trans-Saharan slave trade on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 The trans-Saharan slave trade, also known as the Arab slave trade, was a
The trans-Saharan slave trade, also known as the Arab slave trade, was a
 Paul Lovejoy estimates that around 6 million black slaves were transported across the Sahara between the years 650 AD and 1500 AD. The trans-Saharan slave trade, established in Antiquity, continued during the
Paul Lovejoy estimates that around 6 million black slaves were transported across the Sahara between the years 650 AD and 1500 AD. The trans-Saharan slave trade, established in Antiquity, continued during the  Passage through the Sahara required the expertise of ethnic groups whose lifestyles were uniquely adapted for survival in scorching, arid environments, namely the local Berber tribes and the foreign
Passage through the Sahara required the expertise of ethnic groups whose lifestyles were uniquely adapted for survival in scorching, arid environments, namely the local Berber tribes and the foreign 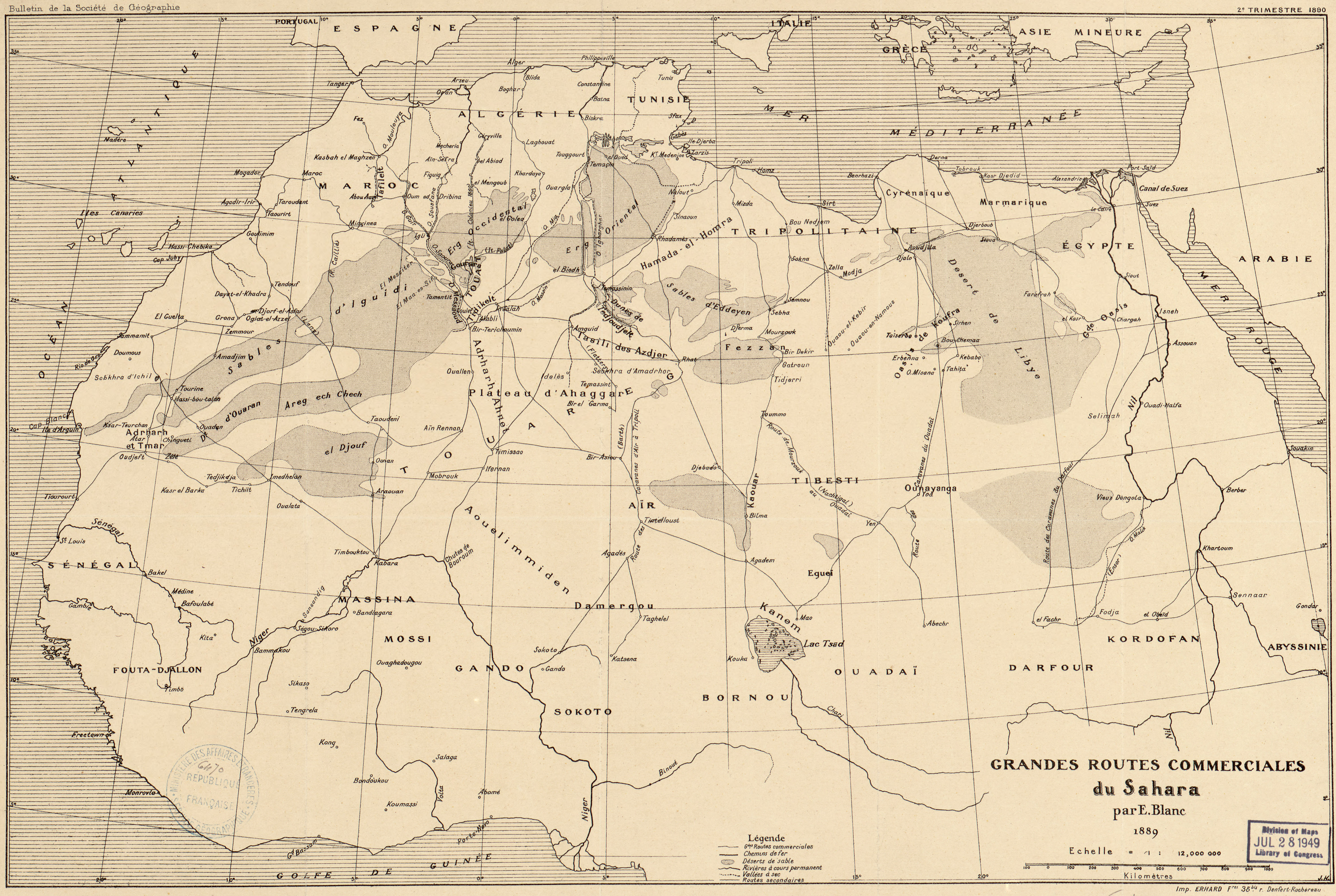

 In Central Africa, during the 16th and 17th centuries, slave traders continued to raid the region as part of the expansion of the Saharan and Nile River slave routes. It is estimated that, in the 17th and 18th centuries, 1.4 million slaves were forced to make the trek through the Sahara Captives were enslaved and shipped to the Mediterranean coast, Europe, Arabia, the Western Hemisphere, or to the slave ports and factories along the West and North Africa coasts or South along the Ubanqui and Congo rivers.Alistair Boddy-Evans
In Central Africa, during the 16th and 17th centuries, slave traders continued to raid the region as part of the expansion of the Saharan and Nile River slave routes. It is estimated that, in the 17th and 18th centuries, 1.4 million slaves were forced to make the trek through the Sahara Captives were enslaved and shipped to the Mediterranean coast, Europe, Arabia, the Western Hemisphere, or to the slave ports and factories along the West and North Africa coasts or South along the Ubanqui and Congo rivers.Alistair Boddy-Evans
Central Africa Republic Timeline – Part 1: From Prehistory to Independence (13 August 1960), A Chronology of Key Events in Central Africa Republic
. About.com 1.2 million slaves are estimated to have been sent through the Sahara in the 19th century. In the 1830s, a period when slave trade flourished,
"Tripoli and Tripolitania: Conflict and Cohesion during the Period of the Barbary Corsairs (1551–1850)"
''Transactions of the Institute of British Geographers'', New Series, Vol. 3, No. 3, Settlement and Conflict in the Mediterranean World. (1978), pp. 285-294. Even though the slave trade was officially abolished in Tripoli by the Firman of 1857, this law was never enforced, and continued in practice at least until the 1890s.Lisa Anderson
">"Nineteenth-Century Reform in Ottoman Libya"
International Journal of Middle East Studies, Vol. 16, No. 3. (Aug., 1984), pp. 325-348. In Tripoli, G. F. Lyon recorded that from 4,000 to 5,000 slaves were processed annually with raids to areas like Kanem-Bornu providing sources of captives. As a witness to the behavior of the slave dealers, Lyon described their behavior in Libya: Other 19th-century European explorers recorded their perilous experiences traveling through the Saharan Desert alongside slave caravans. The explorer
"Tripoli"
''The Geographical Journal'', Vol. 38, No. 5. (Nov., 1911), pp. 487–494. At
The Garamantes and Trans-Saharan Enterprise in Classical Times
{{Africa in topic, Slavery in History of the Sahara Trade routes History of North Africa African slave trade Slavery in Asia Slavery in Morocco Slavery in Algeria Slavery in Tunisia Slavery in Libya Slavery in Egypt Slavery in Saudi Arabia Anti-black racism in Africa Anti-black racism in Asia Forced migration Genocides in Asia History of slavery in the Muslim world Trans-Saharan slave trade Death marches Genocide of indigenous peoples in Africa
 The trans-Saharan slave trade, also known as the Arab slave trade, was a
The trans-Saharan slave trade, also known as the Arab slave trade, was a slave trade Slave trade may refer to:
* History of slavery - overview of slavery
It may also refer to slave trades in specific countries, areas:
* Al-Andalus slave trade
* Atlantic slave trade
** Brazilian slave trade
** Bristol slave trade
** Danish sl ...
in which slaves were mainly transported across the Sahara
The Sahara (, ) is a desert spanning across North Africa. With an area of , it is the largest hot desert in the world and the list of deserts by area, third-largest desert overall, smaller only than the deserts of Antarctica and the northern Ar ...
. Most were moved from sub-Saharan Africa
Sub-Saharan Africa is the area and regions of the continent of Africa that lie south of the Sahara. These include Central Africa, East Africa, Southern Africa, and West Africa. Geopolitically, in addition to the list of sovereign states and ...
to North Africa
North Africa (sometimes Northern Africa) is a region encompassing the northern portion of the African continent. There is no singularly accepted scope for the region. However, it is sometimes defined as stretching from the Atlantic shores of t ...
to be sold to Mediterranean and Middle Eastern civilizations; a small percentage went in the other direction.
Estimates of the total number of black
Black is a color that results from the absence or complete absorption of visible light. It is an achromatic color, without chroma, like white and grey. It is often used symbolically or figuratively to represent darkness.Eva Heller, ''P ...
slaves moved from sub-Saharan Africa to the Arab world
The Arab world ( '), formally the Arab homeland ( '), also known as the Arab nation ( '), the Arabsphere, or the Arab states, comprises a large group of countries, mainly located in West Asia and North Africa. While the majority of people in ...
range from 6 to 10 million, and the trans-Saharan trade routes conveyed a significant number of this total, with one estimate tallying around 7.2 million slaves crossing the Sahara from the mid-7th century until the 20th century when it was abolished. The Arabs
Arabs (, , ; , , ) are an ethnic group mainly inhabiting the Arab world in West Asia and North Africa. A significant Arab diaspora is present in various parts of the world.
Arabs have been in the Fertile Crescent for thousands of yea ...
managed and operated the trans-Saharan slave trade, although Berbers
Berbers, or the Berber peoples, also known as Amazigh or Imazighen, are a diverse grouping of distinct ethnic groups indigenous to North Africa who predate the arrival of Arab migrations to the Maghreb, Arabs in the Maghreb. Their main connec ...
were also actively involved.
Alongside sub-Saharan Africans, Turks, Iranians, Europeans
Europeans are the focus of European ethnology, the field of anthropology related to the various ethnic groups that reside in the states of Europe. Groups may be defined by common ancestry, language, faith, historical continuity, etc. There are ...
and Berbers were among the people traded by the Arabs, with the trade being practised throughout the Arab world, primarily in Western Asia
West Asia (also called Western Asia or Southwest Asia) is the westernmost region of Asia. As defined by most academics, UN bodies and other institutions, the subregion consists of Anatolia, the Arabian Peninsula, Iran, Mesopotamia, the Armenian ...
, North Africa, East Africa, and Europe.
Early trans-Saharan slave trade
Records of slave trading and transportation in the Sahara date as far back as the 3rd millennium BC during the reign of the Egyptian kingSneferu
Sneferu or Soris (c. 2600 BC) was an ancient Egyptian monarch and the first pharaoh of the Fourth Dynasty of Egypt, during the earlier half of the Old Kingdom period (26th century BC). He introduced major innovations in the design and constructio ...
who crossed the fourth cataract
A cataract is a cloudy area in the lens (anatomy), lens of the eye that leads to a visual impairment, decrease in vision of the eye. Cataracts often develop slowly and can affect one or both eyes. Symptoms may include faded colours, blurry or ...
of the Nile
The Nile (also known as the Nile River or River Nile) is a major north-flowing river in northeastern Africa. It flows into the Mediterranean Sea. The Nile is the longest river in Africa. It has historically been considered the List of river sy ...
into what is today modern Sudan
Sudan, officially the Republic of the Sudan, is a country in Northeast Africa. It borders the Central African Republic to the southwest, Chad to the west, Libya to the northwest, Egypt to the north, the Red Sea to the east, Eritrea and Ethiopi ...
to capture slaves and send them north. These raids for prisoners of war, who subsequently became slaves, were a regular occurrence in the ancient Nile Valley and Africa. During times of conquest and after winning battles, the ancient Nubians
Nubians () ( Nobiin: ''Nobī,'' ) are a Nilo-Saharan speaking ethnic group indigenous to the region which is now northern Sudan and southern Egypt. They originate from the early inhabitants of the central Nile valley, believed to be one of th ...
were taken as slaves by the ancient Egyptians.
The Garamantes
The Garamantes (; ) were ancient peoples, who may have descended from Berbers, Berber tribes, Toubous, Toubou tribes, and Saharan Pastoral period, pastoralists that settled in the Fezzan region by at least 1000 BC and established a civilization t ...
relied heavily on slave labor from sub-Saharan Africa. They used slaves in their own communities to construct and maintain underground irrigation systems known to Berbers
Berbers, or the Berber peoples, also known as Amazigh or Imazighen, are a diverse grouping of distinct ethnic groups indigenous to North Africa who predate the arrival of Arab migrations to the Maghreb, Arabs in the Maghreb. Their main connec ...
as '' foggara''. Ancient Greek
Ancient Greek (, ; ) includes the forms of the Greek language used in ancient Greece and the classical antiquity, ancient world from around 1500 BC to 300 BC. It is often roughly divided into the following periods: Mycenaean Greek (), Greek ...
historian Herodotus
Herodotus (; BC) was a Greek historian and geographer from the Greek city of Halicarnassus (now Bodrum, Turkey), under Persian control in the 5th century BC, and a later citizen of Thurii in modern Calabria, Italy. He wrote the '' Histori ...
recorded in the 5th century BC that the Garamantes enslaved cave-dwelling Ethiopians, known as Troglodytae
The Troglodytae (, ''Trōglodytai''), or Troglodyti (literally "cave goers"), were people mentioned in various locations by many ancient Greek and Roman geographers and historians, including Herodotus (5th century BCE), Agatharchides (2nd centur ...
, chasing them with chariots.
In the early Roman Empire
The Roman Empire ruled the Mediterranean and much of Europe, Western Asia and North Africa. The Roman people, Romans conquered most of this during the Roman Republic, Republic, and it was ruled by emperors following Octavian's assumption of ...
, the city of Lepcis established a slave market
A slave market is a place where slaves are bought and sold. These markets are a key phenomenon in the history of slavery.
Asia
Central Asia
Since antiquity, cities along the Silk road of Central Asia, had been centers of slave trade. In ...
to buy and sell slaves from the Bantu African interior. In the 5th century AD, Roman Carthage
Roman Carthage was an important city in ancient Rome, located in modern-day Tunisia. Approximately 100 years after the destruction of Punic Carthage in 146 BC, a new city of the same name (Latin '' Carthāgō'') was built on the same land by t ...
was trading in black slaves brought across the Sahara. The empire imposed customs tax on the trade of slaves. Black slaves seem to have been valued as household slaves for their exotic appearance. Some historians argue that the scale of slave trade in this period may have been higher than medieval times due to the high demand for slaves in the Roman Empire. However the slave trade through the Sahara in antiquity may have been small and rare as Saharan trade didn't reach large dimensions until the Arabs
Arabs (, , ; , , ) are an ethnic group mainly inhabiting the Arab world in West Asia and North Africa. A significant Arab diaspora is present in various parts of the world.
Arabs have been in the Fertile Crescent for thousands of yea ...
and Berbers introduced large numbers of camels into the desert.
The Ancient Garamantian caravan trade route between the coast of Tripolitania across the Sahara to Lake Chad
Lake Chad (, Kanuri language, Kanuri: ''Sádǝ'', ) is an endorheic freshwater lake located at the junction of four countries: Nigeria, Niger, Chad, and Cameroon, in western and central Africa respectively, with a catchment area in excess of . ...
transported foremost circus animals, gold, cabochon
A cabochon (; ) is a gemstone that has been shaped and polished, as opposed to faceted. The resulting form is usually a convex (rounded) obverse with a flat reverse. Cabochon was the default method of preparing gemstones before gemstone cuttin ...
and raw material for food processing and perfume manufacture, but also slaves; the African slave trade was however likely limited prior to the Islamic period, and African slaves appeared to have been few in the Roman Empire, where they were viewed as exotic luxury slaves.
Trans-Saharan slave trade in the Middle Ages
 Paul Lovejoy estimates that around 6 million black slaves were transported across the Sahara between the years 650 AD and 1500 AD. The trans-Saharan slave trade, established in Antiquity, continued during the
Paul Lovejoy estimates that around 6 million black slaves were transported across the Sahara between the years 650 AD and 1500 AD. The trans-Saharan slave trade, established in Antiquity, continued during the Middle Ages
In the history of Europe, the Middle Ages or medieval period lasted approximately from the 5th to the late 15th centuries, similarly to the post-classical period of global history. It began with the fall of the Western Roman Empire and ...
. Following the early 8th-century conquest of North Africa, Arabs, Berbers, and other ethnic groups ventured into Sub-Saharan Africa
Sub-Saharan Africa is the area and regions of the continent of Africa that lie south of the Sahara. These include Central Africa, East Africa, Southern Africa, and West Africa. Geopolitically, in addition to the list of sovereign states and ...
first along the Nile Valley
The Nile (also known as the Nile River or River Nile) is a major north-flowing river in northeastern Africa. It flows into the Mediterranean Sea. The Nile is the longest river in Africa. It has historically been considered the longest river i ...
towards Nubia
Nubia (, Nobiin language, Nobiin: , ) is a region along the Nile river encompassing the area between the confluence of the Blue Nile, Blue and White Nile, White Niles (in Khartoum in central Sudan), and the Cataracts of the Nile, first cataract ...
, and also across the Sahara
The Sahara (, ) is a desert spanning across North Africa. With an area of , it is the largest hot desert in the world and the list of deserts by area, third-largest desert overall, smaller only than the deserts of Antarctica and the northern Ar ...
towards West Africa. They were interested in the trans-Saharan trade, especially in slaves, as there was a constant demand for slaves in the eastern Arab nations and Constantinople
Constantinople (#Names of Constantinople, see other names) was a historical city located on the Bosporus that served as the capital of the Roman Empire, Roman, Byzantine Empire, Byzantine, Latin Empire, Latin, and Ottoman Empire, Ottoman empire ...
. The Muslim slave traders distinguished themselves from the peoples on the other side of the Sahara, referring to these African populations as ''Zanj'' or ''Sudan'' meaning "black".
Arabs would routinely acquire slaves through violent raiding, followed by capturing them and sending them on dangerous forced marches across the Sahara to slave markets where they would be treated as chattel i.e. as personal property
Personal property is property that is movable. In common law systems, personal property may also be called chattels or personalty. In civil law (legal system), civil law systems, personal property is often called movable property or movables—a ...
that can be bought and sold. In North Africa, the main slave markets were in Morocco
Morocco, officially the Kingdom of Morocco, is a country in the Maghreb region of North Africa. It has coastlines on the Mediterranean Sea to the north and the Atlantic Ocean to the west, and has land borders with Algeria to Algeria–Morocc ...
, Algiers
Algiers is the capital city of Algeria as well as the capital of the Algiers Province; it extends over many Communes of Algeria, communes without having its own separate governing body. With 2,988,145 residents in 2008Census 14 April 2008: Offi ...
, Tripoli and Cairo
Cairo ( ; , ) is the Capital city, capital and largest city of Egypt and the Cairo Governorate, being home to more than 10 million people. It is also part of the List of urban agglomerations in Africa, largest urban agglomeration in Africa, L ...
. Sales were held in public places such as souks. During the era of the Fatimid Caliphate
The Fatimid Caliphate (; ), also known as the Fatimid Empire, was a caliphate extant from the tenth to the twelfth centuries CE under the rule of the Fatimids, an Isma'ili Shi'a dynasty. Spanning a large area of North Africa and West Asia, i ...
(909–1171), the majority of slaves were Europeans taken along European beaches during conflicts.
Aside from raiding, slaves could also be obtained by purchasing them from local black rulers. The 9th century Arab historian Ya'qubi
ʾAbū al-ʿAbbās ʾAḥmad bin ʾAbī Yaʿqūb bin Ǧaʿfar bin Wahb bin Waḍīḥ al-Yaʿqūbī (died 897/8), commonly referred to simply by his nisba al-Yaʿqūbī, was an Arab Muslim geographer.
Life
Ya'qubi was born in Baghdad to a fam ...
states:
Indeed, few Sub-Saharan African rulers would resist the slave trade, while many chiefs would become middlemen in the trafficking, rounding up members of nearby villages to be sold to visiting merchants. The 12th century Arab geographer al-Idrisi
Abu Abdullah Muhammad al-Idrisi al-Qurtubi al-Hasani as-Sabti, or simply al-Idrisi (; ; 1100–1165), was an Arab Muslim geographer and cartographer who served in the court of King Roger II at Palermo, Sicily. Muhammad al-Idrisi was born in C ...
noted that Sub-Saharan Africans would also participate in slave raiding stating that:
Al-Idrisi would also describe the different methods Muslim merchants would use to enslave blacks, recording that some would "steal the children of the Zanj using dates...lure them with dates and lead them from place to place, until they seize them, take them out of the country and transport them to their own countries". In 1353, the Berber explorer Ibn Battuta
Ibn Battuta (; 24 February 13041368/1369), was a Maghrebi traveller, explorer and scholar. Over a period of 30 years from 1325 to 1354, he visited much of Africa, the Middle East, Asia and the Iberian Peninsula. Near the end of his life, Ibn ...
would record accompanying a trade caravan to Morocco which carried 600 black female slaves who were to be used as domestic servants and concubines
Concubinage is an interpersonal and sexual relationship between two people in which the couple does not want to, or cannot, enter into a full marriage. Concubinage and marriage are often regarded as similar, but mutually exclusive.
During the e ...
. When Battuta visited the ancient African kingdom of Mali he recounted that the local inhabitants vied with each other in the number of slaves and servants they had, and was himself given a slave boy as a "hospitality gift."
The routes taken by slave caravans transporting slaves depended on their destination. Slaves headed to Egypt would be carried by boat down the Nile and slaves headed to Arabia would be sent to ports on the Red Sea
The Red Sea is a sea inlet of the Indian Ocean, lying between Africa and Asia. Its connection to the ocean is in the south, through the Bab-el-Mandeb Strait and the Gulf of Aden. To its north lie the Sinai Peninsula, the Gulf of Aqaba, and th ...
such as Suakin
Suakin or Sawakin (, Beja: ''Oosook'') is a port city in northeastern Sudan, on the west coast of the Red Sea. It was formerly the region's chief port, but is now secondary to Port Sudan, about north.
Suakin used to be considered the height ...
and Assab
Assab or Aseb (, ) is a port city in the Southern Red Sea Region of Eritrea. It is situated on the west coast of the Red Sea.
Languages spoken in Assab are predominantly Afar language, Afar, Tigrinya language, Tigrinya, and Arabic. After the Ita ...
. Slaves headed to North Africa would have to take the Saharan trade routes which had been in use since around 1000 BC. These include routes such as the ones from Tripoli–Ghadames
Ghadames or Ghadamis ( Ghadamsi: ⵄⴰⴷⴻⵎⴻⵙ / ''Ɛadēməs'' �adeːməs , ) is an oasis town in the Nalut District of the Tripolitania region in northwestern Libya.
Ghadamès, known as 'the pearl of the desert', stands in an oa ...
–Ghat
Ghat (), a term used in the Indian subcontinent, to refer to the series of steps leading down to a body of water or wharf, such as a bathing or cremation place along the banks of a river or pond, the Ghats in Varanasi, Dhobi Ghat or the Aap ...
– Hoggar–Gao
Gao (or Gawgaw/Kawkaw) is a city in Mali and the capital of the Gao Region. The city is located on the River Niger, east-southeast of Timbuktu on the left bank at the junction with the Tilemsi valley.
For much of its history Gao was an imp ...
connecting modern-day Libya to Nigeria, the Tripoli-Fezzan
Fezzan ( , ; ; ; ) is the southwestern region of modern Libya. It is largely desert, but broken by mountains, uplands, and dry river valleys (wadis) in the north, where oases enable ancient towns and villages to survive deep in the otherwise in ...
-Bornu route, connecting Libya to areas of what are today Chad
Chad, officially the Republic of Chad, is a landlocked country at the crossroads of North Africa, North and Central Africa. It is bordered by Libya to Chad–Libya border, the north, Sudan to Chad–Sudan border, the east, the Central Afric ...
, Niger
Niger, officially the Republic of the Niger, is a landlocked country in West Africa. It is a unitary state Geography of Niger#Political geography, bordered by Libya to the Libya–Niger border, north-east, Chad to the Chad–Niger border, east ...
, and Cameroon
Cameroon, officially the Republic of Cameroon, is a country in Central Africa. It shares boundaries with Nigeria to the west and north, Chad to the northeast, the Central African Republic to the east, and Equatorial Guinea, Gabon, and the R ...
, and the east–west route connecting Egypt to Ghana
Ghana, officially the Republic of Ghana, is a country in West Africa. It is situated along the Gulf of Guinea and the Atlantic Ocean to the south, and shares borders with Côte d’Ivoire to the west, Burkina Faso to the north, and Togo to t ...
, Mali
Mali, officially the Republic of Mali, is a landlocked country in West Africa. It is the List of African countries by area, eighth-largest country in Africa, with an area of over . The country is bordered to the north by Algeria, to the east b ...
, and Songhai. Kanem–Bornu– Zawila was another route to North Africa as the Kanem–Bornu Empire
The Kanem–Bornu Empire was an empire based around Lake Chad that once ruled areas which are now part of Nigeria, Niger, Cameroon, Libya, Algeria, Sudan, and Chad. The empire was sustained by the prosperous trans-Saharan trade and was one of the ...
in the eastern part of Niger
Niger, officially the Republic of the Niger, is a landlocked country in West Africa. It is a unitary state Geography of Niger#Political geography, bordered by Libya to the Libya–Niger border, north-east, Chad to the Chad–Niger border, east ...
was an active part of the trans-Saharan slave trade for centuries, and the trade formed the basis of the empire's prosperity.
 Passage through the Sahara required the expertise of ethnic groups whose lifestyles were uniquely adapted for survival in scorching, arid environments, namely the local Berber tribes and the foreign
Passage through the Sahara required the expertise of ethnic groups whose lifestyles were uniquely adapted for survival in scorching, arid environments, namely the local Berber tribes and the foreign Bedouins
The Bedouin, Beduin, or Bedu ( ; , singular ) are pastorally nomadic Arab tribes who have historically inhabited the desert regions in the Arabian Peninsula, North Africa, the Levant, and Mesopotamia (Iraq). The Bedouin originated in the Sy ...
from Arabia
The Arabian Peninsula (, , or , , ) or Arabia, is a peninsula in West Asia, situated north-east of Africa on the Arabian plate. At , comparable in size to India, the Arabian Peninsula is the largest peninsula in the world.
Geographically, the ...
. For example, the Tuareg
The Tuareg people (; also spelled Twareg or Touareg; endonym, depending on variety: ''Imuhaɣ'', ''Imušaɣ'', ''Imašeɣăn'' or ''Imajeɣăn'') are a large Berber ethnic group, traditionally nomadic pastoralists, who principally inhabit th ...
and others who are indigenous to Libya facilitated, taxed and partly organized the trade from the south along the trans-Saharan trade routes. Various nomadic peoples played critical roles as guards, guides, and camel drivers. As a result, they were granted autonomy and treated as allies by governments of North Africa. Oases were vital waystations for caravans and those such as Awjila
Awjila (Arabic: أوجلة; Latin: ''Augila'') is an oasis town in the Al Wahat District in the Cyrenaica region of northeastern Libya. Since classical times, it has been known as a place where high-quality dates are farmed. The oasis was ment ...
, Ghadames, and Kufra
Kufra () is a basinBertarelli (1929), p. 514. and oasis group in the Kufra District of southeastern Cyrenaica in Libya. At the end of the 19th century, Kufra became the centre and holy place of the Senussi order. It also played a minor role in ...
in Libya allowed both north–south and east–west travel. Even with expert help the passage could still prove deadly to merchants and slaves. Sometimes whole caravans of thousands of people could disappear without a trace.
The goods exchanged in the trans-Saharan slave trade varied. In the 10th century, the Muslim scholar Mutahhar ibn Tahir al-Maqdisi described the trade between the Islamic world and Sub-Saharan Africa as consisting of food and clothing being imported into Sub-Saharan Africa while slaves, gold, and coconuts were exported out of Sub-Saharan Africa. Later, the 16th century Andalusian writer Leo Africanus
Johannes Leo Africanus (born al-Ḥasan ibn Muḥammad ibn Aḥmad al-Wazzān al-Zayyātī al-Fasī, ; – ) was an Andalusi diplomat and author who is best known for his 1526 book '' Cosmographia et geographia de Affrica'', later publish ...
wrote that traders from Morocco would bring horses, European cloth, clothing, sugar, books, and brass vessels to Sudan in order to exchange them for slaves, civet
A civet () is a small, lean, mostly nocturnal mammal native to tropical Asia and Africa, especially the tropical forests. The term ''civet'' applies to over a dozen different species, mostly from the family Viverridae. Most of the species's div ...
s and gold. According to Africanus, the sultan
Sultan (; ', ) is a position with several historical meanings. Originally, it was an Arabic abstract noun meaning "strength", "authority", "rulership", derived from the verbal noun ', meaning "authority" or "power". Later, it came to be use ...
of Bornu would accept payment for slaves only in horses, with an exchange rate of up to twenty slaves for one horse.
The range of tasks given to slaves was varied and included servile labor utilized for "irrigation
Irrigation (also referred to as watering of plants) is the practice of applying controlled amounts of water to land to help grow crops, landscape plants, and lawns. Irrigation has been a key aspect of agriculture for over 5,000 years and has bee ...
, pastoralism
Pastoralism is a form of animal husbandry where domesticated animals (known as "livestock") are released onto large vegetated outdoor lands (pastures) for grazing, historically by nomadic people who moved around with their herds. The anim ...
, mining
Mining is the Resource extraction, extraction of valuable geological materials and minerals from the surface of the Earth. Mining is required to obtain most materials that cannot be grown through agriculture, agricultural processes, or feasib ...
, transport
Transport (in British English) or transportation (in American English) is the intentional Motion, movement of humans, animals, and cargo, goods from one location to another. Mode of transport, Modes of transport include aviation, air, land tr ...
, public works
Public works are a broad category of infrastructure projects, financed and procured by a government body for recreational, employment, and health and safety uses in the greater community. They include public buildings ( municipal buildings, ...
, proto-industry, and construction
Construction are processes involved in delivering buildings, infrastructure, industrial facilities, and associated activities through to the end of their life. It typically starts with planning, financing, and design that continues until the a ...
." In general black slaves were used as laborers, servants and eunuch
A eunuch ( , ) is a male who has been castration, castrated. Throughout history, castration often served a specific social function. The earliest records for intentional castration to produce eunuchs are from the Sumerian city of Lagash in the 2 ...
s. Some female slaves could be used for labor, but most would be used for domestic chores and concubinage. Eunuchs, who were around seven times more expensive than non-castrated males could be used as harem guards, administrators, tutor, secretaries, commercial agents, and even concubines. Due to strictures within Islamic law, slaves would not usually be castrated
Castration is any action, surgical, chemical, or otherwise, by which a male loses use of the testicles: the male gonad. Surgical castration is bilateral orchiectomy (excision of both testicles), while chemical castration uses pharmaceutical ...
within Muslim territory and therefore would be castrated before being sent across the Sahara. Sometimes slaves were castrated after purchase in North African slave markets. Conditions within the mining industry were notoriously harsh especially the salt mines of Basra
Basra () is a port city in Iraq, southern Iraq. It is the capital of the eponymous Basra Governorate, as well as the List of largest cities of Iraq, third largest city in Iraq overall, behind Baghdad and Mosul. Located near the Iran–Iraq bor ...
where tens of thousands of black slaves toiled in extremely miserable conditions living on insufficient amounts of food. This poor treatment led to the bloody Zanj Rebellion
The Zanj Rebellion ( ) was a major revolt against the Abbasid Caliphate, which took place from 869 until 883. Begun near the city of Basra in present-day southern Iraq and led by one Ali ibn Muhammad, the insurrection involved both enslaved and ...
or "black revolution". Ya'qubi records that both male and female slaves were employed in the copper mines of Upper Egypt
Upper Egypt ( ', shortened to , , locally: ) is the southern portion of Egypt and is composed of the Nile River valley south of the delta and the 30th parallel North. It thus consists of the entire Nile River valley from Cairo south to Lake N ...
. The Qarmatian Republic of eastern Arabia is said to have employed 30,000 blacks slaves to perform all difficult labor. Some black slaves served in the military forces of North Africa. For example, the Zirid dynasty
The Zirid dynasty (), Banu Ziri (), was a Sanhaja Berber dynasty from what is now Algeria which ruled the central Maghreb from 972 to 1014 and Ifriqiya (eastern Maghreb) from 972 to 1148.
Descendants of Ziri ibn Manad, a military leader of t ...
used black slaves imported from Sudan via Zawila.
In some instances, Christians
A Christian () is a person who follows or adheres to Christianity, a monotheistic Abrahamic religion based on the life and teachings of Jesus Christ. Christians form the largest religious community in the world. The words '' Christ'' and ''C ...
in Africa would acquiesce to Muslims' demands that they be provided with slaves. In 641 AD during the treaty known as the Baqt
The Baqt (or Bakt) (بقط) was a 7th-century treaty between the Christian state of Makuria and the new Muslim rulers of Egypt. Lasting almost seven hundred years, it is by some measures the longest-lasting treaty in history. The name comes ei ...
was signed establishing an agreement between the Nubian Christian state of Makuria
Makuria ( Old Nubian: , ''Dotawo''; ; ) was a medieval Nubian kingdom in what is today northern Sudan and southern Egypt. Its capital was Dongola (Old Nubian: ') in the fertile Dongola Reach, and the kingdom is sometimes known by the name of ...
and the new Muslim rulers of Egypt, in which the Nubians agreed to give Muslim traders more privileges of trade in addition to sending 442 slaves every year to Cairo as tribute. This treaty remained intact for 600 years all while the slave trade within Nubia continued unimpeded.
In the Muslim culture
Islamic cultures or Muslim cultures refers to the historic cultural practices that developed among the various peoples living in the Muslim world. These practices, while not always religious in nature, are generally influenced by aspects of Islam ...
of the Middle Ages, blackness became increasingly identified with slavery. This was justified by appeals to a specific interpretation of the biblical story of Curse of Ham that posited Ham
Ham is pork from a leg cut that has been preserved by wet or dry curing, with or without smoking."Bacon: Bacon and Ham Curing" in '' Chambers's Encyclopædia''. London: George Newnes, 1961, Vol. 2, p. 39. As a processed meat, the term '' ...
had been cursed by Noah
Noah (; , also Noach) appears as the last of the Antediluvian Patriarchs (Bible), patriarchs in the traditions of Abrahamic religions. His story appears in the Hebrew Bible (Book of Genesis, chapters 5–9), the Quran and Baháʼí literature, ...
in two ways, the first, the turning of his skin black, and the second, that his descendants would be doomed to slavery. Muslim slave traders would use this as a pretext to enslave blacks, including black Muslims. In the late 14th century, a black king of Bornu wrote a letter to the sultan of Egypt complaining of the continual slave raids perpetrated by Arab tribesmen, which were devastating his lands and resulting in the mass enslavement of the black Muslim population of the region. In Al-Andalus
Al-Andalus () was the Muslim-ruled area of the Iberian Peninsula. The name refers to the different Muslim states that controlled these territories at various times between 711 and 1492. At its greatest geographical extent, it occupied most o ...
, the area of medieval Iberia
The Iberian Peninsula ( ), also known as Iberia, is a peninsula in south-western Europe. Mostly separated from the rest of the European landmass by the Pyrenees, it includes the territories of peninsular Spain and Continental Portugal, compri ...
under Islamic control, black Muslims could be legally held as slaves in slavery in Al-Andalus. This all occurred despite the orthodox Muslim jurist position that no Muslim, regardless of race, could be enslaved. Even as late as the 19th century, many of the common people in Islamic society still believed that enslavement based on skin color, rather than based on religion, was approved by the religious laws of Islam.
In 1416, al-Maqrizi told how pilgrims coming from Takrur
Takrur, Tekrur or Tekrour ( 500 – c. 1456) was a state based in the Senegal River in modern day Senegal which was at its height in the 11th and 12th centuries, roughly parallel to the Ghana Empire. It lasted in some form into the 18th ...
(near the Senegal River
The Senegal River ( or "Senegal" - compound of the Serer term "Seen" or "Sene" or "Sen" (from Roog Seen, Supreme Deity in Serer religion) and "O Gal" (meaning "body of water")); , , , ) is a river in West Africa; much of its length mark ...
) brought 1,700 slaves with them to Mecca
Mecca, officially Makkah al-Mukarramah, is the capital of Mecca Province in the Hejaz region of western Saudi Arabia; it is the Holiest sites in Islam, holiest city in Islam. It is inland from Jeddah on the Red Sea, in a narrow valley above ...
. In the late 16th century, access to slaves in the areas of the former Songhai Empire
The Songhai Empire was a state located in the western part of the Sahel during the 15th and 16th centuries. At its peak, it was one of the largest African empires in history. The state is known by its historiographical name, derived from its lar ...
in West Africa were cut off due to the anarchy in the area caused by the Moroccan armies' invasion of Songhai headed by al-Mansur
Abū Jaʿfar ʿAbd Allāh ibn Muḥammad al-Manṣūr (; ; 714 – 6 October 775) usually known simply as by his laqab al-Manṣūr () was the second Abbasid caliph, reigning from 754 to 775 succeeding his brother al-Saffah (). He is known ...
. This necessitated the substitution of the former Songhai route with the Benghazi
Benghazi () () is the List of cities in Libya, second-most-populous city in Libya as well as the largest city in Cyrenaica, with an estimated population of 859,000 in 2023. Located on the Gulf of Sidra in the Mediterranean Sea, Mediterranean, Ben ...
– Wadai route and others through Sudan. After Europeans had settled in the Gulf of Guinea
The Gulf of Guinea (French language, French: ''Golfe de Guinée''; Spanish language, Spanish: ''Golfo de Guinea''; Portuguese language, Portuguese: ''Golfo da Guiné'') is the northeasternmost part of the tropical Atlantic Ocean from Cape Lopez i ...
, the trans-Saharan slave trade became less important.
Arabs were sometimes made into slaves in the trans-Saharan slave trade. In Mecca, Arab women were sold as slaves according to Ibn Butlan, and certain rulers in West Africa had slave girls of Arab origin. According to al-Maqrizi
Al-Maqrīzī (, full name Taqī al-Dīn Abū al-'Abbās Aḥmad ibn 'Alī ibn 'Abd al-Qādir ibn Muḥammad al-Maqrīzī, ; 1364–1442) was a medieval Egyptian historian and biographer during the Mamluk era, known for his interest in the Fat ...
, slave girls with lighter skin were sold to West Africans on hajj
Hajj (; ; also spelled Hadj, Haj or Haji) is an annual Islamic pilgrimage to Mecca, Saudi Arabia, the holiest city for Muslims. Hajj is a mandatory religious duty for capable Muslims that must be carried out at least once in their lifetim ...
. Ibn Battuta met an Arab slave girl near Timbuktu in Mali in 1353. Battuta wrote that the slave girl was fluent in Arabic, from Damascus, and her master's name was Farbá Sulaymán. Besides his Damascus slave girl and a secretary fluent in Arabic, Arabic was also understood by Farbá himself. The West African states also imported highly trained slave soldiers.
Under the Saadi dynasty
The Saadi Sultanate (), also known as the Sharifian Sultanate (), was a state which ruled present-day Morocco and parts of Northwest Africa in the 16th and 17th centuries. It was led by the Saadi dynasty, an Arab Sharifism, Sharifian dynasty.
...
, Morocco's sugar industry was dependent on Sub-Saharan African slave labor. According to Paul Berthier, the need for slave labor on Moroccan sugar plantations was a major reason for the 16th century Saadian invasion of the Songhai Empire
The Moroccan invasion of the Songhai Empire began with an expedition sent in 1590 by Sultan Ahmad al-Mansur of the Saadian dynasty, which ruled over Morocco at the time. The Saadian army, led by Judar Pasha, arrived in the Niger valley region (i ...
.
Late trans-Saharan slave trade
 In Central Africa, during the 16th and 17th centuries, slave traders continued to raid the region as part of the expansion of the Saharan and Nile River slave routes. It is estimated that, in the 17th and 18th centuries, 1.4 million slaves were forced to make the trek through the Sahara Captives were enslaved and shipped to the Mediterranean coast, Europe, Arabia, the Western Hemisphere, or to the slave ports and factories along the West and North Africa coasts or South along the Ubanqui and Congo rivers.Alistair Boddy-Evans
In Central Africa, during the 16th and 17th centuries, slave traders continued to raid the region as part of the expansion of the Saharan and Nile River slave routes. It is estimated that, in the 17th and 18th centuries, 1.4 million slaves were forced to make the trek through the Sahara Captives were enslaved and shipped to the Mediterranean coast, Europe, Arabia, the Western Hemisphere, or to the slave ports and factories along the West and North Africa coasts or South along the Ubanqui and Congo rivers.Alistair Boddy-EvansCentral Africa Republic Timeline – Part 1: From Prehistory to Independence (13 August 1960), A Chronology of Key Events in Central Africa Republic
. About.com 1.2 million slaves are estimated to have been sent through the Sahara in the 19th century. In the 1830s, a period when slave trade flourished,
Ghadames
Ghadames or Ghadamis ( Ghadamsi: ⵄⴰⴷⴻⵎⴻⵙ / ''Ɛadēməs'' �adeːməs , ) is an oasis town in the Nalut District of the Tripolitania region in northwestern Libya.
Ghadamès, known as 'the pearl of the desert', stands in an oa ...
was handling 2,500 slaves a year.K. S. McLachlan"Tripoli and Tripolitania: Conflict and Cohesion during the Period of the Barbary Corsairs (1551–1850)"
''Transactions of the Institute of British Geographers'', New Series, Vol. 3, No. 3, Settlement and Conflict in the Mediterranean World. (1978), pp. 285-294. Even though the slave trade was officially abolished in Tripoli by the Firman of 1857, this law was never enforced, and continued in practice at least until the 1890s.Lisa Anderson
">"Nineteenth-Century Reform in Ottoman Libya"
International Journal of Middle East Studies, Vol. 16, No. 3. (Aug., 1984), pp. 325-348. In Tripoli, G. F. Lyon recorded that from 4,000 to 5,000 slaves were processed annually with raids to areas like Kanem-Bornu providing sources of captives. As a witness to the behavior of the slave dealers, Lyon described their behavior in Libya: Other 19th-century European explorers recorded their perilous experiences traveling through the Saharan Desert alongside slave caravans. The explorer
Gustav Nachtigal
Gustav Nachtigal (; born 23 February 1834 – 20 April 1885) was a German military surgeon and explorer of Central and West Africa. He is further known as the German Empire's consul-general for Tunisia and Commissioner for West Africa. His miss ...
reported finding numerous bones at desert springs that had run dry. Nachtigal estimated that for every one slave that successfully arrived at the market three or four had either died or escaped. Cold could also kill in the desert as the explorer Heinrich Barth relayed a story that the vizier of Bornu had lost forty slaves in a single night in Libya. A British account described one hundred skeletons.
By 1858, the British consul in Tripoli had recorded that more than 66% of the value shipped across the Sahara was made up by slaves. The British Consul in Benghazi
Benghazi () () is the List of cities in Libya, second-most-populous city in Libya as well as the largest city in Cyrenaica, with an estimated population of 859,000 in 2023. Located on the Gulf of Sidra in the Mediterranean Sea, Mediterranean, Ben ...
wrote in 1875 that the slave trade had reached an enormous scale and that the slaves who were sold in Alexandria
Alexandria ( ; ) is the List of cities and towns in Egypt#Largest cities, second largest city in Egypt and the List of coastal settlements of the Mediterranean Sea, largest city on the Mediterranean coast. It lies at the western edge of the Nile ...
and Constantinople
Constantinople (#Names of Constantinople, see other names) was a historical city located on the Bosporus that served as the capital of the Roman Empire, Roman, Byzantine Empire, Byzantine, Latin Empire, Latin, and Ottoman Empire, Ottoman empire ...
had quadrupled in price. This trade, he wrote, was encouraged by the local government
Local government is a generic term for the lowest tiers of governance or public administration within a particular sovereign state.
Local governments typically constitute a subdivision of a higher-level political or administrative unit, such a ...
. By the mid 19th century, it is possible that nearly 10,000 slaves were being transported to North Africa yearly. The Muslim historian Ahmad ibn Khalid an-Nasiri bemoaned the "unlimited enslavement of blacks" in 19th century North Africa "where men traffic them like beasts or worse" and where the majority of slaves were Muslims who should have been exempt from slavery because of their religious status.
Slaves were marched in shackles from across the Sahara via the Trans-Saharan slave trade to the Nile, while dying from exposure and swollen feet.
Adolf Vischer wrote in an article published in 1911 that: "...it has been said that slave traffic is still going on on the Benghazi– Wadai route, but it is difficult to test the truth of such an assertion as, in any case, the traffic is carried on secretly".Adolf Vischer"Tripoli"
''The Geographical Journal'', Vol. 38, No. 5. (Nov., 1911), pp. 487–494. At
Kufra
Kufra () is a basinBertarelli (1929), p. 514. and oasis group in the Kufra District of southeastern Cyrenaica in Libya. At the end of the 19th century, Kufra became the centre and holy place of the Senussi order. It also played a minor role in ...
, the Egyptian traveller Ahmed Hassanein Bey found out in 1916 that he could buy a girl slave for five pounds sterling while in 1923 he found that the price had risen to 30 to 40 pounds sterling. Another traveler, the Danish convert to Islam Knud Holmboe, crossed the Italian Libya
Libya (; ) was a colony of Fascist Italy (1922–1943), Italy located in North Africa, in what is now modern Libya, between 1934 and 1943. It was formed from the unification of the colonies of Italian Cyrenaica, Cyrenaica and Italian Tripolitan ...
n desert in 1930, and was told that slavery is still practiced in Kufra and that he could buy a slave girl for 30 pounds sterling at the Thursday slave market
A slave market is a place where slaves are bought and sold. These markets are a key phenomenon in the history of slavery.
Asia
Central Asia
Since antiquity, cities along the Silk road of Central Asia, had been centers of slave trade. In ...
.
According to James Richardson's testimony, when he visited Ghadames, most slaves were from Bornu. According to Raëd Bader, based on estimates of the Trans-Saharan trade, between 1700 and 1880 Tunisia received 100,000 black slaves, compared to only 65,000 entering Algeria, 400,000 in Libya, 515,000 in Morocco and 800,000 in Egypt.
Abolition
After the establishment of the British and Foreign Anti-Slavery Society in 1839 to fight slave trading in the Mediterranean,Ahmad I ibn Mustafa
Ahmad I (), 2 December 1805 Ibn Abi Dhiaf, ''Présent des hommes de notre temps. Chroniques des rois de Tunis et du pacte fondamental'', vol. IV, éd. Maison tunisienne de l'édition, Tunis, 1990, p. 12 – 30 May 1855Ibn Abi Dhiaf, ''op. cit.'' ...
, Bey of Tunis
Bey, also spelled as Baig, Bayg, Beigh, Beig, Bek, Baeg, Begh, or Beg, is a Turkic languages, Turkic title for a chieftain, and a royal, aristocratic title traditionally applied to people with special lineages to the leaders or rulers of various ...
, agreed to outlaw exporting, importing, and selling slaves in 1842, and he made slavery illegal in 1846. In 1848, France
France, officially the French Republic, is a country located primarily in Western Europe. Overseas France, Its overseas regions and territories include French Guiana in South America, Saint Pierre and Miquelon in the Atlantic Ocean#North Atlan ...
outlawed slavery in Algeria
Algeria, officially the People's Democratic Republic of Algeria, is a country in the Maghreb region of North Africa. It is bordered to Algeria–Tunisia border, the northeast by Tunisia; to Algeria–Libya border, the east by Libya; to Alger ...
.
Despite the British outlawing the slave trade in 1833, Turco-Egyptian troops of Muhammad Ali of Egypt
Muhammad Ali (4 March 1769 – 2 August 1849) was the Ottoman Empire, Ottoman Albanians, Albanian viceroy and governor who became the ''de facto'' ruler of History of Egypt under the Muhammad Ali dynasty, Egypt from 1805 to 1848, widely consi ...
continued to export approximately 20,000 slaves annually from Sudan. Merchant princes such as Al-Zubayr Rahma Mansur, appointed khedive
Khedive ( ; ; ) was an honorific title of Classical Persian origin used for the sultans and grand viziers of the Ottoman Empire, but most famously for the Khedive of Egypt, viceroy of Egypt from 1805 to 1914.Adam Mestyan"Khedive" ''Encyclopaedi ...
in 1873, controlled trade in Bahr el Ghazal Bahr el-Ghazal (, also transliterated ''Bahr al-Ghazal'', ''Baḥr al-Ghazāl'', ''Bahr el-Gazel'', or versions of these without the hyphen) may refer to two distinct places, both named after ephemeral or dry rivers.
Chad
* Bahr el-Ghazal (wadi in ...
and the routes to Kordofan
Kordofan ( ') is a former province of central Sudan. In 1994 it was divided into three new federal states: North Kordofan, South Kordofan and West Kordofan. In August 2005, West Kordofan State was abolished and its territory divided between N ...
and Darfur
Darfur ( ; ) is a region of western Sudan. ''Dār'' is an Arabic word meaning "home f – the region was named Dardaju () while ruled by the Daju, who migrated from Meroë , and it was renamed Dartunjur () when the Tunjur ruled the area. ...
.
In 1929, the Sanusi center of Kufra
Kufra () is a basinBertarelli (1929), p. 514. and oasis group in the Kufra District of southeastern Cyrenaica in Libya. At the end of the 19th century, Kufra became the centre and holy place of the Senussi order. It also played a minor role in ...
in the Sahara was pointed out as a center of the (Trans-Saharan) slave trade.
The Italians reported to the Advisory Committee of Experts on Slavery
The Advisory Committee of Experts on Slavery (ACE) was a permanent committee of the League of Nations, inaugurated in 1933. It was the first permanent slavery committee of the League of Nations, which was founded after a decade of work addre ...
in the 1930s that all former slaves in Italian Tripolitania
Italian Tripolitania was an Italian colony, located in present-day western Libya, that existed from 1911 to 1934. It was part of the territory conquered from the Ottoman Empire after the Italo-Turkish War in 1911. Italian Tripolitania included th ...
- slavery in Libya was since long formally abolished - were free to leave their former Arab owners if they wished, but that they stayed because they were socially depressed; and that in the oases of Cyrenaica and the interiour of Sanusiya, the Trans-Saharan slave trade had been erased in parallel with Italian conquest, during which 900 slaves had been freed in the Kufra slave market.Miers, S. (2003). Slavery in the Twentieth Century: The Evolution of a Global Problem. Storbritannien: AltaMira Press. 226
In 1936, the report to the Advisory Committee of Experts on Slavery
The Advisory Committee of Experts on Slavery (ACE) was a permanent committee of the League of Nations, inaugurated in 1933. It was the first permanent slavery committee of the League of Nations, which was founded after a decade of work addre ...
from the French, British and Italian stated that they all surveyed the water sources along the caravan routes in the Sahara to combat the Trans-Saharan slave trade from Nigeria to North Africa. In 1937, the report to the Advisory Committee of Experts on Slavery
The Advisory Committee of Experts on Slavery (ACE) was a permanent committee of the League of Nations, inaugurated in 1933. It was the first permanent slavery committee of the League of Nations, which was founded after a decade of work addre ...
, both France and Spain assured that they actively fought the slave raids from the Trans-Saharan slave traders, and in 1938, the French claimed that they had secured control over the border areas alongside Morocco and Algeria and effectively prevented the trans-Saharan slave trade in that area.Miers, S. (2003). Slavery in the Twentieth Century: The Evolution of a Global Problem. USA: AltaMira Press. p. 279 Slavery was not abolished in Mauritania
Mauritania, officially the Islamic Republic of Mauritania, is a sovereign country in Maghreb, Northwest Africa. It is bordered by the Atlantic Ocean to the west, Western Sahara to Mauritania–Western Sahara border, the north and northwest, ...
until 1981.
In the 1980s, during the Second Sudanese Civil War
The Second Sudanese Civil War was a conflict from 1983 to 2005 between the central Sudanese government and the Sudan People's Liberation Army/Movement, Sudan People's Liberation Army. It was largely a continuation of the First Sudanese Civil Wa ...
, there was a resurgence of the Sudanese slave trade under the National Islamic Front
The National Islamic Front (NIF; ; transliterated: ''al-Jabhah al-Islamiyah al-Qawmiyah'') was an Islamist political organization founded in 1976 and led by Dr. Hassan al-Turabi that influenced the Sudanese government starting in 1979, and d ...
and groups such as the Baqqara and Rizeigat.
Slavery in the post-Gaddafi Libya
Since the beginning of the Libyan Civil War of 2011, that saw the overthrow ofMuammar Gaddafi
Muammar Muhammad Abu Minyar al-Gaddafi (20 October 2011) was a Libyan military officer, revolutionary, politician and political theorist who ruled Libya from 1969 until Killing of Muammar Gaddafi, his assassination by Libyan Anti-Gaddafi ...
's regime by NATO
The North Atlantic Treaty Organization (NATO ; , OTAN), also called the North Atlantic Alliance, is an intergovernmental organization, intergovernmental Transnationalism, transnational military alliance of 32 Member states of NATO, member s ...
-backed anti-Gaddafi forces
The anti-Gaddafi forces, also known as the Libyan opposition or Libyan rebels, were Libyan groups that opposed and militarily defeated the government of Muammar Gaddafi during the First Libyan Civil War in 2011, killing him in the process. The A ...
, Libya has been plagued by instability and migrants with little cash and no papers have become vulnerable. Libya is a major exit point for African migrants heading to Europe. The International Organization for Migration
The International Organization for Migration (IOM) is a United Nations related organization working in the field of migration. The organization implements operational assistance programmes for Human migration, migrants, including internally displa ...
(IOM) published a report in April 2017 showing that many of the migrants from West Africa
West Africa, also known as Western Africa, is the westernmost region of Africa. The United Nations geoscheme for Africa#Western Africa, United Nations defines Western Africa as the 16 countries of Benin, Burkina Faso, Cape Verde, The Gambia, Gha ...
heading to Europe are sold as slaves after being detained by people smugglers or militia groups. African countries south of Libya were targeted for slave trading and transferred to Libyan slave markets instead. According to the victims, the price is higher for migrants with skills like painting and tiling. Slaves are often ransom
Ransom refers to the practice of holding a prisoner or item to extort money or property to secure their release. It also refers to the sum of money paid by the other party to secure a captive's freedom.
When ransom means "payment", the word ...
ed to their families and in the meantime until ransom
Ransom refers to the practice of holding a prisoner or item to extort money or property to secure their release. It also refers to the sum of money paid by the other party to secure a captive's freedom.
When ransom means "payment", the word ...
can be tortured, forced to work, sometimes to death and eventually executed or left to starve if they can't pay for too long. Women are often raped and used as sex slave
Sexual slavery and sexual exploitation is an attachment of any ownership right over one or more people with the intent of coercing or otherwise forcing them to engage in sexual activities. This includes forced labor that results in sexual ...
s and sold to brothel
A brothel, strumpet house, bordello, bawdy house, ranch, house of ill repute, house of ill fame, or whorehouse is a place where people engage in Human sexual activity, sexual activity with prostitutes. For legal or cultural reasons, establis ...
s and private Libyan clients. Many child migrants also suffer from abuse and child rape in Libya.
After receiving unverified CNN video of a November 2017 slave auction in Libya, a human trafficker told Al-Jazeera
Al Jazeera Media Network (AJMN; , ) is a private-media conglomerate headquartered in Wadi Al Sail, Doha, funded in part by the government of Qatar. The network's flagship channels include Al Jazeera Arabic and Al Jazeera English, which pr ...
(a Qatari TV station with interests in Libya) that hundreds of migrants are bought and sold across the country every week. Migrants who have gone through Libyan detention centres have shown signs of many human rights abuses such as severe abuse, including electric shocks, burns, lashes and even skinning, stated the director of health services on the Italian island of Lampedusa
Lampedusa ( , , ; ; ) is the largest island of the Italian Pelagie Islands in the Mediterranean Sea.
The ''comune'' of Lampedusa e Linosa is part of the Sicilian province of Agrigento which also includes the smaller islands of Linosa and Lamp ...
to Euronews
Euronews (stylised in lowercase) is a pan-European television news broadcasting, news network, headquartered in Lyon, France. It is a provider of livestreamed news, which can be viewed in Europe and North Africa via satellite, and in most of the ...
.
A Libyan group known as the Asma Boys have antagonized migrants from other parts of Africa from at least as early as 2000, destroying their property. Nigerian migrants in January 2018 gave accounts of abuses in detention centres, including being leased or sold as slaves. Videos of Sudanese migrants being burnt and whipped for ransom, were released later on by their families on social media. In June 2018, the United Nations applied sanctions against four Libyans (including a Coast Guard commander) and two Eritreans for their criminal leadership of slave trade networks.
Routes
According to professor Ibrahima Baba Kaké, there were four main slavery routes to North Africa, from east to west of Africa, from theMaghreb
The Maghreb (; ), also known as the Arab Maghreb () and Northwest Africa, is the western part of the Arab world. The region comprises western and central North Africa, including Algeria, Libya, Mauritania, Morocco, and Tunisia. The Maghreb al ...
to the Sudan
Sudan, officially the Republic of the Sudan, is a country in Northeast Africa. It borders the Central African Republic to the southwest, Chad to the west, Libya to the northwest, Egypt to the north, the Red Sea to the east, Eritrea and Ethiopi ...
, from Tripolitania
Tripolitania (), historically known as the Tripoli region, is a historic region and former province of Libya.
The region had been settled since antiquity, first coming to prominence as part of the Carthaginian empire. Following the defeat ...
to central Sudan and from Egypt to the Middle East. Caravan trails, set up in the 9th century, went past the oasis of the Sahara; travel was difficult and uncomfortable. Since Ancient Rome
In modern historiography, ancient Rome is the Roman people, Roman civilisation from the founding of Rome, founding of the Italian city of Rome in the 8th century BC to the Fall of the Western Roman Empire, collapse of the Western Roman Em ...
, long convoys had transported slaves.
See also
*Baqt
The Baqt (or Bakt) (بقط) was a 7th-century treaty between the Christian state of Makuria and the new Muslim rulers of Egypt. Lasting almost seven hundred years, it is by some measures the longest-lasting treaty in history. The name comes ei ...
* Barbary slave trade
The Barbary slave trade involved the capture and selling of European slaves at slave markets in the largely independent Ottoman Barbary states. European slaves were captured by Barbary pirates in slave raids on ships and by raids on coastal ...
* Comoros slave trade
* Haratin
The Haratin (, singular ''Ḥarṭānī''), also spelled Haratine or Harratin, are an ethnic group found in western Sahel and southwestern Maghreb. The Haratin are mostly found in modern Mauritania (where they form a plurality), Morocco, Western ...
* Indian Ocean slave trade
The Indian Ocean slave trade, sometimes known as the East African slave trade, involved the capture and transportation of predominately sub-Saharan African slaves along the coasts, such as the Swahili Coast and the Horn of Africa, and through ...
* Red Sea slave trade
The Red Sea slave trade, sometimes known as the Islamic slave trade, Arab slave trade, or Oriental slave trade, was a slave trade across the Red Sea trafficking Africans from Sub-Saharan Africa in the African continent to slavery in the A ...
* Zanzibar slave trade
* Comoros slave trade
* Trans-Sahara Highway
* Trans-Saharan trade
* Slavery in ancient Egypt
Slavery in ancient Egypt existed at least since the Old Kingdom period. Discussions of slavery in Pharaonic Egypt are complicated by terminology used by the Egyptians to refer to different classes of servitude over the course of dynastic h ...
* Slavery in ancient Rome
Slavery in ancient Rome played an important role in society and the economy. Unskilled or low-skill slaves labored in the fields, mines, and mills with few opportunities for advancement and little chance of freedom. Skilled and educated slaves ...
* Slavery in Africa
Slavery has historically been widespread in Africa. Systems of servitude and slavery were once commonplace in parts of Africa, as they were in much of the rest of the Ancient history, ancient and Post-classical history, medieval world. When t ...
* Human trafficking in Chad
* Slavery in Libya
* Slavery in Mali
* Slavery in Mauritania
Slavery has been called "deeply rooted" in the structure of the northwest African country of Mauritania and estimated to be "closely tied" to the ethnic composition of the country, although it has also been estimated that "Widespread slavery was ...
* Slavery in Niger
* Slavery in Nigeria
References
Further reading
The Garamantes and Trans-Saharan Enterprise in Classical Times
{{Africa in topic, Slavery in History of the Sahara Trade routes History of North Africa African slave trade Slavery in Asia Slavery in Morocco Slavery in Algeria Slavery in Tunisia Slavery in Libya Slavery in Egypt Slavery in Saudi Arabia Anti-black racism in Africa Anti-black racism in Asia Forced migration Genocides in Asia History of slavery in the Muslim world Trans-Saharan slave trade Death marches Genocide of indigenous peoples in Africa