Victor Skumin on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Victor Andreevich Skumin ( rus, Ви́ктор Андре́евич Ску́мин, p=ˈvʲiktər ɐnˈdrʲejɪvʲɪtɕ ˈskumʲɪn, born 30 August 1948) is a Russian and Soviet scientist,
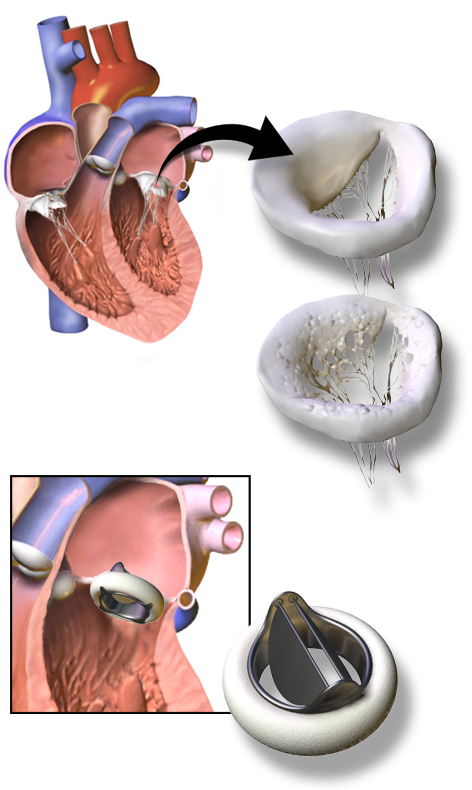 ''Skumin syndrome'' () was described by Skumin in 1978. as a ''cardioprosthetic psychopathological syndrome'', associated with mechanical heart valve implant and manifested by irrational fear,
''Skumin syndrome'' () was described by Skumin in 1978. as a ''cardioprosthetic psychopathological syndrome'', associated with mechanical heart valve implant and manifested by irrational fear,
 In the
In the
World Organisation of Culture of Health
{{DEFAULTSORT:Skumin, Victor 1948 births 20th-century Russian philosophers 20th-century Russian writers 21st-century Russian philosophers 21st-century Russian writers Cosmists Kharkiv National Medical University people Living people New Age writers People from Penza Oblast Russian psychiatrists Russian transhumanists Soviet psychiatrists Soviet scientists Spiritual writers Russian scientists
psychiatrist
A psychiatrist is a physician who specializes in psychiatry. Psychiatrists are physicians who evaluate patients to determine whether their symptoms are the result of a physical illness, a combination of physical and mental ailments or strictly ...
, philosopher and writer.
After graduating from the Kharkiv National Medical University in 1973, he became a psychotherapist in Kiev Institute of Cardiovascular Surgery. In 1978, he described a new disease, the Skumin syndrome. He introduced a method of psychotherapy
Psychotherapy (also psychological therapy, talk therapy, or talking therapy) is the use of Psychology, psychological methods, particularly when based on regular Conversation, personal interaction, to help a person change behavior, increase hap ...
and self-improvement
Personal development or self-improvement consists of activities that develops a person's capabilities and potential, enhance quality of life, and facilitate the realization of dreams and aspirations. Personal development may take place over the c ...
based on optimistic autosuggestion
Autosuggestion is a psychological technique related to the placebo effect, developed by pharmacist Émile Coué at the beginning of the 20th century. It is a form of self-induced suggestion in which individuals guide their own thoughts, feelings ...
for psychological rehabilitation of cardiosurgical patients (1979).
From 1980 to 1990, he was professor of psychotherapy at the Kharkiv Medical Academy of Post-graduate Education
Kharkiv Medical Academy of Post-graduate Education is a Ukrainian university in Kharkiv.
History
The Kharkiv Medical Academy of Postgraduate Education was established on 11 November 1923 and was called “ Ukrainian State Institute for Advanc ...
. The main result of his scientific activity was the discovery of the "syndrome of the neurotic phantom of somatic disease" and a "concept of the mental constituent of a chronic somatic disease".
From 1990 to 1994, Skumin held positions as chaired professor of psychology
Psychology is the scientific study of mind and behavior. Its subject matter includes the behavior of humans and nonhumans, both consciousness, conscious and Unconscious mind, unconscious phenomena, and mental processes such as thoughts, feel ...
and pedagogy
Pedagogy (), most commonly understood as the approach to teaching, is the theory and practice of learning, and how this process influences, and is influenced by, the social, political, and psychological development of learners. Pedagogy, taken ...
, and of physical education
Physical education is an academic subject taught in schools worldwide, encompassing Primary education, primary, Secondary education, secondary, and sometimes tertiary education. It is often referred to as Phys. Ed. or PE, and in the United Stat ...
and Health life at the Kharkiv State Academy of Culture. In 1994, he was elected to the post of the President-founder of the World Organisation of Culture of Health (Moscow
Moscow is the Capital city, capital and List of cities and towns in Russia by population, largest city of Russia, standing on the Moskva (river), Moskva River in Central Russia. It has a population estimated at over 13 million residents with ...
). In 1995, Skumin became the first editor-in-chief of the journal '' To Health via Culture''. He is known for inventing a popular term "Culture of Health" (1968).
Besides psychiatry
Psychiatry is the medical specialty devoted to the diagnosis, treatment, and prevention of deleterious mental disorder, mental conditions. These include matters related to cognition, perceptions, Mood (psychology), mood, emotion, and behavior.
...
and psychology, Skumin writes on healthy lifestyle, yoga
Yoga (UK: , US: ; 'yoga' ; ) is a group of physical, mental, and spiritual practices or disciplines that originated with its own philosophy in ancient India, aimed at controlling body and mind to attain various salvation goals, as pra ...
, and philosophy. He co-authored series of illustrated books and articles on Agni Yoga
Agni Yoga () or the Living Ethics (), or the Teaching of Life (), is a Neo-Theosophical religious doctrine transmitted by Helena Roerich and Nicholas Roerich from 1920. The term ''Agni Yoga'' means "Mergence with Divine Fire" or "Path to Me ...
, Roerichism
Roerichism or RerikhismPhilip Walters. ''Religion, State & Society''. Volume 28, Issue 1, 2000. Quote from the ''Editorial'': "'Rerikhism' is an example of a thoroughly Russian new religious movement". (Russian: Рерихи́зм, Рерих ...
, Russian cosmism
Russian cosmism (Russian: Русский космизм), or simply cosmism, is a philosophical and cultural movement that emerged in late 19th- and early 20th-century Russia, integrating science, religion, and metaphysics into a unified worldvie ...
, transhumanism
Transhumanism is a philosophical and intellectual movement that advocates the human enhancement, enhancement of the human condition by developing and making widely available new and future technologies that can greatly enhance longevity, cogni ...
, and New Age
New Age is a range of Spirituality, spiritual or Religion, religious practices and beliefs that rapidly grew in Western world, Western society during the early 1970s. Its highly eclecticism, eclectic and unsystematic structure makes a precise d ...
. He wrote books of fiction and lyrics for several songs.
Early life and education
Victor Skumin was born on 30 August 1948 inPenza Oblast
Penza Oblast () is a federal subjects of Russia, federal subject of Russia (an oblast). Its administrative center is the types of inhabited localities in Russia, city of Penza. As of the Russian Census (2010), 2010 Census, its population was ...
, RSFSR
The Russian Soviet Federative Socialist Republic (Russian SFSR or RSFSR), previously known as the Russian Socialist Federative Soviet Republic and the Russian Soviet Republic, and unofficially as Soviet Russia,Declaration of Rights of the labo ...
, where his father – Andrew Skumin
The Skumin family ( rus, Ску́мин, p=ˈskumʲɪn) is a prominent Lithuanian nobility, Lithuanian, Polish nobility, Polish and Russian nobility, Russian noble family.
Notable people with the surname
*:ru:Скумин-Тышкевич, Але ...
( rus, Андре́й Ску́мин, p=ɐnˈdrʲej ˈskumʲɪn) – was an officer
An officer is a person who has a position of authority in a hierarchical organization. The term derives from Old French ''oficier'' "officer, official" (early 14c., Modern French ''officier''), from Medieval Latin ''officiarius'' "an officer," fro ...
of MGB of the USSR. He was the Colonel
Colonel ( ; abbreviated as Col., Col, or COL) is a senior military Officer (armed forces), officer rank used in many countries. It is also used in some police forces and paramilitary organizations.
In the 17th, 18th, and 19th centuries, a colon ...
of Justice, WWII
World War II or the Second World War (1 September 1939 – 2 September 1945) was a World war, global conflict between two coalitions: the Allies of World War II, Allies and the Axis powers. World War II by country, Nearly all of the wo ...
Veteran. After the birth of Victor, the family moved to the city of Kazan
Kazan; , IPA: Help:IPA/Tatar, ɑzanis the largest city and capital city, capital of Tatarstan, Russia. The city lies at the confluence of the Volga and the Kazanka (river), Kazanka Rivers, covering an area of , with a population of over 1. ...
, where his father was appointed to the post of Chairman of the Military Tribunal
Military justice (or military law) is the body of laws and procedures governing members of the armed forces. Many nation-states have separate and distinct bodies of law that govern the conduct of members of their armed forces. Some states us ...
of the Internal Troops of the Volga Military District
The Volga Military District (PriVO) was a military district of the Soviet Union and the Russian Federation that existed from 1918 to 1989 and 1992 to 2001.
The district headquarters was located at Kazan, Saratov and Kuibyshev (Samara) at differen ...
.
The family many times moved from one city to another, where Andrew Skumin was appointed to a new post. These cities, in particular, were Penza
Penza (, ) is the largest types of inhabited localities in Russia, city and administrative center of Penza Oblast, Russia. It is located on the Sura (river), Sura River, southeast of Moscow. As of the 2010 Russian census, 2010 Census, Penza had ...
, Chelyabinsk
Chelyabinsk; , is the administrative center and largest types of inhabited localities in Russia, city of Chelyabinsk Oblast, Russia. It is the List of cities and towns in Russia by population, seventh-largest city in Russia, with a population ...
, and Petrozavodsk
Petrozavodsk (, ; Karelian language, Karelian, Veps language, Vepsian and ) is the capital city of the Republic of Karelia, Russia, which stretches along the western shore of Lake Onega for some . The population of the city is 280,890 as of 2022.
...
. For this reason, he studied in various educational institutions
An educational institution is a place where people of different ages gain an education, including preschools, childcare, primary-elementary schools, secondary-high schools, and universities. They provide a large variety of learning environments a ...
.
Skumin studied medicine at the Kharkiv National Medical University. The history of the higher medical school in Kharkiv
Kharkiv, also known as Kharkov, is the second-largest List of cities in Ukraine, city in Ukraine.
is more than 200 years long and closely connected with the history of Vasily Karazin Kharkiv National University, because it sprang from its Medical Faculty. The University – one of the oldest University of the Russian Empire
The Russian Empire was an empire that spanned most of northern Eurasia from its establishment in November 1721 until the proclamation of the Russian Republic in September 1917. At its height in the late 19th century, it covered about , roughl ...
and the Soviet Union
The Union of Soviet Socialist Republics. (USSR), commonly known as the Soviet Union, was a List of former transcontinental countries#Since 1700, transcontinental country that spanned much of Eurasia from 1922 until Dissolution of the Soviet ...
– was founded in 1804, a decree about its foundation was signed by the Emperor of Russia
The emperor and autocrat of all Russia (, ), also translated as emperor and autocrat of all the Russias, was the official title of the List of Russian monarchs, Russian monarch from 1721 to 1917.
The title originated in connection with Russia's ...
Alexander I Alexander I may refer to:
* Alexander I of Macedon, king of Macedon from 495 to 454 BC
* Alexander I of Epirus (370–331 BC), king of Epirus
* Alexander I Theopator Euergetes, surnamed Balas, ruler of the Seleucid Empire 150-145 BC
* Pope Alex ...
, and the first Statutes of the University were approved at that time. In the Kharkiv University were laid high scientific standards. Its history is connected with the names of the Nobel Laureates
The Nobel Prizes (, ) are awarded annually by the Royal Swedish Academy of Sciences, the Swedish Academy, the Karolinska Institutet, and the Norwegian Nobel Committee to individuals and organizations who make outstanding contributions in th ...
– Lev Landau
Lev Davidovich Landau (; 22 January 1908 – 1 April 1968) was a Soviet physicist who made fundamental contributions to many areas of theoretical physics. He was considered as one of the last scientists who were universally well-versed and ma ...
, Simon Kuznets
Simon Smith Kuznets ( ; rus, Семён Абра́мович Кузне́ц, p=sʲɪˈmʲɵn ɐˈbraməvʲɪtɕ kʊzʲˈnʲets; April 30, 1901 – July 8, 1985) was a Russian-born American economist and statistician who received the 1971 Nobe ...
, Élie Metchnikoff
Ilya Ilyich Mechnikov (; – 15 July 1916), also spelled Élie Metchnikoff, was a zoologist from the Russian Empire of Moldavian noble ancestry and alshereat archive.org best known for his research in immunology (study of immune systems) and ...
– and other distinguished scientists.
Skumin graduated the Medical University in 1973 with diploma with honours. In 1968, when he was still a medical student
A medical school is a tertiary educational institution, professional school, or forms a part of such an institution, that teaches medicine, and awards a professional degree for physicians. Such medical degrees include the Bachelor of Medicine, ...
, he proposed the term ''Culture of Health'' (), which has become widespread. The main task of a Culture of Health is to implement innovative health programs that support a holistic approach to physical, mental and spiritual well-being.
Victor Skumin is married. He has two sons – Andrew and Maxim, as well as granddaughter Alice Skumina and grandson Alexey Skumin.
Contribution to psychiatry and psychotherapy
Cardiac surgery
Skumin researched from 1976 to 1980 psychological and psychiatric problems of cardiac surgery under the mentorship of Nikolai Amosov, who was the founder and first director of the Kiev Institute of Cardiovascular Surgery. This Institute was the first to conduct surgical treatment of heart diseases in theUkrainian SSR
The Ukrainian Soviet Socialist Republic, abbreviated as the Ukrainian SSR, UkrSSR, and also known as Soviet Ukraine or just Ukraine, was one of the Republics of the Soviet Union, constituent republics of the Soviet Union from 1922 until 1991. ...
(since 1955), the Institute began to conduct operations with extracorporeal
An extracorporeal procedure is a medical procedure which is performed outside the body. Extracorporeal devices are the artificial organs that remain outside the body while treating a patient. Extracorporeal devices are useful in hemodialysis and ...
circulation (1958), and mitral valve replacement
Mitral valve replacement is a procedure whereby the diseased mitral valve of a patient's heart is replaced by either a mechanical or tissue (bioprosthetic) valve.
The mitral valve may need to be replaced because:
* The valve is leaky ( mitral v ...
s (1963). In 1961, Amosov was awarded Lenin Prize
The Lenin Prize (, ) was one of the most prestigious awards of the Soviet Union for accomplishments relating to science, literature, arts, architecture, and technology. It was originally created on June 23, 1925, and awarded until 1934. During ...
for the work of surgery.
Since a valve replacement is a heart
The heart is a muscular Organ (biology), organ found in humans and other animals. This organ pumps blood through the blood vessels. The heart and blood vessels together make the circulatory system. The pumped blood carries oxygen and nutrie ...
surgical procedure, it requires placing the patient on cardiopulmonary bypass
Cardiopulmonary bypass (CPB) or heart-lung machine, also called the pump or CPB pump, is a machine that temporarily takes over the function of the heart and lungs during open-heart surgery by maintaining the circulation of blood and oxygen throug ...
. With a valve replacement surgery, there are some risks
In simple terms, risk is the possibility of something bad happening. Risk involves uncertainty about the effects/implications of an activity with respect to something that humans value (such as health, well-being, wealth, property or the environ ...
. Skumin researched a neuropsychological and psychopathologic changes following open heart surgery, nonpsychotic mental disorders in patients with valvular heart disease
Valvular heart disease is any cardiovascular disease process involving one or more of the four valves of the heart (the aortic and mitral valves on the left side of heart and the pulmonic and tricuspid valves on the right side of heart). The ...
before and after surgery, associated with mechanical artificial heart valve (MHV) implant.
An artificial heart valve is a device implanted in the heart of a patient with valvular heart disease, congenital heart defect
A congenital heart defect (CHD), also known as a congenital heart anomaly, congenital cardiovascular malformation, and congenital heart disease, is a defect in the structure of the heart or great vessels that is present at birth. A congenital h ...
, etc. When one or two of the four heart valve
A heart valve is a biological one-way valve that allows blood to flow in one direction through the chambers of the heart. A mammalian heart usually has four valves. Together, the valves determine the direction of blood flow through the heart. Hea ...
s malfunctions, the medical choice may be to replace the natural valve with an artificial valve. There are three major types of mechanical valves with many modifications on these designs. This requires open heart surgery. The mechanical valves are made from metal and pyrolytic carbon
Pyrolytic carbon is a material similar to graphite, but with some covalent bonding between its graphene sheets as a result of imperfections in its production.
Pyrolytic carbon is man-made and is thought not to be found in nature.Ratner, Buddy D ...
, and can last a lifetime. All MHV function in the human body creating a unique sound effects and vibration. Patients with mechanical valves must take blood-thinning medications to prevent clot
A thrombus ( thrombi) is a solid or semisolid aggregate from constituents of the blood (platelets, fibrin, red blood cells, white blood cells) within the circulatory system during life. A blood clot is the final product of the blood coagulatio ...
ting. The choice of which valve type to use depends upon the patient's age, medical condition, preferences with medication, and lifestyle.
 ''Skumin syndrome'' () was described by Skumin in 1978. as a ''cardioprosthetic psychopathological syndrome'', associated with mechanical heart valve implant and manifested by irrational fear,
''Skumin syndrome'' () was described by Skumin in 1978. as a ''cardioprosthetic psychopathological syndrome'', associated with mechanical heart valve implant and manifested by irrational fear, anxiety
Anxiety is an emotion characterised by an unpleasant state of inner wikt:turmoil, turmoil and includes feelings of dread over Anticipation, anticipated events. Anxiety is different from fear in that fear is defined as the emotional response ...
, depression and sleep disorder
A sleep disorder, or somnipathy, is a medical disorder affecting an individual's sleep patterns, sometimes impacting physical, mental, social, and emotional functioning. Polysomnography and actigraphy are tests commonly ordered for diagnosing sle ...
. This syndrome
A syndrome is a set of medical signs and symptoms which are correlated with each other and often associated with a particular disease or disorder. The word derives from the Greek language, Greek σύνδρομον, meaning "concurrence". When a sy ...
is often accompanied by asthenia
Weakness is a symptom of many different medical conditions. The causes are many and can be divided into conditions that have true or perceived muscle weakness. True muscle weakness is a primary symptom of a variety of skeletal muscle diseases, ...
. Alain Carpentier – a member of the French Academy of Sciences
The French Academy of Sciences (, ) is a learned society, founded in 1666 by Louis XIV at the suggestion of Jean-Baptiste Colbert, to encourage and protect the spirit of French Scientific method, scientific research. It was at the forefron ...
and the head the Department of Cardiovascular Surgery at the Hôpital Européen Georges-Pompidou in Paris – believed in 2011 that Skumin syndrome develops in a quarter of the patients with an artificial heart valve. It is possible that a similar problem arises in the conduct of operations to implement an artificial heart
An artificial heart is a artificial organ, device that replaces the human heart, heart. Artificial hearts are typically used as a bridge to heart transplantation, but ongoing research aims to develop a device that could permanently replace the ...
.
The Russia's international news agency ''RIA Novosti
RIA Novosti (), sometimes referred to as RIAN () or RIA (), is a Russian state-owned domestic news agency. On 9 December 2013, by a decree of Vladimir Putin, it was liquidated and its assets and workforce were transferred to the newly created ...
'', operating under the purview of the Russian Ministry of Communications and Mass Media, wrote about this problem (2014),
The methods and the main principles of such therapy and neuropsychological rehabilitation are described and its efficacy was demonstrated. Skumin proposed mixture
In chemistry, a mixture is a material made up of two or more different chemical substances which can be separated by physical method. It is an impure substance made up of 2 or more elements or compounds mechanically mixed together in any proporti ...
subsequently named after him. Skumin's mixture () is a medicine with a sedative effect, affecting the central nervous system
The central nervous system (CNS) is the part of the nervous system consisting primarily of the brain, spinal cord and retina. The CNS is so named because the brain integrates the received information and coordinates and influences the activity o ...
. It is used to treat Skumin syndrome, light forms of heart failure, anxiety and sleep disorders, and asthenia. The medicine is known to be well tolerated, with no contra-indications, except sensitivity. The formula contains Adonis vernalis
''Adonis vernalis'', known variously as pheasant's eye, spring pheasant's eye, yellow pheasant's eye and false hellebore, is a perennial plant, perennial flowering plant in the buttercup family Ranunculaceae. It is found in dry meadows and steppe ...
, Crataegus
''Crataegus'' (), commonly called hawthorn, quickthorn, thornapple, Voss, E. G. 1985. ''Michigan Flora: A guide to the identification and occurrence of the native and naturalized seed-plants of the state. Part II: Dicots (Saururaceae–Cornacea ...
, Valerian root, Leonurus cardiaca
''Leonurus cardiaca'', known as motherwort, is an herbaceous perennial plant in the mint family, Lamiaceae. Other common names include throw-wort, lion's ear, and lion's tail. Lion's tail is also a common name for ''Leonotis leonurus'', and lion' ...
, Eucalyptus
''Eucalyptus'' () is a genus of more than 700 species of flowering plants in the family Myrtaceae. Most species of ''Eucalyptus'' are trees, often Mallee (habit), mallees, and a few are shrubs. Along with several other genera in the tribe Eucalyp ...
, Peppermint
Peppermint (''Mentha'' × ''piperita'') is a Hybrid (biology), hybrid species of Mentha, mint, a cross between Mentha aquatica, watermint and spearmint. Indigenous to Europe and the Middle East, the plant is now widely spread and cultivated in m ...
, and Rose hip
The rose hip or rosehip, also called rose haw and rose hep, is the accessory fruit of the various species of rose plant. It is typically red to orange, but ranges from dark purple to black in some species. Rose hips begin to form after pollina ...
.
For psychological rehabilitation, Skumin improved psychological function by calming the nervous system, enhancing relaxation, increasing body awareness and decreasing general anxiety.
In 1979, Skumin created a special modification of mind control method for psychological rehabilitation of cardiosurgical patients. This method is based on autogenic training
Autogenic training is a relaxation technique first published by the German and Nazi psychiatrist Johannes Heinrich Schultz in 1932. The technique involves repetitions of a set of visualisations accompanied by vocal suggestions that induce a sta ...
. Autogenic training is a relaxation technique
A relaxation technique (also known as relaxation training) is any method, process, procedure, or activity that helps a person to relax; attain a state of increased calmness; or otherwise reduce levels of pain, anxiety, stress or anger. Relaxat ...
developed by the psychiatrist Johannes Heinrich Schultz
Johannes Heinrich Schultz (20 June 1884 – 19 September 1970) was a German psychiatrist and psychotherapist. Schultz is known for the development of autogenic training.
Life
He studied medicine in Lausanne, Göttingen (where he met Karl Jas ...
. He emphasized parallels to techniques in yoga
Yoga (UK: , US: ; 'yoga' ; ) is a group of physical, mental, and spiritual practices or disciplines that originated with its own philosophy in ancient India, aimed at controlling body and mind to attain various salvation goals, as pra ...
and meditation
Meditation is a practice in which an individual uses a technique to train attention and awareness and detach from reflexive, "discursive thinking", achieving a mentally clear and emotionally calm and stable state, while not judging the meditat ...
. It is a method for influencing one's autonomic nervous system
The autonomic nervous system (ANS), sometimes called the visceral nervous system and formerly the vegetative nervous system, is a division of the nervous system that operates viscera, internal organs, smooth muscle and glands. The autonomic nervo ...
. The technique involves the daily practice of sessions that last around 15 minutes, usually in the morning, at lunch time, and in the evening. During each session, the practitioner will repeat a set of visualisations that induce a state of relaxation. Each session can be practiced in a position chosen amongst a set of recommended postures.
The technique of the Skumin mind control method () involves the use of two standard postures: sitting meditation and lying down meditation. This method of psychotraining includes five psychological exercises: the first is "the relaxation", the second one is "the warming", the third one is "the zero gravity", the fourth one is "the target autosuggestion
Autosuggestion is a psychological technique related to the placebo effect, developed by pharmacist Émile Coué at the beginning of the 20th century. It is a form of self-induced suggestion in which individuals guide their own thoughts, feelings ...
", and the fifth exercise is "the psychological activation". Each session contain explanation of the theory and practice of each new exercise as it is reached. The therapeutic effect is achieved by the neutralization of traumatic emotional experiences and the progressive reorganization of the psychic structures to include previously unacceptable mental contents, too. This method of psychotherapy has found application in medical practice, in particular in the treatment of phobia
A phobia is an anxiety disorder, defined by an irrational, unrealistic, persistent and excessive fear of an object or situation. Phobias typically result in a rapid onset of fear and are usually present for more than six months. Those affected ...
s, headache
A headache, also known as cephalalgia, is the symptom of pain in the face, head, or neck. It can occur as a migraine, tension-type headache, or cluster headache. There is an increased risk of Depression (mood), depression in those with severe ...
s, etc.
Skumin's priority on the description of this syndrome and the establishment of effective methods of treatment and rehabilitation of cardiosurgical patients confirmed Nikolai Amosov and Yakov Bendet, Alain Carpentier, and many others. The Higher Attestation Commission under the USSR Council of Ministers awarded him for this research study the degree of Candidate of Sciences
A Candidate of Sciences is a Doctor of Philosophy, PhD-equivalent academic research degree in all the post-Soviet countries with the exception of Ukraine, and until the 1990s it was also awarded in Central and Eastern European countries. It is ...
(1980). It is a first post-graduate scientific degree in some former Eastern Bloc
The Eastern Bloc, also known as the Communist Bloc (Combloc), the Socialist Bloc, the Workers Bloc, and the Soviet Bloc, was an unofficial coalition of communist states of Central and Eastern Europe, Asia, Africa, and Latin America that were a ...
countries.
Gastroenterology
From 1980 to 1990, he worked as professor ofpsychotherapy
Psychotherapy (also psychological therapy, talk therapy, or talking therapy) is the use of Psychology, psychological methods, particularly when based on regular Conversation, personal interaction, to help a person change behavior, increase hap ...
at the Kharkiv Medical Academy of Post-graduate Education
Kharkiv Medical Academy of Post-graduate Education is a Ukrainian university in Kharkiv.
History
The Kharkiv Medical Academy of Postgraduate Education was established on 11 November 1923 and was called “ Ukrainian State Institute for Advanc ...
. During this period Skumin investigated mental health disorder
A mental disorder, also referred to as a mental illness, a mental health condition, or a psychiatric disability, is a behavioral or mental pattern that causes significant distress or impairment of personal functioning. A mental disorder is ...
in chronic diseases of the digestive system
The human digestive system consists of the gastrointestinal tract plus the accessory organs of digestion (the tongue, salivary glands, pancreas, liver, and gallbladder). Digestion involves the breakdown of food into smaller and smaller compone ...
in children and adolescents.
A most significant life event in the first years of life is a disease, especially if it is of early onset, severe, life-threatening, with an uncertain prognosis, and with the necessity of frequent diagnostic and therapeutic interventions. Psychological implications are a significant part of the illness, not a marginal component; they can affect prognosis and outcome. Various laboratory tests, physical examination
In a physical examination, medical examination, clinical examination, or medical checkup, a medical practitioner examines a patient for any possible medical signs or symptoms of a Disease, medical condition. It generally consists of a series of ...
s, and surgeries on these individuals show no evidence supporting the idea that these exaggerating symptom
Signs and symptoms are diagnostic indications of an illness, injury, or condition.
Signs are objective and externally observable; symptoms are a person's reported subjective experiences.
A sign for example may be a higher or lower temperature ...
s are present.
In particular, Skumin studied the patients, aged from 6 to 17, suffering from diseases of the gastrointestinal tract. Most of them have revealed a negative psychological attitude to the dietotherapy they received. A system of special measures has been developed including three main elements: (1) psychotherapeutic mediation of dietotherapy before its administration and in the process of the therapy; (2) creation of the psychologic attitude to the diet adherence; (3) alteration of the patient's taste stereotype. Realization of such measures has been conducive to higher effectiveness of the dietotherapy.
Based on studies into the mental sphere of gastroenterological patients, he systematized borderline neurotic and personality disorders
Personality disorders (PD) are a class of mental health conditions characterized by enduring maladaptive patterns of behavior, cognition, and inner experience, exhibited across many contexts and deviating from those accepted by the culture. T ...
on the clinical and etiopathogenetic basis. He studied the psychosocial problems that may affect children or teenagers who have the chronic gastrointestinal disease. A system of measures aimed at early diagnosis
Diagnosis (: diagnoses) is the identification of the nature and cause of a certain phenomenon. Diagnosis is used in a lot of different academic discipline, disciplines, with variations in the use of logic, analytics, and experience, to determine " ...
, correction, therapy and prophylaxis
Preventive healthcare, or prophylaxis, is the application of healthcare measures to prevent diseases.Hugh R. Leavell and E. Gurney Clark as "the science and art of preventing disease, prolonging life, and promoting physical and mental health a ...
of borderline conditions and psychosocial readaptation of patients is scientifically based. The main result of his scientific activity was the discovery of the "syndrome
A syndrome is a set of medical signs and symptoms which are correlated with each other and often associated with a particular disease or disorder. The word derives from the Greek language, Greek σύνδρομον, meaning "concurrence". When a sy ...
of the neurotic phantom of somatic disease" (a specific psychopathological complex of symptom
Signs and symptoms are diagnostic indications of an illness, injury, or condition.
Signs are objective and externally observable; symptoms are a person's reported subjective experiences.
A sign for example may be a higher or lower temperature ...
s) and a "concept of the mental constituent of a chronic somatic disease".
Skumin defended his doctoral thesis in Moscow at the Serbsky State Scientific Center for Social and Forensic Psychiatry (1988). The Higher Attestation Commission Higher Attestation Commission (, , abbreviated Cyrillic: ВАК, Latin: VAK) is a name of a national government agency in Russia, Ukraine and some other post-Soviet states that oversees awarding of advanced academic degrees. Due to translation diff ...
awarded him for this research study the degree of Doktor Nauk
A Doctor of Sciences, abbreviated д-р наук or д. н.; ; ; ; is a higher doctoral degree in the Russian Empire, Soviet Union and many Commonwealth of Independent States countries. One of the prerequisites of receiving a Doctor of Science ...
in Medicine ( Doctor of Medical Sciences – Dr.scient.med.). It is a higher doctoral degree
A doctorate (from Latin ''doctor'', meaning "teacher") or doctoral degree is a postgraduate academic degree awarded by universities and some other educational institutions, derived from the ancient formalism '' licentia docendi'' ("licence to teach ...
which may be earned after the Candidate of Sciences
A Candidate of Sciences is a Doctor of Philosophy, PhD-equivalent academic research degree in all the post-Soviet countries with the exception of Ukraine, and until the 1990s it was also awarded in Central and Eastern European countries. It is ...
(which is informally regarded in Russia and many other post-Soviet states
The post-Soviet states, also referred to as the former Soviet Union or the former Soviet republics, are the independent sovereign states that emerged/re-emerged from the dissolution of the Soviet Union in 1991. Prior to their independence, they ...
as equivalent to PhD obtained in countries in which PhD is not the highest academic degree
An academic degree is a qualification awarded to a student upon successful completion of a course of study in higher education, usually at a college or university. These institutions often offer degrees at various levels, usually divided into und ...
).
Culture of Health, Agni Yoga and Theosophy
From 1990 to 1994, Skumin held positions as Professor by the Chair ofPsychology
Psychology is the scientific study of mind and behavior. Its subject matter includes the behavior of humans and nonhumans, both consciousness, conscious and Unconscious mind, unconscious phenomena, and mental processes such as thoughts, feel ...
and Pedagogy
Pedagogy (), most commonly understood as the approach to teaching, is the theory and practice of learning, and how this process influences, and is influenced by, the social, political, and psychological development of learners. Pedagogy, taken ...
, and Professor by the Chair of Physical Education
Physical education is an academic subject taught in schools worldwide, encompassing Primary education, primary, Secondary education, secondary, and sometimes tertiary education. It is often referred to as Phys. Ed. or PE, and in the United Stat ...
and Health life at the Kharkiv State Academy of Culture. Skumin completed research of theoretical and practical issues of culture of health, which he developed throughout his scientific and pedagogical activity. These methods, he has introduced in the training course for the students of the Academy: ''The Foundations of a Culture of Health''.
His scientific and pedagogical work Skumin combine with a social activity. In 1994, he was elected to the post of the President-founder of the World Organisation of Culture of Health (WOCH) — International social movement "To Health via Culture" (). Coat of arms of the WOCH contain a symbol of Roerichism
Roerichism or RerikhismPhilip Walters. ''Religion, State & Society''. Volume 28, Issue 1, 2000. Quote from the ''Editorial'': "'Rerikhism' is an example of a thoroughly Russian new religious movement". (Russian: Рерихи́зм, Рерих ...
.
The organization operates in accordance with the registered in Ministry of Justice of the Russian Federation
The Ministry of Justice of the Russian Federation () is a ministry of the Government of Russia responsible for the legal system and penal system.
The Ministry of Justice is the federal authority for operating Russia's courts and correctional ...
Charter. Key element of a Culture of Health is implement innovative health programs that support a holistic approach to physical, mental and spiritual well-being both inside and outside the workplace.
 In the
In the Russian Orthodox Church
The Russian Orthodox Church (ROC; ;), also officially known as the Moscow Patriarchate (), is an autocephaly, autocephalous Eastern Orthodox Church, Eastern Orthodox Christian church. It has 194 dioceses inside Russia. The Primate (bishop), p ...
the social activities of this international organization qualifies as an ideology of the Living Ethics
Agni Yoga () or the Living Ethics (), or the Teaching of Life (), is a Neo-Theosophical religious doctrine transmitted by Helena Roerich and Nicholas Roerich from 1920. The term ''Agni Yoga'' means "Mergence with Divine Fire" or "Path to Merge ...
and New Age
New Age is a range of Spirituality, spiritual or Religion, religious practices and beliefs that rapidly grew in Western world, Western society during the early 1970s. Its highly eclecticism, eclectic and unsystematic structure makes a precise d ...
(NA),
The relationship between the Skumin's doctrine and Roerichism
Roerichism or RerikhismPhilip Walters. ''Religion, State & Society''. Volume 28, Issue 1, 2000. Quote from the ''Editorial'': "'Rerikhism' is an example of a thoroughly Russian new religious movement". (Russian: Рерихи́зм, Рерих ...
is also confirmed by some scientists, such as Goraschuk V. P., Professor of H.S. Skovoroda Kharkiv National Pedagogical University. In 2004, he wrote in his thesis for a Doctor's degree on speciality "general pedagogics and history of pedagogics",
Agni Yoga
Agni Yoga () or the Living Ethics (), or the Teaching of Life (), is a Neo-Theosophical religious doctrine transmitted by Helena Roerich and Nicholas Roerich from 1920. The term ''Agni Yoga'' means "Mergence with Divine Fire" or "Path to Me ...
is a philosophical teaching which embraces all sides of being—from cosmological problems, down to daily human life. This teaching is based on the books written by Helena
Helena may refer to:
People
*Helena (given name), a given name (including a list of people and characters with the name)
*Katri Helena (born 1945), Finnish singer
* Saint Helena (disambiguation), this includes places
Places
Greece
* Helena ...
and Nicholas Roerich
Nikolai Konstantinovich Rerikh (), better known as Nicholas Roerich (; October 9, 1874 – December 13, 1947), was a Russian painter, writer, archaeologist, theosophist, philosopher, and public figure. In his youth he was influenced by Russ ...
in the first half of the 20th century. The New Age movement is a spiritual movement that developed in Western nations
The Western world, also known as the West, primarily refers to various nations and states in Western Europe, Northern America, and Australasia; with some debate as to whether those in Eastern Europe and Latin America also constitute the West. ...
during the 1970s. The movement is characterised by a holistic
Holism is the interdisciplinary idea that systems possess properties as wholes apart from the properties of their component parts. Julian Tudor Hart (2010''The Political Economy of Health Care''pp.106, 258
The aphorism "The whole is greater than t ...
view of the cosmos, a belief in an emergent Age of Aquarius
The Age of Aquarius, in astrology, is either the current or forthcoming astrological age, depending on the method of calculation. Astrologers maintain that an astrological age is a product of the Earth's slow precessional rotation and lasts f ...
an emphasis on self-spirituality and the authority of the self, a focus on healing (particularly with alternative therapies).
Professor Verhorubova and professor Lobanova from Tomsk State Pedagogical University
Tomsk State Pedagogical University () is a university in Tomsk, Russia. It is the successor of the Tomsk Teaching Institute founded in 1902. The foreign languages department started in 1939 as one of the first five departments of the University. ...
argued (2012) that in accordance with the concept of a culture of health, proposed by Skumin, the culture – spiritual, mental, and physical – determines the status of human health. And health – spiritual, mental, physical – is a prerequisite for achieving a higher level of culture.
The essence of the teachings of the culture of health, reveals professor of University of Luhansk
The Luhansk University, officially the Luhansk Taras Shevchenko National University (, ) or Lugansk State Pedagogical University (), is the oldest university in Donbas region and has a reputation as one of Ukraine's most prestigious universiti ...
N. Gribok. He wrote at 2009,
The Culture of Health means recognizing health's central importance in the lives. Expounding the philosophical aspects of his Doctrine of Culture of Health, Skumin referred to the works of Helena Blavatsky
Helena Petrovna Blavatsky (; – 8 May 1891), often known as Madame Blavatsky, was a Russian-born Mysticism, mystic and writer who emigrated to the United States where she co-founded the Theosophical Society in 1875. She gained an internat ...
, Helena and Nicholas Roerich, Konstantin Tsiolkovsky
Konstantin Eduardovich Tsiolkovsky (; rus, Константин Эдуардович Циолковский, p=kənstɐnʲˈtʲin ɪdʊˈardəvʲɪtɕ tsɨɐlˈkofskʲɪj, a=Ru-Konstantin Tsiolkovsky.oga; – 19 September 1935) was a Russi ...
, and Alexander Chizhevsky
Alexander Leonidovich Chizhevsky ( rus, Алекса́ндр Леони́дович Чиже́вский, p=tɕɪˈʐɛfskʲɪj; 7 February 1897 – 20 December 1964) was a Soviet Union, Soviet-era interdisciplinary scientist, a biophysics, biophy ...
. In some of his publications, he argues that the Culture of Health will play an important role in the creation of a human spiritual society into the Solar System
The Solar SystemCapitalization of the name varies. The International Astronomical Union, the authoritative body regarding astronomical nomenclature, specifies capitalizing the names of all individual astronomical objects but uses mixed "Sola ...
.
He elaborated on the theosophical conceptions of spiritual evolution
Spiritual evolution, also called higher evolution, is the idea that the mind or spirit, in analogy to biological evolution, collectively evolves from a simple form dominated by nature, to a higher form dominated by the spiritual or divine. It is d ...
and proposed (1990) a classification of ''Homo spiritalis'' (Latin
Latin ( or ) is a classical language belonging to the Italic languages, Italic branch of the Indo-European languages. Latin was originally spoken by the Latins (Italic tribe), Latins in Latium (now known as Lazio), the lower Tiber area aroun ...
: ''spiritual man''), the sixth root race, consisting of eight subraces: HS0 Anabiosis spiritalis, HS1 Scientella spiritalis, HS2 Aurora spiritalis, HS3 Ascensus spiritalis, HS4 Vocatus spiritalis, HS5 Illuminatio spiritalis, НS6 Creatio spiritalis, and HS7 Servitus spiritalis. According to Skumin:
*''Anabiosis spiritalis'' is spirituality in the potential of unmanifest accumulations of personality, the charge of the fires of spiritual creation;
*''Scientella spiritalis'' is the cordial presentiment of the presence and demands of the spirit, spiritualization of the fire of centers, glimpses of self-consciousness of a spiritual person;
*''Aurora spiritalis'' is the imperative of the spirit, the action of the spiritual fire of the centers in the heart, the kindling of the fire of the spirit, the formation of the orientation of the personality to the spiritual improvement of life;
*''Ascensus spiritalis'' is the dawn of spiritual aspirations, the action of the fire of the spirit in the heart, searching spiritual work, aspiration of self-consciousness to merge with the One Spirit;
*''Vocatus spiritalis'' is the maturation of spiritual accumulations, the purposeful spiritual creation, self-awareness and realization of a person as a warrior of the spirit;
*''IIluminatio spiritalis'' is the beginning of the fiery transmutation, the lighting of the achievement fire; revealing the identity of man - the earthly carrier of the Thoughts of the One Spirit;
*''Creatio Spiritalis'' is the beginning of fiery creation, the action of the fire of achievement in the heart, the revealing self-consciousness of man as the earthly carrier of the Light of the One Spirit;
*''Servitus Spiritalis'' is the carrying a consciously accepted duty-commission, the synthesis of spirituality in the clarity of knowledge of a ''fiery man''.
So, the culture of health is an integral sphere of knowledge that develops and solves theoretical and practical tasks of harmonious development of people's spiritual, mental, and physical strength, health improvement of biosocial environment that provides a higher life creative level on this basis (by Skumin and Bobina, 1994).
Literary and publishing activities
Skumin wrote several books of fiction, and also essays. He is the author of music and lyrics of several songs. Among them anthem "To Health via Culture". This anthem consists of four stanzas. The capital letters each of the four stanzas form the wordAgni
Agni ( ) is the Deva (Hinduism), Hindu god of fire. As the Guardians of the directions#Aṣṭa-Dikpāla ("Guardians of Eight Directions"), guardian deity of the southeast direction, he is typically found in southeast corners of Hindu temples. ...
.
In 1995, Skumin became the first editor-in-chief (EIC) of "The Journal To Health Via Culture". This journal of the World Organisation of Culture of Health (″World Health Culture Organization″) received an International Standard Serial Number
An International Standard Serial Number (ISSN) is an eight-digit to uniquely identify a periodical publication (periodical), such as a magazine. The ISSN is especially helpful in distinguishing between serials with the same title. ISSNs a ...
(ISSN) 0204-3440. The main topics of the magazine are the dissemination of ideas of Culture of Health, holistic medicine
Alternative medicine refers to practices that aim to achieve the healing effects of conventional medicine, but that typically lack biological plausibility, testability, repeatability, or supporting evidence of effectiveness. Such practices ar ...
, and Roerichism
Roerichism or RerikhismPhilip Walters. ''Religion, State & Society''. Volume 28, Issue 1, 2000. Quote from the ''Editorial'': "'Rerikhism' is an example of a thoroughly Russian new religious movement". (Russian: Рерихи́зм, Рерих ...
. The Organization also has its own publishing house ("To Health via Culture").
Skumin wrote many books and articles on a variety medical and spiritual topics advocating a holistic approach to health. He is the author or co-author of a series illustrated books on the Culture of Health, Agni Yoga
Agni Yoga () or the Living Ethics (), or the Teaching of Life (), is a Neo-Theosophical religious doctrine transmitted by Helena Roerich and Nicholas Roerich from 1920. The term ''Agni Yoga'' means "Mergence with Divine Fire" or "Path to Me ...
, and Roerichism
Roerichism or RerikhismPhilip Walters. ''Religion, State & Society''. Volume 28, Issue 1, 2000. Quote from the ''Editorial'': "'Rerikhism' is an example of a thoroughly Russian new religious movement". (Russian: Рерихи́зм, Рерих ...
.
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
Trivia
*According to a study conducted in 2015, Skumin was included in "Russia team on medicine". This list includes fifty-three famous Russian medical scientists from the Russian Federation, theSoviet Union
The Union of Soviet Socialist Republics. (USSR), commonly known as the Soviet Union, was a List of former transcontinental countries#Since 1700, transcontinental country that spanned much of Eurasia from 1922 until Dissolution of the Soviet ...
, and the Russian Empire
The Russian Empire was an empire that spanned most of northern Eurasia from its establishment in November 1721 until the proclamation of the Russian Republic in September 1917. At its height in the late 19th century, it covered about , roughl ...
who were born in 1757—1950. Physicians of all specialities listed here. Among them Vladimir Bekhterev
Vladimir Mikhailovich Bekhterev ( rus, Влади́мир Миха́йлович Бе́хтерев, p=ˈbʲextʲɪrʲɪf; 20 January 1857 – 24 December 1927) was a Russian neurologist and the father of objective psychology. He is best known fo ...
, Vladimir Demikhov
Vladimir Petrovich Demikhov (; 31 July 1916 – 22 November 1998) was a Soviet Russian scientist and organ transplantation pioneer, who performed several transplants in the 1940s and 1950s, including the transplantation of a heart into an anim ...
, Sergei Korsakoff, Ivan Pavlov
Ivan Petrovich Pavlov (, ; 27 February 1936) was a Russian and Soviet experimental neurologist and physiologist known for his discovery of classical conditioning through his experiments with dogs. Pavlov also conducted significant research on ...
, Nikolay Pirogov
Nikolay Ivanovich Pirogov (Russian: Николай Иванович Пирогов; – ) was a Russian scientist, medical doctor, pedagogue, public figure, and corresponding member of the Russian Academy of Sciences (1847), one of the most wi ...
, Ivan Sechenov
Ivan Mikhaylovich Sechenov (; – ) is a world-renowned medical scientist, physiologist, psychologist, academician of the Russian Academy of Sciences, and founder of Russian physiology and psychology, he is a pioneer in the field of central ner ...
.
*In the online poll "The Name of Russia", completed in 2017, Skumin by a wide margin is on first position in the section "The Glory of Russia". Also in the top 10 leaders in "The Glory of Russia" are Fyodor Dostoyevsky
Fyodor Mikhailovich Dostoevsky. () was a Russian novelist, short story writer, essayist and journalist. He is regarded as one of the greatest novelists in both Russian literature, Russian and world literature, and many of his works are consider ...
, Alexander Pushkin
Alexander Sergeyevich Pushkin () was a Russian poet, playwright, and novelist of the Romantic era.Basker, Michael. Pushkin and Romanticism. In Ferber, Michael, ed., ''A Companion to European Romanticism''. Oxford: Blackwell, 2005. He is consid ...
, Seraphim of Sarov
Seraphim of Sarov (; – ), born Prókhor Isídorovich Moshnín (Mashnín) �ро́хор Иси́дорович Мошни́н (Машни́н) is one of the most renowned Russian saints and is venerated in the Eastern Orthodox Church and t ...
, Joseph Stalin
Joseph Vissarionovich Stalin (born Dzhugashvili; 5 March 1953) was a Soviet politician and revolutionary who led the Soviet Union from 1924 until Death and state funeral of Joseph Stalin, his death in 1953. He held power as General Secret ...
(Jughashvili). At the same time Skumin is on fifteenth position in the section "The Shame of Russia". Mikhail Gorbachev
Mikhail Sergeyevich Gorbachev (2 March 1931 – 30 August 2022) was a Soviet and Russian politician who served as the last leader of the Soviet Union from 1985 to dissolution of the Soviet Union, the country's dissolution in 1991. He served a ...
and Boris Berezovsky are in fourteenth and sixteenth positions in this list, and on the top of the rating "The Shame of Russia" are Alexander Lukashenko
Alexander Grigoryevich Lukashenko (also transliterated as Alyaksandr Ryhoravich Lukashenka; born 30 August 1954) is a Belarusian politician who has been the first and only president of Belarus since the office's establishment in 1994, making hi ...
and Vladimir Putin
Vladimir Vladimirovich Putin (born 7 October 1952) is a Russian politician and former intelligence officer who has served as President of Russia since 2012, having previously served from 2000 to 2008. Putin also served as Prime Minister of Ru ...
.
See also
References
External links
*World Organisation of Culture of Health
{{DEFAULTSORT:Skumin, Victor 1948 births 20th-century Russian philosophers 20th-century Russian writers 21st-century Russian philosophers 21st-century Russian writers Cosmists Kharkiv National Medical University people Living people New Age writers People from Penza Oblast Russian psychiatrists Russian transhumanists Soviet psychiatrists Soviet scientists Spiritual writers Russian scientists