Zika on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Zika fever, also known as Zika virus disease or simply Zika, is an infectious disease caused by the
 Most people who are infected have no or few symptoms. Otherwise the most common signs and symptoms of Zika fever are
Most people who are infected have no or few symptoms. Otherwise the most common signs and symptoms of Zika fever are
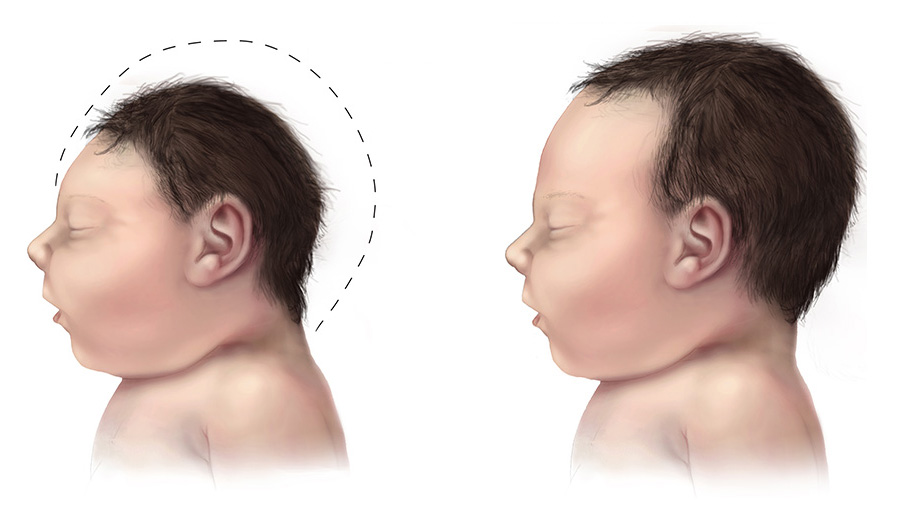 The disease spreads from mother to child in the womb and can cause multiple problems, most notably
The disease spreads from mother to child in the womb and can cause multiple problems, most notably
 In April 1947, as part of studies sponsored by the
In April 1947, as part of studies sponsored by the
 Genetic analyses of Zika virus strains suggest that Zika first entered the Americas between May and December 2013. It was first detected in the
Genetic analyses of Zika virus strains suggest that Zika first entered the Americas between May and December 2013. It was first detected in the
Managing Zika in babies
(CDC)
Species Profile – Zika Virus Disease
National Invasive Species Information Center,
Zika virus
Zika virus (ZIKV; pronounced or ) is a member of the virus family ''Flaviviridae''. It is spread by daytime-active ''Aedes'' mosquitoes, such as '' A. aegypti'' and '' A. albopictus''. Its name comes from the Ziika Forest of Uganda, where ...
. Most cases have no symptoms, but when present they are usually mild and can resemble dengue fever
Dengue fever is a mosquito-borne disease caused by dengue virus, prevalent in tropical and subtropical areas. Asymptomatic infections are uncommon, mild cases happen frequently; if symptoms appear, they typically begin 3 to 14 days after i ...
. Symptoms may include fever
Fever or pyrexia in humans is a symptom of an anti-infection defense mechanism that appears with Human body temperature, body temperature exceeding the normal range caused by an increase in the body's temperature Human body temperature#Fever, s ...
, red eyes, joint pain
Arthralgia () literally means 'joint pain'. Specifically, arthralgia is a symptom of injury, infection, illness (in particular arthritis), or an allergic reaction to medication
Medication (also called medicament, medicine, pharmaceutic ...
, headache, and a maculopapular rash
A maculopapular rash is a type of rash characterized by a flat, red area on the skin that is covered with small confluent bumps. It may only appear red in lighter-skinned people. The term "maculopapular" is a compound: '' macules'' are small, fla ...
. Symptoms generally last less than seven days. It has not caused any reported deaths during the initial infection. Mother-to-child transmission during pregnancy can cause microcephaly
Microcephaly (from Neo-Latin ''microcephalia'', from Ancient Greek μικρός ''mikrós'' "small" and κεφαλή ''kephalé'' "head") is a medical condition involving a smaller-than-normal head. Microcephaly may be present at birth or it m ...
and other brain malformations in some babies. Infections in adults have been linked to Guillain–Barré syndrome
Guillain–Barré syndrome (GBS) is a rapid-onset Paralysis, muscle weakness caused by the immune system damaging the peripheral nervous system. Typically, both sides of the body are involved, and the initial symptoms are changes in sensation ...
(GBS).
Zika fever is mainly spread via the bite of mosquitoes
Mosquitoes, the Culicidae, are a family of small flies consisting of 3,600 species. The word ''mosquito'' (formed by '' mosca'' and diminutive ''-ito'') is Spanish and Portuguese for ''little fly''. Mosquitoes have a slender segmented body, ...
of the ''Aedes
''Aedes'' (also known as the tiger mosquito) is a genus of mosquitoes originally found in tropical and subtropical zones, but now found on all continents except Antarctica. Some species have been spread by human activity: ''Aedes albopictus'', ...
'' type. It can also be sexually transmitted and potentially spread by blood transfusion
Blood transfusion is the process of transferring blood products into a person's Circulatory system, circulation intravenously. Transfusions are used for various medical conditions to replace lost components of the blood. Early transfusions used ...
s. Infections in pregnant women can spread to the baby. Diagnosis is by testing the blood, urine, or saliva for the presence of the virus's RNA
Ribonucleic acid (RNA) is a polymeric molecule that is essential for most biological functions, either by performing the function itself (non-coding RNA) or by forming a template for the production of proteins (messenger RNA). RNA and deoxyrib ...
when the person is sick, or the blood for antibodies
An antibody (Ab) or immunoglobulin (Ig) is a large, Y-shaped protein belonging to the immunoglobulin superfamily which is used by the immune system to identify and neutralize antigens such as bacteria and viruses, including those that caus ...
after symptoms are present more than a week.
Prevention involves decreasing mosquito bites in areas where the disease occurs and proper condom use. Efforts to prevent bites include the use of insect repellent
An insect repellent (also commonly called "bug spray" or "bug deterrent") is a substance applied to the skin, clothing, or other surfaces to discourage insects (and arthropods in general) from landing or climbing on that surface. Insect repellent ...
, covering much of the body with clothing, mosquito nets, and getting rid of standing water where mosquitoes reproduce. There is no effective vaccine
A vaccine is a biological Dosage form, preparation that provides active acquired immunity to a particular infectious disease, infectious or cancer, malignant disease. The safety and effectiveness of vaccines has been widely studied and verifi ...
. Health officials recommended that women in areas affected by the 2015–16 Zika outbreak consider putting off pregnancy and that pregnant women not travel to these areas. While there is no specific treatment, paracetamol
Paracetamol, or acetaminophen, is a non-opioid analgesic and antipyretic agent used to treat fever and mild to moderate pain. It is a widely available over-the-counter drug sold under various brand names, including Tylenol and Panadol.
Parac ...
(acetaminophen) may help with the symptoms. Hospital admission is rarely necessary.
The virus that causes the disease was first isolated in Africa in 1947. The first documented outbreak among people occurred in 2007 in the Federated States of Micronesia
The Federated States of Micronesia (, abbreviated FSM), or simply Micronesia, is an island country in Micronesia, a region of Oceania. The federation encompasses the majority of the Caroline Islands (excluding Palau) and consists of four Admin ...
. An outbreak started in Brazil in 2015, and spread to the Americas, Pacific, Asia, and Africa. This led the World Health Organization
The World Health Organization (WHO) is a list of specialized agencies of the United Nations, specialized agency of the United Nations which coordinates responses to international public health issues and emergencies. It is headquartered in Gen ...
to declare it a Public Health Emergency of International Concern in February 2016. The emergency was lifted in November 2016, but 84 countries still reported cases as of March 2017. The last proven case of Zika spread in the Continental United States was in 2017.
Signs and symptoms
 Most people who are infected have no or few symptoms. Otherwise the most common signs and symptoms of Zika fever are
Most people who are infected have no or few symptoms. Otherwise the most common signs and symptoms of Zika fever are fever
Fever or pyrexia in humans is a symptom of an anti-infection defense mechanism that appears with Human body temperature, body temperature exceeding the normal range caused by an increase in the body's temperature Human body temperature#Fever, s ...
, rash
A rash is a change of the skin that affects its color, appearance, or texture.
A rash may be localized in one part of the body, or affect all the skin. Rashes may cause the skin to change color, itch, become warm, bumpy, chapped, dry, cracke ...
, conjunctivitis
Conjunctivitis, also known as pink eye or Madras eye, is inflammation of the conjunctiva, the thin, clear layer that covers the white surface of the eye and the inner eyelid. It makes the eye appear pink or reddish. Pain, burning, scratchiness ...
(red eyes), muscle
Muscle is a soft tissue, one of the four basic types of animal tissue. There are three types of muscle tissue in vertebrates: skeletal muscle, cardiac muscle, and smooth muscle. Muscle tissue gives skeletal muscles the ability to muscle contra ...
and joint pain
Arthralgia () literally means 'joint pain'. Specifically, arthralgia is a symptom of injury, infection, illness (in particular arthritis), or an allergic reaction to medication
Medication (also called medicament, medicine, pharmaceutic ...
, and headache, which are similar to signs and symptoms of dengue
Dengue fever is a mosquito-borne disease caused by dengue virus, prevalent in tropical and subtropical areas. Asymptomatic infections are uncommon, mild cases happen frequently; if symptoms appear, they typically begin 3 to 14 days after ...
and chikungunya
Chikungunya is an infection caused by the chikungunya virus (CHIKV). The disease was first identified in 1952 in Tanzania and named based on the Kimakonde words for "to become contorted". Chikungunya has become a global health concern due to ...
fever. The time from a mosquito bite to developing symptoms is not yet known, but is probably a few days to a week. The disease lasts for several days to a week. It is usually mild enough for people not to go to a hospital.
Due to being in the same family as dengue, there has been concern that it could cause similar bleeding disorders. However that has only been documented in one case, with blood seen in semen, also known as hematospermia.
Guillain–Barré syndrome
Zika virus infections have been strongly associated withGuillain–Barré syndrome
Guillain–Barré syndrome (GBS) is a rapid-onset Paralysis, muscle weakness caused by the immune system damaging the peripheral nervous system. Typically, both sides of the body are involved, and the initial symptoms are changes in sensation ...
(GBS), which is a rapid onset of muscle weakness caused by the immune system damaging the peripheral nervous system, and which can progress to paralysis. While both GBS and Zika infection can simultaneously occur in the same individual, it is difficult to definitively identify Zika virus as the cause of GBS. Though Zika virus has been shown to infect human Schwann cells
Schwann cells or neurolemmocytes (named after German physiologist Theodor Schwann) are the principal glia of the peripheral nervous system (PNS). Glial cells function to support neurons and in the PNS, also include Satellite glial cell, satellite ...
. Several countries affected by Zika outbreaks have reported increases in the rate of new cases of GBS. During the 2013–2014 outbreak in French Polynesia there were 42 reported cases of GBS over three months, compared to between 3 and 10 annually before the outbreak.
Pregnancy
 The disease spreads from mother to child in the womb and can cause multiple problems, most notably
The disease spreads from mother to child in the womb and can cause multiple problems, most notably microcephaly
Microcephaly (from Neo-Latin ''microcephalia'', from Ancient Greek μικρός ''mikrós'' "small" and κεφαλή ''kephalé'' "head") is a medical condition involving a smaller-than-normal head. Microcephaly may be present at birth or it m ...
, in the baby. The full range of birth defects caused by infection during pregnancy is not known, but they appear to be common, with large-scale abnormalities seen in up to 42% of live births. The most common observed associations have been abnormalities with brain and eye development such as microcephaly and chorioretinal scarring. Less commonly there have been systemic abnormalities such as hydrops fetalis
Hydrops fetalis or hydrops foetalis is a condition in the fetus characterized by an accumulation of fluid, or edema, in at least two fetal compartments. By comparison, hydrops allantois or hydrops amnion is an accumulation of excessive fluid in ...
, where there is abnormal accumulation of fluid in the fetus. These abnormalities can lead to intellectual problems, seizure
A seizure is a sudden, brief disruption of brain activity caused by abnormal, excessive, or synchronous neuronal firing. Depending on the regions of the brain involved, seizures can lead to changes in movement, sensation, behavior, awareness, o ...
s, vision problems
Visual or vision impairment (VI or VIP) is the partial or total inability of visual perception. In the absence of treatment such as corrective eyewear, assistive devices, and medical treatment, visual impairment may cause the individual difficul ...
, hearing problems, problems feeding and slow development.
Whether the stage of pregnancy at which the mother becomes infected affects the risk to the fetus is not well understood, nor is whether other risk factors affect outcomes. One group has estimated the risk of a baby developing microcephaly at about 1% when the mother is infected during the first trimester, with the risk of developing microcephaly becoming uncertain beyond the first trimester. Affected babies might appear normal but actually have brain abnormalities; infection in newborns could also lead to brain damage.
Cause
Reservoir
Zika virus
Zika virus (ZIKV; pronounced or ) is a member of the virus family ''Flaviviridae''. It is spread by daytime-active ''Aedes'' mosquitoes, such as '' A. aegypti'' and '' A. albopictus''. Its name comes from the Ziika Forest of Uganda, where ...
is a mosquito
Mosquitoes, the Culicidae, are a Family (biology), family of small Diptera, flies consisting of 3,600 species. The word ''mosquito'' (formed by ''Musca (fly), mosca'' and diminutive ''-ito'') is Spanish and Portuguese for ''little fly''. Mos ...
- borne flavivirus closely related to the dengue and yellow fever viruses. While mosquitoes are the vector
Vector most often refers to:
* Euclidean vector, a quantity with a magnitude and a direction
* Disease vector, an agent that carries and transmits an infectious pathogen into another living organism
Vector may also refer to:
Mathematics a ...
, the main reservoir
A reservoir (; ) is an enlarged lake behind a dam, usually built to water storage, store fresh water, often doubling for hydroelectric power generation.
Reservoirs are created by controlling a watercourse that drains an existing body of wa ...
species remains unknown, though serological evidence has been found in both West African monkeys and rodents.
Transmission
Transmission is via the bite of mosquitoes from the genus ''Aedes
''Aedes'' (also known as the tiger mosquito) is a genus of mosquitoes originally found in tropical and subtropical zones, but now found on all continents except Antarctica. Some species have been spread by human activity: ''Aedes albopictus'', ...
'', primarily ''Aedes aegypti
''Aedes aegypti'' ( or from Greek 'hateful' and from Latin, meaning 'of Egypt'), sometimes called the Egyptian mosquito, dengue mosquito or yellow fever mosquito, is a mosquito that spreads diseases like dengue fever, yellow fever, malar ...
'' in tropical regions. It has also been isolated from '' Ae. africanus'', '' Ae. apicoargenteus'', '' Ae. luteocephalus'', '' Ae. albopictus,'' '' Ae. vittatus'' and '' Ae. furcifer''. During the 2007 outbreak on Yap Island in the South Pacific, '' Aedes hensilli'' was the vector, while ''Aedes polynesiensis
''Aedes polynesiensis'', the Polynesian tiger mosquito, is only found in the Oceania, South Pacific on the islands of Austral Islands, Cook Islands, Ellice Islands, Fiji, Fiji Islands, Hoorn Islands, Marquesas Islands, Pitcairn Island, Samoa Isla ...
'' spread the virus in French Polynesia in 2013.
Zika virus can also spread by sexual transmission from infected men to their partners. Zika virus has been isolated from semen
Semen, also known as seminal fluid, is a bodily fluid that contains spermatozoon, spermatozoa which is secreted by the male gonads (sexual glands) and other sexual organs of male or hermaphrodite, hermaphroditic animals. In humans and placen ...
samples, with one person having 100,000 times more virus in semen than blood or urine, two weeks after being infected. It is unclear why levels in semen can be higher than other body fluids, and it is also unclear how long infectious virus can remain in semen. There have also been cases of men with no symptoms of Zika virus infection transmitting the disease. The CDC has recommended that all men who have travelled to affected areas should wait at least 6 months before trying to attempt conception, regardless of whether they were ill. To date there have been no reported sexual transmissions from women to their sexual partners. Oral, anal, or vaginal sex can spread the disease.
Cases of vertical perinatal transmission
A vertically transmitted infection is an infection caused by pathogenic bacteria or viruses that use mother-to-child transmission, that is, transmission directly from the mother to an embryo, fetus, or baby during pregnancy or childbirth. It ca ...
have been reported. The CDC recommends that women with Zika fever should wait at least 8 weeks after they start having symptoms of the disease before attempting to conceive. There have been no reported cases of transmission from breastfeeding, but infectious virus has been found in breast milk.
Like other flaviviruses it could potentially be transmitted by blood transfusion
Blood transfusion is the process of transferring blood products into a person's Circulatory system, circulation intravenously. Transfusions are used for various medical conditions to replace lost components of the blood. Early transfusions used ...
and several affected countries have developed strategies to screen blood donors. The U.S. FDA has recommended universal screening of blood products for Zika. The virus is detected in 3% of asymptomatic blood donors in French Polynesia.
Pathophysiology
In fruit flies microcephaly appears to be caused by the flavivirid virus proteinNS4A
Nonstructural protein 4A (NS4A) is a viral protein found in the hepatitis C virus
The hepatitis C virus (HCV) is a small (55–65 nm in size), enveloped, positive-sense single-stranded RNA virus of the family ''Flaviviridae''. The hepatitis ...
, which can disrupt brain growth by hijacking a pathway that regulates the growth of new neurons.
Diagnosis
It is difficult to diagnose Zika virus infection based on clinical signs and symptoms alone due to overlaps with otherarbovirus
Arbovirus is an informal name for any virus that is Transmission (medicine), transmitted by arthropod Vector (epidemiology), vectors. The term ''arbovirus'' is a portmanteau word (''ar''thropod-''bo''rne ''virus''). ''Tibovirus'' (''ti''ck-''bo ...
es that are endemic to similar areas. The US Centers for Disease Control and Prevention
The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) is the National public health institutes, national public health agency of the United States. It is a Federal agencies of the United States, United States federal agency under the United S ...
(CDC) advises that "based on the typical clinical features, the differential diagnosis for Zika virus infection is broad. In addition to dengue, other considerations include leptospirosis
Leptospirosis is a blood infection caused by the bacterium ''Leptospira'' that can infect humans, dogs, rodents and many other wild and domesticated animals. Signs and symptoms can range from none to mild (headaches, Myalgia, muscle pains, a ...
, malaria
Malaria is a Mosquito-borne disease, mosquito-borne infectious disease that affects vertebrates and ''Anopheles'' mosquitoes. Human malaria causes Signs and symptoms, symptoms that typically include fever, Fatigue (medical), fatigue, vomitin ...
, rickettsia
''Rickettsia'' is a genus of nonmotile, gram-negative, nonspore-forming, highly pleomorphic bacteria that may occur in the forms of cocci (0.1 μm in diameter), bacilli (1–4 μm long), or threads (up to about 10 μm long). The genus was n ...
, group A streptococcus, rubella
Rubella, also known as German measles or three-day measles, is an infection caused by the rubella virus. This disease is often mild, with half of people not realizing that they are infected. A rash may start around two weeks after exposure and ...
, measles
Measles (probably from Middle Dutch or Middle High German ''masel(e)'', meaning "blemish, blood blister") is a highly contagious, Vaccine-preventable diseases, vaccine-preventable infectious disease caused by Measles morbillivirus, measles v ...
, and parvovirus, enterovirus
''Enterovirus'' is a genus of positive-sense single-stranded RNA viruses associated with several human and mammalian diseases. Enteroviruses are named by their transmission-route through the intestine ('enteric' meaning intestinal).
Serologic ...
, adenovirus
Adenoviruses (members of the family ''Adenoviridae'') are medium-sized (90–100 nm), nonenveloped (without an outer lipid bilayer) viruses with an icosahedral nucleocapsid containing a double-stranded DNA genome. Their name derives from t ...
, and alphavirus infections (e.g., chikungunya, Mayaro, Ross River, Barmah Forest, O'nyong'nyong, and Sindbis viruses)."
In small case series, routine chemistry
Chemistry is the scientific study of the properties and behavior of matter. It is a physical science within the natural sciences that studies the chemical elements that make up matter and chemical compound, compounds made of atoms, molecules a ...
and complete blood count
A complete blood count (CBC), also known as a full blood count (FBC) or full haemogram (FHG), is a set of medical laboratory tests that provide cytometry, information about the cells in a person's blood. The CBC indicates the counts of white blo ...
s have been normal in most patients. A few have been reported to have mild leukopenia
Leukopenia () is a decrease in the number of white blood cells (leukocytes). It places individuals at increased risk of infection as white blood cells are the body's primary defense against infections.
Signs and symptoms
Symptoms may include:
* s ...
, thrombocytopenia
In hematology, thrombocytopenia is a condition characterized by abnormally low levels of platelets (also known as thrombocytes) in the blood. Low levels of platelets in turn may lead to prolonged or excessive bleeding. It is the most common coag ...
, and elevated liver transaminases.
Zika virus can be identified by reverse transcriptase PCR (RT-PCR) in acutely ill patients. However, the period of viremia can be short and the World Health Organization
The World Health Organization (WHO) is a list of specialized agencies of the United Nations, specialized agency of the United Nations which coordinates responses to international public health issues and emergencies. It is headquartered in Gen ...
(WHO) recommends RT-PCR testing be done on serum collected within 1 to 3 days of symptom onset or on saliva samples collected during the first 3 to 5 days. When evaluating paired samples, Zika virus was detected more frequently in saliva than serum. Urine samples can be collected and tested up to 14 days after the onset of symptoms, as the virus has been seen to survive longer in the urine than either saliva or serum. The longest period of having a detectable level of the virus has been 11 days and the Zika virus does not appear to establish latency.
Later on, serology
Serology is the scientific study of Serum (blood), serum and other body fluids. In practice, the term usually refers to the medical diagnosis, diagnostic identification of Antibody, antibodies in the serum. Such antibodies are typically formed in r ...
for the detection of specific IgM and IgG antibodies to the Zika virus can be used. IgM antibodies can be detectable within 3 days of the onset of illness. Serological cross-reactions with closely related flaviviruses such as dengue and West Nile virus
West Nile virus (WNV) is a single-stranded RNA virus that causes West Nile fever. It is a member of the family ''Flaviviridae'', from the genus ''Flavivirus'', which also contains the Zika virus, dengue virus, and yellow fever virus. The virus ...
as well as vaccines to flaviviruses are possible. As of 2019, the FDA
The United States Food and Drug Administration (FDA or US FDA) is a federal agency of the Department of Health and Human Services. The FDA is responsible for protecting and promoting public health through the control and supervision of food ...
has authorized two tests to detect Zika virus antibodies.
Screening in pregnancy
The CDC recommends screening some pregnant women even if they do not have symptoms of infection. Pregnant women who have traveled to affected areas should be tested between two and twelve weeks after their return from travel. Due to the difficulties with ordering and interpreting tests for Zika virus, the CDC also recommends that healthcare providers contact their local health department for assistance. For women living in affected areas, the CDC has recommended testing at the firstprenatal
Prenatal development () involves the embryonic development, development of the embryo and of the fetus during a viviparity, viviparous animal's gestation. Prenatal development starts with fertilization, in the germinal stage of embryonic develop ...
visit with a doctor as well as in the mid-second trimester, though this may be adjusted based on local resources and the local burden of Zika virus. Additional testing should be done for any signs of Zika virus disease. Women with positive test results for Zika virus infection should have their fetus monitored by ultrasound
Ultrasound is sound with frequency, frequencies greater than 20 Hertz, kilohertz. This frequency is the approximate upper audible hearing range, limit of human hearing in healthy young adults. The physical principles of acoustic waves apply ...
every three to four weeks to monitor fetal anatomy and growth.
Infant testing
For infants with suspectedcongenital
A birth defect is an abnormal condition that is present at childbirth, birth, regardless of its cause. Birth defects may result in disability, disabilities that may be physical disability, physical, intellectual disability, intellectual, or dev ...
Zika virus disease, the CDC recommends testing with both serologic and molecular assays such as RT-PCR, IgM ELISA
The enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) (, ) is a commonly used analytical biochemistry assay, first described by Eva Engvall and Peter Perlmann in 1971. The assay is a solid-phase type of enzyme immunoassay (EIA) to detect the presence of ...
and plaque reduction neutralization test (PRNT). RT-PCR of the infants serum and urine should be performed in the first two days of life. Newborns with a mother who was potentially exposed and who have positive blood tests, microcephaly or intracranial calcifications should have further testing including a thorough physical investigation for neurologic abnormalities, dysmorphic features, splenomegaly, hepatomegaly, and rash or other skin lesions. Other recommended tests are cranial ultrasound, hearing evaluation, and eye examination. Testing should be done for any abnormalities encountered as well as for other congenital infections such as syphilis
Syphilis () is a sexually transmitted infection caused by the bacterium ''Treponema pallidum'' subspecies ''pallidum''. The signs and symptoms depend on the stage it presents: primary, secondary, latent syphilis, latent or tertiary. The prim ...
, toxoplasmosis
Toxoplasmosis is a parasitic disease caused by ''Toxoplasma gondii'', an apicomplexan. Infections with toxoplasmosis are associated with a variety of neuropsychiatric and behavioral conditions. Occasionally, people may have a few weeks or month ...
, rubella, cytomegalovirus
''Cytomegalovirus'' (CMV) (from ''cyto-'' 'cell' via Greek - 'container' + 'big, megalo-' + -''virus'' via Latin 'poison') is a genus of viruses in the order '' Herpesvirales'', in the family '' Herpesviridae'', in the subfamily '' Betaherp ...
infection, lymphocytic choriomeningitis
Lymphocytic choriomeningitis (LCM) is a rodent-borne viral infectious disease that presents as aseptic meningitis, encephalitis or meningoencephalitis. Its causative agent is lymphocytic choriomeningitis virus (LCMV), a member of the family '' ...
virus infection, and herpes simplex virus
Herpes simplex virus 1 and 2 (HSV-1 and HSV-2) are two members of the Herpesviridae#Human herpesvirus types, human ''Herpesviridae'' family, a set of viruses that produce Viral disease, viral infections in the majority of humans. Both HSV-1 a ...
. Some tests should be repeated up to 6 months later as there can be delayed effects, particularly with hearing.
Infant feeding in areas of Zika virus transmission
In response to the widespread transmission of the Zika virus during the 2016 outbreak and concerns about viral genetic material detected in breast milk theWorld Health Organization
The World Health Organization (WHO) is a list of specialized agencies of the United Nations, specialized agency of the United Nations which coordinates responses to international public health issues and emergencies. It is headquartered in Gen ...
(WHO) released a Guideline for infant feeding in areas of Zika virus transmission, first in 2016 and updated in 2021, where the evidence showed that despite the detection of Zika virus in breast milk, there is unclear evidence of transmission to the infant, and considering that Zika virus infection among infants is mild, the balance between desirable and undesirable effects favors breastfeeding versus not breastfeeding. According to the 2021WHO guidelines:
* Infants born to mothers with suspected, probable, or confirmed Zika virus infection or who reside in or have traveled to areas of ongoing Zika virus transmission should be fed according to normal infant feeding guidelines. They should start breastfeeding within one hour of birth, be exclusively breastfed for six months, and have timely introduction of adequate, safe, and properly fed complementary foods while continuing breastfeeding up to two years of age or beyond.
* Infants fed with expressed breast milk from mothers with suspected, probable, or confirmed Zika virus infection or who reside in or have traveled to areas of ongoing Zika virus transmission should be fed according to normal infant feeding guidelines (strong recommendation, very-low certainty of evidence).
* Among infants (0–12 months) affected by complications associated with Zika virus infection, infant feeding practices should be modified (such as adjusting the environment, postural correction, or thickening feeds) to achieve and maintain optimal possible infant growth and development (strong recommendation, very- low certainty of evidence).
* Mothers and caregivers of infants affected by complications associated with Zika virus (such as feeding difficulties) should receive skilled support from health-care workers to initiate and sustain optimal infant feeding practices
Prevention
The virus is spread by mosquitoes, making mosquito avoidance an important element of disease control. The CDC recommends that individuals: * Cover exposed skin by wearing long-sleeved shirts and long pants treated withpermethrin
Permethrin is a medication and an insecticide. As a medication, it is used to treat scabies and lice. It is applied to the skin as a cream or lotion. As an insecticide, it can be sprayed onto outer clothing or mosquito nets to kill the insects ...
.
* Use an insect repellent containing DEET
''N'',''N''-Diethyl-''meta''-toluamide, also called diethyltoluamide or DEET (, from DET, the initials of di- + ethyl + toluamide), is the oldest, one of the most effective, and most common active ingredients in commercial insect repellents. ...
, picaridin
Icaridin, also known as picaridin, is an insect repellent which can be used directly on skin or clothing. It has broad efficacy against various arthropods such as mosquitos, ticks, gnats, flies and fleas, and is almost colorless and odorless. A s ...
, oil of lemon eucalyptus (OLE), or ethyl butylacetylaminopropionate (IR3535)
* Always follow product directions and reapply as directed
* If you are also using sunscreen, apply sunscreen first, let it dry, then apply insect repellent
* Follow package directions when applying repellent on children. Avoid applying repellent to their hands, eyes, or mouth
* Stay and sleep in screened-in or air-conditioned rooms
* Use a bed net
A mosquito net is a type of meshed curtain or cloth that is circumferentially draped over a bed or a sleeping area to offer the sleeper barrier protection against bites and stings from mosquitos, flies, and other pest insects, and thus ag ...
if the area where you are sleeping is exposed to the outdoors
* Cover cribs, strollers, and carriers with mosquito netting for babies under 2 months old.
The CDC also recommends strategies for controlling mosquitoes such as eliminating standing water, repairing septic tank
A septic tank is an underground chamber made of concrete, fiberglass, or plastic through which domestic wastewater (sewage) flows for basic sewage treatment. Settling and anaerobic digestion processes reduce solids and organics, but the treatment ...
s, and using screens on doors and windows. Spraying insecticide
Insecticides are pesticides used to kill insects. They include ovicides and larvicides used against insect eggs and larvae, respectively. The major use of insecticides is in agriculture, but they are also used in home and garden settings, i ...
is used to kill flying mosquitoes and larvicide can be used in water containers.
Because Zika virus can be sexually transmitted, men who have gone to an area where Zika fever is occurring should be counseled to either abstain from sex or use condom
A condom is a sheath-shaped Barrier contraception, barrier device used during sexual intercourse to reduce the probability of pregnancy or a Sexually transmitted disease, sexually transmitted infection (STI). There are both external condo ...
s for 6 months after travel if their partner is pregnant or could potentially become pregnant. Breastfeeding
Breastfeeding, also known as nursing, is the process where breast milk is fed to a child. Infants may suck the milk directly from the breast, or milk may be extracted with a Breast pump, pump and then fed to the infant. The World Health Orga ...
is still recommended by the WHO, even by women who have had Zika fever. There have been no recorded cases of Zika transmission to infants through breastfeeding, though the replicative virus has been detected in breast milk.
When returning from travel, with or without symptoms, it is suggested that prevention of mosquito bites continue for 3 weeks in order to reduce the risk of virus transmission to uninfected mosquitos.
CDC travel alert
Because of the "growing evidence of a link between Zika and microcephaly", in January 2016, the CDC issued a travel alert advising pregnant women to consider postponing travel to countries and territories with ongoing local transmission of Zika virus. Later, the advice was updated to caution pregnant women to avoid these areas entirely if possible and, if travel is unavoidable, to protect themselves from mosquito bites. Male partners of pregnant women and couples contemplating pregnancy who must travel to areas where Zika is active are advised to use condoms or abstain from sex. The agency also suggested that women thinking about becoming pregnant should consult with their physicians before traveling. In September 2016, the CDC travel advisories included: * Cape Verde * Many parts of the Caribbean: Anguilla, Antigua and Barbuda, Aruba, The Bahamas, Barbados, Bonaire, British Virgin Islands, Cayman Islands, Cuba, Curaçao, Dominica, Dominican Republic, Grenada, Guadeloupe, Haiti, Jamaica, Martinique, Puerto Rico, Saba, Saint Saint Barthélemy, Saint Lucia, Saint Martin, Saint Vincent and the Grenadines, Sint Eustatius, Sint Maarten, Trinidad and Tobago, and the U.S. Virgin Islands * Central America: Belize, Costa Rica, El Salvador, Guatemala, Honduras, Nicaragua, and Panama * Mexico * Most of South America: Argentina, Bolivia, Brazil, Colombia, Ecuador, French Guiana, Guyana, Paraguay, Peru, Suriname, and Venezuela * Several Pacific Islands: American Samoa, Fiji, Marshall Islands, Micronesia, New Caledonia, Papua New Guinea, Samoa, and Tonga * In Asia: Singapore, Malaysia, Brunei In December 2020, no active Zika outbreaks were reported by the CDC.WHO response
Both the regionalPan American Health Organization
The Pan American Health Organization (PAHO) is a specialized agency of the United Nations (UN) in charge of international health cooperation in the Americas. It fosters technical cooperation among member countries to fight communicable and non ...
(PAHO) as well as the WHO have issued statements of concern about the widespread public health impact of the Zika virus and its links to GBS and microcephaly. The WHO Director-General, Margaret Chan, issued a statement in February 2016 "declaring that the recent cluster of microcephaly cases and other neurological disorders reported in Brazil, following a similar cluster in French Polynesia in 2014, constitutes a Public Health Emergency of International Concern." The declaration allowed the WHO to coordinate international response to the virus as well as gave its guidance the force of international law
International law, also known as public international law and the law of nations, is the set of Rule of law, rules, norms, Customary law, legal customs and standards that State (polity), states and other actors feel an obligation to, and generall ...
under the International Health Regulations
The International Health Regulations (IHR), first adopted by the World Health Assembly in 1969 and last revised in 2005, are legally binding rules that only apply to the WHO that is an instrument that aims for international collaboration "to prev ...
. The declaration was ended in November 2016.
Vaccine
As of 2016, there was no available vaccine. Development was a priority of the USNational Institutes of Health
The National Institutes of Health (NIH) is the primary agency of the United States government responsible for biomedical and public health research. It was founded in 1887 and is part of the United States Department of Health and Human Service ...
(NIH), but officials stated that development of a vaccine could take years. To speed new drug development
Drug development is the process of bringing a new pharmaceutical drug to the market once a lead compound has been identified through the process of drug discovery. It includes preclinical research on microorganisms and animals, filing for regu ...
regulatory strategies were proposed by the WHO and NIH. Animal and early human studies were underway as of September 2016. As of December 2019, there were several vaccine candidates in various stages of development.
Mosquito control
Disease control in the affected countries currently centers around mosquito control. Several approaches are available for the management of ''Aedes aegypti
''Aedes aegypti'' ( or from Greek 'hateful' and from Latin, meaning 'of Egypt'), sometimes called the Egyptian mosquito, dengue mosquito or yellow fever mosquito, is a mosquito that spreads diseases like dengue fever, yellow fever, malar ...
'' mosquito populations, including the destruction of larval breeding sites (the aquatic pools in which eggs are laid and larvae hatch before mosquito development into flying adults); and, insecticides targeting either the larval stages, adult mosquitoes or both. Additionally, a whole host of novel technologies are under current development for mosquito control and the World Health Organization has recently lent its support for the accelerated development of modern methods for mosquito control such as the use of ''Wolbachia
''Wolbachia'' is a genus of gram-negative bacteria infecting many species of arthropods and filarial nematodes. The symbiotic relationship ranges from parasitism to obligate mutualism. It is one of the most common parasitic microbes of arthrop ...
'' bacteria to render mosquitoes resistant to the virus, and, the release of sterilized male mosquitoes that breed with wild female mosquitoes to give rise to non-viable offspring (offspring that do not survive to the biting, adult stage).
Oxitec's genetically modified OX513A mosquito was approved by Brazil's National Biosecurity Technical Commission (CTNBio) in April 2014 and it was being used to try to combat mosquitoes carrying the Zika virus
Zika virus (ZIKV; pronounced or ) is a member of the virus family ''Flaviviridae''. It is spread by daytime-active ''Aedes'' mosquitoes, such as '' A. aegypti'' and '' A. albopictus''. Its name comes from the Ziika Forest of Uganda, where ...
in the town of Piracicaba
Piracicaba ( ) is a Municipalities of Brazil, Brazilian municipality located in the Interior of São Paulo, interior of São Paulo (state), São Paulo state, in the Southeast Region, Brazil, Southeast Region of Brazil. It serves as the main city ...
, São Paulo in 2016.
In the 1940s and 1950s, the ''Aedes aegypti
''Aedes aegypti'' ( or from Greek 'hateful' and from Latin, meaning 'of Egypt'), sometimes called the Egyptian mosquito, dengue mosquito or yellow fever mosquito, is a mosquito that spreads diseases like dengue fever, yellow fever, malar ...
'' mosquito was eradicated on some Caribbean islands and in at least eighteen Latin American countries. Decreasing political will and presumably available money, mosquito resistance to insecticide, and a pace of urbanization that exceeded eradication efforts led to this mosquito's comeback.
Machine Learning and Zika virus monitoring
Due to the difficulty of diagnosing the Zika virus early, as many cases are asymptomatic, machine learning techniques have emerged as a potentially promising solution for improving the prediction and surveillance of virus outbreaks. This approach would track the virus’s spread by analyzing genetic data, media, and climate history to identify environmental changes that allow Aedes mosquitoes to thrive. Such insights could aid in early warning and preventative efforts. However, challenges remain in integrating these methods into healthcare systems and ensuring the data quality used for accurate predictions.Treatment
There is currently no specific treatment for Zika virus infection. Care is supportive with the treatment of pain, fever, and itching. Some authorities have recommended against usingaspirin
Aspirin () is the genericized trademark for acetylsalicylic acid (ASA), a nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug (NSAID) used to reduce pain, fever, and inflammation, and as an antithrombotic. Specific inflammatory conditions that aspirin is ...
and other NSAIDs as these have been associated with hemorrhagic syndrome when used for other flaviviruses. Additionally, aspirin use is generally avoided in children when possible due to the risk of Reye syndrome.
Zika virus was poorly studied until the major outbreak in 2015, and no specific antiviral treatments are available as yet. Advice to pregnant women is to avoid any risk of infection so far as possible, as once infected there is little that can be done beyond supportive treatment.
Outcomes
Most of the time, Zika fever resolves on its own in two to seven days, but rarely, some people developGuillain–Barré syndrome
Guillain–Barré syndrome (GBS) is a rapid-onset Paralysis, muscle weakness caused by the immune system damaging the peripheral nervous system. Typically, both sides of the body are involved, and the initial symptoms are changes in sensation ...
. The fetus of a pregnant woman who has Zika fever may die or be born with congenital central nervous system malformations, like microcephaly
Microcephaly (from Neo-Latin ''microcephalia'', from Ancient Greek μικρός ''mikrós'' "small" and κεφαλή ''kephalé'' "head") is a medical condition involving a smaller-than-normal head. Microcephaly may be present at birth or it m ...
.
Some individuals have reported experiencing symptoms similar to those they had during their initial Zika virus infection, such as arthralgia, muscle aches, and fatigue, months after recovery. Although these symptoms are not typical, they can persist for months, though they tend to be less severe than during the acute phase of infection. This underscores the importance of ongoing research to understand better the long-term health effects of contracting the Zika virus.
Epidemiology
 In April 1947, as part of studies sponsored by the
In April 1947, as part of studies sponsored by the Rockefeller Foundation
The Rockefeller Foundation is an American private foundation and philanthropic medical research and arts funding organization based at 420 Fifth Avenue, New York City. The foundation was created by Standard Oil magnate John D. Rockefeller (" ...
into yellow fever, 6 caged rhesus monkeys were placed in the canopy of the Zika Forest of Uganda. On April 18 one of the monkeys (no. 776) developed a fever and blood samples revealed the first known case of Zika fever. Population surveys at the time in Uganda found 6.1% of individuals to be seropositive for Zika. The first human cases were reported in Nigeria in 1954. A few outbreaks have been reported in tropical Africa and some areas in Southeast Asia. Until recently there were no documented cases of Zika virus in the Indian subcontinent
The Indian subcontinent is a physiographic region of Asia below the Himalayas which projects into the Indian Ocean between the Bay of Bengal to the east and the Arabian Sea to the west. It is now divided between Bangladesh, India, and Pakista ...
, however, the first cases were reported in 2017 from Gujarat state and Tamil Nadu, more cases were reported in Rajasthan state involving an outbreak of 153 reported cases and in a pregnant women living in Kerala state. A 1954 study assessing blood samples from several people from different states found antibodies
An antibody (Ab) or immunoglobulin (Ig) is a large, Y-shaped protein belonging to the immunoglobulin superfamily which is used by the immune system to identify and neutralize antigens such as bacteria and viruses, including those that caus ...
to Zika in healthy people in India which could indicate past exposure, though it could also be due to cross-reaction with other flaviviruses.
By using phylogenetic
In biology, phylogenetics () is the study of the evolutionary history of life using observable characteristics of organisms (or genes), which is known as phylogenetic inference. It infers the relationship among organisms based on empirical dat ...
analysis of Asian strains, it was estimated that Zika virus had moved to Southeast Asia by 1945. In 1977–1978, Zika virus infection was described as a cause of fever in Indonesia. Before 2007, there were only 13 reported natural infections with Zika virus, all with a mild, self-limited febrile illness. As of July 2019, evidence of local transmission from mosquitoes to humans has been reported in a total of 87 countries from four of six WHO Regions; African, Americas, South-East Asia and Western Pacific.
Since the previous epidemiological update in 2019, Kenya and India have been added to the list of countries with confirmed local Zika virus transmission.
Yap Islands
The first major outbreak, with 185 confirmed cases, was reported in 2007 in the Yap Islands of the Federated States of Micronesia. A total of 108 cases were confirmed by PCR or serology and 72 additional cases were suspected. The most common symptoms were rash, fever, arthralgia, and conjunctivitis, and no deaths were reported. The mosquito '' Aedes hensilli'', which was the predominant species identified in Yap during the outbreak, was probably the main transmission vector. While the way of introduction of the virus on Yap Island remains uncertain, it is likely to have happened through the introduction of infected mosquitoes or a human infected with a strain related to those in Southeast Asia. This was also the first time Zika fever had been reported outside Africa and Asia. Before the Yap Island outbreak, only 14 human cases had ever been reported.Oceania
In 2013–2014, several outbreaks of Zika were reported inFrench Polynesia
French Polynesia ( ; ; ) is an overseas collectivity of France and its sole #Governance, overseas country. It comprises 121 geographically dispersed islands and atolls stretching over more than in the Pacific Ocean, South Pacific Ocean. The t ...
, New Caledonia
New Caledonia ( ; ) is a group of islands in the southwest Pacific Ocean, southwest of Vanuatu and east of Australia. Located from Metropolitan France, it forms a Overseas France#Sui generis collectivity, ''sui generis'' collectivity of t ...
, Easter Island
Easter Island (, ; , ) is an island and special territory of Chile in the southeastern Pacific Ocean, at the southeasternmost point of the Polynesian Triangle in Oceania. The island is renowned for its nearly 1,000 extant monumental statues, ...
and the Cook Islands
The Cook Islands is an island country in Polynesia, part of Oceania in the South Pacific Ocean. It consists of 15 islands whose total land area is approximately . The Cook Islands' Exclusive Economic Zone (EEZ) covers of ocean. Avarua is its ...
. The source of the virus was thought to be an independent introduction of the virus from Southeast Asia
Southeast Asia is the geographical United Nations geoscheme for Asia#South-eastern Asia, southeastern region of Asia, consisting of the regions that are situated south of China, east of the Indian subcontinent, and northwest of the Mainland Au ...
, unrelated to the Yap Islands outbreak.
Americas
 Genetic analyses of Zika virus strains suggest that Zika first entered the Americas between May and December 2013. It was first detected in the
Genetic analyses of Zika virus strains suggest that Zika first entered the Americas between May and December 2013. It was first detected in the Western Hemisphere
The Western Hemisphere is the half of the planet Earth that lies west of the Prime Meridian (which crosses Greenwich, London, United Kingdom) and east of the 180th meridian.- The other half is called the Eastern Hemisphere. Geopolitically, ...
in February 2014, and rapidly spread throughout South
South is one of the cardinal directions or compass points. The direction is the opposite of north and is perpendicular to both west and east.
Etymology
The word ''south'' comes from Old English ''sūþ'', from earlier Proto-Germanic ''*sunþa ...
and Central America, reaching Mexico in November 2015. In 2016 it established local transmission in Florida and Texas. The first death in the United States due to Zika occurred in February 2016.
In May 2015, Brazil officially reported its first 16 cases of the illness. Although, a case of illness was reported in March 2015 in a returning traveller. According to the Brazilian Health Ministry, as of November 2015 there was no official count of the number of people infected with the virus in Brazil, since the disease is not subject to compulsory notification. Even so, cases were reported in 14 states of the country. Mosquito-borne Zika virus is suspected to be the cause of 2,400 possible cases of microcephaly and 29 infant deaths in Brazil in 2015 (of the 2400 or so notified cases in 2015, 2165 were under investigation in December 2015, 134 were confirmed and 102 were ruled out for microcephaly).
The Brazilian Health Ministry has reported at least 2,400 suspected cases of microcephaly in the country in 2015 as of 12 December, and 29 fatalities. Before the Zika outbreak, only an average of 150 to 200 cases per year were reported in Brazil. In the state of Pernambuco
Pernambuco ( , , ) is a States of Brazil, state of Brazil located in the Northeast Region, Brazil, Northeast region of the country. With an estimated population of 9.5 million people as of 2024, it is the List of Brazilian states by population, ...
the reported rates of microcephaly in 2015 are 77 times higher than in the previous 5 years. A model using data from a Zika outbreak in French Polynesia estimated the risk of microcephaly in children born to mothers who acquired Zika virus in the first trimester to be 1%.
On 24 January 2016, the WHO warned that the virus is likely to spread to nearly all countries of the Americas, since its vector, the mosquito ''Aedes aegypti'', is found in all countries in the region, except for Canada
Canada is a country in North America. Its Provinces and territories of Canada, ten provinces and three territories extend from the Atlantic Ocean to the Pacific Ocean and northward into the Arctic Ocean, making it the world's List of coun ...
and continental
Continental may refer to:
Places
* Continental, Arizona, a small community in Pima County, Arizona, US
* Continental, Ohio, a small town in Putnam County, US
Arts and entertainment
* ''Continental'' (album), an album by Saint Etienne
* Continen ...
Chile
Chile, officially the Republic of Chile, is a country in western South America. It is the southernmost country in the world and the closest to Antarctica, stretching along a narrow strip of land between the Andes, Andes Mountains and the Paci ...
. The mosquito and dengue fever have been detected in Chile's Easter Island, some away from its closest point in mainland Chile, since 2002.
In February 2016, WHO declared the outbreak a Public Health Emergency of International Concern as evidence grew that Zika is a cause of birth defects and neurological problems. In April 2016, WHO stated there is a scientific consensus, based on preliminary evidence, that Zika is a cause of microcephaly
Microcephaly (from Neo-Latin ''microcephalia'', from Ancient Greek μικρός ''mikrós'' "small" and κεφαλή ''kephalé'' "head") is a medical condition involving a smaller-than-normal head. Microcephaly may be present at birth or it m ...
in infants and Guillain–Barré syndrome
Guillain–Barré syndrome (GBS) is a rapid-onset Paralysis, muscle weakness caused by the immune system damaging the peripheral nervous system. Typically, both sides of the body are involved, and the initial symptoms are changes in sensation ...
in adults. Studies of this and prior outbreaks have found Zika infection during pregnancy to be associated with early pregnancy loss and other pregnancy problems. In the Americas the number of cases peaked during the first half of 2016 and declined through 2017–2018, with a total of 31,587 suspected, probable, and confirmed cases of ZIKV disease were reported in the Region of the Americas. Of these, 3,473 (11%) were laboratory-confirmed. Transmission persists at low levels in some areas and is not uniformly distributed within countries.
Asia
In 2016 imported or locally transmitted Zika was reported in all the countries of Asia except Brunei, Hong Kong, Myanmar and Nepal. Serological surveys have indicated that Zika virus isendemic
Endemism is the state of a species being found only in a single defined geographic location, such as an island, state, nation, country or other defined zone; organisms that are indigenous to a place are not endemic to it if they are also foun ...
in most areas of Asia, though at a low level. While there was a sharp rise in the number of cases of Zika detected in Singapore after the 2016 Summer Olympics
The 2016 Summer Olympics (), officially the Games of the XXXI Olympiad () and officially branded as Rio 2016, were an international multi-sport event held from 5 to 21 August 2016 in Rio de Janeiro, Brazil, with preliminary events i ...
in Brazil, genetic analysis revealed that the strains were more closely related to strains from Thailand than from those causing the epidemic in the Americas.History
Origin of the name
It is named after the Zika Forest nearEntebbe
Entebbe is a city in Central Region, Uganda, Central Uganda which is located on Lake Victoria peninsula, approximately southwest of the Ugandan capital city, Kampala. Entebbe was once the seat of government for the Protectorate of Uganda pri ...
, Uganda
Uganda, officially the Republic of Uganda, is a landlocked country in East Africa. It is bordered to the east by Kenya, to the north by South Sudan, to the west by the Democratic Republic of the Congo, to the south-west by Rwanda, and to the ...
, where the Zika virus was first identified.
Microcephaly and other infant disorders
Zika virus was first identified in the late 1940s in Kampala, Uganda, Africa but was first confirmed in Brazil. Since it was first identified, Zika has been found in more than 27 countries and territories. Following the initial Zika outbreak in Northeastern Brazil in May 2015, physicians observed a tremendous surge of reports of infants born withmicrocephaly
Microcephaly (from Neo-Latin ''microcephalia'', from Ancient Greek μικρός ''mikrós'' "small" and κεφαλή ''kephalé'' "head") is a medical condition involving a smaller-than-normal head. Microcephaly may be present at birth or it m ...
, with 20 times the number of expected cases. Many of these cases have since been confirmed, leading WHO officials to project that approximately 2,500 infants will be found to have been born in Brazil with Zika-related microcephaly.
Proving that Zika causes these effects was difficult and complex for several reasons. For example, the effects on an infant might not be seen until months after the mother's initial infection, long after the time when Zika is easily detected in the body. In addition, research was needed to determine the mechanism by which Zika produced these effects.
Since the initial outbreak, studies that use several different methods found evidence of a link, leading public health officials to conclude that it appears increasingly likely the virus is linked to microcephaly and miscarriage. On 1 February 2016, the World Health Organization
The World Health Organization (WHO) is a list of specialized agencies of the United Nations, specialized agency of the United Nations which coordinates responses to international public health issues and emergencies. It is headquartered in Gen ...
declared recently reported clusters of microcephaly and other neurological disorders a Public Health Emergency of International Concern (PHEIC). On 8 March 2016, the WHO Committee reconfirmed that the association between Zika and neurological disorders is of global concern.
The Zika virus was first linked with newborn microcephaly during the Brazil Zika virus outbreak. In 2015, there were 2,782 suspected cases of microcephaly compared with 147 in 2014 and 167 in 2013. Confirmation of many of the recent cases is pending, and it is difficult to estimate how many cases went unreported before the recent awareness of the risk of virus infections.
In November 2015, the Zika virus was isolated in a newborn baby from the northeastern state
State most commonly refers to:
* State (polity), a centralized political organization that regulates law and society within a territory
**Sovereign state, a sovereign polity in international law, commonly referred to as a country
**Nation state, a ...
of Ceará
Ceará (, ) is one of the 26 states of Brazil, located in the Northeast Region, Brazil, northeastern part of the country, on the Atlantic Ocean, Atlantic coast. It is the List of Brazilian states by population, eighth-largest Brazilian State by ...
, Brazil, with microcephaly and other congenital disorder
A birth defect is an abnormal condition that is present at childbirth, birth, regardless of its cause. Birth defects may result in disability, disabilities that may be physical disability, physical, intellectual disability, intellectual, or dev ...
s. ''The Lancet
''The Lancet'' is a weekly peer-reviewed general medical journal, founded in England in 1823. It is one of the world's highest-impact academic journals and also one of the oldest medical journals still in publication.
The journal publishes ...
'' medical journal reported in January 2016 that the Brazilian Ministry of Health had confirmed 134 cases of microcephaly "believed to be associated with Zika virus infection" with an additional 2,165 cases in 549 counties
A county () is a geographic region of a country used for administrative or other purposesL. Brookes (ed.) '' Chambers Dictionary''. Edinburgh: Chambers Harrap Publishers Ltd, 2005. in some nations. The term is derived from the Old French denoti ...
in 20 states remaining under investigation. An analysis of 574 cases of microcephaly in Brazil during 2015 and the first week of 2016, reported in March 2016, found an association with maternal illness involving rash and fever during the first trimester of pregnancy. During this period, 12 Brazilian states reported increases of at least 3 standard deviation
In statistics, the standard deviation is a measure of the amount of variation of the values of a variable about its Expected value, mean. A low standard Deviation (statistics), deviation indicates that the values tend to be close to the mean ( ...
s (SDs) in cases of microcephaly compared with 2000–14, with the northeastern states of Bahia, Paraíba
Paraíba ( , ; ) is a states of Brazil, state of Brazil. It is located in the Brazilian Northeast, and it is bordered by Rio Grande do Norte to the north, Ceará to the west, Pernambuco to the south and the Atlantic Ocean to the east. Paraíba i ...
and Pernambuco
Pernambuco ( , , ) is a States of Brazil, state of Brazil located in the Northeast Region, Brazil, Northeast region of the country. With an estimated population of 9.5 million people as of 2024, it is the List of Brazilian states by population, ...
reporting increases of more than 20 SDs.
In January 2016, a baby in Oahu
Oahu (, , sometimes written Oahu) is the third-largest and most populated island of the Hawaiian Islands and of the U.S. state of Hawaii. The state capital, Honolulu, is on Oahu's southeast coast. The island of Oahu and the uninhabited Northwe ...
, Hawaii, was born with microcephaly, the first case in the United States of brain damage linked to the virus. The baby and mother tested positive for a past Zika virus infection. The mother, who had probably acquired the virus while traveling in Brazil in May 2015 during the early stages of her pregnancy, had reported her bout of Zika. She recovered before relocating to Hawaii. Her pregnancy had progressed normally, and the baby's condition was not known until birth.
In February 2016, ocular disorders in newborns have been linked to Zika virus infection. In one study in Pernambuco state in Brazil, about 40 percent of babies with Zika-related microcephaly also had scarring of the retina with spots, or pigment alteration. On 20 February 2016, Brazilian scientists announced that they had successfully sequenced the Zika virus genome and expressed hope that this would help in both developing a vaccine and in determining the nature of any link to birth defects.
Also in February 2016, rumors
A rumor (American English), or rumour (British English; American and British English spelling differences#-our, -or, see spelling differences; derived from Latin 'noise'), is an unverified piece of information circulating among people, especial ...
that microcephaly is caused by the use of the larvicide pyriproxyfen in drinking water
Drinking water or potable water is water that is safe for ingestion, either when drunk directly in liquid form or consumed indirectly through food preparation. It is often (but not always) supplied through taps, in which case it is also calle ...
were refuted by scientists. "It's important to state that some localities that do not use pyriproxyfen also had reported cases of microcephaly", read a Brazilian government statement. The Brazilian government also refuted conspiracy theories
A conspiracy theory is an explanation for an event or situation that asserts the existence of a conspiracy (generally by powerful sinister groups, often political in motivation), when other explanations are more probable.Additional sources:
*
...
that chickenpox and rubella vaccinations or genetically modified mosquitoes were causing increases in microcephaly.
Researchers also suspected that the Zika virus could be transmitted by a pregnant woman to her baby ("vertical transmission
Vertical transmission of symbionts is the transfer of a microbial symbiont from the parent directly to the offspring. Many metazoan species carry symbiotic bacteria which play a mutualistic, commensal, or parasitic role. A symbiont is acq ...
"). This remained unproven until February 2016, when a paper by Calvet et al. was published, showing not only the Zika virus genome found in the amniotic fluid but also IgM antibodies against the virus. This means that not only can the virus cross the placental barrier, but also the antibodies produced by the mother can reach the fetus, which suggests that vertical transmission is plausible in these cases. One other study published in March 2016 by Mlakar and colleagues analyzed autopsy tissues from a fetus with microcephaly that was probably related to Zika virus; researchers found ZIKV in the brain tissue and suggested that the brain injuries were probably associated with the virus, which also shed a light on the vertical transmission theory. Also in March 2016, first solid evidence was reported on how the virus affects the development of the brain, indicating that it appears to preferentially kill developing brain cells.
The first cases of birth defects linked to Zika in Colombia and in Panama were reported in March 2016. In the same month, researchers published a prospective cohort study that found profound impacts in 29 percent of infants of mothers infected with Zika, some of whom were infected late in pregnancy. This study did not suffer from some of the difficulties of studying Zika: the study followed women who presented to a Rio de Janeiro clinic with fever and rash within the last five days. The women were then tested for Zika using PCR, then the progress of the pregnancies was followed using ultrasound.
Guillain–Barré syndrome
A high rate of the autoimmune diseaseGuillain–Barré syndrome
Guillain–Barré syndrome (GBS) is a rapid-onset Paralysis, muscle weakness caused by the immune system damaging the peripheral nervous system. Typically, both sides of the body are involved, and the initial symptoms are changes in sensation ...
(GBS), noted in the French Polynesia outbreak, has also been found in the outbreak that began in Brazil. Laboratory analysis found Zika infections in some patients with GBS in Brazil, El Salvador, Suriname, and Venezuela, and the WHO declared on 22 March 2016 that Zika appeared to be "implicated" in GBS infection and that if the pattern was confirmed it would represent a global public health crisis.
Research
Mechanism
Early in the 2015–16 Zika virus epidemic, research was begun to understand how the Zika virus causes microcephaly and other neurological disorders. However, with the 2019 election ofJair Bolsonaro
Jair Messias Bolsonaro (; born 21 March 1955) is a Brazilian politician and former military officer who served as the 38th president of Brazil from 2019 to 2023. He previously served as a member of Brazil's Chamber of Deputies (Brazil), Chamb ...
in Brazil, who cut funding for research, and the emergence of the COVID-19 pandemic
The COVID-19 pandemic (also known as the coronavirus pandemic and COVID pandemic), caused by severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2), began with an disease outbreak, outbreak of COVID-19 in Wuhan, China, in December ...
in early 2020, most Zika-related research projects were abandoned or reduced.
It may involve infection of the primary neural stem cells
In multicellular organisms, stem cells are undifferentiated or partially differentiated cells that can change into various types of cells and proliferate indefinitely to produce more of the same stem cell. They are the earliest type of cell ...
of the fetal brain, known as neural progenitor cells. The main roles of brain stem cells are to proliferate until the correct number is achieved, and then to produce neurons
A neuron (American English), neurone (British English), or nerve cell, is an membrane potential#Cell excitability, excitable cell (biology), cell that fires electric signals called action potentials across a neural network (biology), neural net ...
through the process of neurogenesis
Neurogenesis is the process by which nervous system cells, the neurons, are produced by neural stem cells (NSCs). This occurs in all species of animals except the porifera (sponges) and placozoans. Types of NSCs include neuroepithelial cells ( ...
. Zika proteins NS4A and NS4B have also been shown to directly suppress neurogenesis. Infection of brain stem cells can cause cell death, which reduces the production of future neurons and leads to a smaller brain. Zika also appears to have an equal tropism
In biology, a tropism is a phenomenon indicating the growth or turning movement of an organism, usually a plant, in response to an environmental stimulus (physiology), stimulus. In tropisms, this response is dependent on the direction of the s ...
for cells of the developing eye, leading to high rates of eye abnormalities as well.
In addition to inducing cell death, infection of neural progenitor cells may alter the process of cell proliferation, causing a depletion in the pool of progenitor cells. A large number of cases of microcephaly
Microcephaly (from Neo-Latin ''microcephalia'', from Ancient Greek μικρός ''mikrós'' "small" and κεφαλή ''kephalé'' "head") is a medical condition involving a smaller-than-normal head. Microcephaly may be present at birth or it m ...
have been associated with inherited gene mutations, and specifically with mutations that lead to dysfunction of the mitotic spindle
In cell biology, the spindle apparatus is the cytoskeletal structure of eukaryotic cells that forms during cell division to separate sister chromatids between daughter cells. It is referred to as the mitotic spindle during mitosis, a process ...
. There is some evidence that Zika virus may directly or indirectly interfere with mitotic
Mitosis () is a part of the cell cycle in eukaryotic cells in which replicated chromosomes are separated into two new nuclei. Cell division by mitosis is an equational division which gives rise to genetically identical cells in which the t ...
function, this may play a role in altering cell proliferation.
Another line of research considers that Zika, unlike other flaviviruses, may target developing brain cells after it crosses the placenta, and considers the resulting damage likely to be the result of inflammation
Inflammation (from ) is part of the biological response of body tissues to harmful stimuli, such as pathogens, damaged cells, or irritants. The five cardinal signs are heat, pain, redness, swelling, and loss of function (Latin ''calor'', '' ...
as a byproduct of the immune response
An immune response is a physiological reaction which occurs within an organism in the context of inflammation for the purpose of defending against exogenous factors. These include a wide variety of different toxins, viruses, intra- and extracellula ...
to the infection of those cells.
Mosquito control
Some experimental prevention methods include breeding and releasing mosquitoes that have been genetically modified to prevent them from transmitting pathogens, or have been infected with the ''Wolbachia
''Wolbachia'' is a genus of gram-negative bacteria infecting many species of arthropods and filarial nematodes. The symbiotic relationship ranges from parasitism to obligate mutualism. It is one of the most common parasitic microbes of arthrop ...
'' bacterium, believed to inhibit the spread of viruses. A strain of ''Wolbachia'' helped to reduce the vector competence of the Zika virus in infected ''Aedes aegypti'' released in Medellin, Colombia.
Gene drive is a technique for changing wild populations, for instance to combat insects so they cannot transmit diseases (in particular mosquitoes in the cases of malaria and Zika). Another method which been researched aims to render male mosquitoes infertile by nuclear radiation in the hope to reduce populations; this is done with a cobalt-60
Cobalt-60 (Co) is a synthetic radioactive isotope of cobalt with a half-life of 5.2714 years. It is produced artificially in nuclear reactors. Deliberate industrial production depends on neutron activation of bulk samples of the monoisotop ...
gamma cell irradiator. In 2016 the World Health Organization
The World Health Organization (WHO) is a list of specialized agencies of the United Nations, specialized agency of the United Nations which coordinates responses to international public health issues and emergencies. It is headquartered in Gen ...
encouraged field trials of transgenic male ''Aedes aegypti'' mosquitoes developed by Oxitec to try to halt the spread of the Zika virus.
Potential application in Glioblastoma treatment
Recent studies have explored the use of the Zika virus (ZIKV) as a potential treatment for glioblastoma multiforme (GBM), a highly aggressive brain cancer. GBM has a median survival rate of about 15 months due to limited treatment options and high tumor recurrence rates. Oncolytic virotherapy, which uses specific viruses to target and destroy cancer cells, has shown promise as an alternative treatment for GBM. One study investigated the oncolytic potential of live-attenuated vaccine strains of Zika virus (ZIKV-LAV) against human GBM cells in vitro. The study found that ZIKV-LAV selectively infected and killed GBM cells without affecting terminally differentiated neurons or primary endothelial cells. ZIKV-LAV induced cell death through apoptosis and pyroptosis, two forms of programmed cell death.Victorio, C. B. L., Novera, W., Ganasarajah, A., Ong, J., Thomas, M., Wu, J., Toh, H. S. Y., Sun, A. X., Ooi, E. E., & Chacko, A.-M. (2024). Repurposing of Zika virus live-attenuated vaccine (ZIKV-LAV) strains as oncolytic viruses targeting human glioblastoma multiforme cells. ''Journal of Translational Medicine, 22''(1), 93. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12967-024-04930-4. This research highlights the potential of ZIKV-LAV as a treatment for GBM through oncolytic virotherapy. However, further clinical trials and research are necessary to assess its efficacy in human patients.See also
* Climate change and infectious diseasesReferences
External links
Managing Zika in babies
(CDC)
Species Profile – Zika Virus Disease
National Invasive Species Information Center,
United States National Agricultural Library
The United States National Agricultural Library (NAL) is one of the world's largest agricultural research libraries, and serves as a national library of the United States and as the library of the United States Department of Agriculture. Locate ...
. Lists general information and resources for White-Nose Syndrome.
{{Authority control
Insect-borne diseases
Sexually transmitted diseases and infections
Zika virus
Wikipedia medicine articles ready to translate
Articles containing video clips
Wikipedia infectious disease articles ready to translate