Watershed Delineation on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Watershed delineation is the process of identifying the boundary of a watershed, also referred to as a catchment, 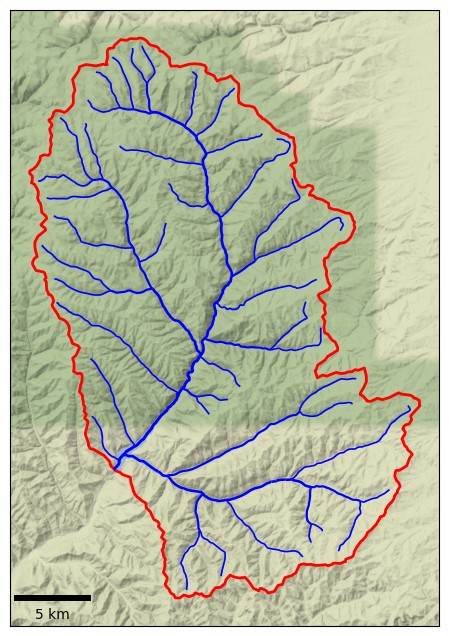 Computerized methods for watershed delineation use digital elevation models (DEMs), datasets that represent the height of the Earth's land surface. Computerized watershed delineation may be done using specialized hydrologic modeling software such as WMS,
Computerized methods for watershed delineation use digital elevation models (DEMs), datasets that represent the height of the Earth's land surface. Computerized watershed delineation may be done using specialized hydrologic modeling software such as WMS,
 For "manual" watershed delination, one must know how to read and interpret a topographic map, for example to identify ridges, valleys, and the direction of steepest slope. Even in the computer era, manual watershed delineation is still a useful skill, in order to check whether watersheds generated with software are correct.
Instructions for manual watershed delineation can be found in some textbooks in geography or environmental management, in government pamphlets, or in online video tutorials.
According to the US Geological Survey, there are 5 steps to manual watershed delineation:
# Find the point of interest along a stream on the map. This is the "watershed outlet" or "pour point."
# Imagine or draw surface water flow lines that point downhill perpendicular to the topographic contours (this is the steepest direction).
# Mark the location of topographical high points (peaks) around the stream.
# Mark the points along contours that divide flows towards or away from the stream (ridges).
# Connect the dots to delineate the watershed.
General Rules:
* The watershed boundary should be perpendicular to contour lines where it crosses them.
* The watershed boundary must not cross rivers or streams other than at the outlet. (In some cases, a blue line representing a man-made canal or pipeline may traverse your watershed boundary.)
* The watershed boundary should run along ridgelines and connect high points.
One disadvantage to manual watershed delineation is that it is subject to errors and the individual judgment of the analyst. The Illinois Environmental Protection Agency wrote, "bear in mind that delineating a watershed is an inexact science. Any two people, even if both are experts, will come up with slightly different boundaries."
Especially for smaller watersheds and when accurate results are important, field reconnaissance may be needed to find features that are not shown on maps. "Going out into the field allows you to identify human alterations, such as road ditches, storm sewers and culverts that could change the direction of waters flow and thus change the watershed boundaries."
For "manual" watershed delination, one must know how to read and interpret a topographic map, for example to identify ridges, valleys, and the direction of steepest slope. Even in the computer era, manual watershed delineation is still a useful skill, in order to check whether watersheds generated with software are correct.
Instructions for manual watershed delineation can be found in some textbooks in geography or environmental management, in government pamphlets, or in online video tutorials.
According to the US Geological Survey, there are 5 steps to manual watershed delineation:
# Find the point of interest along a stream on the map. This is the "watershed outlet" or "pour point."
# Imagine or draw surface water flow lines that point downhill perpendicular to the topographic contours (this is the steepest direction).
# Mark the location of topographical high points (peaks) around the stream.
# Mark the points along contours that divide flows towards or away from the stream (ridges).
# Connect the dots to delineate the watershed.
General Rules:
* The watershed boundary should be perpendicular to contour lines where it crosses them.
* The watershed boundary must not cross rivers or streams other than at the outlet. (In some cases, a blue line representing a man-made canal or pipeline may traverse your watershed boundary.)
* The watershed boundary should run along ridgelines and connect high points.
One disadvantage to manual watershed delineation is that it is subject to errors and the individual judgment of the analyst. The Illinois Environmental Protection Agency wrote, "bear in mind that delineating a watershed is an inexact science. Any two people, even if both are experts, will come up with slightly different boundaries."
Especially for smaller watersheds and when accurate results are important, field reconnaissance may be needed to find features that are not shown on maps. "Going out into the field allows you to identify human alterations, such as road ditches, storm sewers and culverts that could change the direction of waters flow and thus change the watershed boundaries."
 Additionally, some methods allow for "fencing ridgelines" and burning in flow pathways through lakes. Some methods also enforce a small slope onto flat areas so that flow will continue to move toward the outlet. The step of "burning in" stream channels involves artificially deepening the channel, by subtracting a large elevation value from pixels that represent the channel. This ensures that once flow has entered the channel, it will stay there rather than jumping out and flowing overland or into another channel. Some algorithms infer the location of channels automatically from the DEM. Better results are usually obtained by burning in mapped stream channels, or channels derived from satellite or aerial imagery.
There are several different algorithms available for calculating flow direction from a DEM. The first method, introduced by Australian geographers O'Callaghan and Mark in 1984, is referred to as D8. Water flows from a pixel to one of 8 possible directions to a neighboring cell (including diagonally), based on the direction of steepest slope. There are disadvantages to this method as water flow is limited to 8 directions, separated by 45°, which may result in unrealistic flow patterns. Also, because all of the flow is routed in one direction, the D8 method is unable to model situations where the flow diverges, such as on convex hillsides, in a
Additionally, some methods allow for "fencing ridgelines" and burning in flow pathways through lakes. Some methods also enforce a small slope onto flat areas so that flow will continue to move toward the outlet. The step of "burning in" stream channels involves artificially deepening the channel, by subtracting a large elevation value from pixels that represent the channel. This ensures that once flow has entered the channel, it will stay there rather than jumping out and flowing overland or into another channel. Some algorithms infer the location of channels automatically from the DEM. Better results are usually obtained by burning in mapped stream channels, or channels derived from satellite or aerial imagery.
There are several different algorithms available for calculating flow direction from a DEM. The first method, introduced by Australian geographers O'Callaghan and Mark in 1984, is referred to as D8. Water flows from a pixel to one of 8 possible directions to a neighboring cell (including diagonally), based on the direction of steepest slope. There are disadvantages to this method as water flow is limited to 8 directions, separated by 45°, which may result in unrealistic flow patterns. Also, because all of the flow is routed in one direction, the D8 method is unable to model situations where the flow diverges, such as on convex hillsides, in a
 This list is non-exhaustive, as many organizations and territories have produced their own watershed map data and have published via the web. Notable datasets include:
* United States Watershed Boundary Dataset,
This list is non-exhaustive, as many organizations and territories have produced their own watershed map data and have published via the web. Notable datasets include:
* United States Watershed Boundary Dataset,
website
(continually updated) * Canadian National Hydrographic Network Watershed Boundaries
website
* HydroBasins
website
(global, 2013) * Hydrologic Derivatives for Modeling and Applications (HDMA), (global, 2017) * MERIT-Basins
website
(global, 2021) * Hydrography90m,website
(2022, global, shows smaller headwater streams)
drainage basin
A drainage basin is an area of land in which all flowing surface water converges to a single point, such as a river mouth, or flows into another body of water, such as a lake or ocean. A basin is separated from adjacent basins by a perimeter, ...
, or river basin. It is an important step in many areas of environmental science, engineering, and management, for example to study flooding, aquatic habitat, or water pollution.
The activity of watershed delineation is typically performed by geographers, scientists, and engineers. Historically, watershed delineation was done by hand on paper topographic map
In modern mapping, a topographic map or topographic sheet is a type of map characterized by large- scale detail and quantitative representation of relief features, usually using contour lines (connecting points of equal elevation), but histori ...
s, sometimes supplemented with field research. In the 1980s, automated methods were developed for watershed delineation with computers and electronic data, and these are now in widespread use.
 Computerized methods for watershed delineation use digital elevation models (DEMs), datasets that represent the height of the Earth's land surface. Computerized watershed delineation may be done using specialized hydrologic modeling software such as WMS,
Computerized methods for watershed delineation use digital elevation models (DEMs), datasets that represent the height of the Earth's land surface. Computerized watershed delineation may be done using specialized hydrologic modeling software such as WMS, geographic information system
A geographic information system (GIS) consists of integrated computer hardware and Geographic information system software, software that store, manage, Spatial analysis, analyze, edit, output, and Cartographic design, visualize Geographic data ...
software like ArcGIS
ArcGIS is a family of client, server and online geographic information system (GIS) software developed and maintained by Esri.
ArcGIS was first released in 1982 as ARC/INFO, a command line-based GIS. ARC/INFO was later merged into ArcGIS De ...
or QGIS
QGIS is a geographic information system (GIS) software that is free and open-source. QGIS supports Windows, macOS, and Linux. It supports viewing, editing, printing, and analysis of geospatial data in a range of data formats. Its name comes from ...
, or with programming languages like Python
Python may refer to:
Snakes
* Pythonidae, a family of nonvenomous snakes found in Africa, Asia, and Australia
** ''Python'' (genus), a genus of Pythonidae found in Africa and Asia
* Python (mythology), a mythical serpent
Computing
* Python (prog ...
or R.
Watersheds are a fundamental geographic unit in hydrology
Hydrology () is the scientific study of the movement, distribution, and management of water on Earth and other planets, including the water cycle, water resources, and drainage basin sustainability. A practitioner of hydrology is called a hydro ...
, the science concerned with the movement, distribution, and management of water on Earth. Delineating watersheds may be considered an application of hydrography
Hydrography is the branch of applied sciences which deals with the measurement and description of the physical features of oceans, seas, coastal areas, lakes and rivers, as well as with the prediction of their change over time, for the primary ...
, the branch of applied sciences which deals with the measurement and description of the physical features of oceans, seas, coastal areas, lakes and rivers. It is also related to geomorphometry
Geomorphometry, or geomorphometrics ( + + ), is the science and practice of measuring the characteristics of terrain, the shape of the surface of the Earth, and the effects of this surface form on human and natural geography. It gathers various m ...
, the quantitative science of analyzing land surfaces. Watershed delineation continues to be an active area of research, with scientists and programmers developing new algorithms and methods, and making use of increasingly high-resolution data from aerial or satellite remote sensing
Remote sensing is the acquisition of information about an physical object, object or phenomenon without making physical contact with the object, in contrast to in situ or on-site observation. The term is applied especially to acquiring inform ...
.
Manual watershed delineation
The conventional method of finding a watershed boundary is to draw it by hand on a papertopographic map
In modern mapping, a topographic map or topographic sheet is a type of map characterized by large- scale detail and quantitative representation of relief features, usually using contour lines (connecting points of equal elevation), but histori ...
, or on a transparent overlay. The watershed area can then be estimated using a planimeter
A planimeter, also known as a platometer, is a measuring instrument used to determine the area of an arbitrary two-dimensional shape.
Construction
There are several kinds of planimeters, but all operate in a similar way. The precise way in whic ...
, by overlaying graph paper and counting grid cells, or the result can be digitized for use with mapping software. The same process can be done on a computer, sketching the watershed boundary (with a mouse or stylus) over a digital copy of a topographic map. This is referred to as "heads up digitizing" or "on-screen digitizing."
 For "manual" watershed delination, one must know how to read and interpret a topographic map, for example to identify ridges, valleys, and the direction of steepest slope. Even in the computer era, manual watershed delineation is still a useful skill, in order to check whether watersheds generated with software are correct.
Instructions for manual watershed delineation can be found in some textbooks in geography or environmental management, in government pamphlets, or in online video tutorials.
According to the US Geological Survey, there are 5 steps to manual watershed delineation:
# Find the point of interest along a stream on the map. This is the "watershed outlet" or "pour point."
# Imagine or draw surface water flow lines that point downhill perpendicular to the topographic contours (this is the steepest direction).
# Mark the location of topographical high points (peaks) around the stream.
# Mark the points along contours that divide flows towards or away from the stream (ridges).
# Connect the dots to delineate the watershed.
General Rules:
* The watershed boundary should be perpendicular to contour lines where it crosses them.
* The watershed boundary must not cross rivers or streams other than at the outlet. (In some cases, a blue line representing a man-made canal or pipeline may traverse your watershed boundary.)
* The watershed boundary should run along ridgelines and connect high points.
One disadvantage to manual watershed delineation is that it is subject to errors and the individual judgment of the analyst. The Illinois Environmental Protection Agency wrote, "bear in mind that delineating a watershed is an inexact science. Any two people, even if both are experts, will come up with slightly different boundaries."
Especially for smaller watersheds and when accurate results are important, field reconnaissance may be needed to find features that are not shown on maps. "Going out into the field allows you to identify human alterations, such as road ditches, storm sewers and culverts that could change the direction of waters flow and thus change the watershed boundaries."
For "manual" watershed delination, one must know how to read and interpret a topographic map, for example to identify ridges, valleys, and the direction of steepest slope. Even in the computer era, manual watershed delineation is still a useful skill, in order to check whether watersheds generated with software are correct.
Instructions for manual watershed delineation can be found in some textbooks in geography or environmental management, in government pamphlets, or in online video tutorials.
According to the US Geological Survey, there are 5 steps to manual watershed delineation:
# Find the point of interest along a stream on the map. This is the "watershed outlet" or "pour point."
# Imagine or draw surface water flow lines that point downhill perpendicular to the topographic contours (this is the steepest direction).
# Mark the location of topographical high points (peaks) around the stream.
# Mark the points along contours that divide flows towards or away from the stream (ridges).
# Connect the dots to delineate the watershed.
General Rules:
* The watershed boundary should be perpendicular to contour lines where it crosses them.
* The watershed boundary must not cross rivers or streams other than at the outlet. (In some cases, a blue line representing a man-made canal or pipeline may traverse your watershed boundary.)
* The watershed boundary should run along ridgelines and connect high points.
One disadvantage to manual watershed delineation is that it is subject to errors and the individual judgment of the analyst. The Illinois Environmental Protection Agency wrote, "bear in mind that delineating a watershed is an inexact science. Any two people, even if both are experts, will come up with slightly different boundaries."
Especially for smaller watersheds and when accurate results are important, field reconnaissance may be needed to find features that are not shown on maps. "Going out into the field allows you to identify human alterations, such as road ditches, storm sewers and culverts that could change the direction of waters flow and thus change the watershed boundaries."
Automated or computerized watershed delineation
Using computer software to delineate watersheds can be much faster than manual methods. It may also be more consistent, as it removes analyst's subjectivity. Automatic methods of watershed delineation have been in use since the 1980s, and are now in widespread use in the science and engineering communities. Researchers have even used computer methods to delineate watersheds on Mars. Automated watershed delineation methods use digital data of the earth's elevation, aDigital Elevation Model
A digital elevation model (DEM) or digital surface model (DSM) is a 3D computer graphics representation of elevation data to represent terrain or overlaying objects, commonly of a planet, Natural satellite, moon, or asteroid. A "global DEM" refer ...
, or DEM. Typically, algorithms use the method of "steepest slope" to calculate the flow direction from a grid cell (or pixel) to one of its neighbors.
It is possible to use DEMs in different formats for watershed delineation, such as a Triangular Irregular Network
In computer graphics, a triangulated irregular network (TIN) is a representation of a continuous surface consisting entirely of triangular facets (a triangle mesh), used mainly as Discrete Global Grid in primary elevation modeling.
The verti ...
(TIN), or Hexagonal tiling
In geometry, the hexagonal tiling or hexagonal tessellation is a regular tiling of the Euclidean plane, in which exactly three hexagons meet at each vertex. It has Schläfli symbol of or (as a Truncation (geometry), truncated triangular tiling ...
however most contemporary algorithms make use of a regular rectangular grid. In the 1980s and 1990s, digital elevation models were often obtained by scanning and digitizing the contours on paper topographic maps, which were then converted to a TIN or a gridded DEM. More recently, the DEM is obtained by aerial or satellite remote sensing
Remote sensing is the acquisition of information about an physical object, object or phenomenon without making physical contact with the object, in contrast to in situ or on-site observation. The term is applied especially to acquiring inform ...
, using stereophotogrammetry
Photogrammetry is the science and technology of obtaining reliable information about physical objects and the environment through the process of recording, measuring and interpreting photographic images and patterns of electromagnetic radiant ima ...
, lidar
Lidar (, also LIDAR, an acronym of "light detection and ranging" or "laser imaging, detection, and ranging") is a method for determining ranging, ranges by targeting an object or a surface with a laser and measuring the time for the reflected li ...
, or radar
Radar is a system that uses radio waves to determine the distance ('' ranging''), direction ( azimuth and elevation angles), and radial velocity of objects relative to the site. It is a radiodetermination method used to detect and track ...
.
To use a rectangular grid DEM for watershed delineation, it must first be processed or "conditioned" in order to return realistic results. The result is sometimes referred to as a "hydro-enforced" DEM or a "HydroDEM." Most of the software packages listed below can perform these functions on a "raw" DEM, or analysts can download hydrologically-conditioned DEMs such as the near-global HydroSHEDS, MERIT-Hydro, or EDNA for the continental United States. The usual steps for hydrologic conditioning of a DEM are:
# Fill sinks.
# "Burn in" the stream channels.
# Calculate flow direction.
# Calculate flow accumulation.
 Additionally, some methods allow for "fencing ridgelines" and burning in flow pathways through lakes. Some methods also enforce a small slope onto flat areas so that flow will continue to move toward the outlet. The step of "burning in" stream channels involves artificially deepening the channel, by subtracting a large elevation value from pixels that represent the channel. This ensures that once flow has entered the channel, it will stay there rather than jumping out and flowing overland or into another channel. Some algorithms infer the location of channels automatically from the DEM. Better results are usually obtained by burning in mapped stream channels, or channels derived from satellite or aerial imagery.
There are several different algorithms available for calculating flow direction from a DEM. The first method, introduced by Australian geographers O'Callaghan and Mark in 1984, is referred to as D8. Water flows from a pixel to one of 8 possible directions to a neighboring cell (including diagonally), based on the direction of steepest slope. There are disadvantages to this method as water flow is limited to 8 directions, separated by 45°, which may result in unrealistic flow patterns. Also, because all of the flow is routed in one direction, the D8 method is unable to model situations where the flow diverges, such as on convex hillsides, in a
Additionally, some methods allow for "fencing ridgelines" and burning in flow pathways through lakes. Some methods also enforce a small slope onto flat areas so that flow will continue to move toward the outlet. The step of "burning in" stream channels involves artificially deepening the channel, by subtracting a large elevation value from pixels that represent the channel. This ensures that once flow has entered the channel, it will stay there rather than jumping out and flowing overland or into another channel. Some algorithms infer the location of channels automatically from the DEM. Better results are usually obtained by burning in mapped stream channels, or channels derived from satellite or aerial imagery.
There are several different algorithms available for calculating flow direction from a DEM. The first method, introduced by Australian geographers O'Callaghan and Mark in 1984, is referred to as D8. Water flows from a pixel to one of 8 possible directions to a neighboring cell (including diagonally), based on the direction of steepest slope. There are disadvantages to this method as water flow is limited to 8 directions, separated by 45°, which may result in unrealistic flow patterns. Also, because all of the flow is routed in one direction, the D8 method is unable to model situations where the flow diverges, such as on convex hillsides, in a river delta
A river delta is a landform, archetypically triangular, created by the deposition of the sediments that are carried by the waters of a river, where the river merges with a body of slow-moving water or with a body of stagnant water. The creat ...
, or in branched or braided river
A braided river (also called braided channel or braided stream) consists of a network of river channel (geography), channels separated by small, often temporary, islands called ''braid bars'' or, in British English usage, ''aits'' or ''eyots''.
...
s. Alternative algorithms have been proposed and implemented to overcome this limitation, such as D∞. Nevertheless, the D8 algorithm remains in widespread use, and has been used to create important datasets such as HydroBasins and MERIT-Basins.
Computerized watershed delineation is not always correct. Some errors stem from incorrectly placing the watershed outlet on the digital river network, or "snapping the pour point." Another class of errors stems from inaccuracies in the digital terrain data, or where its resolution is too coarse to capture flow pathways. In general, DEMs with higher spatial resolution can more realistically describe topography of the land surface and flow direction. However, there is a tradeoff, as a finer grid with more pixels increases computing time. Nevertheless, even high-resolution data may not adequately capture flow pathways in complex environments like cities and suburbs, where flow is directed by curbs, culverts, and storm drains. Finally, some errors can result from the algorithm or the choice of parameters.
Because errors are common, some authorities insist that the results of automated delineation must be carefully checked. The US Geological Survey's standards for the US Watershed Boundary Dataset allow the use of software "to generate intermediate or “draft” boundary lines," which then must be verified by the analyst by overlaying them on a computer display over basemaps (scanned topographic maps, aerial photographs) to verify their accuracy.
Software for watershed delineation
Some of the first watershed delineation software was written in FORTRAN, such as CATCH and DEDNM. Watershed delineation tools are a part of severalGeographic Information System
A geographic information system (GIS) consists of integrated computer hardware and Geographic information system software, software that store, manage, Spatial analysis, analyze, edit, output, and Cartographic design, visualize Geographic data ...
software packages such as ArcGIS
ArcGIS is a family of client, server and online geographic information system (GIS) software developed and maintained by Esri.
ArcGIS was first released in 1982 as ARC/INFO, a command line-based GIS. ARC/INFO was later merged into ArcGIS De ...
, QGIS
QGIS is a geographic information system (GIS) software that is free and open-source. QGIS supports Windows, macOS, and Linux. It supports viewing, editing, printing, and analysis of geospatial data in a range of data formats. Its name comes from ...
, and GRASS GIS
''Geographic Resources Analysis Support System'' (commonly termed ''GRASS GIS'') is a geographic information system (GIS) software suite used for geospatial data management and analysis, image processing, producing graphics and maps, spatial and ...
. There are standalone programs for watershed delineation such as TauDEM. Watershed delineation tools are also incorporated into some hydrologic modeling software packages.
Software developers have also published libraries or modules in several languages (see list below). Many of these packages are free and open source, which means they can be expanded or adapted by those willing and able to write or modify code. Finally, there are web applications for delineating watersheds. Some of these web apps have extra features for science and engineering like calculating flow statistics or watershed land cover types (e.g.: StreamStats, Model My Watershed).
Standalone watershed delineation software
* TauDEM, Toolbox for ArcGIS, or command line executable for Windows. * TOPAZ, from the US Department of Agriculture, Windows executable.Hydrologic Modeling Software with Watershed Delineation Capability
*WMS (hydrology software)
SMS (Surface-water Modeling System) is a complete program for building and simulating surface water models from Aquaveo. It features 1D and 2D modeling and a unique conceptual model approach. Currently supported models include ADCIRC, CMS-FLOW2D ...
* SWAT model
SWAT (soil and water assessment tool) is a river basin scale model developed to quantify the impact of land management practices in large, complex watersheds. SWAT is a public domain software enabled model actively supported by the USDA Agricultur ...
* BASINS
* BasinMaker, for use with the RAVEN software suite, for parts of US and Canada only
* WEAP Model
GIS-based software
* ESRIArcGIS
ArcGIS is a family of client, server and online geographic information system (GIS) software developed and maintained by Esri.
ArcGIS was first released in 1982 as ARC/INFO, a command line-based GIS. ARC/INFO was later merged into ArcGIS De ...
or the ArcGIS online web application
* GRASS GIS
''Geographic Resources Analysis Support System'' (commonly termed ''GRASS GIS'') is a geographic information system (GIS) software suite used for geospatial data management and analysis, image processing, producing graphics and maps, spatial and ...
, modules r.water, r.watershed, and r.stream
* QGIS
QGIS is a geographic information system (GIS) software that is free and open-source. QGIS supports Windows, macOS, and Linux. It supports viewing, editing, printing, and analysis of geospatial data in a range of data formats. Its name comes from ...
* SAGA GIS
System for Automated Geoscientific Analyses (SAGA GIS) is a geographic information system (GIS) computer program, used to edit spatial data. It is free and open-source software, developed originally by a small team at the Department of Physical Ge ...
* Whitebox Geospatial Analysis Tools
Whitebox Geospatial Analysis Tools (GAT) is an Open-source software, open-source and cross-platform Geographic information system (GIS) and remote sensing software package that is distributed under the GNU General Public License. It has been ...
* ILWIS
Integrated Land and Water Information System (ILWIS) is a geographic information system (GIS) and remote sensing software for both vector and raster processing. Its features include digitizing, editing, analysis and display of data, and production ...
* TerrSet
TerrSet (formerly IDRISI) is an integrated geographic information system (GIS) and remote sensing software developed by Clark Labs at Clark University for the analysis and display of digital geospatial information. TerrSet is a PC raster-based s ...
(formerly IDRISI)
* TNTmips
TNTmips is a geospatial analysis system providing a fully featured GIS, RDBMS, and automated image processing system with CAD, TIN, surface modeling, map layout and innovative data publishing tools. TNTmips has a single integrated system with an i ...
* MapWindow GIS
* Manifold System
Manifold System is a geographic information system (GIS) software package developed by Manifold Software Limited that runs on Microsoft Windows. Manifold System handles both vector and raster data, includes spatial SQL, a built-in Internet Map Se ...
*
Web Applications
* Global Watersheds, web app and API * Stream Stats, from the US Geological Survey, allows you to delineate watersheds in the US only * Model My Watershed, by theStroud Water Research Center
The Stroud Water Research Center (the Stroud Center) is a not-for-profit organization performing freshwater research, environmental education, and watershed restoration; it is headquartered in Avondale, Pennsylvania. It was co-founded in 1967 by ...
, US only, can delineate watersheds based on an outlet point, and perform analyses related to water quality
* Ontario Watershed Information Tool, for the province of Ontario in Canada
Vector datasets of pre-delineated watersheds
There are a number of vector datasets representing watersheds as polygons that can be displayed and analyzed with GIS or other software. In these datasets, the entire land surface is divided into "subwatersheds" or "unit catchments." Individual unit watersheds can be combined or merged to find larger watersheds. The unit catchments have linkedhydrological code
A hydrological code or hydrologic unit code is a sequence of numbers or letters (a '' geocode'') that identify a hydrological unit or feature, such as a river, river reach, lake, or area like a drainage basin (also called watershed in North Ameri ...
data or similar metadata to create a flow network
In graph theory, a flow network (also known as a transportation network) is a directed graph where each edge has a capacity and each edge receives a flow. The amount of flow on an edge cannot exceed the capacity of the edge. Often in operations re ...
, so flow pathways and connections can be determined via network analysis.
 This list is non-exhaustive, as many organizations and territories have produced their own watershed map data and have published via the web. Notable datasets include:
* United States Watershed Boundary Dataset,
This list is non-exhaustive, as many organizations and territories have produced their own watershed map data and have published via the web. Notable datasets include:
* United States Watershed Boundary Dataset,website
(continually updated) * Canadian National Hydrographic Network Watershed Boundaries
website
* HydroBasins
website
(global, 2013) * Hydrologic Derivatives for Modeling and Applications (HDMA), (global, 2017) * MERIT-Basins
website
(global, 2021) * Hydrography90m,website
(2022, global, shows smaller headwater streams)
References
{{reflist Drainage basins Hydrology Geomorphology