Vascular Anomaly on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
A vascular anomaly is any of a range of lesions from a simple
 A
A
 * Capillary malformation (also known as port-wine stains): Capillary malformations are flat, reddish lesions that typically affect the skin, mostly around the head and the neck, and which darken with age, in contrast to birthmarks such as salmon patch, Nevus simplex or vascular stain, which lighten or disappear within the first few years of life. Capillary malformations constitute 11% of the vascular malformations. Syndromes associated with capillary malformations are:
* Capillary malformation (also known as port-wine stains): Capillary malformations are flat, reddish lesions that typically affect the skin, mostly around the head and the neck, and which darken with age, in contrast to birthmarks such as salmon patch, Nevus simplex or vascular stain, which lighten or disappear within the first few years of life. Capillary malformations constitute 11% of the vascular malformations. Syndromes associated with capillary malformations are: 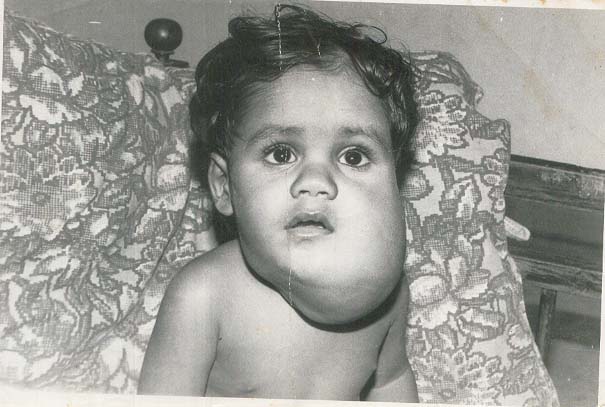 * Lymphatic malformation is a benign growth of the lymphatic system. They result from a blockage or defect of the lymphatic vessels as they are forming. 28% of all vascular malformations are lymphatic malformations. Lymphatic malformations can be treated with
* Lymphatic malformation is a benign growth of the lymphatic system. They result from a blockage or defect of the lymphatic vessels as they are forming. 28% of all vascular malformations are lymphatic malformations. Lymphatic malformations can be treated with
birthmark
A birthmark is a congenital, benign irregularity on the skin which is present at birth or appears shortly after birth—usually in the first month. Birthmarks can occur anywhere on the skin. They are caused by overgrowth of blood vessels, melanocy ...
to a large tumor
A neoplasm () is a type of abnormal and excessive growth of tissue. The process that occurs to form or produce a neoplasm is called neoplasia. The growth of a neoplasm is uncoordinated with that of the normal surrounding tissue, and persists ...
that may be disfiguring. They are caused by a disorder of the vascular system
In vertebrates, the circulatory system is a system of organs that includes the heart, blood vessels, and blood which is circulated throughout the body. It includes the cardiovascular system, or vascular system, that consists of the heart a ...
. A vascular anomaly is a localized defect in blood vessel
Blood vessels are the tubular structures of a circulatory system that transport blood throughout many Animal, animals’ bodies. Blood vessels transport blood cells, nutrients, and oxygen to most of the Tissue (biology), tissues of a Body (bi ...
s or lymph vessel
The lymphatic vessels (or lymph vessels or lymphatics) are thin-walled vessels (tubes), structured like blood vessels, that carry lymph. As part of the lymphatic system, lymph vessels are complementary to the cardiovascular system. Lymph vessel ...
s. These defects are characterized by an increased number of vessels, and vessels that are both enlarged and heavily curved. Some vascular anomalies are congenital
A birth defect is an abnormal condition that is present at childbirth, birth, regardless of its cause. Birth defects may result in disability, disabilities that may be physical disability, physical, intellectual disability, intellectual, or dev ...
, others appear within weeks to years after birth, and others are acquired by trauma
Trauma most often refers to:
*Psychological trauma, in psychology and psychiatric medicine, refers to severe mental and emotional injury caused by distressing events
*Traumatic injury, sudden physical injury caused by an external force, which doe ...
or during pregnancy. Inherited vascular anomalies are also described and often present with a number of lesions that increase with age. Vascular anomalies can also be a part of a syndrome
A syndrome is a set of medical signs and symptoms which are correlated with each other and often associated with a particular disease or disorder. The word derives from the Greek language, Greek σύνδρομον, meaning "concurrence". When a sy ...
.
The estimated prevalence of vascular anomalies is 4.5%. Vascular anomalies can occur throughout the whole body, but in 60% of patients they are localized in the head and neck region.
Vascular anomalies can present in various ways: when situated deep below the skin, they appear blue, and are often called cavernous
The cavernous sinus within the human head is one of the dural venous sinuses creating a cavity called the lateral sellar compartment bordered by the temporal bone of the skull and the sphenoid bone, lateral to the sella turcica.
Structure
The cav ...
. Superficial vascular anomalies appear as red-coloured stains and are associated with vascular anomalies affecting the dermis
The dermis or corium is a layer of skin between the epidermis (skin), epidermis (with which it makes up the cutis (anatomy), cutis) and subcutaneous tissues, that primarily consists of dense irregular connective tissue and cushions the body from s ...
. Historically, vascular anomalies have been labeled with descriptive terms, according to the food they resembled (port wine, strawberry, cherry, salmon patch). This imprecise terminology has caused diagnostic confusion, blocked communication and even caused incorrect treatment, as it does not differentiate between various vascular anomalies. However, in 1982, Mulliken introduced a classification that replaced these descriptive terms and gave direction to the management of various vascular anomalies. This classification, based on clinical features, natural history and cellular characteristics, divides vascular anomalies into two groups: vascular tumor
A vascular tumor is a vascular anomaly where a tumor forms from cells that make blood or lymph vessels; a soft tissue growth that can be either benign or malignant. Examples of vascular tumors include hemangiomas, hemangioendotheliomas, Kapo ...
s and vascular malformation
A vascular malformation is a type of vascular anomaly. They may cause aesthetic problems as they have a growth cycle, and can continue to grow throughout life.
Vascular malformations of the brain include those involving capillaries, and those in ...
s.
Although vascular tumors and vascular malformations can resemble each other, there are important differences between both.
Vascular tumors
Vascular tumor
A vascular tumor is a vascular anomaly where a tumor forms from cells that make blood or lymph vessels; a soft tissue growth that can be either benign or malignant. Examples of vascular tumors include hemangiomas, hemangioendotheliomas, Kapo ...
s, include hemangiomas
A hemangioma or haemangioma is a usually benign vascular tumor derived from blood vessel cell types. The most common form, seen in infants, is an infantile hemangioma, known colloquially as a "strawberry mark", most commonly presenting on the s ...
, the most common tumor
A neoplasm () is a type of abnormal and excessive growth of tissue. The process that occurs to form or produce a neoplasm is called neoplasia. The growth of a neoplasm is uncoordinated with that of the normal surrounding tissue, and persists ...
s in infants, occurring in 1-2%, and higher in 10% of premature infants of very low birth weight. Vascular tumors are characterized by an overgrowth of normal vessels, which show increased endothelial proliferation. They are typically present at birth, but can appear within a couple of weeks after birth or during infancy. The four most common types are: infantile hemangioma
An infantile hemangioma (IH), sometimes called a strawberry mark due to appearance, is a type of benign vascular tumor or anomaly that affects babies. Other names include capillary hemangioma, "strawberry hemangioma", strawberry birthmark and ...
, congenital hemangioma
A vascular tumor is a vascular anomaly where a tumor forms from cells that make blood or lymph vessels; a soft tissue growth that can be either benign or malignant. Examples of vascular tumors include hemangiomas, hemangioendotheliomas, Kaposi ...
, kaposiform hemangioendothelioma
A vascular tumor is a vascular anomaly where a tumor forms from cells that make blood or lymph vessels; a soft tissue growth that can be either benign or malignant. Examples of vascular tumors include hemangiomas, hemangioendotheliomas, Kapos ...
and pyogenic granuloma
A pyogenic granuloma or lobular capillary hemangioma is a vascular tumor that occurs on both mucosa and skin, and appears as an overgrowth of tissue due to irritation, physical trauma, or hormonal factors. It is often found to involve the gums, ...
.
Infantile hemangioma
Infantile hemangioma
An infantile hemangioma (IH), sometimes called a strawberry mark due to appearance, is a type of benign vascular tumor or anomaly that affects babies. Other names include capillary hemangioma, "strawberry hemangioma", strawberry birthmark and ...
is the most common vascular tumor. It is a benign tumor, which occurs in 4-5% of Caucasian
Caucasian may refer to:
Common meanings
*Anything from the Caucasus region or related to it
** Ethnic groups in the Caucasus
** ''Caucasian Exarchate'' (1917–1920), an ecclesiastical exarchate of the Russian Orthodox Church in the Caucasus re ...
infants, but rarely in dark skinned infants. It occurs in 20% of low weight premature infants and 2.2 to 4.5 times more frequently in females. IH most commonly presents in the head and neck region (60%), but also involves the trunk
Trunk may refer to:
Biology
* Trunk (anatomy), synonym for torso
* Trunk (botany), a tree's central superstructure, and the stem of woody plants
* Trunk of corpus callosum, in neuroanatomy
* Elephant trunk, the proboscis of an elephant
Comput ...
and extremities. One third of these lesions is present at birth as a telangiectatic stain or ecchymotic area. During the first four weeks of life, 70% to 90% appear. Lesions that are situated beneath the skin may not appear until 3 to 4 months of age, when the tumor is large enough. During the first 9 months, IH undergoes rapid growth, which is faster than the growth of the child. This is called the proliferating phase. After 9 months, the growth of the tumor will decrease and equal the growth of the child for about 3 months. After 12 months, the tumor will start to involute and might even disappear. Involution occurs in one-third of patient by the age of 3 years, in 50% by the age of 5 years and in 72% by the age of 7 years. Involution may result in residual telangiectasias, pallor, atrophy, textural changes and sometimes fibrofatty residuum.
Since 90% of IH is small, localized and asymptomatic
Asymptomatic (or clinically silent) is an adjective categorising the medical conditions (i.e., injuries or diseases) that patients carry but without experiencing their symptoms, despite an explicit diagnosis (e.g., a positive medical test).
P ...
, treatment mainly consists of observation and awaiting until involution is complete. IH can be treated with corticosteroids
Corticosteroids are a class of steroid hormones that are produced in the adrenal cortex of vertebrates, as well as the synthetic analogues of these hormones. Two main classes of corticosteroids, glucocorticoids and mineralocorticoids, are invol ...
, which accelerate involution: in 95% of patients, growth is stabilized and 75% of tumors decrease in size. Intralesional corticosteroids are most effective, but may require additional injections, as the effect is only temporarily. Systemic corticosteroids may cause a number of side-effects and are only used in problematic IH, which is too large to treat with intralesional injections.
During the proliferating phase, the tumor is highly vascular. Patients who undergo operative treatment during this period, are at risk for blood loss. Moreover, surgery during this phase, often leads to an inferior aesthetic
Aesthetics (also spelled esthetics) is the branch of philosophy concerned with the nature of beauty and taste, which in a broad sense incorporates the philosophy of art.Slater, B. H.Aesthetics ''Internet Encyclopedia of Philosophy,'' , acces ...
outcome. However, patients may require intervention during childhood, because 50% of IH leave residual fibrofatty tissue, redundant skin, or damaged structures after involution. Waiting until involution is completed, ensures that the least amount of fibro fatty residuum and excess skin is resected, giving the smallest possible scar. Another option for treatment is the pulsed-dye laser. After involution residual telangiectasias can be treated with laser therapy
Laser medicine is the use of lasers in medical diagnosis, treatments, or therapies, such as laser photodynamic therapy, photorejuvenation, and laser surgery.
The word ''laser'' stands for "light amplification by stimulated emission of radiatio ...
.
Congenital hemangioma
Congenital hemangioma can be distinguished from infantile hemangioma because it is fully developed at birth. It forms during prenatal life and has reached its maximal size at birth. Congenital hemangioma can even be diagnosed in utero byprenatal ultrasound
Obstetric ultrasonography, or prenatal ultrasound, is the use of medical ultrasonography in pregnancy, in which sound waves are used to create real-time visual images of the developing embryo or fetus in the uterus (womb). The procedure is a stand ...
. Unlike IH, CH is more common in the extremities, has an equal sex distribution, and is solitary, with an average diameter of 5 cm. It commonly presents in the head and neck and in the lower extremities.
Congenital hemangioma are divided into 2 subgroups: the rapidly involuting congenital hemangiomas (RICHs) and the non-involuting congenital hemangiomas(NICHs).
The rapidly involuting congenital hemangioma, RICH, presents at birth as a solitary raised tumor with a central depression, scar, or ulceration
An ulcer is a discontinuity or break in a bodily membrane that impedes normal function of the affected Organ (biology), organ. According to Robbins's pathology, "ulcer is the breach of the continuity of skin, epithelium or mucous membrane caus ...
surrounded by a rim of pallor. It is noted for its involution, which typically begins several weeks after birth and is completed no later than 14 months of age. After regression RICH may cause a residual deformity, such as atrophic skin and subcutaneous tissue. It mainly affects the limbs (52%), but also the head and neck region (42%) and the trunk (6%).
The non-involuting congenital hemangioma, NICH, presents as a solitary, well-circumscribed reddish-pink to purple plaque with central telangiectasia
Telangiectasias (), also known as spider veins, are small dilated blood vessels that can occur near the surface of the skin or mucous membranes, measuring between 0.5 and 1 millimeter in diameter. These dilated blood vessels can develop anywhere ...
and hypopigmented rim. In contrast to RICH, NICH does not involute and rarely ulcerates. It persists into late childhood and can even mimic a vascular malformation by growing commensurately with the child. Although NICH can resemble RICH in its external appearance, it can be differentiated from RICH by a greater elevation and coarse telangiectases. It mainly affects the head and neck region (43%), but also the limbs (38%) and the trunk (19%).
Surgical resection
Segmental resection, or segmentectomy, is a surgical procedure to remove part of an organ or gland as a sub-type of resection, which might involve removing the whole body part. It may also be used to remove a tumor and the normal tissue around it ...
for congenital hemangiomas is rarely needed, because RICH undergoes postnatal regression and NICH is benign and often asymptomatic. Resection may be indicated to improve the appearance of the affected area, as long as the surgical scar is less noticeable than the lesion. Other indications are problematic ulcers with persistent bleeding or chronic infection
Chronic may refer to:
* Chronic condition, a condition or disease that is persistent or otherwise long-lasting in its effects
* Chronic toxicity, a substance with toxic effects after continuous or repeated exposure
* Chronic (film), ''Chronic'' ...
.
Although most NICH lesions are non-problematic and do not cause significant deformity, the threshold for resection of NICH is lower, because it neither involutes, nor responds to pharmacotherapy. RICH tumors are observed until involution is completed. Involuted RICH may leave behind atrophic tissue, which can be reconstructed with autologous grafts. It is often best to postpone excision until regression is complete.
There are effective pharmacologic treatments, which include intralesional corticosteroid injection, systemic corticosteroid injection, interferon α-2a or α-2b and angiogenic inhibitors. The use of corticosteroids leads to accelerated regression in 30%, stabilization of growth in 40%, lightening of color and softening of the tumor. However, 30% shows minimal or no response. Another drug treatment is interferon α-2a or α-2b. It is often used for patients who did not respond to corticosteroids. Although the response rate is much slower, it has been successful for 80% of children treated. The most serious side effect of interferon is a spastic diplegia
Spastic diplegia is a form of cerebral palsy (CP) that primarily affects the legs, with possible considerable asymmetry between the two sides. It is a chronic neuromuscular condition of hypertonia and spasticity in the muscles of the lower e ...
. Other therapeutic options are embolization and pulsed-dye laser, which improves residual telangiectasias in RICH and in NICH.
Kaposiform hemangioendothelioma
Kaposiform hemangioendothelioma
A vascular tumor is a vascular anomaly where a tumor forms from cells that make blood or lymph vessels; a soft tissue growth that can be either benign or malignant. Examples of vascular tumors include hemangiomas, hemangioendotheliomas, Kapos ...
(KHE) is a rare vascular neoplasm that is locally aggressive but without metastatic potential. It occurs particularly in the skin
Skin is the layer of usually soft, flexible outer tissue covering the body of a vertebrate animal, with three main functions: protection, regulation, and sensation.
Other animal coverings, such as the arthropod exoskeleton, have different ...
, deep soft tissue, retroperitoneum
The retroperitoneal space (retroperitoneum) is the anatomical space (sometimes a potential space) behind (''retro'') the peritoneum. It has no specific delineating anatomical structures. Organs are retroperitoneal if they have peritoneum on their ...
, mediastinum
The mediastinum (from ;: mediastina) is the central compartment of the thoracic cavity. Surrounded by loose connective tissue, it is a region that contains vital organs and structures within the thorax, mainly the heart and its vessels, the eso ...
, and rarely in bone
A bone is a rigid organ that constitutes part of the skeleton in most vertebrate animals. Bones protect the various other organs of the body, produce red and white blood cells, store minerals, provide structure and support for the body, ...
. Although lesions occur solitary, they often involve large areas of the body, such as the head/neck region (40%), trunk (30%), or extremity (30%).
Usually, it is present at birth as a flat, reddish-purple, tense and edematous
Edema (American English), also spelled oedema (British English), and also known as fluid retention, swelling, dropsy and hydropsy, is the build-up of fluid in the body's tissue. Most commonly, the legs or arms are affected. Symptoms may inclu ...
lesion.
Although half of lesions are congenital, 58% of KHE develop during infancy, 32% between age 1 and 10 years (32%) and 10% after 11 years of age. Moreover, adult onset has been described too with mainly males being affected. Both sexes are affected equally in children.
Lesions are often greater than 5 cm in diameter and can cause visible deformity and pain. During early childhood, KHE may enlarge and after 2 years of age, it may partially regress. Though, it usually persists longterm. In addition, 50% of patients have coagulopathy
Coagulopathy (also called a bleeding disorder) is a condition in which the blood's ability to coagulate (form clots) is impaired. This condition can cause a tendency toward prolonged or excessive bleeding ( bleeding diathesis), which may occur s ...
due to thrombocytopenia
In hematology, thrombocytopenia is a condition characterized by abnormally low levels of platelets (also known as thrombocytes) in the blood. Low levels of platelets in turn may lead to prolonged or excessive bleeding. It is the most common coag ...
(<25,000/mm3), presenting with petechiae
A petechia (; : petechiae) is a small red or purple spot ( 1 cm in diameter) and purpura (3 to 10 mm in diameter). The term is typically used in the plural (petechiae), since a single petechia is seldom noticed or significant.
Causes Physical ...
and bleeding. This is called the Kasabach–Merritt syndrome
Kasabach–Merritt syndrome (KMS), also known as hemangioma with thrombocytopenia, is a rare disease, usually of infants, in which a vascular tumor leads to decreased platelet counts and sometimes other bleeding problems, which can be life-threat ...
, which is caused by trapping of platelets and other clotting factors within the tumor. Kasabach-Merritt Phenomenon is less likely in patients with lesions less than 8 cm. As two-thirds of adult-onset KHE tumors are less than 2 cm, KHE in adults is rarely associated with Kasabach-Merritt Phenomenon.
Patients with KHE and Kasabach-Merritt Phenomenon present with petechiae and ecchymosis
A bruise, also known as a contusion, is a type of hematoma of tissue, the most common cause being capillaries damaged by trauma, causing localized bleeding that extravasates into the surrounding interstitial tissues. Most bruises occur clo ...
.
Most KHE tumors are diffuse involving multiple tissue planes and important structures. Resection of KHE is thus often difficult. Treatment of kaposiform hemangioendothelioma is therefore medical. The primary drug is interferon alfa
Interferon alfa ( INN) or HuIFN-alpha-Le, trade name Multiferon, is a pharmaceutical drug composed of natural interferon alpha (IFN-α), obtained from the leukocyte fraction of human blood following induction with Sendai virus. Interferon alfa co ...
, which is successful in 50% of children. Another option is vincristine
Vincristine, also known as leurocristine and sold under the brand name Oncovin among others, is a chemotherapy medication used to treat a number of types of cancer. This includes acute lymphocytic leukemia, acute myeloid leukemia, Hodgkin lym ...
, which has many side-effects, but has a response rate of 90%. Drug therapy is often used in shrinking the tumor and treating the coagulopathy. However, many of these kaposiform hemangioendotheliomas do not completely regress and remain as a much smaller asymptomatic tumor. However, KHE still has a high mortality rate of 30%. Although complete surgical removal with a large margin has the best reported outcome, it is usually not done because of the risk of bleeding, extensiveness, and the anatomic site of the lesion.
Operative management may be possible for small or localized lesions. Removal of larger areas also may be indicated for symptomatic patients or for patients who have failed pharmacotherapy. Resection is not required for lesions that are not causing functional problems, because KHE is benign and because resection could cause deformity.
Pyogenic granuloma
pyogenic granuloma
A pyogenic granuloma or lobular capillary hemangioma is a vascular tumor that occurs on both mucosa and skin, and appears as an overgrowth of tissue due to irritation, physical trauma, or hormonal factors. It is often found to involve the gums, ...
, is a small benign vascular tumor
A vascular tumor is a vascular anomaly where a tumor forms from cells that make blood or lymph vessels; a soft tissue growth that can be either benign or malignant. Examples of vascular tumors include hemangiomas, hemangioendotheliomas, Kapo ...
that primarily involves the skin (88.2%) and mucous membranes. Pyogenic granuloma appears as a red macule that grows rapidly, turns into a papule and eventually becomes pedunculated, being attached to a narrow stalk. The average diameter of these lesions is 6.5 mm. Although these lesions are small, they are often complicated by bleeding, crusting and ulceration. Microscopically, pyogenic granulomas are characterized by vascular proliferation amidst granulation tissue
Granulation tissue is new connective tissue and microscopic blood vessels that form on the surfaces of a wound during the healing process. Granulation tissue typically grows from the base of a wound and is able to fill wounds of almost any size ...
and chronic inflammatory infiltrate.
Pyogenic granulomas are rarely congenital. It commonly develops in infants: 42.1% develops within the first 5 years of life. This vascular tumor is twice as common in males as in females and 25% of lesions seem to be associated with trauma, an underlying cutaneous condition, pregnancy, hormonal alterations and medications. Pyogenic granulomas can also arise within a capillary malformation. Of all pyogenic granulomas, 62% is distributed on the head or neck, occurring mainly on the cheek and in the oral cavity. Lesions on the face may cause visible deformity.
Numerous treatment methods have been described for pyogenic granuloma. Lesions involving the reticular dermis
The dermis or corium is a layer of skin between the epidermis (with which it makes up the cutis) and subcutaneous tissues, that primarily consists of dense irregular connective tissue and cushions the body from stress and strain. It is divided in ...
, may be out of the reach of pulsed-dye laser, cautery or shave excision and therefore have a recurrence rate of 43.5%. Definitive management requires full-thickness skin excision. Other options are curettage
Curettage ( or ), in medical procedures, is the use of a curette (French, meaning "scoop" Mosby's Medical, Nursing & Allied Health Dictionary, Fourth Edition, Mosby-Year Book 1994, p. 422) to remove tissue by scraping or scooping.
Curettages ...
or laser therapy
Laser medicine is the use of lasers in medical diagnosis, treatments, or therapies, such as laser photodynamic therapy, photorejuvenation, and laser surgery.
The word ''laser'' stands for "light amplification by stimulated emission of radiatio ...
. Furthermore, thorough curettage and cauterization are often used for small lesions and full-thickness excision for larger lesion.
Vascular malformations
Vascular malformation
A vascular malformation is a type of vascular anomaly. They may cause aesthetic problems as they have a growth cycle, and can continue to grow throughout life.
Vascular malformations of the brain include those involving capillaries, and those in ...
is a collective term for different disorders of the vasculature
In vertebrates, the circulatory system is a system of organs that includes the heart, blood vessels, and blood which is circulated throughout the body. It includes the cardiovascular system, or vascular system, that consists of the heart an ...
(errors in vascular development). It can be a disorder of the capillaries
A capillary is a small blood vessel, from 5 to 10 micrometres in diameter, and is part of the microcirculation system. Capillaries are microvessels and the smallest blood vessels in the body. They are composed of only the tunica intima (the in ...
, arteries
An artery () is a blood vessel in humans and most other animals that takes oxygenated blood away from the heart in the systemic circulation to one or more parts of the body. Exceptions that carry deoxygenated blood are the pulmonary arteries in ...
, veins
Veins () are blood vessels in the circulatory system of humans and most other animals that carry blood towards the heart. Most veins carry deoxygenated blood from the tissues back to the heart; exceptions are those of the pulmonary and fetal c ...
and lymphatic vessels
The lymphatic vessels (or lymph vessels or lymphatics) are thin-walled vessels (tubes), structured like blood vessels, that carry lymph. As part of the lymphatic system, lymph vessels are complementary to the cardiovascular system. Lymph vessel ...
or a disorder of a combination of these (lesions are named based on the primary vessel that is malformed). A vascular malformation consists of a cluster of deformed vessels, due to an error in vascular development (dysmorphogenesis
Morphogenesis (from the Greek ''morphê'' shape and ''genesis'' creation, literally "the generation of form") is the biological process that causes a cell, tissue or organism to develop its shape. It is one of three fundamental aspects of develo ...
). However, endothelial turnover is stable in these defects. Congenital vascular malformations are always already present at birth, although they are not always visible. In contrast to vascular tumors, vascular malformations do not have a growth phase, nor an involution phase. Vascular malformations tend to grow proportionately with the child. Vascular malformations never regress, but persist throughout life.
Vascular malformations can be divided into slow-flow, fast-flow and complex-combined types.
Slow-flow vascular malformations
 * Capillary malformation (also known as port-wine stains): Capillary malformations are flat, reddish lesions that typically affect the skin, mostly around the head and the neck, and which darken with age, in contrast to birthmarks such as salmon patch, Nevus simplex or vascular stain, which lighten or disappear within the first few years of life. Capillary malformations constitute 11% of the vascular malformations. Syndromes associated with capillary malformations are:
* Capillary malformation (also known as port-wine stains): Capillary malformations are flat, reddish lesions that typically affect the skin, mostly around the head and the neck, and which darken with age, in contrast to birthmarks such as salmon patch, Nevus simplex or vascular stain, which lighten or disappear within the first few years of life. Capillary malformations constitute 11% of the vascular malformations. Syndromes associated with capillary malformations are: Sturge–Weber syndrome
Sturge–Weber syndrome, sometimes referred to as encephalotrigeminal angiomatosis, is a rare congenital neurocutaneous disorder (also known as phakomatoses). It is often associated with port-wine stains of the face, glaucoma, seizures, intellect ...
and Klippel–Trénaunay syndrome
Klippel–Trénaunay syndrome, formerly Klippel–Trénaunay–Weber syndrome and sometimes angioosteohypertrophy syndrome and hemangiectatic hypertrophy, is a rare congenital medical condition in which blood vessels and/or lymph vessels fail to f ...
. Capillary malformations can be treated with IPL-(Intensed-pulsed-light)-therapy or surgical resection
Segmental resection, or segmentectomy, is a surgical procedure to remove part of an organ or gland as a sub-type of resection, which might involve removing the whole body part. It may also be used to remove a tumor and the normal tissue around it ...
.
* Venous malformation is a bluish lesion compressible on palpation; the masses enlarge with physical activity or if in a dependent position. The bluish lesion is caused by dilated venous vessels. Venous malformations can be painful in the morning due to stasis and microthrombi within the veins. Venous malformations usually occur in the head and neck. Venous malformations are the most common vascular anomaly, making up 40% of all vascular malformations. They can be treated with sclerotherapy
Sclerotherapy (the word reflects the Greek ''skleros'', meaning ''hard'')
is a procedure used to treat blood vessel malformations ( vascular malformations) and also malformations of the lymphatic system. A medication is injected into the vessels ...
and surgical resection.
 * Lymphatic malformation is a benign growth of the lymphatic system. They result from a blockage or defect of the lymphatic vessels as they are forming. 28% of all vascular malformations are lymphatic malformations. Lymphatic malformations can be treated with
* Lymphatic malformation is a benign growth of the lymphatic system. They result from a blockage or defect of the lymphatic vessels as they are forming. 28% of all vascular malformations are lymphatic malformations. Lymphatic malformations can be treated with sclerotherapy
Sclerotherapy (the word reflects the Greek ''skleros'', meaning ''hard'')
is a procedure used to treat blood vessel malformations ( vascular malformations) and also malformations of the lymphatic system. A medication is injected into the vessels ...
and surgical resection.
Fast flow vascular malformations
All fast-flow malformations are malformations involving arteries. They constitute about 14% of all vascular malformations. * Arterial malformation *Arteriovenous fistula
An arteriovenous fistula is an abnormal connection or passageway between an artery and a vein. It may be congenital, surgically created for hemodialysis treatments, or acquired due to pathologic process, such as trauma or erosion of an arteri ...
(AVF) : a lesion with a direct communication via fistulae between an artery and a vein.
* Arteriovenous malformation
An arteriovenous malformation (AVM) is an abnormal connection between arteries and veins, bypassing the capillary system. Usually congenital, this vascular anomaly is widely known because of its occurrence in the central nervous system (usually ...
: a lesion with a direct connection between an artery and a vein, without an intervening capillary bed, but with an interposed nidus of dysplastic vascular channels in between.
Combined-complex vascular malformations
a combination of various vascular malformations. They are 'complex' because they involve a combination of two different types of vessels. * CVM: capillary venous malformation * CLM: capillary lymphatic malformation * LVM: lymphatic venous malformation * CLVM: capillary lymphatic venous malformation. CLVM is associated withKlippel–Trénaunay syndrome
Klippel–Trénaunay syndrome, formerly Klippel–Trénaunay–Weber syndrome and sometimes angioosteohypertrophy syndrome and hemangiectatic hypertrophy, is a rare congenital medical condition in which blood vessels and/or lymph vessels fail to f ...
* AVM-LM: Arteriovenous malformation- lymphatic malformation
* CM-AVM: capillary malformation- arteriovenous malformation
Research
The international organization dedicated to the research of vascular anomalies is the ''International Society for the Study of Vascular Anomalies (ISSVA)'' made up of multi-disciplinary doctors, scientists and healthcare providers. Geographical vascular anomaly organizations exist as well. For example, in Australia and New Zealand ''The Australian Vascular Anomalies Network''.Terminology
The International Society for the Study of Vascular Anomalies (ISSVA) classification is a basic and systematic classification of vascular anomalies with international acceptance. Terminology used widely in the past such as lymphangioma are outdated. Newer research may only reference ISSVA terminology and, as a consequence, sources of information can be missed by doctors and patients unaware of the ISSVA convention.References
{{Vascular anomalies Vascular diseases