V-weapon on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]

 V-weapons, known in original German as (, German: "retaliatory weapons", "reprisal weapons"), were a particular set of long-range
V-weapons, known in original German as (, German: "retaliatory weapons", "reprisal weapons"), were a particular set of long-range
Rocket V2 – The "Third Bridge Operation", July 1944An overview of all the deadly V-impacts in Belgium
{{V-weapons World War II strategic bombing Reprisals


 V-weapons, known in original German as (, German: "retaliatory weapons", "reprisal weapons"), were a particular set of long-range
V-weapons, known in original German as (, German: "retaliatory weapons", "reprisal weapons"), were a particular set of long-range artillery
Artillery consists of ranged weapons that launch Ammunition, munitions far beyond the range and power of infantry firearms. Early artillery development focused on the ability to breach defensive walls and fortifications during sieges, and l ...
weapons designed for strategic bombing during World War II
World War II (1939–1945) involved sustained strategic bombing of railways, harbours, cities, workers' and civilian housing, and industrial districts in enemy territory. Strategic bombing as a military strategy is distinct both from close ...
, particularly strategic bombing
Strategic bombing is a systematically organized and executed military attack from the air which can utilize strategic bombers, long- or medium-range missiles, or nuclear-armed fighter-bomber aircraft to attack targets deemed vital to the enemy' ...
and aerial bombing of cities
The aerial bombing of cities is an optional element of strategic bombing, which became widespread in warfare during World War I. The bombing of cities grew to a vast scale in World War II and is still practiced today. The development of aeri ...
. They were the V-1, a pulsejet
file:Pulse Jet Engine.PNG, 300px, Diagram of a valved pulsejet. 1 - Air enters through valve and is mixed with fuel. 2 - The mixture is ignited, expands, closes the valve and exits through the tailpipe, creating thrust.3 - Low pressure in the engi ...
-powered cruise missile
A cruise missile is an unmanned self-propelled guided missile that sustains flight through aerodynamic lift for most of its flight path. Cruise missiles are designed to deliver a large payload over long distances with high precision. Modern cru ...
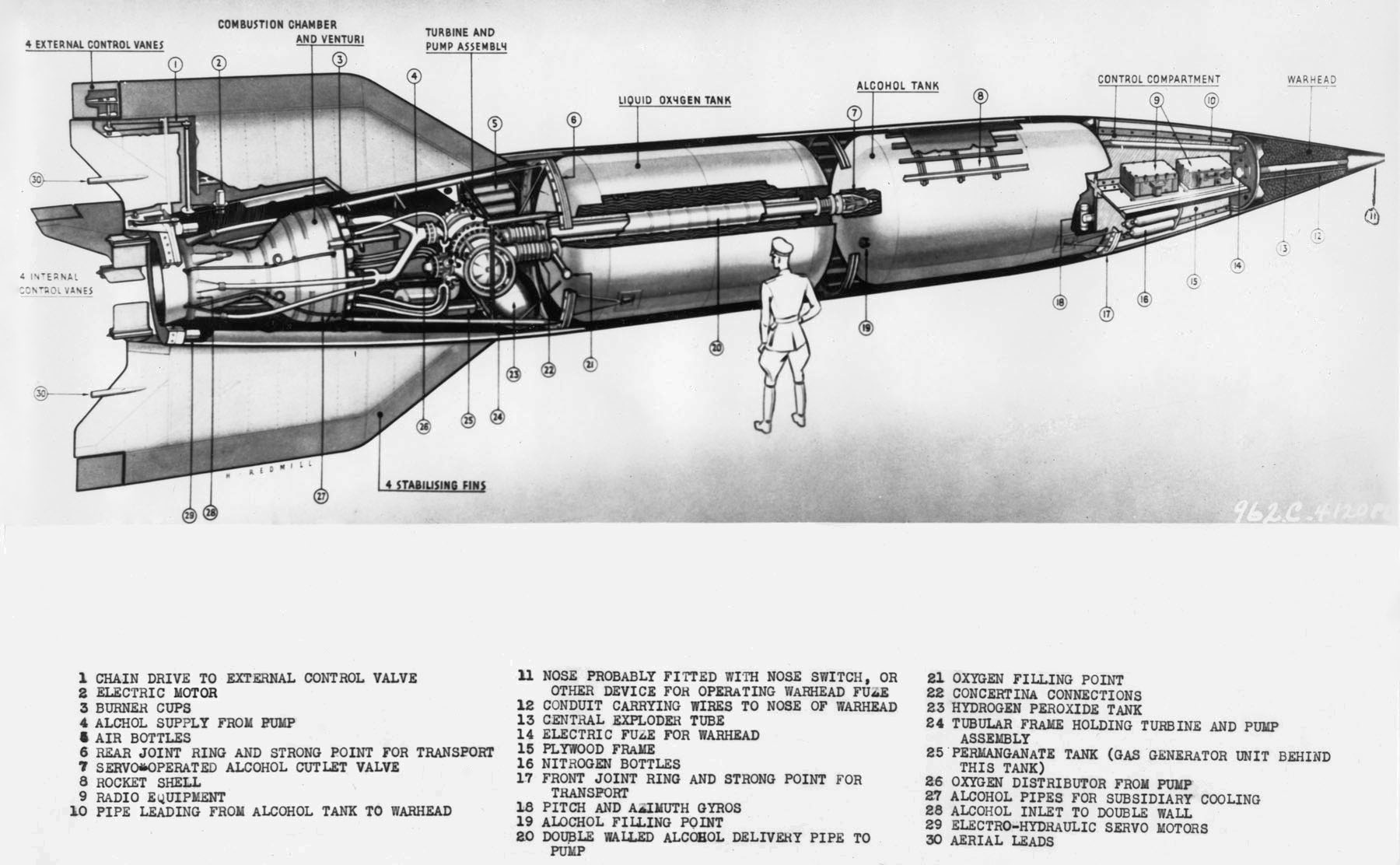
; the V-2, a liquid-fueled ballistic missile
A ballistic missile is a type of missile that uses projectile motion to deliver warheads on a target. These weapons are powered only during relatively brief periods—most of the flight is unpowered. Short-range ballistic missiles (SRBM) typic ...
; and the V-3 cannon. Germany intended to use all of these weapons in a military campaign against Britain
Britain most often refers to:
* Great Britain, a large island comprising the countries of England, Scotland and Wales
* The United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Ireland, a sovereign state in Europe comprising Great Britain and the north-eas ...
, though only the V-1 and V-2 were so used in a campaign conducted 1944–45. After the invasion of western Europe by the Allies, these weapons were also employed against targets on the mainland of Europe, mainly in France and Belgium. Strategic bombing
Strategic bombing is a systematically organized and executed military attack from the air which can utilize strategic bombers, long- or medium-range missiles, or nuclear-armed fighter-bomber aircraft to attack targets deemed vital to the enemy' ...
with V-weapons killed approximately 18,000 people, mostly civilians. The cities of London
London is the Capital city, capital and List of urban areas in the United Kingdom, largest city of both England and the United Kingdom, with a population of in . London metropolitan area, Its wider metropolitan area is the largest in Wester ...
, Antwerp
Antwerp (; ; ) is a City status in Belgium, city and a Municipalities of Belgium, municipality in the Flemish Region of Belgium. It is the capital and largest city of Antwerp Province, and the third-largest city in Belgium by area at , after ...
and Liège
Liège ( ; ; ; ; ) is a City status in Belgium, city and Municipalities in Belgium, municipality of Wallonia, and the capital of the Liège Province, province of Liège, Belgium. The city is situated in the valley of the Meuse, in the east o ...
were the main targets.
V-weapons formed part of the range of the so-called ( superweapons, or "wonderweapons") of Nazi Germany
Nazi Germany, officially known as the German Reich and later the Greater German Reich, was the German Reich, German state between 1933 and 1945, when Adolf Hitler and the Nazi Party controlled the country, transforming it into a Totalit ...
.
Development
As early as 28 June 1940, a strategic bombing rationale had been advanced for the A4 (V-2 rocket) being developed at a meeting between Army Ordnance Chief Emil Leeb and Commander-in-Chief of the Wehrmacht,Walther von Brauchitsch
Walther Heinrich Alfred Hermann von Brauchitsch (4 October 1881 – 18 October 1948) was a German ''Generalfeldmarschall'' (Field Marshal) and Commander-in-Chief (''Oberbefehlshaber'') of the German Army during the first two years of World War ...
. Following the relative failure of the Baedeker Raids in Britain in 1942, development of both flying bomb and rocket accelerated, with Britain designated as the target. On 29 September 1943, Albert Speer
Berthold Konrad Hermann Albert Speer (; ; 19 March 1905 – 1 September 1981) was a German architect who served as Reich Ministry of Armaments and War Production, Minister of Armaments and War Production in Nazi Germany during most of W ...
publicly promised retribution against the mass bombing of German cities by a "secret weapon". Then the official 24 June 1944 Reich Propaganda Ministry announcement of the " Vergeltungswaffe 1" guided missile
A missile is an airborne ranged weapon capable of Propulsion, self-propelled flight aided usually by a propellant, jet engine or rocket motor.
Historically, 'missile' referred to any projectile that is thrown, shot or propelled towards a targ ...
implied that there would be another such weapon. After the first operational A-4 launch in September 1944, the rocket was renamed the V-2. (although no one knows exactly who gave it this name). However, the V-2 operations manual distributed to firing batteries continued to use the A-4 name for the rocket.
Allen Dulles, head of the American secret service OSS in Switzerland, was in contact with the Austrian resistance group around the priest Heinrich Maier from 1943 onwards. Through this Dulles received crucial information and plans about Peenemünde, the V-1 and the V-2 rocket
The V2 (), with the technical name ''Aggregat (rocket family), Aggregat-4'' (A4), was the world's first long-range missile guidance, guided ballistic missile. The missile, powered by a liquid-propellant rocket engine, was developed during the S ...
.
Use against Britain and Mainland Europe 1944–45
V-1
Beginning in October 1943, launch sites for the V-1 were constructed in Northern France, along the coast fromCalais
Calais ( , , traditionally , ) is a French port city in the Pas-de-Calais department, of which it is a subprefecture. Calais is the largest city in Pas-de-Calais. The population of the city proper is 67,544; that of the urban area is 144,6 ...
to Le Havre
Le Havre is a major port city in the Seine-Maritime department in the Normandy (administrative region), Normandy region of northern France. It is situated on the right bank of the estuary of the Seine, river Seine on the English Channel, Channe ...
. Aerial bombing attacks on these sites by the Allied airforce were only partially successful, and by June 1944 they were ready for action. Prompted by the Normandy Landings
The Normandy landings were the landing operations and associated airborne operations on 6 June 1944 of the Allies of World War II, Allied invasion of Normandy in Operation Overlord during the Second World War. Codenamed Operation Neptune and ...
of 6 June, in the early morning of 13 June 1944, the first V-1 flying bomb attack was carried out on London. Ten missiles were launched, of which four reached England. The first of these impacted near Swanscombe, causing no casualties. At Bethnal Green
Bethnal Green is an area in London, England, and is located in the London Borough of Tower Hamlets. It is in east London and part of the East End of London, East End. The area emerged from the small settlement which developed around the common la ...
, however, a bridge was destroyed, six people killed and nine injured. The attacks became sustained at a rate of about 100 a day. With the first attack the British put their pre-planned Operation Diver (after their codename "Diver" used for the V-1) into action.
The buzzing sound of the V-1's pulse jet engine
In medicine, the pulse refers to the rhythmic pulsations (expansion and contraction) of an artery in response to the cardiac cycle (heartbeat). The pulse may be felt (palpated) in any place that allows an artery to be compressed near the surface ...
was likened by some to "a motor cycle in bad running order". As it reached its target and dived, there would be a distinct sound of the propulsion unit spluttering and cutting out; the eerie hush before impact which followed was quite terrifying, according to observers. The brief interval of silence before detonation was also a warning to seek shelter (later V-1s were corrected to have the originally intended power dive). At least one business in London advertised how quickly a patron could access a nearby shelter. Despite this, the cloudy and rainy conditions of June and July aided the effectiveness of the weapon, and casualties were high. By late August a million and a half people had left London, and the rate of work production was affected. By the late summer and autumn, however, increasingly effective countermeasures against the V-1 were taken, and people started returning to London.
A total of 9,251 V-1s were fired at targets in Britain, with the vast majority aimed at London; 2,515 reached the city, killing 6,184 civilians and injuring 17,981. Croydon
Croydon is a large town in South London, England, south of Charing Cross. Part of the London Borough of Croydon, a Districts of England, local government district of Greater London; it is one of the largest commercial districts in Greater Lond ...
to the south, on the flight path of the V-1s, suffered severely, taking 142 hits.
V-2
V-2 rocket launching sites were set up by the Germans aroundThe Hague
The Hague ( ) is the capital city of the South Holland province of the Netherlands. With a population of over half a million, it is the third-largest city in the Netherlands. Situated on the west coast facing the North Sea, The Hague is the c ...
in the Netherlands on 6 September 1944. The first was launched from here against London on 8 September 1944 and took an estimated 5 minutes to fly the from the Hague to London, where it struck at 6:43pm on 8 September on Chiswick
Chiswick ( ) is a district in West London, split between the London Borough of Hounslow, London Boroughs of Hounslow and London Borough of Ealing, Ealing. It contains Hogarth's House, the former residence of the 18th-century English artist Wi ...
, causing 13 casualties. As the V-2 explosions came without warning, the government initially attempted to conceal their cause by blaming them on defective gas mains. However, the public was not fooled and soon began sardonically referring to the V-2s as "Flying gas pipes".
By October the offensive became sustained. A particularly devastating strike was on 25 November 1944, when a V-2 exploded at the Woolworths store in New Cross Road, killing 168 people and seriously injuring 121. Intercepting the supersonic V-2 missiles in flight proved virtually impossible, and other countermeasures, such as bombing the launch sites, were fairly ineffectual. Sustained bombardment continued until March 1945. The final missiles arrived on 27 March 1945, with one of them killing 134 people and injuring 49 when it hit a block of flats in Stepney
Stepney is an area in the London Borough of Tower Hamlets in the East End of London. Stepney is no longer officially defined, and is usually used to refer to a relatively small area. However, for much of its history the place name was applied to ...
.
1,115 V-2s were fired at the United Kingdom. The vast majority of them were aimed at London, though about 40 targeted (and missed) Norwich
Norwich () is a cathedral city and district of the county of Norfolk, England, of which it is the county town. It lies by the River Wensum, about north-east of London, north of Ipswich and east of Peterborough. The population of the Norwich ...
. They killed an estimated 2,754 people in London, with another 6,523 injured. A further 2,917 service personnel were killed as a result of the V-weapon campaign. Since the V-2 was supersonic and could not be heard (and was rarely seen) as it approached the target, its psychological effect "suffered in comparison to the V-1".
The V-weapon offensive ended in March 1945, with the last V-2 landing in Kent
Kent is a Ceremonial counties of England, ceremonial county in South East England. It is bordered by Essex across the Thames Estuary to the north, the Strait of Dover to the south-east, East Sussex to the south-west, Surrey to the west, and Gr ...
on March 27, and the last enemy-action incident of any kind on British soil occurred at 09:00 on 29 March 1945 when a V-1 struck a Hertfordshire
Hertfordshire ( or ; often abbreviated Herts) is a ceremonial county in the East of England and one of the home counties. It borders Bedfordshire to the north-west, Cambridgeshire to the north-east, Essex to the east, Greater London to the ...
field. In terms of casualties, their effects had been less than their inventors hoped or their victims feared, though the damage to property was extensive, with 20,000 houses a day being damaged at the height of the campaign, causing a massive housing crisis in south-east England in late 1944 and early 1945.
The existential horror of the V-2 attack on London is the theme of Thomas Pynchon
Thomas Ruggles Pynchon Jr. ( , ; born May 8, 1937) is an American novelist noted for his dense and complex novels. His fiction and non-fiction writings encompass a vast array of subject matter, Literary genre, genres and Theme (narrative), th ...
's novel '' Gravity's Rainbow''.
V-2s were launched against Antwerp
Antwerp (; ; ) is a City status in Belgium, city and a Municipalities of Belgium, municipality in the Flemish Region of Belgium. It is the capital and largest city of Antwerp Province, and the third-largest city in Belgium by area at , after ...
and Liège
Liège ( ; ; ; ; ) is a City status in Belgium, city and Municipalities in Belgium, municipality of Wallonia, and the capital of the Liège Province, province of Liège, Belgium. The city is situated in the valley of the Meuse, in the east o ...
in Belgium; the attack on Antwerp was to prevent use of the Port of Antwerp which was essential for Allied logistics. In the six months following liberation in September 1944, Belgian towns were targeted by German V-weapons. A total of 2,342 V-weapons (mostly of the more advanced V-2 type) fell in a radius around Antwerp alone. A post-war SHAEF
Supreme Headquarters Allied Expeditionary Force (SHAEF; ) was the headquarters of the Commander of Allies of World War II, Allied forces in northwest Europe, from late 1943 until the end of World War II. US General Dwight D. Eisenhower was the ...
report estimated V-Bombs had been responsible for killing 5,000 people and injuring a further 21,000, mostly in the cities of Antwerp and Liège.
On 17 March 1945 eleven V-2 rockets were fired at the Ludendorf rail bridge across the Rhine at Remagen
Remagen () is a town in Germany in the state of Rhineland-Palatinate, in the district of Ahrweiler (district), Ahrweiler. It is about a one-hour drive from Cologne, just south of Bonn, the former West Germany, West German seat of government. It i ...
on Hitler's orders (see Battle of Remagen). This was the only time they were fired at a tactical target or at a target in Germany; the nearest hit to the target was away; and one hit Cologne, to the north. The General Staff were against their use as they were inaccurate and could kill German citizens and troops, but Hitler was desperate to destroy the Allied bridgehead across the Rhine. They were launched by Batterie SS Abt. 500 at Hellendoorn in the Netherlands, about to the north.
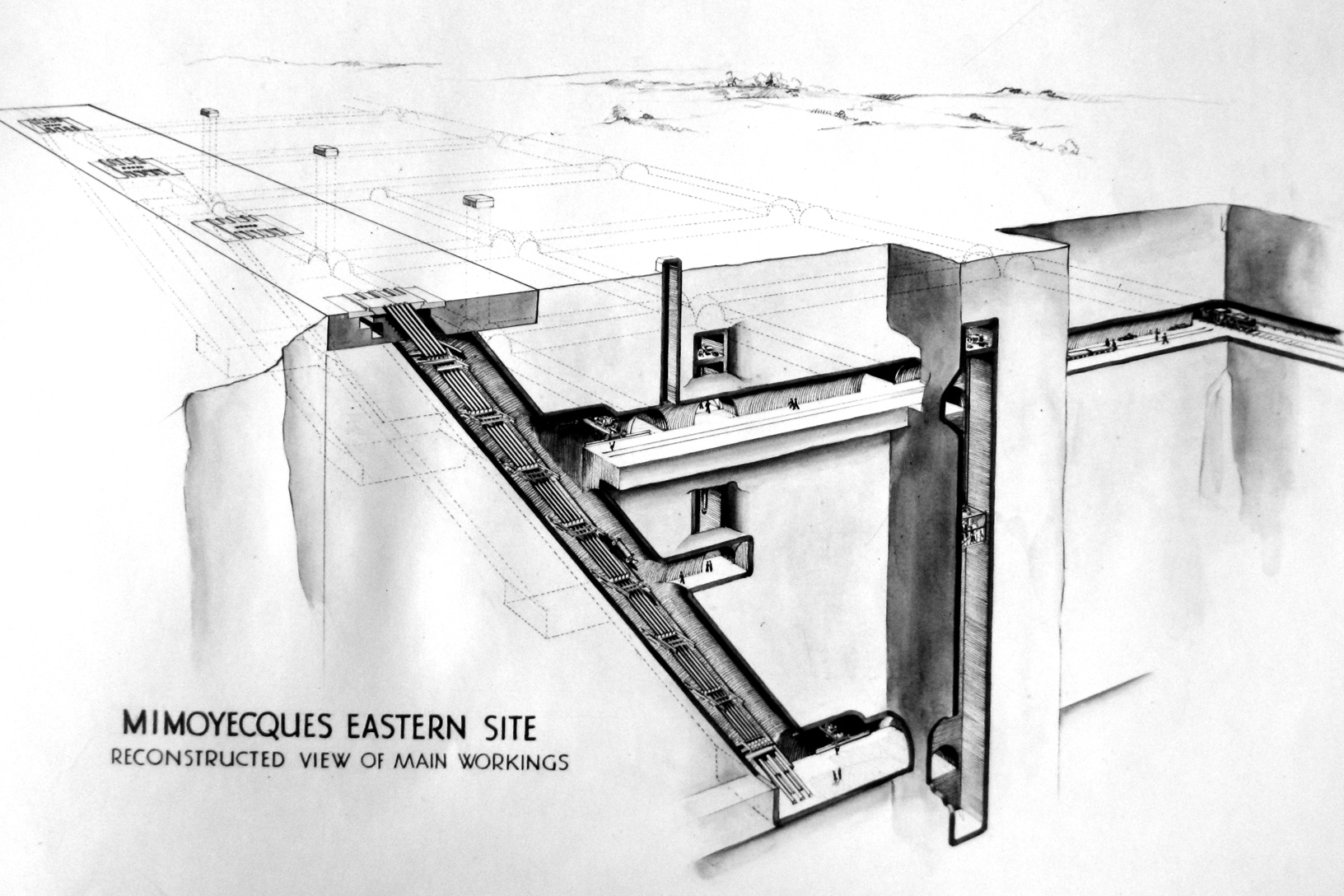
V-3
The V-3 cannon, also designed to fire on London, was never used for this purpose due to Allied attacks on the launch facilities, especially the fortress of Mimoyecques, and the offensive in northern Europe in 1944, overrunning the launch sites. Consequently, its use was diverted, in the winter of 1944, to bombardLuxembourg
Luxembourg, officially the Grand Duchy of Luxembourg, is a landlocked country in Western Europe. It is bordered by Belgium to the west and north, Germany to the east, and France on the south. Its capital and most populous city, Luxembour ...
, with minimal result.Max Hastings (2004) ''Armageddon: The Battle for Germany 1944–1945'': 196.
V-4
The term V-4 has been applied by later writers to a number of projects and systems but in no case is this supported by period German documentation. Things it has been assigned to include the German nuclear program during World War II the A9 rocket and the Fieseler Fi 103R Reichenberg. The name has also been applied to a solid fuel rocket named the Rheinbote (Rhine Messenger). A salvo of 24 was fired at Antwerp on 24 December 1944, but they were "woefully inaccurate" and after another salvo was launched at the port SS Lieutenant General Hans Kammler gave up on the programme.See also
* Aggregat series *Peenemünde
Peenemünde (, ) is a municipality on the Baltic Sea island of Usedom in the Vorpommern-Greifswald district in Mecklenburg-Vorpommern in north-eastern Germany. It is part of the ''Amt (country subdivision), Amt'' (collective municipality) of Used ...
*Operation Hydra (1943)
Operation Hydra was an attack by RAF Bomber Command on a German scientific research centre at Peenemünde on the night of 17/18 August 1943. Group Captain John Searby, commanding officer of No. 83 Squadron RAF, commanded the operation, the fir ...
* Operation Most III
*Operation Crossbow
''Crossbow'' was the code name in World War II for Anglo-American operations against the German V-weapons, long range reprisal weapons (V-weapons) programme. The primary V-weapons were the V-1 flying bomb and V-2 rocket, which were launched agai ...
References
External links
Rocket V2 – The "Third Bridge Operation", July 1944
{{V-weapons World War II strategic bombing Reprisals