Unison (ISP) on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 In
In

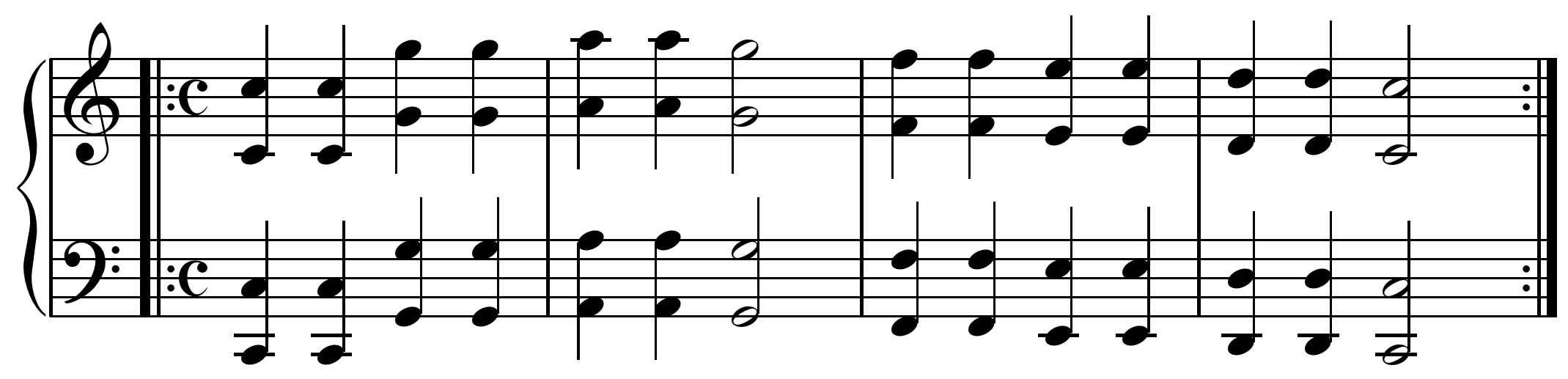 In orchestral music ''unison'' can mean the simultaneous playing of a note (or a series of notes constituting a
In orchestral music ''unison'' can mean the simultaneous playing of a note (or a series of notes constituting a
 In
In music
Music is the arrangement of sound to create some combination of Musical form, form, harmony, melody, rhythm, or otherwise Musical expression, expressive content. Music is generally agreed to be a cultural universal that is present in all hum ...
, unison is two or more musical parts that sound either the same pitch or pitches separated by intervals of one or more octave
In music, an octave (: eighth) or perfect octave (sometimes called the diapason) is an interval between two notes, one having twice the frequency of vibration of the other. The octave relationship is a natural phenomenon that has been referr ...
s, usually at the same time. ''Rhythmic unison'' is another term for homorhythm
In music, a homorhythm or homometer is a texture having a "similarity of rhythm in all parts"Griffiths, Paul (2005). ''The Penguin Companion to Classical Music'', p.375. . or "very similar rhythm" as would be used in simple hymn or chorale settin ...
.
Definition
Unison or perfect unison (also called a prime, or perfect prime)Benward & Saker (2003), p. 53. may refer to the (pseudo-) interval formed by a tone and its duplication (in German, ''Unisono'', ''Einklang'', or ''Prime''), for example C–C, as differentiated from thesecond
The second (symbol: s) is a unit of time derived from the division of the day first into 24 hours, then to 60 minutes, and finally to 60 seconds each (24 × 60 × 60 = 86400). The current and formal definition in the International System of U ...
, C–D, etc. In the unison the two pitches have the ratio of 1:1 or 0 half step
A semitone, also called a minor second, half step, or a half tone, is the smallest musical interval commonly used in Western tonal music, and it is considered the most dissonant when sounded harmonically.
It is defined as the interval between ...
s and zero cents. Although two tones in unison are considered to be the same pitch, they are still perceivable as coming from separate sources, whether played on instruments of a different type: ; or of the same type: . This is because a pair of tones in unison come from different locations or can have different "colors" (timbre
In music, timbre (), also known as tone color or tone quality (from psychoacoustics), is the perceived sound of a musical note, sound or tone. Timbre distinguishes sounds according to their source, such as choir voices and musical instrument ...
s), i.e. come from different musical instrument
A musical instrument is a device created or adapted to make Music, musical sounds. In principle, any object that produces sound can be considered a musical instrument—it is through purpose that the object becomes a musical instrument. A person ...
s or human voices. Voices with different colors have, as sound waves, different waveform
In electronics, acoustics, and related fields, the waveform of a signal is the shape of its Graph of a function, graph as a function of time, independent of its time and Magnitude (mathematics), magnitude Scale (ratio), scales and of any dis ...
s. These waveforms have the same fundamental frequency
Frequency is the number of occurrences of a repeating event per unit of time. Frequency is an important parameter used in science and engineering to specify the rate of oscillatory and vibratory phenomena, such as mechanical vibrations, audio ...
but differ in the amplitudes of their higher harmonic
In physics, acoustics, and telecommunications, a harmonic is a sinusoidal wave with a frequency that is a positive integer multiple of the ''fundamental frequency'' of a periodic signal. The fundamental frequency is also called the ''1st har ...
s. The unison is considered the most consonant
In articulatory phonetics, a consonant is a speech sound that is articulated with complete or partial closure of the vocal tract, except for the h sound, which is pronounced without any stricture in the vocal tract. Examples are and pronou ...
interval while the near unison is considered the most dissonant
In music, consonance and dissonance are categorizations of simultaneous or successive sounds. Within the Western tradition, some listeners associate consonance with sweetness, pleasantness, and acceptability, and dissonance with harshness, unple ...
. The unison is also the easiest interval to tune. The unison is abbreviated as "P1".
However, the unison was questioned by Zarlino
Gioseffo Zarlino (31 January or 22 March 1517 – 4 February 1590) was an Italian music theorist and composer of the Renaissance. He made a large contribution to the theory of counterpoint as well as to musical tuning.
Life and career
Zarlino w ...
as an interval for lacking contrast and compared to a point in geometry:
Performance ensembles

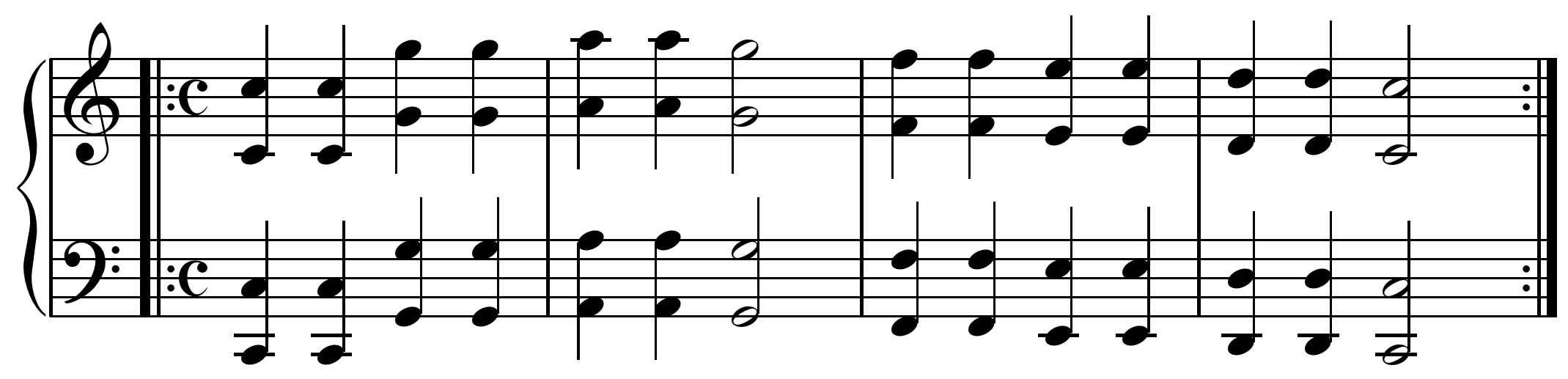 In orchestral music ''unison'' can mean the simultaneous playing of a note (or a series of notes constituting a
In orchestral music ''unison'' can mean the simultaneous playing of a note (or a series of notes constituting a melody
A melody (), also tune, voice, or line, is a linear succession of musical tones that the listener perceives as a single entity. In its most literal sense, a melody is a combination of Pitch (music), pitch and rhythm, while more figurativel ...
) by different instruments, either at the same pitch; or in a different octave
In music, an octave (: eighth) or perfect octave (sometimes called the diapason) is an interval between two notes, one having twice the frequency of vibration of the other. The octave relationship is a natural phenomenon that has been referr ...
, for example, cello
The violoncello ( , ), commonly abbreviated as cello ( ), is a middle pitched bowed (sometimes pizzicato, plucked and occasionally col legno, hit) string instrument of the violin family. Its four strings are usually intonation (music), tuned i ...
and double bass
The double bass (), also known as the upright bass, the acoustic bass, the bull fiddle, or simply the bass, is the largest and lowest-pitched string instrument, chordophone in the modern orchestra, symphony orchestra (excluding rare additions ...
(''all'unisono''). Typically a section string player plays unison with the rest of the section. Occasionally the Italian word ''divisi
In musical terminology, ''divisi'', or as typically printed ''“div.,”'' is an instruction to divide a single section of instruments into multiple subsections. This usually applies to the violins of the string section in an orchestra, although v ...
'' (meaning ''divided'', abbrev. ''div.'') marks a point where an instrumental section, typically the first violins, is to be divided into two groups for rendering passages that might, for example, include full chords
Chord or chords may refer to:
Art and music
* Chord (music), an aggregate of musical pitches sounded simultaneously
** Guitar chord, a chord played on a guitar, which has a particular tuning
* The Chords (British band), 1970s British mod ...
. Thus, in the ''divisi'' first violins the "outside" players (nearer the audience) might play the top note of the chord, while the "inside" seated players play the middle note, and the second violins play the bottom note. At the point where the first violins no longer play ''divisi'', the score may indicate this with ''unison'' (abbrev. ''unis.'').
When an entire choir
A choir ( ), also known as a chorale or chorus (from Latin ''chorus'', meaning 'a dance in a circle') is a musical ensemble of singers. Choral music, in turn, is the music written specifically for such an ensemble to perform or in other words ...
sings the main melody, the choir usually sings in unison. Music in which all the notes sung are in unison is called monophonic
Monaural sound or monophonic sound (often shortened to mono) is sound intended to be heard as if it were emanating from one position. This contrasts with stereophonic sound or ''stereo'', which uses two separate audio channels to reproduce sou ...
. In a choir with two or more sections, such as for different vocal range
Vocal range is the range of pitches that a human voice can phonate. A common application is within the context of singing, where it is used as a defining characteristic for classifying singing voices into voice types. It is also a topic of stud ...
s, each section typically sings in unison. Part singing is when two or more voices sing different notes. Homophony
In music, homophony (;, Greek: ὁμόφωνος, ''homóphōnos'', from ὁμός, ''homós'', "same" and φωνή, ''phōnē'', "sound, tone") is a texture in which a primary part is supported by one or more additional strands that provide ...
is when choir members sing different pitches but with the same rhythm. Polyphony
Polyphony ( ) is a type of musical texture consisting of two or more simultaneous lines of independent melody, as opposed to a musical texture with just one voice ( monophony) or a texture with one dominant melodic voice accompanied by chord ...
is when the chorus sings multiple independent melodies.
Synthesizer
Onsynthesizer
A synthesizer (also synthesiser or synth) is an electronic musical instrument that generates audio signals. Synthesizers typically create sounds by generating waveforms through methods including subtractive synthesis, additive synthesis a ...
s, the term ''unison'' is used to describe two or more oscillator
Oscillation is the repetitive or periodic variation, typically in time, of some measure about a central value (often a point of equilibrium) or between two or more different states. Familiar examples of oscillation include a swinging pendulum ...
s generating the same pitch/notes as each other, which can result in a fatter or thicker sound (especially if tiny changes are made to each oscillator's tuning).
However, if each oscillator is tuned so far from the other oscillators that they aren't generating the same note then technically they aren't in unison.
If they are playing the same note but in a different octave then they are still in unison. For example, a melody consisting of A-B-C-B-A-A-A if played in a different octave is still A-B-C-B-A-A-A therefore this is still considered as ''in unison''.
Unison refers to ''everything doing the same thing''.
See also
* List of musical intervals *List of pitch intervals
Below is a list of intervals expressible in terms of a prime limit (see Terminology), completed by a choice of intervals in various equal subdivisions of the octave or of other intervals.
For commonly encountered harmonic or melodic intervals ...
References
Further reading
* Apel, Willi, ed., ''Harvard Dictionary of Music'', Second Edition, Revised and Enlarged. The Belknap Press of Harvard University Press, Cambridge, Massachusetts, 1969. . {{Intervals Just tuning and intervals Perfect intervals 3-limit tuning and intervals