Turing Statue Surrey on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Alan Mathison Turing (; 23 June 1912 – 7 June 1954) was an English
 Turing's parents enrolled him at St Michael's, a primary school at 20 Charles Road,
Turing's parents enrolled him at St Michael's, a primary school at 20 Charles Road,
 Although
Although
 On 4 September 1939, the day after the UK declared war on Germany, Turing reported to Bletchley Park, the wartime station of GC&CS.Copeland, 2006 p. 378. Like all others who came to Bletchley, he was required to sign the
On 4 September 1939, the day after the UK declared war on Germany, Turing reported to Bletchley Park, the wartime station of GC&CS.Copeland, 2006 p. 378. Like all others who came to Bletchley, he was required to sign the
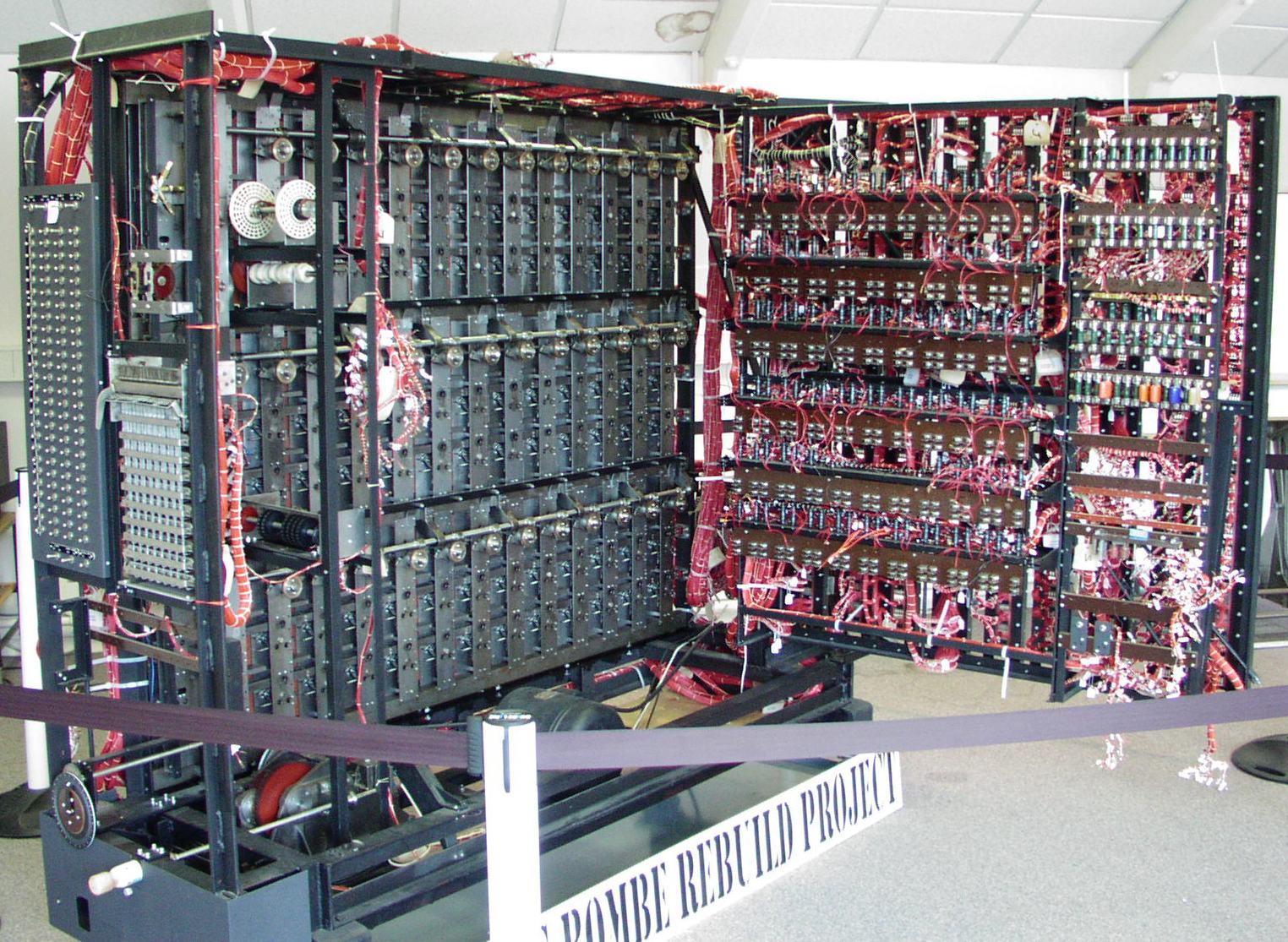 The bombe searched for possible correct settings used for an Enigma message (i.e., rotor order, rotor settings and plugboard settings) using a suitable '' crib'': a fragment of probable
The bombe searched for possible correct settings used for an Enigma message (i.e., rotor order, rotor settings and plugboard settings) using a suitable '' crib'': a fragment of probable
 Turing decided to tackle the particularly difficult problem of cracking the German naval use of Enigma "because no one else was doing anything about it and I could have it to myself". In December 1939, Turing solved the essential part of the naval
Turing decided to tackle the particularly difficult problem of cracking the German naval use of Enigma "because no one else was doing anything about it and I could have it to myself". In December 1939, Turing solved the essential part of the naval
 Between 1945 and 1947, Turing lived in Hampton, London, while he worked on the design of the
Between 1945 and 1947, Turing lived in Hampton, London, while he worked on the design of the
 On 8 June 1954, at his house at 43 Adlington Road,
On 8 June 1954, at his house at 43 Adlington Road,  It has also been suggested that Turing's belief in
It has also been suggested that Turing's belief in
Oral history interview with Nicholas C. Metropolis
Charles Babbage Institute, University of Minnesota. Metropolis was the first director of computing services at Los Alamos National Laboratory; topics include the relationship between Turing and
How Alan Turing Cracked The Enigma Code
Imperial War Museums
Alan Turing Year
CiE 2012: Turing Centenary Conference
Science in the Making
Alan Turing's papers in the Royal Society's archives
Alan Turing
site maintained by
short biography
AlanTuring.net – Turing Archive for the History of Computing
by
The Turing Digital Archive
nbsp;– contains scans of some unpublished documents and material from the King's College, Cambridge archive
Alan Turing Papers
– University of Manchester Library, Manchester *
Sherborne School Archives
– holds papers relating to Turing's time at Sherborne School
Alan Turing and the ‘Nature of Spirit’
(Old Shirburnian Society)
Alan Turing OBE, PhD, FRS (1912-1954)
(Old Shirburnian Society)
Alan Turing plaques
recorded on openplaques.org
Alan Turing
archive on New Scientist {{DEFAULTSORT:Turing, Alan Alan Turing, 1912 births 1954 deaths 1954 suicides 20th-century atheists 20th-century English LGBTQ people 20th-century English mathematicians 20th-century English philosophers Academics of the University of Manchester Institute of Science and Technology Academics of the University of Manchester Alumni of King's College, Cambridge Bayesian statisticians Bletchley Park people British anti-fascists British artificial intelligence researchers British cryptographers British people of World War II Castrated people Computability theorists Computer chess people Computer designers English atheists English computer scientists English gay sportsmen English inventors English LGBTQ scientists English logicians English male long-distance runners British male long-distance runners English people of Irish descent English people of Scottish descent Enigma machine Fellows of King's College, Cambridge Fellows of the Royal Society Foreign Office personnel of World War II Former Protestants Gay academics Gay scientists GCHQ people History of computing in the United Kingdom LGBTQ mathematicians LGBTQ philosophers LGBTQ track and field athletes LGBTQ people who died by suicide Officers of the Order of the British Empire People convicted for homosexuality in the United Kingdom People educated at Sherborne School People from Maida Vale People from Wilmslow People who have received posthumous pardons Princeton University alumni Recipients of British royal pardons Scientists of the National Physical Laboratory (United Kingdom) Suicides by cyanide poisoning Suicides in England Theoretical biologists British theoretical computer scientists
mathematician
A mathematician is someone who uses an extensive knowledge of mathematics in their work, typically to solve mathematical problems. Mathematicians are concerned with numbers, data, quantity, mathematical structure, structure, space, Mathematica ...
, computer scientist
A computer scientist is a scientist who specializes in the academic study of computer science.
Computer scientists typically work on the theoretical side of computation. Although computer scientists can also focus their work and research on ...
, logic
Logic is the study of correct reasoning. It includes both formal and informal logic. Formal logic is the study of deductively valid inferences or logical truths. It examines how conclusions follow from premises based on the structure o ...
ian, cryptanalyst
Cryptanalysis (from the Greek ''kryptós'', "hidden", and ''analýein'', "to analyze") refers to the process of analyzing information systems in order to understand hidden aspects of the systems. Cryptanalysis is used to breach cryptographic se ...
, philosopher
Philosophy ('love of wisdom' in Ancient Greek) is a systematic study of general and fundamental questions concerning topics like existence, reason, knowledge, Value (ethics and social sciences), value, mind, and language. It is a rational an ...
and theoretical biologist. He was highly influential in the development of theoretical computer science
Theoretical computer science is a subfield of computer science and mathematics that focuses on the Abstraction, abstract and mathematical foundations of computation.
It is difficult to circumscribe the theoretical areas precisely. The Associati ...
, providing a formalisation of the concepts of algorithm
In mathematics and computer science, an algorithm () is a finite sequence of Rigour#Mathematics, mathematically rigorous instructions, typically used to solve a class of specific Computational problem, problems or to perform a computation. Algo ...
and computation
A computation is any type of arithmetic or non-arithmetic calculation that is well-defined. Common examples of computation are mathematical equation solving and the execution of computer algorithms.
Mechanical or electronic devices (or, hist ...
with the Turing machine
A Turing machine is a mathematical model of computation describing an abstract machine that manipulates symbols on a strip of tape according to a table of rules. Despite the model's simplicity, it is capable of implementing any computer algori ...
, which can be considered a model of a general-purpose computer
A computer is a machine that can be Computer programming, programmed to automatically Execution (computing), carry out sequences of arithmetic or logical operations (''computation''). Modern digital electronic computers can perform generic set ...
. Turing is widely considered to be the father of theoretical computer science.
Born in London, Turing was raised in southern England
Southern England, also known as the South of England or the South, is a sub-national part of England. Officially, it is made up of the southern, south-western and part of the eastern parts of England, consisting of the statistical regions of ...
. He graduated from King's College, Cambridge
King's College, formally The King's College of Our Lady and Saint Nicholas in Cambridge, is a List of colleges of the University of Cambridge, constituent college of the University of Cambridge. The college lies beside the River Cam and faces ...
, and in 1938, earned a doctorate degree from Princeton University
Princeton University is a private university, private Ivy League research university in Princeton, New Jersey, United States. Founded in 1746 in Elizabeth, New Jersey, Elizabeth as the College of New Jersey, Princeton is the List of Colonial ...
. During World War II
World War II or the Second World War (1 September 1939 – 2 September 1945) was a World war, global conflict between two coalitions: the Allies of World War II, Allies and the Axis powers. World War II by country, Nearly all of the wo ...
, Turing worked for the Government Code and Cypher School
The Government Code and Cypher School (GC&CS) was a British signals intelligence agency set up in 1919. During the First World War, the British Army and Royal Navy had separate signals intelligence agencies, MI1b and NID25 (initially known as R ...
at Bletchley Park
Bletchley Park is an English country house and Bletchley Park estate, estate in Bletchley, Milton Keynes (Buckinghamshire), that became the principal centre of Allies of World War II, Allied World War II cryptography, code-breaking during the S ...
, Britain's codebreaking
Cryptanalysis (from the Greek ''kryptós'', "hidden", and ''analýein'', "to analyze") refers to the process of analyzing information systems in order to understand hidden aspects of the systems. Cryptanalysis is used to breach cryptographic secu ...
centre that produced Ultra
Ultra may refer to:
Science and technology
* Ultra (cryptography), the codename for cryptographic intelligence obtained from signal traffic in World War II
* Adobe Ultra, a vector-keying application
* Sun Ultra series, a brand of computer work ...
intelligence. He led Hut 8, the section responsible for German naval cryptanalysis. Turing devised techniques for speeding the breaking of German cipher
In cryptography, a cipher (or cypher) is an algorithm for performing encryption or decryption—a series of well-defined steps that can be followed as a procedure. An alternative, less common term is ''encipherment''. To encipher or encode i ...
s, including improvements to the pre-war Polish bomba method, an electromechanical
Electromechanics combine processes and procedures drawn from electrical engineering and mechanical engineering. Electromechanics focus on the interaction of electrical and mechanical systems as a whole and how the two systems interact with each ...
machine that could find settings for the Enigma machine
The Enigma machine is a cipher device developed and used in the early- to mid-20th century to protect commercial, diplomatic, and military communication. It was employed extensively by Nazi Germany during World War II, in all branches of the W ...
. He played a crucial role in cracking intercepted messages that enabled the Allies
An alliance is a relationship among people, groups, or states that have joined together for mutual benefit or to achieve some common purpose, whether or not an explicit agreement has been worked out among them. Members of an alliance are calle ...
to defeat the Axis powers
The Axis powers, originally called the Rome–Berlin Axis and also Rome–Berlin–Tokyo Axis, was the military coalition which initiated World War II and fought against the Allies of World War II, Allies. Its principal members were Nazi Ge ...
in the Battle of the Atlantic
The Battle of the Atlantic, the longest continuous military campaign in World War II, ran from 1939 to the defeat of Nazi Germany in 1945, covering a major part of the naval history of World War II. At its core was the Allies of World War II, ...
and other engagements.
After the war, Turing worked at the National Physical Laboratory, where he designed the Automatic Computing Engine
The Automatic Computing Engine (ACE) was a British early Electronic storage, electronic Serial computer, serial stored-program computer design by Alan Turing. Turing completed the ambitious design in late 1945, having had experience in the yea ...
, one of the first designs for a stored-program computer. In 1948, Turing joined Max Newman
Maxwell Herman Alexander Newman, FRS (7 February 1897 – 22 February 1984), generally known as Max Newman, was a British mathematician and codebreaker. His work in World War II led to the construction of Colossus, the world's first operatio ...
's Computing Machine Laboratory at the University of Manchester
The University of Manchester is a public university, public research university in Manchester, England. The main campus is south of Manchester city centre, Manchester City Centre on Wilmslow Road, Oxford Road. The University of Manchester is c ...
, where he contributed to the development of early Manchester computers
The Manchester computers were an innovative series of Von Neumann architecture, stored-program Computer, electronic computers developed during the 30-year period between 1947 and 1977 by a small team at the Victoria University of Manchester, Uni ...
and became interested in mathematical biology
Mathematical and theoretical biology, or biomathematics, is a branch of biology which employs theoretical analysis, mathematical models and abstractions of living organisms to investigate the principles that govern the structure, development ...
. Turing wrote on the chemical basis of morphogenesis
Morphogenesis (from the Greek ''morphê'' shape and ''genesis'' creation, literally "the generation of form") is the biological process that causes a cell, tissue or organism to develop its shape. It is one of three fundamental aspects of deve ...
and predicted oscillating chemical reactions such as the Belousov–Zhabotinsky reaction
A Belousov–Zhabotinsky reaction, or BZ reaction, is one of a class of reactions that serve as a classical example of non-equilibrium thermodynamics, resulting in the establishment of a nonlinear chemical oscillator. The only common element in ...
, first observed in the 1960s. Despite these accomplishments, he was never fully recognised during his lifetime because much of his work was covered by the Official Secrets Act
An Official Secrets Act (OSA) is legislation that provides for the protection of Classified information, state secrets and official information, mainly related to national security. However, in its unrevised form (based on the UK Official Secret ...
.
In 1952, Turing was prosecuted for homosexual acts. He accepted hormone treatment, a procedure commonly referred to as chemical castration
Chemical castration is castration via anaphrodisiac drugs, whether to reduce libido and sexual activity, management of cancer, to treat cancer, or otherwise. Unlike orchiectomy, surgical castration, where the gonads are removed through an incision ...
, as an alternative to prison. Turing died on 7 June 1954, aged 41, from cyanide poisoning
Cyanide poisoning is poisoning that results from exposure to any of a number of forms of cyanide. Early symptoms include headache, dizziness, fast heart rate, shortness of breath, and vomiting. This phase may then be followed by seizures, slo ...
. An inquest determined his death as suicide, but the evidence is also consistent with accidental poisoning.
Following a campaign in 2009, British prime minister Gordon Brown
James Gordon Brown (born 20 February 1951) is a British politician who served as Prime Minister of the United Kingdom and Leader of the Labour Party (UK), Leader of the Labour Party from 2007 to 2010. Previously, he was Chancellor of the Ex ...
made an official public apology for "the appalling way uringwas treated". Queen Elizabeth II
Elizabeth II (Elizabeth Alexandra Mary; 21 April 19268 September 2022) was Queen of the United Kingdom and other Commonwealth realms from 6 February 1952 until Death and state funeral of Elizabeth II, her death in 2022. ...
granted a pardon
A pardon is a government decision to allow a person to be relieved of some or all of the legal consequences resulting from a criminal conviction. A pardon may be granted before or after conviction for the crime, depending on the laws of the j ...
in 2013. The term "Alan Turing law
"Alan Turing law" is an informal term for the portion of the Policing and Crime Act 2017 which serves in UK law to pardon men who were cautioned or convicted under obsolete laws criminalising homosexual acts. The provision is named after Ala ...
" is used informally to refer to a 2017 law in the UK that retroactively pardoned men cautioned or convicted under historical legislation that outlawed homosexual acts.
Turing left an extensive legacy in mathematics and computing which has become widely recognised with statues and many things named after him, including an annual award for computing innovation. His portrait appears on the Bank of England £50 note
The Bank of England £50 note is a sterling banknote circulated in the United Kingdom. It is the highest denomination of banknote currently issued for public circulation by the Bank of England. The current note, the second of this denomination ...
, first released on 23 June 2021 to coincide with his birthday. The audience vote in a 2019 BBC series named Turing the greatest person of the 20th century.
Early life and education
Family
Turing was born inMaida Vale
Maida Vale ( ) is an affluent residential district in North West London, England, north of Paddington, southwest of St John's Wood and south of Kilburn, on Edgware Road. It is part of the City of Westminster and is northwest of Charing C ...
, London, while his father, Julius Mathison Turing, was on leave from his position with the Indian Civil Service
The Indian Civil Service (ICS), officially known as the Imperial Civil Service, was the higher civil service of the British Empire in India during British Raj, British rule in the period between 1858 and 1947.
Its members ruled over more than 3 ...
(ICS) of the British Raj government at Chatrapur, then in the Madras Presidency
The Madras Presidency or Madras Province, officially called the Presidency of Fort St. George until 1937, was an administrative subdivision (province) of British India and later the Dominion of India. At its greatest extent, the presidency i ...
and presently in Odisha
Odisha (), formerly Orissa (List of renamed places in India, the official name until 2011), is a States and union territories of India, state located in East India, Eastern India. It is the List of states and union territories of India by ar ...
state, in India
India, officially the Republic of India, is a country in South Asia. It is the List of countries and dependencies by area, seventh-largest country by area; the List of countries by population (United Nations), most populous country since ...
. Turing's father was the son of a clergyman, the Rev. John Robert Turing, from a Scottish family of merchants that had been based in the Netherlands and included a baronet
A baronet ( or ; abbreviated Bart or Bt) or the female equivalent, a baronetess (, , or ; abbreviation Btss), is the holder of a baronetcy, a hereditary title awarded by the British Crown. The title of baronet is mentioned as early as the 14th ...
. Turing's mother, Julius's wife, was Ethel Sara Turing (), daughter of Edward Waller Stoney, chief engineer of the Madras Railways. The Stoneys were a Protestant
Protestantism is a branch of Christianity that emphasizes Justification (theology), justification of sinners Sola fide, through faith alone, the teaching that Salvation in Christianity, salvation comes by unmerited Grace in Christianity, divin ...
Anglo-Irish
Anglo-Irish people () denotes an ethnic, social and religious grouping who are mostly the descendants and successors of the English Protestant Ascendancy in Ireland. They mostly belong to the Anglican Church of Ireland, which was the State rel ...
gentry
Gentry (from Old French , from ) are "well-born, genteel and well-bred people" of high social class, especially in the past. ''Gentry'', in its widest connotation, refers to people of good social position connected to Landed property, landed es ...
family from both County Tipperary
County Tipperary () is a Counties of Ireland, county in Republic of Ireland, Ireland. It is in the Provinces of Ireland, province of Munster and the Southern Region, Ireland, Southern Region. The county is named after the town of Tipperary (tow ...
and County Longford
County Longford () is a Counties of Ireland, county in Republic of Ireland, Ireland. It is in the Provinces of Ireland, province of Leinster. It is named after the town of Longford. Longford County Council is the Local government in the Republic ...
, while Ethel herself had spent much of her childhood in County Clare
County Clare () is a Counties of Ireland, county in the Provinces of Ireland, province of Munster in the Southern Region, Ireland, Southern part of Republic of Ireland, Ireland, bordered on the west by the Atlantic Ocean. Clare County Council ...
. Julius and Ethel married on 1 October 1907 at the Church of Ireland St. Bartholomew's Church on Clyde Road in Ballsbridge
Ballsbridge () (from historic Ball's Bridge) is an affluent neighbourhood of the city of Dublin, the capital of Ireland. The area is largely situated north and west of a three-arch stone bridge across the River Dodder, on the south side of the ...
, Dublin
Dublin is the capital and largest city of Republic of Ireland, Ireland. Situated on Dublin Bay at the mouth of the River Liffey, it is in the Provinces of Ireland, province of Leinster, and is bordered on the south by the Dublin Mountains, pa ...
.
Julius's work with the ICS brought the family to British India, where his grandfather had been a general in the Bengal Army
The Bengal Army was the army of the Bengal Presidency, one of the three presidencies of British India within the British Empire.
The presidency armies, like the presidencies themselves, belonged to the East India Company (EIC) until the Gover ...
. However, both Julius and Ethel wanted their children to be brought up in Britain, so they moved to Maida Vale
Maida Vale ( ) is an affluent residential district in North West London, England, north of Paddington, southwest of St John's Wood and south of Kilburn, on Edgware Road. It is part of the City of Westminster and is northwest of Charing C ...
, London, where Alan Turing was born on 23 June 1912, as recorded by a blue plaque
A blue plaque is a permanent sign installed in a public place in the United Kingdom, and certain other countries and territories, to commemorate a link between that location and a famous person, event, or former building on the site, serving a ...
on the outside of the house of his birth, later the Colonnade Hotel. Turing had an elder brother, John Ferrier Turing, father of Dermot Turing, 12th Baronet of the Turing baronets. In 1922, he discovered ''Natural Wonders Every Child Should Know'' by Edwin Tenney Brewster. He credited it with opening his eyes to science.
Turing's father's civil service commission was still active during Turing's childhood years, and his parents travelled between Hastings
Hastings ( ) is a seaside town and Borough status in the United Kingdom, borough in East Sussex on the south coast of England,
east of Lewes and south east of London. The town gives its name to the Battle of Hastings, which took place to th ...
in the United Kingdom and India, leaving their two sons to stay with a retired Army
An army, ground force or land force is an armed force that fights primarily on land. In the broadest sense, it is the land-based military branch, service branch or armed service of a nation or country. It may also include aviation assets by ...
couple. At Hastings, Turing stayed at Baston Lodge, Upper Maze Hill, St Leonards-on-Sea
St Leonards-on-Sea (commonly known as St Leonards) is a town and seaside resort in the borough of Hastings in East Sussex, England. It has been part of the borough since the late 19th century and lies to the west of central Hastings. The origin ...
, now marked with a blue plaque. The plaque was unveiled on 23 June 2012, the centenary of Turing's birth.
Very early in life, Turing's parents purchased a house in Guildford
Guildford () is a town in west Surrey, England, around south-west of central London. As of the 2011 census, the town has a population of about 77,000 and is the seat of the wider Borough of Guildford, which had around inhabitants in . The nam ...
in 1927, and Turing lived there during school holidays. The location is also marked with a blue plaque.
School
 Turing's parents enrolled him at St Michael's, a primary school at 20 Charles Road,
Turing's parents enrolled him at St Michael's, a primary school at 20 Charles Road, St Leonards-on-Sea
St Leonards-on-Sea (commonly known as St Leonards) is a town and seaside resort in the borough of Hastings in East Sussex, England. It has been part of the borough since the late 19th century and lies to the west of central Hastings. The origin ...
, from the age of six to nine. The headmistress recognised his talent, noting that she "...had clever boys and hardworking boys, but Alan is a genius".
Between January 1922 and 1926, Turing was educated at Hazelhurst Preparatory School, an independent school in the village of Frant
Frant is a village and civil parish in the Wealden District of East Sussex, England, on the Kentish border about three miles (5 km) south of Royal Tunbridge Wells.
When the iron industry was at its height, much of the village was owned by ...
in Sussex (now East Sussex
East Sussex is a Ceremonial counties of England, ceremonial county in South East England. It is bordered by Kent to the north-east, West Sussex to the west, Surrey to the north-west, and the English Channel to the south. The largest settlement ...
). In 1926, at the age of 13, he went on to Sherborne School
Sherborne School is a full-boarding school for boys aged 13 to 18 located beside Sherborne Abbey in the Dorset town of Sherborne. The school has been in continuous operation on the same site for over 1,300 years. It was founded in 705 AD by Ald ...
, an independent boarding school in the market town of Sherborne
Sherborne is a market town and civil parishes in England, civil parish in north west Dorset, in South West England. It is sited on the River Yeo (South Somerset), River Yeo, on the edge of the Blackmore Vale, east of Yeovil. The parish include ...
in Dorset, where he boarded at Westcott House. The first day of term coincided with the 1926 General Strike, in Britain, but Turing was so determined to attend that he rode his bicycle unaccompanied from Southampton
Southampton is a port City status in the United Kingdom, city and unitary authority in Hampshire, England. It is located approximately southwest of London, west of Portsmouth, and southeast of Salisbury. Southampton had a population of 253, ...
to Sherborne, stopping overnight at an inn.
Turing's natural inclination towards mathematics and science did not earn him respect from some of the teachers at Sherborne, whose definition of education placed more emphasis on the classics
Classics, also classical studies or Ancient Greek and Roman studies, is the study of classical antiquity. In the Western world, ''classics'' traditionally refers to the study of Ancient Greek literature, Ancient Greek and Roman literature and ...
. His headmaster wrote to his parents: "I hope he will not fall between two stools. If he is to stay at public school, he must aim at becoming ''educated''. If he is to be solely a ''Scientific Specialist'', he is wasting his time at a public school". Despite this, Turing continued to show remarkable ability in the studies he loved, solving advanced problems in 1927 without having studied even elementary calculus
Calculus is the mathematics, mathematical study of continuous change, in the same way that geometry is the study of shape, and algebra is the study of generalizations of arithmetic operations.
Originally called infinitesimal calculus or "the ...
. In 1928, aged 16, Turing encountered Albert Einstein
Albert Einstein (14 March 187918 April 1955) was a German-born theoretical physicist who is best known for developing the theory of relativity. Einstein also made important contributions to quantum mechanics. His mass–energy equivalence f ...
's work; not only did he grasp it, but it is possible that he managed to deduce Einstein's questioning of Newton's laws of motion
Newton's laws of motion are three physical laws that describe the relationship between the motion of an object and the forces acting on it. These laws, which provide the basis for Newtonian mechanics, can be paraphrased as follows:
# A body re ...
from a text in which this was never made explicit.
Christopher Morcom
At Sherborne, Turing formed a significant friendship with fellow pupil Christopher Collan Morcom (13 July 1911 – 13 February 1930), who has been described as Turing's first love. Their relationship provided inspiration in Turing's future endeavours, but it was cut short by Morcom's death, in February 1930, from complications of bovine tuberculosis, contracted after drinking infected cow's milk some years previously. The event caused Turing great sorrow. He coped with his grief by working that much harder on the topics of science and mathematics that he had shared with Morcom. In a letter to Morcom's mother, Frances Isobel Morcom (née Swan), Turing wrote: Turing's relationship with Morcom's mother continued long after Morcom's death, with her sending gifts to Turing, and him sending letters, typically on Morcom's birthday. A day before the third anniversary of Morcom's death (13 February 1933), he wrote to Mrs. Morcom: Some have speculated that Morcom's death was the cause of Turing'satheism
Atheism, in the broadest sense, is an absence of belief in the Existence of God, existence of Deity, deities. Less broadly, atheism is a rejection of the belief that any deities exist. In an even narrower sense, atheism is specifically the ...
and materialism
Materialism is a form of monism, philosophical monism according to which matter is the fundamental Substance theory, substance in nature, and all things, including mind, mental states and consciousness, are results of material interactions. Acco ...
. Apparently, at this point in his life he still believed in such concepts as a spirit, independent of the body and surviving death. In a later letter, also written to Morcom's mother, Turing wrote:
University and work on computability
After graduating from Sherborne, Turing applied for several Cambridge colleges scholarships, includingTrinity
The Trinity (, from 'threefold') is the Christian doctrine concerning the nature of God, which defines one God existing in three, , consubstantial divine persons: God the Father, God the Son (Jesus Christ) and God the Holy Spirit, thr ...
and King's, eventually earning an £80 per annum scholarship (equivalent to about £4,300 as of 2023) to study at the latter. There, Turing studied the undergraduate course in Schedule B from February 1931 to November 1934 at King's College, Cambridge
King's College, formally The King's College of Our Lady and Saint Nicholas in Cambridge, is a List of colleges of the University of Cambridge, constituent college of the University of Cambridge. The college lies beside the River Cam and faces ...
, where he was awarded first-class honours in mathematics. His dissertation, ''On the Gaussian error function'', written during his senior year and delivered in November 1934 (with a deadline date of 6 December) proved a version of the central limit theorem
In probability theory, the central limit theorem (CLT) states that, under appropriate conditions, the Probability distribution, distribution of a normalized version of the sample mean converges to a Normal distribution#Standard normal distributi ...
. It was finally accepted on 16 March 1935. By spring of that same year, Turing started his master's course ( Part III)—which he completed in 1937—and, at the same time, he published his first paper, a one-page article called ''Equivalence of left and right almost periodicity'' (sent on 23 April), featured in the tenth volume of the ''Journal of the London Mathematical Society
The London Mathematical Society (LMS) is one of the United Kingdom's learned societies for mathematics (the others being the Royal Statistical Society (RSS), the Institute of Mathematics and its Applications (IMA), the Edinburgh Mathematical S ...
''. Later that year, Turing was elected a Fellow
A fellow is a title and form of address for distinguished, learned, or skilled individuals in academia, medicine, research, and industry. The exact meaning of the term differs in each field. In learned society, learned or professional society, p ...
of King's College on the strength of his dissertation where he served as a lecturer
Lecturer is an academic rank within many universities, though the meaning of the term varies somewhat from country to country. It generally denotes an academic expert who is hired to teach on a full- or part-time basis. They may also conduct re ...
. However, and, unknown to Turing, this version of the theorem he proved in his paper, had already been proven, in 1922, by Jarl Waldemar Lindeberg
Jarl Waldemar Lindeberg (4 August 1876, Helsinki – 24 December 1932, Helsinki) was a Finnish mathematician known for work on the central limit theorem.
Life and work
Lindeberg was son of a teacher at the Helsinki Polytechnical Institute and a ...
. Despite this, the committee found Turing's methods original and so regarded the work worthy of consideration for the fellowship. Abram Besicovitch's report for the committee went so far as to say that if Turing's work had been published before Lindeberg's, it would have been "an important event in the mathematical literature of that year".
Between the springs of 1935 and 1936, at the same time as Alonzo Church
Alonzo Church (June 14, 1903 – August 11, 1995) was an American computer scientist, mathematician, logician, and philosopher who made major contributions to mathematical logic and the foundations of theoretical computer science. He is bes ...
, Turing worked on the decidability of problems, starting from Gödel's incompleteness theorems
Gödel's incompleteness theorems are two theorems of mathematical logic that are concerned with the limits of in formal axiomatic theories. These results, published by Kurt Gödel in 1931, are important both in mathematical logic and in the phi ...
. In mid-April 1936, Turing sent Max Newman the first draft typescript of his investigations. That same month, Church published his ''An Unsolvable Problem of Elementary Number Theory'', with similar conclusions to Turing's then-yet unpublished work. Finally, on 28 May of that year, he finished and delivered his 36-page paper for publication called "On Computable Numbers, with an Application to the Entscheidungsproblem
Turing's proof is a proof by Alan Turing, first published in November 1936 with the title "On Computable Numbers, with an Application to the ". It was the second proof (after Church's theorem) of the negation of Hilbert's ; that is, the conjectu ...
". It was published in the ''Proceedings of the London Mathematical Society'' journal in two parts, the first on 30 November and the second on 23 December. In this paper, Turing reformulated Kurt Gödel
Kurt Friedrich Gödel ( ; ; April 28, 1906 – January 14, 1978) was a logician, mathematician, and philosopher. Considered along with Aristotle and Gottlob Frege to be one of the most significant logicians in history, Gödel profoundly ...
's 1931 results on the limits of proof and computation, replacing Gödel's universal arithmetic-based formal language with the formal and simple hypothetical devices that became known as Turing machine
A Turing machine is a mathematical model of computation describing an abstract machine that manipulates symbols on a strip of tape according to a table of rules. Despite the model's simplicity, it is capable of implementing any computer algori ...
s. The ''Entscheidungsproblem
In mathematics and computer science, the ; ) is a challenge posed by David Hilbert and Wilhelm Ackermann in 1928. It asks for an algorithm that considers an inputted statement and answers "yes" or "no" according to whether it is universally valid ...
'' (decision problem) was originally posed by German mathematician David Hilbert
David Hilbert (; ; 23 January 1862 – 14 February 1943) was a German mathematician and philosopher of mathematics and one of the most influential mathematicians of his time.
Hilbert discovered and developed a broad range of fundamental idea ...
in 1928. Turing proved that his "universal computing machine" would be capable of performing any conceivable mathematical computation if it were representable as an algorithm
In mathematics and computer science, an algorithm () is a finite sequence of Rigour#Mathematics, mathematically rigorous instructions, typically used to solve a class of specific Computational problem, problems or to perform a computation. Algo ...
. He went on to prove that there was no solution to the ''decision problem'' by first showing that the halting problem
In computability theory (computer science), computability theory, the halting problem is the problem of determining, from a description of an arbitrary computer program and an input, whether the program will finish running, or continue to run for ...
for Turing machines is undecidable: it is not possible to decide algorithmically whether a Turing machine will ever halt. This paper has been called "easily the most influential math paper in history".
 Although
Although Turing's proof
Turing's proof is a proof by Alan Turing, first published in November 1936 with the title "On Computable Numbers, with an Application to the ". It was the second proof (after Church's theorem) of the negation of Hilbert's ; that is, the conjectu ...
was published shortly after Church's equivalent proof using his lambda calculus
In mathematical logic, the lambda calculus (also written as ''λ''-calculus) is a formal system for expressing computability, computation based on function Abstraction (computer science), abstraction and function application, application using var ...
, Turing's approach is considerably more accessible and intuitive than Church's. It also included a notion of a 'Universal Machine' (now known as a universal Turing machine
In computer science, a universal Turing machine (UTM) is a Turing machine capable of computing any computable sequence, as described by Alan Turing in his seminal paper "On Computable Numbers, with an Application to the Entscheidungsproblem". Co ...
), with the idea that such a machine could perform the tasks of any other computation machine (as indeed could Church's lambda calculus). According to the Church–Turing thesis
In Computability theory (computation), computability theory, the Church–Turing thesis (also known as computability thesis, the Turing–Church thesis, the Church–Turing conjecture, Church's thesis, Church's conjecture, and Turing's thesis) ...
, Turing machines and the lambda calculus are capable of computing anything that is computable. John von Neumann
John von Neumann ( ; ; December 28, 1903 – February 8, 1957) was a Hungarian and American mathematician, physicist, computer scientist and engineer. Von Neumann had perhaps the widest coverage of any mathematician of his time, in ...
acknowledged that the central concept of the modern computer was due to Turing's paper. To this day, Turing machines are a central object of study in theory of computation
In theoretical computer science and mathematics, the theory of computation is the branch that deals with what problems can be solved on a model of computation, using an algorithm, how efficiently they can be solved or to what degree (e.g., app ...
.
From September 1936 to July 1938, Turing spent most of his time studying under Church at Princeton University
Princeton University is a private university, private Ivy League research university in Princeton, New Jersey, United States. Founded in 1746 in Elizabeth, New Jersey, Elizabeth as the College of New Jersey, Princeton is the List of Colonial ...
, in the second year as a Jane Eliza Procter Visiting Fellow. In addition to his purely mathematical work, he studied cryptology and also built three of four stages of an electro-mechanical binary multiplier
A binary multiplier is an electronic circuit used in digital electronics, such as a computer, to multiply two binary numbers.
A variety of computer arithmetic techniques can be used to implement a digital multiplier. Most techniques involve com ...
. In June 1938, he obtained his PhD from the Department of Mathematics at Princeton; his dissertation, '' Systems of Logic Based on Ordinals'', introduced the concept of ordinal logic and the notion of relative computing, in which Turing machines are augmented with so-called oracles, allowing the study of problems that cannot be solved by Turing machines. John von Neumann wanted to hire him as his postdoctoral assistant, but he went back to the United Kingdom.
Career and research
When Turing returned to Cambridge, he attended lectures given in 1939 byLudwig Wittgenstein
Ludwig Josef Johann Wittgenstein ( ; ; 26 April 1889 – 29 April 1951) was an Austrian philosopher who worked primarily in logic, the philosophy of mathematics, the philosophy of mind, and the philosophy of language.
From 1929 to 1947, Witt ...
about the foundations of mathematics
Foundations of mathematics are the mathematical logic, logical and mathematics, mathematical framework that allows the development of mathematics without generating consistency, self-contradictory theories, and to have reliable concepts of theo ...
. The lectures have been reconstructed verbatim, including interjections from Turing and other students, from students' notes. Turing and Wittgenstein argued and disagreed, with Turing defending formalism and Wittgenstein propounding his view that mathematics does not discover any absolute truths, but rather invents them.
Cryptanalysis
During the Second World War, Turing was a leading participant in the breaking of German ciphers atBletchley Park
Bletchley Park is an English country house and Bletchley Park estate, estate in Bletchley, Milton Keynes (Buckinghamshire), that became the principal centre of Allies of World War II, Allied World War II cryptography, code-breaking during the S ...
. The historian and wartime codebreaker Asa Briggs
Asa Briggs, Baron Briggs (7 May 1921 – 15 March 2016) was an English historian. He was a leading specialist on the Victorian era, and the foremost historian of broadcasting in Britain. Briggs achieved international recognition during his lon ...
has said, "You needed exceptional talent, you needed genius at Bletchley and Turing's was that genius."
From September 1938, Turing worked part-time with the Government Code and Cypher School
The Government Code and Cypher School (GC&CS) was a British signals intelligence agency set up in 1919. During the First World War, the British Army and Royal Navy had separate signals intelligence agencies, MI1b and NID25 (initially known as R ...
(GC&CS), the British codebreaking organisation. He concentrated on cryptanalysis of the Enigma cipher machine used by Nazi Germany
Nazi Germany, officially known as the German Reich and later the Greater German Reich, was the German Reich, German state between 1933 and 1945, when Adolf Hitler and the Nazi Party controlled the country, transforming it into a Totalit ...
, together with Dilly Knox
Alfred Dillwyn "Dilly" Knox, CMG (23 July 1884 – 27 February 1943) was an English classics scholar and papyrologist at King's College, Cambridge and a codebreaker. As a member of the Room 40 codebreaking unit he helped decrypt the Zimme ...
, a senior GC&CS codebreaker. Soon after the July 1939 meeting near Warsaw
Warsaw, officially the Capital City of Warsaw, is the capital and List of cities and towns in Poland, largest city of Poland. The metropolis stands on the Vistula, River Vistula in east-central Poland. Its population is officially estimated at ...
at which the Polish Cipher Bureau gave the British and French details of the wiring of Enigma machine's rotors and their method of decrypting Enigma machine
The Enigma machine is a cipher device developed and used in the early- to mid-20th century to protect commercial, diplomatic, and military communication. It was employed extensively by Nazi Germany during World War II, in all branches of the W ...
's messages, Turing and Knox developed a broader solution. The Polish method relied on an insecure indicator
Indicator may refer to:
Biology
* Environmental indicator of environmental health (pressures, conditions and responses)
* Ecological indicator of ecosystem health (ecological processes)
* Health indicator, which is used to describe the health o ...
procedure that the Germans were likely to change, which they in fact did in May 1940. Turing's approach was more general, using crib-based decryption for which he produced the functional specification of the bombe
The bombe () was an Electromechanics, electro-mechanical device used by British cryptologists to help decipher German Enigma machine, Enigma-machine-encrypted secret messages during World War II. The United States Navy, US Navy and United Sta ...
(an improvement on the Polish Bomba).
 On 4 September 1939, the day after the UK declared war on Germany, Turing reported to Bletchley Park, the wartime station of GC&CS.Copeland, 2006 p. 378. Like all others who came to Bletchley, he was required to sign the
On 4 September 1939, the day after the UK declared war on Germany, Turing reported to Bletchley Park, the wartime station of GC&CS.Copeland, 2006 p. 378. Like all others who came to Bletchley, he was required to sign the Official Secrets Act
An Official Secrets Act (OSA) is legislation that provides for the protection of Classified information, state secrets and official information, mainly related to national security. However, in its unrevised form (based on the UK Official Secret ...
, in which he agreed not to disclose anything about his work at Bletchley, with severe legal penalties for violating the Act.
Specifying the bombe was the first of five major cryptanalytical advances that Turing made during the war. The others were: deducing the indicator procedure used by the German navy; developing a statistical procedure dubbed ''Banburismus
Banburismus was a Cryptanalysis, cryptanalytic process developed by Alan Turing at Bletchley Park in United Kingdom, Britain during the Second World War. It was used by Bletchley Park's Hut 8 to help break German ''Kriegsmarine'' (naval) message ...
'' for making much more efficient use of the bombes; developing a procedure dubbed ''Turingery
Turingery in ''Testery Methods 1942–1944'' or Turing's method (playfully dubbed Turingismus by Peter Ericsson, Peter Hilton and Donald Michie) was a manual codebreaking method devised in July 1942 by the mathematician and cryptanalyst Alan Turi ...
'' for working out the cam settings of the wheels of the Lorenz SZ 40/42 (''Tunny'') cipher machine and, towards the end of the war, the development of a portable secure voice
Secure voice (alternatively secure speech or ciphony) is a term in cryptography for the encryption of voice communication over a range of communication types such as radio, telephone or Voice over IP, IP.
History
The implementation of voice en ...
scrambler at Hanslope Park that was codenamed Delilah.
By using statistical techniques to optimise the trial of different possibilities in the code breaking process, Turing made an innovative contribution to the subject. He wrote two papers discussing mathematical approaches, titled ''The Applications of Probability to Cryptography'' and ''Paper on Statistics of Repetitions'', which were of such value to GC&CS and its successor GCHQ
Government Communications Headquarters (GCHQ) is an intelligence and security organisation responsible for providing signals intelligence (SIGINT) and information assurance (IA) to the government and armed forces of the United Kingdom. Primar ...
that they were not released to the UK National Archives
The National Archives (TNA; ) is a non-ministerial department of the Government of the United Kingdom. Its parent department is the Department for Culture, Media and Sport of the United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Ireland. It is the ...
until April 2012, shortly before the centenary of his birth. A GCHQ mathematician, "who identified himself only as Richard," said at the time that the fact that the contents had been restricted under the Official Secrets Act for some 70 years demonstrated their importance, and their relevance to post-war cryptanalysis:
Turing had a reputation for eccentricity at Bletchley Park. He was known to his colleagues as "Prof" and his treatise on Enigma was known as the "Prof's Book". According to historian Ronald Lewin, Jack Good, a cryptanalyst who worked with Turing, said of his colleague:
Peter Hilton
Peter John Hilton (7 April 1923Peter Hilton, "On all Sorts of Automorphisms", ''The American Mathematical Monthly'', 92(9), November 1985, p. 6506 November 2010) was a British mathematician, noted for his contributions to homotopy theory and f ...
recounted his experience working with Turing in Hut 8 in his "Reminiscences of Bletchley Park" from ''A Century of Mathematics in America:''
Hilton echoed similar thoughts in the Nova PBS
The Public Broadcasting Service (PBS) is an American public broadcaster and non-commercial, free-to-air television network based in Arlington, Virginia. PBS is a publicly funded nonprofit organization and the most prominent provider of educat ...
documentary ''Decoding Nazi Secrets''.
While working at Bletchley, Turing, who was a talented long-distance runner
Long-distance running, or endurance running, is a form of continuous running over distances of at least . Physiologically, it is largely Aerobic exercise, aerobic in nature and requires stamina as well as mental strength.
Within endurance ru ...
, occasionally ran the to London when he was needed for meetings, and he was capable of world-class marathon standards. Turing tried out for the 1948 British Olympic team, but he was hampered by an injury. His tryout time for the marathon was only 11 minutes slower than British silver medallist Thomas Richards' Olympic race time of 2 hours 35 minutes. He was Walton Athletic Club's best runner, a fact discovered when he passed the group while running alone. When asked why he ran so hard in training he replied:
Due to the problems of counterfactual history
Counterfactual history (also virtual history) is a form of historiography that attempts to answer the ''wikt:what if, What if?'' questions that arise from counterfactuals, counterfactual conditions. Counterfactual history seeks by "conjecturing ...
, it is hard to estimate the precise effect Ultra intelligence had on the war. However, official war historian Harry Hinsley
Sir Francis Harry Hinsley, (26 November 1918 – 16 February 1998) was an English intelligence officer and historian. He worked at Bletchley Park during the Second World War and wrote widely on the history of international relations and Briti ...
estimated that this work shortened the war in Europe by more than two years but added the caveat that this did not account for the use of the atomic bomb and other eventualities. Transcript of a lecture given on Tuesday 19 October 1993 at Cambridge University
At the end of the war, a memo was sent to all those who had worked at Bletchley Park, reminding them that the code of silence dictated by the Official Secrets Act did not end with the war but would continue indefinitely. Thus, even though Turing was appointed an Officer of the Order of the British Empire
The Most Excellent Order of the British Empire is a British order of chivalry, rewarding valuable service in a wide range of useful activities. It comprises five classes of awards across both civil and military divisions, the most senior two o ...
(OBE) in 1946 by King George VI
George VI (Albert Frederick Arthur George; 14 December 1895 – 6 February 1952) was King of the United Kingdom and the Dominions of the British Commonwealth from 11 December 1936 until Death and state funeral of George VI, his death in 1952 ...
for his wartime services, his work remained secret for many years.
Bombe
Within weeks of arriving at Bletchley Park, Turing had specified an electromechanical machine called thebombe
The bombe () was an Electromechanics, electro-mechanical device used by British cryptologists to help decipher German Enigma machine, Enigma-machine-encrypted secret messages during World War II. The United States Navy, US Navy and United Sta ...
, which could break Enigma more effectively than the Polish '' bomba kryptologiczna'', from which its name was derived. The bombe, with an enhancement suggested by mathematician Gordon Welchman
William Gordon Welchman OBE (15 June 1906 – 8 October 1985) was an English mathematician. During World War II, he worked at Britain's secret decryption centre at Bletchley Park, where he was one of the most important contributors. In 1948, a ...
, became one of the primary tools, and the major automated one, used to attack Enigma-enciphered messages.
 The bombe searched for possible correct settings used for an Enigma message (i.e., rotor order, rotor settings and plugboard settings) using a suitable '' crib'': a fragment of probable
The bombe searched for possible correct settings used for an Enigma message (i.e., rotor order, rotor settings and plugboard settings) using a suitable '' crib'': a fragment of probable plaintext
In cryptography, plaintext usually means unencrypted information pending input into cryptographic algorithms, usually encryption algorithms. This usually refers to data that is transmitted or stored unencrypted.
Overview
With the advent of comp ...
. For each possible setting of the rotors (which had on the order of 1019 states, or 1022 states for the four-rotor U-boat variant), the bombe performed a chain of logical deductions based on the crib, implemented electromechanically.
The bombe detected when a contradiction had occurred and ruled out that setting, moving on to the next. Most of the possible settings would cause contradictions and be discarded, leaving only a few to be investigated in detail. A contradiction would occur when an enciphered letter would be turned back into the same plaintext letter, which was impossible with the Enigma. The first bombe was installed on 18 March 1940.
Action This Day
By late 1941, Turing and his fellow cryptanalystsGordon Welchman
William Gordon Welchman OBE (15 June 1906 – 8 October 1985) was an English mathematician. During World War II, he worked at Britain's secret decryption centre at Bletchley Park, where he was one of the most important contributors. In 1948, a ...
, Hugh Alexander and Stuart Milner-Barry were frustrated. Building on the work of the Poles, they had set up a good working system for decrypting Enigma signals, but their limited staff and bombes meant they could not translate all the signals. In the summer, they had considerable success, and shipping losses had fallen to under 100,000 tons a month; however, they badly needed more resources to keep abreast of German adjustments. They had tried to get more people and fund more bombes through the proper channels, but had failed.
On 28 October they wrote directly to Winston Churchill
Sir Winston Leonard Spencer Churchill (30 November 1874 – 24 January 1965) was a British statesman, military officer, and writer who was Prime Minister of the United Kingdom from 1940 to 1945 (Winston Churchill in the Second World War, ...
explaining their difficulties, with Turing as the first named. They emphasised how small their need was compared with the vast expenditure of men and money by the forces and compared with the level of assistance they could offer to the forces. As Andrew Hodges
Andrew Philip Hodges ( ; born 1949) is a British mathematician, author and emeritus senior research fellow at Wadham College, Oxford.
Education
Hodges was born in London in 1949 and educated at Birkbeck, University of London, where he was award ...
, biographer of Turing, later wrote, "This letter had an electric effect." Churchill wrote a memo to General Ismay, which read: "ACTION THIS DAY. Make sure they have all they want on extreme priority and report to me that this has been done." On 18 November, the chief of the secret service reported that every possible measure was being taken. The cryptographers at Bletchley Park did not know of the Prime Minister's response, but as Milner-Barry recalled, "All that we did notice was that almost from that day the rough ways began miraculously to be made smooth." More than two hundred bombes were in operation by the end of the war.
Hut 8 and the naval Enigma
 Turing decided to tackle the particularly difficult problem of cracking the German naval use of Enigma "because no one else was doing anything about it and I could have it to myself". In December 1939, Turing solved the essential part of the naval
Turing decided to tackle the particularly difficult problem of cracking the German naval use of Enigma "because no one else was doing anything about it and I could have it to myself". In December 1939, Turing solved the essential part of the naval indicator
Indicator may refer to:
Biology
* Environmental indicator of environmental health (pressures, conditions and responses)
* Ecological indicator of ecosystem health (ecological processes)
* Health indicator, which is used to describe the health o ...
system, which was more complex than the indicator systems used by the other services.
That same night, he also conceived of the idea of ''Banburismus
Banburismus was a Cryptanalysis, cryptanalytic process developed by Alan Turing at Bletchley Park in United Kingdom, Britain during the Second World War. It was used by Bletchley Park's Hut 8 to help break German ''Kriegsmarine'' (naval) message ...
'', a sequential statistical technique (what Abraham Wald
Abraham Wald (; ; , ; – ) was a Hungarian and American mathematician and statistician who contributed to decision theory, geometry and econometrics, and founded the field of sequential analysis. One of his well-known statistical works was ...
later called sequential analysis
In statistics, sequential analysis or sequential hypothesis testing is statistical analysis where the sample size is not fixed in advance. Instead data is evaluated as it is collected, and further sampling is stopped in accordance with a pre-defi ...
) to assist in breaking the naval Enigma, "though I was not sure that it would work in practice, and was not, in fact, sure until some days had actually broken". For this, he invented a measure of weight of evidence that he called the '' ban''. ''Banburismus'' could rule out certain sequences of the Enigma rotors, substantially reducing the time needed to test settings on the bombes. Later this sequential process of accumulating sufficient weight of evidence using decibans (one tenth of a ban) was used in cryptanalysis of the Lorenz cipher
Cryptanalysis of the Lorenz cipher was the process that enabled the British to read high-level German army messages during World War II. The British Government Code and Cypher School (GC&CS) at Bletchley Park decrypted many communications betwee ...
.
Turing travelled to the United States in November 1942 and worked with US Navy cryptanalysts on the naval Enigma and bombe construction in Washington. He also visited their Computing Machine Laboratory in Dayton, Ohio
Dayton () is a city in Montgomery County, Ohio, United States, and its county seat. It is the List of cities in Ohio, sixth-most populous city in Ohio, with a population of 137,644 at the 2020 United States census, 2020 census. The Dayton metro ...
.
Turing's reaction to the American bombe design was far from enthusiastic:
During this trip, he also assisted at Bell Labs
Nokia Bell Labs, commonly referred to as ''Bell Labs'', is an American industrial research and development company owned by Finnish technology company Nokia. With headquarters located in Murray Hill, New Jersey, Murray Hill, New Jersey, the compa ...
with the development of secure speech devices. He returned to Bletchley Park in March 1943. During his absence, Hugh Alexander had officially assumed the position of head of Hut 8, although Alexander had been ''de facto'' head for some time (Turing having little interest in the day-to-day running of the section). Turing became a general consultant for cryptanalysis at Bletchley Park.
Alexander wrote of Turing's contribution:
Turingery
In July 1942, Turing devised a technique termed ''Turingery
Turingery in ''Testery Methods 1942–1944'' or Turing's method (playfully dubbed Turingismus by Peter Ericsson, Peter Hilton and Donald Michie) was a manual codebreaking method devised in July 1942 by the mathematician and cryptanalyst Alan Turi ...
'' (or jokingly ''Turingismus'') for use against the Lorenz cipher
The Lorenz SZ40, SZ42a and SZ42b were German Rotor machine, rotor stream cipher machines used by the German Army (Wehrmacht), German Army during World War II. They were developed by C. Lorenz AG in Berlin. The model name ''SZ'' is derived from ' ...
messages produced by the Germans' new ''Geheimschreiber'' (secret writer) machine. This was a teleprinter
A teleprinter (teletypewriter, teletype or TTY) is an electromechanical device that can be used to send and receive typed messages through various communications channels, in both point-to-point (telecommunications), point-to-point and point- ...
rotor cipher attachment codenamed ''Tunny'' at Bletchley Park. Turingery was a method of ''wheel-breaking'', i.e., a procedure for working out the cam settings of Tunny's wheels. He also introduced the Tunny team to Tommy Flowers
Thomas Harold Flowers Order of the British Empire, MBE (22 December 1905 – 28 October 1998) was an English engineer with the British General Post Office. During World War II, Flowers designed and built Colossus computer, Colossus, the world's ...
who, under the guidance of Max Newman
Maxwell Herman Alexander Newman, FRS (7 February 1897 – 22 February 1984), generally known as Max Newman, was a British mathematician and codebreaker. His work in World War II led to the construction of Colossus, the world's first operatio ...
, went on to build the Colossus computer
Colossus was a set of computers developed by British cryptanalysis, codebreakers in the years 1943–1945 to help in the cryptanalysis of the Lorenz cipher. Colossus used vacuum tube, thermionic valves (vacuum tubes) to perform Boolean algebra ...
, the world's first programmable digital electronic computer, which replaced a simpler prior machine (the Heath Robinson
William Heath Robinson (31 May 1872 – 13 September 1944) was an English cartoonist, illustrator and artist who drew whimsically elaborate machines to achieve simple objectives.
The earliest citation in the ''Oxford English Dictionary'' f ...
), and whose superior speed allowed the statistical decryption techniques to be applied usefully to the messages. Some have mistakenly said that Turing was a key figure in the design of the Colossus computer. Turingery and the statistical approach of Banburismus undoubtedly fed into the thinking about cryptanalysis of the Lorenz cipher
Cryptanalysis of the Lorenz cipher was the process that enabled the British to read high-level German army messages during World War II. The British Government Code and Cypher School (GC&CS) at Bletchley Park decrypted many communications betwee ...
, but he was not directly involved in the Colossus development.
Delilah
Following his work atBell Labs
Nokia Bell Labs, commonly referred to as ''Bell Labs'', is an American industrial research and development company owned by Finnish technology company Nokia. With headquarters located in Murray Hill, New Jersey, Murray Hill, New Jersey, the compa ...
in the US, Turing pursued the idea of electronic enciphering of speech in the telephone system. In the latter part of the war, he moved to work for the Secret Service's Radio Security Service (later HMGCC) at Hanslope Park. At the park, he further developed his knowledge of electronics with the assistance of REME
The Corps of Royal Electrical and Mechanical Engineers (REME ) is the maintenance arm of the British Army
The British Army is the principal Army, land warfare force of the United Kingdom. the British Army comprises 73,847 regular full ...
officer Donald Bayley. Together they undertook the design and construction of a portable secure voice
Secure voice (alternatively secure speech or ciphony) is a term in cryptography for the encryption of voice communication over a range of communication types such as radio, telephone or Voice over IP, IP.
History
The implementation of voice en ...
communications machine codenamed ''Delilah
Delilah ( ; , meaning "delicate";Gesenius's ''Hebrew-Chaldee Lexicon'' ; ) is a woman mentioned in the sixteenth chapter of the Book of Judges in the Hebrew Bible. She is loved by Samson, a Nazirite who possesses great strength and serves as t ...
''. The machine was intended for different applications, but it lacked the capability for use with long-distance radio transmissions. In any case, Delilah was completed too late to be used during the war. Though the system worked fully, with Turing demonstrating it to officials by encrypting and decrypting a recording of a Winston Churchill
Sir Winston Leonard Spencer Churchill (30 November 1874 – 24 January 1965) was a British statesman, military officer, and writer who was Prime Minister of the United Kingdom from 1940 to 1945 (Winston Churchill in the Second World War, ...
speech, Delilah was not adopted for use. Turing also consulted with Bell Labs on the development of SIGSALY
SIGSALY (also known as the X System, Project X, Ciphony I, and the Green Hornet) was a secure voice, secure speech system used in World War II for the highest-level Allies of World War II, Allied communications. It pioneered a number of digital co ...
, a secure voice system that was used in the later years of the war.
Early computers and the Turing test
 Between 1945 and 1947, Turing lived in Hampton, London, while he worked on the design of the
Between 1945 and 1947, Turing lived in Hampton, London, while he worked on the design of the ACE
An ace is a playing card, die or domino with a single pip. In the standard French deck, an ace has a single suit symbol (a heart, diamond, spade, or a club) located in the middle of the card, sometimes large and decorated, especially in the ...
(Automatic Computing Engine) at the National Physical Laboratory (NPL). He presented a paper on 19 February 1946, which was the first detailed design of a stored-program computer
A stored-program computer is a computer that stores program instructions in electronically, electromagnetically, or optically accessible memory. This contrasts with systems that stored the program instructions with plugboards or similar mechani ...
. Von Neumann's incomplete ''First Draft of a Report on the EDVAC
The ''First Draft of a Report on the EDVAC'' (commonly shortened to ''First Draft'') is an incomplete 101-page document written by John von Neumann and distributed on June 30, 1945 by Herman Goldstine, security officer on the classified ENIAC pr ...
'' had predated Turing's paper, but it was much less detailed and, according to John R. Womersley
John Ronald Womersley (20 June 1907 – 7 March 1958) was a British mathematician and computer scientist who made important contributions to computer development, and hemodynamics. Nowadays he is principally remembered for his contribution to Hem ...
, Superintendent of the NPL Mathematics Division, it "contains a number of ideas which are Dr. Turing's own".
Although ACE was a feasible design, the effect of the Official Secrets Act
An Official Secrets Act (OSA) is legislation that provides for the protection of Classified information, state secrets and official information, mainly related to national security. However, in its unrevised form (based on the UK Official Secret ...
surrounding the wartime work at Bletchley Park made it impossible for Turing to explain the basis of his analysis of how a computer installation involving human operators would work. This led to delays in starting the project and he became disillusioned. In late 1947 he returned to Cambridge for a sabbatical year during which he produced a seminal work on ''Intelligent Machinery'' that was not published in his lifetime. While he was at Cambridge, the Pilot ACE
The Pilot ACE (Automatic Computing Engine) was one of the first computers built in the United Kingdom. Built at the National Physical Laboratory (NPL) in the early 1950s, it was also one of the earliest general-purpose, stored-program computer ...
was being built in his absence. It executed its first program on 10 May 1950, and a number of later computers around the world owe much to it, including the English Electric DEUCE
The DEUCE (''Digital Electronic Universal Computing Engine'') was one of the earliest British commercially available computers, built by English Electric from 1955. It was the production version of the Pilot ACE, itself a cut-down version of ...
and the American Bendix G-15
The Bendix G-15 is a computer introduced in 1956 by the Bendix Corporation, Computer Division, Los Angeles, California. It is about and weighs about . The G-15 has a drum memory of 2,160 29-bit words, along with 20 words used for special purpos ...
. The full version of Turing's ACE was not built until after his death.
According to the memoirs of the German computer pioneer Heinz Billing from the Max Planck Institute for Physics, published by Genscher, Düsseldorf, there was a meeting between Turing and Konrad Zuse
Konrad Ernst Otto Zuse (; ; 22 June 1910 – 18 December 1995) was a German civil engineer, List of pioneers in computer science, pioneering computer scientist, inventor and businessman. His greatest achievement was the world's first programm ...
. It took place in Göttingen
Göttingen (, ; ; ) is a college town, university city in Lower Saxony, central Germany, the Capital (political), capital of Göttingen (district), the eponymous district. The River Leine runs through it. According to the 2022 German census, t ...
in 1947. The interrogation had the form of a colloquium. Participants were Womersley, Turing, Porter from England and a few German researchers like Zuse, Walther, and Billing (for more details see Herbert Bruderer, ''Konrad Zuse und die Schweiz'').
In 1948, Turing was appointed reader in the Mathematics Department at the University of Manchester
The University of Manchester is a public university, public research university in Manchester, England. The main campus is south of Manchester city centre, Manchester City Centre on Wilmslow Road, Oxford Road. The University of Manchester is c ...
. He lived at "Copper Folly", 43 Adlington Road, in Wilmslow
Wilmslow ( ) is a market town and civil parish in the borough of Cheshire East in Cheshire, England. It is south of Manchester. At the 2021 United Kingdom census, 2021 census the parish had a population of 26,213 and the built up area had a p ...
. A year later, he became deputy director of the Computing Machine Laboratory, where he worked on software for one of the earliest stored-program computers—the Manchester Mark 1
The Manchester Mark 1 was one of the earliest stored-program computers, developed at the Victoria University of Manchester, England from the Manchester Baby (operational in June 1948). Work began in August 1948, and the first version was operat ...
. Turing wrote the first version of the Programmer's Manual for this machine, and was recruited by Ferranti as a consultant in the development of their commercialised machine, the Ferranti Mark 1. He continued to be paid consultancy fees by Ferranti until his death. During this time, he continued to do more abstract work in mathematics, and in "Computing Machinery and Intelligence
"Computing Machinery and Intelligence" is a seminal paper written by Alan Turing on the topic of artificial intelligence. The paper, published in 1950 in ''Mind (journal), Mind'', was the first to introduce his concept of what is now known as th ...
", Turing addressed the problem of artificial intelligence
Artificial intelligence (AI) is the capability of computer, computational systems to perform tasks typically associated with human intelligence, such as learning, reasoning, problem-solving, perception, and decision-making. It is a field of re ...
, and proposed an experiment that became known as the Turing test
The Turing test, originally called the imitation game by Alan Turing in 1949,. Turing wrote about the ‘imitation game’ centrally and extensively throughout his 1950 text, but apparently retired the term thereafter. He referred to ‘ iste ...
, an attempt to define a standard for a machine to be called "intelligent". The idea was that a computer could be said to "think" if a human interrogator could not tell it apart, through conversation, from a human being. In the paper, Turing suggested that rather than building a program to simulate the adult mind, it would be better to produce a simpler one to simulate a child's mind and then to subject it to a course of education. A reversed form of the Turing test is widely used on the Internet; the CAPTCHA
Completely Automated Public Turing Test to tell Computers and Humans Apart (CAPTCHA) ( ) is a type of challenge–response authentication, challenge–response turing test used in computing to determine whether the user is human in order to de ...
test is intended to determine whether the user is a human or a computer.
In 1948, Turing, working with his former undergraduate colleague, D.G. Champernowne, began writing a chess
Chess is a board game for two players. It is an abstract strategy game that involves Perfect information, no hidden information and no elements of game of chance, chance. It is played on a square chessboard, board consisting of 64 squares arran ...
program for a computer that did not yet exist. By 1950, the program was completed and dubbed the Turochamp. In 1952, he tried to implement it on a Ferranti Mark 1
The Ferranti Mark 1, also known as the Manchester Electronic Computer in its sales literature, and thus sometimes called the Manchester Ferranti, was produced by British electrical engineering firm Ferranti Ltd. It was the world's first commer ...
, but lacking enough power, the computer was unable to execute the program. Instead, Turing "ran" the program by flipping through the pages of the algorithm and carrying out its instructions on a chessboard, taking about half an hour per move. The game was recorded. According to Garry Kasparov
Garry Kimovich Kasparov (born Garik Kimovich Weinstein on 13 April 1963) is a Russian Grandmaster (chess), chess grandmaster, former World Chess Champion (1985–2000), political activist and writer. His peak FIDE chess Elo rating system, ra ...
, Turing's program "played a recognizable game of chess". The program lost to Turing's colleague Alick Glennie, although it is said that it won a game against Champernowne's wife, Isabel.
His Turing test was a significant, characteristically provocative, and lasting contribution to the debate regarding artificial intelligence, which continues after more than half a century.
Pattern formation and mathematical biology
When Turing was 39 years old in 1951, he turned tomathematical biology
Mathematical and theoretical biology, or biomathematics, is a branch of biology which employs theoretical analysis, mathematical models and abstractions of living organisms to investigate the principles that govern the structure, development ...
, finally publishing his masterpiece "The Chemical Basis of Morphogenesis
"The Chemical Basis of Morphogenesis" is an article that the English mathematician Alan Turing wrote in 1952. It describes how patterns in nature, such as stripes and spirals, can arise naturally from a homogeneous, uniform state. The theory, w ...
" in January 1952. He was interested in morphogenesis
Morphogenesis (from the Greek ''morphê'' shape and ''genesis'' creation, literally "the generation of form") is the biological process that causes a cell, tissue or organism to develop its shape. It is one of three fundamental aspects of deve ...
, the development of patterns and shapes in biological organisms. He suggested that a system of chemicals reacting with each other and diffusing across space, termed a reaction–diffusion system
Reaction–diffusion systems are mathematical models that correspond to several physical phenomena. The most common is the change in space and time of the concentration of one or more chemical substances: local chemical reactions in which the su ...
, could account for "the main phenomena of morphogenesis". He used systems of partial differential equations
In mathematics, a partial differential equation (PDE) is an equation which involves a multivariable function and one or more of its partial derivatives.
The function is often thought of as an "unknown" that solves the equation, similar to how ...
to model catalytic chemical reactions. For example, if a catalyst A is required for a certain chemical reaction to take place, and if the reaction produced more of the catalyst A, then we say that the reaction is autocatalytic, and there is positive feedback that can be modelled by nonlinear differential equations. Turing discovered that patterns could be created if the chemical reaction not only produced catalyst A, but also produced an inhibitor B that slowed down the production of A. If A and B then diffused through the container at different rates, then you could have some regions where A dominated and some where B did. To calculate the extent of this, Turing would have needed a powerful computer, but these were not so freely available in 1951, so he had to use linear approximations to solve the equations by hand. These calculations gave the right qualitative results, and produced, for example, a uniform mixture that oddly enough had regularly spaced fixed red spots. The Russian biochemist Boris Belousov had performed experiments with similar results, but could not get his papers published because of the contemporary prejudice that any such thing violated the second law of thermodynamics
The second law of thermodynamics is a physical law based on Universal (metaphysics), universal empirical observation concerning heat and Energy transformation, energy interconversions. A simple statement of the law is that heat always flows spont ...
. Belousov was not aware of Turing's paper in the ''Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society
''Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society'' is a scientific journal published by the Royal Society. In its earliest days, it was a private venture of the Royal Society's secretary. It was established in 1665, making it the second journ ...
''.
Although published before the structure and role of DNA
Deoxyribonucleic acid (; DNA) is a polymer composed of two polynucleotide chains that coil around each other to form a double helix. The polymer carries genetic instructions for the development, functioning, growth and reproduction of al ...
was understood, Turing's work on morphogenesis remains relevant today and is considered a seminal piece of work in mathematical biology. One of the early applications of Turing's paper was the work by James Murray explaining spots and stripes on the fur of cats, large and small. Further research in the area suggests that Turing's work can partially explain the growth of "feathers, hair follicles, the branching pattern of lungs, and even the left-right asymmetry that puts the heart on the left side of the chest". In 2012, Sheth, et al. found that in mice, removal of Hox genes
Hox genes, a subset of homeobox genes, are a group of related genes that specify regions of the body plan of an embryo along the head-tail axis of animals. Hox proteins encode and specify the characteristics of 'position', ensuring that the c ...
causes an increase in the number of digits without an increase in the overall size of the limb, suggesting that Hox genes control digit formation by tuning the wavelength of a Turing-type mechanism. Later papers were not available until ''Collected Works of A. M. Turing'' was published in 1992.
A study conducted in 2023 confirmed Turing's mathematical model hypothesis. Presented by the American Physical Society
The American Physical Society (APS) is a not-for-profit membership organization of professionals in physics and related disciplines, comprising nearly fifty divisions, sections, and other units. Its mission is the advancement and diffusion of ...
, the experiment involved growing chia seed
Chia seeds ( ) are the edible seeds of ''Salvia hispanica'', a flowering plant in the Mentha, mint family (Lamiaceae) native to central and southern Mexico, or of the related ''Salvia columbariae'', ''Salvia polystachia'', or ''Salvia tiliifolia' ...
s in even layers within trays, later adjusting the available moisture. Researchers experimentally tweaked the factors which appear in the Turing equations, and, as a result, patterns resembling those seen in natural environments emerged. This is believed to be the first time that experiments with living vegetation have verified Turing's mathematical insight.
Personal life
Treasure
In the 1940s, Turing became worried about losing his savings in the event of a German invasion. In order to protect it, he bought two silver bars weighing and worth £250 (in 2022, £8,000 adjusted for inflation, £48,000 at spot price) and buried them in a wood near Bletchley Park. Upon returning to dig them up, Turing found that he was unable to break his own code describing where exactly he had hidden them. This, along with the fact that the area had been renovated, meant that he never regained the silver.Engagement
In 1941, Turing proposed marriage to Hut 8 colleagueJoan Clarke
Joan Elisabeth Lowther Murray, MBE (''née'' Clarke; 24 June 1917 – 4 September 1996) was an English cryptanalyst and numismatist who worked as a code-breaker at Bletchley Park during the Second World War. Although she did not personally ...
, a fellow mathematician and cryptanalyst, but their engagement was short-lived. After admitting his homosexuality to his fiancée, who was reportedly "unfazed" by the revelation, Turing decided that he could not go through with the marriage.
Homosexuality and indecency conviction
In December 1951, Turing met Arnold Murray, a 19-year-old unemployed man. Turing was walking along Manchester's Oxford Road when he met Murray just outside theRegal Cinema
The Regal Cinema is an Art deco movie theatre located at Colaba Causeway, in Mumbai, India. Built by Framji Sidhwa, the first film to be aired at the Regal was the Laurel and Hardy work '' The Devil's Brother'' in 1933.
According to the '' ...
and invited him to lunch. The two agreed to meet again and in January 1952 began an intimate relationship. On 23 January, Turing's house in Wilmslow was burgled. Murray told Turing that he and the burglar were acquainted, and Turing reported the crime to the police. During the investigation, he acknowledged a sexual relationship with Murray. Homosexual acts were criminal offences in the United Kingdom at that time, and both men were charged with "gross indecency
Gross indecency is a crime in some parts of the English-speaking world, originally used to criminalize sexual activity between men that fell short of sodomy, which required penetration. The term was first used in British law in a statute of the ...
" under Section 11 of the Criminal Law Amendment Act 1885
The Criminal Law Amendment Act 1885 ( 48 & 49 Vict. c. 69), or "An Act to make further provision for the Protection of Women and Girls, the suppression of brothels, and other purposes," was an Act of the Parliament of the United Kingdom, the la ...
. Initial committal proceedings for the trial were held on 27 February during which Turing's solicitor "reserved his defence", i.e., did not argue or provide evidence against the allegations. The proceedings were held at the Sessions House
A sessions house in the United Kingdom was historically a courthouse that served as a dedicated court of quarter sessions, where criminal trials were held four times a year on quarter days. Sessions houses were also used for other purposes to do w ...
in Knutsford
Knutsford () is a market town and civil parish in the Cheshire East district, in Cheshire, England; it is located south-west of Manchester, north-west of Macclesfield and south-east of Warrington. The population of the parish at the 2021 Uni ...
.
Turing was later convinced by the advice of his brother and his own solicitor, and he entered a plea of guilty. The case, '' Regina v. Turing and Murray,'' was brought to trial on 31 March 1952. Turing was convicted and given a choice between imprisonment and probation. His probation would be conditional on his agreement to undergo hormonal
A hormone (from the Greek participle , "setting in motion") is a class of signaling molecules in multicellular organisms that are sent to distant organs or tissues by complex biological processes to regulate physiology and behavior. Hormones a ...
physical changes designed to reduce libido
In psychology, libido (; ) is psychic drive or energy, usually conceived of as sexual in nature, but sometimes conceived of as including other forms of desire. The term ''libido'' was originally developed by Sigmund Freud, the pioneering origin ...
, known as "chemical castration
Chemical castration is castration via anaphrodisiac drugs, whether to reduce libido and sexual activity, management of cancer, to treat cancer, or otherwise. Unlike orchiectomy, surgical castration, where the gonads are removed through an incision ...
". He accepted the option of injections of what was then called stilboestrol (now known as diethylstilbestrol
Diethylstilbestrol (DES), also known as stilbestrol or stilboestrol, is a nonsteroidal estrogen medication, which is presently rarely used. In the past, it was widely used for a variety of indications, including pregnancy support for those with ...
or DES), a synthetic oestrogen
Estrogen (also spelled oestrogen in British English; see spelling differences) is a category of sex hormone responsible for the development and regulation of the female reproductive system and secondary sex characteristics. There are three m ...
; this feminization of his body was continued for the course of one year. The treatment rendered Turing impotent and caused breast tissue to form. In a letter, Turing wrote that "no doubt I shall emerge from it all a different man, but quite who I've not found out". Murray was given a conditional discharge.
Turing's conviction led to the removal of his security clearance and barred him from continuing with his cryptographic consultancy for GCHQ
Government Communications Headquarters (GCHQ) is an intelligence and security organisation responsible for providing signals intelligence (SIGINT) and information assurance (IA) to the government and armed forces of the United Kingdom. Primar ...
, the British signals intelligence
Signals intelligence (SIGINT) is the act and field of intelligence-gathering by interception of ''signals'', whether communications between people (communications intelligence—abbreviated to COMINT) or from electronic signals not directly u ...
agency that had evolved from GC&CS in 1946, though he kept his academic post. His trial took place only months after the defection to the Soviet Union of Guy Burgess
Guy Francis de Moncy Burgess (16 April 1911 – 30 August 1963) was a British diplomat and Soviet double agent, and a member of the Cambridge Five spy ring that operated from the mid-1930s to the early years of the Cold War era. His defection ...
and Donald Maclean, in summer 1951, after which the Foreign Office started to consider anyone known to be homosexual as a potential security risk.
Turing was denied entry into the United States after his conviction in 1952, but was free to visit other European countries. In the summer of 1952 he visited Norway which was more tolerant of homosexuals. Among the various men he met there was one named Kjell Carlson. Kjell intended to visit Turing in the UK but the authorities intercepted Kjell's postcard detailing his travel arrangements and were able to intercept and deport him before the two could meet. It was also during this time that Turing started consulting a psychiatrist, Dr Franz Greenbaum, with whom he got on well and who subsequently became a family friend.
Death
 On 8 June 1954, at his house at 43 Adlington Road,
On 8 June 1954, at his house at 43 Adlington Road, Wilmslow
Wilmslow ( ) is a market town and civil parish in the borough of Cheshire East in Cheshire, England. It is south of Manchester. At the 2021 United Kingdom census, 2021 census the parish had a population of 26,213 and the built up area had a p ...
, Turing's housekeeper found him dead. A post mortem was held that evening, which determined that he had died the previous day at age 41 with cyanide poisoning
Cyanide poisoning is poisoning that results from exposure to any of a number of forms of cyanide. Early symptoms include headache, dizziness, fast heart rate, shortness of breath, and vomiting. This phase may then be followed by seizures, slo ...
cited as the cause of death. When his body was discovered, an apple lay half-eaten beside his bed, and although the apple was not tested for cyanide, it was speculated that this was the means by which Turing had consumed a fatal dose.
Turing's brother, John, identified the body the following day and took the advice given by Dr. Greenbaum to accept the verdict of the inquest
An inquest is a judicial inquiry in common law jurisdictions, particularly one held to determine the cause of a person's death. Conducted by a judge, jury, or government official, an inquest may or may not require an autopsy carried out by a cor ...
, as there was little prospect of establishing that the death was accidental. The inquest was held the following day, which determined the cause of death to be suicide. Turing's remains were cremated at Woking Crematorium
Woking Crematorium is a crematorium in Woking, a large town in the west of Surrey, England. Established in 1878, it was the first custom-built crematorium in the United Kingdom and is closely linked to the history of cremation in the UK.
Locat ...
just two days later on 12 June 1954, with just his mother, brother, and Lyn Newman attending, and his ashes were scattered in the gardens of the crematorium, just as his father's had been. Turing's mother was on holiday in Italy at the time of his death and returned home after the inquest. She never accepted the verdict of suicide.
Philosopher Jack Copeland
Brian Jack Copeland (born 1950) is Professor of Philosophy at the University of Canterbury, Christchurch, New Zealand, and author of books on the computing pioneer Alan Turing.
Education
Copeland was educated at the University of Oxford, obt ...
has questioned various aspects of the coroner's historical verdict. He suggested an alternative explanation for the cause of Turing's death: the accidental inhalation of cyanide fumes from an apparatus used to electroplate gold onto spoons. The potassium cyanide
Potassium cyanide is a compound with the formula KCN. It is a colorless salt, similar in appearance to sugar, that is highly soluble in water. Most KCN is used in gold mining, organic synthesis, and electroplating. Smaller applications include ...
was used to dissolve the gold. Turing had such an apparatus set up in his tiny spare room. Copeland noted that the autopsy findings were more consistent with inhalation than with ingestion of the poison. Turing also habitually ate an apple before going to bed, and it was not unusual for the apple to be discarded half-eaten. Furthermore, Turing had reportedly borne his legal setbacks and hormone treatment (which had been discontinued a year previously) "with good humour" and had shown no sign of despondency before his death. He even set down a list of tasks that he intended to complete upon returning to his office after the holiday weekend. Turing's mother believed that the ingestion was accidental, resulting from her son's careless storage of laboratory chemicals. Turing biographer Andrew Hodges
Andrew Philip Hodges ( ; born 1949) is a British mathematician, author and emeritus senior research fellow at Wadham College, Oxford.
Education
Hodges was born in London in 1949 and educated at Birkbeck, University of London, where he was award ...
theorised that Turing deliberately made his death look accidental in order to shield his mother from the knowledge that he had killed himself.
Doubts on the suicide thesis have been also cast by John W. Dawson Jr. who, in his review of Hodges' book, recalls "Turing's vulnerable position in the Cold War political climate" and points out that "Turing was found dead by a maid, who discovered him 'lying neatly in his bed'—hardly what one would expect of "a man fighting for life against the suffocation induced by cyanide poisoning." Turing had given no hint of suicidal inclinations to his friends and had made no effort to put his affairs in order.
Hodges and a later biographer, David Leavitt, have both speculated that Turing was re-enacting a scene from the Walt Disney
Walter Elias Disney ( ; December 5, 1901December 15, 1966) was an American animator, film producer, voice actor, and entrepreneur. A pioneer of the Golden age of American animation, American animation industry, he introduced several develop ...
film ''Snow White and the Seven Dwarfs
"Snow White" is a German fairy tale, first written down in the early 19th century. The Brothers Grimm published it in 1812 in the first edition of their collection ''Grimms' Fairy Tales'', numbered as Tale 53. The original title was ''Sneewittch ...
'' (1937), his favourite fairy tale. Both men noted that (in Leavitt's words) he took "an especially keen pleasure in the scene where the Wicked Queen immerses her apple in the poisonous brew".
 It has also been suggested that Turing's belief in
It has also been suggested that Turing's belief in fortune-telling
Fortune telling is the spiritual practice of predicting information about a person's life. Melton, J. Gordon. (2008). ''The Encyclopedia of Religious Phenomena''. Visible Ink Press. pp. 115–116. The scope of fortune telling is in principle ...
may have caused his depressed mood. As a youth, Turing had been told by a fortune-teller that he would be a genius. In mid-May 1954, shortly before his death, Turing again decided to consult a fortune-teller during a day-trip to St Annes-on-Sea with the Greenbaum family. According to the Greenbaums' daughter, Barbara:
Government apology and pardon
In August 2009, British programmerJohn Graham-Cumming
John Graham-Cumming is a British software engineer and writer best known for starting a successful petition to the Government of the United Kingdom asking for an apology for its persecution of Alan Turing. UK Prime Minister Gordon Brown issued ...
started a petition urging the British government to apologise for Turing's prosecution as a homosexual. The petition received more than 30,000 signatures. The prime minister, Gordon Brown
James Gordon Brown (born 20 February 1951) is a British politician who served as Prime Minister of the United Kingdom and Leader of the Labour Party (UK), Leader of the Labour Party from 2007 to 2010. Previously, he was Chancellor of the Ex ...
, acknowledged the petition, releasing a statement on 10 September 2009 apologising and describing the treatment of Turing as "appalling":
In December 2011, William Jones and his member of Parliament, John Leech, created an e-petition requesting that the British government pardon
A pardon is a government decision to allow a person to be relieved of some or all of the legal consequences resulting from a criminal conviction. A pardon may be granted before or after conviction for the crime, depending on the laws of the j ...
Turing for his conviction of "gross indecency":
The petition gathered over 37,000 signatures, and was submitted to Parliament by the Manchester MP John Leech but the request was discouraged by Justice Minister Lord McNally, who said:
John Leech, the MP for Manchester Withington
Manchester Withington is a Constituencies of the Parliament of the United Kingdom, constituency represented in the House of Commons of the United Kingdom, House of Commons of the UK Parliament since 2015 by Jeff Smith (British politician), Jeff ...
(2005–15), submitted several bills to Parliament and led a high-profile campaign to secure the pardon. Leech made the case in the House of Commons that Turing's contribution to the war made him a national hero and that it was "ultimately just embarrassing" that the conviction still stood. Leech continued to take the bill through Parliament and campaigned for several years, gaining the public support of numerous leading scientists, including Stephen Hawking
Stephen William Hawking (8January 194214March 2018) was an English theoretical physics, theoretical physicist, cosmologist, and author who was director of research at the Centre for Theoretical Cosmology at the University of Cambridge. Between ...
. At the British premiere of a film based on Turing's life, ''The Imitation Game
''The Imitation Game'' is a 2014 American biographical film, biographical thriller film directed by Morten Tyldum and written by Graham Moore (writer), Graham Moore, based on the 1983 biography ''Alan Turing: The Enigma'' by Andrew Hodges. The ...
'', the producers thanked Leech for bringing the topic to public attention and securing Turing's pardon. Leech is now regularly described as the "architect" of Turing's pardon and subsequently the Alan Turing Law which went on to secure pardons for 75,000 other men and women convicted of similar crimes.
On 26 July 2012, a bill was introduced in the House of Lords
The House of Lords is the upper house of the Parliament of the United Kingdom. Like the lower house, the House of Commons of the United Kingdom, House of Commons, it meets in the Palace of Westminster in London, England. One of the oldest ext ...
to grant a statutory pardon to Turing for offences under section 11 of the Criminal Law Amendment Act 1885, of which he was convicted on 31 March 1952. Late in the year in a letter to ''The Daily Telegraph
''The Daily Telegraph'', known online and elsewhere as ''The Telegraph'', is a British daily broadsheet conservative newspaper published in London by Telegraph Media Group and distributed in the United Kingdom and internationally. It was found ...
'', the physicist Stephen Hawking and 10 other signatories including the Astronomer Royal
Astronomer Royal is a senior post in the Royal Households of the United Kingdom. There are two officers, the senior being the astronomer royal dating from 22 June 1675; the junior is the astronomer royal for Scotland dating from 1834. The Astro ...
Lord Rees, President of the Royal Society
The president of the Royal Society (PRS), also known as the Royal Society of London, is the elected Head of the Royal Society who presides over meetings of the society's council.
After an informal meeting (a lecture) by Christopher Wren at Gres ...
Sir Paul Nurse, Jean Barker, Baroness Trumpington, Lady Trumpington (who worked for Turing during the war) and John Sharkey, Baron Sharkey, Lord Sharkey (the bill's sponsor) called on Prime Minister David Cameron to act on the pardon request. The government indicated it would support the bill, and it passed its third reading in the House of Lords in October.
At the bill's second reading in the House of Commons of the United Kingdom, House of Commons on 29 November 2013, Conservative MP Christopher Chope objected to the bill, delaying its passage. The bill was due to return to the House of Commons on 28 February 2014, but before the bill could be debated in the House of Commons, the government elected to proceed under the royal prerogative of mercy. On 24 December 2013, Queen Elizabeth II
Elizabeth II (Elizabeth Alexandra Mary; 21 April 19268 September 2022) was Queen of the United Kingdom and other Commonwealth realms from 6 February 1952 until Death and state funeral of Elizabeth II, her death in 2022. ...
signed a pardon
A pardon is a government decision to allow a person to be relieved of some or all of the legal consequences resulting from a criminal conviction. A pardon may be granted before or after conviction for the crime, depending on the laws of the j ...
for Turing's conviction for "gross indecency", with immediate effect. Announcing the pardon, Lord Chancellor Chris Grayling said Turing deserved to be "remembered and recognised for his fantastic contribution to the war effort" and not for his later criminal conviction. The Queen pronounced Turing pardoned in August 2014. It was only the fourth royal pardon granted since the conclusion of the Second World War. Pardons are normally granted only when the person is technically innocent, and a request has been made by the family or other interested party; neither condition was met in regard to Turing's conviction.
In September 2016, the government announced its intention to expand this retroactive exoneration to other men convicted of similar historical indecency offences, in what was described as an "Alan Turing law
"Alan Turing law" is an informal term for the portion of the Policing and Crime Act 2017 which serves in UK law to pardon men who were cautioned or convicted under obsolete laws criminalising homosexual acts. The provision is named after Ala ...
". The Alan Turing law is now an informal term for the law in the United Kingdom, contained in the Policing and Crime Act 2017, which serves as an amnesty law to retroactively pardon men who were cautioned or convicted under historical legislation that outlawed homosexual acts. The law applies in England and Wales.
On 19 July 2023, Sexual orientation and the military of the United Kingdom#Official apology to veterans, following an apology to LGBT veterans from the UK Government, Secretary of State for Defence, Defence Secretary Ben Wallace (politician), Ben Wallace suggested Turing should be honoured with a permanent statue on the Fourth plinth#Proposals for permanent statues, fourth plinth of Trafalgar Square, describing Turing as "probably the greatest war hero, in my book, of the Second World War, [whose] achievements shortened the war, saved thousands of lives, helped defeat the Nazis. And his story is a sad story of a society and how it treated him."
See also
* Legacy of Alan Turing * List of things named after Alan TuringReferences
Notes
Citations
Works cited
* * * * * * ** in * * * * * * * *Further reading
Articles
* * * * * * *Books
* * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * (originally published in 1983); basis of the film ''The Imitation Game
''The Imitation Game'' is a 2014 American biographical film, biographical thriller film directed by Morten Tyldum and written by Graham Moore (writer), Graham Moore, based on the 1983 biography ''Alan Turing: The Enigma'' by Andrew Hodges. The ...
''
*
*
*
*
* Turing's mother, who survived him by many years, wrote this 157-page biography of her son, glorifying his life. It was published in 1959, and so could not cover his war work. Scarcely 300 copies were sold (Sara Turing to Lyn Newman, 1967, Library of St John's College, Cambridge). The six-page foreword by Lyn Irvine includes reminiscences and is more frequently quoted. It was re-published by Cambridge University Press in 2012, to honour the centenary of his birth, and included a new foreword by Martin Davis (mathematician), Martin Davis, as well as a never-before-published memoir by Turing's older brother John F. Turing.
* (originally published in 1959 by W. Heffer & Sons, Ltd)
*
* This 1986 Hugh Whitemore play tells the story of Turing's life and death. In the original West End and Broadway runs, Derek Jacobi played Turing and he recreated the role in a 1997 television film based on the play made jointly by the BBC and WGBH-TV, WGBH, Boston. The play is published by Amber Lane Press, Oxford, ASIN: B000B7TM0Q
*
*
External links
Oral history interview with Nicholas C. Metropolis
Charles Babbage Institute, University of Minnesota. Metropolis was the first director of computing services at Los Alamos National Laboratory; topics include the relationship between Turing and
John von Neumann
John von Neumann ( ; ; December 28, 1903 – February 8, 1957) was a Hungarian and American mathematician, physicist, computer scientist and engineer. Von Neumann had perhaps the widest coverage of any mathematician of his time, in ...
How Alan Turing Cracked The Enigma Code
Imperial War Museums
Alan Turing Year
CiE 2012: Turing Centenary Conference
Science in the Making
Alan Turing's papers in the Royal Society's archives
Alan Turing
site maintained by
Andrew Hodges
Andrew Philip Hodges ( ; born 1949) is a British mathematician, author and emeritus senior research fellow at Wadham College, Oxford.
Education
Hodges was born in London in 1949 and educated at Birkbeck, University of London, where he was award ...
including short biography
AlanTuring.net – Turing Archive for the History of Computing
by
Jack Copeland
Brian Jack Copeland (born 1950) is Professor of Philosophy at the University of Canterbury, Christchurch, New Zealand, and author of books on the computing pioneer Alan Turing.
Education
Copeland was educated at the University of Oxford, obt ...
The Turing Digital Archive
nbsp;– contains scans of some unpublished documents and material from the King's College, Cambridge archive
Alan Turing Papers
– University of Manchester Library, Manchester *
Sherborne School Archives
– holds papers relating to Turing's time at Sherborne School
Alan Turing and the ‘Nature of Spirit’
(Old Shirburnian Society)
Alan Turing OBE, PhD, FRS (1912-1954)
(Old Shirburnian Society)
Alan Turing plaques
recorded on openplaques.org
Alan Turing
archive on New Scientist {{DEFAULTSORT:Turing, Alan Alan Turing, 1912 births 1954 deaths 1954 suicides 20th-century atheists 20th-century English LGBTQ people 20th-century English mathematicians 20th-century English philosophers Academics of the University of Manchester Institute of Science and Technology Academics of the University of Manchester Alumni of King's College, Cambridge Bayesian statisticians Bletchley Park people British anti-fascists British artificial intelligence researchers British cryptographers British people of World War II Castrated people Computability theorists Computer chess people Computer designers English atheists English computer scientists English gay sportsmen English inventors English LGBTQ scientists English logicians English male long-distance runners British male long-distance runners English people of Irish descent English people of Scottish descent Enigma machine Fellows of King's College, Cambridge Fellows of the Royal Society Foreign Office personnel of World War II Former Protestants Gay academics Gay scientists GCHQ people History of computing in the United Kingdom LGBTQ mathematicians LGBTQ philosophers LGBTQ track and field athletes LGBTQ people who died by suicide Officers of the Order of the British Empire People convicted for homosexuality in the United Kingdom People educated at Sherborne School People from Maida Vale People from Wilmslow People who have received posthumous pardons Princeton University alumni Recipients of British royal pardons Scientists of the National Physical Laboratory (United Kingdom) Suicides by cyanide poisoning Suicides in England Theoretical biologists British theoretical computer scientists