Urethral Stricture on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
A urethral stricture is a narrowing of the
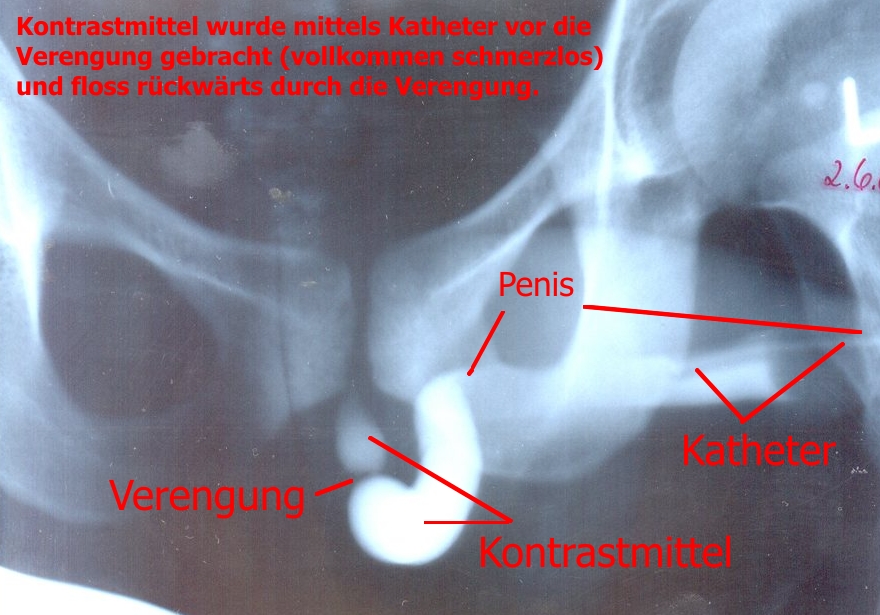 *
*
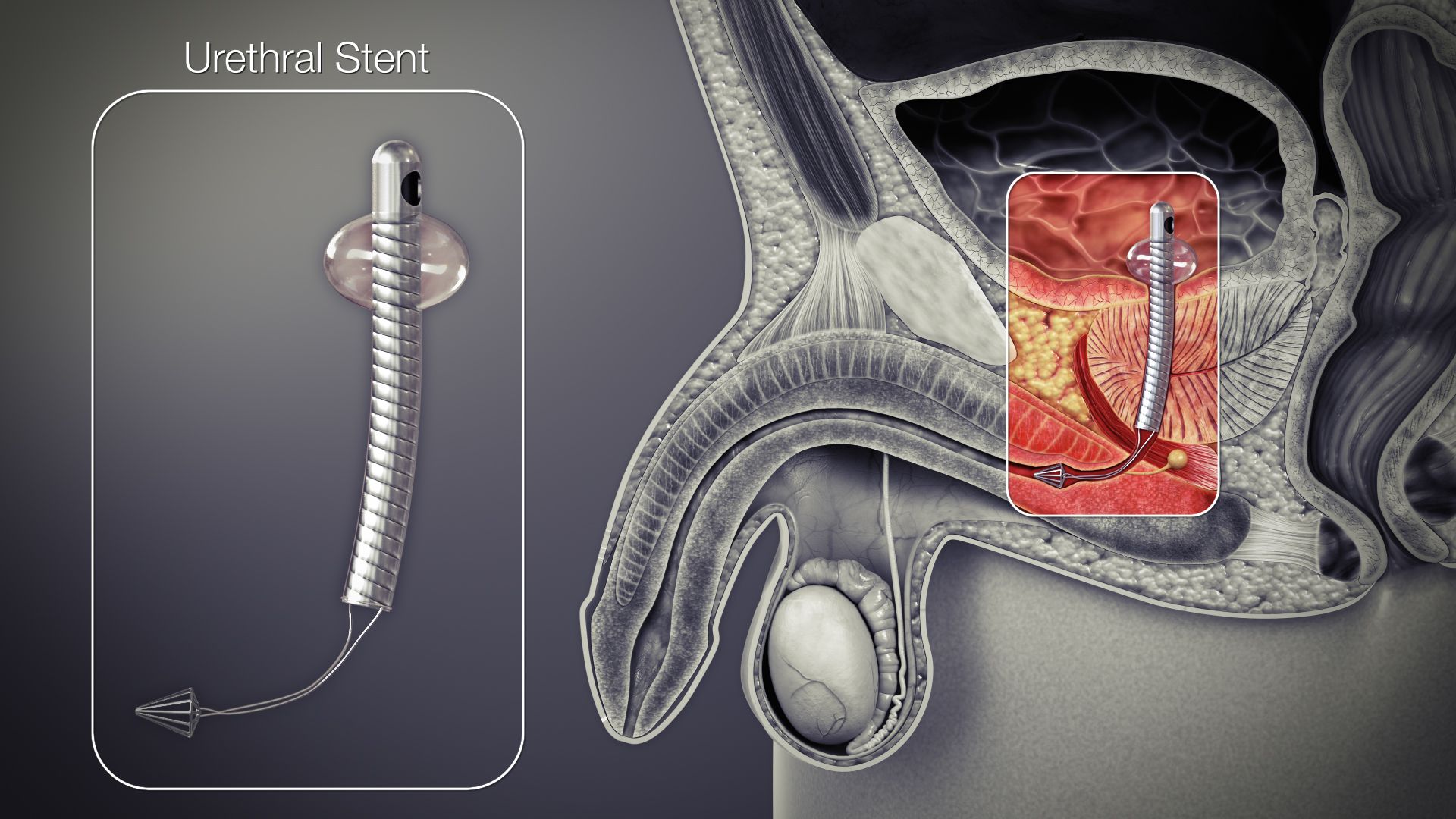 A permanent urethral stent was approved for use in men with bulbar urethral strictures in 1996, but was recently removed from the market.
A temporary thermoexpandable urethral stent (Memotherm) is available in Europe but is not currently approved for use in the United States.
A permanent urethral stent was approved for use in men with bulbar urethral strictures in 1996, but was recently removed from the market.
A temporary thermoexpandable urethral stent (Memotherm) is available in Europe but is not currently approved for use in the United States.
urethra
The urethra (: urethras or urethrae) is the tube that connects the urinary bladder to the urinary meatus, through which Placentalia, placental mammals Urination, urinate and Ejaculation, ejaculate.
The external urethral sphincter is a striated ...
, the tube connected to the bladder
The bladder () is a hollow organ in humans and other vertebrates that stores urine from the kidneys. In placental mammals, urine enters the bladder via the ureters and exits via the urethra during urination. In humans, the bladder is a distens ...
that allows urination
Urination is the release of urine from the bladder through the urethra in Placentalia, placental mammals, or through the cloaca in other vertebrates. It is the urinary system's form of excretion. It is also known medically as micturition, v ...
. The narrowing reduces the flow of urine
Urine is a liquid by-product of metabolism in humans and many other animals. In placental mammals, urine flows from the Kidney (vertebrates), kidneys through the ureters to the urinary bladder and exits the urethra through the penile meatus (mal ...
and makes it more difficult or even painful to empty the bladder.
Urethral stricture is caused by injury, instrumentation, infection, and certain non-infectious forms of urethritis
Urethritis is the inflammation of the urethra. The most common symptoms include painful or difficult urination and urethral discharge. It is a commonly treatable condition usually caused by infection with bacteria. This bacterial infection is ...
. The condition is more common in men due to their longer urethra.
Signs and symptoms
The hallmark sign of urethral stricture is a weak urinary stream. Other symptoms include: * Splaying of the urinary stream * Urinary frequency * Urinary urgency * Straining to urinate * Pain during urination *Urinary tract infection
A urinary tract infection (UTI) is an infection that affects a part of the urinary tract. Lower urinary tract infections may involve the bladder (cystitis) or urethra (urethritis) while upper urinary tract infections affect the kidney (pyel ...
* Prostatitis
Prostatitis is an umbrella term for a variety of medical conditions that incorporate bacterial and non-bacterial origin illnesses in the pelvic region. In contrast with the plain meaning of the word (which means "inflammation of the prostate"), the ...
* Inability to completely empty the bladder.
Some people with severe urethral strictures are completely unable to urinate. This is referred to as acute urinary retention
Urinary retention is an inability to completely empty the bladder. Onset can be sudden or gradual. When of sudden onset, symptoms include an inability to urinate and lower abdominal pain. When of gradual onset, symptoms may include urinary incont ...
, and is a medical emergency
A medical emergency is an acute injury or illness that poses an immediate risk to a person's life or long-term health, sometimes referred to as a situation risking "life or limb". These emergencies may require assistance from another, qualified ...
. Hydronephrosis
Hydronephrosis is the hydrostatic dilation of the renal pelvis and Renal calyx, calyces as a result of obstruction to urine flow downstream. Alternatively, hydroureter describes the dilation of the ureter, and hydronephroureter describes the dila ...
and kidney failure
Kidney failure, also known as renal failure or end-stage renal disease (ESRD), is a medical condition in which the kidneys can no longer adequately filter waste products from the blood, functioning at less than 15% of normal levels. Kidney fa ...
may also occur.
Complications
*Urinary retention
Urinary retention is an inability to completely empty the bladder. Onset can be sudden or gradual. When of sudden onset, symptoms include an inability to urinate and lower abdominal pain. When of gradual onset, symptoms may include urinary incont ...
* Prostatitis
Prostatitis is an umbrella term for a variety of medical conditions that incorporate bacterial and non-bacterial origin illnesses in the pelvic region. In contrast with the plain meaning of the word (which means "inflammation of the prostate"), the ...
* Bladder dysfunction
* Urethral diverticulum
In medicine or biology, a diverticulum is an outpouching of a hollow (or a fluid-filled) structure in the body. Depending upon which layers of the structure are involved, diverticula are described as being either true or false.
In medicine, t ...
* Periurethral abscess
* Fournier's gangrene
* Urethral
The urethra (: urethras or urethrae) is the tube that connects the urinary bladder to the urinary meatus, through which placental mammals urinate and ejaculate.
The external urethral sphincter is a striated muscle that allows voluntary control ...
fistula
In anatomy, a fistula (: fistulas or fistulae ; from Latin ''fistula'', "tube, pipe") is an abnormal connection (i.e. tube) joining two hollow spaces (technically, two epithelialized surfaces), such as blood vessels, intestines, or other h ...
* Bilateral hydronephrosis
Hydronephrosis is the hydrostatic dilation of the renal pelvis and Renal calyx, calyces as a result of obstruction to urine flow downstream. Alternatively, hydroureter describes the dilation of the ureter, and hydronephroureter describes the dila ...
* Urinary infections
* Urinary calculus
Calculus is the mathematics, mathematical study of continuous change, in the same way that geometry is the study of shape, and algebra is the study of generalizations of arithmetic operations.
Originally called infinitesimal calculus or "the ...
Causes
Urethral strictures most commonly result from injury, urethral instrumentation, infection, non-infectious inflammatory conditions of the urethra, and after priorhypospadias
Hypospadias is a common malformation in fetal development of the penis in which the urethra does not open from its usual location on the head of the penis. It is the second-most common birth defect of the male reproductive system, affecting about ...
surgery. Less common causes include congenital urethral strictures and those resulting from malignancy.
Urethral strictures after blunt trauma can generally be divided into two sub-types;
* Pelvic fracture-associated urethral disruption occurs in as many as 15% of severe pelvic fractures. These injuries are typically managed with suprapubic tube placement and delayed urethroplasty 3 months later. Early endoscopic realignment may be used in select cases instead of a suprapubic tube, but these patients should be monitored closely as vast majority of them will require urethroplasty.
* Blunt trauma to the perineum compresses the bulbar urethra against the pubic symphysis, causing a "crush" injury. These patients are typically treated with suprapubic tube and delayed urethroplasty.
Other specific causes of urethral stricture include:
* Instrumentation (e.g., after transurethral resection of prostate, transurethral resection of bladder tumor, or endoscopic kidney surgery)
* Infection (typically with gonorrhea
Gonorrhoea or gonorrhea, colloquially known as the clap, is a sexually transmitted infection (STI) caused by the bacterium ''Neisseria gonorrhoeae''. Infection may involve the genitals, mouth, or rectum.
Gonorrhea is spread through sexual c ...
)
* Lichen sclerosus
Lichen sclerosus (LS) is a chronic, inflammatory skin disease, of unknown cause, which can affect any body part of any person, but has a strong preference for the genitals (penis, vulva), and is also known as balanitis xerotica obliterans when i ...
* Surgery to address hypospadias can result in a delayed urethral stricture, even decades after the original surgery.
Diagnosis
Among ways to diagnose this condition is: *
* Cystoscopy
Cystoscopy is endoscopy of the urinary bladder via the urethra. It is carried out with a cystoscope.
The urethra is the tube that carries urine from the bladder to the outside of the body.
The cystoscope has lenses like a telescope or microscop ...
* Urethrography
Treatment
Initial treatment usually involves urethral dilation (widening the tube) orurethrotomy
A urethrotomy is an operation which involves incision of the urethra, especially for relief of a stricture. It is most often performed in the outpatient setting, with the patient (usually) being discharged from the hospital or surgery center wit ...
, where the stricture is cut away with a cystoscope
Cystoscopy is endoscopy of the urinary bladder via the urethra. It is carried out with a cystoscope.
The urethra is the tube that carries urine from the bladder to the outside of the body.
The cystoscope has lenses like a telescope or microscop ...
.
Dilation and urethrotomy
Urethral dilation and otherendoscopic
An endoscopy is a procedure used in medicine to look inside the body. The endoscopy procedure uses an endoscope to examine the interior of a hollow organ or cavity of the body. Unlike many other medical imaging techniques, endoscopes are insert ...
approaches such as direct vision internal urethrotomy (DVIU), laser urethrotomy, and self intermittent dilation are the most commonly used treatments for urethral stricture. However, these approaches are associated with low success rates and may worsen the stricture, making future attempts to surgically repair the urethra more difficult.
A Cochrane review found that performing intermittent self-dilatation may confer a reduced risk of recurrent urethral stricture after endoscopic treatment, but the evidence
Evidence for a proposition is what supports the proposition. It is usually understood as an indication that the proposition is truth, true. The exact definition and role of evidence vary across different fields. In epistemology, evidence is what J ...
is weak.
Urethroplasty
Urethroplasty
Urethroplasty is the surgical repair of an injury or defect within the walls of the urethra. Trauma, iatrogenic injury and infections are the most common causes of urethral injury/defect requiring repair. Urethroplasty is regarded as the gold st ...
refers to any open reconstruction of the urethra. Success rates range from 85% to 95% and depend on a variety of clinical factors, such as stricture as the cause, length, location, and caliber.Santucci RA, Mario LA, McAninch JW. Anastomotic urethroplasty for bulbar urethral stricture: analysis of 168 patients. J Urol. 2002 Apr;167(4):1715-9.Figler BD, Malaeb BS, Dy GW, Voelzke BB, Wessells H. Impact of graft position on failure of single-stage bulbar urethroplasties with buccal mucosa graft. Urology. 2013 Nov;82(5):1166-70.Barbagli G1, Sansalone S, Romano G, Lazzeri M. Bulbar urethroplasty: transecting vs. nontransecting techniques. Curr Opin Urol. 2012 Nov;22(6):474-7.Bello JO. Impact of preoperative patient characteristics on posturethroplasty recurrence: the significance of stricture length and prior treatments. Niger J Surg. 2016; 22(2):86-89 Urethroplasty can be performed safely on men of all ages.
In the posterior urethra, anastomotic urethroplasty (with or without preservation of bulbar arteries) is typically performed after removing scar tissue.
In the bulbar urethra, the most common types of urethroplasty are anastomotic (with or without preservation of corpus spongiosum and bulbar arteries) and substitution with buccal mucosa graft, full-thickness skin graft
Skin grafting, a type of graft (surgery), graft surgery, involves the organ transplant, transplantation of skin without a defined circulation. The transplanted biological tissue, tissue is called a skin graft.
Surgeons may use skin grafting to ...
, or split thickness skin graft. These are nearly always done in a single setting (or stage).
In the penile urethra, anastomotic urethroplasties are rare because they can lead to chordee (penile curvature due to a shortened urethra). Instead, most penile urethroplasties are substitution procedures utilizing buccal mucosa graft, full-thickness skin graft, or split-thickness skin graft. These can be done in one or more settings, depending on stricture location, severity, cause and patient or surgeon preference.
Urethral stent
 A permanent urethral stent was approved for use in men with bulbar urethral strictures in 1996, but was recently removed from the market.
A temporary thermoexpandable urethral stent (Memotherm) is available in Europe but is not currently approved for use in the United States.
A permanent urethral stent was approved for use in men with bulbar urethral strictures in 1996, but was recently removed from the market.
A temporary thermoexpandable urethral stent (Memotherm) is available in Europe but is not currently approved for use in the United States.
Emergency treatment
When in acute urinary retention, treatment of the urethral stricture or diversion is an emergency. Options include: * Urethral dilatation and catheter placement. This can be performed in theEmergency Department
An emergency department (ED), also known as an accident and emergency department (A&E), emergency room (ER), emergency ward (EW) or casualty department, is a medical treatment facility specializing in emergency medicine, the Acute (medicine), ...
, a practitioner's office or an operating room. The advantage of this approach is that the urethra may remain patent for a period of time after the dilation, though long-term success rates are low.
* Insertion of a suprapubic catheter
A suprapubic cystostomy or suprapubic catheter (SPC) (also known as a vesicostomy or epicystostomy) is a surgically created connection between the urinary bladder and the skin used to drain urine from the bladder in individuals with obstruction ...
with catheter drainage system. This procedure is performed in an Operating Room, Emergency Department or practitioner's office. The advantage of this approach is that it does not disrupt the scar and interfere with future definitive surgery.
Ongoing care
Following urethroplasty, patients should be monitored for a minimum of 1 year, since the vast majority of recurrences occur within 1 year. Because of the high rate of recurrence following dilation and other endoscopic approaches, the provider must maintain a high index of suspicion for recurrence when the patient presents with obstructive voiding symptoms or urinary tract infection.Research
Urethrotomy vs. urethroplasty
Comparing the two surgical procedures, a UK trial found that both urethrotomy and urethroplasty are effective in treating urethral narrowing in the bulbar region. At the same time the more invasive urethroplasty had longer-lasting benefit and was associated with fewer re-interventions. The results were integrated into the new UK guidelines on the treatment urethral narrowing by British Association of Urological Surgeons.Bioengineering
The use of bioengineered urethral tissue is promising, but still in the early stages. The Wake Forest Institute of Regenerative Medicine has pioneered the first bioengineered human urethra and in 2006 implanted urethral tissue grown on bioabsorbable scaffolding (approximating the size and shape of the affected areas) in five young (human) males who had congenital defects, physical trauma, or an unspecified disorder necessitating urethral reconstruction. As of March 2011, all five recipients report the transplants have functioned well.Cell therapy approach through endoscopy
Buccal mucosal tissue harvested under local anesthesia after culturing in the lab when applied as cells through endoscopy after urethrotomy in a pilot study (BEES HAUS Procedure) has yielded encouraging results. This procedure has subsequently been standardised for in vitro cell culture, then in animal models of urethral stricture for both morphological engraftment of the buccal cells onto the site of the urethral injury and also immunohistochemically by negative and positive markers confirming that the transplanted cells are the ones that got engrafted covering the wounded surface of the urethra, leading to possible prevention of recurrence of the stricture. Clinically, this procedure has been started as an application recently in Japan as per the regenerative medicine law of Japan.References
External links
{{Authority control Urethra disorders Male genital disorders