|
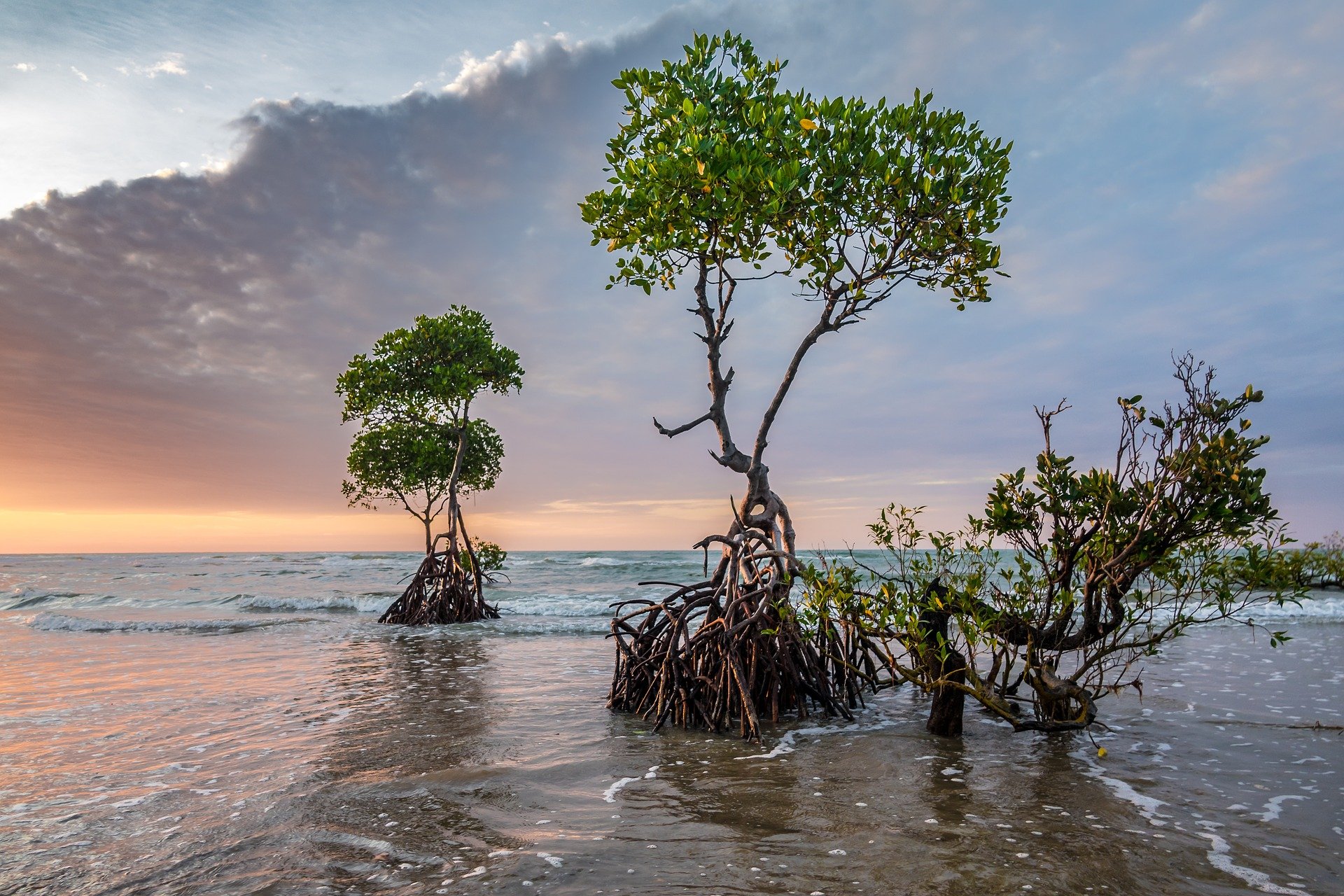
Mangrove Forest
Mangrove forests, also called mangrove swamps, mangrove thickets or mangals, are productive wetlands that occur in coastal intertidal zones. Mangrove forests grow mainly at tropical and subtropical latitudes because mangrove trees cannot withstand freezing temperatures. There are about 80 different species of mangroves, all of which grow in areas with low-oxygen soil, where slow-moving waters allow fine sediments to accumulate.What is a mangrove forest? National Ocean Service, NOAA. Updated: 25 March 2021. Retrieved: 4 October 2021. Many mangrove forests can be recognised by their dense tangle of prop roots that make the trees appear to be standing on stilts above the water. This tangle of roots allows the trees to handle the daily rise and fall of tides, as most mangroves get flooded at least twice per day. The roo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Blue Carbon
Blue carbon is a concept within climate change mitigation that refers to "biologically driven carbon fluxes and storage in marine systems that are amenable to management". Most commonly, it refers to the role that tidal marshes, mangroves and Seagrass meadow, seagrass meadows can play in carbon sequestration. These ecosystems can play an important role for climate change mitigation and ecosystem-based adaptation. However, when blue carbon ecosystems are degraded or lost, they release carbon back to the atmosphere, thereby adding to greenhouse gas emissions. The methods for ''blue carbon management'' fall into the category of "ocean-based biological carbon dioxide removal (CDR) methods".Canadell, J. G., P. M. S. Monteiro, M. H. Costa, L. Cotrim da Cunha, P. M. Cox, A. V. Eliseev, S. Henson, M. Ishii, S. Jaccard, C. Koven, A. Lohila, P. K. Patra, S. Piao, J. Rogelj, S. Syampungani, S. Zaehle, and K. Zickfeld, 2021Chapter 5: Global Carbon and other Biogeochemical Cycles and Feedbacks ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mangroves At Sunset
A mangrove is a shrub or tree that grows mainly in coastal saline water, saline or brackish water. Mangroves grow in an equatorial climate, typically along coastlines and tidal rivers. They have particular adaptations to take in extra oxygen and remove salt, allowing them to tolerate conditions that kill most plants. The term is also used for tropical coastal vegetation consisting of such species. Mangroves are taxonomically diverse due to convergent evolution in several plant families. They occur worldwide in the tropics and subtropics and even some temperate coastal areas, mainly between latitudes 30° N and 30° S, with the greatest mangrove area within 5° of the equator. Mangrove plant families first appeared during the Late Cretaceous to Paleocene epochs and became widely distributed in part due to the plate tectonics, movement of tectonic plates. The oldest known fossils of Nypa fruticans, mangrove palm date to 75 million years ago. Mangroves are salt-tolerant ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Intertidal Zone
The intertidal zone or foreshore is the area above water level at low tide and underwater at high tide; in other words, it is the part of the littoral zone within the tidal range. This area can include several types of habitats with various species of life, such as sea stars, sea urchins, and many species of coral with regional differences in biodiversity. Sometimes it is referred to as the ''littoral zone'' or '' seashore'', although those can be defined as a wider region. The intertidal zone also includes steep rocky cliffs, sandy beaches, bogs or wetlands (e.g., vast mudflats). This area can be a narrow strip, such as in Pacific islands that have only a narrow tidal range, or can include many meters of shoreline where shallow beach slopes interact with high tidal excursion. The peritidal zone is similar but somewhat wider, extending from above the highest tide level to below the lowest. Organisms in the intertidal zone are well-adapted to their environment, facing high ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tropical Cyclone
A tropical cyclone is a rapidly rotating storm system with a low-pressure area, a closed low-level atmospheric circulation, strong winds, and a spiral arrangement of thunderstorms that produce heavy rain and squalls. Depending on its location and strength, a tropical cyclone is called a hurricane (), typhoon (), tropical storm, cyclonic storm, tropical depression, or simply cyclone. A hurricane is a strong tropical cyclone that occurs in the Atlantic Ocean or northeastern Pacific Ocean. A typhoon is the same thing which occurs in the northwestern Pacific Ocean. In the Indian Ocean and South Pacific, comparable storms are referred to as "tropical cyclones". In modern times, on average around 80 to 90 named tropical cyclones form each year around the world, over half of which develop hurricane-force winds of or more. Tropical cyclones tropical cyclogenesis, typically form over large bodies of relatively warm water. They derive their energy through the evaporation of water ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Erosion
Erosion is the action of surface processes (such as Surface runoff, water flow or wind) that removes soil, Rock (geology), rock, or dissolved material from one location on the Earth's crust#Crust, Earth's crust and then sediment transport, transports it to another location where it is deposit (geology), deposited. Erosion is distinct from weathering which involves no movement. Removal of rock or soil as clastic sediment is referred to as ''physical'' or ''mechanical'' erosion; this contrasts with ''chemical'' erosion, where soil or rock material is removed from an area by Solvation, dissolution. Eroded sediment or solutes may be transported just a few millimetres, or for thousands of kilometres. Agents of erosion include rainfall; bedrock wear in rivers; coastal erosion by the sea and Wind wave, waves; glacier, glacial Plucking (glaciation), plucking, Abrasion (geology), abrasion, and scour; areal flooding; Aeolian processes, wind abrasion; groundwater processes; and Mass wastin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Colloidal Particle
Particle size is a notion introduced for comparing dimensions of solid particles ('' flecks''), liquid particles (''droplets''), or gaseous particles ('' bubbles''). The notion of particle size applies to particles in colloids, in ecology, in granular material (whether airborne or not), and to particles that form a granular material (see also grain size). Measurement There are several methods for measuring particle size and particle size distribution. Some of them are based on light, other on ultrasound,Dukhin, A. S. and Goetz, P. J. ''Characterization of liquids, nano- and micro- particulates and porous bodies using Ultrasound'', Elsevier, 2017 or electric field, or gravity, or centrifugation. The use of sieves is a common measurement technique, however this process can be more susceptible to human error and is time consuming. Technology such as dynamic image analysis (DIA) can make particle size distribution analyses much easier. This approach can be seen in instruments lik ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Heavy Metals
upright=1.2, Crystals of lead.html" ;"title="osmium, a heavy metal nearly twice as dense as lead">osmium, a heavy metal nearly twice as dense as lead Heavy metals is a controversial and ambiguous term for metallic elements with relatively high density, densities, atomic weights, or atomic numbers. The criteria used, and whether metalloids are included, vary depending on the author and context and it has been argued that the term "heavy metal" should be avoided. A heavy metal may be defined on the basis of density, atomic number or chemical behaviour. More specific definitions have been published, none of which have been widely accepted. The definitions surveyed in this article encompass up to 96 out of the 118 known chemical elements; only mercury, lead and bismuth meet all of them. Despite this lack of agreement, the term (plural or singular) is widely used in science. A density of more than 5 g/cm3 is sometimes quoted as a commonly used criterion and is used in the b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anoxic Waters
Anoxic waters are areas of sea water, fresh water, or groundwater that are depleted of dissolved oxygen. The US Geological Survey defines anoxic groundwater as those with dissolved oxygen concentration of less than 0.5 milligrams per litre. Anoxic waters can be contrasted with hypoxic waters, which are low (but not lacking) in dissolved oxygen. Often, hypoxia is defined as waters that have less than 2 milligrams per litre of dissolved oxygen. This condition is generally found in areas that have restricted water exchange. In most cases, oxygen is prevented from reaching the deeper levels by a physical barrier, as well as by a pronounced density stratification, in which, for instance, denser, colder or hypersaline waters rest at the bottom of a basin. Anoxic conditions will occur if the rate of oxidation of organic matter by bacteria is greater than the supply of dissolved oxygen. Anoxic waters are a natural phenomenon, and have occurred throughout geological history. The Permia ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oyster
Oyster is the common name for a number of different families of salt-water bivalve molluscs that live in marine or brackish habitats. In some species, the valves are highly calcified, and many are somewhat irregular in shape. Many, but not all oysters, are in the superfamily Ostreoidea. Some species of oyster are commonly consumed and are regarded as a delicacy in some localities. Some types of pearl oysters are harvested for the pearl produced within the mantle. Others, such as the translucent Windowpane oysters, are harvested for their shells. Etymology The word ''oyster'' comes from Old French , and first appeared in English during the 14th century. The French derived from the Latin , the feminine form of , which is the Latinisation (literature), latinisation of the Ancient Greek () 'oyster'. Compare () 'bone'. Types True oysters True oysters are members of the family Ostreidae. This family includes the edible oysters, which mainly belong to the genera '' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tidal Flooding
Tidal flooding, also known as sunny day flooding or nuisance flooding, is the temporary inundation of low-lying areas, especially streets, during exceptionally high tide events, such as at full and new moons. The highest tides of the year may be known as the king tide, with the month varying by location. These kinds of floods tend not to be a high risk to property or human safety, but further stress coastal infrastructure in low-lying areas. This kind of flooding is becoming more common in cities and other human-occupied coastal areas as sea level rise associated with climate change and other human-related environmental impacts such as coastal erosion and land subsidence increase the vulnerability of infrastructure. Geographies faced with these issues can utilize coastal management practices to mitigate the effects in some areas, but increasingly these kinds of floods may develop into coastal flooding that requires managed retreat or other more extensive climate change adapta ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Salinity
Salinity () is the saltiness or amount of salt (chemistry), salt dissolved in a body of water, called saline water (see also soil salinity). It is usually measured in g/L or g/kg (grams of salt per liter/kilogram of water; the latter is dimensionless and equal to per mille, ‰). Salinity is an important factor in determining many aspects of the chemistry of natural waters and of biological processes within it, and is a state function, thermodynamic state variable that, along with temperature and pressure, governs physical characteristics like the density and heat capacity of the water. A contour line of constant salinity is called an ''isohaline'', or sometimes ''isohale''. Definitions Salinity in rivers, lakes, and the ocean is conceptually simple, but technically challenging to define and measure precisely. Conceptually the salinity is the quantity of dissolved salt content of the water. Salts are compounds like sodium chloride, magnesium sulfate, potassium nitrate, and sod ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hypoxia (environmental)
Hypoxia (''hypo'': 'below', ''oxia'': 'oxygenated') refers to low oxygen conditions. Hypoxia is problematic for air-breathing organisms, yet it is essential for many anaerobic organisms. Hypoxia applies to many situations, but usually refers to the atmosphere and natural waters. Atmospheric hypoxia Atmospheric hypoxia occurs naturally at high altitudes. Total atmospheric pressure decreases as altitude increases, causing a lower partial pressure of oxygen, which is defined as hypobaric hypoxia. Oxygen remains at 20.9% of the total gas mixture, differing from hypoxic hypoxia, where the percentage of oxygen in the air (or blood) is decreased. This is common in the sealed burrows of some subterranean animals, such as blesmols. Atmospheric hypoxia is also the basis of altitude training, which is a standard part of training for elite athletes. Several companies mimic hypoxia using normobaric artificial atmosphere. Aquatic hypoxia An aquatic system lacking dissolved oxygen (0% ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |