Western Cordillera (North America) on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The North American Cordillera, sometimes also called the Western Cordillera of North America, the Western Cordillera, or the Pacific Cordillera, is the
The Cordillera
',
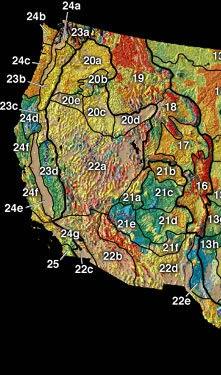 The North American Cordillera extends from the
The North American Cordillera extends from the
Earth
', pp. 534–535, Macmillan, 1986. Its mountain ranges generally run north-to-south along three main belts: the
"Comparative phylogeography of north-western north america: A synthesis"
In: Silverton, J., Antonovics, J. (Eds.), ''Integrating Ecology and Evolution in a Spatial Context''. The 14th Special Symposium of the British Ecological Society. British Ecolological Society, Blackwell Science Ltd., Ch. 15, pp. 319–339. Generally speaking, it will be convenient here to consider these three belts going west to east, and north to south. In
Merriam-Webster's Geographical Dictionary
', Merriam-Webster, 1997, pp. 219 and 1087, To the west of the Sierra Madre Occidental, the
 The
The
 The
The
Landforms of British Columbia
'', BC Govt, 1976
World Geomorphology
', Cambridge University Press, 1990, p. 88, . The Sierra Madre Oriental spans about . Mexico's Gulf Coastal Plain lies to the east of the range, between the mountains and the Gulf of Mexico coast. The Mexican Plateau lies to the west of the range.
 The
The
North America
North America is a continent in the Northern Hemisphere, Northern and Western Hemisphere, Western hemispheres. North America is bordered to the north by the Arctic Ocean, to the east by the Atlantic Ocean, to the southeast by South Ameri ...
n portion of the American Cordillera
The American Cordillera ( ) is a chain of mountain ranges (cordilleras), consisting of an almost continuous sequence of mountain ranges that form the western "backbone" of the Americas. Aconcagua is the highest peak of the chain. It is also the ...
, the mountain chain system along the Pacific coast
Pacific coast may be used to reference any coastline that borders the Pacific Ocean.
Geography Americas North America
Countries on the western side of North America have a Pacific coast as their western or south-western border. One of th ...
of the Americas
The Americas, sometimes collectively called America, are a landmass comprising the totality of North America and South America.''Webster's New World College Dictionary'', 2010 by Wiley Publishing, Inc., Cleveland, Ohio. When viewed as a sing ...
. The North American Cordillera covers an extensive area of mountain range
A mountain range or hill range is a series of mountains or hills arranged in a line and connected by high ground. A mountain system or mountain belt is a group of mountain ranges with similarity in form, structure, and alignment that have aris ...
s, intermontane
Intermontane is a physiographic adjective formed from the prefix " inter-" (''signifying among, between, amid, during, within, mutual, reciprocal'') and the adjective "montane" (inhabiting, or growing in mountainous regions, especially cool, mo ...
basins
Basin may refer to:
Geography and geology
* Depression (geology)
** Back-arc basin, a submarine feature associated with island arcs and subduction zones
** Debris basin, designed to prevent damage from debris flow
** Drainage basin (hydrology), ...
, and plateau
In geology and physical geography, a plateau (; ; : plateaus or plateaux), also called a high plain or a tableland, is an area of a highland consisting of flat terrain that is raised sharply above the surrounding area on at least one side. ...
s in Western
Western may refer to:
Places
*Western, Nebraska, a village in the US
*Western, New York, a town in the US
*Western Creek, Tasmania, a locality in Australia
*Western Junction, Tasmania, a locality in Australia
*Western world, countries that id ...
and Northwestern Canada, Western United States
The Western United States (also called the American West, the Western States, the Far West, the Western territories, and the West) is List of regions of the United States, census regions United States Census Bureau.
As American settlement i ...
, and Mexico
Mexico, officially the United Mexican States, is a country in North America. It is the northernmost country in Latin America, and borders the United States to the north, and Guatemala and Belize to the southeast; while having maritime boundar ...
, including much of the territory west of the Great Plains
The Great Plains is a broad expanse of plain, flatland in North America. The region stretches east of the Rocky Mountains, much of it covered in prairie, steppe, and grassland. They are the western part of the Interior Plains, which include th ...
.
The precise boundaries of this cordillera and its subregions, as well as the names of its various features, may differ depending on the definitions in each country or jurisdiction, and also depending on the scientific field; this cordillera is a particularly prominent subject in the scientific field of physical geography
Physical geography (also known as physiography) is one of the three main branches of geography. Physical geography is the branch of natural science which deals with the processes and patterns in the natural environment such as the atmosphere, h ...
.Melanie Ostopowich (2005) The Cordillera
',
Weigl Educational Publishers Limited
Weigl Educational Publishers Limited is a publishing house in Canada, one of the country's largest.
Linda A. Weigl founded the company in 1979 as a textbook publisher. First based in Saskatchewan, the company moved to Alberta in 1984, and now has ...
, , pp. 6, 12, and 20: "The Cordillera is one of the seven geographic regions in Canada".
Major features
 The North American Cordillera extends from the
The North American Cordillera extends from the U.S. state
In the United States, a state is a constituent political entity, of which there are 50. Bound together in a political union, each state holds governmental jurisdiction over a separate and defined geographic territory where it shares its so ...
of Alaska
Alaska ( ) is a non-contiguous U.S. state on the northwest extremity of North America. Part of the Western United States region, it is one of the two non-contiguous U.S. states, alongside Hawaii. Alaska is also considered to be the north ...
to the southern border of Mexico
Mexico, officially the United Mexican States, is a country in North America. It is the northernmost country in Latin America, and borders the United States to the north, and Guatemala and Belize to the southeast; while having maritime boundar ...
, and includes some of the highest peaks on the continent.Frank Press
Frank Press (December 4, 1924 – January 29, 2020) was an American geophysicist. He was an advisor to four U.S. presidents, and later served two consecutive terms as president of the U.S. National Academy of Sciences (1981–1993). He was the a ...
and Raymond Siever Earth
', pp. 534–535, Macmillan, 1986. Its mountain ranges generally run north-to-south along three main belts: the
Pacific Coast Ranges
The Pacific Coast Ranges (officially gazetted as the Pacific Mountain System in the United States; ; ) are the series of mountain ranges that stretch along the West Coast of North America from Alaska south to Northern and Central Mexico. Althoug ...
in the west, the Nevadan belt in the middle (including the Sierra Nevada
The Sierra Nevada ( ) is a mountain range in the Western United States, between the Central Valley of California and the Great Basin. The vast majority of the range lies in the state of California, although the Carson Range spur lies primari ...
), and the Laramide belt in the east (including the Rocky Mountains
The Rocky Mountains, also known as the Rockies, are a major mountain range and the largest mountain system in North America. The Rocky Mountains stretch in great-circle distance, straight-line distance from the northernmost part of Western Can ...
and the Black Hills
The Black Hills is an isolated mountain range rising from the Great Plains of North America in western South Dakota and extending into Wyoming, United States. Black Elk Peak, which rises to , is the range's highest summit. The name of the range ...
).
These three orogenic belts
An orogenic belt, orogen, or mobile belt, is a zone of Earth's crust affected by orogeny. An orogenic belt develops when a continental plate crumples and is uplifted to form one or more mountain ranges; this involves a series of geological proc ...
(also called "orogens") arose due to the engagement of tectonic plates
Plate tectonics (, ) is the scientific theory that the Earth's lithosphere comprises a number of large tectonic plates, which have been slowly moving since 3–4 billion years ago. The model builds on the concept of , an idea developed durin ...
which deformed the Earth's lithosphere
A lithosphere () is the rigid, outermost rocky shell of a terrestrial planet or natural satellite. On Earth, it is composed of the crust and the lithospheric mantle, the topmost portion of the upper mantle that behaves elastically on time ...
(crust and uppermost mantle). For example, the Laramide orogeny
The Laramide orogeny was a time period of mountain building in western North America, which started in the Late Cretaceous, 80 to 70 million years ago, and ended 55 to 35 million years ago. The exact duration and ages of beginning and end of the o ...
changed the topography
Topography is the study of the forms and features of land surfaces. The topography of an area may refer to the landforms and features themselves, or a description or depiction in maps.
Topography is a field of geoscience and planetary sci ...
of the central Rocky Mountains and adjoining Laramide regions (from central Montana to central New Mexico) during the Late Cretaceous
The Late Cretaceous (100.5–66 Ma) is the more recent of two epochs into which the Cretaceous Period is divided in the geologic time scale. Rock strata from this epoch form the Upper Cretaceous Series. The Cretaceous is named after ''cre ...
80 million years ago. Prior to this time the Rocky Mountain region was occupied by a broad basin. Further topographical evolution occurred during the Eocene
The Eocene ( ) is a geological epoch (geology), epoch that lasted from about 56 to 33.9 million years ago (Ma). It is the second epoch of the Paleogene Period (geology), Period in the modern Cenozoic Era (geology), Era. The name ''Eocene'' comes ...
(55–50 million years ago) and Oligocene
The Oligocene ( ) is a geologic epoch (geology), epoch of the Paleogene Geologic time scale, Period that extends from about 33.9 million to 23 million years before the present ( to ). As with other older geologic periods, the rock beds that defin ...
(34–23 million years ago), but since that time, the region has been relatively stable.D. Alt and D. Hyndman. (1995). Northwest Exposures: A Geological Story of the North West. Mountain Press Publishing Company, Missoula, MontanaS. Brunsfeld, J. Sullivan, D. Soltis, and P. Sotis (2001)"Comparative phylogeography of north-western north america: A synthesis"
In: Silverton, J., Antonovics, J. (Eds.), ''Integrating Ecology and Evolution in a Spatial Context''. The 14th Special Symposium of the British Ecological Society. British Ecolological Society, Blackwell Science Ltd., Ch. 15, pp. 319–339. Generally speaking, it will be convenient here to consider these three belts going west to east, and north to south. In
Alaska
Alaska ( ) is a non-contiguous U.S. state on the northwest extremity of North America. Part of the Western United States region, it is one of the two non-contiguous U.S. states, alongside Hawaii. Alaska is also considered to be the north ...
, south of the Interior Plains area, is the Rocky Mountain System, then the Intermontane Basins and Ranges, and in the southern part of the state are the Pacific Mountains and Valleys. In the Alaska panhandle
Southeast Alaska, often abbreviated to southeast or southeastern, and sometimes called the Alaska(n) panhandle, is the southeastern portion of the U.S. state of Alaska, bordered to the east and north by the northern half of the Canadian provi ...
, the mainland mountain ranges and offshore islands (the Alexander Archipelago
The Alexander Archipelago () is a archipelago (group of islands) in North America lying off the southeastern coast of Alaska. It contains about 1,100 islands, the tops of submerged coastal mountains that rise steeply from the Pacific Ocean. Deep ...
) are extensions of respective ranges further south.
In Canada, the North American Cordillera is usually divided into three physiographic regions: the western system, the interior system, and the eastern system. The western system includes the Coast Mountains
The Coast Mountains () are a major mountain range in the Pacific Coast Ranges of western North America, extending from southwestern Yukon through the Alaska Panhandle and virtually all of the British Columbia Coast, Coast of British Columbia sout ...
, the interior system includes the Columbia Mountains
The Columbia Mountains are a group of mountain ranges along the Upper Columbia River in British Columbia, Montana, Idaho and Washington (state), Washington. The mountain range covers 135,952 km² (52,491 sq mi). The range is bounded by th ...
, and the eastern system includes the Canadian Rockies
The Canadian Rockies () or Canadian Rocky Mountains, comprising both the Alberta Rockies and the British Columbian Rockies, is the Canadian segment of the North American Rocky Mountains. It is the easternmost part of the Canadian Cordillera, w ...
.
At its midsection between San Francisco
San Francisco, officially the City and County of San Francisco, is a commercial, Financial District, San Francisco, financial, and Culture of San Francisco, cultural center of Northern California. With a population of 827,526 residents as of ...
, California
California () is a U.S. state, state in the Western United States that lies on the West Coast of the United States, Pacific Coast. It borders Oregon to the north, Nevada and Arizona to the east, and shares Mexico–United States border, an ...
, and Denver
Denver ( ) is a List of municipalities in Colorado#Consolidated city and county, consolidated city and county, the List of capitals in the United States, capital and List of municipalities in Colorado, most populous city of the U.S. state of ...
, Colorado
Colorado is a U.S. state, state in the Western United States. It is one of the Mountain states, sharing the Four Corners region with Arizona, New Mexico, and Utah. It is also bordered by Wyoming to the north, Nebraska to the northeast, Kansas ...
, the North American Cordillera is about wide, and its physiographic provinces at this midpoint are as follows, going from west to east: the Pacific Coast Ranges, the Central Valley, the Sierra Nevada, the Basin and Range Province
The Basin and Range Province is a vast United States physiographic region, physiographic region covering much of the inland Western United States and Northern Mexico, northwestern Mexico. It is defined by unique basin and range topography, charac ...
(forming many narrow ranges and valleys), the Colorado Plateau
The Colorado Plateau is a physiographic and desert region of the Intermontane Plateaus, roughly centered on the Four Corners region of the Southwestern United States. This plateau covers an area of 336,700 km2 (130,000 mi2) within w ...
, and the Rocky Mountains. In the United States, another major feature of the Cordillera is the Columbia Plateau
The Columbia Plateau is an important geology, geologic and geography, geographic region that lies across parts of the U.S. states of Washington (state), Washington, Oregon, and Idaho. It is a wide flood basalt plateau between the Cascade Range a ...
, located north of California between the Cascade Range
The Cascade Range or Cascades is a major mountain range of western North America, extending from southern British Columbia through Washington (state), Washington and Oregon to Northern California. It includes both non-volcanic mountains, such as m ...
– which is a northern extension of the Sierra Nevada – and the Rocky Mountains.
In Mexico, the Sierra Madre Occidental
The Sierra Madre Occidental is a major mountain range system of the North American Cordillera, that runs northwest–southeast through northwestern and western Mexico, and along the Gulf of California. The Sierra Madre is part of the American C ...
, and the Sierra Madre Oriental
The Sierra Madre Oriental () is a mountain range in northeastern Mexico. The Sierra Madre Oriental is part of the American Cordillera, a chain of mountain ranges (cordillera) that consists of an almost continuous sequence of mountain ranges that ...
further east, surround the Mexican Plateau
The Central Mexican Plateau, also known as the Mexican Altiplano (), is a large arid-to-semiarid plateau that occupies much of northern and central Mexico. Averaging above sea level, it extends from the United States border in the north to the T ...
.Merriam-Webster's Geographical Dictionary
', Merriam-Webster, 1997, pp. 219 and 1087, To the west of the Sierra Madre Occidental, the
Peninsular Ranges
The Peninsular Ranges (also called the Lower California province) are a group of mountain ranges that stretch from Southern California to the southern tip of the Baja California peninsula; they are part of the North American Pacific Coast Range ...
border the Pacific Ocean, and the Sierra Madre del Sur
The Sierra Madre del Sur is a mountain range in southern Mexico, extending from southern Michoacán east through Guerrero, to the Isthmus of Tehuantepec in eastern Oaxaca.
Geography
The Sierra Madre del Sur joins with the Eje Volcánico Transv ...
is the southern extension of the Peninsular Ranges.''Encyclopedia Americana: the International Reference Work'', Volume 18: "Sierra Madre del Sur. — This sierra, which crosses the states of Colima, Michoacan, Guerrero, and Oaxaca, is the continuation of the Sierra de Baja California and the other mountain ranges linked with it." (Americana Corporation 1961). Sierra Madre means "Mother Range" in Spanish.
The Nevadan belt runs up and down the middle of the North American Cordillera. Therefore, the intermontane areas of the cordillera can be divided up into the areas east of the Nevadan belt, and those west of the Nevadan belt.
Pacific Coast Belt
The Pacific Coast Ranges, comprising the Pacific Coast Belt, parallel the North American Pacific Coast, and comprise several mountain systems. Along theBritish Columbia
British Columbia is the westernmost Provinces and territories of Canada, province of Canada. Situated in the Pacific Northwest between the Pacific Ocean and the Rocky Mountains, the province has a diverse geography, with rugged landscapes that ...
and Alaska coasts, the mountains intermix with the sea in a complex maze of fjords
In physical geography, a fjord (also spelled fiord in New Zealand English; ) is a long, narrow sea inlet with steep sides or cliffs, created by a glacier. Fjords exist on the coasts of Antarctica, the Arctic, and surrounding landmasses of the no ...
, with thousands of islands. Off the Southern California coast, the Channel Islands
The Channel Islands are an archipelago in the English Channel, off the French coast of Normandy. They are divided into two Crown Dependencies: the Jersey, Bailiwick of Jersey, which is the largest of the islands; and the Bailiwick of Guernsey, ...
archipelago
An archipelago ( ), sometimes called an island group or island chain, is a chain, cluster, or collection of islands. An archipelago may be in an ocean, a sea, or a smaller body of water. Example archipelagos include the Aegean Islands (the o ...
of the Santa Monica Mountains
The Santa Monica Mountains are a coastal mountain range in Southern California, next to the Pacific Ocean. It is part of the Transverse Ranges. The Santa Monica Mountains National Recreation Area encompasses this mountain range. Because of its p ...
extends for .
Southern Alaska ranges
In southern Alaska, the primary mountain ranges are theAlaska Range
The Alaska Range is a relatively narrow, mountain range in the Southcentral Alaska, southcentral region of the U.S. state of Alaska, from Lake Clark at its southwest endSources differ as to the exact delineation of the Alaska Range. ThBoard on G ...
, Wrangell Mountains
The Wrangell Mountains are a high mountain range of eastern Alaska in the United States. Much of the range is included in Wrangell-Saint Elias National Park and Preserve. The Wrangell Mountains are almost entirely volcanic in origin, and they i ...
, Saint Elias Mountains
The Saint Elias Mountains () are a subgroup of the Pacific Coast Ranges, located in southeastern Alaska in the United States, Southwestern Yukon and the very far northwestern part of British Columbia in Canada. The range spans Wrangell-St. Elias ...
, Kenai Mountains
The Kenai Mountains ( Dena'ina: ''Yaghanen Dghili'') are a mountain range in the U.S. state of Alaska. They extend northeast from the southern end of the Kenai Peninsula to the Chugach Mountains, and have an average elevation of 3,000 to 5,00 ...
, Chugach Mountains
The Chugach Mountains of southern Alaska are the northernmost of the several mountain ranges that make up the Pacific Coast Ranges of the western edge of North America. The range is about long and wide, and extends from the Knik and Turnag ...
, and Talkeetna Mountains
The Talkeetna Mountains (''Dghelaay tahwt’aene'' in Ahtna) () are a mountain range in Alaska. The Matanuska and Susitna River valleys, with towns such as Trapper Creek, Talkeetna, Wasilla, Palmer, Sutton, and Chickaloon, roughly bound th ...
.
Western System of Canada
The Yukon Ranges comprise themountain
A mountain is an elevated portion of the Earth's crust, generally with steep sides that show significant exposed bedrock. Although definitions vary, a mountain may differ from a plateau in having a limited summit area, and is usually higher t ...
s in the southeastern part of the U.S. state
In the United States, a state is a constituent political entity, of which there are 50. Bound together in a political union, each state holds governmental jurisdiction over a separate and defined geographic territory where it shares its so ...
of Alaska
Alaska ( ) is a non-contiguous U.S. state on the northwest extremity of North America. Part of the Western United States region, it is one of the two non-contiguous U.S. states, alongside Hawaii. Alaska is also considered to be the north ...
and most of the Yukon
Yukon () is a Provinces and territories of Canada, territory of Canada, bordering British Columbia to the south, the Northwest Territories to the east, the Beaufort Sea to the north, and the U.S. state of Alaska to the west. It is Canada’s we ...
, Canada. This range has an area of .
The Coast Mountains
The Coast Mountains () are a major mountain range in the Pacific Coast Ranges of western North America, extending from southwestern Yukon through the Alaska Panhandle and virtually all of the British Columbia Coast, Coast of British Columbia sout ...
run from the lower Fraser River
The Fraser River () is the longest river within British Columbia, Canada, rising at Fraser Pass near Blackrock Mountain (Canada), Blackrock Mountain in the Rocky Mountains and flowing for , into the Strait of Georgia just south of the City of V ...
and the Fraser Canyon
The Fraser Canyon is a major landform of the Fraser River where it descends rapidly through narrow rock gorges in the Coast Mountains en route from the Interior Plateau of British Columbia to the Fraser Valley. Colloquially, the term "Fraser Ca ...
northwestward, separating the Interior Plateau
The Interior Plateau comprises a large region of the Interior of British Columbia, and lies between the Cariboo and Monashee Mountains on the east, and the Hazelton Mountains, Coast Mountains and Cascade Range on the west.''Landforms of Bri ...
from the Pacific Ocean.Wilson, Robert J. ''Geology and Economic Minerals of Canada'', p. 26 (Geological Survey of Canada, Department of Energy, Mines and Resources, 1976). Their coastal flank is characterized by an intense network of fjords and associated islands, very similar to the Norwegian coastline
The coastline of Norway is formed along the Skagerrak, North Sea, Norwegian Sea, and Barents Sea. This considers only the mainland coastline and excludes Svalbard.
A straight line along Norway's sea borders (the coastal perimeter) is long. Alo ...
, while their inland side against the plateau transitions to the high plateau in dryland valleys notable for a series of large lakes similar to the alpine lakes of southern Switzerland, beginning in deep mountains and ending in flatland. They are subdivided in three main groupings, the Pacific Ranges
The Pacific Ranges are the southernmost subdivision of the Coast Mountains portion of the Pacific Cordillera. Located entirely within British Columbia, British Columbia, Canada, they run northwest from the lower stretches of the Fraser River to B ...
between the Fraser and Bella Coola, the Kitimat Ranges
The Kitimat Ranges are one of the three main subdivisions of the Coast Mountains in British Columbia, Canada, the others being the Pacific Ranges to the south and the Boundary Ranges to the north.
Geography
The Kitimat Ranges lie between the Na ...
from there northwards to the Nass River
The Nass River is a river in northern British Columbia, Canada. It flows from the Coast Mountains southwest to Nass Bay, a sidewater of Portland Inlet, which connects to the North Pacific Ocean via the Dixon Entrance. Nass Bay joins Portland I ...
, and the Boundary Ranges
The Boundary Ranges, also known in the singular and as the Alaska Boundary Range, are the largest and most northerly subrange of the Coast Mountains. They begin at the Nass River, near the southern end of the Alaska Panhandle in the Canadian pro ...
from there to their terminus in the Yukon
Yukon () is a Provinces and territories of Canada, territory of Canada, bordering British Columbia to the south, the Northwest Territories to the east, the Beaufort Sea to the north, and the U.S. state of Alaska to the west. It is Canada’s we ...
Territory at Champagne Pass and Chilkat Pass northwest of Haines, Alaska
Haines (Tlingit: ''Deishú'') is a census-designated place located in Haines Borough, Alaska, United States. It is in the northern part of the Alaska Panhandle and near Glacier Bay National Park and Preserve. As of the 2020 census, the popul ...
. The Saint Elias Mountains
The Saint Elias Mountains () are a subgroup of the Pacific Coast Ranges, located in southeastern Alaska in the United States, Southwestern Yukon and the very far northwestern part of British Columbia in Canada. The range spans Wrangell-St. Elias ...
lie to their west and northwest, while the Yukon Ranges and Yukon Basin lie to their north. On the inland side of the Boundary Ranges are the Tahltan
The Tahltan or Nahani are a First Nations people of the Athabaskan-speaking ethnolinguistic group who live in northern British Columbia around Telegraph Creek, Dease Lake, and Iskut. The Tahltan constitute the fourth division of the ''Nahan ...
and Tagish Highland
The Tagish Highland is an upland area on the inland side of the northernmost Boundary Ranges of the Coast Mountains, spanning far northwestern British Columbia from Atlin Lake to the area of the pass at Champagne, Yukon between the Alsek and Y ...
s and also the Skeena Mountains
The Skeena Mountains, also known as the Skeenas, are a subrange of the Interior Mountains of northern British Columbia, Canada, essentially flanking the upper basin of the Skeena River. They lie just inland from the southern end of the Boundary ...
, part of the Interior Mountains
The Interior Mountains or Northern Interior Mountains are the semi-official names for an expansive collection of mountain ranges that comprises much of the northern half of the Canadian province of British Columbia and a large area of southern Yu ...
system, which also extend southwards on the inland side of the Kitimat Ranges
The Kitimat Ranges are one of the three main subdivisions of the Coast Mountains in British Columbia, Canada, the others being the Pacific Ranges to the south and the Boundary Ranges to the north.
Geography
The Kitimat Ranges lie between the Na ...
.
The terrain of the main spine of the Coast Mountains is typified by heavy glaciation, including several very large icefields of varying elevation. Of the three subdivisions, the Pacific Ranges are the highest and are crowned by Mount Waddington
Mount Waddington, once known as Mystery Mountain, is the highest peak in the Coast Mountains of British Columbia, Canada. Although it is lower than Mount Fairweather and Mount Quincy Adams, which straddle the United States border between Alaska ...
, while the Boundary Ranges contain the largest icefields, the Juneau Icefield
The Juneau Icefield is an ice field located just north of Juneau, Alaska, Juneau, Alaska, continuing north through the border with British Columbia, extending through an area of in the Coast Mountains, Coast Range ranging north to south and east ...
being the largest. The Kitimat Ranges are lower and less glacier-covered than either of the other two groupings, but are extremely rugged and dense.
The Coast Mountains are made of igneous
Igneous rock ( ), or magmatic rock, is one of the three main rock types, the others being sedimentary and metamorphic. Igneous rocks are formed through the cooling and solidification of magma or lava.
The magma can be derived from partial ...
and metamorphic rock
Metamorphic rocks arise from the transformation of existing rock to new types of rock in a process called metamorphism. The original rock ( protolith) is subjected to temperatures greater than and, often, elevated pressure of or more, caus ...
from an episode of arc volcanism
A volcanic arc (also known as a magmatic arc) is a belt of volcanoes formed above a subducting oceanic tectonic plate, with the belt arranged in an arc shape as seen from above. Volcanic arcs typically parallel an oceanic trench, with the arc lo ...
related to subduction
Subduction is a geological process in which the oceanic lithosphere and some continental lithosphere is recycled into the Earth's mantle at the convergent boundaries between tectonic plates. Where one tectonic plate converges with a second p ...
of the Kula and Farallon Plates during the Laramide orogeny
The Laramide orogeny was a time period of mountain building in western North America, which started in the Late Cretaceous, 80 to 70 million years ago, and ended 55 to 35 million years ago. The exact duration and ages of beginning and end of the o ...
about 100 million years ago. The widespread granite
Granite ( ) is a coarse-grained (phanerite, phaneritic) intrusive rock, intrusive igneous rock composed mostly of quartz, alkali feldspar, and plagioclase. It forms from magma with a high content of silica and alkali metal oxides that slowly coo ...
forming the Coast Mountains formed when magma intruded and cooled at depth beneath volcanoes of the Coast Range Arc, whereas the metamorphic formed when intruding magma heated the surrounding rock to produce schist
Schist ( ) is a medium-grained metamorphic rock generally derived from fine-grained sedimentary rock, like shale. It shows pronounced ''schistosity'' (named for the rock). This means that the rock is composed of mineral grains easily seen with a l ...
.
The Insular Mountains
The Insular Mountains are a range of mountains in the Pacific Coast Ranges on the Coast of British Columbia, Canada, comprising the Vancouver Island Ranges and Queen Charlotte Mountains. The Insular Mountains are rugged, particularly on Vanco ...
extend from Vancouver Island
Vancouver Island is an island in the northeastern Pacific Ocean and part of the Canadian province of British Columbia. The island is in length, in width at its widest point, and in total area, while are of land. The island is the largest ...
in the south to Haida Gwaii
Haida Gwaii (; / , literally "Islands of the Haida people"), previously known as the Queen Charlotte Islands, is an archipelago located between off the British Columbia Coast, northern Pacific coast in the Canadian province of British Columbia ...
in the north on the British Columbia Coast
The British Columbia Coast, popularly referred to as the BC Coast or simply the Coast, is a geographic region of the Provinces and territories of Canada, Canadian province of British Columbia. As the entire western continental coastline of Canada ...
. It contains two main mountain ranges, the Vancouver Island Ranges
The Vancouver Island Ranges, formerly called the Vancouver Island Mountains, are a series of mountain ranges extending along the length of Vancouver Island which has an area of . The Vancouver Island Ranges comprise the central and largest part ...
on Vancouver Island and the Queen Charlotte Mountains on Haida Gwaii.
Pacific Border Province in contiguous U.S.
 The
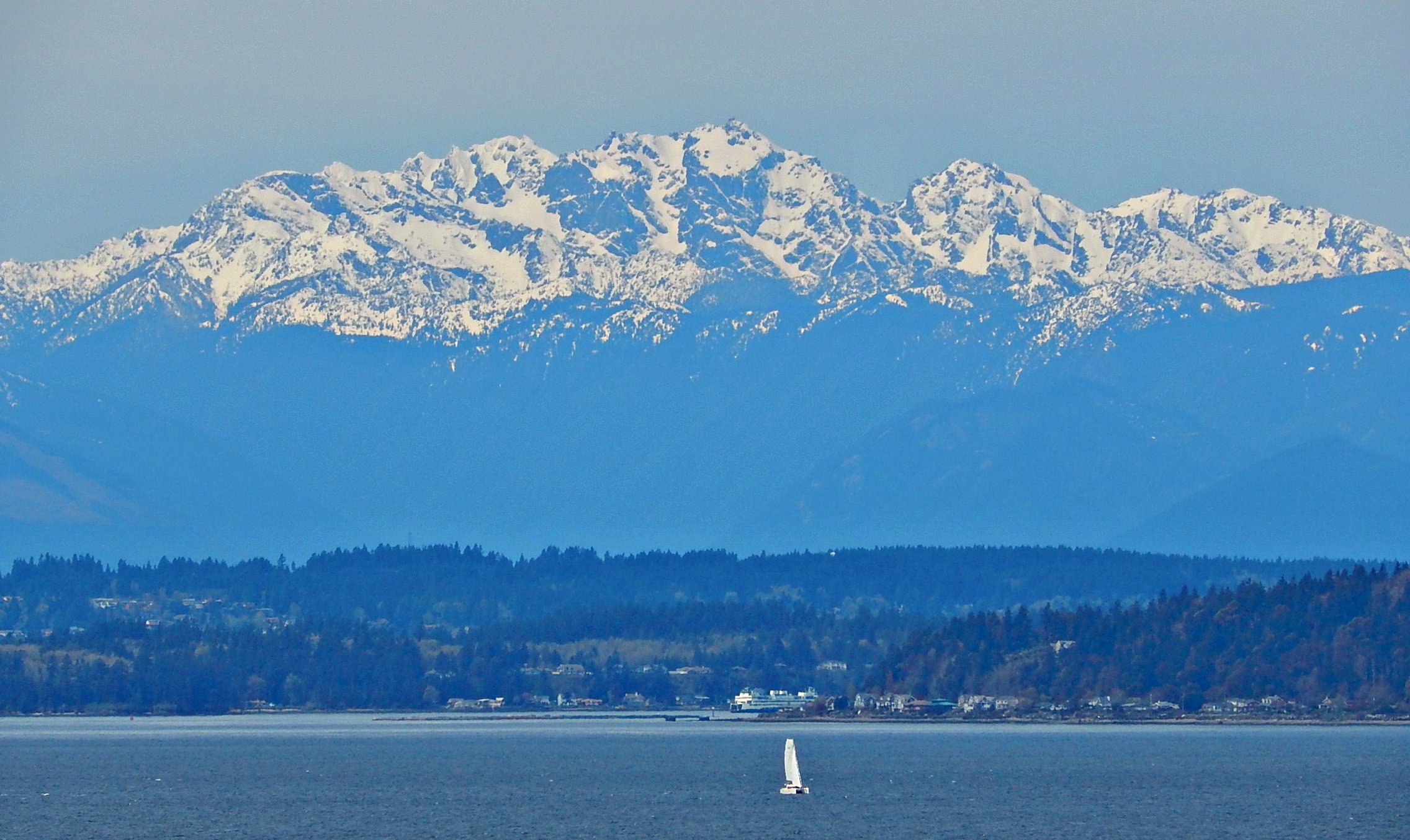
The Olympic Mountains
The Olympic Mountains are a mountain range on the Olympic Peninsula of the Pacific Northwest of the United States. The mountains, part of the Pacific Coast Ranges, are not especially high – Mount Olympus (Washington), Mount Olympus is the high ...
is a mountain range
A mountain range or hill range is a series of mountains or hills arranged in a line and connected by high ground. A mountain system or mountain belt is a group of mountain ranges with similarity in form, structure, and alignment that have aris ...
on the Olympic Peninsula
The Olympic Peninsula is a large peninsula in Western Washington that lies across Puget Sound from Seattle, and contains Olympic National Park. It is bounded on the west by the Pacific Ocean, the north by the Strait of Juan de Fuca, and the ...
of western Washington
Washington most commonly refers to:
* George Washington (1732–1799), the first president of the United States
* Washington (state), a state in the Pacific Northwest of the United States
* Washington, D.C., the capital of the United States
** A ...
in the United States
The United States of America (USA), also known as the United States (U.S.) or America, is a country primarily located in North America. It is a federal republic of 50 U.S. state, states and a federal capital district, Washington, D.C. The 48 ...
. The mountain
A mountain is an elevated portion of the Earth's crust, generally with steep sides that show significant exposed bedrock. Although definitions vary, a mountain may differ from a plateau in having a limited summit area, and is usually higher t ...
s, part of the Pacific Coast Ranges
The Pacific Coast Ranges (officially gazetted as the Pacific Mountain System in the United States; ; ) are the series of mountain ranges that stretch along the West Coast of North America from Alaska south to Northern and Central Mexico. Althoug ...
, are not especially high – Mount Olympus
Mount Olympus (, , ) is an extensive massif near the Thermaic Gulf of the Aegean Sea, located on the border between Thessaly and Macedonia (Greece), Macedonia, between the regional units of Larissa (regional unit), Larissa and Pieria (regional ...
is the highest at – but the western slopes of the Olympics rise directly out of the Pacific Ocean
The Pacific Ocean is the largest and deepest of Earth's five Borders of the oceans, oceanic divisions. It extends from the Arctic Ocean in the north to the Southern Ocean, or, depending on the definition, to Antarctica in the south, and is ...
and are the wettest place in the contiguous 48 states. Most of the mountains are protected within the bounds of the Olympic National Park
Olympic National Park is a national park of the United States located in Washington, on the Olympic Peninsula. The park has four regions: the Pacific coastline, alpine areas, the west-side temperate rainforest, and the forests of the drier e ...
.
South of the Olympics lies the Chehalis River valley representing a break in elevation and drainages, followed by the Willapa Hills
The Willapa Hills is a geologic, physiographic, and geographic region in southwest Washington. When described as a physiographical province, the Willapa Hills are bounded by the Pacific Ocean to the west, the Columbia River to the south, the Olymp ...
. The highest peak in the Willapa Hills is Boistfort Peak with an elevation of . This region represents the lowest of the upland ares in the Pacific Coast Ranges.
The Oregon Coast Range
The Oregon Coast Range, often called simply the Coast Range and sometimes the Pacific Coast Range, is a mountain range, in the Pacific Coast Ranges Physiographic regions of the world, physiographic region, in the United States, U.S. state of Or ...
is the part of the Coast Range system that is denoted as between the mouth of the Columbia River
The Columbia River (Upper Chinook language, Upper Chinook: ' or '; Sahaptin language, Sahaptin: ''Nch’i-Wàna'' or ''Nchi wana''; Sinixt dialect'' '') is the largest river in the Pacific Northwest region of North America. The river headwater ...
and the Middle Fork Coquille River. It is about long. The highest peak is Marys Peak
Marys Peak (formerly Mary's Peak and sometimes still spelled this way) is a mountain in Benton County, Oregon, Benton County, Oregon, United States, just southwest of Philomath, Oregon, Philomath. The Kalapuya people call the peak "chatímanwi" ...
, at .
The California Coast Ranges
The Coast Ranges of California span from Del Norte County, California, Del Norte or Humboldt County, California, south to Santa Barbara County, California, Santa Barbara County. The other three coastal California mountain ranges are the Trans ...
are one of the eleven traditional geomorphic provinces of California. This province includes several – but not all – mountain ranges along the California coast (the Transverse Ranges
The Transverse Ranges are a group of mountain ranges of Southern California, in the Pacific Coast Ranges physiographic region in North America. The Transverse Ranges begin at the southern end of the California Coast Ranges and lie within Santa Ba ...
, Peninsular Ranges
The Peninsular Ranges (also called the Lower California province) are a group of mountain ranges that stretch from Southern California to the southern tip of the Baja California peninsula; they are part of the North American Pacific Coast Range ...
, and Klamath Mountains
The Klamath Mountains are a rugged and lightly populated mountain range in northwestern California and southwestern Oregon in the western United States. As a mountain system within both the greater Pacific Coast Ranges and the California Coast R ...
are not included).
Western mountain ranges of Mexico
TheSierra Madre del Sur
The Sierra Madre del Sur is a mountain range in southern Mexico, extending from southern Michoacán east through Guerrero, to the Isthmus of Tehuantepec in eastern Oaxaca.
Geography
The Sierra Madre del Sur joins with the Eje Volcánico Transv ...
mountains in southwestern Mexico form a southern extension of the Peninsular Ranges
The Peninsular Ranges (also called the Lower California province) are a group of mountain ranges that stretch from Southern California to the southern tip of the Baja California peninsula; they are part of the North American Pacific Coast Range ...
of Baja California
Baja California, officially the Free and Sovereign State of Baja California, is a state in Mexico. It is the northwesternmost of the 32 federal entities of Mexico. Before becoming a state in 1952, the area was known as the North Territory of B ...
. The Peninsular Ranges are separated from the Sierra Madre del Sur by an expanse of ocean.
Nevadan belt
The Nevadan belt is located between the Pacific coast belt and the Laramide belt. ''Nevada'' means "snow-covered" in Spanish.Interior System of Canada
In Canada, the Northern Interior Mountains are a northern extension of the Columbia Mountains. They include the Hazelton Mountains,Cassiar Mountains
The Cassiar Mountains () are the most northerly group of the Northern Interior Mountains in the Canadian province of British Columbia and also extend slightly into the southernmost Yukon Territory. They lie north and west of the Omineca Mountain ...
, Omineca Mountains
The Omineca Mountains, also known as "the Ominecas", are a group of remote mountain ranges in the Boreal Cordillera of north-central British Columbia, Canada. They are bounded by the Finlay River on the north, the Rocky Mountain Trench (here fil ...
, and Skeena Mountains
The Skeena Mountains, also known as the Skeenas, are a subrange of the Interior Mountains of northern British Columbia, Canada, essentially flanking the upper basin of the Skeena River. They lie just inland from the southern end of the Boundary ...
.
 The
The Columbia Mountains
The Columbia Mountains are a group of mountain ranges along the Upper Columbia River in British Columbia, Montana, Idaho and Washington (state), Washington. The mountain range covers 135,952 km² (52,491 sq mi). The range is bounded by th ...
are a designation in British Columbia for a group of four ranges lying between the Rocky Mountain Trench
The Rocky Mountain Trench, also known as the Valley of a Thousand Peaks or simply the Trench, is a large valley on the western side of the northern part of North America's Rocky Mountains. The Trench is both visually and cartographically a ...
(to the east) and the Interior Plateau
The Interior Plateau comprises a large region of the Interior of British Columbia, and lies between the Cariboo and Monashee Mountains on the east, and the Hazelton Mountains, Coast Mountains and Cascade Range on the west.''Landforms of Bri ...
(to the west). These ranges are the Cariboo Mountains
The Cariboo Mountains are the northernmost subrange of the Columbia Mountains, which run down into the Spokane area of the United States and include the Selkirks, Monashees and Purcells. The Cariboo Mountains are entirely within the province ...
, which are the northernmost and sometimes considered to be part of the Interior Plateau, the Selkirk Mountains
The Selkirk Mountains are a mountain range spanning the northern portion of the Idaho Panhandle, eastern Washington, and southeastern British Columbia which are part of a larger grouping of mountains, the Columbia Mountains. They begin at Mic ...
, the Purcell Mountains
The Purcell Mountains are a mountain range in southeastern British Columbia, Canada. They are a subrange of the Columbia Mountains, which includes the Selkirk, Monashee, and Cariboo Mountains. They are located on the west side of the Rocky Mo ...
, and the Monashee Mountains
The Monashee Mountains are a mountain range lying mostly in British Columbia, Canada, extending into the U.S. state of Washington. They stretch from north to south and from east to west. They are a sub-range of the Columbia Mountains. The hig ...
.
The Columbia Mountains are classified as being in Canada's interior system, rather than its eastern system. However, the Columbia Mountains are an extension of mountains in the United States that are considered part of the Rocky Mountains, and therefore the Columbia Mountains are often treated as being part of the Rockies.
The Selkirks and Purcells lie entirely within the basin of the Columbia River, while the Monashees lie to the river's west on its southward course from its Big Bend and are flanked on the west by the basin of the Thompson and Okanagan River
The Okanogan River (known as the Okanagan River in Canada) is a tributary of the Columbia River, approximately 115 mi (185 km) long, in southern British Columbia and north central Washington. It drains a scenic plateau region called t ...
s. There are many named subranges of all four subgroupings, particularly in the Selkirks and Monashees. The southward extension of the Selkirks, Purcells and Monashees into the United States are reckoned to be part of the Rocky Mountains
The Rocky Mountains, also known as the Rockies, are a major mountain range and the largest mountain system in North America. The Rocky Mountains stretch in great-circle distance, straight-line distance from the northernmost part of Western Can ...
and the designation Columbia Mountains is not used there (the Purcells, also, go by the name "Percell Mountains" in the United States). The Salish
Salish () may refer to:
* Salish peoples, a group of First Nations/Native Americans
** Coast Salish peoples, several First Nations/Native American groups in the coastal regions of the Pacific Northwest
** Interior Salish peoples, several First Na ...
and Cabinet Mountains
The Cabinet Mountains are part of the Rocky Mountains, located in northwest Montana and the Idaho panhandle, in the United States. The mountains cover an area of . The Cabinet Mountains lie south of the Purcell Mountains, between the Kootenai R ...
south of the Kootenai River
The Kootenay River or Kootenai River is a major river of the Northwest Plateau in southeastern British Columbia, Canada, and northern Montana and Idaho in the United States. It is one of the uppermost major tributaries of the Columbia River, ...
are essentially part of the same landform, but are officially designated part of the Rocky Mountains in the United States.
To the west of the Monashees and Cariboos, there are three intermediary upland areas which are transitional between the mountain ranges and the plateaus flanking the Fraser Fraser may refer to:
Places Antarctica
* Fraser Point, South Orkney Islands
Australia
* Fraser, Australian Capital Territory, a suburb in the Canberra district of Belconnen
* Division of Fraser (Australian Capital Territory), a former federal ...
and Thompson River
The Thompson River is the largest tributary of the Fraser River, flowing through the south-central portion of British Columbia, Canada. The Thompson River has two main branches, the South Thompson River and the North Thompson River. The river ...
s. These Quesnel, Shuswap, and Okanagan Highland
The Okanagan Highland is an elevated hilly plateau area in British Columbia, Canada, and the U.S. state of Washington (where it is spelled Okanogan Highlands). Rounded mountains with elevations up to above sea level and deep, narrow valleys ar ...
s are sometimes considered as being part of the neighbouring ranges rather than the plateaus and are often spoken of that way locally but are formally designated as being part of the Interior Plateau
The Interior Plateau comprises a large region of the Interior of British Columbia, and lies between the Cariboo and Monashee Mountains on the east, and the Hazelton Mountains, Coast Mountains and Cascade Range on the west.''Landforms of Bri ...
. The southernmost extends into Washington, where it is named by the American spelling Okanogan Highland (and was the first-named of these groupings).S. Holland, Landforms of British Columbia
'', BC Govt, 1976
Cascade–Sierra Mountains in contiguous U.S.
TheCascade Range
The Cascade Range or Cascades is a major mountain range of western North America, extending from southern British Columbia through Washington (state), Washington and Oregon to Northern California. It includes both non-volcanic mountains, such as m ...
(called the Cascade Mountains
The Cascade Range or Cascades is a major mountain range of western North America, extending from southern British Columbia through Washington and Oregon to Northern California. It includes both non-volcanic mountains, such as many of those in the ...
in Canada) extends from northern California
Northern California (commonly shortened to NorCal) is a geocultural region that comprises the northern portion of the U.S. state of California, spanning the northernmost 48 of the state's List of counties in California, 58 counties. Northern Ca ...
in the United States to British Columbia
British Columbia is the westernmost Provinces and territories of Canada, province of Canada. Situated in the Pacific Northwest between the Pacific Ocean and the Rocky Mountains, the province has a diverse geography, with rugged landscapes that ...
, Canada. It consists of non-volcanic and volcanic
A volcano is commonly defined as a vent or fissure in the crust of a planetary-mass object, such as Earth, that allows hot lava, volcanic ash, and gases to escape from a magma chamber below the surface.
On Earth, volcanoes are most often fo ...
mountains: all of the known historic eruptions in the contiguous United States have been from the volcanoes of the Cascade Volcanic Arc. The highest peak in the Cascade Range is Mount Rainier
Mount Rainier ( ), also known as Tahoma, is a large active stratovolcano in the Cascade Range of the Pacific Northwest in the United States. The mountain is located in Mount Rainier National Park about south-southeast of Seattle. With an off ...
(), a stratovolcano
A stratovolcano, also known as a composite volcano, is a typically conical volcano built up by many alternating layers (strata) of hardened lava and tephra. Unlike shield volcanoes, stratovolcanoes are characterized by a steep profile with ...
. The small portion of the Cascade Range in Canada is called the Cascade Mountains or Canadian Cascades, and in its southwestern area is similar in terrain to the area north of Glacier Peak
Glacier Peak or Dakobed (known in the Sauk-Suiattle dialect of the Lushootseed language as "Tda-ko-buh-ba" or "Takobia") is the most isolated of the five major stratovolcanoes (composite volcanoes) of the Cascade Volcanoes, Cascade Volcanic Arc ...
, known as the North Cascades
The North Cascades are a section of the Cascade Range of western North America. They span the border between the Provinces and territories of Canada, Canadian province of British Columbia and the U.S. state of Washington (state), Washington and ...
, and its northern and eastern extremities verge on the Thompson Plateau
The Thompson Plateau forms the southern portion of the Interior Plateau of British Columbia, Canada, lying to the west of Okanagan Lake, south of the Thompson River and east of (although never adjoining it) the Fraser River. At its most southern ...
in a less rugged fashion than in most other parts of the range. The North Cascades are very different in character from the series of high volcanic stratovolcanoes from Rainier southwards to Mount Shasta
Mount Shasta ( ; Shasta people, Shasta: ''Waka-nunee-Tuki-wuki''; Karuk language, Karuk: ''Úytaahkoo'') is a Volcano#Volcanic activity, potentially active stratovolcano at the southern end of the Cascade Range in Siskiyou County, California. A ...
and Lassen Peak
Lassen Peak ( ), commonly referred to as Mount Lassen, is a lava dome volcano in Lassen Volcanic National Park in Northern California. Located in the Shasta Cascade region above the northern Sacramento Valley, it is the southernmost active vo ...
, and are more severely alpine and steeply rugged, particularly the Skagit Range
The Skagit Range ( , ) is a subrange of the Cascade Range in southwestern British Columbia, Canada and northwestern Washington, United States, which are known in Canada as the Canadian Cascades or, officially, the Cascade Mountains. It is also k ...
. Inland portions of the range are dryland and plateau-like in character, such as the Okanagan Range
The Okanagan Range or Okanogan Range is a small subrange of the Cascade Range straddling the border between British Columbia and Washington (U.S. state), Washington south of the Similkameen River on the inland side of the range. The range is the ...
, which lies along the Cascades' northeastern margin, separated by the Similkameen River.
The Sierra Nevada
The Sierra Nevada ( ) is a mountain range in the Western United States, between the Central Valley of California and the Great Basin. The vast majority of the range lies in the state of California, although the Carson Range spur lies primari ...
forms an inland mountain spine of northern California, extending from the terminus of the Cascade Range
The Cascade Range or Cascades is a major mountain range of western North America, extending from southern British Columbia through Washington (state), Washington and Oregon to Northern California. It includes both non-volcanic mountains, such as m ...
south of Lassen Peak
Lassen Peak ( ), commonly referred to as Mount Lassen, is a lava dome volcano in Lassen Volcanic National Park in Northern California. Located in the Shasta Cascade region above the northern Sacramento Valley, it is the southernmost active vo ...
southwards along the east flank of the Central Valley of California
The Central Valley is a broad, elongated, flat valley that dominates the interior of California, United States. It is wide and runs approximately from north-northwest to south-southeast, inland from and parallel to the Pacific coast. It cover ...
to the Transverse Ranges
The Transverse Ranges are a group of mountain ranges of Southern California, in the Pacific Coast Ranges physiographic region in North America. The Transverse Ranges begin at the southern end of the California Coast Ranges and lie within Santa Ba ...
, forming a mountain region of complex terrain and varied geology which separates the Central Valley from the Great Basin
The Great Basin () is the largest area of contiguous endorheic watersheds, those with no outlets to the ocean, in North America. It spans nearly all of Nevada, much of Utah, and portions of California, Idaho, Oregon, Wyoming, and Baja Californi ...
to the east. The mean height of the mountain summits in the Sierra Nevada gradually increases from north to south, culminating at Mount Whitney
Mount Whitney (Paiute: ''Too-man-i-goo-yah'' or ''Too-man-go-yah'') is a mountain in the Sierra Nevada mountain range of California, and the highest point in the contiguous United States, with an elevation of . It lies in East–Central Califor ...
(), the highest point in the contiguous United States
The contiguous United States, also known as the U.S. mainland, officially referred to as the conterminous United States, consists of the 48 adjoining U.S. states and the District of Columbia of the United States in central North America. The te ...
. From east to west, the Sierra is wedge-shaped: the west slope gradually rises and the east slope forms a steep escarpment
An escarpment is a steep slope or long cliff that forms as a result of faulting or erosion and separates two relatively level areas having different elevations.
Due to the similarity, the term '' scarp'' may mistakenly be incorrectly used inte ...
, particularly so in the southern portion.
The northern Sierra surface rocks are predominantly volcanic, while the southern Sierra granitic batholith
A batholith () is a large mass of intrusive rock, intrusive igneous rock (also called plutonic rock), larger than in area, that forms from cooled magma deep in the Earth's crust. Batholiths are almost always made mostly of felsic or intermediate ...
has been sculpted by glaciers into dramatic U-shaped valley
U-shaped valleys, also called trough valleys or glacial troughs, are formed by the process of Glacial period, glaciation. They are characteristic of mountain glaciation in particular. They have a characteristic U shape in cross-section, with s ...
s and thin ridges called arête
An arête ( ; ) is a narrow ridge of rock that separates two valleys. It is typically formed when two glaciers erode parallel U-shaped valleys. Arêtes can also form when two glacial cirques erode headwards towards one another, although frequ ...
s.
Sierra Madre Occidental in Mexico
TheSierra Madre Occidental
The Sierra Madre Occidental is a major mountain range system of the North American Cordillera, that runs northwest–southeast through northwestern and western Mexico, and along the Gulf of California. The Sierra Madre is part of the American C ...
mountain range is a southern extension of the Sierra Nevada. The range extends from near the Arizona border down to the Sierra Madre del Sur, along the western mainland of Mexico. The high plateau that is formed by the range is cut by deep river valleys.
Laramide Belt
The Laramide belt is on the side of the North American Cordillera most distant from the Pacific Coast Ranges. It is named for the Laramie Mountains of easternWyoming
Wyoming ( ) is a landlocked U.S. state, state in the Mountain states, Mountain West subregion of the Western United States, Western United States. It borders Montana to the north and northwest, South Dakota and Nebraska to the east, Idaho t ...
(in turn named for Jacques La Ramee
Jacques La Ramée (June 8, 1784 – 1821) was a French-Canadian and Métis coureur des bois, frontiersman, trapper, fur trader, hunter, explorer, and mountain man who lived in what is now the U.S. state of Wyoming, having settled there i ...
, a trapper who disappeared in the Laramie Mountains in 1820 and was never heard from again).
Alaska and Eastern System of Canada
TheBrooks Range
The Brooks Range (Gwich’in language, Gwich'in: ''Gwazhał'') is a mountain range in far northern North America stretching some from west to east across northern Alaska into Canada's Yukon Territory. Reaching a peak elevation of on Mount Isto, ...
includes the northernmost of the major mountain systems of the North American Cordillera, and extends along an east–west axis across northern Alaska
Alaska ( ) is a non-contiguous U.S. state on the northwest extremity of North America. Part of the Western United States region, it is one of the two non-contiguous U.S. states, alongside Hawaii. Alaska is also considered to be the north ...
from near the northern opening of the Bering Strait
The Bering Strait ( , ; ) is a strait between the Pacific and Arctic oceans, separating the Chukchi Peninsula of the Russian Far East from the Seward Peninsula of Alaska. The present Russia–United States maritime boundary is at 168° 58' ...
to the northern Yukon
Yukon () is a Provinces and territories of Canada, territory of Canada, bordering British Columbia to the south, the Northwest Territories to the east, the Beaufort Sea to the north, and the U.S. state of Alaska to the west. It is Canada’s we ...
Territory. Major subranges include the British Mountains
The British Mountains are a mountain range in Yukon, Canada
Canada is a country in North America. Its Provinces and territories of Canada, ten provinces and three territories extend from the Atlantic Ocean to the Pacific Ocean and no ...
and Richardson Mountains
The Richardson Mountains are a mountain range located west of the mouth of the Mackenzie River in northern Yukon, Canada. They parallel the northernmost part of the boundary between Yukon and Northwest Territories.
Although some sources consider ...
, towards their eastern end, and at their farthest west is the De Long Mountains
The De Long Mountains are a mountain range in the North Slope Borough of the U.S. state of Alaska. The range is located at the west end of the Brooks Range
The Brooks Range (Gwich’in language, Gwich'in: ''Gwazhał'') is a mountain range in fa ...
. The Brooks Range forms the northern flank of the lower Yukon River
The Yukon River is a major watercourse of northwestern North America. From its source in British Columbia, it flows through Canada's territory of Yukon (itself named after the river). The lower half of the river continues westward through the U.S ...
basin, separating it from Alaska's North Slope region, facing the Beaufort Sea
The Beaufort Sea ( ; ) is a marginal sea of the Arctic Ocean, located north of the Northwest Territories, Yukon, and Alaska, and west of the Canadian Arctic Archipelago. The sea is named after Sir Francis Beaufort, a Hydrography, hydrographer. T ...
. The Brooks Range is considered part of (or an extension of) the Rockies
The Rocky Mountains, also known as the Rockies, are a major mountain range and the largest mountain system in North America. The Rocky Mountains stretch in straight-line distance from the northernmost part of Western Canada, to New Mexico in ...
. South of the Brooks Range are the Mackenzie Mountains
The Mackenzie Mountains are a Canadian mountain range forming part of the Yukon–Northwest Territories boundary between the Liard and Peel rivers. The range is named in honour of Canada's second prime minister, Alexander Mackenzie. Nahanni ...
and the Canadian Rockies
The Canadian Rockies () or Canadian Rocky Mountains, comprising both the Alberta Rockies and the British Columbian Rockies, is the Canadian segment of the North American Rocky Mountains. It is the easternmost part of the Canadian Cordillera, w ...
.
Rocky Mountain System in contiguous U.S.
In theRocky Mountains
The Rocky Mountains, also known as the Rockies, are a major mountain range and the largest mountain system in North America. The Rocky Mountains stretch in great-circle distance, straight-line distance from the northernmost part of Western Can ...
, the highest peak is Mount Elbert
Mount Elbert is the highest summit of the Rocky Mountains of North America. With an elevation of , it is also the highest point in the U.S. state of Colorado and the second-highest summit in the contiguous United States after Mount Whitney, w ...
in Colorado
Colorado is a U.S. state, state in the Western United States. It is one of the Mountain states, sharing the Four Corners region with Arizona, New Mexico, and Utah. It is also bordered by Wyoming to the north, Nebraska to the northeast, Kansas ...
at above sea level. The American Rockies rise steeply over the Interior Plains
The Interior Plains is a vast physiographic region that spreads across the Laurentian craton of central North America, extending along the east flank of the Rocky Mountains from the Gulf Coast region to the Arctic Beaufort Sea. In Canada, it ...
to the east, and over the Great Basin
The Great Basin () is the largest area of contiguous endorheic watersheds, those with no outlets to the ocean, in North America. It spans nearly all of Nevada, much of Utah, and portions of California, Idaho, Oregon, Wyoming, and Baja Californi ...
to the west, and extend south to the Rio Grande
The Rio Grande ( or ) in the United States or the Río Bravo (del Norte) in Mexico (), also known as Tó Ba'áadi in Navajo language, Navajo, is one of the principal rivers (along with the Colorado River) in the Southwestern United States a ...
in New Mexico. The United States definition of the Rockies includes the Cabinet and Salish Mountains
The Salish Mountains are located in the northwest corner of the U.S. State of Montana. Much of the range is bordered on the east by Flathead Lake. With peaks ranging from just under 7,000 feet tall to named hills that are a little short of 3,600 f ...
of Idaho and Montana, whereas their counterparts north of the Kootenai River
The Kootenay River or Kootenai River is a major river of the Northwest Plateau in southeastern British Columbia, Canada, and northern Montana and Idaho in the United States. It is one of the uppermost major tributaries of the Columbia River, ...
, the Columbia Mountains
The Columbia Mountains are a group of mountain ranges along the Upper Columbia River in British Columbia, Montana, Idaho and Washington (state), Washington. The mountain range covers 135,952 km² (52,491 sq mi). The range is bounded by th ...
, are sometimes considered a separate system lying to the west of the huge Rocky Mountain Trench
The Rocky Mountain Trench, also known as the Valley of a Thousand Peaks or simply the Trench, is a large valley on the western side of the northern part of North America's Rocky Mountains. The Trench is both visually and cartographically a ...
which runs the length of British Columbia.
Sierra Madre Oriental in Mexico
TheSierra Madre Oriental
The Sierra Madre Oriental () is a mountain range in northeastern Mexico. The Sierra Madre Oriental is part of the American Cordillera, a chain of mountain ranges (cordillera) that consists of an almost continuous sequence of mountain ranges that ...
mountains in eastern Mexico are a southern extension of the Rocky Mountains
The Rocky Mountains, also known as the Rockies, are a major mountain range and the largest mountain system in North America. The Rocky Mountains stretch in great-circle distance, straight-line distance from the northernmost part of Western Can ...
.Edwin Bridges. World Geomorphology
', Cambridge University Press, 1990, p. 88, . The Sierra Madre Oriental spans about . Mexico's Gulf Coastal Plain lies to the east of the range, between the mountains and the Gulf of Mexico coast. The Mexican Plateau lies to the west of the range.
Intermontane areas seaward from the Nevadan belt
The Nevadan belt runs down the middle of the North American Cordillera. Therefore, the intermontane areas can be divided up into the areas east of the Nevadan belt, and those west of the Nevadan belt.Canadian portion
TheInterior Plateau
The Interior Plateau comprises a large region of the Interior of British Columbia, and lies between the Cariboo and Monashee Mountains on the east, and the Hazelton Mountains, Coast Mountains and Cascade Range on the west.''Landforms of Bri ...
is the northern continuation of the Columbia Plateau
The Columbia Plateau is an important geology, geologic and geography, geographic region that lies across parts of the U.S. states of Washington (state), Washington, Oregon, and Idaho. It is a wide flood basalt plateau between the Cascade Range a ...
, and covers much of inland British Columbia
British Columbia is the westernmost Provinces and territories of Canada, province of Canada. Situated in the Pacific Northwest between the Pacific Ocean and the Rocky Mountains, the province has a diverse geography, with rugged landscapes that ...
. The Cariboo Mountains
The Cariboo Mountains are the northernmost subrange of the Columbia Mountains, which run down into the Spokane area of the United States and include the Selkirks, Monashees and Purcells. The Cariboo Mountains are entirely within the province ...
and Monashee Mountains
The Monashee Mountains are a mountain range lying mostly in British Columbia, Canada, extending into the U.S. state of Washington. They stretch from north to south and from east to west. They are a sub-range of the Columbia Mountains. The hig ...
lie to the east, the Canadian Cascades are to the southwest, and the Hazelton Mountains and Coast Range to the west and northwest.
Within the Interior plateau, the Shuswap Highland
The Shuswap Highland is a plateau-like hilly area of in British Columbia, Canada
Canada is a country in North America. Its Provinces and territories of Canada, ten provinces and three territories extend from the Atlantic Ocean to the P ...
consists of a portion of the foothills between the Thompson Plateau
The Thompson Plateau forms the southern portion of the Interior Plateau of British Columbia, Canada, lying to the west of Okanagan Lake, south of the Thompson River and east of (although never adjoining it) the Fraser River. At its most southern ...
and Bonaparte Plateau
The Bonaparte Plateau, in British Columbia, Canada, is a sub-plateau of the Thompson Plateau which extends to the Quesnel River and lies between the Cariboo Mountains on the east and the Fraser River on the west. The Thompson Plateau is itself ...
on the west, and the Monashee Mountains
The Monashee Mountains are a mountain range lying mostly in British Columbia, Canada, extending into the U.S. state of Washington. They stretch from north to south and from east to west. They are a sub-range of the Columbia Mountains. The hig ...
and Cariboo Mountains
The Cariboo Mountains are the northernmost subrange of the Columbia Mountains, which run down into the Spokane area of the United States and include the Selkirks, Monashees and Purcells. The Cariboo Mountains are entirely within the province ...
on the east and northeast.
Also within the Interior plateau, the Thompson Plateau
The Thompson Plateau forms the southern portion of the Interior Plateau of British Columbia, Canada, lying to the west of Okanagan Lake, south of the Thompson River and east of (although never adjoining it) the Fraser River. At its most southern ...
forms the southern portion of the Interior Plateau. It is bordered on the south by the Canadian Cascades and on the north by the Thompson River
The Thompson River is the largest tributary of the Fraser River, flowing through the south-central portion of British Columbia, Canada. The Thompson River has two main branches, the South Thompson River and the North Thompson River. The river ...
.
The Okanagan Highland is the part of the Interior Plateau to the east of the Thompson Plateau, and is bounded by the Okanagan River
The Okanogan River (known as the Okanagan River in Canada) is a tributary of the Columbia River, approximately 115 mi (185 km) long, in southern British Columbia and north central Washington. It drains a scenic plateau region called t ...
on the west, the Shuswap River The basin of the Shuswap River (pronounced /ˈʃuːʃwɑːp/) lies northeast of the Okanagan Valley in British Columbia, originating in the central Monashee Mountains. It is the upper part of the drainage better known to British Columbians as bel ...
on the north, and the Kettle River on the east side. The Okanagan Highland is described as being a hilly plateau, and is located in southern British Columbia
British Columbia is the westernmost Provinces and territories of Canada, province of Canada. Situated in the Pacific Northwest between the Pacific Ocean and the Rocky Mountains, the province has a diverse geography, with rugged landscapes that ...
and northern Washington
Washington most commonly refers to:
* George Washington (1732–1799), the first president of the United States
* Washington (state), a state in the Pacific Northwest of the United States
* Washington, D.C., the capital of the United States
** A ...
. The Interior Plateau also includes the Quesnel Highland
The Quesnel Highland is a geographic area in the Central Interior of the Canadian province of British Columbia. As defined by BC government geographer in ''Landforms of British Columbia'', an account and analysis of British Columbia geography t ...
, Fraser Plateau
The Fraser Plateau is an intermontane plateau. It is one of the main subdivisions of the Interior Plateau located in the Central Interior of British Columbia.
Geography
The region includes the Cariboo Plateau and Chilcotin Plateau, and the adj ...
, Nechako Plateau
The Nechako Plateau is the northernmost subdivision of the Interior Plateau, one of the main geographic regions of the Canadian province of British Columbia. It spans the basin of the Nechako River and its tributaries the Stuart River and Enda ...
, and McGregor Plateau
The McGregor Plateau is a sub-plateau of the Nechako Plateau, the northernmost major subdivision of the Interior Plateau spanning the inland regions of the Pacific Northwest. Located in British Columbia, Canada, to the east of the city of Prince ...
.
Portion in contiguous U.S.
California's Central Valley is a large, flat valley that dominates the central portion ofCalifornia
California () is a U.S. state, state in the Western United States that lies on the West Coast of the United States, Pacific Coast. It borders Oregon to the north, Nevada and Arizona to the east, and shares Mexico–United States border, an ...
, stretching inland and parallel to the Pacific Ocean
The Pacific Ocean is the largest and deepest of Earth's five Borders of the oceans, oceanic divisions. It extends from the Arctic Ocean in the north to the Southern Ocean, or, depending on the definition, to Antarctica in the south, and is ...
coast. Its northern half is referred to as the Sacramento Valley
The Sacramento Valley is the area of the Central Valley of the U.S. state of California that lies north of the Sacramento–San Joaquin River Delta and is drained by the Sacramento River. It encompasses all or parts of ten Northern California ...
, and its southern half as the San Joaquin Valley
The San Joaquin Valley ( ; Spanish language in California, Spanish: ''Valle de San Joaquín'') is the southern half of California's Central Valley (California), Central Valley. Famed as a major breadbasket, the San Joaquin Valley is an importa ...
. The two-halves meet at the huge Sacramento-San Joaquin River Delta of the Sacramento and San Joaquin Rivers, which along with their tributaries drain the majority of the valley and flow into San Francisco Bay
San Francisco Bay (Chochenyo language, Chochenyo: 'ommu) is a large tidal estuary in the United States, U.S. state of California, and gives its name to the San Francisco Bay Area. It is dominated by the cities of San Francisco, California, San ...
. The Central Valley covers an area of approximately , making it slightly smaller than the state of West Virginia
West Virginia is a mountainous U.S. state, state in the Southern United States, Southern and Mid-Atlantic (United States), Mid-Atlantic regions of the United States.The United States Census Bureau, Census Bureau and the Association of American ...
and about 13.7% of California's total area. The Central Valley is wide, with the Sierra Nevada
The Sierra Nevada ( ) is a mountain range in the Western United States, between the Central Valley of California and the Great Basin. The vast majority of the range lies in the state of California, although the Carson Range spur lies primari ...
to the east and the Coast Ranges
The Pacific Coast Ranges (officially gazetted as the Pacific Mountain System in the United States; ; ) are the series of mountain ranges that stretch along the West Coast of North America from Alaska south to Northern and Central Mexico. Althoug ...
to the west.
In northwestern Oregon, the fertile Willamette Valley
The Willamette Valley ( ) is a valley in Oregon, in the Pacific Northwest region of the United States. The Willamette River flows the entire length of the valley and is surrounded by mountains on three sides: the Cascade Range to the east, the ...
lies between the Oregon Coast Range
The Oregon Coast Range, often called simply the Coast Range and sometimes the Pacific Coast Range, is a mountain range, in the Pacific Coast Ranges Physiographic regions of the world, physiographic region, in the United States, U.S. state of Or ...
and the Cascades; this depression continues north into Washington as the Puget Trough.
Mexican portion
TheGulf of California
The Gulf of California (), also known as the Sea of Cortés (''Mar de Cortés'') or Sea of Cortez, or less commonly as the Vermilion Sea (''Mar Vermejo''), is a marginal sea of the Pacific Ocean that separates the Baja California peninsula from ...
is a body of water that separates the Peninsular Ranges
The Peninsular Ranges (also called the Lower California province) are a group of mountain ranges that stretch from Southern California to the southern tip of the Baja California peninsula; they are part of the North American Pacific Coast Range ...
from the Sierra Madre Occidental
The Sierra Madre Occidental is a major mountain range system of the North American Cordillera, that runs northwest–southeast through northwestern and western Mexico, and along the Gulf of California. The Sierra Madre is part of the American C ...
on the Mexican mainland. The Gulf of California is long and wide, with an area of , a mean depth of , and a volume of .
Intermontane areas inland from the Nevadan belt
Canadian portion
TheRocky Mountain Trench
The Rocky Mountain Trench, also known as the Valley of a Thousand Peaks or simply the Trench, is a large valley on the western side of the northern part of North America's Rocky Mountains. The Trench is both visually and cartographically a ...
is a large valley that extends approximately from Flathead Lake
Flathead Lake (, ) is a large natural lake in northwest Montana, United States.
The lake is a remnant of the ancient, massive glacial dammed lake, Glacial Lake Missoula, Lake Missoula, of the era of the last interglacial. Flathead Lake is a nat ...
, Montana
Montana ( ) is a landlocked U.S. state, state in the Mountain states, Mountain West subregion of the Western United States. It is bordered by Idaho to the west, North Dakota to the east, South Dakota to the southeast, Wyoming to the south, an ...
, to the Liard River
The Liard River of the Boreal forest of Canada, North American boreal forest flows through Yukon, British Columbia and the Northwest Territories, Canada. Rising in the Saint Cyr Range of the Pelly Mountains in southeastern Yukon, it flows sout ...
, just south of the British Columbia
British Columbia is the westernmost Provinces and territories of Canada, province of Canada. Situated in the Pacific Northwest between the Pacific Ocean and the Rocky Mountains, the province has a diverse geography, with rugged landscapes that ...
–Yukon
Yukon () is a Provinces and territories of Canada, territory of Canada, bordering British Columbia to the south, the Northwest Territories to the east, the Beaufort Sea to the north, and the U.S. state of Alaska to the west. It is Canada’s we ...
border near Watson Lake, Yukon
Watson Lake is a town in Yukon, Canada, located at mile 635 on the Alaska Highway close to the British Columbia border. It had a population of 1,133 in 2021. The town is named for Frank Watson, an American-born trapper and prospector, who settled ...
. The trench bottom is wide and ranges from above sea level. The general orientation of the Trench is almost uniformly pointing north. Some of its topography
Topography is the study of the forms and features of land surfaces. The topography of an area may refer to the landforms and features themselves, or a description or depiction in maps.
Topography is a field of geoscience and planetary sci ...
has been carved into glacial valley
U-shaped valleys, also called trough valleys or glacial troughs, are formed by the process of glaciation. They are characteristic of mountain glaciation in particular. They have a characteristic U shape in cross-section, with steep, straight s ...
s, but it is primarily a byproduct of faulting
In geology, a fault is a planar fracture or discontinuity in a volume of rock across which there has been significant displacement as a result of rock-mass movements. Large faults within Earth's crust result from the action of plate tectonic ...
. The Trench separates the Rocky Mountains
The Rocky Mountains, also known as the Rockies, are a major mountain range and the largest mountain system in North America. The Rocky Mountains stretch in great-circle distance, straight-line distance from the northernmost part of Western Can ...
on its east from the Columbia Mountains
The Columbia Mountains are a group of mountain ranges along the Upper Columbia River in British Columbia, Montana, Idaho and Washington (state), Washington. The mountain range covers 135,952 km² (52,491 sq mi). The range is bounded by th ...
and the Cassiar Mountains
The Cassiar Mountains () are the most northerly group of the Northern Interior Mountains in the Canadian province of British Columbia and also extend slightly into the southernmost Yukon Territory. They lie north and west of the Omineca Mountain ...
on its west. It is up to wide, if measured peak-to-peak.
For convenience the Rocky Mountain Trench may be divided into northern and southern sections. The dividing point reflects the separation of north and easterly flows to the Arctic Ocean versus south and westerly flows to the Pacific Ocean. A break in the valley system at around 54°N near Prince George, British Columbia
British Columbia is the westernmost Provinces and territories of Canada, province of Canada. Situated in the Pacific Northwest between the Pacific Ocean and the Rocky Mountains, the province has a diverse geography, with rugged landscapes that ...
may be used for this purpose. There are three main mountain ranges in the Canadian area named the Rocky Mountains, the Columbia Mountains, and the Coast Mountains.
Portion in contiguous U.S.
 The
The Columbia Plateau
The Columbia Plateau is an important geology, geologic and geography, geographic region that lies across parts of the U.S. states of Washington (state), Washington, Oregon, and Idaho. It is a wide flood basalt plateau between the Cascade Range a ...
is a geologic
Geology (). is a branch of natural science concerned with the Earth and other astronomical objects, the rocks of which they are composed, and the processes by which they change over time. Modern geology significantly overlaps all other Earth s ...
and geographic
Geography (from Ancient Greek ; combining 'Earth' and 'write', literally 'Earth writing') is the study of the lands, features, inhabitants, and phenomena of Earth. Geography is an all-encompassing discipline that seeks an understanding o ...
region that lies across parts of the U.S. state
In the United States, a state is a constituent political entity, of which there are 50. Bound together in a political union, each state holds governmental jurisdiction over a separate and defined geographic territory where it shares its so ...
s of Washington
Washington most commonly refers to:
* George Washington (1732–1799), the first president of the United States
* Washington (state), a state in the Pacific Northwest of the United States
* Washington, D.C., the capital of the United States
** A ...
, Oregon
Oregon ( , ) is a U.S. state, state in the Pacific Northwest region of the United States. It is a part of the Western U.S., with the Columbia River delineating much of Oregon's northern boundary with Washington (state), Washington, while t ...
, and Idaho
Idaho ( ) is a landlocked U.S. state, state in the Pacific Northwest and Mountain states, Mountain West subregions of the Western United States. It borders Montana and Wyoming to the east, Nevada and Utah to the south, and Washington (state), ...
. It is a wide flood basalt
A flood basalt (or plateau basalt) is the result of a giant volcanic eruption or series of eruptions that covers large stretches of land or the ocean floor with basalt lava. Many flood basalts have been attributed to the onset of a hotspot (geolo ...
plateau between the Cascade Range
The Cascade Range or Cascades is a major mountain range of western North America, extending from southern British Columbia through Washington (state), Washington and Oregon to Northern California. It includes both non-volcanic mountains, such as m ...
and the Rocky Mountains
The Rocky Mountains, also known as the Rockies, are a major mountain range and the largest mountain system in North America. The Rocky Mountains stretch in great-circle distance, straight-line distance from the northernmost part of Western Can ...
, cut through by the Columbia River
The Columbia River (Upper Chinook language, Upper Chinook: ' or '; Sahaptin language, Sahaptin: ''Nch’i-Wàna'' or ''Nchi wana''; Sinixt dialect'' '') is the largest river in the Pacific Northwest region of North America. The river headwater ...
. In one of various usages, the term " Columbia Basin" refers to more or less the same area as the Columbia Plateau.
The Basin and Range province
The Basin and Range Province is a vast United States physiographic region, physiographic region covering much of the inland Western United States and Northern Mexico, northwestern Mexico. It is defined by unique basin and range topography, charac ...
covers most of the state of Nevada
Nevada ( ; ) is a landlocked state in the Western United States. It borders Oregon to the northwest, Idaho to the northeast, California to the west, Arizona to the southeast, and Utah to the east. Nevada is the seventh-most extensive, th ...
and parts of the states of Arizona
Arizona is a U.S. state, state in the Southwestern United States, Southwestern region of the United States, sharing the Four Corners region of the western United States with Colorado, New Mexico, and Utah. It also borders Nevada to the nort ...
, California
California () is a U.S. state, state in the Western United States that lies on the West Coast of the United States, Pacific Coast. It borders Oregon to the north, Nevada and Arizona to the east, and shares Mexico–United States border, an ...
, Idaho
Idaho ( ) is a landlocked U.S. state, state in the Pacific Northwest and Mountain states, Mountain West subregions of the Western United States. It borders Montana and Wyoming to the east, Nevada and Utah to the south, and Washington (state), ...
, New Mexico
New Mexico is a state in the Southwestern United States, Southwestern region of the United States. It is one of the Mountain States of the southern Rocky Mountains, sharing the Four Corners region with Utah, Colorado, and Arizona. It also ...
, Oregon
Oregon ( , ) is a U.S. state, state in the Pacific Northwest region of the United States. It is a part of the Western U.S., with the Columbia River delineating much of Oregon's northern boundary with Washington (state), Washington, while t ...
, Texas
Texas ( , ; or ) is the most populous U.S. state, state in the South Central United States, South Central region of the United States. It borders Louisiana to the east, Arkansas to the northeast, Oklahoma to the north, New Mexico to the we ...
, Utah
Utah is a landlocked state in the Mountain states, Mountain West subregion of the Western United States. It is one of the Four Corners states, sharing a border with Arizona, Colorado, and New Mexico. It also borders Wyoming to the northea ...
, and Wyoming
Wyoming ( ) is a landlocked U.S. state, state in the Mountain states, Mountain West subregion of the Western United States, Western United States. It borders Montana to the north and northwest, South Dakota and Nebraska to the east, Idaho t ...
, as well as much of northern Mexico
Mexico, officially the United Mexican States, is a country in North America. It is the northernmost country in Latin America, and borders the United States to the north, and Guatemala and Belize to the southeast; while having maritime boundar ...
. It is an extremely arid region characterized by basin and range
Basin and range topography is characterized by alternating parallel mountain ranges and valleys. It is a result of crustal extension due to mantle upwelling, gravitational collapse, crustal thickening, or relaxation of confining stresses. The e ...
topography.
The Colorado Plateau
The Colorado Plateau is a physiographic and desert region of the Intermontane Plateaus, roughly centered on the Four Corners region of the Southwestern United States. This plateau covers an area of 336,700 km2 (130,000 mi2) within w ...
is an area of high desert located in Arizona
Arizona is a U.S. state, state in the Southwestern United States, Southwestern region of the United States, sharing the Four Corners region of the western United States with Colorado, New Mexico, and Utah. It also borders Nevada to the nort ...
, New Mexico
New Mexico is a state in the Southwestern United States, Southwestern region of the United States. It is one of the Mountain States of the southern Rocky Mountains, sharing the Four Corners region with Utah, Colorado, and Arizona. It also ...
, Colorado
Colorado is a U.S. state, state in the Western United States. It is one of the Mountain states, sharing the Four Corners region with Arizona, New Mexico, and Utah. It is also bordered by Wyoming to the north, Nebraska to the northeast, Kansas ...
, and Utah
Utah is a landlocked state in the Mountain states, Mountain West subregion of the Western United States. It is one of the Four Corners states, sharing a border with Arizona, Colorado, and New Mexico. It also borders Wyoming to the northea ...
, bisected by the Colorado River
The Colorado River () is one of the principal rivers (along with the Rio Grande) in the Southwestern United States and in northern Mexico. The river, the List of longest rivers of the United States (by main stem), 5th longest in the United St ...
which flows westward through the southern part, and the Green River which flows south from the northernmost part of the plateau. The Green is a tributary of the Colorado, the confluence being west of Moab, Utah in Canyonlands National Park.
Mexican portion
TheMexican Plateau
The Central Mexican Plateau, also known as the Mexican Altiplano (), is a large arid-to-semiarid plateau that occupies much of northern and central Mexico. Averaging above sea level, it extends from the United States border in the north to the T ...
is one of six distinct physiographic sections of the Basin and Range Province
The Basin and Range Province is a vast United States physiographic region, physiographic region covering much of the inland Western United States and Northern Mexico, northwestern Mexico. It is defined by unique basin and range topography, charac ...
, which in turn is part of the Intermontane Plateaus physiographic division. It is a large arid-to-semiarid plateau
In geology and physical geography, a plateau (; ; : plateaus or plateaux), also called a high plain or a tableland, is an area of a highland consisting of flat terrain that is raised sharply above the surrounding area on at least one side. ...
that occupies much of northern and central Mexico
Mexico, officially the United Mexican States, is a country in North America. It is the northernmost country in Latin America, and borders the United States to the north, and Guatemala and Belize to the southeast; while having maritime boundar ...
. Averaging above sea level, it extends from the United States border in the north to the Trans-Mexican Volcanic Belt
The Trans-Mexican Volcanic Belt (), also known as the Transvolcanic Belt and locally as the (''Snowy Mountain Range''), is an active volcanic belt that covers central-southern Mexico. Several of its highest peaks have snow all year long, and dur ...
in the south and is bounded by the Sierra Madre Occidental
The Sierra Madre Occidental is a major mountain range system of the North American Cordillera, that runs northwest–southeast through northwestern and western Mexico, and along the Gulf of California. The Sierra Madre is part of the American C ...
and Sierra Madre Oriental
The Sierra Madre Oriental () is a mountain range in northeastern Mexico. The Sierra Madre Oriental is part of the American Cordillera, a chain of mountain ranges (cordillera) that consists of an almost continuous sequence of mountain ranges that ...
to the west and east, respectively.
A low east–west mountain range in the state of Zacatecas
Zacatecas, officially the Free and Sovereign State of Zacatecas, is one of the Political divisions of Mexico, 31 states of Mexico. It is divided into Municipalities of Zacatecas, 58 municipalities and its capital city is Zacatecas City, Zacatec ...
divides the plateau into northern and southern sections. These two sections, called the Northern Plateau (Spanish: ''Mesa del Norte'') and Central Plateau (Spanish: ''Mesa Central''), are now generally regarded by geographers as sections of one plateau.
See also
* List of ecoregions in North America (CEC): Western CordilleraReferences
External links
* {{Authority control Mountain ranges of North America Geologic provinces of Canada Geologic provinces of the United States Geology of Mexico Lists of mountain ranges Mountain ranges of Canada Mountain ranges of the United States Mountain ranges of Mexico Cordilleras