ZIU-9 on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
ZiU-9, or ZIU-9 (
 The electrical equipment of the ZiU-9 had some minor differences from the ZiU-5. The power of the main motor was increased. The indirect
The electrical equipment of the ZiU-9 had some minor differences from the ZiU-5. The power of the main motor was increased. The indirect
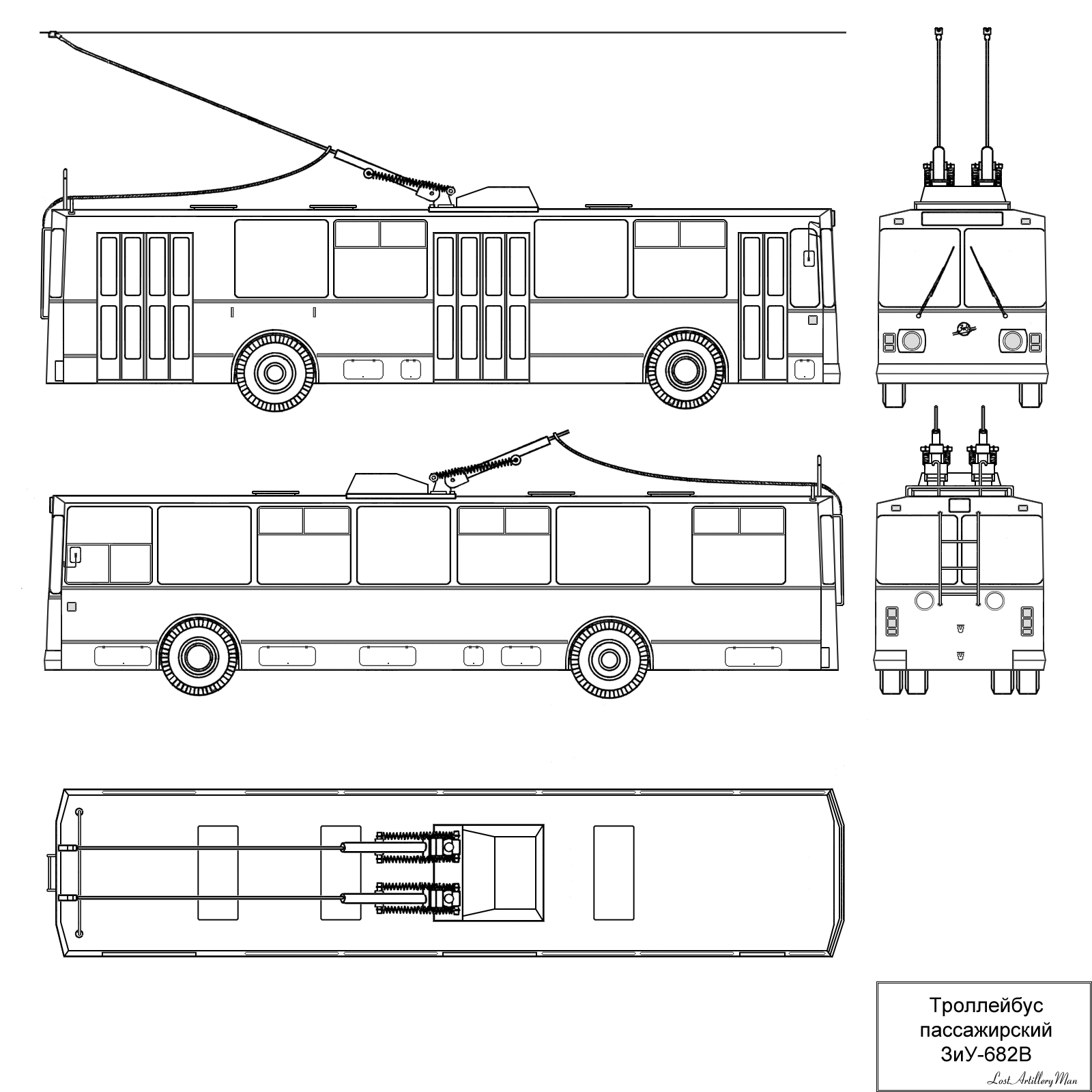
 At the end of 1976, mass production of the updated ZiU-682V began, which replaced the ZiU-682B, the key difference being leaf springs instead of track bars. Since 1976, the number of fixtures in the cabin has been reduced from 12 to 11, every other window in the cabin lost air vents. Since 1978, front ceiling hatch was removed, and the pole storage hooks became electric powered.
Since 1983, changed the shape and location of the front and rear position lamps. Lights original form, informally called "boats" have been replaced by unified and offset edges closer to route indicators. In 1985, similar design changes underwent external signal lights and turn indicators.
From March through May 1984 trolleybuses were produced without the low-level rear accumulation area, which was due to the need to strengthen the base structure of the body in the rear overhang. In 1985, the nameplate trolley was partially aligned with the standards forming the
At the end of 1976, mass production of the updated ZiU-682V began, which replaced the ZiU-682B, the key difference being leaf springs instead of track bars. Since 1976, the number of fixtures in the cabin has been reduced from 12 to 11, every other window in the cabin lost air vents. Since 1978, front ceiling hatch was removed, and the pole storage hooks became electric powered.
Since 1983, changed the shape and location of the front and rear position lamps. Lights original form, informally called "boats" have been replaced by unified and offset edges closer to route indicators. In 1985, similar design changes underwent external signal lights and turn indicators.
From March through May 1984 trolleybuses were produced without the low-level rear accumulation area, which was due to the need to strengthen the base structure of the body in the rear overhang. In 1985, the nameplate trolley was partially aligned with the standards forming the
 By the end of 1980, individual trolley components manufactured at that time were almost 20 years old, making them significantly outdated. Therefore, simultaneously with the launch of a series of recent modifications to the ZiU- 682V, preparations were made to produce a more profound modernization of the model trolley, which was designated ZiU- 682G. Experienced instances ZiU- 682G were released in 1988, and since February 1, 1991, the plant has fully passed on its production.
In addition to the changes already introduced earlier models ZiU 682V0A - and - ZiU 682V0B model ZiU- 682G have received the following differences. Front, under the windshield, placed the intake grille. Changed the location of windows with vents along the starboard side. Undergone significant redevelopment salon trolley. Most of the seats along the left side of the body were replaced with a double row on row, which increased the number of standing places. Changed the design of seats themselves and their handrails. Big changes undergone cab. Partition behind the driver, which had previously oval window became deaf; extended sliding door in the driver's cabin. In the cabin itself changed the layout of the dashboard, which became made of black plastic. Control of external light devices was moved to the steering column. On a dedicated right panel were only control door opening, the wiper switch, and the alarm. Other switches were transferred to the new control panel by trolley to the left of the driver's side near the window. Redesigned suspension and brake pedals at the same time control approached the car.
On the other hand, the ZiU- 682G was supplied to provincial towns from 1993 to 2000. Compared to the previous model, the ZiU- 682V had significantly lighter load-bearing elements of the frame component of the supporting frame (apparently, to reduce cost). As a result, in severe operating conditions (e.g. in Nizhny Novgorod) over 5 years, these structural elements had a tendency to corrode to the extent that they could be punctured with the gentle tap of a screwdriver.
Since 1997, the base modification in mass production became ZiU- 682G -012 (ZiU- 682G0A). An external difference between the new modification was the reduced height of the cab's side window, which also has another location pane. Minor changes have been planning the cabin. It was adapted for the domestic market modification export version trolley ZiU- 682G -010, the production of which began in 1992.
Based on ZiU- 682G -012 began the further modernization of trolley conducted mainly commissioned Mosgortransa (as most other Russian cities at that time became insolvent) and divided into several stages. For low voltage power generator instead of 63.3701 and auxiliary engine DC - 661B was set low noise static converter. Been improved waterproofing and grounding. The trolleybuses began to possess higher corrosion protection, a number of components now composed of aluminum, stainless steel, and fiberglass. In parallel with ZiU- 682G -012, in 1998, production began for the transition to modification ZiU- 682G -014 (ZiU- 682G0E), which replaced the old sofas in the lounge with individual padded seats, applied laser (source?) Heaters cabin windows. This version is also equipped with a static converter.
By the end of 1980, individual trolley components manufactured at that time were almost 20 years old, making them significantly outdated. Therefore, simultaneously with the launch of a series of recent modifications to the ZiU- 682V, preparations were made to produce a more profound modernization of the model trolley, which was designated ZiU- 682G. Experienced instances ZiU- 682G were released in 1988, and since February 1, 1991, the plant has fully passed on its production.
In addition to the changes already introduced earlier models ZiU 682V0A - and - ZiU 682V0B model ZiU- 682G have received the following differences. Front, under the windshield, placed the intake grille. Changed the location of windows with vents along the starboard side. Undergone significant redevelopment salon trolley. Most of the seats along the left side of the body were replaced with a double row on row, which increased the number of standing places. Changed the design of seats themselves and their handrails. Big changes undergone cab. Partition behind the driver, which had previously oval window became deaf; extended sliding door in the driver's cabin. In the cabin itself changed the layout of the dashboard, which became made of black plastic. Control of external light devices was moved to the steering column. On a dedicated right panel were only control door opening, the wiper switch, and the alarm. Other switches were transferred to the new control panel by trolley to the left of the driver's side near the window. Redesigned suspension and brake pedals at the same time control approached the car.
On the other hand, the ZiU- 682G was supplied to provincial towns from 1993 to 2000. Compared to the previous model, the ZiU- 682V had significantly lighter load-bearing elements of the frame component of the supporting frame (apparently, to reduce cost). As a result, in severe operating conditions (e.g. in Nizhny Novgorod) over 5 years, these structural elements had a tendency to corrode to the extent that they could be punctured with the gentle tap of a screwdriver.
Since 1997, the base modification in mass production became ZiU- 682G -012 (ZiU- 682G0A). An external difference between the new modification was the reduced height of the cab's side window, which also has another location pane. Minor changes have been planning the cabin. It was adapted for the domestic market modification export version trolley ZiU- 682G -010, the production of which began in 1992.
Based on ZiU- 682G -012 began the further modernization of trolley conducted mainly commissioned Mosgortransa (as most other Russian cities at that time became insolvent) and divided into several stages. For low voltage power generator instead of 63.3701 and auxiliary engine DC - 661B was set low noise static converter. Been improved waterproofing and grounding. The trolleybuses began to possess higher corrosion protection, a number of components now composed of aluminum, stainless steel, and fiberglass. In parallel with ZiU- 682G -012, in 1998, production began for the transition to modification ZiU- 682G -014 (ZiU- 682G0E), which replaced the old sofas in the lounge with individual padded seats, applied laser (source?) Heaters cabin windows. This version is also equipped with a static converter.
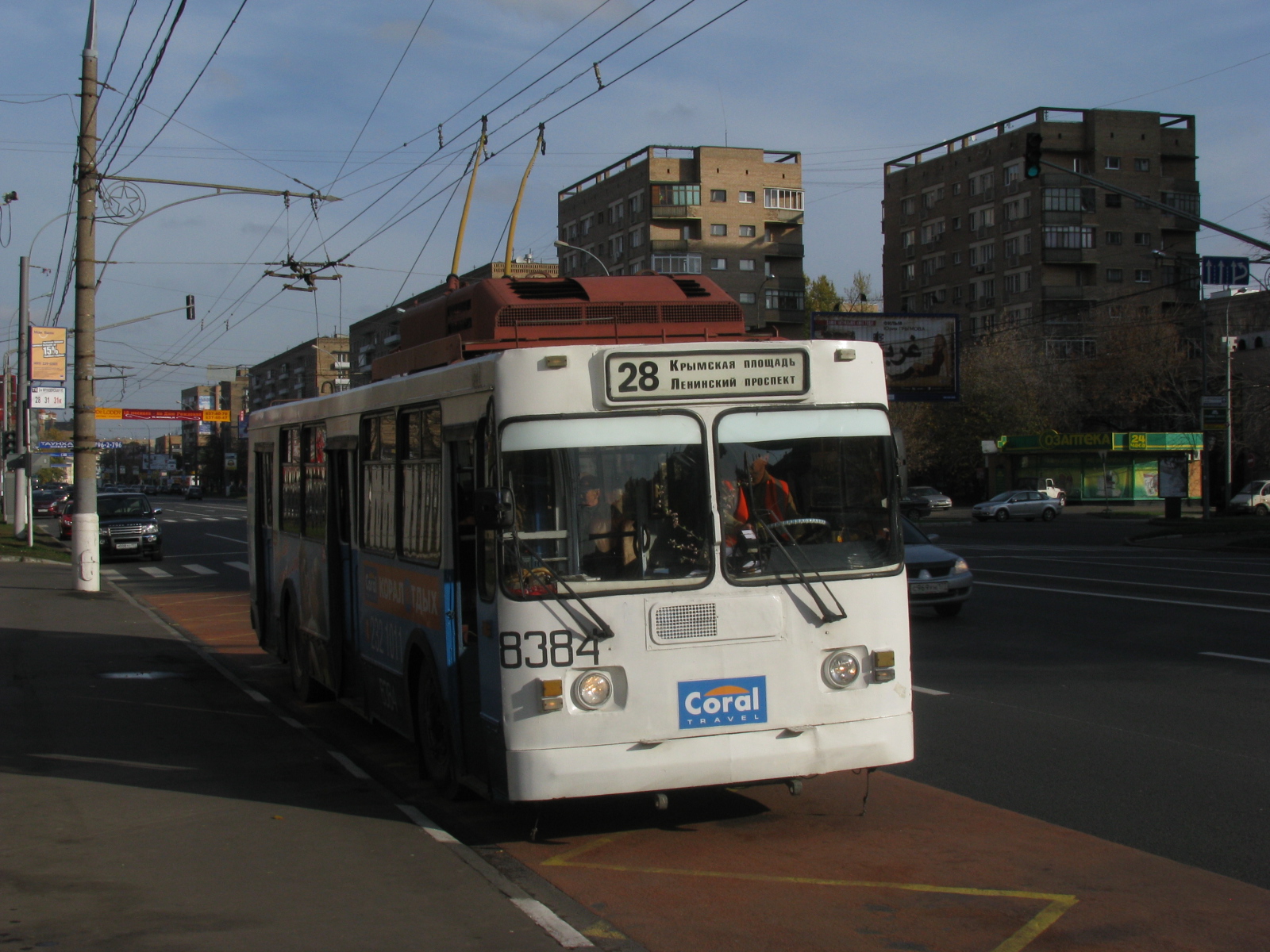 As a result of the continuation of the modernization of the trolley in the same 1998 there was a modification, the ZiU- 682G -016 (ZiU- 682G0M), which became the base model. Exterior siding boards became run from extruded galvanized steel sheets, which improved the appearance of the trolley and increased its corrosion resistance. Casement doors were subjected to additional treatment with a special rustproofing compound. A great deal of work was done to improve the electrical trolley : applied dielectric coating rods susceptor set travel stops rods, improved insulation chicanery, installed in the cab indicator of leakage currents, improved design -board covers and sealing side compartments, redesigned heater. Also applied to the trolley locking system running with the doors open.
Back in the mid-1990s, it became apparent that the location of electrical equipment underneath the trolley did not meet modern requirements of the current equipment, because it does not protect it from moisture, anti-icing agents or other debris and damaging conditions, and also allows the bus to drag the assembly through puddles should their depth exceed ten centimeters. In 1995, the model was designed as the ZiU- 52642, which is a major upgrade to the ZiU- 682G with the removal of electrical equipment on the roof of the trolley and other changes. However, for various reasons, the model series did not go.
The first production series with the removal of part of the apparatus on the roof became ZiU- 682G -017 (ZiU- 682G0H), launched in 2000. Unlike experienced ZiU- 52642 equipped with a Thyristor-pulse control system, modification ZiU- 682G -017 remained equipped with classical, uneconomical and unsupported acceptable smoothness
As a result of the continuation of the modernization of the trolley in the same 1998 there was a modification, the ZiU- 682G -016 (ZiU- 682G0M), which became the base model. Exterior siding boards became run from extruded galvanized steel sheets, which improved the appearance of the trolley and increased its corrosion resistance. Casement doors were subjected to additional treatment with a special rustproofing compound. A great deal of work was done to improve the electrical trolley : applied dielectric coating rods susceptor set travel stops rods, improved insulation chicanery, installed in the cab indicator of leakage currents, improved design -board covers and sealing side compartments, redesigned heater. Also applied to the trolley locking system running with the doors open.
Back in the mid-1990s, it became apparent that the location of electrical equipment underneath the trolley did not meet modern requirements of the current equipment, because it does not protect it from moisture, anti-icing agents or other debris and damaging conditions, and also allows the bus to drag the assembly through puddles should their depth exceed ten centimeters. In 1995, the model was designed as the ZiU- 52642, which is a major upgrade to the ZiU- 682G with the removal of electrical equipment on the roof of the trolley and other changes. However, for various reasons, the model series did not go.
The first production series with the removal of part of the apparatus on the roof became ZiU- 682G -017 (ZiU- 682G0H), launched in 2000. Unlike experienced ZiU- 52642 equipped with a Thyristor-pulse control system, modification ZiU- 682G -017 remained equipped with classical, uneconomical and unsupported acceptable smoothness
 Since September 2009, JSC "Trolza" in accordance with an obtained production license started production of trolleybuses ZiU-682G-016.04 and ZiU-682G-016.05. And apparently, these trolleys and constructive modifications almost completely replicate their predecessors ZiU-682G-016.02 and ZiU-682G-016.03. As changes in the rank of permanent options included installing electronic route signs and a marquee in the passenger compartment and ABS that ZiU-682G-ZiU 016.02 and 016.03-682G-performed by the customer.
Since September 2009, JSC "Trolza" in accordance with an obtained production license started production of trolleybuses ZiU-682G-016.04 and ZiU-682G-016.05. And apparently, these trolleys and constructive modifications almost completely replicate their predecessors ZiU-682G-016.02 and ZiU-682G-016.03. As changes in the rank of permanent options included installing electronic route signs and a marquee in the passenger compartment and ABS that ZiU-682G-ZiU 016.02 and 016.03-682G-performed by the customer.

 In
In
ZiU-9 on the Nizhny Novgorod tram site
(in Russian)
(English, somewhat dated) {{commons category, ZiU-9 Trolleybuses
Cyrillic
The Cyrillic script ( ) is a writing system used for various languages across Eurasia. It is the designated national script in various Slavic, Turkic, Mongolic, Uralic, Caucasian and Iranic-speaking countries in Southeastern Europe, Ea ...
: ЗиУ-9) is a Soviet
The Union of Soviet Socialist Republics. (USSR), commonly known as the Soviet Union, was a List of former transcontinental countries#Since 1700, transcontinental country that spanned much of Eurasia from 1922 until Dissolution of the Soviet ...
(and later Russia
Russia, or the Russian Federation, is a country spanning Eastern Europe and North Asia. It is the list of countries and dependencies by area, largest country in the world, and extends across Time in Russia, eleven time zones, sharing Borders ...
n) trolleybus
A trolleybus (also known as trolley bus, trolley coach, trackless trolley, trackless tramin the 1910s and 1920sJoyce, J.; King, J. S.; and Newman, A. G. (1986). ''British Trolleybus Systems'', pp. 9, 12. London: Ian Allan Publishing. .or troll ...
. Other names for the ZiU-9 are ZiU-682 and HTI-682 (Cyrillic
The Cyrillic script ( ) is a writing system used for various languages across Eurasia. It is the designated national script in various Slavic, Turkic, Mongolic, Uralic, Caucasian and Iranic-speaking countries in Southeastern Europe, Ea ...
: ЗиУ-682 and ХТИ-682). The ZiU acronym stands for "Zavod imeni Uritskogo", which means a factory named after Moisei Uritsky
Moisei Solomonovich Uritsky (; ; – 30 August 1918), also known by his pen-name Boretsky () was a Bolshevik revolutionary leader in Russia. After the October Revolution, he was the chief of the Cheka secret police of the Petrograd Soviet. ...
, the Russian revolutionary. Before 1996 this acronym was also a trademark of the vehicle manufacturer ''Trolza
Trolza (), formerly known as the Uritsky factory or simply Uritsky,Bushell, Chris; and Stonham, Peter (eds.) (1987). ''Jane's Urban Transport Systems 1987'', pp. 603–605. London: Jane's Publishing Company. . was a trolleybus manufacturer in ...
''. The ZiU-9 was first built in 1966, although it was only put into mass production in 1972 and it was still assembled along with other more advanced trolleybus vehicles in the Trolza
Trolza (), formerly known as the Uritsky factory or simply Uritsky,Bushell, Chris; and Stonham, Peter (eds.) (1987). ''Jane's Urban Transport Systems 1987'', pp. 603–605. London: Jane's Publishing Company. . was a trolleybus manufacturer in ...
(former ZiU) factory until 2015. The total number of produced ZiU-9s exceeds 42,000 vehicles making it the most produced trolleybus in the world. Many copies of the ZiU-9 were made in other factories of the former Soviet bloc. Following the Soviet era, many cities still utilize the ZiU-9 as their primary trolleybus; for example Cheboksary, Ryazan, Vinnitsa and others.
History and development
The explosive development of trolleybus systems in theSoviet Union
The Union of Soviet Socialist Republics. (USSR), commonly known as the Soviet Union, was a List of former transcontinental countries#Since 1700, transcontinental country that spanned much of Eurasia from 1922 until Dissolution of the Soviet ...
in the 1960s required a large number of trolleybuses to operate on said systems. The mainstay of the contemporary Soviet trolleybus fleet, the ZiU-5
The ZiU-5 (in Russian ''ЗиУ-5'') is a Soviet Union, Soviet trolleybus model that was built by the Uritsky (company), Uritsky factory. The ZiU acronym stands for ''Zavod imeni Uritskogo'' (in Russian ''Завод имени Урицкого'', ' ...
, was not sufficient for large urban passenger transfers as it was more suited for medium-size cities rather than large megapolises such as Moscow
Moscow is the Capital city, capital and List of cities and towns in Russia by population, largest city of Russia, standing on the Moskva (river), Moskva River in Central Russia. It has a population estimated at over 13 million residents with ...
or Saint Petersburg
Saint Petersburg, formerly known as Petrograd and later Leningrad, is the List of cities and towns in Russia by population, second-largest city in Russia after Moscow. It is situated on the Neva, River Neva, at the head of the Gulf of Finland ...
. In addition, the ZiU-5 had an aluminium
Aluminium (or aluminum in North American English) is a chemical element; it has chemical symbol, symbol Al and atomic number 13. It has a density lower than that of other common metals, about one-third that of steel. Aluminium has ...
exterior, which was expensive and complicated from a technological point of view. The two doors in the ZiU-5 hull ends did not work well in overcrowded situations which were quite common in Soviet public transportation.
The ZiU-9 was a quite successful attempt to solve these problems. It has one extra door compared to the ZiU-5. The middle and rear doors are wider, to allow for enhanced passenger flow. The small door at the front end of the vehicle is smaller, yet nonetheless comfortable for the driver and for outgoing passengers. The exterior of the ZiU-9 is made of welded steel
Steel is an alloy of iron and carbon that demonstrates improved mechanical properties compared to the pure form of iron. Due to steel's high Young's modulus, elastic modulus, Yield (engineering), yield strength, Fracture, fracture strength a ...
and is significantly cheaper and simpler than the exterior of the ZiU-5.
 The electrical equipment of the ZiU-9 had some minor differences from the ZiU-5. The power of the main motor was increased. The indirect
The electrical equipment of the ZiU-9 had some minor differences from the ZiU-5. The power of the main motor was increased. The indirect resistor
A resistor is a passive two-terminal electronic component that implements electrical resistance as a circuit element. In electronic circuits, resistors are used to reduce current flow, adjust signal levels, to divide voltages, bias active e ...
-based power control system was slightly modified to deal with the increased power of the traction motor. While western designers developed new semiconductor
A semiconductor is a material with electrical conductivity between that of a conductor and an insulator. Its conductivity can be modified by adding impurities (" doping") to its crystal structure. When two regions with different doping level ...
-based control devices, Soviet engineers decided to retain the old resistor-based system for ease of maintenance. The first prototype vehicles were tested in Moscow in 1971 and were approved for mass production after some minor design adjustments.
The '9' in the vehicle name was the initial project index of the design team. However, after launching mass production, the new trolleybus received a new index, '682' from the unified classification of non-rail public transport vehicles. All series went by the ZiU-682 designation, but the number '682' proved difficult to pronounce and the shorter '9' still lives in the everyday language of drivers and servicemen. In 1986, a new classification was introduced and the former ZiU-682 was designated as HTI-682. However, this was not the end of the vehicle's cycle of renaming; the Russian acronym HTI in the Cyrillic alphabet is ХТИ, and these three Cyrillic letters in 1995 were confused with the Latin letters XTU which then became the official name of the vehicle.
Production
ZiU-9
The first prototype, ZiU-9, was built in 1966, with the second prototype being built in 1970. Elements of the appearance and number of design decisions were borrowed from contemporary to the time foreign firmsMAN
A man is an adult male human. Before adulthood, a male child or adolescent is referred to as a boy.
Like most other male mammals, a man's genome usually inherits an X chromosome from the mother and a Y chromosome from the f ...
and Chausson.
ZiU-9A
The ZiU-9A was an experimental version with a wide body up to 2680 mm. With one prototype made in 1968.ZiU-682B
In August 1972, the first production series, the ZiU-682B, began production. Early trolley cars differed from later releases. Models prior to 1974 had angular wheel arches rather than circular ones. The first batch of trolleybuses used the outdated DC-207G engine, which was replaced by the DC-210 110 kW engine in 1973. Suspension on the first ZiU-682B was pneumatic, with track bars as guiding elements (which were later replaced with leaf springs). The rear area had a lowered floor, to reduce the number of steps at the back door, thus allowing the loading of wheelchairs, prams, and large items. However, this "advantage" was leveled by a high handrail on the steps separating the rear and middle doors. The transition from a high floor in the cabin to a lower back floor was facilitated by sloping the aisle between the rear wheel arches, which caused inconvenience to passengers at peak hours (especially in winter), standing on an icy ramp. In 1991 developers replaced the high-speed separator handrail attached to the door, but by this time all storage sites were at three stages from sidewalk level. For natural ventilation, the roof of the cabin was equipped with four ceiling hatches, and sliding side window panes. Currently, the only instance of ZIU-9B is preserved and operated in the city ofZaporozhye
Zaporizhzhia, formerly known as Aleksandrovsk or Oleksandrivsk until 1921, is a city in southeast Ukraine, situated on the banks of the Dnieper River. It is the administrative centre of Zaporizhzhia Oblast. Zaporizhzhia has a population of
...
and has the side number 562.
ZiU-682V (B00/B0A)
VIN code
A vehicle identification number (VIN; also called a chassis number or frame number) is a unique code, including a serial number, used by the automotive industry to identify individual motor vehicles, towed vehicles, motorcycles, scooters a ...
, which led to a change in marking HTI682V00.
Since 1988, the plant switched to production modifications ZiU- 682V -012 (ZiU- 682V0A) powered DC -213 capacity of 115 kW. Since 1989, the electrical noise filters shroud became smaller and flatter. In 1989, production started in parallel transition modification ZiU- 682V0B on which the electric drive door opener was replaced with a pneumatic system.
ZiU-682G
 By the end of 1980, individual trolley components manufactured at that time were almost 20 years old, making them significantly outdated. Therefore, simultaneously with the launch of a series of recent modifications to the ZiU- 682V, preparations were made to produce a more profound modernization of the model trolley, which was designated ZiU- 682G. Experienced instances ZiU- 682G were released in 1988, and since February 1, 1991, the plant has fully passed on its production.
In addition to the changes already introduced earlier models ZiU 682V0A - and - ZiU 682V0B model ZiU- 682G have received the following differences. Front, under the windshield, placed the intake grille. Changed the location of windows with vents along the starboard side. Undergone significant redevelopment salon trolley. Most of the seats along the left side of the body were replaced with a double row on row, which increased the number of standing places. Changed the design of seats themselves and their handrails. Big changes undergone cab. Partition behind the driver, which had previously oval window became deaf; extended sliding door in the driver's cabin. In the cabin itself changed the layout of the dashboard, which became made of black plastic. Control of external light devices was moved to the steering column. On a dedicated right panel were only control door opening, the wiper switch, and the alarm. Other switches were transferred to the new control panel by trolley to the left of the driver's side near the window. Redesigned suspension and brake pedals at the same time control approached the car.
On the other hand, the ZiU- 682G was supplied to provincial towns from 1993 to 2000. Compared to the previous model, the ZiU- 682V had significantly lighter load-bearing elements of the frame component of the supporting frame (apparently, to reduce cost). As a result, in severe operating conditions (e.g. in Nizhny Novgorod) over 5 years, these structural elements had a tendency to corrode to the extent that they could be punctured with the gentle tap of a screwdriver.
Since 1997, the base modification in mass production became ZiU- 682G -012 (ZiU- 682G0A). An external difference between the new modification was the reduced height of the cab's side window, which also has another location pane. Minor changes have been planning the cabin. It was adapted for the domestic market modification export version trolley ZiU- 682G -010, the production of which began in 1992.
Based on ZiU- 682G -012 began the further modernization of trolley conducted mainly commissioned Mosgortransa (as most other Russian cities at that time became insolvent) and divided into several stages. For low voltage power generator instead of 63.3701 and auxiliary engine DC - 661B was set low noise static converter. Been improved waterproofing and grounding. The trolleybuses began to possess higher corrosion protection, a number of components now composed of aluminum, stainless steel, and fiberglass. In parallel with ZiU- 682G -012, in 1998, production began for the transition to modification ZiU- 682G -014 (ZiU- 682G0E), which replaced the old sofas in the lounge with individual padded seats, applied laser (source?) Heaters cabin windows. This version is also equipped with a static converter.
By the end of 1980, individual trolley components manufactured at that time were almost 20 years old, making them significantly outdated. Therefore, simultaneously with the launch of a series of recent modifications to the ZiU- 682V, preparations were made to produce a more profound modernization of the model trolley, which was designated ZiU- 682G. Experienced instances ZiU- 682G were released in 1988, and since February 1, 1991, the plant has fully passed on its production.
In addition to the changes already introduced earlier models ZiU 682V0A - and - ZiU 682V0B model ZiU- 682G have received the following differences. Front, under the windshield, placed the intake grille. Changed the location of windows with vents along the starboard side. Undergone significant redevelopment salon trolley. Most of the seats along the left side of the body were replaced with a double row on row, which increased the number of standing places. Changed the design of seats themselves and their handrails. Big changes undergone cab. Partition behind the driver, which had previously oval window became deaf; extended sliding door in the driver's cabin. In the cabin itself changed the layout of the dashboard, which became made of black plastic. Control of external light devices was moved to the steering column. On a dedicated right panel were only control door opening, the wiper switch, and the alarm. Other switches were transferred to the new control panel by trolley to the left of the driver's side near the window. Redesigned suspension and brake pedals at the same time control approached the car.
On the other hand, the ZiU- 682G was supplied to provincial towns from 1993 to 2000. Compared to the previous model, the ZiU- 682V had significantly lighter load-bearing elements of the frame component of the supporting frame (apparently, to reduce cost). As a result, in severe operating conditions (e.g. in Nizhny Novgorod) over 5 years, these structural elements had a tendency to corrode to the extent that they could be punctured with the gentle tap of a screwdriver.
Since 1997, the base modification in mass production became ZiU- 682G -012 (ZiU- 682G0A). An external difference between the new modification was the reduced height of the cab's side window, which also has another location pane. Minor changes have been planning the cabin. It was adapted for the domestic market modification export version trolley ZiU- 682G -010, the production of which began in 1992.
Based on ZiU- 682G -012 began the further modernization of trolley conducted mainly commissioned Mosgortransa (as most other Russian cities at that time became insolvent) and divided into several stages. For low voltage power generator instead of 63.3701 and auxiliary engine DC - 661B was set low noise static converter. Been improved waterproofing and grounding. The trolleybuses began to possess higher corrosion protection, a number of components now composed of aluminum, stainless steel, and fiberglass. In parallel with ZiU- 682G -012, in 1998, production began for the transition to modification ZiU- 682G -014 (ZiU- 682G0E), which replaced the old sofas in the lounge with individual padded seats, applied laser (source?) Heaters cabin windows. This version is also equipped with a static converter.
ZiU-682G-016, 017 and 018
 As a result of the continuation of the modernization of the trolley in the same 1998 there was a modification, the ZiU- 682G -016 (ZiU- 682G0M), which became the base model. Exterior siding boards became run from extruded galvanized steel sheets, which improved the appearance of the trolley and increased its corrosion resistance. Casement doors were subjected to additional treatment with a special rustproofing compound. A great deal of work was done to improve the electrical trolley : applied dielectric coating rods susceptor set travel stops rods, improved insulation chicanery, installed in the cab indicator of leakage currents, improved design -board covers and sealing side compartments, redesigned heater. Also applied to the trolley locking system running with the doors open.
Back in the mid-1990s, it became apparent that the location of electrical equipment underneath the trolley did not meet modern requirements of the current equipment, because it does not protect it from moisture, anti-icing agents or other debris and damaging conditions, and also allows the bus to drag the assembly through puddles should their depth exceed ten centimeters. In 1995, the model was designed as the ZiU- 52642, which is a major upgrade to the ZiU- 682G with the removal of electrical equipment on the roof of the trolley and other changes. However, for various reasons, the model series did not go.
The first production series with the removal of part of the apparatus on the roof became ZiU- 682G -017 (ZiU- 682G0H), launched in 2000. Unlike experienced ZiU- 52642 equipped with a Thyristor-pulse control system, modification ZiU- 682G -017 remained equipped with classical, uneconomical and unsupported acceptable smoothness
As a result of the continuation of the modernization of the trolley in the same 1998 there was a modification, the ZiU- 682G -016 (ZiU- 682G0M), which became the base model. Exterior siding boards became run from extruded galvanized steel sheets, which improved the appearance of the trolley and increased its corrosion resistance. Casement doors were subjected to additional treatment with a special rustproofing compound. A great deal of work was done to improve the electrical trolley : applied dielectric coating rods susceptor set travel stops rods, improved insulation chicanery, installed in the cab indicator of leakage currents, improved design -board covers and sealing side compartments, redesigned heater. Also applied to the trolley locking system running with the doors open.
Back in the mid-1990s, it became apparent that the location of electrical equipment underneath the trolley did not meet modern requirements of the current equipment, because it does not protect it from moisture, anti-icing agents or other debris and damaging conditions, and also allows the bus to drag the assembly through puddles should their depth exceed ten centimeters. In 1995, the model was designed as the ZiU- 52642, which is a major upgrade to the ZiU- 682G with the removal of electrical equipment on the roof of the trolley and other changes. However, for various reasons, the model series did not go.
The first production series with the removal of part of the apparatus on the roof became ZiU- 682G -017 (ZiU- 682G0H), launched in 2000. Unlike experienced ZiU- 52642 equipped with a Thyristor-pulse control system, modification ZiU- 682G -017 remained equipped with classical, uneconomical and unsupported acceptable smoothness Rheostat
A potentiometer is a three-terminal (electronics), terminal resistor with a sliding or rotating contact that forms an adjustable voltage divider. If only two terminals are used, one end and the wiper, it acts as a variable resistor or rheostat.
...
- contactor control system, electrical equipment factory "Dinamo" conventional platen doors. Some of the changes undergone interior, in particular, have been installed interior lights more modern form. From 2002 to request the trolley began to be produced in variants with altered appearance cabin (this applied fiberglass pad).
ZiU-682G-016.02 and ZiU-682G-016.03
Since October 2002, commercially produced modification ZiU- 682G - 016.02, which is a further development of the model ZiU- 682G -018. Siding boards made of seamless steel sheet paneling front of the trolley were combined with the use of fiberglass panels; the front bumper was also made of fiberglass. Passenger cabin windows are tinted glass, and a new panoramic windshield was installed. Increased corrosion protection was added to the body, including the use of conductive soils firm «Sikkens» in lap welds, phosphate protective coating, as well as additional coverage of the base, sides, front and rear of the protective coating. On trolley mounted traction motor DC - 213A production Moscow factory "Dinamo" 110 kW. Control system - rheostat- contactor. Most of traction electric trolley put to the roof. Collectors located on the roof, power resistors, group controller, radioreaktory circuit breaker WB -7 (there is an option to install instead of the WB -7 breaker manual AV- 8 in the cab at the rear), a static converter (IPT-600/28 or BP -3G), stroke limiter rods. Behind the driver is case inside of which has an electric panel protective relays. In this regard, the first window on the left side of the passenger compartment has reduced dimensions, there is no passenger seat facing the front wheel arch. Interior lighting passenger compartment carried fluorescent fixtures have modes full, partial, and emergency lighting. Passenger room is equipped with separate comfortable seats (which, however, often criticized for full passengers trouble and inconvenience). Two passenger seats are equipped to transport people with limited mobility. Parking brake acts on the brakes the drive wheels of energy storage, control of air in the cab of the crane. The hydraulic oil tank is equipped with a power steering oil level warning device. To improve the electrical introduced fiberglass boards, electrical insulation flaps passenger doors from the body, external electrical insulation rod current collectors, insulation monitoring device UKI, emergency switch, the imposition of mostly electric traction kit from under the floor to the roof, technological track on the roof to move attendants, rear stopper rods pantographs fitted to three electrical insulators, locking the trolley system with open doors, emergency (spare) the passenger area lighting system ANTI passenger doors, emergency exits through the windows of the cabin, equipment service doors from inside and outside governments to open in an emergency installation on the roof of a high-speed circuit-breaker with remote control, etc. The trolley ZiU- 682G - 016.03 has also been produced commercially since 2004. Its main difference from ZiU - 682G - 016.02 is that the frame (base) body is made of an open profile (sill), which increases the rigidity and makes it more resistant to corrosion. Trolleybus body ZiU- 682G 016.03 - welded frame construction. Optionally, the vehicle may be installed with a swing-slide-type front double door (which is especially important for use in Moscow, as one must pay for travel validation). Since September 2009, in connection with the termination of a license to manufacture trolleybuses, issue ZiU 682G016.02 - and - ZiU 682G016.03 were discontinued.ZiU-682G-016.04 and ZiU-682G-016.05
 Since September 2009, JSC "Trolza" in accordance with an obtained production license started production of trolleybuses ZiU-682G-016.04 and ZiU-682G-016.05. And apparently, these trolleys and constructive modifications almost completely replicate their predecessors ZiU-682G-016.02 and ZiU-682G-016.03. As changes in the rank of permanent options included installing electronic route signs and a marquee in the passenger compartment and ABS that ZiU-682G-ZiU 016.02 and 016.03-682G-performed by the customer.
Since September 2009, JSC "Trolza" in accordance with an obtained production license started production of trolleybuses ZiU-682G-016.04 and ZiU-682G-016.05. And apparently, these trolleys and constructive modifications almost completely replicate their predecessors ZiU-682G-016.02 and ZiU-682G-016.03. As changes in the rank of permanent options included installing electronic route signs and a marquee in the passenger compartment and ABS that ZiU-682G-ZiU 016.02 and 016.03-682G-performed by the customer.
Modifications as of 2012
Note that in approximately 2003 JSC "Trolza" changed several notations for produced models of the ZiU- 682G family, considering them all modifications ZiU- 682G -016 (VIN- code starts with all modifications XTU682G0M). As of 2010, the manufacturer offers the following serial modifications (listed in order of increasing number of changes compared to ZiU- 682G) * ZiU- 682G -016 (012) - a basic model similar ZiU- 682G -012 (delivery in the form of a body 1st version) * ZiU- 682G -016 (018) - modification, similar ZiU- 682G -018, and has a slight performance improvement ZiU- 682G -016 (delivery in the form of a body 1st version) * ZiU- 682G - 016.02 (delivery in the form of a body 1st version) * ZiU- 682G - 016.03 (delivery in the form of a body 1st version) * ZiU- 682G - 016.04 * ZiU- 682G - 016.05 In 2009, Trolza developed a modified ZiU- 682G - 016.07. This machine has a total 016.04 with a different numbering and control system - TrSU " Chergos " instead of the standard rheostat- contactor. The only instance in operation in Murmansk. The serial production for the ZiU-9 was discontinued in 2014 due to a lack of demand for the model.Clones produced by other companies
Many factories in modernRussia
Russia, or the Russian Federation, is a country spanning Eastern Europe and North Asia. It is the list of countries and dependencies by area, largest country in the world, and extends across Time in Russia, eleven time zones, sharing Borders ...
or Belarus
Belarus, officially the Republic of Belarus, is a landlocked country in Eastern Europe. It is bordered by Russia to the east and northeast, Ukraine to the south, Poland to the west, and Lithuania and Latvia to the northwest. Belarus spans an a ...
developed their unlicensed or semi-licensed copies of the ZiU-9 design. They may have different designations and trademarks, but in the colloquial language all of them are referred to as "ZiU-9 clones".
* AKSM 100, AKSM 101 and their various modifications built by Belkommunmash
OJSC "Holding Management Company "Belkommunmash" (, Belkamunmash), is a Belarusian manufacturer of electric public transport vehicles. The enterprise was based on a tram and trolleybus repair facility which was opened in 1973. Today it is the lead ...
(Minsk)
* BTZ -5276 and modifications built by manufacturer Bashkir Trolleybus Plant ( Ufa)
* VZTM -5284 and modifications built by manufacturer Volgograd Plant of Transport Engineering (Volgograd
Volgograd,. formerly Tsaritsyn. (1589–1925) and Stalingrad. (1925–1961), is the largest city and the administrative centre of Volgograd Oblast, Russia. The city lies on the western bank of the Volga, covering an area of , with a population ...
)
* VMZ -170 built by manufacturer Vologda Mechanical Plant (JSC " Trans- Alpha", Vologda
Vologda (, ) is a types of inhabited localities in Russia, city and the administrative center of Vologda Oblast, Russia, located on the river Vologda (river), Vologda within the watershed of the Northern Dvina. Population:
The city serves as ...
)
* Trolleybuses production "Nizhtroll" (Nizhny Novgorod
Nizhny Novgorod ( ; rus, links=no, Нижний Новгород, a=Ru-Nizhny Novgorod.ogg, p=ˈnʲiʐnʲɪj ˈnovɡərət, t=Lower Newtown; colloquially shortened to Nizhny) is a city and the administrative centre of Nizhny Novgorod Oblast an ...
), officially passing as overhaul reconditioning
* CT- 682G production "Siberian trolley" (Novosibirsk
Novosibirsk is the largest city and administrative centre of Novosibirsk Oblast and the Siberian Federal District in Russia. As of the 2021 Russian census, 2021 census, it had a population of 1,633,595, making it the most populous city in Siber ...
), officially passing as overhaul reconditioning
* MTRZ - 6223 Moscow trolleybus production plant - modernization of the ZiU -682 for Moscow
Moscow is the Capital city, capital and List of cities and towns in Russia by population, largest city of Russia, standing on the Moskva (river), Moskva River in Central Russia. It has a population estimated at over 13 million residents with ...
* ZiU -682 ZiU BTRM production "Barnaul trolleybus repair shops " (Barnaul
Barnaul (, ) is the largest types of inhabited localities in Russia, city and administrative centre of Altai Krai, Russia, located at the confluence of the Barnaulka and Ob (river), Ob rivers in the West Siberian Plain. As of the Russian Censu ...
), officially passing as overhaul reconditioning
* MTRZ - 6223 Altayelektrotrans production " CAU " Altayelektrotrans " " (Barnaul
Barnaul (, ) is the largest types of inhabited localities in Russia, city and administrative centre of Altai Krai, Russia, located at the confluence of the Barnaulka and Ob (river), Ob rivers in the West Siberian Plain. As of the Russian Censu ...
)
* ZiU -682 Barnaul production of " Company " Altai electric transport company " " (Barnaul)
Operators
 In
In Hungary
Hungary is a landlocked country in Central Europe. Spanning much of the Pannonian Basin, Carpathian Basin, it is bordered by Slovakia to the north, Ukraine to the northeast, Romania to the east and southeast, Serbia to the south, Croatia and ...
, ZiU-9 trolleys still operate in recent years, but they have been retired in Debrecen
Debrecen ( ; ; ; ) is Hungary's cities of Hungary, second-largest city, after Budapest, the regional centre of the Northern Great Plain Regions of Hungary, region and the seat of Hajdú-Bihar County. A city with county rights, it was the large ...
( DKV), Budapest
Budapest is the Capital city, capital and List of cities and towns of Hungary, most populous city of Hungary. It is the List of cities in the European Union by population within city limits, tenth-largest city in the European Union by popul ...
( BKV), and Szeged
Szeged ( , ; see also #Etymology, other alternative names) is List of cities and towns of Hungary#Largest cities in Hungary, the third largest city of Hungary, the largest city and regional centre of the Southern Great Plain and the county seat ...
(SzKT
The Szeged Transport Ltd. () is the name of the transport company of the city of Szeged, Hungary.
Aims
The Szeged Transport Ltd.'s aims are: the operation of electric track-based transport, a public pay parking system, vehicle rescue and transport ...
). Originally 174 of them were used in the capital city of Budapest
Budapest is the Capital city, capital and List of cities and towns of Hungary, most populous city of Hungary. It is the List of cities in the European Union by population within city limits, tenth-largest city in the European Union by popul ...
, and a few dozen more in other cities. Regardless, some buses are still in working condition and are used occasionally by retro and heritage trolley services.
ZiU-9s formerly or are currently employed in all ex-USSR countries except the Baltic states. They have also been in service in Belgrade
Belgrade is the Capital city, capital and List of cities in Serbia, largest city of Serbia. It is located at the confluence of the Sava and Danube rivers and at the crossroads of the Pannonian Basin, Pannonian Plain and the Balkan Peninsula. T ...
ever since the Yugoslav period.
They were also sold to Greece
Greece, officially the Hellenic Republic, is a country in Southeast Europe. Located on the southern tip of the Balkan peninsula, it shares land borders with Albania to the northwest, North Macedonia and Bulgaria to the north, and Turkey to th ...
, Argentina
Argentina, officially the Argentine Republic, is a country in the southern half of South America. It covers an area of , making it the List of South American countries by area, second-largest country in South America after Brazil, the fourt ...
, and Colombia
Colombia, officially the Republic of Colombia, is a country primarily located in South America with Insular region of Colombia, insular regions in North America. The Colombian mainland is bordered by the Caribbean Sea to the north, Venezuel ...
. In the latter, the EDTU (Empresa Distrital de Transportes Urbanos) was a larger operator of these buses; they were in a very bad conservation state in the former Eastern Bloc countries. Three buses were on loan in 1973 for testing purposes in Helsinki
Helsinki () is the Capital city, capital and most populous List of cities and towns in Finland, city in Finland. It is on the shore of the Gulf of Finland and is the seat of southern Finland's Uusimaa region. About people live in the municipali ...
, Finland
Finland, officially the Republic of Finland, is a Nordic country in Northern Europe. It borders Sweden to the northwest, Norway to the north, and Russia to the east, with the Gulf of Bothnia to the west and the Gulf of Finland to the south, ...
.
Greek donation
In 2004, theILPAP
I.L.P.A.P. () was a public Greek company, part of the Athens Urban Transport Organisation, responsible for the operation of the trolleybuses network. ILPAP was founded on December 14, 1970, and since 1998 the company was owned by the Athens Urba ...
, the operator of the trolleybuses in Athens
Athens ( ) is the Capital city, capital and List of cities and towns in Greece, largest city of Greece. A significant coastal urban area in the Mediterranean, Athens is also the capital of the Attica (region), Attica region and is the southe ...
and Piraeus
Piraeus ( ; ; , Ancient: , Katharevousa: ) is a port city within the Athens urban area ("Greater Athens"), in the Attica region of Greece. It is located southwest of Athens city centre along the east coast of the Saronic Gulf in the Ath ...
, Greece
Greece, officially the Hellenic Republic, is a country in Southeast Europe. Located on the southern tip of the Balkan peninsula, it shares land borders with Albania to the northwest, North Macedonia and Bulgaria to the north, and Turkey to th ...
donated nearly all of its old ZiU-9 trolleybuses to the city of Belgrade
Belgrade is the Capital city, capital and List of cities in Serbia, largest city of Serbia. It is located at the confluence of the Sava and Danube rivers and at the crossroads of the Pannonian Basin, Pannonian Plain and the Balkan Peninsula. T ...
and to Georgia (country)
Georgia is a country in the Caucasus region on the coast of the Black Sea. It is located at the intersection of Eastern Europe and West Asia, and is today generally regarded as part of Europe. It is bordered to the north and northeast by Russ ...
. One was donated to the East Anglia Transport Museum
The East Anglia Transport Museum is an open-air transport museum, with numerous historic public transport vehicles (including many in full working order). It is located in Carlton Colville a suburb of Lowestoft, Suffolk. It is the only museum ...
.
Belgrade has had ZiU-9 trolleybuses since the late 1970s. In 2010 a public action was made to save Belgrade's first ZiU-9 from being scrapped.
In fiction
See also
*ZiU-10
ZiU-10 (Zavod imeni Uritskogo, Russian language, Russian for Uritsky Factory) or ZIU-10 (),Murray, Alan (2000). ''World Trolleybus Encyclopaedia'', pp. 75, 114. Yateley, Hampshire, UK: Trolleybooks. . also referred to as ZIU-683, is a model of tro ...
* ZiU-9 EMU
References
External links
ZiU-9 on the Nizhny Novgorod tram site
(in Russian)
(English, somewhat dated) {{commons category, ZiU-9 Trolleybuses