Vidharba on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Vidarbha (Pronunciation: id̪Éɾb汃 is a geographical region in the
 According to the Hindu epic ''
According to the Hindu epic '' The coins and inscriptions from the period of Paramara king Jagadeva have been found in the northern parts the region. An inscription discovered at Jainad names Jagadeva as the son of the Paramara king Udayaditya (reigned c. 1060â1086). Scholar M. H. Krishna argued that the
The coins and inscriptions from the period of Paramara king Jagadeva have been found in the northern parts the region. An inscription discovered at Jainad names Jagadeva as the son of the Paramara king Udayaditya (reigned c. 1060â1086). Scholar M. H. Krishna argued that the
 Vidarbha lies in
Vidarbha lies in
 The
The
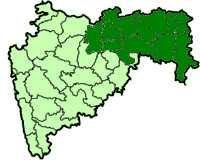 The Vidarbha movement started in the 1930s demanding a separate state of Vidarbha. The demand has been raised at times due to perceived neglect of the region by the
The Vidarbha movement started in the 1930s demanding a separate state of Vidarbha. The demand has been raised at times due to perceived neglect of the region by the
west India
Western India is a loosely defined region of India consisting of western states of Republic of India. The Ministry of Home Affairs in its Western Zonal Council Administrative division includes the states of Goa, Gujarat, and Maharashtra al ...
n state
State most commonly refers to:
* State (polity), a centralized political organization that regulates law and society within a territory
**Sovereign state, a sovereign polity in international law, commonly referred to as a country
**Nation state, a ...
of Maharashtra
Maharashtra () is a state in the western peninsular region of India occupying a substantial portion of the Deccan Plateau. It is bordered by the Arabian Sea to the west, the Indian states of Karnataka and Goa to the south, Telangana to th ...
. Forming the eastern part of the state, it comprises Amravati
Amravati (/Marathi phonology, ÉmáµÉ¾ÉÊáµt̪iË/) is a city in Maharashtra located in the Vidarbha region. It is the ninth largest city in Maharashtra, India & second largest city in the Vidarbha region in terms of population. It is the ...
and Nagpur
Nagpur (; ISO 15919, ISO: ''NÄgapura'') is the second capital and third-largest city of the Indian state of Maharashtra. It is called the heart of India because of its central geographical location. It is the largest and most populated city i ...
divisions. As per the 2011 Census, the region had a population of 23,003,179. The region occupies 31.6% of the total area and is home to 21.3% of the total population of Maharashtra. Situated in central India, it borders the state of Madhya Pradesh
Madhya Pradesh (; ; ) is a state in central India. Its capital is Bhopal and the largest city is Indore, Indore. Other major cities includes Gwalior, Jabalpur, and Sagar, Madhya Pradesh, Sagar. Madhya Pradesh is the List of states and union te ...
to the north, Chhattisgarh
Chhattisgarh (; ) is a landlocked States and union territories of India, state in Central India. It is the List of states and union territories of India by area, ninth largest state by area, and with a population of roughly 30 million, the List ...
to the east, Telangana
Telangana is a States and union territories of India, state in India situated in the Southern India, south-central part of the Indian subcontinent on the high Deccan Plateau. It is the List of states and union territories of India by area, ele ...
to the south and Marathwada
Marathwada () is a geographical region of the States and territories of India, Indian state of Maharashtra. It was formed during the Nizam of Hyderabad, Nizam's rule and was part of the then Hyderabad State. The region coincides with the Aurang ...
and Uttar Maharashtra regions of Maharashtra to the west.
According to the Hindu epic ''Mahabharata
The ''MahÄbhÄrata'' ( ; , , ) is one of the two major Sanskrit Indian epic poetry, epics of ancient India revered as Smriti texts in Hinduism, the other being the ''Ramayana, RÄmÄyaá¹a''. It narrates the events and aftermath of the Kuru ...
'', Rukmini
Rukmini (, ) is a Devi, Hindu goddess and the first queen of Krishna. She is described as the chief of Krishna's wives in DvÄrakÄ. Rukmini is revered as the avatar of Lakshmi and is venerated primarily in Warkari, and Haridasa tradition, and ...
, the wife of lord Krishna
Krishna (; Sanskrit language, Sanskrit: à¤à¥à¤·à¥à¤£, ) is a major deity in Hinduism. He is worshipped as the eighth avatar of Vishnu and also as the Supreme God (Hinduism), Supreme God in his own right. He is the god of protection, c ...
, was born to Bhishmaka, the king of the Vidarbha kingdom. Vidarbha was part of the Satavahana Empire
The Satavahanas (; ''SÄdavÄhana'' or ''SÄtavÄhana'', IAST: ), also referred to as the Andhras (also ''Andhra-bhá¹tyas'' or ''Andhra-jatiyas'') in the Puranas, were an ancient Indian dynasty. Most modern scholars believe that the Satavaha ...
during 1st to 2nd century CE). The coins and inscriptions from the period of Paramara king Jagadeva, the son of the Udayaditya (reigned c. 1060â1086) have been found in the northern parts the region. According to the ''Ain-i-Akbari
The ''Ain-i-Akbari'' (), or the "Administration of Akbar", is a 16th-century detailed document regarding the administration of the Mughal Empire under Emperor Akbar, written by his court historian, Abu'l Fazl, in the Persian language. It forms ...
'', the region was part of Berar Subah
The Berar Subah () was one of the Subahs (provinces) of the Mughal Empire, in Central India from 1596 to 1724. It bordered Golconda, Ahmandagar (both conquered in 1601), Kandesh and Malwa provinces as well as the independent and tributary kin ...
, in the Medieval period
In the history of Europe, the Middle Ages or medieval period lasted approximately from the 5th to the late 15th centuries, similarly to the post-classical period of World history (field), global history. It began with the fall of the West ...
. In 1680, the region was captured by Sambhaji
Sambhaji (Sambhajiraje Shivajiraje Bhonsle, ; 14 May 1657 â 11 March 1689), also known as Shambhuraje, ruled from 1681 to 1689 as the second king ( Chhatrapati) of the Maratha Empire, a prominent state in early modern India. He was the elde ...
, the son of Shivaji
Shivaji I (Shivaji Shahaji Bhonsale, ; 19 February 1630 â 3 April 1680) was an Indian ruler and a member of the Bhonsle dynasty. Shivaji carved out his own independent kingdom from the Sultanate of Bijapur that formed the genesis of the ...
, who was the founder of Maratha empire
The Maratha Empire, also referred to as the Maratha Confederacy, was an early modern India, early modern polity in the Indian subcontinent. It comprised the realms of the Peshwa and four major independent List of Maratha dynasties and states, Ma ...
. In 1724, Asaf Jah, who later became the Nizam of Hyderabad
Nizam of Hyderabad was the title of the ruler of Hyderabad State ( part of the Indian state of Telangana, and the Kalyana-Karnataka region of Karnataka). ''Nizam'' is a shortened form of (; ), and was the title bestowed upon Asaf Jah I wh ...
, declared independence and brought most of the region under his nominal rule. The administration and right of collecting taxes were held by the Marathas. In 1803, following the defeat of the Marathas, the region came under the rule of British East India Company
The East India Company (EIC) was an English, and later British, joint-stock company that was founded in 1600 and dissolved in 1874. It was formed to Indian Ocean trade, trade in the Indian Ocean region, initially with the East Indies (South A ...
. Later, the British Empire
The British Empire comprised the dominions, Crown colony, colonies, protectorates, League of Nations mandate, mandates, and other Dependent territory, territories ruled or administered by the United Kingdom and its predecessor states. It bega ...
took control of the region from the British East India Company in 1857, and the region was part of Berar and Central Provinces
The Central Provinces was a province of British India. It comprised British conquests from the Mughals and Marathas in central India, and covered parts of present-day Madhya Pradesh, Chhattisgarh and Maharashtra states. Nagpur was the primary ...
. After Indian Independence in 1947, the region remained a part of the Central Provinces and Berar
The Central Provinces and Berar was a province of British India and later the Dominion of India which existed from 1903 to 1950. It was formed by the merger of the Central Provinces with the province of Berar, which was territory leased by the ...
. After the Re-organization of Indian states, majority of the region became part of Bombay State
Bombay State was a large Indian state created in 1950 from the erstwhile Bombay Province, with other regions being added to it in the succeeding years. Bombay Province (in British India roughly equating to the present-day Indian state of Mah ...
in 1957. After the bifurcation of Bombay State
Bombay State was a large Indian state created in 1950 from the erstwhile Bombay Province, with other regions being added to it in the succeeding years. Bombay Province (in British India roughly equating to the present-day Indian state of Mah ...
, into Gujarat
Gujarat () is a States of India, state along the Western India, western coast of India. Its coastline of about is the longest in the country, most of which lies on the Kathiawar peninsula. Gujarat is the List of states and union territories ...
and Maharashtra
Maharashtra () is a state in the western peninsular region of India occupying a substantial portion of the Deccan Plateau. It is bordered by the Arabian Sea to the west, the Indian states of Karnataka and Goa to the south, Telangana to th ...
, the region became part of Maharashtra
Maharashtra () is a state in the western peninsular region of India occupying a substantial portion of the Deccan Plateau. It is bordered by the Arabian Sea to the west, the Indian states of Karnataka and Goa to the south, Telangana to th ...
.
The GDP
Gross domestic product (GDP) is a monetary measure of the total market value of all the final goods and services produced and rendered in a specific time period by a country or countries. GDP is often used to measure the economic performance o ...
of the region is estimated to be 2023-24. The economy of the region is largely dependent on agriculture
Agriculture encompasses crop and livestock production, aquaculture, and forestry for food and non-food products. Agriculture was a key factor in the rise of sedentary human civilization, whereby farming of domesticated species created ...
with oranges and cotton
Cotton (), first recorded in ancient India, is a soft, fluffy staple fiber that grows in a boll, or protective case, around the seeds of the cotton plants of the genus '' Gossypium'' in the mallow family Malvaceae. The fiber is almost pure ...
being the major crops. The region also holds considerable mineral resources and forest cover. The region is economically under developed compared to the rest of Maharashtra with considerable poverty
Poverty is a state or condition in which an individual lacks the financial resources and essentials for a basic standard of living. Poverty can have diverse Biophysical environmen ...
and malnutrition
Malnutrition occurs when an organism gets too few or too many nutrients, resulting in health problems. Specifically, it is a deficiency, excess, or imbalance of energy, protein and other nutrients which adversely affects the body's tissues a ...
. Agriculture is largely dependent on seasonal monsoons
A monsoon () is traditionally a seasonal reversing wind accompanied by corresponding changes in precipitation but is now used to describe seasonal changes in atmospheric circulation and precipitation associated with annual latitudinal oscil ...
and the region receives very less rainfall due to its location in the rain shadow
A rain shadow is an area of significantly reduced rainfall behind a mountainous region, on the side facing away from prevailing winds, known as its leeward side.
Evaporated moisture from body of water, bodies of water (such as oceans and larg ...
region of the Western Ghats. Drought
A drought is a period of drier-than-normal conditions.Douville, H., K. Raghavan, J. Renwick, R.P. Allan, P.A. Arias, M. Barlow, R. Cerezo-Mota, A. Cherchi, T.Y. Gan, J. Gergis, D. Jiang, A. Khan, W. Pokam Mba, D. Rosenfeld, J. Tierney, ...
s and famines are common with more than 1.4 lakh farmer suicide
Suicide is the act of intentionally causing one's own death.
Risk factors for suicide include mental disorders, physical disorders, and substance abuse. Some suicides are impulsive acts driven by stress (such as from financial or ac ...
s in the period 1997 to 2006.
The largest and major city in the region is Nagpur
Nagpur (; ISO 15919, ISO: ''NÄgapura'') is the second capital and third-largest city of the Indian state of Maharashtra. It is called the heart of India because of its central geographical location. It is the largest and most populated city i ...
and other major towns include Amravati
Amravati (/Marathi phonology, ÉmáµÉ¾ÉÊáµt̪iË/) is a city in Maharashtra located in the Vidarbha region. It is the ninth largest city in Maharashtra, India & second largest city in the Vidarbha region in terms of population. It is the ...
, Akola, Chandrapur and Gondia. Varhadi and Zadi dialects of Marathi
Marathi may refer to:
*Marathi people, an Indo-Aryan ethnolinguistic group of Maharashtra, India
**Marathi people (Uttar Pradesh), the Marathi people in the Indian state of Uttar Pradesh
*Marathi language, the Indo-Aryan language spoken by the Mar ...
is widely spoken. There have been demands for a separate state of Vidarbha, due to perceived neglect from the Government of Maharashtra
The Government of Maharashtra is the executive branch of the Indian states of india, state of Maharashtra. The government is led by the List of chief ministers of Maharashtra, chief minister (currently Devendra Fadnavis since 5 December 2024) ...
. While the demand is supported by major political parties BJP and Congress
A congress is a formal meeting of the representatives of different countries, constituent states, organizations, trade unions, political parties, or other groups. The term originated in Late Middle English to denote an encounter (meeting of ...
, it is opposed by Shiv Sena
Shiv Sena (1966â2022) (; ; SS) was a right-wing Marathi regionalist Hindutva-based political party in India founded in 1966 by Bal Thackeray, who was later succeeded by Uddhav Thackeray. The party is split into two parties: the Uddha ...
, one of the major regional political parties in the state.
History
 According to the Hindu epic ''
According to the Hindu epic ''Mahabharata
The ''MahÄbhÄrata'' ( ; , , ) is one of the two major Sanskrit Indian epic poetry, epics of ancient India revered as Smriti texts in Hinduism, the other being the ''Ramayana, RÄmÄyaá¹a''. It narrates the events and aftermath of the Kuru ...
'' and other '''' scriptures, princess Rukmini
Rukmini (, ) is a Devi, Hindu goddess and the first queen of Krishna. She is described as the chief of Krishna's wives in DvÄrakÄ. Rukmini is revered as the avatar of Lakshmi and is venerated primarily in Warkari, and Haridasa tradition, and ...
considered to be an incarnation of the goddess Lakshmi
Lakshmi (; , , sometimes spelled Laxmi, ), also known as Shri (, , ), is one of the principal goddesses in Hinduism, revered as the goddess of wealth, fortune, prosperity, beauty, fertility, sovereignty, and abundance. She along with Parvat ...
and the wife of lord Krishna
Krishna (; Sanskrit language, Sanskrit: à¤à¥à¤·à¥à¤£, ) is a major deity in Hinduism. He is worshipped as the eighth avatar of Vishnu and also as the Supreme God (Hinduism), Supreme God in his own right. He is the god of protection, c ...
, was born to Bhishmaka, the king of the Vidarbha kingdom. Vidarbha was part of the Satavahana Empire
The Satavahanas (; ''SÄdavÄhana'' or ''SÄtavÄhana'', IAST: ), also referred to as the Andhras (also ''Andhra-bhá¹tyas'' or ''Andhra-jatiyas'') in the Puranas, were an ancient Indian dynasty. Most modern scholars believe that the Satavaha ...
during 1st to 2nd century CE), ascertained by the Satavahana coins found in Pauni.
 The coins and inscriptions from the period of Paramara king Jagadeva have been found in the northern parts the region. An inscription discovered at Jainad names Jagadeva as the son of the Paramara king Udayaditya (reigned c. 1060â1086). Scholar M. H. Krishna argued that the
The coins and inscriptions from the period of Paramara king Jagadeva have been found in the northern parts the region. An inscription discovered at Jainad names Jagadeva as the son of the Paramara king Udayaditya (reigned c. 1060â1086). Scholar M. H. Krishna argued that the Chalukya
The Chalukya dynasty () was a Classical Indian dynasty that ruled large parts of southern and central India between the 6th and the 12th centuries. During this period, they ruled as three related yet individual dynasties. The earliest dynas ...
king Someshvara was known by the title "Jagadeva" ("Lord of the world") in the northern part of his kingdom, and it was he who issued these coins. However, all the known Chalukya coins featured Kannada script
The Kannada script ( IAST: ''Kannaá¸a lipi''; obsolete: Kanarese or Canarese script in English) is an abugida of the Brahmic family, used to write Kannada, one of the Dravidian languages of South India especially in the state of Karnataka. I ...
, while the coins of Jagadeva featured the Nagari script used by the Paramaras.
According to the ''Ain-i-Akbari
The ''Ain-i-Akbari'' (), or the "Administration of Akbar", is a 16th-century detailed document regarding the administration of the Mughal Empire under Emperor Akbar, written by his court historian, Abu'l Fazl, in the Persian language. It forms ...
'', the region was part of Berar Subah
The Berar Subah () was one of the Subahs (provinces) of the Mughal Empire, in Central India from 1596 to 1724. It bordered Golconda, Ahmandagar (both conquered in 1601), Kandesh and Malwa provinces as well as the independent and tributary kin ...
, known as the Gulshan-e-Berar in the Medieval period
In the history of Europe, the Middle Ages or medieval period lasted approximately from the 5th to the late 15th centuries, similarly to the post-classical period of World history (field), global history. It began with the fall of the West ...
. In 1680, the region was captured by Sambhaji
Sambhaji (Sambhajiraje Shivajiraje Bhonsle, ; 14 May 1657 â 11 March 1689), also known as Shambhuraje, ruled from 1681 to 1689 as the second king ( Chhatrapati) of the Maratha Empire, a prominent state in early modern India. He was the elde ...
, the son of Shivaji
Shivaji I (Shivaji Shahaji Bhonsale, ; 19 February 1630 â 3 April 1680) was an Indian ruler and a member of the Bhonsle dynasty. Shivaji carved out his own independent kingdom from the Sultanate of Bijapur that formed the genesis of the ...
who was the founder of Maratha empire
The Maratha Empire, also referred to as the Maratha Confederacy, was an early modern India, early modern polity in the Indian subcontinent. It comprised the realms of the Peshwa and four major independent List of Maratha dynasties and states, Ma ...
. In 1724, following a battle at Buldana
Buldhana (Marathi pronunciation: ) is a city and a Municipal Council in the Indian state of Maharashtra, established on 17 February 1893. It is the administrative headquarters of Buldhana District in the Amravati Division. Buldhana is the secon ...
, Asaf Jah defeated the Mughal governor and declared independence. Most of the region came under the nominal rule of Jah, who later became the Nizam of Hyderabad
Nizam of Hyderabad was the title of the ruler of Hyderabad State ( part of the Indian state of Telangana, and the Kalyana-Karnataka region of Karnataka). ''Nizam'' is a shortened form of (; ), and was the title bestowed upon Asaf Jah I wh ...
, though the administration and right of collecting chauth
Chauth (from ) was a regular tax or tribute imposed from the early 18th century by the Maratha Empire in the Indian subcontinent. It was an annual tax nominally levied at 25% on revenue or produce, hence the name, on lands that were under nominal M ...
were held by the Marathas. In 1803, following the defeat of the Marathas, the region came under the rule of British East India Company
The East India Company (EIC) was an English, and later British, joint-stock company that was founded in 1600 and dissolved in 1874. It was formed to Indian Ocean trade, trade in the Indian Ocean region, initially with the East Indies (South A ...
.
Later, the British Empire
The British Empire comprised the dominions, Crown colony, colonies, protectorates, League of Nations mandate, mandates, and other Dependent territory, territories ruled or administered by the United Kingdom and its predecessor states. It bega ...
took control of the region from the British East India Company in 1857. After Indian Independence in 1947, the region was part of the Bombay State
Bombay State was a large Indian state created in 1950 from the erstwhile Bombay Province, with other regions being added to it in the succeeding years. Bombay Province (in British India roughly equating to the present-day Indian state of Mah ...
. After the States Reorganisation Act
The States Reorganisation Act, 1956 was a major reform of the boundaries of India's States and union territories of India, states and territories, organising them along linguistic lines.
Although additional changes to India's state boundaries ...
, which re-organized state boundaries, majority of the region became part of Maharashtra
Maharashtra () is a state in the western peninsular region of India occupying a substantial portion of the Deccan Plateau. It is bordered by the Arabian Sea to the west, the Indian states of Karnataka and Goa to the south, Telangana to th ...
.
Geography
 Vidarbha lies in
Vidarbha lies in Central India
Central India refers to a geographical region of India that generally includes the states of Chhattisgarh and Madhya Pradesh.
The Central Zonal Council, established by the Government of India, includes these states as well as Uttar Prades ...
on the northern part of the Deccan Plateau
The Deccan is a plateau extending over an area of and occupies the majority of the Indian peninsula. It stretches from the Satpura Range, Satpura and Vindhya Ranges in the north to the northern fringes of Tamil Nadu in the south. It is bound ...
. It borders the state of Madhya Pradesh
Madhya Pradesh (; ; ) is a state in central India. Its capital is Bhopal and the largest city is Indore, Indore. Other major cities includes Gwalior, Jabalpur, and Sagar, Madhya Pradesh, Sagar. Madhya Pradesh is the List of states and union te ...
to the north, Chhattisgarh
Chhattisgarh (; ) is a landlocked States and union territories of India, state in Central India. It is the List of states and union territories of India by area, ninth largest state by area, and with a population of roughly 30 million, the List ...
to the east, Telangana
Telangana is a States and union territories of India, state in India situated in the Southern India, south-central part of the Indian subcontinent on the high Deccan Plateau. It is the List of states and union territories of India by area, ele ...
to the south and Marathwada
Marathwada () is a geographical region of the States and territories of India, Indian state of Maharashtra. It was formed during the Nizam of Hyderabad, Nizam's rule and was part of the then Hyderabad State. The region coincides with the Aurang ...
and Uttar Maharashtra regions of Maharashtra to the west. It lies in the rain shadow
A rain shadow is an area of significantly reduced rainfall behind a mountainous region, on the side facing away from prevailing winds, known as its leeward side.
Evaporated moisture from body of water, bodies of water (such as oceans and larg ...
region of the Western Ghats and the terrain is largely flat. The Satpura Range
The Satpura Range, formerly also known as the Seeonee Hills, is a range of hills in central India. The range rises in eastern Gujarat running east through the border of Maharashtra and Madhya Pradesh and ends in Chhattisgarh. The range paralle ...
lies to the north of Vidarbha region with Melghat in Amravati district
Amravati district (Marathi pronunciation: Help:IPA/Marathi, mɾaËÊÉt̪iË is a Districts of Maharashtra, district of Maharashtra state in central India. It is the administrative headquarter of Amravati division, which is one of the two ...
forming part of the southern offshoot of the Satpura Range. Large basalt
Basalt (; ) is an aphanite, aphanitic (fine-grained) extrusive igneous rock formed from the rapid cooling of low-viscosity lava rich in magnesium and iron (mafic lava) exposed at or very near the planetary surface, surface of a terrestrial ...
ic rock formations exists throughout the region, part of the 66-million-year-old volcanic Deccan Traps
The Deccan Traps are a large igneous province of west-central India (17â24°N, 73â74°E). They are one of the largest volcanic features on Earth, taking the form of a large shield volcano. They consist of many layers of solidified flood ...
. Bhandara and Gondia district are entirely occupied by metamorphic rock and alluvium, making their geology unique in Maharashtra. The Poorna river basin lies in Western Vidarbha and comprises Akola, Amaravati and Buldhana districts. The region has extremely high innate soil and water salinity.
Administration
Vidarbha has 11 districts divided into two divisions:Amravati
Amravati (/Marathi phonology, ÉmáµÉ¾ÉÊáµt̪iË/) is a city in Maharashtra located in the Vidarbha region. It is the ninth largest city in Maharashtra, India & second largest city in the Vidarbha region in terms of population. It is the ...
(earlier Berar) and Nagpur
Nagpur (; ISO 15919, ISO: ''NÄgapura'') is the second capital and third-largest city of the Indian state of Maharashtra. It is called the heart of India because of its central geographical location. It is the largest and most populated city i ...
divisions.
Each district has a collector's office which is responsible for day-to-day administration. The District Collector
The district magistrate, also known as the district collector or deputy commissioner, is a career civil servant who serves as the executive head of a district's administration in India. The specific name depends on the state or union territo ...
is a Central Indian Government IAS appointee who is in charge of the governance of a district in a state.
Demographics
Vidarbha has a total population of according to the 2011 India census. The region occupies 31.6% of the total area and is home to 21.3% of the total population of Maharashtra. According to the 2011 census,Hinduism
Hinduism () is an Hypernymy and hyponymy, umbrella term for a range of Indian religions, Indian List of religions and spiritual traditions#Indian religions, religious and spiritual traditions (Sampradaya, ''sampradaya''s) that are unified ...
was the principal religion in the state at 76.91% of the total population, while Buddhists
Buddhism, also known as Buddhadharma and Dharmavinaya, is an Indian religion and philosophical tradition based on teachings attributed to the Buddha, a wandering teacher who lived in the 6th or 5th century BCE. It is the world's fourth ...
constituted 13.08 of the total population. Vidarbha accounts for 45.91% of total Buddhists in Maharashtra
Maharashtra () is a state in the western peninsular region of India occupying a substantial portion of the Deccan Plateau. It is bordered by the Arabian Sea to the west, the Indian states of Karnataka and Goa to the south, Telangana to th ...
.
The largest city in the region is Nagpur
Nagpur (; ISO 15919, ISO: ''NÄgapura'') is the second capital and third-largest city of the Indian state of Maharashtra. It is called the heart of India because of its central geographical location. It is the largest and most populated city i ...
and other major cities include Amravati
Amravati (/Marathi phonology, ÉmáµÉ¾ÉÊáµt̪iË/) is a city in Maharashtra located in the Vidarbha region. It is the ninth largest city in Maharashtra, India & second largest city in the Vidarbha region in terms of population. It is the ...
, Akola, Chandrapur and Gondia.
Language and culture
As per the 2011 census, 73.72% of the population speaksMarathi
Marathi may refer to:
*Marathi people, an Indo-Aryan ethnolinguistic group of Maharashtra, India
**Marathi people (Uttar Pradesh), the Marathi people in the Indian state of Uttar Pradesh
*Marathi language, the Indo-Aryan language spoken by the Mar ...
, 8.30% Hindi
Modern Standard Hindi (, ), commonly referred to as Hindi, is the Standard language, standardised variety of the Hindustani language written in the Devanagari script. It is an official language of India, official language of the Government ...
, 6.23% Urdu
Urdu (; , , ) is an Indo-Aryan languages, Indo-Aryan language spoken chiefly in South Asia. It is the Languages of Pakistan, national language and ''lingua franca'' of Pakistan. In India, it is an Eighth Schedule to the Constitution of Indi ...
, 2.58% Lambadi
Lambadi, Lambani, Lamani or Banjari is a Western Indo-Aryan language spoken by the Banjara people across India. The language does not have a native script.
Regional dialects are divided between the Banjara of Maharashtra (written in Devanaga ...
, 1.83% Gondi, 1.10% Korku and 1.02% Telugu as their first language. Varhadi and Zadi dialects of Marathi
Marathi may refer to:
*Marathi people, an Indo-Aryan ethnolinguistic group of Maharashtra, India
**Marathi people (Uttar Pradesh), the Marathi people in the Indian state of Uttar Pradesh
*Marathi language, the Indo-Aryan language spoken by the Mar ...
are widely spoken.
Hindu
Hindus (; ; also known as SanÄtanÄ«s) are people who religiously adhere to Hinduism, also known by its endonym SanÄtana Dharma. Jeffery D. Long (2007), A Vision for Hinduism, IB Tauris, , pp. 35â37 Historically, the term has also be ...
festivals like Holi
Holi () is a major Hindu festival celebrated as the Festival of Colours, Love and Spring.The New Oxford Dictionary of English (1998) p. 874 "Holi /'hÉÊli:/ noun a Hindu spring festival ...".Yudit Greenberg, Encyclopedia of Love in World ...
, Diwali
Diwali (), also called Deepavali (IAST: ''DÄ«pÄvalÄ«'') or Deepawali (IAST: ''DÄ«pÄwalÄ«''), is the Hindu festival of lights, with variations celebrated in other Indian religions such as Jainism and Sikhism. It symbolises the spiritual v ...
and Dasara are celebrated throughout the region.
The Nagpur Central Museum ( 1863) maintains collections from the region.
Economy
 The
The GDP
Gross domestic product (GDP) is a monetary measure of the total market value of all the final goods and services produced and rendered in a specific time period by a country or countries. GDP is often used to measure the economic performance o ...
of the region is estimated to be 2022-23. The region also holds considerable mineral resources and forest cover. The region is economically under developed compared to the rest of Maharashtra with considerable poverty
Poverty is a state or condition in which an individual lacks the financial resources and essentials for a basic standard of living. Poverty can have diverse Biophysical environmen ...
and malnutrition
Malnutrition occurs when an organism gets too few or too many nutrients, resulting in health problems. Specifically, it is a deficiency, excess, or imbalance of energy, protein and other nutrients which adversely affects the body's tissues a ...
.
The economy of the region is largely dependent on agriculture
Agriculture encompasses crop and livestock production, aquaculture, and forestry for food and non-food products. Agriculture was a key factor in the rise of sedentary human civilization, whereby farming of domesticated species created ...
with oranges and cotton
Cotton (), first recorded in ancient India, is a soft, fluffy staple fiber that grows in a boll, or protective case, around the seeds of the cotton plants of the genus '' Gossypium'' in the mallow family Malvaceae. The fiber is almost pure ...
being the major crops. Agriculture is largely dependent on seasonal monsoons
A monsoon () is traditionally a seasonal reversing wind accompanied by corresponding changes in precipitation but is now used to describe seasonal changes in atmospheric circulation and precipitation associated with annual latitudinal oscil ...
and the region receives very less rainfall. Drought
A drought is a period of drier-than-normal conditions.Douville, H., K. Raghavan, J. Renwick, R.P. Allan, P.A. Arias, M. Barlow, R. Cerezo-Mota, A. Cherchi, T.Y. Gan, J. Gergis, D. Jiang, A. Khan, W. Pokam Mba, D. Rosenfeld, J. Tierney, ...
s and famines are common with more than 1.4 lakh farmer suicides in the period 1997 to 2006. Though the federal government
A federation (also called a federal state) is an entity characterized by a political union, union of partially federated state, self-governing provinces, states, or other regions under a #Federal governments, federal government (federalism) ...
has provided relief packages aimed at the region, with corruption rampant in the region. Columnist and journalist P Sainath opined that the relief packages were destined to fail as corruption in the government meant that little impact happened on the ground.
Nagpur is a major hub for business and healthcare. MIHAN is the major cargo hub in the region, operational out of Nagpur Airport.
Nagpur also hosts Information Technology
Information technology (IT) is a set of related fields within information and communications technology (ICT), that encompass computer systems, software, programming languages, data processing, data and information processing, and storage. Inf ...
Special Economic Zone
A special economic zone (SEZ) is an area in which the business and trade laws are different from the rest of the country. SEZs are located within a country's national borders, and their aims include increasing trade balance, employment, increas ...
(IT SEZ). for information-technology companies. Amravati and Yavatmal are known for cotton production. Chandrapur has a thermal power station
A thermal power station, also known as a thermal power plant, is a type of power station in which the heat energy generated from various fuel sources (e.g., coal, natural gas, nuclear fuel, etc.) is converted to electrical energy. The heat ...
, which is one of the biggest in India. There are other heavy industries and mines in the region.
The region has mineral resources with coal and manganese
Manganese is a chemical element; it has Symbol (chemistry), symbol Mn and atomic number 25. It is a hard, brittle, silvery metal, often found in minerals in combination with iron. Manganese was first isolated in the 1770s. It is a transition m ...
, the major minerals. Iron ore and limestone
Limestone is a type of carbonate rock, carbonate sedimentary rock which is the main source of the material Lime (material), lime. It is composed mostly of the minerals calcite and aragonite, which are different Polymorphism (materials science) ...
have also been identified as potential mining resources. Chandrapur district contributes 29% of all mineral output of Maharashtra.
Education
Sports and recreation
Cricket
Cricket is a Bat-and-ball games, bat-and-ball game played between two Sports team, teams of eleven players on a cricket field, field, at the centre of which is a cricket pitch, pitch with a wicket at each end, each comprising two Bail (cr ...
is the most popular sport in the region. Nagpur's Vidarbha Cricket Association Ground (VCA) hosted international cricket matches. In 2008, the new Vidarbha Cricket Association Stadium was built in Jamtha.
The eastern part of Vidarbha consists of Maharashtra's oldest National Park
A national park is a nature park designated for conservation (ethic), conservation purposes because of unparalleled national natural, historic, or cultural significance. It is an area of natural, semi-natural, or developed land that is protecte ...
, the Tadoba Andhari Tiger Reserve, one of the Project Tiger Reserves. Shegaon
Shegaon is a city and municipal council in the Buldana district, Buldhana district in the Indian States and territories of India, state of Maharashtra. Shegaon has become a pilgrimage centre due to the influence of Shri Sant Gajanan Maharaj, w ...
is a place of pilgrimage with temples attributed to the Hindu saint Gajanan Maharaj who lived there. Chikhaldara in Amravati district is a hill station
A hill station is a touristic town located at a higher elevation than the nearby plain or valley. The English term was originally used mostly in Western imperialism in Asia, colonial Asia, but also in Africa (albeit rarely), for towns founded by ...
and popular tourist destination.
Politics
Vidarbha has tenLok Sabha
The Lok Sabha, also known as the House of the People, is the lower house of Parliament of India which is Bicameralism, bicameral, where the upper house is Rajya Sabha. Member of Parliament, Lok Sabha, Members of the Lok Sabha are elected by a ...
constituencies. Nagpur district
Nagpur district (Marathi pronunciation: Help:IPA/Marathi, aËÉ¡puËɾ is a Districts of Maharashtra, district in the Vidarbha region of Maharashtra state in central India. The city of Nagpur is the district administrative centre. The district ...
has two seats Nagpur
Nagpur (; ISO 15919, ISO: ''NÄgapura'') is the second capital and third-largest city of the Indian state of Maharashtra. It is called the heart of India because of its central geographical location. It is the largest and most populated city i ...
and Ramtek, while Gadchiroli-Chimur Lok Sabha constituency is spread across districts of Chandrapur, Gadchiroli
Gadchiroli ( ¡ÉÉtÍ¡ÊiɾoliË is a city and a municipal council
A municipal council is the legislative body of a municipality or local government area. Depending on the location and classification of the municipality it may be known as ...
and Gondia. Yavatmal and Washim district
Washim district (Marathi pronunciation: Help:IPA/Marathi, aËÊim is a List of districts of Maharashtra, district in Maharashtra, India. The headquarters is at Washim. The area of the district is .
Officer
Members of Parliament
*Sanjay De ...
s form part of YavatmalâWashim Lok Sabha constituency
YavatmalâWashim Lok Sabha constituency is one of the 48 Lok Sabha (lower house of the Indian parliament) constituencies of Maharashtra state in western India. This constituency was created on 19 February 2008 as a part of the implementation of ...
. Other seats include Akola, Amravati
Amravati (/Marathi phonology, ÉmáµÉ¾ÉÊáµt̪iË/) is a city in Maharashtra located in the Vidarbha region. It is the ninth largest city in Maharashtra, India & second largest city in the Vidarbha region in terms of population. It is the ...
, Bhandara, Buldhana, Gondia, and Wardha. Amravati and Ramtek seats are reserved for Scheduled Caste candidates, while Gadchiroli-Chimur is reserved for Scheduled Tribes. In the Maharashtra Legislative Assembly
The Maharashtra Legislative Assembly (ISO: ''MahÄrÄá¹£á¹ra VidhÄna SabhÄ'') is the lower house of the bicameral legislature of Maharashtra state in western India. It consists of 288 members directly elected from single-seat constituenci ...
, the region is represented by 62 Vidhan Sabha
The State Legislative Assembly, also known as the Vidhan Sabha or the Saasana Sabha, is a legislative body in each of the states and certain union territories of India. Members of the legislative assembly are often directly elected to serve fiv ...
seats.
Demand for statehood
 The Vidarbha movement started in the 1930s demanding a separate state of Vidarbha. The demand has been raised at times due to perceived neglect of the region by the
The Vidarbha movement started in the 1930s demanding a separate state of Vidarbha. The demand has been raised at times due to perceived neglect of the region by the Government of Maharashtra
The Government of Maharashtra is the executive branch of the Indian states of india, state of Maharashtra. The government is led by the List of chief ministers of Maharashtra, chief minister (currently Devendra Fadnavis since 5 December 2024) ...
. While the demand is supported by major political parties BJP and Congress
A congress is a formal meeting of the representatives of different countries, constituent states, organizations, trade unions, political parties, or other groups. The term originated in Late Middle English to denote an encounter (meeting of ...
, it is opposed by Shiv Sena
Shiv Sena (1966â2022) (; ; SS) was a right-wing Marathi regionalist Hindutva-based political party in India founded in 1966 by Bal Thackeray, who was later succeeded by Uddhav Thackeray. The party is split into two parties: the Uddha ...
, one of the major regional political parties in the state. Political economist Shrikant Jichkar opposed the separation of the region from Maharashtra, stating that it was not sustainable. He noted that income from available natural resources would not be able to balance the subsidies given by the government, whose cooperation would be vital to any development and that the division introduces societal risks due to dividing of the Marathi-speaking state.
See also
* Dehani lift irrigation scheme * List of cities in Vidarbha * List of Maratha dynasties and states * Manav Vikas Mission *Proposed states and territories of India
The constitutional power to create new states and union territories in India is solely reserved with the Parliament of India, which can do so by announcing new states/union territories, separating territory from an existing state or merging tw ...
References
External links
{{Proposed states and territories of India Regions of India Regions of Maharashtra Proposed states and union territories of India