USS Archer-Fish (SS-311) on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
USS ''Archerfish'' (SS/AGSS-311) was a ''Balao''-class
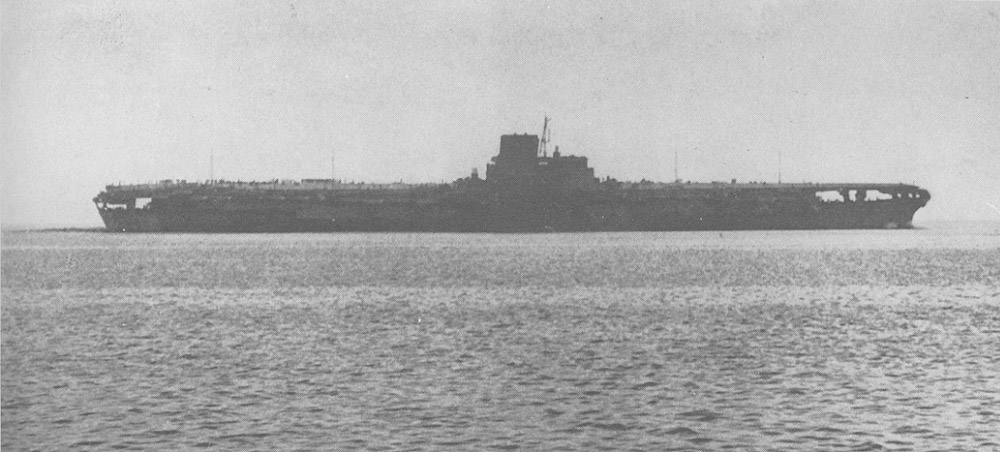 Enright ordered the carrier tracked from ahead in preparation for an attack from below. After six hours, the enemy carrier turned back into ''Archerfish''s path, and ''Archerfish'' got into an attack position. ''Archerfish'' submerged and fired six torpedoes, four of which found their mark. Enright deliberately set the torpedoes to run shallow () in hopes of
Enright ordered the carrier tracked from ahead in preparation for an attack from below. After six hours, the enemy carrier turned back into ''Archerfish''s path, and ''Archerfish'' got into an attack position. ''Archerfish'' submerged and fired six torpedoes, four of which found their mark. Enright deliberately set the torpedoes to run shallow () in hopes of
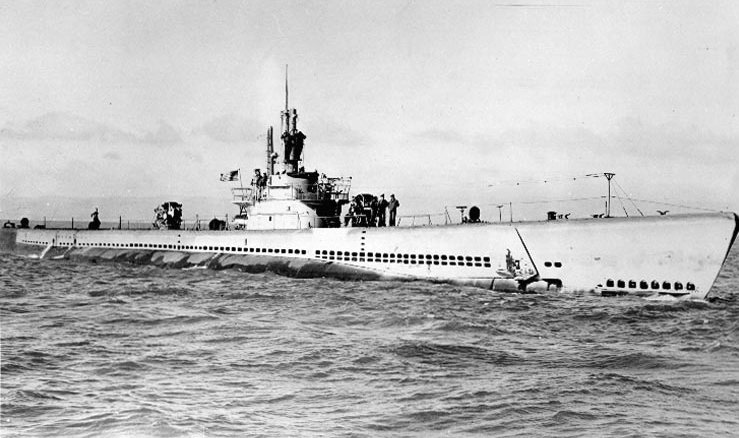 Following completion of the yard work, ''Archerfish'' sailed on 14 June, for
Following completion of the yard work, ''Archerfish'' sailed on 14 June, for
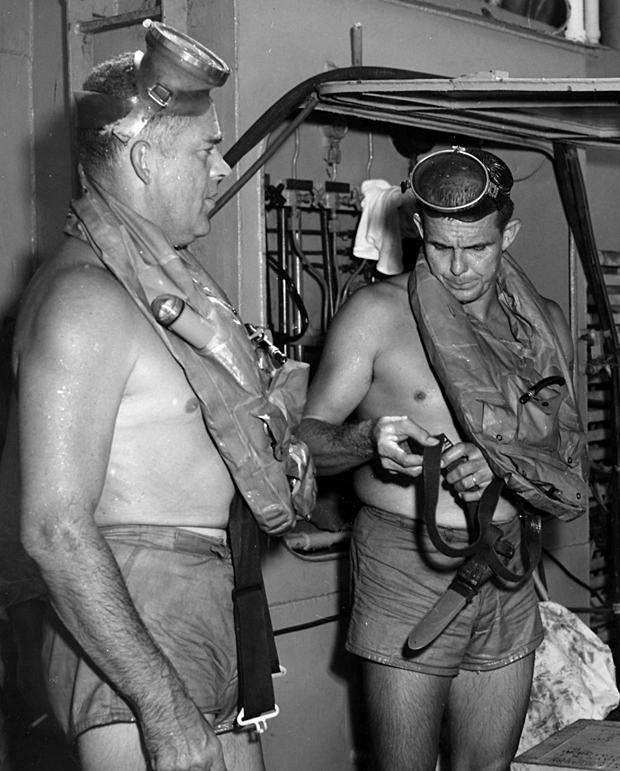 On 2 October 1959, approximately 15 miles southwest of Key West, over Vestal Shoal, ''Archerfish'' bottomed at . Commander
On 2 October 1959, approximately 15 miles southwest of Key West, over Vestal Shoal, ''Archerfish'' bottomed at . Commander
 Presidential Unit Citation
* Asiatic-Pacific Campaign Medal with seven
Presidential Unit Citation
* Asiatic-Pacific Campaign Medal with seven 
Official website: USS ''Archerfish''
{{DEFAULTSORT:Archerfish (Ss-311) 1943 ships Balao-class submarines Cold War submarines of the United States Ships built in Kittery, Maine Ships sunk as targets Maritime incidents in 1968 Shipwrecks in the Pacific Ocean Shipwrecks of the California coast World War II submarines of the United States
submarine
A submarine (often shortened to sub) is a watercraft capable of independent operation underwater. (It differs from a submersible, which has more limited underwater capability.) The term "submarine" is also sometimes used historically or infor ...
. She was the first ship of the United States Navy
The United States Navy (USN) is the naval warfare, maritime military branch, service branch of the United States Department of Defense. It is the world's most powerful navy with the largest Displacement (ship), displacement, at 4.5 millio ...
to be named for the archerfish
The archerfish (also known as spinner fish or archer fish) or Toxotidae are a monotypic family (although some include a second genus) of perciform tropical fish known for their unique predation technique of "shooting down" land-based insects a ...
. ''Archerfish'' is best known for sinking the Japan
Japan is an island country in East Asia. Located in the Pacific Ocean off the northeast coast of the Asia, Asian mainland, it is bordered on the west by the Sea of Japan and extends from the Sea of Okhotsk in the north to the East China Sea ...
ese aircraft carrier
An aircraft carrier is a warship that serves as a seagoing airbase, equipped with a full-length flight deck and hangar facilities for supporting, arming, deploying and recovering carrier-based aircraft, shipborne aircraft. Typically it is the ...
''Shinano'' in November 1944, the largest warship ever sunk by a submarine. For this achievement, she received a Presidential Unit Citation after World War II
World War II or the Second World War (1 September 1939 – 2 September 1945) was a World war, global conflict between two coalitions: the Allies of World War II, Allies and the Axis powers. World War II by country, Nearly all of the wo ...
.
Construction and commissioning
''Archerfish''skeel
The keel is the bottom-most longitudinal structural element of a watercraft, important for stability. On some sailboats, it may have a fluid dynamics, hydrodynamic and counterbalancing purpose as well. The keel laying, laying of the keel is often ...
was laid down on 22 January 1943 in the Portsmouth Navy Yard
The Portsmouth Naval Shipyard (PNS), often called the Portsmouth Navy Yard, is a United States Navy shipyard on Seavey's Island in Kittery, Maine, bordering Portsmouth, New Hampshire. The naval yard lies along the southern boundary of Maine on ...
in Kittery, Maine
Kittery is a town in York County, Maine, United States, and the oldest incorporated town in Maine. Home to the Portsmouth Naval Shipyard on Seavey's Island, Kittery includes Badger's Island, the seaside district of Kittery Point, and part of ...
. She was launched on 28 May 1943, sponsored by Malvina Thompson
Malvina "Tommy" Thompson (1893 – April 12, 1953) was a private secretary and personal aide to First Lady Eleanor Roosevelt. She was a pioneer of the East Wing staff, being the first staffer for a First Lady of the United States who was not a ...
, the personal secretary to first lady Eleanor Roosevelt
Anna Eleanor Roosevelt ( ; October 11, 1884November 7, 1962) was an American political figure, diplomat, and activist. She was the longest-serving First Lady of the United States, first lady of the United States, during her husband Franklin D ...
. The boat was commissioned on 4 September 1943.
World War II
''Archerfish'' underwent shakedown training through the first part of November off theNew England
New England is a region consisting of six states in the Northeastern United States: Connecticut, Maine, Massachusetts, New Hampshire, Rhode Island, and Vermont. It is bordered by the state of New York (state), New York to the west and by the ...
coast, and headed for Hawaii
Hawaii ( ; ) is an island U.S. state, state of the United States, in the Pacific Ocean about southwest of the U.S. mainland. One of the two Non-contiguous United States, non-contiguous U.S. states (along with Alaska), it is the only sta ...
via the Panama Canal
The Panama Canal () is an artificial waterway in Panama that connects the Caribbean Sea with the Pacific Ocean. It cuts across the narrowest point of the Isthmus of Panama, and is a Channel (geography), conduit for maritime trade between th ...
. She arrived at Pearl Harbor
Pearl Harbor is an American lagoon harbor on the island of Oahu, Hawaii, west of Honolulu. It was often visited by the naval fleet of the United States, before it was acquired from the Hawaiian Kingdom by the U.S. with the signing of the Reci ...
on 29 November 1943 and joined the Pacific Fleet.
First four patrols, December 1943 – September 1944
After receiving voyage repairs and undergoing training exercises, ''Archerfish'' got under way on 23 December, for her first war patrol. She paused atMidway Atoll
Midway Atoll (colloquialism, colloquial: Midway Islands; ; ) is a atoll in the North Pacific Ocean. Midway Atoll is an insular area of the United States and is an Insular area#Unorganized unincorporated territories, unorganized and unincorpo ...
on 27 December, to refuel before proceeding to her patrol area north of Taiwan
Taiwan, officially the Republic of China (ROC), is a country in East Asia. The main geography of Taiwan, island of Taiwan, also known as ''Formosa'', lies between the East China Sea, East and South China Seas in the northwestern Pacific Ocea ...
. During this patrol, she attacked three ships, but scored no kills before returning to Midway on 16 February 1944 for repairs and training.
The submarine stood out of Midway on 16 March 1944 on her second war patrol but encountered no Japanese targets during her 42 days at sea, mostly near the Palau Islands
Palau, officially the Republic of Palau, is an island country in the Micronesia subregion of Oceania in the western Pacific Ocean. The Republic of Palau consists of approximately 340 islands and is the western part of the Caroline Islands, w ...
. She returned to the Submarine Base at Pearl Harbor via Johnston Island
Johnston Atoll is an unincorporated territory of the United States, under the jurisdiction of the United States Air Force (USAF). The island is closed to public entry, and limited access for management needs is only granted by a letter of autho ...
on 27 April, to commence refitting.
A month and a day later, ''Archerfish'' left Pearl Harbor, bound for the Bonin Islands
The Bonin Islands, also known as the , is a list of islands of Japan, Japanese archipelago of over 30 subtropical and Island#Tropical islands, tropical islands located around SSE of Tokyo and northwest of Guam. The group as a whole has a total ...
area and her third patrol. She was assigned lifeguard duty during the strikes against Iwo Jima
is one of the Japanese Volcano Islands, which lie south of the Bonin Islands and together with them make up the Ogasawara Subprefecture, Ogasawara Archipelago. Together with the Izu Islands, they make up Japan's Nanpō Islands. Although sout ...
on 4 July, and rescued downed aviator Ensign John B. Anderson before returning to Midway on 15 July.
After a refit alongside submarine tender
A submarine tender, in British English a submarine depot ship, is a type of depot ship that supplies and supports submarines.
Development
Submarines are small compared to most oceangoing vessels, and generally cannot carry large amounts of foo ...
and training exercises, ''Archerfish'' got under way again on 7 August, to begin another patrol. She prowled the waters off Honshū
, historically known as , is the largest of the four main islands of Japan. It lies between the Pacific Ocean (east) and the Sea of Japan (west). It is the seventh-largest island in the world, and the second-most populous after the Indonesian ...
for more than a month without bagging any enemy ships, and returned to Pearl Harbor
Pearl Harbor is an American lagoon harbor on the island of Oahu, Hawaii, west of Honolulu. It was often visited by the naval fleet of the United States, before it was acquired from the Hawaiian Kingdom by the U.S. with the signing of the Reci ...
on 29 September, after 53 days at sea.
Fifth patrol, October–December 1944: Sinking ''Shinano''
''Archerfish'' left Hawaii on 30 October, under the command ofCommander
Commander (commonly abbreviated as Cmdr.) is a common naval officer rank as well as a job title in many army, armies. Commander is also used as a rank or title in other formal organizations, including several police forces. In several countri ...
Joseph F. Enright, visited Saipan
Saipan () is the largest island and capital of the Northern Mariana Islands, an unincorporated Territories of the United States, territory of the United States in the western Pacific Ocean. According to 2020 estimates by the United States Cens ...
on 9 November, for quick voyage repairs, and departed two days later to carry out her next patrol, in which her primary mission was to provide lifeguard services for the first B-29 Superfortress
The Boeing B-29 Superfortress is a retired American four-engined Propeller (aeronautics), propeller-driven heavy bomber, designed by Boeing and flown primarily by the United States during World War II and the Korean War. Named in allusion to ...
strikes against Tokyo
Tokyo, officially the Tokyo Metropolis, is the capital of Japan, capital and List of cities in Japan, most populous city in Japan. With a population of over 14 million in the city proper in 2023, it is List of largest cities, one of the most ...
. On 28 November, she received word that no air raids would be launched that day, giving her carte blanche to roam the waters near Tokyo Bay
is a bay located in the southern Kantō region of Japan spanning the coasts of Tokyo, Kanagawa Prefecture, and Chiba Prefecture, on the southern coast of the island of Honshu. Tokyo Bay is connected to the Pacific Ocean by the Uraga Channel. Th ...
. That evening, lookouts spotted what looked like a tanker leaving the bay. It was later discovered that it was actually a large aircraft carrier
An aircraft carrier is a warship that serves as a seagoing airbase, equipped with a full-length flight deck and hangar facilities for supporting, arming, deploying and recovering carrier-based aircraft, shipborne aircraft. Typically it is the ...
screened by three destroyers ( ''Hamakaze'', ''Yukikaze'', ''Isokaze'') and a submarine chaser ( ''Cha-241'').
 Enright ordered the carrier tracked from ahead in preparation for an attack from below. After six hours, the enemy carrier turned back into ''Archerfish''s path, and ''Archerfish'' got into an attack position. ''Archerfish'' submerged and fired six torpedoes, four of which found their mark. Enright deliberately set the torpedoes to run shallow () in hopes of
Enright ordered the carrier tracked from ahead in preparation for an attack from below. After six hours, the enemy carrier turned back into ''Archerfish''s path, and ''Archerfish'' got into an attack position. ''Archerfish'' submerged and fired six torpedoes, four of which found their mark. Enright deliberately set the torpedoes to run shallow () in hopes of capsizing
Capsizing or keeling over occurs when a boat or ship is rolled on its side or further by wave action, instability or wind force beyond the angle of positive static stability or it is upside down in the water. The act of recovering a vessel fr ...
the target by holing it higher up on its hull. He also wanted to increase the chances of a hit in case the torpedoes ran deeper than set. Before ''Archerfish'' descended to to avoid a depth charge
A depth charge is an anti-submarine warfare (ASW) weapon designed to destroy submarine
A submarine (often shortened to sub) is a watercraft capable of independent operation underwater. (It differs from a submersible, which has more limited ...
attack, Enright saw that the carrier was listing to starboard. The crew began picking up loud breaking-up noises from the target shortly after firing the last torpedo. The noises continued for 47 minutes.
The patrol ended at Guam
Guam ( ; ) is an island that is an Territories of the United States, organized, unincorporated territory of the United States in the Micronesia subregion of the western Pacific Ocean. Guam's capital is Hagåtña, Guam, Hagåtña, and the most ...
on 15 December, after 48 days on station. Initially, the Office of Naval Intelligence
The Office of Naval Intelligence (ONI) is the military intelligence agency of the United States Navy. Established in 1882 primarily to advance the Navy's modernization efforts, it is the oldest member of the U.S. Intelligence Community and serv ...
thought that ''Archerfish'' had sunk a cruiser, not believing that there were any carriers in that stretch of ocean. However, Enright had made sketches of the target, and ''Archerfish'' was given credit for sinking a 28,000-ton carrier.
It was only after the war that the Americans learned the identity of ''Archerfish''s quarry: '' Shinano,'' the biggest aircraft carrier ever built at the time. It was originally the third of the s, but had been converted into a 72,000-ton supercarrier after the Battle of Midway
The Battle of Midway was a major naval battle in the Pacific Ocean theater of World War II, Pacific Theater of World War II that took place on 4–7 June 1942, six months after Japan's attack on Pearl Harbor and one month after the Battle of t ...
. Four of ''Archerfish''s six torpedoes had hit, striking the carrier between the anti-torpedo bulge
The anti-torpedo bulge (also known as an anti-torpedo blister) is a form of defence against naval torpedoes occasionally employed in warship construction in the period between the First and Second World Wars. It involved fitting (or retrofittin ...
and the waterline at approximately 03:20. The damage was magnified by the fact that ''Shinano'' had turned south just minutes before Enright loosed his torpedoes, thus exposing her entire side to ''Archerfish''—a nearly ideal firing situation for a submarine. The ship initially continued under way, but it lost power around 06:00. The crew were unable to contain the flooding due to serious design flaws and inexperience, and the carrier capsized just before 11:00. ''Archerfish'' received the Presidential Unit Citation and Enright received the Navy Cross
The Navy Cross is the United States Naval Service's second-highest military decoration awarded for sailors and marines who distinguish themselves for extraordinary heroism in combat with an armed enemy force. The medal is equivalent to the Army ...
for this action. ''Shinano'' is the largest warship to be sunk by a submarine.
Last two patrols, January–September 1945
While her officers and crew spent the holidays at a rest and recreation camp located on Guam, ''Archerfish'' underwent refit at the island. On 10 January 1945, the submarine got underway for her sixth patrol. Enright was in command of "Joe's Jugheads", a three-submarine " wolfpack" comprising ''Archerfish'', , and . This mission took her to waters in theSouth China Sea
The South China Sea is a marginal sea of the Western Pacific Ocean. It is bounded in the north by South China, in the west by the Indochinese Peninsula, in the east by the islands of Taiwan island, Taiwan and northwestern Philippines (mainly Luz ...
off Hong Kong
Hong Kong)., Legally Hong Kong, China in international treaties and organizations. is a special administrative region of China. With 7.5 million residents in a territory, Hong Kong is the fourth most densely populated region in the wor ...
and the southern tip of Formosa
Taiwan, officially the Republic of China (ROC), is a country in East Asia. The island of Taiwan, formerly known to Westerners as Formosa, has an area of and makes up 99% of the land under ROC control. It lies about across the Taiwan Strait f ...
. She damaged one unidentified target and claimed a submarine on 14 February 1945 during this patrol which ended on 3 March, three days earlier than scheduled, due to bow-plane problems. (The submarine sinking was not confirmed until after the war.) ''Archerfish'' touched at Saipan
Saipan () is the largest island and capital of the Northern Mariana Islands, an unincorporated Territories of the United States, territory of the United States in the western Pacific Ocean. According to 2020 estimates by the United States Cens ...
and Pearl Harbor before arriving back in the United States at San Francisco, California
San Francisco, officially the City and County of San Francisco, is a commercial, Financial District, San Francisco, financial, and Culture of San Francisco, cultural center of Northern California. With a population of 827,526 residents as of ...
on 13 March. She then proceeded to the Hunters Point Navy Yard for overhaul and drydocking.
 Following completion of the yard work, ''Archerfish'' sailed on 14 June, for
Following completion of the yard work, ''Archerfish'' sailed on 14 June, for Oahu
Oahu (, , sometimes written Oahu) is the third-largest and most populated island of the Hawaiian Islands and of the U.S. state of Hawaii. The state capital, Honolulu, is on Oahu's southeast coast. The island of Oahu and the uninhabited Northwe ...
. She arrived at Pearl Harbor on 22 June, and commenced voyage repairs and training exercises. The submarine got underway on 10 July, for her seventh and last war patrol, which she conducted in the area off the east coast of Honshū
, historically known as , is the largest of the four main islands of Japan. It lies between the Pacific Ocean (east) and the Sea of Japan (west). It is the seventh-largest island in the world, and the second-most populous after the Indonesian ...
and the south coast of Hokkaidō
is the second-largest island of Japan and comprises the largest and northernmost prefecture, making up its own region. The Tsugaru Strait separates Hokkaidō from Honshu; the two islands are connected by railway via the Seikan Tunnel.
The ...
, providing lifeguard services for Superfortresses striking the Japanese home islands. She was still off Hokkaidō on 15 August, when word of the Japanese capitulation arrived. ''Archerfish'' was one of 12 submarines that entered Tokyo Bay
is a bay located in the southern Kantō region of Japan spanning the coasts of Tokyo, Kanagawa Prefecture, and Chiba Prefecture, on the southern coast of the island of Honshu. Tokyo Bay is connected to the Pacific Ocean by the Uraga Channel. Th ...
on 31 August, and moored alongside Tender USS Proteus (AS-19)
The third USS ''Proteus'' (AS-19) was a in the United States Navy.
Construction and commissioning
''Proteus'' was laid down by the Moore Shipbuilding and Dry Dock Company, Oakland, California, 15 September 1941; launched 12 November 1942; spo ...
, near the Yokosuka Navy Yard
or is a United States Navy base in Yokosuka, Japan. Its mission is to maintain and operate base facilities for the logistic, recreational, administrative support and service of the U.S. Naval Forces Japan, Seventh Fleet and other operating f ...
. After the formal Japanese surrender on 2 September, ''Archerfish'' departed Tokyo Bay
is a bay located in the southern Kantō region of Japan spanning the coasts of Tokyo, Kanagawa Prefecture, and Chiba Prefecture, on the southern coast of the island of Honshu. Tokyo Bay is connected to the Pacific Ocean by the Uraga Channel. Th ...
, bound for Pearl Harbor
Pearl Harbor is an American lagoon harbor on the island of Oahu, Hawaii, west of Honolulu. It was often visited by the naval fleet of the United States, before it was acquired from the Hawaiian Kingdom by the U.S. with the signing of the Reci ...
, and arrived there on 12 September. She was then assigned to Submarine Squadron 1 (SubRon 1) for duty and training.
Post-war
The submarine left Pearl Harbor on 2 January 1946, bound for San Francisco. From 8 January, to 13 March, the ship's force carried out her preinactivation overhaul. On the latter day, she proceeded to theMare Island Naval Shipyard
The Mare Island Naval Shipyard (MINSY or MINS) was the first United States Navy base established on the Pacific Ocean and was in service 142 years from 1854 to 1996. It is located on Mare Island, northeast of San Francisco, in Vallejo, Califor ...
where the final stages of inactivation were completed. ''Archerfish'' was decommissioned on 12 June 1946 and placed in the Pacific Reserve Group berthed at Mare Island.
1952–1955
During theKorean War
The Korean War (25 June 1950 – 27 July 1953) was an armed conflict on the Korean Peninsula fought between North Korea (Democratic People's Republic of Korea; DPRK) and South Korea (Republic of Korea; ROK) and their allies. North Korea was s ...
, many inactive Navy vessels were recommissioned. ''Archerfish'' was chosen for recommissioning on 7 January 1952. She was recommissioned on 7 March and reported for duty to the Pacific Fleet on 26 March. The next day she sailed for three weeks of shakedown training out of San Diego, California
San Diego ( , ) is a city on the Pacific coast of Southern California, adjacent to the Mexico–United States border. With a population of over 1.4 million, it is the List of United States cities by population, eighth-most populous city in t ...
. However, a fire broke out in her maneuvering room on 28 March, and the ship returned to Mare Island under her own power for a restricted availability to have the damage corrected.
With repairs complete on 27 May, ''Archerfish'' held shakedown off the West Coast. She then transited the Panama Canal
The Panama Canal () is an artificial waterway in Panama that connects the Caribbean Sea with the Pacific Ocean. It cuts across the narrowest point of the Isthmus of Panama, and is a Channel (geography), conduit for maritime trade between th ...
and joined the Atlantic Fleet on 3 July. Attached to SubRon 12, she operated out of Key West, Florida
Key West is an island in the Straits of Florida, at the southern end of the U.S. state of Florida. Together with all or parts of the separate islands of Sigsbee Park, Dredgers Key, Fleming Key, Sunset Key, and the northern part of Stock Islan ...
, visiting such places as Santiago
Santiago (, ; ), also known as Santiago de Chile (), is the capital and largest city of Chile and one of the largest cities in the Americas. It is located in the country's central valley and is the center of the Santiago Metropolitan Regi ...
and Guantánamo Bay
Guantánamo Bay (, ) is a bay in Guantánamo Province at the southeastern end of Cuba. It is the largest harbor on the south side of the island and it is surrounded by steep hills which create an enclave that is cut off from its immediate hint ...
, Cuba; Port-au-Prince, Haiti
Port-au-Prince ( ; ; , ) is the capital and most populous city of Haiti. The city's population was estimated at 1,200,000 in 2022 with the metropolitan area estimated at a population of 2,618,894. The metropolitan area is defined by the IHSI ...
; San Juan, Puerto Rico
San Juan ( , ; Spanish for "Saint John the Baptist, John") is the capital city and most populous Municipalities of Puerto Rico, municipality in the Commonwealth (U.S. insular area), Commonwealth of Puerto Rico, an unincorporated territory of the ...
; and Trinidad, British West Indies. The vessel departed Key West on 25 April 1955 and proceeded to the Philadelphia Naval Shipyard
The Philadelphia Naval Shipyard was the first United States Navy shipyard and was historically important for nearly two centuries.
Construction of the original Philadelphia Naval Shipyard began during the American Revolution in 1776 at Front ...
for decommissioning. After completing her inactivation overhaul, the ship was towed to Atlantic Reserve Fleet, New London in New London, Connecticut
New London is a seaport city and a port of entry on the northeast coast of the United States, located at the outlet of the Thames River (Connecticut), Thames River in New London County, Connecticut, which empties into Long Island Sound. The cit ...
, and was decommissioned on 21 October 1955.
Oceanographic work, 1958–1964
''Archerfish'' was reactivated at New London in July 1957, placed back in commission on 1 August, and again joined SubRon 12 at Key West. On 13 January 1958, she got underway for a cruise under the technical supervision of the Navy Hydrographic Office. On this deployment, she visitedRecife
Recife ( , ) is the Federative units of Brazil, state capital of Pernambuco, Brazil, on the northeastern Atlantic Ocean, Atlantic coast of South America. It is the largest urban area within both the North Region, Brazil, North and the Northeast R ...
, Brazil, and Trinidad. Upon completion of that mission she provided services for the fleet training commands at Key West and Guantánamo Bay. (In this time, she also portrayed the in the 1959 movie ''Operation Petticoat
''Operation Petticoat'' is a 1959 American World War II submarine comedy film in Eastmancolor from Universal-International, produced by Robert Arthur, directed by Blake Edwards, and starring Cary Grant and Tony Curtis.
The film tells in flash ...
'' for the underwater and distance scenes and shots.)
 On 2 October 1959, approximately 15 miles southwest of Key West, over Vestal Shoal, ''Archerfish'' bottomed at . Commander
On 2 October 1959, approximately 15 miles southwest of Key West, over Vestal Shoal, ''Archerfish'' bottomed at . Commander George F. Bond
Captain George Foote Bond (November 14, 1915 – January 3, 1983) was a United States Navy physician who was known as a leader in the field of undersea and hyperbaric medicine and the "Father of Saturation Diving".
While serving as Officer-in-C ...
and Chief Engineman Cyril Tuckfield safely completed a 52-second, 302-foot buoyant ascent from the forward escape trunk
Escape or Escaping may refer to:
Arts and media Film
* ''Escape'' (1928 film), a German silent drama film
* ''Escape!'' (film), a 1930 British crime film starring Austin Trevor and Edna Best
* ''Escape'' (1940 film), starring Robert Taylor and ...
. Both men received the Legion of Merit
The Legion of Merit (LOM) is a Awards and decorations of the United States military, military award of the United States Armed Forces that is given for exceptionally meritorious conduct in the performance of outstanding services and achievemen ...
in 1960 for establishing the feasibility of deep submarine escape by locking out.
In early 1960, ''Archerfish'' was chosen to participate in Operation "Sea Scan", a scientific study of marine weather conditions, water composition, ocean depths, and temperature ranges. She entered the Philadelphia Naval Shipyard
The Philadelphia Naval Shipyard was the first United States Navy shipyard and was historically important for nearly two centuries.
Construction of the original Philadelphia Naval Shipyard began during the American Revolution in 1776 at Front ...
in January to be specially equipped for this new mission. During this time, the vessel was redesignated an auxiliary submarine, with hull classification symbol
The United States Navy, United States Coast Guard, and United States National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA) use a hull classification symbol (sometimes called hull code or hull number) to identify their ships by type and by ind ...
AGSS-311. Embarking a team of civilian scientists, she commenced the first phase of "Sea Scan" on 18 May. On the cruise, the submarine visited Portsmouth
Portsmouth ( ) is a port city status in the United Kingdom, city and unitary authority in Hampshire, England. Most of Portsmouth is located on Portsea Island, off the south coast of England in the Solent, making Portsmouth the only city in En ...
, England; Hammerfest
Hammerfest or Hámmárfeasta is a town/cityIn the Norwegian language, the word ''by'' can be translated as "town" or "city". that is also the administrative centre of Hammerfest Municipality in Finnmark county, Norway. It is located on the nor ...
and Bergen
Bergen (, ) is a city and municipalities of Norway, municipality in Vestland county on the Western Norway, west coast of Norway. Bergen is the list of towns and cities in Norway, second-largest city in Norway after the capital Oslo.
By May 20 ...
, Norway; Faslane
His Majesty's Naval Base, Clyde (HMNB Clyde; also HMS ''Neptune''), primarily sited at Faslane on the Gare Loch, is one of three operating bases in the United Kingdom for the Royal Navy (the others being HMNB Devonport and HMNB Portsmouth). It ...
, Scotland; Thule
Thule ( ; also spelled as ''Thylē'') is the most northerly location mentioned in ancient Greek and Roman literature and cartography. First written of by the Greek explorer Pytheas of Massalia (modern-day Marseille, France) in about 320 BC, i ...
, Godthaab
Nuuk (; , formerly ) is the capital (political), capital and List of cities and towns in Greenland, most populous city of Greenland, an autonomous territory in the Kingdom of Denmark. Nuuk is the seat of Government of Greenland, government an ...
, and Julianehab, Greenland
Greenland is an autonomous territory in the Danish Realm, Kingdom of Denmark. It is by far the largest geographically of three constituent parts of the kingdom; the other two are metropolitan Denmark and the Faroe Islands. Citizens of Greenlan ...
; Belfast, Northern Ireland
Belfast (, , , ; from ) is the capital city and principal port of Northern Ireland, standing on the banks of the River Lagan and connected to the open sea through Belfast Lough and the North Channel (Great Britain and Ireland), North Channel ...
; and Halifax, Nova Scotia
Halifax is the capital and most populous municipality of the Provinces and territories of Canada, Canadian province of Nova Scotia, and the most populous municipality in Atlantic Canada. As of 2024, it is estimated that the population of the H ...
, before mooring at New London on 3 December.
After six weeks of upkeep, ''Archerfish'' got underway on 20 January 1961 for the Pacific phase of "Sea Scan", transited the Panama Canal
The Panama Canal () is an artificial waterway in Panama that connects the Caribbean Sea with the Pacific Ocean. It cuts across the narrowest point of the Isthmus of Panama, and is a Channel (geography), conduit for maritime trade between th ...
on 6 February, and proceeded via San Diego to Hawaii. She left Pearl Harbor on 27 March. During her operations the submarine visited Yokosuka
is a city in Kanagawa Prefecture, Japan.
, the city has a population of 373,797, and a population density of . The total area is . Yokosuka is the 11th-most populous city in the Greater Tokyo Area, and the 12th in the Kantō region. The city i ...
and Hakodate
is a Cities of Japan, city and seaports of Japan, port located in Oshima Subprefecture, Hokkaido, Japan. It is the capital city of Oshima Subprefecture. As of January 31, 2024, the city had an estimated population of 239,813 with 138,807 househol ...
, Japan, Hong Kong
Hong Kong)., Legally Hong Kong, China in international treaties and organizations. is a special administrative region of China. With 7.5 million residents in a territory, Hong Kong is the fourth most densely populated region in the wor ...
; Subic Bay
Subic Bay is a bay on the west coast of the island of Luzon in the Philippines, about northwest of Manila Bay. An extension of the South China Sea, its shores were formerly the site of a major United States Navy facility, U.S. Naval Base Subi ...
, Philippines; Bangkok
Bangkok, officially known in Thai language, Thai as Krung Thep Maha Nakhon and colloquially as Krung Thep, is the capital and most populous city of Thailand. The city occupies in the Chao Phraya River delta in central Thailand and has an estim ...
, Thailand; Penang
Penang is a Malaysian state located on the northwest coast of Peninsular Malaysia along the Strait of Malacca. It has two parts: Penang Island, where the capital city, George Town, is located, and Seberang Perai on the Malay Peninsula. Th ...
, Malaya
Malaya refers to a number of historical and current political entities related to what is currently Peninsular Malaysia in Southeast Asia:
Political entities
* British Malaya (1826–1957), a loose collection of the British colony of the Straits ...
; Colombo
Colombo, ( ; , ; , ), is the executive and judicial capital and largest city of Sri Lanka by population. The Colombo metropolitan area is estimated to have a population of 5.6 million, and 752,993 within the municipal limits. It is the ...
, Ceylon
Sri Lanka, officially the Democratic Socialist Republic of Sri Lanka, also known historically as Ceylon, is an island country in South Asia. It lies in the Indian Ocean, southwest of the Bay of Bengal, separated from the Indian subcontinent, ...
; and Fremantle
Fremantle () () is a port city in Western Australia located at the mouth of the Swan River (Western Australia), Swan River in the metropolitan area of Perth, the state capital. Fremantle Harbour serves as the port of Perth. The Western Australi ...
, Australia, and closed out 1961 moored at Yokosuka.
Phase two of Operation "Sea Scan" continued during the early months of 1962 with operations in the western Pacific area and port calls at Sasebo
is a core city located in Nagasaki Prefecture, Japan. It is the second-largest city in Nagasaki Prefecture, after its capital, Nagasaki. , the city had an estimated population of 230,873 in 102,670 households, and a population density of 540 per ...
, Japan, Guam
Guam ( ; ) is an island that is an Territories of the United States, organized, unincorporated territory of the United States in the Micronesia subregion of the western Pacific Ocean. Guam's capital is Hagåtña, Guam, Hagåtña, and the most ...
, and Cebu City
Cebu City, officially the City of Cebu, is a Cities of the Philippines#Legal classification, highly urbanized city in the Central Visayas region of the Philippines. According to the 2020 census, it has a population of 964,169 people, making ...
, Philippines. Early in March, the submarine completed phase two and proceeded via Pago Pago
Pago Pago ( or ; Samoan language, Samoan: )Harris, Ann G. and Esther Tuttle (2004). ''Geology of National Parks''. Kendall Hunt. Page 604. . is the capital of American Samoa. It is in Maoputasi County, American Samoa, Maoputasi County on Tutuila ...
to Pearl Harbor
Pearl Harbor is an American lagoon harbor on the island of Oahu, Hawaii, west of Honolulu. It was often visited by the naval fleet of the United States, before it was acquired from the Hawaiian Kingdom by the U.S. with the signing of the Reci ...
. On 27 April, she entered the San Francisco Naval Shipyard
The Hunters Point Naval Shipyard was a United States Navy shipyard in San Francisco, California, located on of waterfront at Hunters Point in the southeast corner of the city.
Originally, Hunters Point was a commercial shipyard established i ...
for overhaul. After completion of overhaul, the submarine moved to San Diego for a two-week upkeep. She then commenced phase three of "Sea Scan" in the eastern Pacific area, with stops in Pearl Harbor and Midway Atoll
Midway Atoll (colloquialism, colloquial: Midway Islands; ; ) is a atoll in the North Pacific Ocean. Midway Atoll is an insular area of the United States and is an Insular area#Unorganized unincorporated territories, unorganized and unincorpo ...
, and returned to San Diego for the Christmas holidays.
''Archerfish'' departed San Diego on 10 January 1963, bound for Yokosuka, where she began a three-week upkeep period. Following two and one-half months of operations she returned to the United States for a brief visit to San Francisco, California
San Francisco, officially the City and County of San Francisco, is a commercial, Financial District, San Francisco, financial, and Culture of San Francisco, cultural center of Northern California. With a population of 827,526 residents as of ...
, before reentering Pearl Harbor early in May. Late May and most of June were devoted to surveying off the northwest coast of the United States and Canada, with port calls in Portland, Oregon
Portland ( ) is the List of cities in Oregon, most populous city in the U.S. state of Oregon, located in the Pacific Northwest region. Situated close to northwest Oregon at the confluence of the Willamette River, Willamette and Columbia River, ...
; Seattle, Washington
Seattle ( ) is the List of municipalities in Washington, most populous city in the U.S. state of Washington (state), Washington and in the Pacific Northwest region of North America. With a population of 780,995 in 2024, it is the List of Unit ...
; and Vancouver, British Columbia
Vancouver is a major city in Western Canada, located in the Lower Mainland region of British Columbia. As the List of cities in British Columbia, most populous city in the province, the 2021 Canadian census recorded 662,248 people in the cit ...
. The submarine was back in Yokosuka for drydocking in July and August before beginning three months of continuous surveying in the mid-Pacific, broken only by brief fuelling and upkeep stops at Midway and Pearl Harbor. She departed Yokosuka on 25 November, for an extended cruise to the southern hemisphere, arrived in Australia in mid-December and took a three-week holiday in Newcastle
Newcastle usually refers to:
*Newcastle upon Tyne, a city and metropolitan borough in Tyne and Wear, England, United Kingdom
*Newcastle-under-Lyme, a town in Staffordshire, England, United Kingdom
*Newcastle, New South Wales, a metropolitan area ...
and Sydney
Sydney is the capital city of the States and territories of Australia, state of New South Wales and the List of cities in Australia by population, most populous city in Australia. Located on Australia's east coast, the metropolis surrounds Syd ...
. From the latter port, ''Archerfish'' travelled to Guam
Guam ( ; ) is an island that is an Territories of the United States, organized, unincorporated territory of the United States in the Micronesia subregion of the western Pacific Ocean. Guam's capital is Hagåtña, Guam, Hagåtña, and the most ...
for a two-week upkeep in late January 1964 and finally reached Pearl Harbor on 5 March.
Departing Pearl Harbor on 30 March, the ship continued "Sea Scan" operations in the eastern Pacific. She visited San Francisco in April and Vancouver, in May before returning to Pearl Harbor on 25 May, ending the third phase of "Sea Scan".
''Archerfish'' began an extended fourth and final phase of Operation "Sea Scan" when she left Pearl Harbor on 17 June, and headed for the eastern Pacific. She made port calls during July at Seattle and Olympia, Washington
Olympia is the capital city of the U.S. state of Washington. It had a population of 55,605 at the 2020 census, making it the state of Washington's 23rd-most populous city. Olympia is the county seat of Thurston County, and the central city ...
, and returned to Pearl Harbor on 19 August, for a three-week upkeep and drydocking before undertaking a cruise to the South Pacific. The submarine sailed on 9 September, for the Fiji Islands
Fiji, officially the Republic of Fiji, is an island country in Melanesia, part of Oceania in the South Pacific Ocean. It lies about north-northeast of New Zealand. Fiji consists of an archipelago of more than 330 islands—of which about ...
. After briefly touching Suva
Suva (, ) is the Capital city, capital and the most populous city of Fiji. It is the home of the country's largest metropolitan area and serves as its major port. The city is located on the southeast coast of the island of Viti Levu, in Rew ...
, she headed for Auckland
Auckland ( ; ) is a large metropolitan city in the North Island of New Zealand. It has an urban population of about It is located in the greater Auckland Region, the area governed by Auckland Council, which includes outlying rural areas and ...
, New Zealand, for an 11-day visit. Her next stop was Wellington
Wellington is the capital city of New Zealand. It is located at the south-western tip of the North Island, between Cook Strait and the Remutaka Range. Wellington is the third-largest city in New Zealand (second largest in the North Island ...
, New Zealand, but she left New Zealand on 19 October, and arrived in Yokosuka on 6 November. She got underway again on 27 November, to continue survey operations in the Caroline Islands
The Caroline Islands (or the Carolines) are a widely scattered archipelago of tiny islands in the western Pacific Ocean, to the north of New Guinea. Politically, they are divided between the Federated States of Micronesia (FSM) in the cen ...
area. After spending New Year's Eve
In the Gregorian calendar, New Year's Eve refers to the evening, or commonly the entire day, of the last day of the year, 31 December, also known as Old Year's Day. In many countries, New Year's Eve is celebrated with dancing, eating, drinkin ...
in Guam
Guam ( ; ) is an island that is an Territories of the United States, organized, unincorporated territory of the United States in the Micronesia subregion of the western Pacific Ocean. Guam's capital is Hagåtña, Guam, Hagåtña, and the most ...
, the ship sailed for Subic Bay
Subic Bay is a bay on the west coast of the island of Luzon in the Philippines, about northwest of Manila Bay. An extension of the South China Sea, its shores were formerly the site of a major United States Navy facility, U.S. Naval Base Subi ...
, Philippines, where she closed the year in upkeep.
1965–1968
During the remaining three and a half years of her Navy career ''Archerfish'' carried out various research assignments in the eastern Pacific. In early 1968, ''Archerfish'' was declared unfit for further naval service and was struck from theNaval Vessel Register
The ''Naval Vessel Register'' (NVR) is the official inventory of ships and service craft in custody of or titled by the United States Navy. It contains information on ships and service craft that make up the official inventory of the Navy from t ...
on 1 May 1968. She was towed to a target position off San Diego and sunk by a torpedo fired from the submarine on 17 October 1968.
Awards
*battle star
A service star is a miniature bronze or silver five-pointed star in diameter that is authorized to be worn by members of the eight uniformed services of the United States on medals and ribbons to denote an additional award or service period. T ...
s for World War II
World War II or the Second World War (1 September 1939 – 2 September 1945) was a World war, global conflict between two coalitions: the Allies of World War II, Allies and the Axis powers. World War II by country, Nearly all of the wo ...
service
* Navy Occupation Service Medal
The Navy Occupation Service Medal was a military award of the United States Navy which was "Awarded to commemorate the services of Navy, Marine Corps and Coast Guard personnel in the occupation of certain territories of the enemies of the United St ...
with "ASIA" clasp
References
* *External links
*Official website: USS ''Archerfish''
{{DEFAULTSORT:Archerfish (Ss-311) 1943 ships Balao-class submarines Cold War submarines of the United States Ships built in Kittery, Maine Ships sunk as targets Maritime incidents in 1968 Shipwrecks in the Pacific Ocean Shipwrecks of the California coast World War II submarines of the United States