Upper Niger on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The Niger River ( ; ) is the main river of
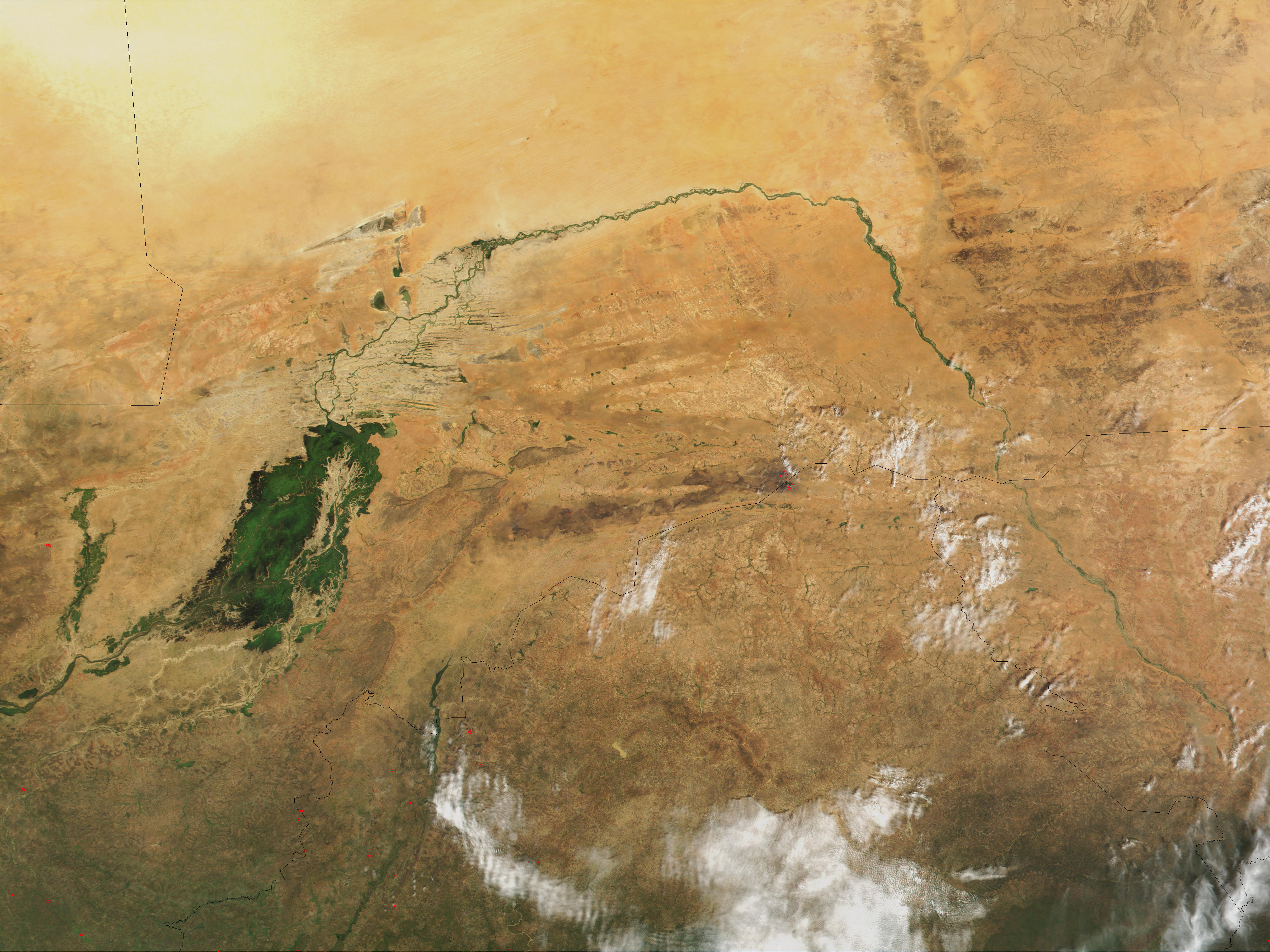 The Niger River is a relatively clear river, carrying only a tenth as much sediment as the Nile because the Niger's headwaters lie in ancient rocks that provide little
The Niger River is a relatively clear river, carrying only a tenth as much sediment as the Nile because the Niger's headwaters lie in ancient rocks that provide little  The river loses nearly two-thirds of its
The river loses nearly two-thirds of its
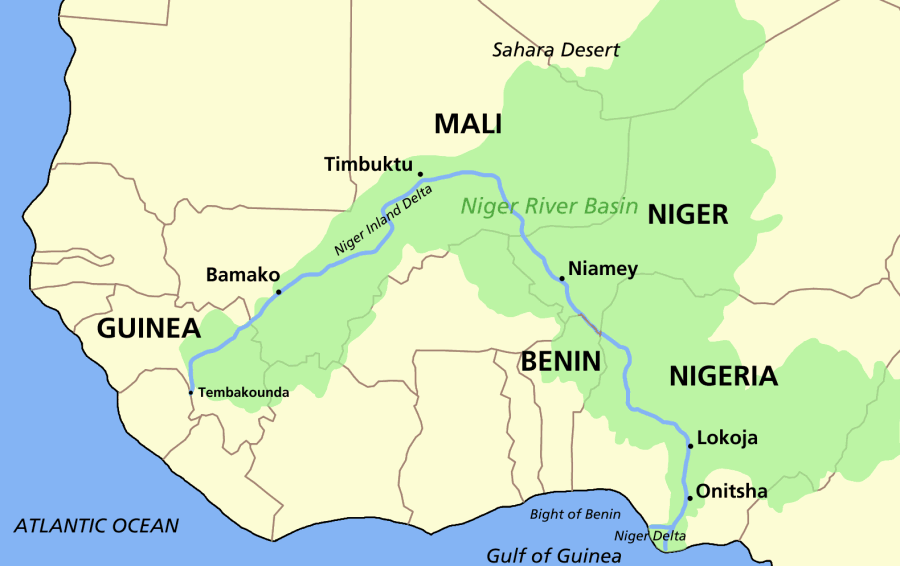 The Niger takes one of the most unusual routes of any major river, a
The Niger takes one of the most unusual routes of any major river, a


 At the end of the African humid period around 5,500 years before present, the modern Sahara Desert, once a
At the end of the African humid period around 5,500 years before present, the modern Sahara Desert, once a
Information and a map of the Niger's watershed
on http://www.wri.org/resources
(link broken)
Niger Currents: Exploring life and technology along the Niger River
*
Bibliography on Water Resources and International Law
Peace Palace Library * {{Authority control Benin–Niger border International rivers of Africa Inner Niger Delta Physiographic sections Rivers of Benin Rivers of Guinea Rivers of Mali Rivers of Niger Rivers of Nigeria Border rivers Lowest points of countries
West Africa
West Africa, also known as Western Africa, is the westernmost region of Africa. The United Nations geoscheme for Africa#Western Africa, United Nations defines Western Africa as the 16 countries of Benin, Burkina Faso, Cape Verde, The Gambia, Gha ...
, extending about . Its drainage basin
A drainage basin is an area of land in which all flowing surface water converges to a single point, such as a river mouth, or flows into another body of water, such as a lake or ocean. A basin is separated from adjacent basins by a perimeter, ...
is in area. Its source is in the Guinea Highlands
The Guinea Highlands is a densely forested mountainous plateau extending from central Guinea through northern Sierra Leone and Liberia to western Ivory Coast. The highlands include a number of mountains, ranges and plateaus, including the Fouta Dj ...
in south-eastern Guinea near the Sierra Leone border. It runs in a crescent shape through Mali, Niger, on the border with Benin and then through Nigeria, discharging through a massive delta
Delta commonly refers to:
* Delta (letter) (Δ or δ), the fourth letter of the Greek alphabet
* D (NATO phonetic alphabet: "Delta"), the fourth letter in the Latin alphabet
* River delta, at a river mouth
* Delta Air Lines, a major US carrier ...
, known as the Niger Delta
The Niger Delta is the delta of the Niger River sitting directly on the Gulf of Guinea on the Atlantic Ocean in Nigeria. It is located within nine coastal southern Nigerian states, which include: all six states from the South South geopolitic ...
, into the Gulf of Guinea
The Gulf of Guinea (French language, French: ''Golfe de Guinée''; Spanish language, Spanish: ''Golfo de Guinea''; Portuguese language, Portuguese: ''Golfo da Guiné'') is the northeasternmost part of the tropical Atlantic Ocean from Cape Lopez i ...
in the Atlantic Ocean
The Atlantic Ocean is the second largest of the world's five borders of the oceans, oceanic divisions, with an area of about . It covers approximately 17% of Earth#Surface, Earth's surface and about 24% of its water surface area. During the ...
. The Niger is the third-longest river in Africa, exceeded by the Nile
The Nile (also known as the Nile River or River Nile) is a major north-flowing river in northeastern Africa. It flows into the Mediterranean Sea. The Nile is the longest river in Africa. It has historically been considered the List of river sy ...
and the Congo River
The Congo River, formerly also known as the Zaire River, is the second-longest river in Africa, shorter only than the Nile, as well as the third-largest river in the world list of rivers by discharge, by discharge volume, following the Amazon Ri ...
. Its main tributary
A tributary, or an ''affluent'', is a stream or river that flows into a larger stream (''main stem'' or ''"parent"''), river, or a lake. A tributary does not flow directly into a sea or ocean. Tributaries, and the main stem river into which they ...
is the Benue River
Benue River (), previously known as the Chadda River or Tchadda, is a major tributary of the Niger River. The size of its catchment basin is 319,000 km2 (123,000 sq mi). Almost its entire length of Approximation, approximately is navigable dur ...
.
Etymology
The Niger has different names in the different languages of the region: * Fula: ''Maayo Jaaliba'' * Manding: ''Jeliba'' or ''Joliba'' "great river" *Tuareg
The Tuareg people (; also spelled Twareg or Touareg; endonym, depending on variety: ''Imuhaɣ'', ''Imušaɣ'', ''Imašeɣăn'' or ''Imajeɣăn'') are a large Berber ethnic group, traditionally nomadic pastoralists, who principally inhabit th ...
: ''Eġərəw n-Igərǝwăn'' "river of rivers"
* Songhay: ''Isa'' "the river"
* Zarma: ''Isa Beeri'' "great river"
* Hausa: ''Kwara''
* Nupe: ''Èdù''
* Yoruba: ''Ọya'' "named after the Yoruba goddess Ọya, who is believed to embody the river"
* Igbo: ''Orimiri'' or ''Orimili'' "great water"
* Ijaw Ijaw may refer to:
*Ijaw people
The Ijaw people, also known as the Izon people, are an ethnic group found in the Niger Delta region in Nigeria, with primary Population, population clusters in Bayelsa State, Bayelsa, Delta State, Delta, and River ...
: ''Toru Beni'' "the river water"
The earliest use of the name "Niger" for the river is by Leo Africanus in his '' Della descrittione dell’Africa et delle cose notabili che ivi sono'', published in Italian in 1550. Nevertheless, "Nigris" was already the name of a river in West Africa, as mentioned by Pliny the Elder and Solinus, among others. Whether this river was the same as the actual Niger, or rather the river also known as Ger (currently known as Oued Guir, in Morocco), is a matter of discussion. This Nigris was said to divide "Africa proper" from the land of the (Western) Ethiopians to the south, and its name (as well as that of the river Ger) might well come from the Berber
Berber or Berbers may refer to:
Ethnic group
* Berbers, an ethnic group native to Northern Africa
* Berber languages, a family of Afro-Asiatic languages
Places
* Berber, Sudan, a town on the Nile
People with the surname
* Ady Berber (1913–196 ...
phrase ''gr-n-grwn'' meaning "river of rivers", as the current Tuareg name for the river Niger. As Timbuktu
Timbuktu ( ; ; Koyra Chiini: ; ) is an ancient city in Mali, situated north of the Niger River. It is the capital of the Tombouctou Region, one of the eight administrative regions of Mali, having a population of 32,460 in the 2018 census.
...
was the southern end of the principal Trans-Saharan trade route to the western Mediterranean
The Mediterranean Sea ( ) is a sea connected to the Atlantic Ocean, surrounded by the Mediterranean basin and almost completely enclosed by land: on the east by the Levant in West Asia, on the north by Anatolia in West Asia and Southern ...
, it was the source of most European knowledge of the region.
Medieval European maps applied the name ''Niger'' to the middle reaches of the river, in modern Mali, but ''Quorra'' (''Kworra'') to the lower reaches in modern Nigeria, as these were not recognized at the time as being the same river. When European colonial powers began to send ships along the west coast of Africa in the 16th and 17th centuries, the Senegal River
The Senegal River ( or "Senegal" - compound of the Serer term "Seen" or "Sene" or "Sen" (from Roog Seen, Supreme Deity in Serer religion) and "O Gal" (meaning "body of water")); , , , ) is a river in West Africa; much of its length mark ...
was often postulated to be the seaward end of the Niger. The Niger Delta, pouring into the Atlantic
The Atlantic Ocean is the second largest of the world's five oceanic divisions, with an area of about . It covers approximately 17% of Earth's surface and about 24% of its water surface area. During the Age of Discovery, it was known for se ...
through mangrove swamps
A mangrove is a shrub or tree that grows mainly in coastal saline or brackish water. Mangroves grow in an equatorial climate, typically along coastlines and tidal rivers. They have particular adaptations to take in extra oxygen and remove sal ...
and thousands of distributaries
A distributary, or a distributary channel is a stream channel that branches off and flows a main stream channel. It is the opposite of a ''tributary'', a stream that flows another stream or river. Distributaries are a result of river bifurca ...
along more than , was thought to be coastal wetlands. It was only with the 18th-century visits of Mungo Park, who travelled down the Niger River and visited the great Sahelian empires of his day, that Europeans correctly identified the course of the Niger and extended the name to its entire course.
The modern nations of Nigeria and Niger
Niger, officially the Republic of the Niger, is a landlocked country in West Africa. It is a unitary state Geography of Niger#Political geography, bordered by Libya to the Libya–Niger border, north-east, Chad to the Chad–Niger border, east ...
take their names from the river, marking contesting national claims by colonial powers of the "upper", "lower" and "middle" Niger river basin during the Scramble for Africa
The Scramble for Africa was the invasion, conquest, and colonialism, colonisation of most of Africa by seven Western European powers driven by the Second Industrial Revolution during the late 19th century and early 20th century in the era of ...
at the end of the 19th century.
Climate
As part of theWest Africa
West Africa, also known as Western Africa, is the westernmost region of Africa. The United Nations geoscheme for Africa#Western Africa, United Nations defines Western Africa as the 16 countries of Benin, Burkina Faso, Cape Verde, The Gambia, Gha ...
Sahel region, the Niger River has a hot climate characterized by very high temperatures year-round; a long, intense dry season from October to May; and a brief, irregular rainy season linked to the West African monsoon.
Geography
 The Niger River is a relatively clear river, carrying only a tenth as much sediment as the Nile because the Niger's headwaters lie in ancient rocks that provide little
The Niger River is a relatively clear river, carrying only a tenth as much sediment as the Nile because the Niger's headwaters lie in ancient rocks that provide little silt
Silt is granular material of a size between sand and clay and composed mostly of broken grains of quartz. Silt may occur as a soil (often mixed with sand or clay) or as sediment mixed in suspension (chemistry), suspension with water. Silt usually ...
. Like the Nile, the Niger floods yearly; this begins in September, peaks in November, and finishes by May. An unusual feature of the river is the Inner Niger Delta, which forms where its gradient
In vector calculus, the gradient of a scalar-valued differentiable function f of several variables is the vector field (or vector-valued function) \nabla f whose value at a point p gives the direction and the rate of fastest increase. The g ...
suddenly decreases. The result is a region of braided streams, marsh
In ecology, a marsh is a wetland that is dominated by herbaceous plants rather than by woody plants.Keddy, P.A. 2010. Wetland Ecology: Principles and Conservation (2nd edition). Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, UK. 497 p More in genera ...
es, and large lakes; the seasonal floods make the Delta extremely productive for both fishing and agriculture.
 The river loses nearly two-thirds of its
The river loses nearly two-thirds of its potential flow
In fluid dynamics, potential flow or irrotational flow refers to a description of a fluid flow with no vorticity in it. Such a description typically arises in the limit of vanishing viscosity, i.e., for an inviscid fluid and with no vorticity pre ...
in the Inner Delta between Ségou
Ségou (; , ) is a town and an Communes of Mali, urban commune in south-central Mali that lies northeast of Bamako on the right bank of the River Niger. The town is the capital of the Ségou Cercle and the Ségou Region. With 130,690 inhabitant ...
and Timbuktu to seepage and evaporation. The water from the Bani River, which flows into the Delta at Mopti
Mopti (Fulfulde: Mobti) is a town and an urban commune in the Inner Niger Delta region of Mali. The town is the capital of the Mopti Cercle and the Mopti Region. Situated 630 km northeast of Bamako, the town lies at the confluence of the ...
, does not compensate for the losses. The average loss is estimated at 31 km3/year but varies considerably between years. The river is then joined by various tributaries
A tributary, or an ''affluent'', is a stream or river that flows into a larger stream ('' main stem'' or ''"parent"''), river, or a lake. A tributary does not flow directly into a sea or ocean. Tributaries, and the main stem river into which the ...
but also loses more water to evaporation. The quantity of water entering Nigeria was estimated at 25 km3/year before the 1980s and at 13.5 km3/year during the 1980s.
The most important tributary is the Benue River which merges with the Niger at Lokoja
Lokoja is a north-central city in Nigeria. It lies at the confluence of the Niger River, Niger and Benue River, Benue list of rivers of Nigeria, rivers and is the capital city of Kogi State. While the Bassa Nge, Yoruba people, Yoruba Oworo peopl ...
in Nigeria. The total volume of tributaries in Nigeria is six times higher than the inflow into Nigeria, with a flow near the mouth of the river standing at 177.0 km3/year before the 1980s and 147.3 km3/year during the 1980s.
Course
boomerang
A boomerang () is a thrown tool typically constructed with airfoil sections and designed to spin about an axis perpendicular to the direction of its flight, designed to return to the thrower. The origin of the word is from Australian Aborigin ...
shape that baffled geographers for two centuries. Its source ( Tembakounda) is 240 km (150 mi) inland from the Atlantic Ocean, but the river runs directly away from the sea into the Sahara Desert
The Sahara (, ) is a desert spanning across North Africa. With an area of , it is the largest hot desert in the world and the list of deserts by area, third-largest desert overall, smaller only than the deserts of Antarctica and the northern Ar ...
, then takes a sharp right turn near the ancient city of Timbuktu and heads southeast to the Gulf of Guinea
The Gulf of Guinea (French language, French: ''Golfe de Guinée''; Spanish language, Spanish: ''Golfo de Guinea''; Portuguese language, Portuguese: ''Golfo da Guiné'') is the northeasternmost part of the tropical Atlantic Ocean from Cape Lopez i ...
. This strange geography apparently came about because the Niger River is two ancient rivers joined together. The upper Niger, from the source west of Timbuktu to the bend in the current river near Timbuktu
Timbuktu ( ; ; Koyra Chiini: ; ) is an ancient city in Mali, situated north of the Niger River. It is the capital of the Tombouctou Region, one of the eight administrative regions of Mali, having a population of 32,460 in the 2018 census.
...
, once emptied into a now dry lake to the east northeast of Timbuktu, while the lower Niger started to the south of Timbuktu and flowed south into the Gulf of Guinea. Over time upstream erosion by the lower Niger resulted in stream capture
Stream capture, river capture, river piracy or stream piracy is a geomorphological phenomenon occurring when a stream or river drainage system or watershed is diverted from its own bed, and flows down to the bed of a neighbouring stream. This ...
of the upper Niger by the lower Niger.
The northern part of the river, known as the ''Niger bend'', is an important area because it is the major river and source of water in that part of the Sahara. This made it the focal point of trade across the western Sahara and the centre of the Sahelian kingdoms of Mali
Mali, officially the Republic of Mali, is a landlocked country in West Africa. It is the List of African countries by area, eighth-largest country in Africa, with an area of over . The country is bordered to the north by Algeria, to the east b ...
and Gao
Gao (or Gawgaw/Kawkaw) is a city in Mali and the capital of the Gao Region. The city is located on the River Niger, east-southeast of Timbuktu on the left bank at the junction with the Tilemsi valley.
For much of its history Gao was an imp ...
. The surrounding Niger River Basin is one of the distinct physiographic sections of the Sudan province, which in turn is part of the larger African massive physiographic division.
Drainage basin
The Niger River basin, located in westernAfrica
Africa is the world's second-largest and second-most populous continent after Asia. At about 30.3 million km2 (11.7 million square miles) including adjacent islands, it covers 20% of Earth's land area and 6% of its total surfac ...
, covers 7.5% of the continent
A continent is any of several large geographical regions. Continents are generally identified by convention (norm), convention rather than any strict criteria. A continent could be a single large landmass, a part of a very large landmass, as ...
and spreads over ten countries.
Niger River basin: areas and rainfall by country
Hydrometric stations on the Niger River

Discharge
Average, minimum and maximum discharge of the Niger River atKoulikoro
Koulikoro ( Bambara: ߞߎߟߌߞߏߙߏ tr. Kulikoro) is a town and urban commune in Mali
Mali, officially the Republic of Mali, is a landlocked country in West Africa. It is the List of African countries by area, eighth-largest country in A ...
(Upper Niger), Niamey
Niamey () is the capital and largest city of Niger. As the Niamey Urban Community (, CUN), it is a Regions of Niger, first-level division of Niger, surrounded by the Tillabéri Region, in the western part of the country. Niamey lies on the Nige ...
(Middle Niger) and Lokoja
Lokoja is a north-central city in Nigeria. It lies at the confluence of the Niger River, Niger and Benue River, Benue list of rivers of Nigeria, rivers and is the capital city of Kogi State. While the Bassa Nge, Yoruba people, Yoruba Oworo peopl ...
(Lower Niger). Period from 2000/06/01 to 2024/05/31.
Average discharge of the Niger River at Niger Delta
The Niger Delta is the delta of the Niger River sitting directly on the Gulf of Guinea on the Atlantic Ocean in Nigeria. It is located within nine coastal southern Nigerian states, which include: all six states from the South South geopolitic ...
(period from 2010 to 2018):
Niger River at Lokoja
Niger River atLokoja
Lokoja is a north-central city in Nigeria. It lies at the confluence of the Niger River, Niger and Benue River, Benue list of rivers of Nigeria, rivers and is the capital city of Kogi State. While the Bassa Nge, Yoruba people, Yoruba Oworo peopl ...
average, minimum and maximum discharge (1946 to 2023):
Tributaries
The main tributaries from the mouth:History

 At the end of the African humid period around 5,500 years before present, the modern Sahara Desert, once a
At the end of the African humid period around 5,500 years before present, the modern Sahara Desert, once a savanna
A savanna or savannah is a mixed woodland-grassland (i.e. grassy woodland) biome and ecosystem characterised by the trees being sufficiently widely spaced so that the canopy does not close. The open canopy allows sufficient light to reach th ...
, underwent desertification
Desertification is a type of gradual land degradation of Soil fertility, fertile land into arid desert due to a combination of natural processes and human activities.
The immediate cause of desertification is the loss of most vegetation. This i ...
. As plant species sharply declined, humans migrated to the fertile Niger River bend region, with abundant resources including plants for grazing and fish. Like in the Fertile Crescent
The Fertile Crescent () is a crescent-shaped region in the Middle East, spanning modern-day Iraq, Israel, Jordan, Lebanon, Palestine, and Syria, together with northern Kuwait, south-eastern Turkey, and western Iran. Some authors also include ...
, many food crops were domesticated
Domestication is a multi-generational mutualistic relationship in which an animal species, such as humans or leafcutter ants, takes over control and care of another species, such as sheep or fungi, to obtain from them a steady supply of reso ...
in the Niger River region, including yams, African rice (Oryza glaberrima
''Oryza glaberrima'', commonly known as African rice, is one of the two domesticated rice species. It was first domesticated and grown in West Africa around 3,000 years ago. In agriculture, it has largely been replaced by higher-yielding Asian ric ...
), and pearl millet
Pearl millet (''Cenchrus americanus'', commonly known as the synonym ''Pennisetum glaucum'') is the most widely grown type of millet. It has been grown in Africa and the Indian subcontinent since prehistoric times. The center of diversity, and ...
. The Sahara aridification
Aridification is the process of a region becoming increasingly arid, or dry. It refers to long term change, rather than seasonal variation.
It is often measured as the reduction of average soil moisture content.
It can be caused by reduced preci ...
may have triggered, or at least accelerated, these domestications. Agriculture, as well as fishing and animal husbandry, led to the rise of settlements like Djenné-Djenno in the Inner Delta, now a World Heritage Site
World Heritage Sites are landmarks and areas with legal protection under an treaty, international treaty administered by UNESCO for having cultural, historical, or scientific significance. The sites are judged to contain "cultural and natural ...
.
The region of the Niger bend, in the Sahel
The Sahel region (; ), or Sahelian acacia savanna, is a Biogeography, biogeographical region in Africa. It is the Ecotone, transition zone between the more humid Sudanian savannas to its south and the drier Sahara to the north. The Sahel has a ...
, was a key origin and destination for trans-Saharan trade, fueling the wealth of great empires such as the Ghana
Ghana, officially the Republic of Ghana, is a country in West Africa. It is situated along the Gulf of Guinea and the Atlantic Ocean to the south, and shares borders with Côte d’Ivoire to the west, Burkina Faso to the north, and Togo to t ...
, Mali, and Songhai Empire
The Songhai Empire was a state located in the western part of the Sahel during the 15th and 16th centuries. At its peak, it was one of the largest African empires in history. The state is known by its historiographical name, derived from its lar ...
s. Major trading ports along the river, including Timbuktu and Gao, became centers of learning and culture. Trade to the Niger bend region also brought Islam to the region in approximately the 14th century CE. Much of the northern Niger basin remains Muslim today, although the southern reaches of the river tend to be Christian.
Classical writings on the interior of the Sahara begin with Ptolemy
Claudius Ptolemy (; , ; ; – 160s/170s AD) was a Greco-Roman mathematician, astronomer, astrologer, geographer, and music theorist who wrote about a dozen scientific treatises, three of which were important to later Byzantine science, Byzant ...
, who mentions two rivers in the desert: the "Gir" (Γειρ) and farther south, the "Nigir" (Νιγειρ). The first has been since identified as the Wadi Ghir on the north-western edge of the Tuat
Tuat, or Touat (), is a natural region of desert in central Algeria that contains a string of small oasis, oases. In the past, the oases were important for Camel caravan, caravans crossing the Sahara.
Geography
Tuat lies to the south of the Gr ...
, along the borders of modern Morocco
Morocco, officially the Kingdom of Morocco, is a country in the Maghreb region of North Africa. It has coastlines on the Mediterranean Sea to the north and the Atlantic Ocean to the west, and has land borders with Algeria to Algeria–Morocc ...
and Algeria
Algeria, officially the People's Democratic Republic of Algeria, is a country in the Maghreb region of North Africa. It is bordered to Algeria–Tunisia border, the northeast by Tunisia; to Algeria–Libya border, the east by Libya; to Alger ...
. This would likely have been as far as Ptolemy would have had consistent records. The Ni-Ger was likely speculation, although the name stuck as that of a river south of the Mediterranean's "known world". Suetonius
Gaius Suetonius Tranquillus (), commonly referred to as Suetonius ( ; – after AD 122), was a Roman historian who wrote during the early Imperial era of the Roman Empire. His most important surviving work is ''De vita Caesarum'', common ...
reports Romans traveling to the "Ger", although in reporting any river's name derived from a Berber
Berber or Berbers may refer to:
Ethnic group
* Berbers, an ethnic group native to Northern Africa
* Berber languages, a family of Afro-Asiatic languages
Places
* Berber, Sudan, a town on the Nile
People with the surname
* Ady Berber (1913–196 ...
language, in which "gher" means "watercourse", confusion could easily arise. Pliny connected these two rivers as one long watercourse which flowed (via lakes and underground sections) into the Nile, a notion which persisted in the Arab and European worlds – and further added the Senegal River as the "Ger" – until the 19th century.
While the true course of the Niger was presumably known to locals, it was a mystery to the outside world until the late 18th century. The connection to the Nile River
The Nile (also known as the Nile River or River Nile) is a major north-flowing river in northeastern Africa. It flows into the Mediterranean Sea. The Nile is the longest river in Africa. It has historically been considered the longest river i ...
was made not simply because this was then known as the great river of "Aethiopia
Ancient Aethiopia, () first appears as a geographical term in classical documents in reference to the skin color of the inhabitants of the upper Nile in northern Sudan, of areas south of the Sahara, and of certain areas in Asia. Its earliest men ...
" (by which all lands south of the desert were called by Classical writers), but because the Nile like the Niger flooded every summer. Through the descriptions of Leo Africanus and even Ibn Battuta
Ibn Battuta (; 24 February 13041368/1369), was a Maghrebi traveller, explorer and scholar. Over a period of 30 years from 1325 to 1354, he visited much of Africa, the Middle East, Asia and the Iberian Peninsula. Near the end of his life, Ibn ...
– despite his visit to the river – the myth connecting the Niger to the Nile persisted.
Many European expeditions to plot the river were unsuccessful. In 1788 the African Association
The Association for Promoting the Discovery of the Interior Parts of Africa (commonly known as the African Association), founded in London on 9 June 1788, was a British club dedicated to the exploration of West Africa, with the mission of discov ...
was formed in England
England is a Countries of the United Kingdom, country that is part of the United Kingdom. It is located on the island of Great Britain, of which it covers about 62%, and List of islands of England, more than 100 smaller adjacent islands. It ...
to promote the exploration of Africa in the hopes of locating the Niger, and in June 1796 the Scottish explorer Mungo Park was the first European to lay eyes on the middle portion of the river since antiquity (and perhaps ever). He wrote an account in 1799, '' Travels in the Interior of Africa''. Park proposed a theory that the Niger and Congo were the same river. Although the Niger Delta would seem like an obvious candidate, it was a maze of streams and swamps that did not look like the head of a great river. He died in 1806 on a second expedition attempting to prove the Niger-Congo connection. The theory became the leading one in Europe. Several failed expeditions followed; however the mystery of the Niger would not be solved for another 25 years, in 1830, when Richard Lander and his brother became the first Europeans to follow the course of the Niger to the ocean.
In 1946, three Frenchmen, Jean Sauvy, Pierre Ponty and movie maker Jean Rouch
Jean Rouch (; 31 May 1917 – 18 February 2004) was a French Filmmaking, filmmaker and anthropologist.
He is considered one of the founders of cinéma vérité in France. Rouch's practice as a filmmaker, for over 60 years in Africa, was char ...
, former civil servants in the African French colonies, set out to travel the entire length of the river, as no one else seemed to have done previously. They travelled from the beginning of the river near Kissidougou in Guinea, walking at first till a raft could be used, then changing to various local crafts as the river broadened and changed. Two of them reached the ocean on March 25, 1947, with Ponty having left the expedition at Niamey
Niamey () is the capital and largest city of Niger. As the Niamey Urban Community (, CUN), it is a Regions of Niger, first-level division of Niger, surrounded by the Tillabéri Region, in the western part of the country. Niamey lies on the Nige ...
, somewhat past the halfway mark. They carried a 16mm movie camera, the resulting footage giving Rouch his first two ethnographic documentaries: "Au pays des mages noirs", and "La chasse à l’hippopotame". A camera was used to illustrate Rouch's subsequent book "Le Niger En Pirogue" (Fernand Nathan, 1954), as well as Sauvy's "Descente du Niger" (L'Harmattan, 2001). A typewriter was brought as well, on which Ponty produced newspaper articles he mailed out whenever possible.
Management and development
The water in the Niger River basin is partially regulated through dams. In Mali the Sélingué Dam on the Sankarani River is mainly used for hydropower but also permits irrigation. Two diversion dams, one at Sotuba just downstream ofBamako
Bamako is the Capital city, capital and largest city of Mali, with a 2022 population of 4,227,569. It is located on the Niger River, near the rapids that divide the upper and middle Niger valleys in the southwestern part of the country.
Bamak ...
, and one at Markala
Markala is a commune in Mali's Ségou Region on the Niger River
The Niger River ( ; ) is the main river of West Africa, extending about . Its drainage basin is in area. Its source is in the Guinea Highlands in south-eastern Guinea near the ...
, just downstream of Ségou
Ségou (; , ) is a town and an Communes of Mali, urban commune in south-central Mali that lies northeast of Bamako on the right bank of the River Niger. The town is the capital of the Ségou Cercle and the Ségou Region. With 130,690 inhabitant ...
, are used to irrigate about 54,000 hectares. In Nigeria the Kainji Dam, Shiroro Dam, Zungeru Dam, and Jebba Dam are used to generate hydropower.
The water resources of the Niger River are under pressure because of increased water abstraction for irrigation. The construction of dams
A dam is a barrier that stops or restricts the flow of surface water or underground streams. Reservoirs created by dams not only suppress floods but also provide water for activities such as irrigation, human consumption, industrial use, ...
for hydropower generation is underway or envisaged in order to alleviate chronic power shortages in the countries of the Niger basin. The FAO
The Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations; . (FAO) is a List of specialized agencies of the United Nations, specialized agency of the United Nations that leads international efforts to defeat hunger and improve nutrition ...
estimates the irrigation potential of all countries in the Niger river basin at 2.8 million hectares. Only 0.93m hectares (ha) were under irrigation in the late 1980s. The irrigation potential was estimated at 1.68m ha in Nigeria 0.56m ha in Mali, and the actual irrigated area was 0.67m ha and 0.19m ha.
See also
* *Notes
References
* * * * *External links
Information and a map of the Niger's watershed
on http://www.wri.org/resources
(link broken)
Niger Currents: Exploring life and technology along the Niger River
*
International law and the Niger River
Bibliography on Water Resources and International Law
Peace Palace Library * {{Authority control Benin–Niger border International rivers of Africa Inner Niger Delta Physiographic sections Rivers of Benin Rivers of Guinea Rivers of Mali Rivers of Niger Rivers of Nigeria Border rivers Lowest points of countries