|
Operation Diver
Operation Diver was the British code name for the V-1 flying bomb campaign launched by the German in 1944 against London and other parts of Britain. Diver was the code name for the V-1, against which the defence consisted of anti-aircraft guns, barrage balloons and fighter aircraft. The British Double-Cross System used double agents to plant false information about the accuracy of the V-1 bombardment. Anti-aircraft guns proved the most effective form of defence in the later stages of the campaign, with the aid of radar-based technology and the proximity fuse. The V-1 campaign from ground launch sites ended by the middle of 1944 with the Allied occupation of the launch sites. Diver Plan The Diver Plan was prepared in early 1944 following the first reports of the weapon in April 1943 and the discovery of its intended launch sites in late 1943. The plan had to be flexible enough to cover the anticipated assault on Britain and the needs of Operation Overlord, the Allied invasion o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cleverly Estate After A Direct Hit From A V1 Rocket, 1945 (6841305380)
Cleverly is a surname. Notable people with the name include: * Barbara Cleverly (born 1940), British author of detective fiction * Charles St George Cleverly (1819–1897), second Surveyor General in Hong Kong * Chris Cleverly (born 1967), British lawyer * Harry Cleverly (1912–1968), American ice hockey and baseball coach at Boston University * James Cleverly (born 1969), British Conservative Member of Parliament * Marcus Cleverly (born 1981), Danish handballer * Nathan Cleverly (born 1987), Welsh boxer * Sir Osmund Somers Cleverly (1891–1966), Principal Private Secretary to the British Prime Minister * Rhian Cleverly Rhian Cleverly (born 11 January 1995) is a Welsh footballer who plays as defender and midfielder for Lewes. She has a single appearance with the Wales national team. Early life, youth and college career Cleverly was born in Griffithstown. She ... (born 1995), Welsh footballer See also * Cleverley, surname with a similar spelling * Cleverly estate, a P ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
East Anglia
East Anglia is an area of the East of England, often defined as including the counties of Norfolk, Suffolk and Cambridgeshire, with parts of Essex sometimes also included. The name derives from the Anglo-Saxon kingdom of the East Angles, a people whose name originated in Anglia (Angeln), in what is now Northern Germany. East Anglia is a predominantly rural region and contains mainly flat or low-lying and agricultural land. The area is known for considerable natural beauty. It shares a long North Sea coastline and contains one of the ten national parks in England, The Broads. Norwich is the largest city in the region. Area Definitions of what constitutes East Anglia vary. The Anglo-Saxon Kingdom of East Anglia, established in the 6th century, originally consisted of the modern counties of Norfolk and Suffolk and expanded west into at least part of Cambridgeshire, typically the northernmost parts known as The Fens. The modern NUTS 2 statistical unit of East Anglia compri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
SCR-584 Radar
The SCR-584 (short for '' Set, Complete, Radio # 584'') was an automatic-tracking microwave radar developed by the MIT Radiation Laboratory during World War II. It was one of the most advanced ground-based radars of its era, and became one of the primary gun laying radars used worldwide well into the 1950s. A trailer-mounted mobile version was the SCR-784. In 1937, America's first fire-control radar, the SCR-268 radar, had proven to be insufficiently accurate due in part to its long wavelength. In 1940, Vannevar Bush, heading the National Defense Research Committee, established the "Microwave Committee" (section D-1) and the "Fire Control" division (D-2) to develop a more advanced radar anti-aircraft system in time to assist the British air-defense effort. In September of that year, a British delegation, the Tizard Mission, revealed to US and Canadian researchers that they had developed a magnetron oscillator operating at the top end of the UHF band (10 cm wavelength/3 GHz), ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Radiation Laboratory At The Massachusetts Institute Of Technology
The Radiation Laboratory, commonly called the Rad Lab, was a microwave and radar research laboratory located at the Massachusetts Institute of Technology (MIT) in Cambridge, Massachusetts. It was first created in October 1940 and operated until 31 December 1945 when its functions were dispersed to industry, other departments within MIT, and in 1951, the newly formed MIT Lincoln Laboratory. The use of microwaves for various radio and radar uses was highly desired before the war, but existing microwave devices like the klystron were far too low powered to be useful. Alfred Lee Loomis, a millionaire and physicist who headed his own private laboratory, organized the Microwave Committee to consider these devices and look for improvements. In early 1940, Winston Churchill organized what became the Tizard Mission to introduce U.S. researchers to several new technologies the UK had been developing. Among these was the cavity magnetron, a leap forward in the creation of microwaves that ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
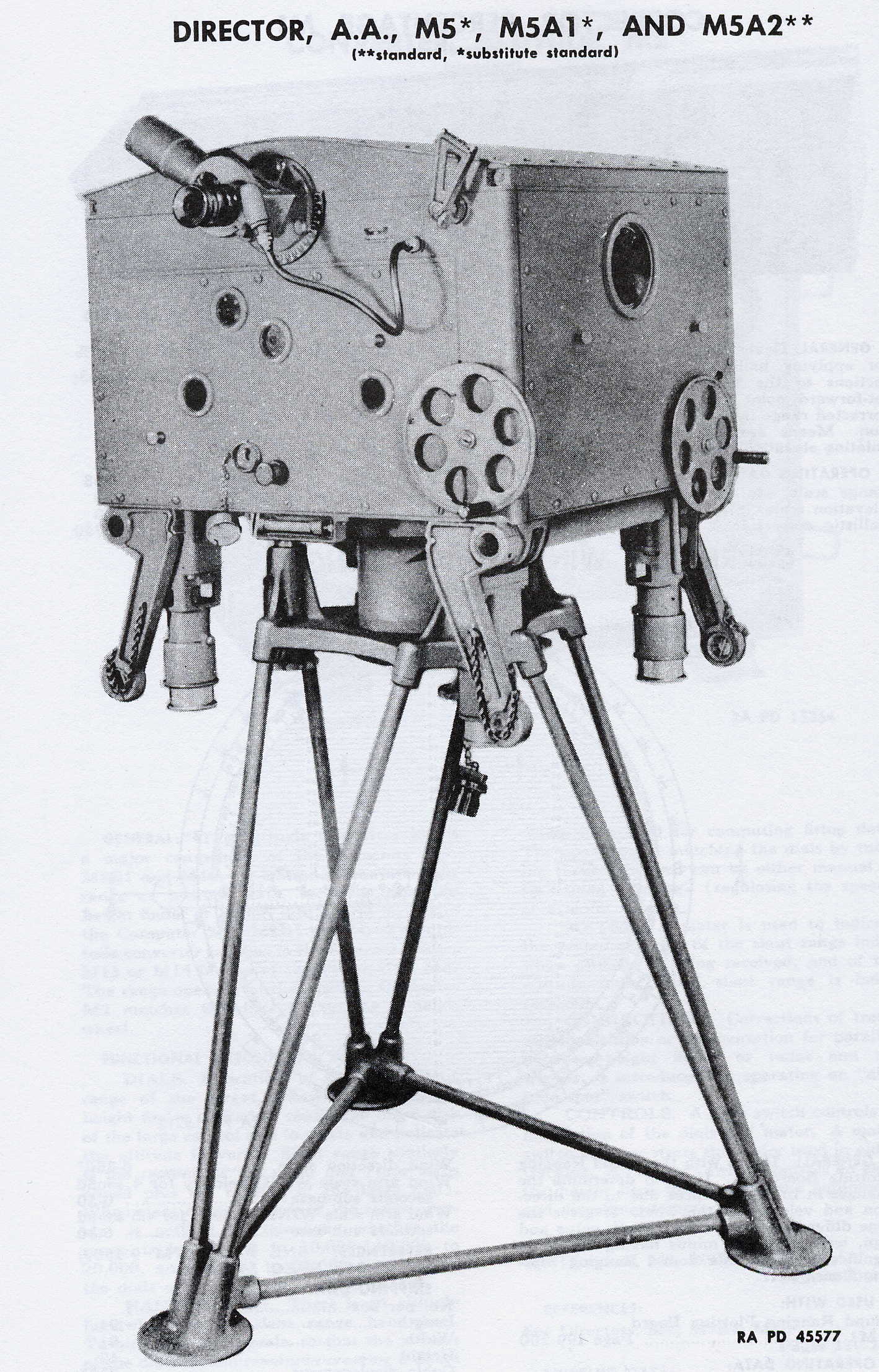
Kerrison Predictor
The Kerrison Predictor was one of the first fully automated anti-aircraft fire-control systems. It was used to automate the aiming of the British Army's Bofors 40 mm guns and provide accurate lead calculations through simple inputs on three main handwheels. The predictor could aim a gun at an aircraft based on simple inputs like the observed speed and the angle to the target. Such devices had been used on ships for gunnery control for some time, and versions such as the Vickers Predictor were available for larger anti-aircraft guns intended to be used against high-altitude bombers. Kerrison's analog computer was the first to be fast enough to be used in the demanding high-speed low-altitude role, which involved very short engagement times and high angular rates. The design was also adopted for use in the United States, where it was produced by Singer Corporation as the M5 Antiaircraft Director, later updated as the M5A1 and M5A2. The M6 was mechanically identical, differing on ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Analogue Computer
An analog computer or analogue computer is a type of computation machine (computer) that uses physical phenomena such as electrical, mechanical, or hydraulic quantities behaving according to the mathematical principles in question (''analog signals'') to model the problem being solved. In contrast, digital computers represent varying quantities symbolically and by discrete values of both time and amplitude (digital signals). Analog computers can have a very wide range of complexity. Slide rules and nomograms are the simplest, while naval gunfire control computers and large hybrid digital/analog computers were among the most complicated. Complex mechanisms for process control and protective relays used analog computation to perform control and protective functions. Analog computers were widely used in scientific and industrial applications even after the advent of digital computers, because at the time they were typically much faster, but they started to become obsolete as ear ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fire-control System
A fire-control system (FCS) is a number of components working together, usually a gun data computer, a director and radar, which is designed to assist a ranged weapon system to target, track, and hit a target. It performs the same task as a human gunner firing a weapon, but attempts to do so faster and more accurately. Naval fire control Origins The original fire-control systems were developed for ships. The early history of naval fire control was dominated by the engagement of targets within visual range (also referred to as direct fire). In fact, most naval engagements before 1800 were conducted at ranges of . Even during the American Civil War, the famous engagement between and was often conducted at less than range. Rapid technical improvements in the late 19th century greatly increased the range at which gunfire was possible. Rifled guns of much larger size firing explosive shells of lighter relative weight (compared to all-metal balls) so greatly increased the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bell Labs
Nokia Bell Labs, commonly referred to as ''Bell Labs'', is an American industrial research and development company owned by Finnish technology company Nokia. With headquarters located in Murray Hill, New Jersey, Murray Hill, New Jersey, the company operates several laboratories in the United States and around the world. As a former subsidiary of the American Telephone and Telegraph Company (AT&T), Bell Labs and its researchers have been credited with the development of radio astronomy, the transistor, the laser, the photovoltaic cell, the charge-coupled device (CCD), information theory, the Unix operating system, and the programming languages B (programming language), B, C (programming language), C, C++, S (programming language), S, SNOBOL, AWK, AMPL, and others, throughout the 20th century. Eleven Nobel Prizes and five Turing Awards have been awarded for work completed at Bell Laboratories. Bell Labs had its origin in the complex corporate organization of the Bell System telepho ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Proximity Fuze
A Proximity Fuse (also VT fuse or "variable time fuze") is a fuse that detonates an explosive device automatically when it approaches within a certain distance of its target. Proximity fuses are designed for elusive military targets such as aircraft and missiles, as well as ships at sea and ground forces. This sophisticated trigger mechanism may increase lethality by 5 to 10 times compared to the common contact fuse or timed fuse. Background Before the invention of the proximity fuze, detonation was induced by direct contact, a timer set at launch, or an altimeter. All of these earlier methods have disadvantages. The probability of a direct hit on a small moving target is low; a shell that just misses the target will not explode. A time- or height-triggered fuze requires good prediction by the gunner and accurate timing by the fuze. If either is wrong, then even accurately aimed shells may explode harmlessly before reaching the target or after passing it. At the start of the Bl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cavity Magnetron
The cavity magnetron is a high-power vacuum tube used in early radar systems and subsequently in microwave ovens and in linear particle accelerators. A cavity magnetron generates microwaves using the interaction of a stream of electrons with a magnetic field, while moving past a series of cavity resonators, which are small, open cavities in a metal block. Electrons pass by the cavities and cause microwaves to oscillate within, similar to the functioning of a whistle producing a tone when excited by an air stream blown past its opening. The resonant frequency of the arrangement is determined by the cavities' physical dimensions. Unlike other vacuum tubes, such as a klystron or a traveling-wave tube (TWT), the magnetron cannot function as an amplifier for increasing the intensity of an applied microwave signal; the magnetron serves solely as an electronic oscillator generating a microwave signal from direct-current electricity supplied to the vacuum tube. The use of magne ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fire Control Radar
A fire-control radar (FCR) is a radar that is designed specifically to provide information (mainly target azimuth, elevation, range and range rate) to a fire-control system in order to direct weapons such that they hit a target. They are sometimes known as narrow beam radars, targeting radars, tracking radars, or in the UK, gun-laying radars. If the radar is used to guide a missile, it is often known as a target illuminator or illuminator radar. A typical fire-control radar emits a narrow, intense beam of radio waves to ensure accurate tracking information and to minimize the chance of losing track of the target. This makes them less suitable for initial detection of the target, and FCRs are often partnered with a medium-range search radar to fill this role. In British terminology, these medium-range systems were known as tactical control radars. Most modern radars have a track-while-scan capability, enabling them to function simultaneously as both fire-control radar and sea ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
QF 3
QF may stand for: Businesses and organisations * Qantas, an Australian airline (IATA:QF) * Qatar Foundation, a non-profit * Quiverfull, a Christian movement Military * Quds Force, an Iranian expeditionary unit * Quick-firing gun, an artillery piece * A gun breech that uses metallic cartridges; see British ordnance terms#QF * Q-Fire, a decoy fire site used in World War II Other uses * Quality factor In physics and engineering, the quality factor or factor is a dimensionless parameter that describes how underdamped an oscillator or resonator is. It is defined as the ratio of the initial energy stored in the resonator to the energy lost in ..., in physics and engineering, a measure of the "quality" of a resonant system {{disambig fr:QF ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |