Tropospheric scatter link on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]

 Tropospheric scatter, also known as troposcatter, is a method of communicating with microwave radio signals over considerable distances – often up to and further depending on frequency of operation, equipment type, terrain, and climate factors. This method of propagation uses the tropospheric scatter phenomenon, where radio waves at
Tropospheric scatter, also known as troposcatter, is a method of communicating with microwave radio signals over considerable distances – often up to and further depending on frequency of operation, equipment type, terrain, and climate factors. This method of propagation uses the tropospheric scatter phenomenon, where radio waves at
 The propagation losses are very high; only about one
The propagation losses are very high; only about one 

 Tropospheric scatter, also known as troposcatter, is a method of communicating with microwave radio signals over considerable distances – often up to and further depending on frequency of operation, equipment type, terrain, and climate factors. This method of propagation uses the tropospheric scatter phenomenon, where radio waves at
Tropospheric scatter, also known as troposcatter, is a method of communicating with microwave radio signals over considerable distances – often up to and further depending on frequency of operation, equipment type, terrain, and climate factors. This method of propagation uses the tropospheric scatter phenomenon, where radio waves at UHF
Ultra high frequency (UHF) is the ITU designation for radio frequencies in the range between 300 megahertz (MHz) and 3 gigahertz (GHz), also known as the decimetre band as the wavelengths range from one meter to one tenth of a meter (on ...
and SHF frequencies are randomly scattered as they pass through the upper layers of the troposphere
The troposphere is the first and lowest layer of the atmosphere of the Earth, and contains 75% of the total mass of the planetary atmosphere, 99% of the total mass of water vapour and aerosols, and is where most weather phenomena occur. From ...
. Radio signals are transmitted in a narrow beam aimed just above the horizon in the direction of the receiver station. As the signals pass through the troposphere, some of the energy is scattered back toward the Earth, allowing the receiver station to pick up the signal.
Normally, signals in the microwave frequency range travel in straight lines, and so are limited to '' line-of-sight'' applications, in which the receiver can be 'seen' by the transmitter. Communication distances are limited by the visual horizon to around . Troposcatter allows microwave communication beyond the horizon. It was developed in the 1950s and used for military communications until communications satellite
A communications satellite is an artificial satellite that relays and amplifies radio telecommunication signals via a transponder; it creates a communication channel between a source transmitter and a receiver at different locations on Ear ...
s largely replaced it in the 1970s.
Because the troposphere is turbulent and has a high proportion of moisture, the tropospheric scatter radio signals are refracted and consequently only a tiny proportion of the transmitted radio energy is collected by the receiving antennas. Frequencies of transmission around are best suited for tropospheric scatter systems as at this frequency the wavelength of the signal interacts well with the moist, turbulent areas of the troposphere, improving signal-to-noise ratios.
Overview
Discovery
Previous toWorld War II
World War II or the Second World War, often abbreviated as WWII or WW2, was a world war that lasted from 1939 to 1945. It involved the World War II by country, vast majority of the world's countries—including all of the great power ...
, prevailing radio physics theory predicted a relationship between frequency and diffraction that suggested radio signals would follow the curvature of the Earth, but that the strength of the effect would fall off rapidly and especially at higher frequencies. However, during the war, there were numerous incidents in which high-frequency radar signals were able to detect targets at ranges far beyond the theoretical calculations. In spite of these repeated instances of anomalous range, the matter was never seriously studied.
In the immediate post-war era, the limitation on television
Television, sometimes shortened to TV, is a telecommunication Media (communication), medium for transmitting moving images and sound. The term can refer to a television set, or the medium of Transmission (telecommunications), television tra ...
construction was lifted in the United States and millions of sets were sold. This drove an equally rapid expansion of new television stations. Based on the same calculations used during the war, the Federal Communications Commission
The Federal Communications Commission (FCC) is an independent agency of the United States federal government that regulates communications by radio, television, wire, satellite, and cable across the United States. The FCC maintains jurisd ...
(FCC) arranged frequency allocations for the new VHF and UHF channels to avoid interference between stations. To everyone's surprise, interference was common, even between widely separated stations. As a result, licenses for new stations were put on hold in what is known as the "television freeze" of 1948.
Bell Labs
Nokia Bell Labs, originally named Bell Telephone Laboratories (1925–1984),
then AT&T Bell Laboratories (1984–1996)
and Bell Labs Innovations (1996–2007),
is an American industrial research and scientific development company owned by mult ...
was among the many organizations that began studying this effect, and concluded it was a previously unknown type of reflection off the tropopause
The tropopause is the atmospheric boundary that demarcates the troposphere from the stratosphere; which are two of the five layers of the atmosphere of Earth. The tropopause is a thermodynamic gradient-stratification layer, that marks the end of ...
. This was limited to higher frequencies, in the UHF and microwave bands, which is why it had not been seen prior to the war when these frequencies were beyond the ability of existing electronics. Although the vast majority of the signal went through the troposphere and on to space, the tiny amount that was reflected was useful if combined with powerful transmitters and very sensitive receivers. In 1952, Bell began experiments with Lincoln Labs, the MIT-affiliated radar
Radar is a detection system that uses radio waves to determine the distance ('' ranging''), angle, and radial velocity of objects relative to the site. It can be used to detect aircraft, ships, spacecraft, guided missiles, motor vehicles, w ...
research lab. Using Lincoln's powerful microwave transmitters and Bell's sensitive receivers, they built several experimental systems to test a variety of frequencies and weather effects. When Bell Canada heard of the system they felt it might be useful for a new communications network in Labrador
, nickname = "The Big Land"
, etymology =
, subdivision_type = Country
, subdivision_name = Canada
, subdivision_type1 = Province
, subdivision_name1 ...
and took one of the systems there for cold weather testing.
In 1954 the results from both test series were complete and construction began on the first troposcatter system, the Pole Vault system that linked Pinetree Line radar systems along the coast of Labrador
, nickname = "The Big Land"
, etymology =
, subdivision_type = Country
, subdivision_name = Canada
, subdivision_type1 = Province
, subdivision_name1 ...
. Using troposcatter reduced the number of stations from 50 microwave relays scatted through the wilderness to only 10, all located at the radar stations. In spite of their higher unit costs, the new network cost half as much to build as a relay system. Pole Vault was quickly followed by similar systems like White Alice, relays on the Mid-Canada Line and the DEW Line, and during the 1960s, across the Atlantic Ocean
The Atlantic Ocean is the second-largest of the world's five oceans, with an area of about . It covers approximately 20% of Earth#Surface, Earth's surface and about 29% of its water surface area. It is known to separate the "Old World" of Afr ...
and Europe as part of NATO
The North Atlantic Treaty Organization (NATO, ; french: Organisation du traité de l'Atlantique nord, ), also called the North Atlantic Alliance, is an intergovernmental military alliance between 30 member states – 28 European and two No ...
's ACE High system.
Use
 The propagation losses are very high; only about one
The propagation losses are very high; only about one trillionth
This list contains selected positive numbers in increasing order, including counts of things, dimensionless quantities and probabilities. Each number is given a name in the short scale, which is used in English-speaking countries, as well as a ...
() of the transmit power is available at the receiver. This demands the use of antennas with extremely large antenna gain
In electromagnetics, an antenna's gain is a key performance parameter which combines the antenna's directivity and radiation efficiency. The term ''power gain'' has been deprecated by IEEE. In a transmitting antenna, the gain describes h ...
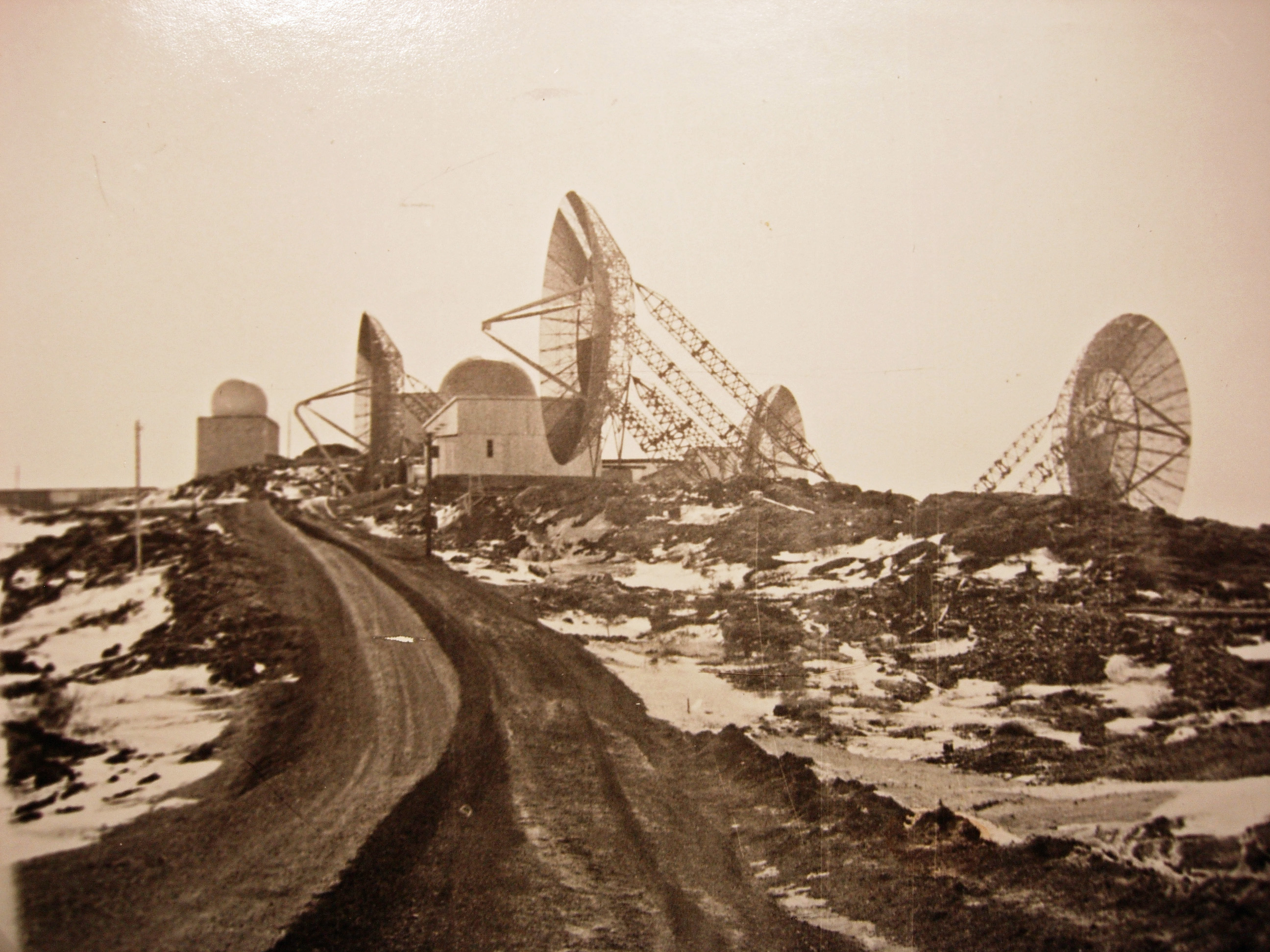
. The original Pole Vault system used large parabolic reflector
A parabolic (or paraboloid or paraboloidal) reflector (or dish or mirror) is a reflective surface used to collect or project energy such as light, sound, or radio waves. Its shape is part of a circular paraboloid, that is, the surface generat ...
dish antennas, but these were soon replaced by billboard antenna
In telecommunications and radar, a reflective array antenna is a class of directive antennas in which multiple driven elements are mounted in front of a flat surface designed to reflect the radio waves in a desired direction. They are a type o ...
s which were somewhat more robust, an important quality given that these systems were often found in harsh locales. Paths were established at distances over . They required antennas ranging from and amplifiers ranging from to . These were analogue systems which were capable of transmitting a few voice channels.
Troposcatter systems have evolved over the years. With communication satellites used for long-distance communication links, current troposcatter systems are employed over shorter distances than previous systems, use smaller antennas and amplifiers, and have much higher bandwidth capabilities. Typical distances are between , though greater distances can be achieved depending on the climate, terrain, and data rate required. Typical antenna sizes range from while typical amplifier sizes range from to . Data rates over can be achieved with today's technology.
Tropospheric scatter is a fairly secure method of propagation as dish alignment is critical, making it extremely difficult to intercept the signals, especially if transmitted across open water, making them highly attractive to military users. Military systems have tended to be ‘thin-line’ tropo – so called because only a narrow bandwidth ‘information’ channel was carried on the tropo system; generally up to 32 analogue ( bandwidth) channels. Modern military systems are "wideband" as they operate 4-16 Mbit/s digital data channels.
Civilian troposcatter systems, such as the British Telecom
BT Group plc (trade name, trading as BT and formerly British Telecom) is a British Multinational corporation, multinational telecommunications holding company headquartered in London, England. It has operations in around 180 countries and is th ...
(BT) North Sea
The North Sea lies between Great Britain, Norway, Denmark, Germany, the Netherlands and Belgium. An epeiric sea on the European continental shelf, it connects to the Atlantic Ocean through the English Channel in the south and the Norwegian S ...
oil communications network, required higher capacity ‘information’ channels than were available using HF (high frequency – to ) radio signals, before satellite technology was available. The BT systems, based at Scousburgh in the Shetland Islands, Mormond Hill
Mormond Hill ( Scottish Gaelic A' Mhormhonadh, meaning the great hill or moor; known as ''Mormounth'' in Old Scots) is a large hill in Aberdeenshire, Scotland, not far from Fraserburgh. Its peak is .Aberdeenshire
Aberdeenshire ( sco, Aiberdeenshire; gd, Siorrachd Obar Dheathain) is one of the 32 council areas of Scotland.
It takes its name from the County of Aberdeen which has substantially different boundaries. The Aberdeenshire Council area incl ...
and Row Brow near Scarborough, were capable of transmitting and receiving 156 analogue ( bandwidth) channels of data and telephony to / from North Sea oil production platforms, using frequency-division multiplexing (FDMX) to combine the channels.
Because of the nature of the turbulence in the troposphere, quadruple diversity propagation paths were used to ensure reliability of the service, equating to about 3 minutes of downtime due to propagation drop out per month. The quadruple space and polarisation diversity systems needed two separate dish antennas (spaced several metres apart) and two differently polarised feed horns – one using vertical polarisation, the other using horizontal polarisation. This ensured that at least one signal path was open at any one time. The signals from the four different paths were recombined in the receiver where a phase corrector removed the phase differences of each signal. Phase differences were caused by the different path lengths of each signal from transmitter to receiver. Once phase corrected, the four signals could be combined additively.
Tropospheric scatter communications networks
The tropospheric scatter phenomenon has been used to build both civilian and military communication links in a number of parts of the world, including: ;Allied Command Europe Highband
Allied Command Europe Highband, better known as ACE High, was a fixed service NATO radiocommunication and early warning system dating back to 1956. After extensive testing ACE High was accepted by NATO to become operational in 1964/1965.
Th ...
(ACE High),
:NATO
The North Atlantic Treaty Organization (NATO, ; french: Organisation du traité de l'Atlantique nord, ), also called the North Atlantic Alliance, is an intergovernmental military alliance between 30 member states – 28 European and two No ...
military radiocommunication and early warning system throughout Europe from the Norwegian-Soviet border to the Turkish-Soviet border.
; BT (British Telecom),
:United Kingdom
The United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Ireland, commonly known as the United Kingdom (UK) or Britain, is a country in Europe, off the north-western coast of the European mainland, continental mainland. It comprises England, Scotlan ...
- Shetland
Shetland, also called the Shetland Islands and formerly Zetland, is a subarctic archipelago in Scotland lying between Orkney, the Faroe Islands and Norway. It is the northernmost region of the United Kingdom.
The islands lie about to the ...
to Mormond Hill
Mormond Hill ( Scottish Gaelic A' Mhormhonadh, meaning the great hill or moor; known as ''Mormounth'' in Old Scots) is a large hill in Aberdeenshire, Scotland, not far from Fraserburgh. Its peak is .Fernmeldeturm Berlin,
:Torfhaus-Berlin, Clenze-Berlin at Cold War times
; Portugal Telecom,
:Serra de Nogueira (northeastern Portugal) to Artzamendi (southwestern France)
; CNCP Telecommunications,
: Tsiigehtchic to Galena Hill, Keno City
: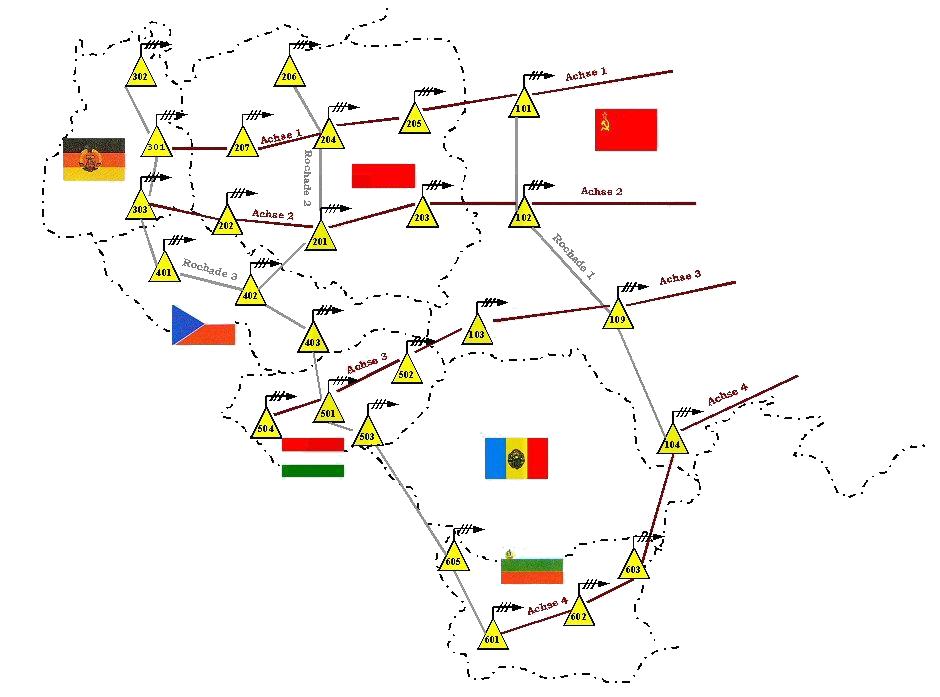 :A Warsaw Pact tropo-scatter network stretching from near
:A Warsaw Pact tropo-scatter network stretching from near  :A single section from
:A single section from
 The U.S. Army and Air Force use tactical tropospheric scatter systems developed by Raytheon for long haul communications. The systems come in two configurations, the original "heavy tropo", and a newer "light tropo" configuration exist. The systems provide four Multiplexing, multiplexed group channels and trunk encryption, and 16 or 32 local analog phone extensions. The U.S. Marine Corps also uses the same device, albeit an older version.
The U.S. Army and Air Force use tactical tropospheric scatter systems developed by Raytheon for long haul communications. The systems come in two configurations, the original "heavy tropo", and a newer "light tropo" configuration exist. The systems provide four Multiplexing, multiplexed group channels and trunk encryption, and 16 or 32 local analog phone extensions. The U.S. Marine Corps also uses the same device, albeit an older version.
Russian tropospheric relay communication network
Tropospheric Scatter Communications - the essentials
* {{Authority control Radio frequency propagation Atmospheric optical phenomena
Hay River Hay River may refer to:
Places
* Hay River, Northwest Territories
* Hay River, Wisconsin
Rivers
* Hay River (Wisconsin)
* Hay River (Canada), a river in Alberta and Northwest Territories, Canada
* Hay River, Northern Territory, Australia
* Hay R ...
- Port Radium - Lady Franklin Point
Lady Franklin Point is a landform in the Canadian Arctic territory of Nunavut. It is located on southwestern Victoria Island in the Coronation Gulf by Austin Bay at the eastern entrance of Dolphin and Union Strait.
The Point is uninhabited but ...
; -
: Guanabo to Florida City
;Project Offices - AT&T Corporation
AT&T Corporation, originally the American Telephone and Telegraph Company, is the subsidiary of AT&T Inc. that provides voice, video, data, and Internet telecommunications and professional services to businesses, consumers, and government agen ...
,
:
:Project Offices is the name sometimes used to refer to several structurally dependable facilities maintained by the ATT Corporation in the Mid-Atlantic states since the mid-th century to house an ongoing, non-public, company project. AT&T began constructing Project Offices in the . Since the inception of the Project Offices program, the company has chosen not to disclose the exact nature of business conducted at Project Offices. However, it has described them as ''central facilities''.
::* Pittsboro, North Carolina
North Carolina () is a state in the Southeastern region of the United States. The state is the 28th largest and 9th-most populous of the United States. It is bordered by Virginia to the north, the Atlantic Ocean to the east, Georgia a ...
::* Buckingham, Virginia
Virginia, officially the Commonwealth of Virginia, is a state in the Mid-Atlantic and Southeastern regions of the United States, between the East Coast of the United States, Atlantic Coast and the Appalachian Mountains. The geography an ...
::* Charlottesville, Virginia
Virginia, officially the Commonwealth of Virginia, is a state in the Mid-Atlantic and Southeastern regions of the United States, between the East Coast of the United States, Atlantic Coast and the Appalachian Mountains. The geography an ...
::* Leesburg, Virginia
Virginia, officially the Commonwealth of Virginia, is a state in the Mid-Atlantic and Southeastern regions of the United States, between the East Coast of the United States, Atlantic Coast and the Appalachian Mountains. The geography an ...
::* Hagerstown, Maryland
Maryland ( ) is a U.S. state, state in the Mid-Atlantic (United States), Mid-Atlantic region of the United States. It shares borders with Virginia, West Virginia, and the District of Columbia to its south and west; Pennsylvania to its north; ...
;Texas Towers - Air defence radars,
:The Texas Towers were a set of three radar
Radar is a detection system that uses radio waves to determine the distance ('' ranging''), angle, and radial velocity of objects relative to the site. It can be used to detect aircraft, ships, spacecraft, guided missiles, motor vehicles, w ...
facilities off the eastern seaboard of the United States
The United States of America (U.S.A. or USA), commonly known as the United States (U.S. or US) or America, is a country primarily located in North America. It consists of 50 U.S. state, states, a Washington, D.C., federal district, five ma ...
which were used for surveillance by the United States Air Force
The United States Air Force (USAF) is the air service branch of the United States Armed Forces, and is one of the eight uniformed services of the United States. Originally created on 1 August 1907, as a part of the United States Army S ...
during the Cold War. Modeled on the offshore oil drilling platform
An oil platform (or oil rig, offshore platform, oil production platform, and similar terms) is a large structure with facilities to extract and process petroleum and natural gas that lie in rock formations beneath the seabed. Many oil platfor ...
s first employed off the Texas
Texas (, ; Spanish language, Spanish: ''Texas'', ''Tejas'') is a state in the South Central United States, South Central region of the United States. At 268,596 square miles (695,662 km2), and with more than 29.1 million residents in 2 ...
coast, they were in operation from 1958 to 1963.
:
; Mid Canada Line,
:A series of five stations (070, 060, 050, 415, 410) in Ontario
Ontario ( ; ) is one of the thirteen provinces and territories of Canada.Ontario is located in the geographic eastern half of Canada, but it has historically and politically been considered to be part of Central Canada. Located in Central C ...
and Quebec
Quebec ( ; )According to the Government of Canada, Canadian government, ''Québec'' (with the acute accent) is the official name in Canadian French and ''Quebec'' (without the accent) is the province's official name in Canadian English is ...
around the lower Hudson Bay. A series of six stations were built in Labrador and Quebec between Goose Bay and Sept-Îles between 1957–1958.
; Pinetree Line, Pole Vault,
: Pole Vault was series of fourteen stations providing communications for Eastern seaboard radar stations of the US/Canadian Pinetree line, running from N-31 Frobisher Bay, Baffin Island to N-22 St. John's, Newfoundland.
; White Alice/ DEW Line/ DEW Training ( Cold War era), /
:A former military and civil communications network with eighty stations stretching up the western seaboard from Port Hardy, Vancouver Island north to Barter Island
Barter Island is an island located on the Arctic coast of the U.S. state of Alaska, east of Arey Island in the Beaufort Sea. It is about four miles (6 km) long and about two miles (3 km) wide at its widest point.
Until the late 19th ...
(BAR), west to Shemya, Alaska
Shemya or Simiya ( ale, Samiyax̂) is a small island in the Semichi Islands group of the Near Islands chain in the Aleutian Islands archipelago southwest of Alaska, at . It has a land area of , and is about southwest of Anchorage, Alaska. It ...
(SYA) in the Aleutian Islands
The Aleutian Islands ( ; ; ale, Unangam Tanangin, "land of the Aleuts"; possibly from the Chukchi ''aliat'', or "island")—also called the Aleut Islands, Aleutic Islands, or, before 1867, the Catherine Archipelago—are a chain of 14 main, ...
(just a few hundred miles from the Soviet Union
The Soviet Union,. officially the Union of Soviet Socialist Republics. (USSR),. was a List of former transcontinental countries#Since 1700, transcontinental country that spanned much of Eurasia from 1922 to 1991. A flagship communist state, ...
) and east across arctic Canada
Canada is a country in North America. Its ten provinces and three territories extend from the Atlantic Ocean to the Pacific Ocean and northward into the Arctic Ocean, covering over , making it the world's second-largest country by tota ...
to Greenland
Greenland ( kl, Kalaallit Nunaat, ; da, Grønland, ) is an island country in North America that is part of the Kingdom of Denmark. It is located between the Arctic and Atlantic oceans, east of the Canadian Arctic Archipelago. Greenland is ...
. Note that not all station were troposcatter, but many were. It also included a training facility for White Alice/DEW line tropo-scatter network located between Pecatonica, Illinois to Streator, Illinois
Streator is a city in LaSalle and Livingston counties in the U.S. state of Illinois. The city is situated on the Vermilion River approximately southwest of Chicago in the prairie and farm land of north-central Illinois. As of the 2020 cens ...
.
; DEW Line (Post Cold War era), /
:Several tropo-scatter networks providing communications for the extensive air-defence radar chain in the far north of Canada and the US.
; North Atlantic Radio System (NARS),
:NATO air-defence network stretching from RAF Fylingdales, via Mormond Hill, UK, Sornfelli
Sornfelli is a mountain plateau on the island of Streymoy in the Faroe Islands about 12 km from the capital Tórshavn (20 km by road). It is the site of a military station at 725m above sea level (asl). The Sornfelli Meteorological Stat ...
(Faroe Islands
The Faroe Islands ( ), or simply the Faroes ( fo, Føroyar ; da, Færøerne ), are a North Atlantic archipelago, island group and an autonomous territory of the Danish Realm, Kingdom of Denmark.
They are located north-northwest of Scotlan ...
), Höfn, Iceland to Keflavik DYE-5, Rockville.
;European Tropospheric Scatter - Army (ET-A),
:A US Army network from RAF Fylingdales to a network in Germany
Germany, officially the Federal Republic of Germany (FRG),, is a country in Central Europe. It is the most populous member state of the European Union. Germany lies between the Baltic and North Sea to the north and the Alps to the sou ...
and a single station in France (Maison Fort
Maison (French for "house") may refer to:
People
* Edna Maison (1892–1946), American silent-film actress
* Jérémy Maison (born 1993), French cyclist
* Leonard Maison, New York state senator 1834–1837
* Nicolas Joseph Maison (1771–1840), Ma ...
). The network became active on 1966.
;486L Mediterranean Communications System (MEDCOM),
: A network covering the Europe
Europe is a large peninsula conventionally considered a continent in its own right because of its great physical size and the weight of its history and traditions. Europe is also considered a subcontinent of Eurasia and it is located enti ...
an coast of the Mediterranean Sea
The Mediterranean Sea is a sea connected to the Atlantic Ocean, surrounded by the Mediterranean Basin and almost completely enclosed by land: on the north by Western and Southern Europe and Anatolia, on the south by North Africa, and on the ...
from San Pablo, Spain in the west to Incirlik Air Base
Incirlik Air Base ( tr, İncirlik Hava Üssü) is a Turkish air base of slightly more than 3320 ac (1335 ha), located in the İncirlik quarter of the city of Adana, Turkey. The base is within an urban area of 1.7 million people, east of ...
, Turkey
Turkey ( tr, Türkiye ), officially the Republic of Türkiye ( tr, Türkiye Cumhuriyeti, links=no ), is a list of transcontinental countries, transcontinental country located mainly on the Anatolia, Anatolian Peninsula in Western Asia, with ...
in the East, with headquarters at Ringstead in Dorset
Dorset ( ; archaically: Dorsetshire , ) is a county in South West England on the English Channel coast. The ceremonial county comprises the unitary authority areas of Bournemouth, Christchurch and Poole and Dorset. Covering an area of ...
, England
England is a country that is part of the United Kingdom. It shares land borders with Wales to its west and Scotland to its north. The Irish Sea lies northwest and the Celtic Sea to the southwest. It is separated from continental Europe ...
. Commissioned by the US Air Force in .
;Royal Air Force
The Royal Air Force (RAF) is the United Kingdom's air and space force. It was formed towards the end of the First World War on 1 April 1918, becoming the first independent air force in the world, by regrouping the Royal Flying Corps (RFC) an ...
,
:Communications to British Forces Germany
British Forces Germany (''BFG'') was the generic name for the three services of the British Armed Forces, made up of service personnel, UK Civil Servants, and dependents (family members), based in Germany. It was established following the Second ...
, running from Swingate
Swingate is a village near Dover in Kent, England. The population of the village is included in the civil parish of Sutton
Sutton (''south settlement'' or ''south town'' in Old English) may refer to:
Places
United Kingdom
England
In alphabet ...
in Kent
Kent is a county in South East England and one of the home counties. It borders Greater London to the north-west, Surrey to the west and East Sussex to the south-west, and Essex to the north across the estuary of the River Thames; it faces ...
to Lammersdorf in Germany
Germany, officially the Federal Republic of Germany (FRG),, is a country in Central Europe. It is the most populous member state of the European Union. Germany lies between the Baltic and North Sea to the north and the Alps to the sou ...
.
; Troposphären-Nachrichtensystem Bars, Warsaw Pact
The Warsaw Pact (WP) or Treaty of Warsaw, formally the Treaty of Friendship, Cooperation and Mutual Assistance, was a collective defense treaty signed in Warsaw, Poland, between the Soviet Union and seven other Eastern Bloc socialist republi ...
 :A Warsaw Pact tropo-scatter network stretching from near
:A Warsaw Pact tropo-scatter network stretching from near Rostok
Rostock (), officially the Hanseatic and University City of Rostock (german: link=no, Hanse- und Universitätsstadt Rostock), is the largest city in the German state of Mecklenburg-Vorpommern and lies in the Mecklenburgian part of the state, c ...
in the DDR (Deutsches Demokratisches Republik), Czechoslovakia
, rue, Чеськословеньско, , yi, טשעכאסלאוואקיי,
, common_name = Czechoslovakia
, life_span = 1918–19391945–1992
, p1 = Austria-Hungary
, image_p1 ...
, Hungary
Hungary ( hu, Magyarország ) is a landlocked country in Central Europe. Spanning of the Carpathian Basin, it is bordered by Slovakia to the north, Ukraine to the northeast, Romania to the east and southeast, Serbia to the south, Croa ...
, Poland
Poland, officially the Republic of Poland, , is a country in Central Europe. Poland is divided into Voivodeships of Poland, sixteen voivodeships and is the fifth most populous member state of the European Union (EU), with over 38 mill ...
, Byelorussia USSR, Ukraine
Ukraine ( uk, Україна, Ukraïna, ) is a country in Eastern Europe. It is the second-largest European country after Russia, which it borders to the east and northeast. Ukraine covers approximately . Prior to the ongoing Russian invas ...
USSR and Bulgaria
Bulgaria (; bg, България, Bǎlgariya), officially the Republic of Bulgaria,, ) is a country in Southeast Europe. It is situated on the eastern flank of the Balkans, and is bordered by Romania to the north, Serbia and North Mac ...
.
;TRRL SEVER,
:A Soviet network stretching across the USSR
The Soviet Union,. officially the Union of Soviet Socialist Republics. (USSR),. was a transcontinental country that spanned much of Eurasia from 1922 to 1991. A flagship communist state, it was nominally a federal union of fifteen nation ...
.
; -  :A single section from
:A single section from Srinigar
Srinagar (English: , ) is the largest city and the summer capital of Jammu and Kashmir, India. It lies in the Kashmir Valley on the banks of the Jhelum River, a tributary of the Indus, and Dal and Anchar lakes. The city is known for its natur ...
, Kashmir, India to Dangara, Tajikistan
Tajikistan (, ; tg, Тоҷикистон, Tojikiston; russian: Таджикистан, Tadzhikistan), officially the Republic of Tajikistan ( tg, Ҷумҳурии Тоҷикистон, Jumhurii Tojikiston), is a landlocked country in Centr ...
, USSR.
;Indian Air Force
The Indian Air Force (IAF) is the air arm of the Indian Armed Forces. Its complement of personnel and aircraft assets ranks third amongst the air forces of the world. Its primary mission is to secure Indian airspace and to conduct aerial w ...
,
:Part of an Air Defence Network covering major air bases, radar installations and missile sites in Northern and central India. The network is being phased out to be replaced with more modern fiber-optic based communication systems.
;Peace Ruby, Spellout, Peace Net,
:An air-defence network set up by the United States
The United States of America (U.S.A. or USA), commonly known as the United States (U.S. or US) or America, is a country primarily located in North America. It consists of 50 U.S. state, states, a Washington, D.C., federal district, five ma ...
prior to the 1979 Islamic Revolution
The Iranian Revolution ( fa, انقلاب ایران, Enqelâb-e Irân, ), also known as the Islamic Revolution ( fa, انقلاب اسلامی, Enqelâb-e Eslâmī), was a series of events that culminated in the overthrow of the Pahlavi dynas ...
. ''Spellout'' built a radar and communications network in the north of Iran. ''PeaceRuby'' built another air-defence network in the south and ''PeaceNet'' integrated the two networks.
; -
:A tropo-scatter system linking Al Manamah, Bahrain
Bahrain ( ; ; ar, البحرين, al-Bahrayn, locally ), officially the Kingdom of Bahrain, ' is an island country in Western Asia. It is situated on the Persian Gulf, and comprises a small archipelago made up of 50 natural islands and an ...
to Dubai
Dubai (, ; ar, دبي, translit=Dubayy, , ) is the most populous city in the United Arab Emirates (UAE) and the capital of the Emirate of Dubai, the most populated of the 7 emirates of the United Arab Emirates.The Government and Politics ...
, United Arab Emirates
The United Arab Emirates (UAE; ar, اَلْإِمَارَات الْعَرَبِيَة الْمُتَحِدَة ), or simply the Emirates ( ar, الِْإمَارَات ), is a country in Western Asia ( The Middle East). It is located at ...
.
; Royal Air Force of Oman,
:A tropo-scatter communications system providing military comms to the former SOAF - Sultan of Oman's Air Force, (now RAFO - Royal Air Force of Oman), across the Sultanate of Oman.
;Royal Saudi Air Force,
:A Royal Saudi Air Force tropo-scatter network linking major airbases and population centres in Saudi Arabia.
;Yemen,
:A single system linking Sana'a with Sa'dah.
;BACK PORCH and Integrated Wideband Communications System (IWCS),
:Two networks run by the United States
The United States of America (U.S.A. or USA), commonly known as the United States (U.S. or US) or America, is a country primarily located in North America. It consists of 50 U.S. state, states, a Washington, D.C., federal district, five ma ...
linking military bases in Thailand and South Vietnam. Stations were located at Bangkok, Ubon Royal Thai Air Force Base, Pleiku, Nha Trang, Vung Chua mountain () Quy Nhon, Monkey Mountain Facility Da Nang, Phu Bai Combat Base, Pr Line () near Da Lat, Hon Cong mountain An Khê, Phu Lam () Saigon, VC Hill () Vũng Tàu and Cần Thơ.
;Phil-Tai-Oki,
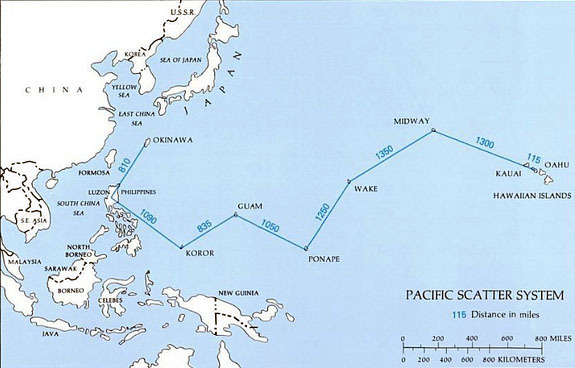
:A system linking the Taiwan with the Philippines and Okinawa.
; Cable & Wireless plc, Cable & Wireless Caribbean network
:A troposcatter link was established by Cable & Wireless in 1960, linking Barbados with Port of Spain, Trinidad. The network was extended further south to Georgetown, Guyana in 1965.
;Japanese Troposcatter Networks,
:Two networks linking Japanese islands from North to South.
Tactical Troposcatter Communication systems
As well as the permanent networks detailed above, there have been many tactical transportable systems produced by several countries: ;Soviet / Russian Troposcatter Systems :MNIRTI R-423-1 Brig-1/R-423-2A Brig-2A/R-423-1KF :MNIRTI R-444 Eshelon / R-444-7,5 Eshelon D :MNIRTI R-420 Atlet-D :NIRTI R-417 Baget/R-417S Baget S :NPP Radiosvyaz R-412 A/B/F/S TORF :MNIRTI R-410/R-410-5,5/R-410-7,5 Atlet / Albatros :MNIRTI R-408/R-408M Baklan ;People's Republic of China (PRoC), People's Liberation Army (PLA) Troposcatter Systems :CETC TS-504 Troposcatter Communication System :CETC TS-510/GS-510 Troposcatter Communication System ;Western Troposcatter Systems :AN/TRC-97 Troposcatter Communication System :AN/TRC-170 Tropospheric Scatter Microwave Radio Terminal :AN/GRC-201 Troposcatter Communication System The U.S. Army and Air Force use tactical tropospheric scatter systems developed by Raytheon for long haul communications. The systems come in two configurations, the original "heavy tropo", and a newer "light tropo" configuration exist. The systems provide four Multiplexing, multiplexed group channels and trunk encryption, and 16 or 32 local analog phone extensions. The U.S. Marine Corps also uses the same device, albeit an older version.
The U.S. Army and Air Force use tactical tropospheric scatter systems developed by Raytheon for long haul communications. The systems come in two configurations, the original "heavy tropo", and a newer "light tropo" configuration exist. The systems provide four Multiplexing, multiplexed group channels and trunk encryption, and 16 or 32 local analog phone extensions. The U.S. Marine Corps also uses the same device, albeit an older version.
See also
* Radio propagation * Non-line-of-sight propagation * Microwave * ACE High - Cold war era NATO European troposcatter network * White Alice Communications System - Cold war era Alaskan tropospheric communications link * List of White Alice Communications System sites * TV-FM DX * Distant Early Warning LineReferences
Citations
Bibliography
*External links
Russian tropospheric relay communication network
Tropospheric Scatter Communications - the essentials
* {{Authority control Radio frequency propagation Atmospheric optical phenomena