Punjab, India, preserved in the memory of those wounded and killed in the Jallianwala Bagh Massacre that took place on t ...
next to it to listen to speakers protesting the Rowlatt Act
The Anarchical and Revolutionary Crimes Act of 1919, popularly known as the Rowlatt Act, was a law, applied during the British India period. It was a legislative council act passed by the Imperial Legislative Council in Delhi on 18
March 1919 ...
and other policies implemented by the British colonial government. A large crowd had gathered, when Colonel Reginald Edward Harry Dyer
Colonel Reginald Edward Harry Dyer, (9 October 186423 July 1927) was a British military officer in the Bengal Army and later the newly constituted British Indian Army. His military career began in the regular British Army, but he soon transfe ...
ordered a detachment of ninety soldiers (drawn from the 9th Gorkha Rifles
The 9th Gorkha Rifles is a Gorkha infantry regiment of the Indian Army and, previously, the British Army. The regiment was initially formed by the British in 1817, and was one of the Gurkha regiments transferred to the Indian Army after independ ...
and the 59th Scinde Rifles) under his command to surround the Jallianwala Bagh, and then open fire into the crowd. 379 were killed and thousands were wounded in the massacre. The massacre
A massacre is an event of killing people who are not engaged in hostilities or are defenseless. It is generally used to describe a targeted killing of civilians Glossary of French words and expressions in English#En masse, en masse by an armed ...
strengthened the opposition to colonial rule throughout India, particularly that from Sikhs. It triggered massive non-violent protests. The protests pressured the British colonial government to transfer the control over the management and treasury of the Golden Temple to an elected organisation called Shiromani Gurudwara Prabandhak Committee (SGPC). The SGPC continues to manage the Golden Temple.
Punjabi Suba movement
ThePunjabi Suba movement
The Punjabi Suba movement was a political movement led by Punjabi-speakers (mainly Sikhs) from 1947 to 1966, demanding the creation of an autonomous ''Punjabi Suba'', or Punjabi-speaking state, in the post-independence Indian state of East Pu ...
was a long-drawn political agitation, launched by the Sikhs
Sikhs (singular Sikh: or ; , ) are an ethnoreligious group who adhere to Sikhism, a religion that originated in the late 15th century in the Punjab region of the Indian subcontinent, based on the revelation of Guru Nanak. The term ''Sikh'' ...
, demanding the creation of a Punjabi Suba, or Punjabi
Punjabi, or Panjabi, most often refers to:
* Something of, from, or related to Punjab, a region in India and Pakistan
* Punjabi language
* Punjabis, Punjabi people
* Punjabi dialects and languages
Punjabi may also refer to:
* Punjabi (horse), a ...
-speaking state, in the post-independence state of East Punjab
East Punjab was a state of Dominion of India from 1947 until 1950. It consisted parts of the Punjab Province of British India that remained in India following the partition of the state between the new dominions of Pakistan and India by the ...
. It was first presented as a policy position in April 1948 by the Shiromani Akali Dal
The Shiromani Akali Dal (SAD) (translation: ''Supreme Eternal Party'') is a centre-right Sikh-centric state political party in Punjab, India. The party is the second-oldest in India, after Congress, being founded in 1920. Although there are ma ...
, after the States Reorganization Commission set up after independence was not effective in the north of the country during its work to delineate states on a linguistic basis. The Golden Temple complex was the main centre of operations of the movement, and important events during the movement that occurred at the gurdwara included the 1955 raid by the government to quash the movement, and the subsequent Amritsar Convention in 1955 to convey Sikh sentiments to the central government. The complex was also the site of speeches, demonstrations, and mass arrests, and where leaders of the movement domiciled in huts during hunger strike
A hunger strike is a method of non-violent resistance where participants fasting, fast as an act of political protest, usually with the objective of achieving a specific goal, such as a policy change. Hunger strikers that do not take fluids are ...
s. The borders of the modern state of Punjab
Punjab () is a States and union territories of India, state in northwestern India. Forming part of the larger Punjab, Punjab region of the Indian subcontinent, the state is bordered by the States and union territories of India, Indian states ...
, along with the official status of the state's native language of Punjabi
Punjabi, or Panjabi, most often refers to:
* Something of, from, or related to Punjab, a region in India and Pakistan
* Punjabi language
* Punjabis, Punjabi people
* Punjabi dialects and languages
Punjabi may also refer to:
* Punjabi (horse), a ...
in the Gurmukhi
Gurmukhī ( , Shahmukhi: ) is an abugida developed from the Laṇḍā scripts, standardized and used by the second Sikh guru, Guru Angad (1504–1552). Commonly regarded as a Sikh script, Gurmukhi is used in Punjab, India as the official scrip ...
script, are the result of the movement, which culminated in the setting of the current borders in 1966.
Operation Blue Star
 The Golden Temple and Akal Takht were occupied by various militant groups in the early 1980s. These included the
The Golden Temple and Akal Takht were occupied by various militant groups in the early 1980s. These included the Dharam Yudh Morcha
The Dharam Yuddh Morcha () ("righteous campaign") was a political movement launched on 4 August 1982, by the Shiromani Akali Dal in partnership with Jarnail Singh Bhindranwale, with its stated aim being the fulfillment of a set of devolutiona ...
led by Sikh fundamentalist Jarnail Singh Bhindranwale
Jarnail Singh Bhindranwale (; born Jarnail Singh Brar; 2 June 1947– 6 June 1984) was a Sikh militant. After Operation Bluestar, he posthumously became the leading figure for the Khalistan movement, although he did not personally advocate for ...
, the Babbar Khalsa, the AISSF and the National Council of Khalistan. In December 1983, the Sikh political party Akali Dal
The Shiromani Akali Dal (SAD) (translation: ''Supreme Eternal Party'') is a Centre-right politics, centre-right Sikhism, Sikh-centric state political party in Punjab, India, Punjab, India. The party is the second-oldest in India, after Indian ...
's President Harchand Singh Longowal
Harchand Singh Longowal (2 January 1932 – 20 August 1985) was the President of the Akali Dal political party during the Punjab insurgency of the 1980s. He had signed the Punjab accord, also known as the Rajiv-Longowal Accord with Rajiv Gandhi ...
had invited Jarnail Singh Bhindranwale
Jarnail Singh Bhindranwale (; born Jarnail Singh Brar; 2 June 1947– 6 June 1984) was a Sikh militant. After Operation Bluestar, he posthumously became the leading figure for the Khalistan movement, although he did not personally advocate for ...
to take up residence in Golden Temple Complex. The Bhindranwale-led group under the military leadership of General Shabeg Singh
Shabeg Singh, PVSM, AVSM (1 May 1924 – 6 June 1984), was an Indian military officer. He had previously served in the British Indian Army and in the Indian Army but later joined the movement of Jarnail Singh Bhindranwale.
He is well known fo ...
had begun to build bunkers and observations posts in and around the Golden Temple. They organised the armed militants present at the Harmandir Sahib
The Golden Temple is a gurdwara located in Amritsar, Punjab, India. It is the pre-eminent spiritual site of Sikhism. It is one of the Holy place, holiest sites in Sikhism, alongside the Gurdwara Darbar Sahib Kartarpur in Kartarpur, Pakistan, ...
in Amritsar in June 1984. The Golden Temple became a place for weapons training for the militants. Shabeg Singh's military expertise is credited with the creation of effective defences of the Gurdwara Complex that made the possibility of a commando operation on foot impossible. Supporters of this militant movement circulated maps showing parts of northwest India, north Pakistan and eastern Afghanistan as historic and future boundaries of the Khalsa Sikhs, with varying claims in different maps.
In June 1984, Prime Minister Indira Gandhi
Indira Priyadarshini Gandhi (Given name, ''née'' Nehru; 19 November 1917 – 31 October 1984) was an Indian politician and stateswoman who served as the Prime Minister of India, prime minister of India from 1966 to 1977 and again from 1980 un ...
ordered the Indian Army to begin Operation Blue Star
Operation Blue Star was a military operation by the Indian Armed Forces conducted between 1 and 10 June 1984 to remove Jarnail Singh Bhindranwale and other Sikh militants from the Golden Temple (Harmandir Sahib), a holy site of Sikhism, and i ...
against the militants. The operation caused severe damage and destroyed the Akal Takht. Numerous soldiers, militants and civilians died in the crossfire, with official estimates of death of 492 civilians and 83 Indian army men. Within days of the Operation Bluestar, some 2,000 Sikh soldiers in India mutinied and attempted to reach Amritsar to liberate the Golden Temple. Within six months, on 31 October 1984, Indira Gandhi's Sikh bodyguards Assassination of Indira Gandhi, assassinated her.
In 1986, Indira Gandhi's son and the next Prime Minister of India Rajiv Gandhi ordered repairs to the Akal Takht Sahib. These repairs were removed and Sikhs rebuilt the Akal Takht Sahib in 1999.
See also
* Golden Temple, Sripuram, Golden Temple, Vellore * Amritsar Jamnagar Expressway * Amritsar Ring Road * Delhi Amritsar Katra Expressway * Gurudwara Sis Ganj Sahib * Hazur Sahib Nanded * List of Gurudwaras * Takht Sri Patna SahibReferences
Citations
General bibliography
* * * * * * * * * * * * * *External links
* {{Authority control 1604 establishments in India Architecture in India Buildings and structures in Amritsar Gurdwaras in Punjab, India Rebuilt buildings and structures in India Religious buildings and structures completed in 1604 Religious buildings and structures with domes Religious tourism in India Tourist attractions in Amritsar 17th-century gurdwaras World Heritage Tentative List for India