|
Nanoflares
A nanoflare is a very small episodic heating event which happens in the corona, the external atmosphere of the Sun. The hypothesis of small impulsive heating events as a possible explanation of the coronal heating was first suggested by Thomas Gold and then later developed and dubbed "nanoflares" by Eugene Parker. According to Parker, a nanoflare arises from an event of magnetic reconnection which converts the energy stored in the solar magnetic field into the motion of the plasma. The fluid plasma motion occurs at length-scales so small that it is soon damped by turbulence and then by viscosity. Damping quickly converts energy into heat, which is conducted by free electrons along the magnetic field lines closest to the place where the nanoflare switches on. In order to heat a region of very high X-ray emission, over an area of one square arcsec on the Sun, a nanoflare of 1017 J should happen every 20 seconds, and 1000 nanoflares per second should occur in a large active re ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Solar Corona
In astronomy, a corona (: coronas or coronae) is the outermost layer of a star's Stellar atmosphere, atmosphere. It is a hot but relatively luminosity, dim region of Plasma (physics), plasma populated by intermittent coronal structures such as solar prominence, prominences, coronal loops, and helmet streamers. The Sun's corona lies above the chromosphere and extends millions of kilometres into outer space. Coronal light is typically obscured by diffuse sky radiation and Glare (vision), glare from the solar disk, but can be easily seen by the naked eye during a total solar eclipse or with a specialized coronagraph. Spectroscopic measurements indicate strong ionization in the corona and a plasma temperature in excess of , much hotter than the surface of the Sun, known as the photosphere. is, in turn, derived . History In 1724, French-Italian astronomer Giacomo F. Maraldi recognized that the aura visible during a solar eclipse belongs to the Sun, not to the Moon. In 1809, Span ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thomas Gold
Thomas Gold (May 22, 1920 – June 22, 2004) was an Austrian-born astrophysicist, who also held British and American citizenship. He was a professor of astronomy at Cornell University, a member of the U.S. National Academy of Sciences, and a Fellow of the Royal Society (London). Gold was one of three young Cambridge scientists who in 1948 proposed the now mostly abandoned "steady state" hypothesis of the universe. Gold's work crossed boundaries of academic and scientific disciplines, into biophysics, astronomy, aerospace engineering, and geophysics. Early life Gold was born on May 22, 1920, in Vienna, Austria, to Max Gold, a wealthy Jewish industrialist (pre-war) who ran one of Austria's largest mining and metal fabrication companies, and German former actress Josefine Martin. Following the economic downfall of the European mining industry in the late 1920s, Max Gold moved his family to Berlin, where he had taken a job as director of a metal trading company.. Following the st ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
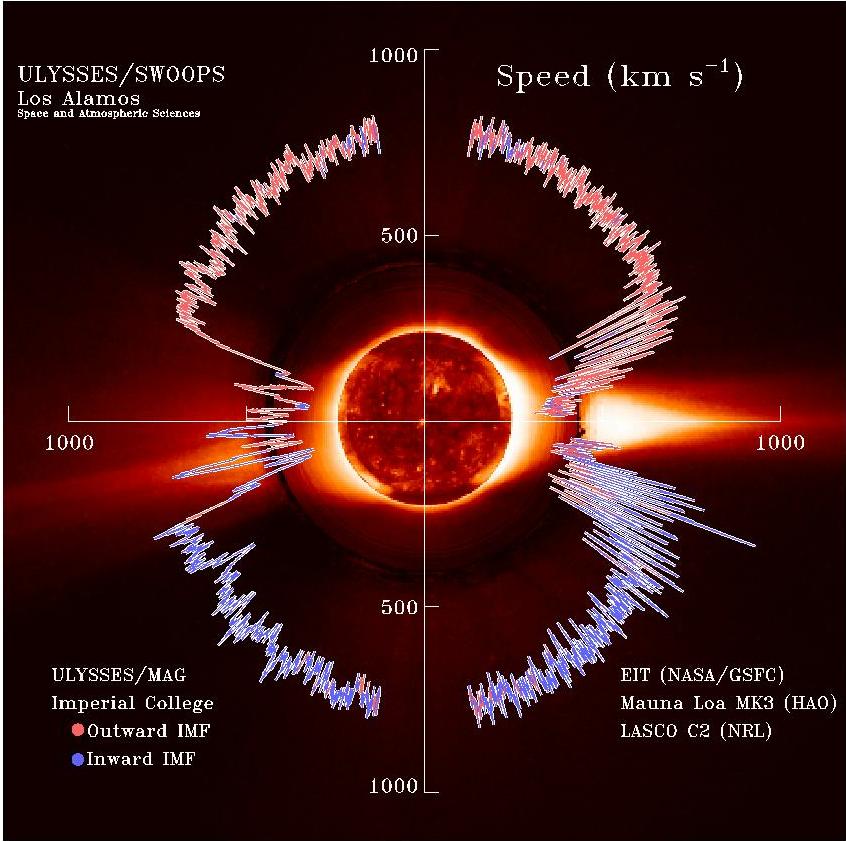
Solar Wind
The solar wind is a stream of charged particles released from the Sun's outermost atmospheric layer, the Stellar corona, corona. This Plasma (physics), plasma mostly consists of electrons, protons and alpha particles with kinetic energy between . The composition of the solar wind plasma also includes a mixture of particle species found in the solar plasma: trace amounts of heavy ions and atomic nuclei of Chemical element, elements such as carbon, nitrogen, oxygen, neon, magnesium, silicon, sulfur, and iron. There are also rarer traces of some other nuclei and isotopes such as phosphorus, titanium, chromium, and nickel's isotopes 58Ni, 60Ni, and 62Ni. Superimposed with the solar-wind plasma is the interplanetary magnetic field. The solar wind varies in density, temperature and speed over time and over Solar coordinate systems#Heliographic, solar latitude and longitude. Its particles can escape the Sun's gravity because of their high energy resulting from the high temperature of t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Solar Magnetic Field
The Sun is the star at the centre of the Solar System. It is a massive, nearly perfect sphere of hot plasma, heated to incandescence by nuclear fusion reactions in its core, radiating the energy from its surface mainly as visible light and infrared radiation with 10% at ultraviolet energies. It is by far the most important source of energy for life on Earth. The Sun has been an object of veneration in many cultures. It has been a central subject for astronomical research since antiquity. The Sun orbits the Galactic Center at a distance of 24,000 to 28,000 light-years. Its distance from Earth defines the astronomical unit, which is about or about 8 light-minutes. Its diameter is about (), 109 times that of Earth. The Sun's mass is about 330,000 times that of Earth, making up about 99.86% of the total mass of the Solar System. The mass of outer layer of the Sun's atmosphere, its ''photosphere'', consists mostly of hydrogen (~73%) and helium (~25%), with much smaller ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Coronal Radiative Losses
In astronomy and in astrophysics, for radiative losses of the solar corona, it is meant the energy flux radiated from the external atmosphere of the Sun (traditionally divided into chromosphere, transition region and corona), and, in particular, the processes of production of the radiation coming from the solar corona and transition region, where the plasma is optically-thin. On the contrary, in the chromosphere, where the temperature decreases from the photospheric value of 6000 K to the minimum of 4400 K, the optical depth is about 1, and the radiation is thermal. The corona extends much further than a solar radius from the photosphere and looks very complex and inhomogeneous in the X-rays images taken by satellites (see the figure on the right taken by the XRT on board Hinode). The structure and dynamics of the corona are dominated by the solar magnetic field. There are strong evidences that even the heating mechanism, responsible for its high temperature of million degr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Solar Flare
A solar flare is a relatively intense, localized emission of electromagnetic radiation in the Sun's atmosphere. Flares occur in active regions and are often, but not always, accompanied by coronal mass ejections, solar particle events, and other eruptive solar phenomena. The occurrence of solar flares varies with the 11-year solar cycle. Solar flares are thought to occur when stored magnetic energy in the Sun's atmosphere accelerates charged particles in the surrounding plasma. This results in the emission of electromagnetic radiation across the electromagnetic spectrum. The typical time profile of these emissions features three identifiable phases: a ''precursor phase'', an ''impulsive phase'' when particle acceleration dominates, and a ''gradual phase'' in which hot plasma injected into the corona by the flare cools by a combination of radiation and conduction of energy back down to the lower atmosphere. The extreme ultraviolet and X-ray radiation from solar flares is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Coronal Mass Ejections
A coronal mass ejection (CME) is a significant ejection of plasma mass from the Sun's corona into the heliosphere. CMEs are often associated with solar flares and other forms of solar activity, but a broadly accepted theoretical understanding of these relationships has not been established. If a CME enters interplanetary space, it is sometimes referred to as an interplanetary coronal mass ejection (ICME). ICMEs are capable of reaching and colliding with Earth's magnetosphere, where they can cause geomagnetic storms, aurorae, and in rare cases damage to electrical power grids. The largest recorded geomagnetic perturbation, resulting presumably from a CME, was the solar storm of 1859. Also known as the ''Carrington Event'', it disabled parts of the newly created United States telegraph network, starting fires and electrically shocking some telegraph operators. Near solar maxima, the Sun produces about three CMEs every day, whereas near solar minima, there is about one CME ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Self-organized Criticality
Self-organized criticality (SOC) is a property of dynamical systems that have a critical point as an attractor. Their macroscopic behavior thus displays the spatial or temporal scale-invariance characteristic of the critical point of a phase transition, but without the need to tune control parameters to a precise value, because the system, effectively, tunes itself as it evolves towards criticality. The concept was put forward by Per Bak, Chao Tang and Kurt Wiesenfeld ("BTW") in a paper , following an earlier paper by Jonathan Katz published in 1987 in ''Physical Review Letters'', and is considered to be one of the mechanisms by which complexity arises in nature. Its concepts have been applied across fields as diverse as geophysics, physical cosmology, evolutionary biology and ecology, bio-inspired computing and optimization (mathematics), economics, quantum gravity, sociology, solar physics, plasma physics, neurobiology and others. SOC is typically observed in slowl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Solar Magnetic Field Lines
Solar may refer to: Astronomy * Of or relating to the Sun ** Solar telescope, a special purpose telescope used to observe the Sun ** A device that utilizes solar energy (e.g. "solar panels") ** Solar calendar, a calendar whose dates indicate the position of the Earth on its revolution around the Sun ** Solar eclipse, an eclipse of a sun in which it is obstructed by the moon ** Solar System, the planetary system made up by the Sun and the objects orbiting it * Solar Maximum Mission, a satellite * SOLAR (ISS), an observatory on International Space Station Music * "Solar" (composition), attributed to Miles Davis * ''Solar'' (Red Garland album), 1962 * ''Solar'' (Taeyang album), 2010 * ''Solar'', a 2011 album by Rubik * "Solar", a song by Northlane from ''Mesmer'', 2017 * "Solar", a song by Sault from ''Air'', 2022 * ”Solar”, a song by Stam1na from ''Taival'', 2018 * SOLAR Records, a record label Geography * Solar (Spanish term), a type of urban site * Solar, County ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chromosphere
A chromosphere ("sphere of color", from the Ancient Greek words χρῶμα (''khrôma'') 'color' and σφαῖρα (''sphaîra'') 'sphere') is the second layer of a Stellar atmosphere, star's atmosphere, located above the photosphere and below the solar transition region and Stellar corona, corona. The term usually refers to the Sun's chromosphere, but not exclusively, since it also refers to the corresponding layer of a stellar atmosphere. The name was suggested by the English astronomer Norman Lockyer after conducting systematic solar observations in order to distinguish the layer from the white-light emitting photosphere. In the solar atmosphere, Sun's atmosphere, the chromosphere is roughly in height, or slightly more than 1% of the Sun's radius at maximum thickness. It possesses a homogeneous layer at the boundary with the photosphere. Narrow jets of Plasma (physics), plasma, called Solar spicule, spicules, rise from this homogeneous region and through the chromosphere, e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Solar Transition Region
The solar transition region is a region of the Sun's atmosphere between the upper chromosphere and corona. It is important because it is the site of several unrelated but important transitions in the physics of the solar atmosphere: * Below, gravity tends to dominate the shape of most features, so that the Sun may often be described in terms of layers and horizontal features (like sunspots); above, dynamic forces dominate the shape of most features, so that the transition region itself is not a well-defined layer at a particular altitude. * Below, most of the helium is not fully ionized, so that it radiates energy very effectively; above, it becomes fully ionized. This has a profound effect on the equilibrium temperature (see below). * Below, the material is opaque to the particular colors associated with spectral lines, so that most spectral lines formed below the transition region are absorption lines in infrared, visible light, and near ultraviolet, while most lines formed ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |