Udmurt Republic on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Udmurtia, officially the Udmurt Republic, is a republic of Russia located in
 On November 4, 1920, the Votyak Autonomous Oblast was formed.''Administrative-Territorial Structure of the Union Republics. 1987.'', p. 57 On January 1, 1932, it was renamed Udmurt Autonomous Oblast, which was then reorganized into the Udmurt ASSR on December 28, 1934. During
On November 4, 1920, the Votyak Autonomous Oblast was formed.''Administrative-Territorial Structure of the Union Republics. 1987.'', p. 57 On January 1, 1932, it was renamed Udmurt Autonomous Oblast, which was then reorganized into the Udmurt ASSR on December 28, 1934. During
"Чувство любви в понимании евреев-ашкенази Удмуртии и Татарстана".
Наука Удмуртии. 2013. №4. С. 131: Комментарии.) as a result up to the 1970s and 1980s the Udmurt variety of Yiddish ('' Udmurtish'') was divided into two linguistic subgroups: the central subgroup (with centers
Jewish studies in the Udmurt Republic: Online. Part 1. Edited by A. Greenberg. February 27, 2015 published. P. 3.
Official website of the Udmurt Republic
{{Use mdy dates, date=October 2014 Regions of Europe with multiple official languages States and territories established in 1990 1990 establishments in Russia 1990 establishments in the Soviet Union Republics of Russia
Eastern Europe
Eastern Europe is a subregion of the Europe, European continent. As a largely ambiguous term, it has a wide range of geopolitical, geographical, ethnic, cultural and socio-economic connotations. Its eastern boundary is marked by the Ural Mountain ...
. It is administratively part of the Volga Federal District
The Volga Federal District ( rus, Приволжский федеральный округ, p=prʲɪˈvolʂskʲɪj fʲɪdʲɪˈralʲnɨj ˈokrʊk) is one of the eight federal districts of Russia, federal districts of Russia. It forms the south ...
. Its capital is the city
A city is a human settlement of a substantial size. The term "city" has different meanings around the world and in some places the settlement can be very small. Even where the term is limited to larger settlements, there is no universally agree ...
of Izhevsk
Izhevsk or Ijevsk (, ; , or ) is the capital city of Udmurtia, Russia. It is situated along the Izh River, west of the Ural Mountains in Eastern Europe. It is the 21st-largest city in Russia, and the most populous in Udmurtia, with over 600,000 ...
.
It was established as the Udmurt (until 1931 — Votskaya) Autonomous Region
An autonomous administrative division (also referred to as an autonomous area, zone, entity, unit, region, subdivision, province, or territory) is a subnational administrative division or territory, internal territory of a sovereign state that has ...
on November 4, 1920.
Name
The name ''Udmurt'' comes from ('meadow people'), where the first part represents the Permic root or ('meadow, glade, turf, greenery'). This is supported by a document dated 1557, in which the Udmurts are referred to as ('meadow people'), alongside the traditional Russian name . The second part means 'person' (cf. Komi , Mari ). It is probably an early borrowing from aScythian
The Scythians ( or ) or Scyths (, but note Scytho- () in composition) and sometimes also referred to as the Pontic Scythians, were an ancient Eastern Iranian equestrian nomadic people who had migrated during the 9th to 8th centuries BC fr ...
language: or ('person, man';
Sanskrit: Manus or Manushya), which is thought to have been borrowed from the Indo-Aryan term ('man, mortal, one who is bound to die'. cf. Old Indic ('young warrior') and ('chariot warrior'), both connected specifically with horses and chariots. The Indo-Europeanists
Indo-European studies () is a field of linguistics and an interdisciplinary field of study dealing with Indo-European languages, both current and extinct. The goal of those engaged in these studies is to amass information about the hypothetical p ...
T. Gamkrelidze and V. Ivanov associate this word with horse-riding Altaic tribes in the Bronze Age
The Bronze Age () was a historical period characterised principally by the use of bronze tools and the development of complex urban societies, as well as the adoption of writing in some areas. The Bronze Age is the middle principal period of ...
.
On the other hand, in the Russian tradition, the name 'meadow people' refers to the inhabitants of the left bank of river in particular. Recently, the most relevant is the version of V. V. Napolskikh and S. K. Belykh. They suppose that ethnonym was borrowed either from Indo-Iranian 'outside, close, last, edge, limit, boundary' or Turkic-Altaic / 'oath (in fidelity), comrade, friend'.
History
 On November 4, 1920, the Votyak Autonomous Oblast was formed.''Administrative-Territorial Structure of the Union Republics. 1987.'', p. 57 On January 1, 1932, it was renamed Udmurt Autonomous Oblast, which was then reorganized into the Udmurt ASSR on December 28, 1934. During
On November 4, 1920, the Votyak Autonomous Oblast was formed.''Administrative-Territorial Structure of the Union Republics. 1987.'', p. 57 On January 1, 1932, it was renamed Udmurt Autonomous Oblast, which was then reorganized into the Udmurt ASSR on December 28, 1934. During World War II
World War II or the Second World War (1 September 1939 – 2 September 1945) was a World war, global conflict between two coalitions: the Allies of World War II, Allies and the Axis powers. World War II by country, Nearly all of the wo ...
, many industrial factories were evacuated from the Ukrainian SSR
The Ukrainian Soviet Socialist Republic, abbreviated as the Ukrainian SSR, UkrSSR, and also known as Soviet Ukraine or just Ukraine, was one of the Republics of the Soviet Union, constituent republics of the Soviet Union from 1922 until 1991. ...
and western borderlands to Udmurtia.
On October 11, 1991, the Supreme Council of the Udmurt ASSR adopted a law according to which the Udmurt ASSR acquired a new name — the Udmurt Republic.
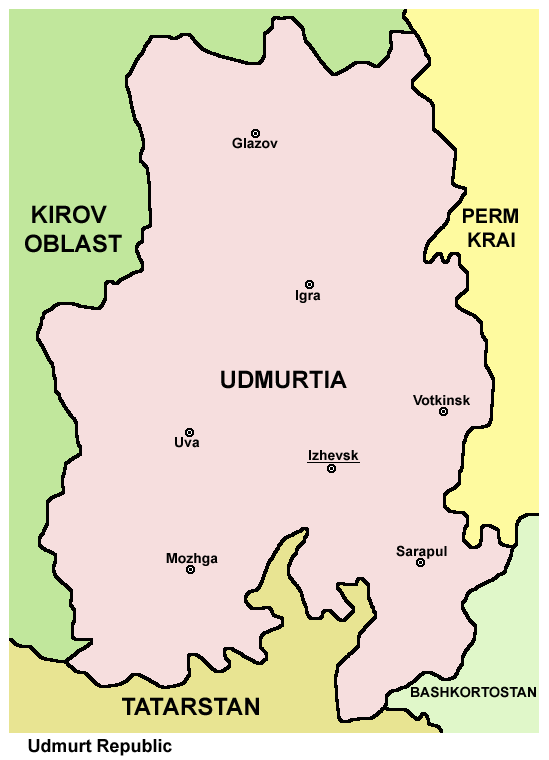
Geography
The republic is located to the west of theUral Mountains
The Ural Mountains ( ),; , ; , or simply the Urals, are a mountain range in Eurasia that runs north–south mostly through Russia, from the coast of the Arctic Ocean to the river Ural (river), Ural and northwestern Kazakhstan.
and borders Kirov, Perm, Bashkortostan
Bashkortostan, officially the Republic of Bashkortostan, sometimes also called Bashkiria, is a republic of Russia between the Volga river and the Ural Mountains in Eastern Europe. The republic borders Perm Krai to the north, Sverdlovsk Oblast ...
, and Tatarstan
Tatarstan, officially the Republic of Tatarstan, sometimes also called Tataria, is a Republics of Russia, republic of Russia located in Eastern Europe. It is a part of the Volga Federal District; and its capital city, capital and largest city i ...
.
Udmurtia is a republic in the Russian Federation, located in Central Russia between the branches of the rivers Kama
''Kama'' (Sanskrit: काम, ) is the concept of pleasure, enjoyment and desire in Hinduism, Buddhism, Jainism, and Sikhism. It can also refer to "desire, wish, longing" in Hindu, Buddhist, Jain, and Sikh literature.Monier Williamsका� ...
and its right tributary the Vyatka.
The city of Izhevsk is the administrative, industrial, and cultural center of Udmurtia. Geographically, it is located not far from Moscow, the capital and largest city of the Russian Federation. The city has a well-developed transport system (including air, land, and water).
Udmurtia borders Kirov Oblast to the west and north, Perm Oblast to the east, and the Bashkortostan and Tatarstan Republics to the south.
Climate
The republic has a moderatecontinental climate
Continental climates often have a significant annual variation in temperature (warm to hot summers and cold winters). They tend to occur in central and eastern parts of the three northern-tier continents (North America, Europe, and Asia), typi ...
, with warm summers and cold, snowy winters. Annual precipitation
In meteorology, precipitation is any product of the condensation of atmospheric water vapor that falls from clouds due to gravitational pull. The main forms of precipitation include drizzle, rain, rain and snow mixed ("sleet" in Commonwe ...
averages 400–600 mm.
Administrative divisions
Demographics
Population: Although as of 2007 the population was declining, the decline was stabilizing and was more pronounced in urban areas. Out of the 19,667 births reported in 2007, 12,631 were in urban areas (11.86 per 1,000) and 7,036 were in rural areas (14.88 per 1,000). Birth rates for rural areas are 25% higher than that of urban areas. Of the total of 21,727 deaths, 14,366 were reported in urban areas (13.49 per 1,000) and 7,361 were in rural areas (15.56 per 1,000). Natural decline of the population was measured at −0.16% for urban areas and an insignificant −0.07% for rural areas (the average for Russia was −0.33% in 2007).Settlements
Vital statistics
Source TFR sourceEthnic groups
According to the 2021 Census,Russians
Russians ( ) are an East Slavs, East Slavic ethnic group native to Eastern Europe. Their mother tongue is Russian language, Russian, the most spoken Slavic languages, Slavic language. The majority of Russians adhere to Eastern Orthodox Church ...
make up 67.7% of the republic's population, while the ethnic Udmurts make up only 24.1%. Other groups include Tatars
Tatars ( )Tatar
in the Collins English Dictionary are a group of Turkic peoples across Eas ...
(5.5%), Mari (0.5%), in the Collins English Dictionary are a group of Turkic peoples across Eas ...
Ukrainians
Ukrainians (, ) are an East Slavs, East Slavic ethnic group native to Ukraine. Their native tongue is Ukrainian language, Ukrainian, and the majority adhere to Eastern Orthodox Church, Eastern Orthodoxy, forming the List of contemporary eth ...
(0.3%), and a host of smaller groups, each accounting for less than 0.5% of the republic's total population.
Over two-thirds of the world population of Udmurts live in the republic.
Religious groups
According to a 2012 survey, 33.1% of the population of Udmurtia adheres to theRussian Orthodox Church
The Russian Orthodox Church (ROC; ;), also officially known as the Moscow Patriarchate (), is an autocephaly, autocephalous Eastern Orthodox Church, Eastern Orthodox Christian church. It has 194 dioceses inside Russia. The Primate (bishop), p ...
, 5% are unaffiliated generic Christians
A Christian () is a person who follows or adheres to Christianity, a monotheistic Abrahamic religion based on the life and teachings of Jesus Christ. Christians form the largest religious community in the world. The words '' Christ'' and ''C ...
, 2% are Eastern Orthodox Christian believers without belonging to any church or members of other Eastern Orthodox church
The Eastern Orthodox Church, officially the Orthodox Catholic Church, and also called the Greek Orthodox Church or simply the Orthodox Church, is List of Christian denominations by number of members, one of the three major doctrinal and ...
es, 4% are Muslim
Muslims () are people who adhere to Islam, a Monotheism, monotheistic religion belonging to the Abrahamic religions, Abrahamic tradition. They consider the Quran, the foundational religious text of Islam, to be the verbatim word of the God ...
s, 2% of the population adheres to the Slavic native faith
The Slavic Native Faith, commonly known as Rodnovery and sometimes as Slavic Neopaganism, is a modern Paganism, modern Pagan religion. Classified as a new religious movement, its practitioners hearken back to the Slavic paganism, historica ...
(Rodnovery) or to Udmurt Vos
Udmurt Vos () is the ethnic religion, ethnic religious revival of the Udmurts, a Finno-Ugric peoples, Finno-Ugrian people inhabiting the republics of Russia, republic of Udmurtia in Russia. Among the Udmurts, as in other Finno-Ugrian republics in t ...
(Udmurt native faith), 1% adheres to forms of Protestantism
Protestantism is a branch of Christianity that emphasizes Justification (theology), justification of sinners Sola fide, through faith alone, the teaching that Salvation in Christianity, salvation comes by unmerited Grace in Christianity, divin ...
, and 1% of the population are Old Believers
Old Believers or Old Ritualists ( Russian: староверы, ''starovery'' or старообрядцы, ''staroobryadtsy'') is the common term for several religious groups, which maintain the old liturgical and ritual practices of the Russian ...
. In addition, 29% of the population declares to be " spiritual but not religious," 19% is atheist
Atheism, in the broadest sense, is an absence of belief in the existence of deities. Less broadly, atheism is a rejection of the belief that any deities exist. In an even narrower sense, atheism is specifically the position that there no ...
, and 3.9% follows other religions or did not give an answer to the question.
The local Russian Orthodox Church is the Metropolitanate of Udmurtia, comprising the Eparchy of Izhevsk (founded 1927) under Bishop and Metropolitan Viktorin (Kostenkov) (2015), the Eparchy of Glazov (founded 1889) under Bishop Viktor (Sergeyev), and the Eparchy of Sarapul (founded 1868) under Bishop Anthony (Prostikhin) (2015).
Jews
Udmurt Jews are a special territorial group of theAshkenazi Jews
Ashkenazi Jews ( ; also known as Ashkenazic Jews or Ashkenazim) form a distinct subgroup of the Jewish diaspora, that emerged in the Holy Roman Empire around the end of the first millennium CE. They traditionally speak Yiddish, a language ...
, which started to be formed in the residential areas of mixed Turkic-speaking (Tatars
Tatars ( )Tatar
in the Collins English Dictionary are a group of Turkic peoples across Eas ...
, Kryashens, in the Collins English Dictionary are a group of Turkic peoples across Eas ...
Bashkirs
The Bashkirs ( , ) or Bashkorts (, ; , ) are a Turkic peoples, Turkic ethnic group indigenous to Russia. They are concentrated in Bashkortostan, a Republics of Russia, republic of the Russian Federation and in the broader historical region of B ...
, Chuvash people
The Chuvash people (, ; , ) also called Chuvash Tatars, are a Turkic ethnic group, a branch of the Oğurs, inhabiting an area stretching from the Idel-Ural region to Siberia.
Most of them live in the Russian republic of Chuvashia and the ...
), Finno-Ugric-speaking ( Udmurts, Mari people
The Mari ( ), also formerly known as the Cheremis or Cheremisses, are a Finno-Ugric peoples, Finno-Ugric people in Eastern Europe, who have traditionally lived along the Volga and Kama River, Kama rivers in Russia. They live mostly in the Mari E ...
) and Slavic-speaking (Russians
Russians ( ) are an East Slavs, East Slavic ethnic group native to Eastern Europe. Their mother tongue is Russian language, Russian, the most spoken Slavic languages, Slavic language. The majority of Russians adhere to Eastern Orthodox Church ...
) population. The Ashkenazi Jews
Ashkenazi Jews ( ; also known as Ashkenazic Jews or Ashkenazim) form a distinct subgroup of the Jewish diaspora, that emerged in the Holy Roman Empire around the end of the first millennium CE. They traditionally speak Yiddish, a language ...
on the territory of the Udmurt Republic first appeared in the 1830s.Шумилов Е.Ф., "Евреи: элита инженерная, торговая, медицинская..." Свое дело. 2001. №11. С. 18. The Udmurt Jewry had formed the local variety on the base of the Yiddish of Udmurtia till the 1930s and features of Yiddish of migrants "joined" into it (in the 1930s and 1940s);Altyntsev A.V., "The Concept of Love in Ashkenazim of Udmurtia and Tatarstan", Nauka Udmurtii. 2013. no. 4 (66), p. 131. (Алтынцев А.В."Чувство любви в понимании евреев-ашкенази Удмуртии и Татарстана".
Наука Удмуртии. 2013. №4. С. 131: Комментарии.) as a result up to the 1970s and 1980s the Udmurt variety of Yiddish ('' Udmurtish'') was divided into two linguistic subgroups: the central subgroup (with centers
Izhevsk
Izhevsk or Ijevsk (, ; , or ) is the capital city of Udmurtia, Russia. It is situated along the Izh River, west of the Ural Mountains in Eastern Europe. It is the 21st-largest city in Russia, and the most populous in Udmurtia, with over 600,000 ...
, Sarapul, and Votkinsk) and the southern subgroup (with centers Kambarka, Alnashi, Agryz, and Naberezhnye Chelny
Naberezhnye Chelny (, ; , ) is the second largest types of inhabited localities in Russia, city in the Republic of Tatarstan, Russia. A major industrial center, Naberezhnye Chelny stands on the Kama River east of Kazan near Nizhnekamsk Reservoi ...
). One of the characteristic features of the Udmurtish is a noticeable number of Udmurt and Tatar loan words.Гольдберг-Алтынцев А.В., "Краткий этнографический обзор группы ашкеназских евреев в Алнашском районе Удмуртской Республики / пер. с англ. яз. А.Й. Каца."Jewish studies in the Udmurt Republic: Online. Part 1. Edited by A. Greenberg. February 27, 2015 published. P. 3.
Culture
Udmurt folklore is understood both in a broad sense (, , - folk knowledge, folk wisdom), and in a narrower one (, - folk poetry, oral poetry). In everyday life, folklore is not divided into genres, it is perceived in unity with material culture, with religious, legal, and ethical aspects. Popular terms-definitions have incorporated the ritual action (, , , , , , ), symbolically figurative and magically forming words (, , , ), musical and choreographic behavior (, , , , ).Notes
References
Sources
* *"СССР. Административно-территориальное деление союзных республик. 1987." (''USSR. Administrative-Territorial Structure of the Union Republics. 1987'') / Составители В. А. Дударев, Н. А. Евсеева. — М.: Изд-во «Известия Советов народных депутатов СССР», 1987. — 673 с.Further reading
*Kalder, Daniel. ''Lost Cosmonaut: Observations of an Anti-tourist''. Scribner Book Company. . *External links
Official website of the Udmurt Republic
{{Use mdy dates, date=October 2014 Regions of Europe with multiple official languages States and territories established in 1990 1990 establishments in Russia 1990 establishments in the Soviet Union Republics of Russia