X-ray Transient on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
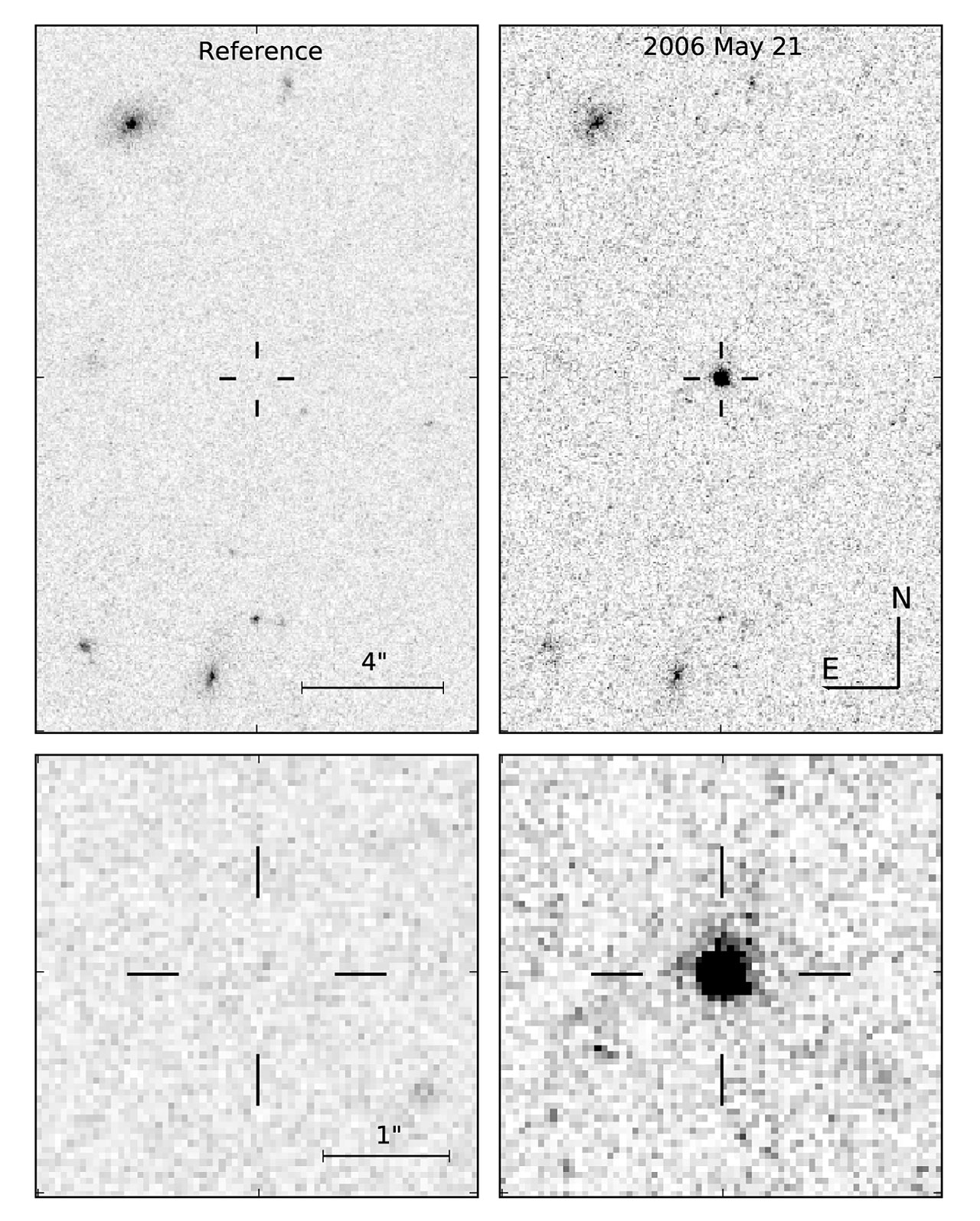 SCP 06F6 is (or was) an
SCP 06F6 is (or was) an
 Unlike Earth's aurorae, which are transient and only occur at times of heightened solar activity,
Unlike Earth's aurorae, which are transient and only occur at times of heightened solar activity,
PTInews.com
/ref> Astrosat will monitor the X-ray sky for new transients, among other scientific focuses.
HETE-2: High Energy Transient Explorer
BATSE: Burst and Transient Source Explorer
Stellar phenomena Astronomical events *X-ray transient
X-ray
An X-ray (also known in many languages as Röntgen radiation) is a form of high-energy electromagnetic radiation with a wavelength shorter than those of ultraviolet rays and longer than those of gamma rays. Roughly, X-rays have a wavelength ran ...
emission occurs from many celestial
Celestial may refer to:
Science
* Objects or events seen in the sky and the following astronomical terms:
** Astronomical object, a naturally occurring physical entity, association, or structure that exists in the observable universe
** Celest ...
objects. These emissions can have a pattern
A pattern is a regularity in the world, in human-made design, or in abstract ideas. As such, the elements of a pattern repeat in a predictable manner. A geometric pattern is a kind of pattern formed of geometric shapes and typically repeated l ...
, occur intermittently, or as a transient astronomical event
Time-domain astronomy is the study of how astronomical objects change with time. Said to have begun with Galileo's '' Letters on Sunspots'', the field has now naturally expanded to encompass variable objects beyond the Solar System. Temporal varia ...
. In X-ray astronomy
X-ray astronomy is an observational branch of astronomy which deals with the study of X-ray observation and detection from astronomical objects. X-radiation is absorbed by the Earth's atmosphere, so instruments to detect X-rays must be taken to ...
many sources have been discovered by placing an X-ray detector
X-ray detectors are devices used to measure the flux, spatial distribution, spectrum, and/or other properties of X-rays.
Detectors can be divided into two major categories: imaging detectors (such as photographic plates and X-ray film (photograp ...
above the Earth
Earth is the third planet from the Sun and the only astronomical object known to Planetary habitability, harbor life. This is enabled by Earth being an ocean world, the only one in the Solar System sustaining liquid surface water. Almost all ...
's atmosphere. Often, the first X-ray source discovered in many constellation
A constellation is an area on the celestial sphere in which a group of visible stars forms Asterism (astronomy), a perceived pattern or outline, typically representing an animal, mythological subject, or inanimate object.
The first constellati ...
s is an X-ray transient. These objects show changing levels of X-ray emission. NRL
The National Rugby League (also known as the NRL Telstra Premiership for sponsorship reasons) is a professional rugby league competition in Oceania which contains clubs from New South Wales, Queensland, Victoria (state), Victoria, the Austral ...
astronomer Dr. Joseph Lazio stated: " ... the sky is known to be full of transient objects emitting at X- and gamma-ray wavelengths, ...". There are a growing number of recurrent X-ray transients. In the sense of traveling as a transient, the only stellar X-ray source that does not belong to a constellation is the Sun
The Sun is the star at the centre of the Solar System. It is a massive, nearly perfect sphere of hot plasma, heated to incandescence by nuclear fusion reactions in its core, radiating the energy from its surface mainly as visible light a ...
. As seen from Earth, the Sun moves from west to east along the ecliptic
The ecliptic or ecliptic plane is the orbital plane of Earth's orbit, Earth around the Sun. It was a central concept in a number of ancient sciences, providing the framework for key measurements in astronomy, astrology and calendar-making.
Fr ...
, passing over the course of one year through the twelve constellations of the Zodiac
The zodiac is a belt-shaped region of the sky that extends approximately 8° north and south celestial latitude of the ecliptic – the apparent path of the Sun across the celestial sphere over the course of the year. Within this zodiac ...
, and Ophiuchus
Ophiuchus () is a large constellation straddling the celestial equator. Its name comes from the Ancient Greek (), meaning "serpent-bearer", and it is commonly represented as a man grasping a snake. The serpent is represented by the constellati ...
.
Exotic X-ray transients
 SCP 06F6 is (or was) an
SCP 06F6 is (or was) an astronomical object
An astronomical object, celestial object, stellar object or heavenly body is a naturally occurring physical entity, association, or structure that exists within the observable universe. In astronomy, the terms ''object'' and ''body'' are of ...
of unknown type, discovered on February 21, 2006, in the constellation Boötes
Boötes ( ) is a constellation in the northern sky, located between 0° and +60° declination, and 13 and 16 hours of right ascension on the celestial sphere. The name comes from , which comes from 'herder, herdsman' or 'plowman' (literally, 'o ...
during a survey of galaxy cluster
A galaxy cluster, or a cluster of galaxies, is a structure that consists of anywhere from hundreds to thousands of galaxies that are bound together by gravity, with typical masses ranging from 1014 to 1015 solar masses. Clusters consist of galax ...
CL 1432.5+3332.8 with the Hubble Space Telescope
The Hubble Space Telescope (HST or Hubble) is a space telescope that was launched into low Earth orbit in 1990 and remains in operation. It was not the Orbiting Solar Observatory, first space telescope, but it is one of the largest and most ...
's Advanced Camera for Surveys
The Advanced Camera for Surveys (ACS) is a third-generation axial instrument aboard the Hubble Space Telescope (HST). The initial design and scientific capabilities of ACS were defined by a team based at Johns Hopkins University. ACS was assembl ...
Wide Field Channel.
The European X-ray satellite XMM Newton made an observation in early August 2006 which appears to show an X-ray glow around SCP 06F6, two orders of magnitude more luminous than that of supernovae.
Nova or supernova
Most astronomical X-ray transient sources have simple and consistent time structures; typically a rapid brightening followed by gradual fading, as in anova
A nova ( novae or novas) is a transient astronomical event that causes the sudden appearance of a bright, apparently "new" star (hence the name "nova", Latin for "new") that slowly fades over weeks or months. All observed novae involve white ...
or supernova
A supernova (: supernovae or supernovas) is a powerful and luminous explosion of a star. A supernova occurs during the last stellar evolution, evolutionary stages of a massive star, or when a white dwarf is triggered into runaway nuclear fusion ...
.
GRO J0422+32
GRO or Gro may refer to:
Organisations
* General Register Office
* General Register Office (Northern Ireland) Technology and science
* Generic receive offload, in computer networking
* GRO structure file format, used by GROMACS
Transportation
* G ...
is an X-ray nova and black hole
A black hole is a massive, compact astronomical object so dense that its gravity prevents anything from escaping, even light. Albert Einstein's theory of general relativity predicts that a sufficiently compact mass will form a black hole. Th ...
candidate that was discovered by the BATSE instrument on the Compton Gamma Ray Observatory
The Compton Gamma Ray Observatory (CGRO) was a space observatory detecting photons with photon energy, energies from 20 kElectronvolt#Properties, eV to 30 GeV, in Earth orbit from 1991 to 2000. The observatory featured four main tel ...
satellite on Aug 5 1992. During the outburst, it was observed to be stronger than the Crab Nebula
The Crab Nebula (catalogue designations M1, NGC 1952, Taurus A) is a supernova remnant and pulsar wind nebula in the constellation of Taurus (constellation), Taurus. The common name comes from a drawing that somewhat resembled a crab with arm ...
gamma-ray source out to photon energies of about 500 keV
In physics, an electronvolt (symbol eV), also written electron-volt and electron volt, is the measure of an amount of kinetic energy gained by a single electron accelerating through an electric potential difference of one volt in vacuum. When us ...
.
Transient binary X-ray source
XTE J1650-500 is a transient binary X-ray source located in theconstellation
A constellation is an area on the celestial sphere in which a group of visible stars forms Asterism (astronomy), a perceived pattern or outline, typically representing an animal, mythological subject, or inanimate object.
The first constellati ...
Ara
Ara may refer to:
Biology
* ''Ara'' (bird), a genus of parrots
* Ara (fish) (''Niphon spinosus''), a species of fish
* L-arabinose operon, also known as ara
Places
* Ara (mountain), a mountain in Armenia
* Ara, Armenia, a village in Armenia
...
. The binary period is 0.32 d.
Soft X-ray transient
" Soft X-ray transients" are composed of some type of compact object (probably a neutron star) and some type of "normal", low-mass star (i.e. a star with a mass of some fraction of the Sun's mass). These objects show changing levels of low-energy, or "soft", X-ray emission, probably produced somehow by variable transfer of mass from the normal star to the compact object. In effect the compact object "gobbles up" the normal star, and the X-ray emission can provide the best view of how this process occurs. Soft X-ray transients Cen X-4 and Apl X-1 were discovered byHakucho
Hakucho (also known as CORSA-b before launch; CORSA stands for Cosmic Radiation Satellite) was Japan's first X-ray astronomy satellite, developed by the Institute of Space and Aeronautical Science (then a division of the University of Tokyo
...
, Japan
Japan is an island country in East Asia. Located in the Pacific Ocean off the northeast coast of the Asia, Asian mainland, it is bordered on the west by the Sea of Japan and extends from the Sea of Okhotsk in the north to the East China Sea ...
's first X-ray astronomy
X-ray astronomy is an observational branch of astronomy which deals with the study of X-ray observation and detection from astronomical objects. X-radiation is absorbed by the Earth's atmosphere, so instruments to detect X-rays must be taken to ...
satellite
A satellite or an artificial satellite is an object, typically a spacecraft, placed into orbit around a celestial body. They have a variety of uses, including communication relay, weather forecasting, navigation ( GPS), broadcasting, scient ...
.
X-ray burster
X-ray burster
X-ray bursters are one class of X-ray binary stars exhibiting X-ray bursts, periodic and rapid increases in luminosity (typically a factor of 10 or greater) that peak in the X-ray region of the electromagnetic spectrum. These astrophysical syste ...
s are one class of X-ray binary stars exhibiting periodic and rapid increases in luminosity
Luminosity is an absolute measure of radiated electromagnetic radiation, electromagnetic energy per unit time, and is synonymous with the radiant power emitted by a light-emitting object. In astronomy, luminosity is the total amount of electroma ...
(typically a factor of 10 or greater) peaked in the X-ray
An X-ray (also known in many languages as Röntgen radiation) is a form of high-energy electromagnetic radiation with a wavelength shorter than those of ultraviolet rays and longer than those of gamma rays. Roughly, X-rays have a wavelength ran ...
regime of the electromagnetic spectrum
The electromagnetic spectrum is the full range of electromagnetic radiation, organized by frequency or wavelength. The spectrum is divided into separate bands, with different names for the electromagnetic waves within each band. From low to high ...
. These astrophysical systems are composed of an accreting compact object
In astronomy, the term compact object (or compact star) refers collectively to white dwarfs, neutron stars, and black holes. It could also include exotic stars if such hypothetical, dense bodies are confirmed to exist. All compact objects have a ...
, typically a neutron star
A neutron star is the gravitationally collapsed Stellar core, core of a massive supergiant star. It results from the supernova explosion of a stellar evolution#Massive star, massive star—combined with gravitational collapse—that compresses ...
or occasionally a black hole
A black hole is a massive, compact astronomical object so dense that its gravity prevents anything from escaping, even light. Albert Einstein's theory of general relativity predicts that a sufficiently compact mass will form a black hole. Th ...
, and a companion 'donor' star; the mass of the donor star is used to categorize the system as either a high mass (above 10 solar mass
The solar mass () is a frequently used unit of mass in astronomy, equal to approximately . It is approximately equal to the mass of the Sun. It is often used to indicate the masses of other stars, as well as stellar clusters, nebulae, galaxie ...
es) or low mass (less than 1 solar mass) X-ray binary, abbreviated as LMXB and HMXB, respectively. X-ray bursters differ observationally from other X-ray transient sources (such as X-ray pulsar
X-ray pulsars or accretion-powered pulsars are a class of astronomical objects that are X-ray sources displaying strict periodic variations in X-ray intensity. The X-ray periods range from as little as a fraction of a second to as much as several m ...
s and soft X-ray transients), showing a sharp rise time (1 – 10 seconds) followed by spectral softening (a property of cooling black bodies). Individual bursts are characterized by an integrated flux of 1039-40 ergs.
Gamma-ray burster
Agamma-ray burst
In gamma-ray astronomy, gamma-ray bursts (GRBs) are extremely energetic events occurring in distant Galaxy, galaxies which represent the brightest and most powerful class of explosion in the universe. These extreme Electromagnetic radiation, ele ...
(GRB) is a highly luminous flash of gamma ray
A gamma ray, also known as gamma radiation (symbol ), is a penetrating form of electromagnetic radiation arising from high energy interactions like the radioactive decay of atomic nuclei or astronomical events like solar flares. It consists o ...
s — the most energetic form of electromagnetic radiation
In physics, electromagnetic radiation (EMR) is a self-propagating wave of the electromagnetic field that carries momentum and radiant energy through space. It encompasses a broad spectrum, classified by frequency or its inverse, wavelength ...
. GRB 970228 was a GRB detected on Feb 28 1997 at 02:58 UTC
Coordinated Universal Time (UTC) is the primary time standard globally used to regulate clocks and time. It establishes a reference for the current time, forming the basis for civil time and time zones. UTC facilitates international communica ...
. Prior to this event, GRBs had only been observed at gamma wavelengths. For several years physicists had expected these bursts to be followed by a longer-lived afterglow
An afterglow in meteorology consists of several atmospheric optical phenomena, with a general definition as a broad arch of whitish or pinkish sunlight in the twilight sky, consisting of the bright segment and the purple light. Purple light mai ...
at longer wavelengths, such as radio waves
Radio waves (formerly called Hertzian waves) are a type of electromagnetic radiation with the lowest frequencies and the longest wavelengths in the electromagnetic spectrum, typically with frequencies below 300 gigahertz (GHz) and wavelengths ...
, x-rays
An X-ray (also known in many languages as Röntgen radiation) is a form of high-energy electromagnetic radiation with a wavelength shorter than those of ultraviolet rays and longer than those of gamma rays. Roughly, X-rays have a wavelength ran ...
, and even visible light
Light, visible light, or visible radiation is electromagnetic radiation that can be perceived by the human eye. Visible light spans the visible spectrum and is usually defined as having wavelengths in the range of 400–700 nanometres (nm ...
. This was the first burst for which such an afterglow was observed.
A transient x-ray source was detected which faded with a power law
In statistics, a power law is a Function (mathematics), functional relationship between two quantities, where a Relative change and difference, relative change in one quantity results in a relative change in the other quantity proportional to the ...
slope in the days following the burst. This x-ray afterglow
An afterglow in meteorology consists of several atmospheric optical phenomena, with a general definition as a broad arch of whitish or pinkish sunlight in the twilight sky, consisting of the bright segment and the purple light. Purple light mai ...
was the first GRB afterglow ever detected.
Transient X-ray pulsars
For some types ofX-ray pulsar
X-ray pulsars or accretion-powered pulsars are a class of astronomical objects that are X-ray sources displaying strict periodic variations in X-ray intensity. The X-ray periods range from as little as a fraction of a second to as much as several m ...
s, the companion star is a Be star
Be stars are a heterogeneous set of stars with B spectral types and emission lines. A narrower definition, sometimes referred to as ''classical Be stars'', is a non-supergiant B star whose spectrum has, or had at some time, one or more Balmer ...
that rotates very rapidly and apparently sheds a disk of gas around its equator. The orbits of the neutron star
A neutron star is the gravitationally collapsed Stellar core, core of a massive supergiant star. It results from the supernova explosion of a stellar evolution#Massive star, massive star—combined with gravitational collapse—that compresses ...
with these companions are usually large and very elliptical in shape. When the neutron star passes nearby or through the Be circumstellar disk, it will capture material and temporarily become an X-ray pulsar. The circumstellar disk around the Be star expands and contracts for unknown reasons, so these are transient X-ray pulsars that are observed only intermittently, often with months to years between episodes of observable X-ray pulsation.
SAX J1808.4-3658 is a transient, accreting millisecond X-ray pulsar
X-ray pulsars or accretion-powered pulsars are a class of astronomical objects that are X-ray sources displaying strict periodic variations in X-ray intensity. The X-ray periods range from as little as a fraction of a second to as much as several m ...
that is intermittent. In addition, X-ray burst
X-ray bursters are one class of X-ray binary stars exhibiting X-ray bursts, periodic and rapid increases in luminosity (typically a factor of 10 or greater) that peak in the X-ray region of the electromagnetic spectrum. These astrophysical syste ...
oscillations and quasi-periodic oscillations in addition to coherent X-ray pulsations have been seen from SAX J1808.4-3658, making it a Rosetta stone for interpretation of the timing behavior of low-mass X-ray binaries.
Supergiant Fast X-ray Transients (SFXTs)
There are a growing number of recurrent X-ray transients, characterized by short outbursts with very fast rise times (~ tens of minutes) and typical durations of a few hours that are associated with OBsupergiant
Supergiants are among the most massive and most luminous stars. Supergiant stars occupy the top region of the Hertzsprung–Russell diagram, with absolute visual magnitudes between about −3 and −8. The temperatures of supergiant stars range ...
s and hence define a new class of massive X-ray binaries: Supergiant Fast X-ray Transients (SFXTs). XTE J1739–302 is one of these. Discovered in 1997, remaining active only one day, with an X-ray spectrum well fitted with a thermal bremsstrahlung
In particle physics, bremsstrahlung (; ; ) is electromagnetic radiation produced by the deceleration of a charged particle when deflected by another charged particle, typically an electron by an atomic nucleus. The moving particle loses kinetic ...
(temperature of ~20 keV), resembling the spectral properties of accreting pulsars, it was at first classified as a peculiar Be/X-ray transient with an unusually short outburst. A new burst was observed on Apr 8 2008 with Swift
Swift or SWIFT most commonly refers to:
* SWIFT, an international organization facilitating transactions between banks
** SWIFT code
* Swift (programming language)
* Swift (bird), a family of birds
It may also refer to:
Organizations
* SWIF ...
.
The Sun as an X-ray transient
The quietSun
The Sun is the star at the centre of the Solar System. It is a massive, nearly perfect sphere of hot plasma, heated to incandescence by nuclear fusion reactions in its core, radiating the energy from its surface mainly as visible light a ...
, although less active than active regions, is awash with dynamic
Dynamics (from Greek δυναμικός ''dynamikos'' "powerful", from δύναμις ''dynamis'' "power") or dynamic may refer to:
Physics and engineering
* Dynamics (mechanics), the study of forces and their effect on motion
Brands and enter ...
processes and transient
Transience or transient may refer to:
Music
* ''Transient'' (album), a 2004 album by Gaelle
* ''Transience'' (Steven Wilson album), 2015
* Transience (Wreckless Eric album)
Science and engineering
* Transient state, when a process variable or ...
events (bright points, nanoflares
A nanoflare is a very small episodic heating event which happens in the corona, the external atmosphere of the Sun.
The hypothesis of small impulsive heating events as a possible explanation of the coronal heating was first suggested by Thoma ...
and jets).
A coronal mass ejection
A coronal mass ejection (CME) is a significant ejection of plasma mass from the Sun's corona into the heliosphere. CMEs are often associated with solar flares and other forms of solar activity, but a broadly accepted theoretical understandin ...
(CME) is an ejected plasma consisting primarily of electron
The electron (, or in nuclear reactions) is a subatomic particle with a negative one elementary charge, elementary electric charge. It is a fundamental particle that comprises the ordinary matter that makes up the universe, along with up qua ...
s and proton
A proton is a stable subatomic particle, symbol , Hydron (chemistry), H+, or 1H+ with a positive electric charge of +1 ''e'' (elementary charge). Its mass is slightly less than the mass of a neutron and approximately times the mass of an e ...
s (in addition to small quantities of heavier elements such as helium, oxygen, and iron), plus the entraining coronal closed magnetic field
A magnetic field (sometimes called B-field) is a physical field that describes the magnetic influence on moving electric charges, electric currents, and magnetic materials. A moving charge in a magnetic field experiences a force perpendicular ...
regions. Small-scale energetic signatures such as plasma heating (observed as compact soft X-ray brightening) may be indicative of impending CMEs. The soft X-ray sigmoid (an S-shaped intensity of soft X-rays) is an observational manifestation of the connection between coronal structure and CME production.
The first detection of a Coronal mass ejection
A coronal mass ejection (CME) is a significant ejection of plasma mass from the Sun's corona into the heliosphere. CMEs are often associated with solar flares and other forms of solar activity, but a broadly accepted theoretical understandin ...
(CME) as such was made on Dec 1 1971 by R. Tousey of the US Naval Research Laboratory
The United States Naval Research Laboratory (NRL) is the corporate research laboratory for the United States Navy and the United States Marine Corps. Located in Washington, DC, it was founded in 1923 and conducts basic scientific research, appl ...
using the 7th Orbiting Solar Observatory ( OSO 7). Earlier observations of coronal transients or even phenomena observed visually during solar eclipses
A solar eclipse occurs when the Moon passes between Earth and the Sun, thereby obscuring the view of the Sun from a small part of Earth, totally or partially. Such an alignment occurs approximately every six months, during the eclipse season i ...
are now understood as essentially the same thing.
The largest geomagnetic perturbation, resulting presumably from a "prehistoric" CME, coincided with the first-observed solar flare
A solar flare is a relatively intense, localized emission of electromagnetic radiation in the Sun's atmosphere. Flares occur in active regions and are often, but not always, accompanied by coronal mass ejections, solar particle events, and ot ...
, in 1859. The flare was observed visually by Richard Christopher Carrington
Richard Christopher Carrington (26 May 1826 – 27 November 1875) was an English astronomer whose 1859 astronomical observations demonstrated the existence of solar flares as well as suggesting their electrical influence upon the Earth and it ...
and the geomagnetic storm
A geomagnetic storm, also known as a magnetic storm, is a temporary disturbance of the Earth's magnetosphere that is driven by interactions between the magnetosphere and large-scale transient Plasma (physics), plasma and magnetic field structur ...
was observed with the recording magnetograph at Kew Gardens
Kew Gardens is a botanical garden, botanic garden in southwest London that houses the "largest and most diverse botany, botanical and mycology, mycological collections in the world". Founded in 1759, from the exotic garden at Kew Park, its li ...
. The same instrument recorded a crotchet, an instantaneous perturbation of the Earth's ionosphere by ionizing soft X-rays
An X-ray (also known in many languages as Röntgen radiation) is a form of high-energy electromagnetic radiation with a wavelength shorter than those of ultraviolet rays and longer than those of gamma rays. Roughly, X-rays have a wavelength ran ...
. This could not easily be understood at the time because it predated the discovery of X-rays (by Roentgen) and the recognition of the ionosphere
The ionosphere () is the ionized part of the upper atmosphere of Earth, from about to above sea level, a region that includes the thermosphere and parts of the mesosphere and exosphere. The ionosphere is ionized by solar radiation. It plays ...
(by Kennelly and Heaviside
Oliver Heaviside ( ; 18 May 1850 – 3 February 1925) was an English mathematician and physicist who invented a new technique for solving differential equations (equivalent to the Laplace transform), independently developed vector calculus, a ...
).
Transient X-rays from Jupiter
 Unlike Earth's aurorae, which are transient and only occur at times of heightened solar activity,
Unlike Earth's aurorae, which are transient and only occur at times of heightened solar activity, Jupiter
Jupiter is the fifth planet from the Sun and the List of Solar System objects by size, largest in the Solar System. It is a gas giant with a Jupiter mass, mass more than 2.5 times that of all the other planets in the Solar System combined a ...
's aurorae are permanent, though their intensity varies from day to day. They consist of three main components: the main ovals, which are bright, narrow (< 1000 km in width) circular features located at approximately 16° from the magnetic poles; the satellite auroral spots, which correspond to the footprints of the magnetic field lines connecting their ionospheres with the ionosphere of Jupiter, and transient polar emissions situated within the main ovals. The auroral emissions were detected in almost all parts of the electromagnetic spectrum from radio waves to X-rays (up to 3 keV).
Detecting X-ray transients
The X-ray monitor ofSolwind
P78-1 or Solwind was a United States satellite launched aboard an Atlas F rocket from Vandenberg Air Force Base in California on February 24, 1979. The satellite's mission was extended by several weeks, so that it operated until it was destroye ...
, designated NRL-608 or XMON, was a collaboration between the Naval Research Laboratory
The United States Naval Research Laboratory (NRL) is the corporate research laboratory for the United States Navy and the United States Marine Corps. Located in Washington, DC, it was founded in 1923 and conducts basic scientific research, appl ...
and Los Alamos National Laboratory
Los Alamos National Laboratory (often shortened as Los Alamos and LANL) is one of the sixteen research and development Laboratory, laboratories of the United States Department of Energy National Laboratories, United States Department of Energy ...
. The monitor consisted of 2 collimated argon proportional counters. The instrument bandwidth of 3-10 keV was defined by the detector window absorption (the window was 0.254 mm beryllium) and the upper level discriminator. The active gas volume (P-10 mixture) was 2.54 cm deep, providing good efficiency up to 10 keV. Counts were recorded in 2 energy channels. Slat collimators defined a FOV of 3° x 30° (FWHM) for each detector; the long axes of the FOVs were perpendicular to each other. The long axes were inclined 45 degrees to the scan direction, allowing localization of transient events to about 1 degree.
The PHEBUS experiment recorded high energy transient events in the range 100 keV to 100 MeV. It consisted of two independent detectors and their associated electronics
Electronics is a scientific and engineering discipline that studies and applies the principles of physics to design, create, and operate devices that manipulate electrons and other Electric charge, electrically charged particles. It is a subfield ...
. Each detector consisted of a bismuth germinate (BGO) crystal 78 mm in diameter
In geometry, a diameter of a circle is any straight line segment that passes through the centre of the circle and whose endpoints lie on the circle. It can also be defined as the longest Chord (geometry), chord of the circle. Both definitions a ...
by 120 mm thick, surrounded by a plastic anti-coincidence jacket. The two detectors were arranged on the spacecraft so as to observe 4 π steradian
The steradian (symbol: sr) or square radian is the unit of solid angle in the International System of Units (SI). It is used in three-dimensional geometry, and is analogous to the radian, which quantifies planar angles. A solid angle in the fo ...
s. The burst mode was triggered when the count rate in the 0.1 to 1.5 MeV energy range exceeded the background level by 8 σ (standard deviations) in either 0.25 or 1.0 seconds. There were 116 channels over the energy range.
Also on board the Granat International Astrophysical Observatory were four WATCH
A watch is a timepiece carried or worn by a person. It is designed to maintain a consistent movement despite the motions caused by the person's activities. A wristwatch is worn around the wrist, attached by a watch strap or another type of ...
instruments that could localize bright sources in the 6 to 180 keV range to within 0.5° using a Rotation Modulation Collimator. Taken together, the instruments' three fields of view covered approximately 75% of the sky. The energy resolution was 30% FWHM
In a distribution, full width at half maximum (FWHM) is the difference between the two values of the independent variable at which the dependent variable is equal to half of its maximum value. In other words, it is the width of a spectrum curve ...
at 60 keV. During quiet periods, count rates in two energy bands (6 to 15 and 15 to 180 keV) were accumulated for 4, 8, or 16 seconds, depending on onboard computer memory availability. During a burst or transient event, count rates were accumulated with a time resolution of 1 s per 36 s.
The Compton Gamma Ray Observatory
The Compton Gamma Ray Observatory (CGRO) was a space observatory detecting photons with photon energy, energies from 20 kElectronvolt#Properties, eV to 30 GeV, in Earth orbit from 1991 to 2000. The observatory featured four main tel ...
(CGRO) carries the Burst and Transient Source Experiment (BATSE) which detects in the 20 keV to 8 MeV range.
WIND was launched on Nov 1 1994. At first, the satellite had a lunar swingby orbit around the Earth. With the assistance of the Moon's gravitational field Wind's apogee was kept over the day hemisphere of the Earth and magnetospheric observations were made. Later in the mission, the Wind spacecraft was inserted into a special "halo" orbit in the solar wind upstream from the Earth, about the sunward Sun-Earth equilibrium point (L1). The satellite has a spin period of ~ 20 seconds, with the spin axis normal to the ecliptic. WIND carries the Transient Gamma-Ray Spectrometer (TGRS) which covers the energy range 15 keV - 10 MeV, with an energy resolution of 2.0 keV @ 1.0 MeV (E/delta E = 500).
The third US Small Astronomy Satellite (SAS-3) was launched on May 7, 1975, with 3 major scientific objectives: 1) determine bright X-ray source locations to an accuracy of 15 arcseconds; 2) study selected sources over the energy range 0.1-55 keV; and 3) continuously search the sky for X-ray novae, flares, and other transient phenomena. It was a spinning satellite with pointing capability. SAS 3 was the first to discover X-rays from a highly magnetic WD binary system, AM Her, discovered X-rays from Algol and HZ 43, and surveyed the soft X-ray background (0.1-0.28 kev).
Tenma
Tenma, known as ASTRO-B before launch (COSPAR 1983-011A, SATCAT 13829), was a Japanese X-ray astronomy
X-ray astronomy is an observational branch of astronomy which deals with the study of X-ray observation and detection from astronomical obje ...
was the second Japanese X-ray astronomy satellite launched on Feb 20 1983. Tenma carried GSFC detectors which had an improved energy resolution (by a factor of 2) compared to proportional counters and performed the first sensitive measurements of the iron spectral region for many astronomical objects. Energy Range: 0.1 keV - 60 keV. Gas Scintillator Proportional Counter: 10 units of 80 cm2 each, FOV ~ 3deg (FWHM), 2 - 60 keV. Transient Source Monitor: 2 - 10 keV.
India
India, officially the Republic of India, is a country in South Asia. It is the List of countries and dependencies by area, seventh-largest country by area; the List of countries by population (United Nations), most populous country since ...
's first dedicated astronomy
Astronomy is a natural science that studies celestial objects and the phenomena that occur in the cosmos. It uses mathematics, physics, and chemistry in order to explain their origin and their overall evolution. Objects of interest includ ...
satellite
A satellite or an artificial satellite is an object, typically a spacecraft, placed into orbit around a celestial body. They have a variety of uses, including communication relay, weather forecasting, navigation ( GPS), broadcasting, scient ...
, scheduled for launch on board the PSLV
The Polar Satellite Launch Vehicle (PSLV) is an expendable medium-lift launch vehicle designed and operated by the Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO). It was developed to allow India to launch its Indian Remote Sensing (IRS) satellite ...
in mid 2010,/ref> Astrosat will monitor the X-ray sky for new transients, among other scientific focuses.
See also
*X-ray astronomy
X-ray astronomy is an observational branch of astronomy which deals with the study of X-ray observation and detection from astronomical objects. X-radiation is absorbed by the Earth's atmosphere, so instruments to detect X-rays must be taken to ...
* X-ray astrophysical sources
References
{{Reflist, 30emExternal links
HETE-2: High Energy Transient Explorer
BATSE: Burst and Transient Source Explorer
Stellar phenomena Astronomical events *X-ray transient