|
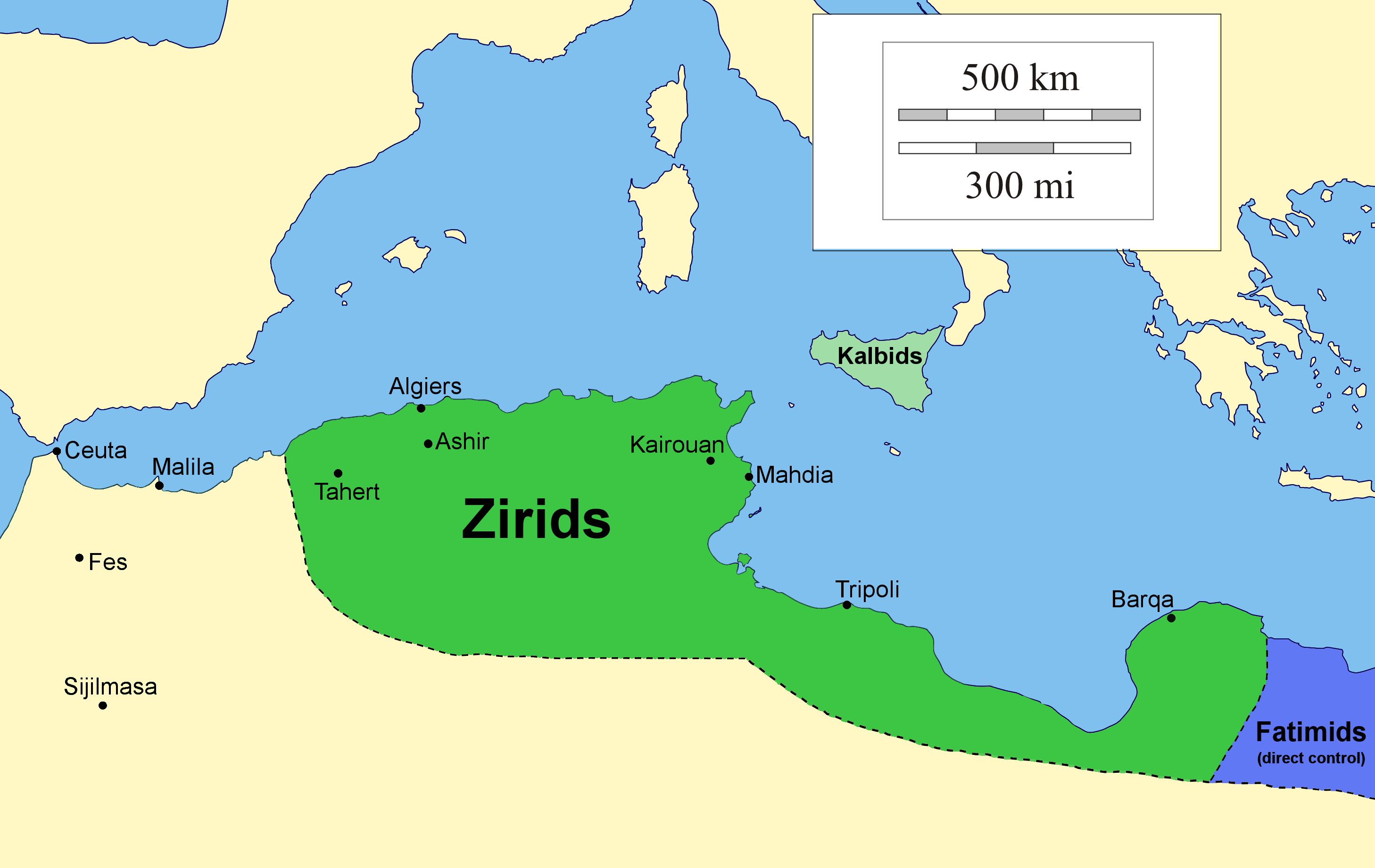
Zirid Dynasty
The Zirid dynasty (), Banu Ziri (), was a Sanhaja Berber dynasty from what is now Algeria which ruled the central Maghreb from 972 to 1014 and Ifriqiya (eastern Maghreb) from 972 to 1148. Descendants of Ziri ibn Manad, a military leader of the Fatimid Caliphate and the eponymous founder of the dynasty, the Zirids were emirs who ruled in the name of the Fatimids. The Zirids gradually established their autonomy in Ifriqiya through military conquest until officially breaking with the Fatimids in the mid-11th century. The rule of the Zirid emirs opened the way to a period in North African history where political power was held by Berber dynasties such as the Almoravid dynasty, Almohad Caliphate, Zayyanid dynasty, Marinid Sultanate and Hafsid dynasty. Under Buluggin ibn Ziri the Zirids extended their control westwards and briefly occupied Fez and much of present-day Morocco after 980, but encountered resistance from the local Zenata Berbers who gave their allegiance to the Cal ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fatimid Caliphate
The Fatimid Caliphate (; ), also known as the Fatimid Empire, was a caliphate extant from the tenth to the twelfth centuries CE under the rule of the Fatimids, an Isma'ili Shi'a dynasty. Spanning a large area of North Africa and West Asia, it ranged from the western Mediterranean in the west to the Red Sea in the east. The Fatimids traced their ancestry to the Islamic prophet Muhammad's daughter Fatima and her husband Ali, the first Shi'a imam. The Fatimids were acknowledged as the rightful imams by different Isma'ili communities as well as by denominations in many other Muslim lands and adjacent regions. Originating during the Abbasid Caliphate, the Fatimids initially conquered Ifriqiya (roughly present-day Tunisia and north-eastern Algeria). They extended their rule across the Mediterranean coast and ultimately made Egypt the center of the caliphate. At its height, the caliphate included—in addition to Egypt—varying areas of the Maghreb, Sicily, the Levant, and the Hej ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Emirate
An emirate is a territory ruled by an emir, a title used by monarchs or high officeholders in the Muslim world. From a historical point of view, an emirate is a political-religious unit smaller than a caliphate. It can be considered equivalent to a principality in non-Muslim contexts. Currently in the world, there are two emirates that are independent states (Kuwait and Qatar), one state ruled by an unrecognised emirate (Afghanistan), and a state that consists of a federation of seven emirates (the United Arab Emirates). A great number of previously independent emirates around the world are now part of larger states. Etymology Etymologically, emirate or amirate ( ' plural: ') is the quality, dignity, office, or territorial competence of any emir (prince, commander, governor, etc.). In English, the term is pronounced or in British English and or in American English. Types Monarchies The United Arab Emirates is a federal state that comprises seven federal emirates, each ad ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Almohad Caliphate
The Almohad Caliphate (; or or from ) or Almohad Empire was a North African Berbers, Berber Muslim empire founded in the 12th century. At its height, it controlled much of the Iberian Peninsula (Al-Andalus) and North Africa (the Maghreb). The Almohad movement was founded by Ibn Tumart among the Berber Masmuda tribes, but the Almohad caliphate and its ruling dynasty, known as the Mu'minid dynasty, were founded after his death by Abd al-Mu'min. * Around 1121, Ibn Tumart was recognized by his followers as the Mahdi, and shortly afterwards he established his base at Tinmel in the Atlas Mountains. Under Abd al-Mu'min (r. 1130–1163), they succeeded in overthrowing the ruling Almoravid dynasty governing the western Maghreb in 1147, when he conquered Marrakesh and declared himself caliph. They then extended their power over all of the Maghreb by 1159. Al-Andalus followed, and all of Muslim Iberia was under Almohad rule by 1172. The turning point of their presence in the Iberian Pe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Almoravid Dynasty
The Almoravid dynasty () was a Berber Muslim dynasty centered in the territory of present-day Morocco. It established an empire that stretched over the western Maghreb and Al-Andalus, starting in the 1050s and lasting until its fall to the Almohads in 1147. The Almoravids emerged from a coalition of the Lamtuna, Gudala, and Massufa, nomadic Berber tribes living in what is now Mauritania and the Western Sahara, traversing the territory between the Draa, the Niger, and the Senegal rivers. During their expansion into the Maghreb, they founded the city of Marrakesh as a capital, . Shortly after this, the empire was divided into two branches: a northern one centered in the Maghreb, led by Yusuf ibn Tashfin and his descendants, and a southern one based in the Sahara, led by Abu Bakr ibn Umar and his descendants. The Almoravids expanded their control to al-Andalus (the Muslim territories in Iberia) and were crucial in temporarily halting the advance of the Christian kingdoms in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Emir
Emir (; ' (), also Romanization of Arabic, transliterated as amir, is a word of Arabic language, Arabic origin that can refer to a male monarch, aristocratic, aristocrat, holder of high-ranking military or political office, or other person possessing actual or ceremonial authority. The title has a history of use in West Asia, East Africa, West Africa, Central Asia, and South Asia. In the modern era, when used as a formal monarchical title, it is roughly synonymous with "prince", applicable both to a son of a hereditary monarch, and to a reigning monarch of a sovereign principality, namely an emirate. The female, feminine form is emira ( '), with the same meaning as "princess". Prior to its use as a monarchical title, the term "emir" was historically used to denote a "commander", "general", or "leader" (for example, Amir al-Mu'min). In contemporary usage, "emir" is also sometimes used as either an honorary or formal title for the head of an Islamic, or Arab (regardless of relig ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ziri Ibn Manad
Ziri ibn Manad or Ziri son of Mennad (died in 971) was the founder of the Zirid dynasty in the Maghreb. Ziri ibn Mennad was a chief of the Takalata branch of the Sanhajah confederation, to which the Kutama Berbers belonged located in the Central Maghreb (Algeria). As an ally of the Fatimids, he assisted in the defeat of the rebellion of Abu Yazid (943–947) by Caliph al-Mansur bi-Nasr Allah, and was rewarded with the governorship of the western provinces, an area that roughly corresponds with modern Algeria north of the Sahara. Ziri had the residence of Achir built south of the future site of Algiers in 935. He summoned masons and joiners from M'sila and Tubna to build the fortress, which, once finished, was filled with scholars, merchants and lawyers. He minted money and began to pay his troops in cash. His son Buluggin ibn Ziri founded the cities of Algiers, Miliana and Médéa (Lamdiya), and rebuilt the settlements destroyed in the revolt. In 959 Ziri successfully co ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ifriqiya
Ifriqiya ( '), also known as al-Maghrib al-Adna (), was a medieval historical region comprising today's Tunisia, eastern Algeria, and Tripolitania (roughly western Libya). It included all of what had previously been the Byzantine province of Africa Proconsularis and extended beyond it, but did not include the Mauretanias. To the south, Ifriqiya was bounded by the semi-arid lands and salt marshes named el-Djerid. The northern boundary fluctuated from as far north as Sicily to the North African coastline, and the western boundary usually reached Béjaïa. Ifriqiya is bordered to the west by the Central Maghreb, with which the borders are fluid depending on the chroniclers and the eras. The capital was briefly Carthage, then Kairouan, Qayrawan (Kairouan), then Mahdia, then Tunis. The Aghlabids, from their base in Kairouan, initiated the invasion of Southern Italy beginning in 827, and established the Emirate of Sicily, which lasted until it was conquered by the Normans, and the s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Maghreb
The Maghreb (; ), also known as the Arab Maghreb () and Northwest Africa, is the western part of the Arab world. The region comprises western and central North Africa, including Algeria, Libya, Mauritania, Morocco, and Tunisia. The Maghreb also includes the territorial dispute, disputed territory of Western Sahara. As of 2018, the region had a population of over 100 million people. The Maghreb is usually defined as encompassing much of the northern part of Africa, including a large portion of the Sahara Desert, but excluding Egypt and the Sudan, which are considered to be located in the Mashriq — the eastern part of the Arab world. The traditional definition of the Maghreb — which restricted its scope to the Atlas Mountains and the coastal plains of Morocco, Algeria, Tunisia and Libya — was expanded in modern times to include Mauritania and the disputed territory of Western Sahara. During the era of al-Andalus on the Iberian Peninsula (711–1492), the Maghreb's inhabita ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Algeria
Algeria, officially the People's Democratic Republic of Algeria, is a country in the Maghreb region of North Africa. It is bordered to Algeria–Tunisia border, the northeast by Tunisia; to Algeria–Libya border, the east by Libya; to Algeria–Niger border, the southeast by Niger; to Algeria–Western Sahara border, the southwest by Mali, Mauritania, and Western Sahara; to Algeria–Morocco border, the west by Morocco; and to the north by the Mediterranean Sea. The capital and List of cities in Algeria, largest city is Algiers, located in the far north on the Mediterranean coast. Inhabited since prehistory, Algeria has been at the crossroads of numerous cultures and civilisations, including the Phoenicians, Numidians, Ancient Rome, Romans, Vandals, and Byzantine Greeks. Its modern identity is rooted in centuries of Arab migrations to the Maghreb, Arab Muslim migration waves since Muslim conquest of the Maghreb, the seventh century and the subsequent Arabization, Arabisation ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Berbers
Berbers, or the Berber peoples, also known as Amazigh or Imazighen, are a diverse grouping of distinct ethnic groups indigenous to North Africa who predate the arrival of Arab migrations to the Maghreb, Arabs in the Maghreb. Their main connections are identified by their usage of Berber languages, most of them mutually unintelligible, which are part of the Afroasiatic languages, Afroasiatic language family. They are indigenous peoples, indigenous to the Maghreb region of North Africa, where they live in scattered communities across parts of Morocco, Algeria, Libya, and to a lesser extent Tunisia, Mauritania, northern Mali and northern Niger. Smaller Berber communities are also found in Burkina Faso and Egypt's Siwa Oasis. Descended from Stone Age tribes of North Africa, accounts of the Imazighen were first mentioned in Egyptian hieroglyphs, Ancient Egyptian writings. From about 2000 BC, Berber languages spread westward from the Nile, Nile Valley across the northern Sahara int ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sanhaja
The Sanhaja (, or زناگة ''Znāga''; , pl. Iẓnagen, and also Aẓnaj, pl. Iẓnajen) were once one of the largest Berbers, Berber tribal confederations, along with the Zenata, Zanata and Masmuda confederations. Many tribes in Algeria, Libya, Mali, Mauritania, Morocco, Niger, Senegal, Tunisia and Western Sahara bore and still carry this ethnonym, especially in its Berber languages, Berber form. Other names for the population include ''Zenaga'', ''Znaga'', ''Sanhája'', ''Sanhâdja'' and ''Senhaja''. Triad Ibn Khaldun and others defined the Sanhaja as a grouping made up of three separate confederations, not as a single confederation. The distinction is usually made with a diacritical point placed above or below that is present in the Arabic text and often lost in English. # Danhāǧa/Sanhaja [Sanhaja of the first type] is a confederation of: Kutama, Kutāma-Igawawen, Zawāwa of the Kabyle people, Kabyle mountains, including some areas like Algiers and Constantine, Algeria, C ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dinar
The dinar () is the name of the principal currency unit in several countries near the Mediterranean Sea, with a more widespread historical use. The English word "dinar" is the transliteration of the Arabic دينار (''dīnār''), which was borrowed via the Syriac language, Syriac ''dīnarā'' from the Latin language , Latin Denarius , ''dēnārius''. The modern gold dinar is a projected bullion gold coin, and is not issued as an official currency by any state. History The modern dinar's historical antecedents are the gold dinar and the silver dirham, the main coin of the medieval Islamic empires, first issued in Islamic calendar, AH 77 (696–697 AD) (Late Antiquity) by Caliph Abd al-Malik ibn Marwan. The word "dinar" derives from the Latin word "denarius, ''dēnārius''," a silver coin of Ancient Roman coinage, ancient Rome, which was first minted about c. 211 BC. The Kushan Empire introduced a gold coin known as the ''dīnāra'' in India in the 1st century ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |