Tox21 on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 Thymocyte selection-associated high mobility group box protein TOX is a
Thymocyte selection-associated high mobility group box protein TOX is a
 Thymocyte selection-associated high mobility group box protein TOX is a
Thymocyte selection-associated high mobility group box protein TOX is a protein
Proteins are large biomolecules and macromolecules that comprise one or more long chains of amino acid residue (biochemistry), residues. Proteins perform a vast array of functions within organisms, including Enzyme catalysis, catalysing metab ...
that in humans is encoded by the ''TOX'' gene
In biology, the word gene has two meanings. The Mendelian gene is a basic unit of heredity. The molecular gene is a sequence of nucleotides in DNA that is transcribed to produce a functional RNA. There are two types of molecular genes: protei ...
. TOX drives T-cell exhaustion and plays a role in innate lymphoid cell development.
Structure
The TOX gene encodes aprotein
Proteins are large biomolecules and macromolecules that comprise one or more long chains of amino acid residue (biochemistry), residues. Proteins perform a vast array of functions within organisms, including Enzyme catalysis, catalysing metab ...
that belongs to a large superfamily of chromatin
Chromatin is a complex of DNA and protein found in eukaryote, eukaryotic cells. The primary function is to package long DNA molecules into more compact, denser structures. This prevents the strands from becoming tangled and also plays important r ...
associated proteins that share an approximately 75 amino acid DNA binding motif, the HMG (high mobility group)-box (named after that found in the canonical member of the family, high mobility group protein 1). Some high mobility group
High-Mobility Group or HMG is a group of chromosomal proteins that are involved in the regulation of DNA-dependent processes such as
transcription, replication, recombination, and DNA repair. History and name
HMG proteins were originally isolate ...
(HMG) box proteins (e.g., LEF1) contain a single HMG box motif and bind DNA in a sequence-specific manner, while other members of this family (e.g., HMGB1
High mobility group box 1 protein, also known as high-mobility group protein 1 (HMG-1) and amphoterin, is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''HMGB1'' gene.
HMG-1 belongs to the high mobility group and contains a HMG-box domain.
Funct ...
) have multiple HMG boxes and bind DNA in a sequence-independent but structure-dependent manner. While TOX has a single HMG-box motif, it is predicted to bind DNA in a sequence-independent manner.
TOX subfamily
TOX is a member of a small subfamily of proteins (TOX2
TOX high mobility group box family member 2, also known as TOX2, is a human gene.
The protein encoded by this gene is a member of a subfamily of transcription factors that also includes TOX, TOX3, and TOX4 that share almost identical HMG-box ...
, TOX3
TOX high mobility group box family member 3, also known as ''TOX3'', is a human gene.
The protein encoded by this gene is a member of a subfamily of transcription factors that also includes '' TOX'', '' TOX2'', and '' TOX4'' that share almost ide ...
, and TOX4
TOX4 (TOX high mobility group box family member 4) also known as KIAA0737, is a human gene
In biology, the word gene has two meanings. The Mendelian gene is a basic unit of heredity. The molecular gene is a sequence of nucleotides in DNA th ...
) that share almost identical HMG-box sequences. TOX2 has been identified to play a role in the differentiation of T follicular helper cell. TOX2 is thought to be a downstream signal of BCL-6. TOX3 has been identified as a breast cancer susceptibility locus. TOX is highly expressed in the thymus
The thymus (: thymuses or thymi) is a specialized primary lymphoid organ of the immune system. Within the thymus, T cells mature. T cells are critical to the adaptive immune system, where the body adapts to specific foreign invaders. The thymus ...
, the site of development of T lymphocyte
T cells (also known as T lymphocytes) are an important part of the immune system and play a central role in the adaptive immune response. T cells can be distinguished from other lymphocytes by the presence of a T-cell receptor (TCR) on their cell ...
s. Knockout mice
A knockout mouse, or knock-out mouse, is a genetically modified mouse (''Mus musculus'') in which researchers have inactivated, or " knocked out", an existing gene by replacing it or disrupting it with an artificial piece of DNA. They are importan ...
that lack TOX have a severe defect in development of certain subsets of T lymphocytes.
Function
T cell exhaustion
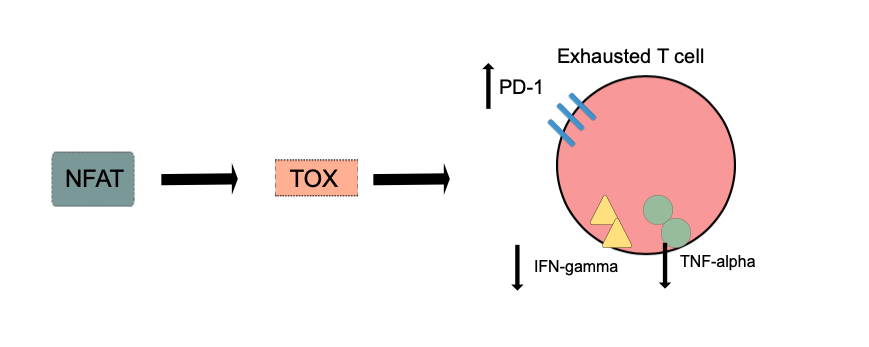
TOX is necessary for T cell persistence but also drivesT cell exhaustion
T cells (also known as T lymphocytes) are an important part of the immune system and play a central role in the adaptive immune response. T cells can be distinguished from other lymphocytes by the presence of a T-cell receptor (TCR) on their cell ...
. An increase in TOX expression is characterized by a weakening of the effector functions of the cytotoxic T cell
A cytotoxic T cell (also known as TC, cytotoxic T lymphocyte, CTL, T-killer cell, cytolytic T cell, CD8+ T-cell or killer T cell) is a T lymphocyte (a type of white blood cell) that kills cancer cells, cells that are infected by intracellular ...
and upregulation of inhibitory receptors on the cytotoxic T cells. TOX promotes the exhausted T cell phenotype through epigenetic
In biology, epigenetics is the study of changes in gene expression that happen without changes to the DNA sequence. The Greek prefix ''epi-'' (ἐπι- "over, outside of, around") in ''epigenetics'' implies features that are "on top of" or "in ...
remodeling. PD-1
Programmed cell death protein 1 (PD-1), (CD279 cluster of differentiation 279). PD-1 is a protein encoded in humans by the ''PDCD1'' gene. PD-1 is a cell surface receptor on T cells and B cells that has a role in regulating the immune system's re ...
is an inhibitory marker on T cells that increases when TOX is unregulated. This allows for cancerous cells to evade the cytotoxic T cells through upregulated expression of PD-L1
Programmed death-ligand 1 (PD-L1) also known as cluster of differentiation 274 (CD274) or B7 homolog 1 (B7-H1) is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''CD274'' gene.
Programmed death-ligand 1 (PD-L1) is a 40kDa type 1 transmembrane prote ...
.
Effector function
Markers of effector functions that are decreased when TOX is overexpressed areKLRG1
Killer cell lectin-like receptor subfamily G member 1 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''KLRG1'' gene.
Function
Natural killer (NK) cells are lymphocytes that can mediate lysis of certain tumor cells and virus-infected cells witho ...
, TNF, and IFN-gamma
Interferon gamma (IFNG or IFN-γ) is a dimerized soluble cytokine that is the only member of the type II class of interferons. The existence of this interferon, which early in its history was known as immune interferon, was described by E. F. ...
. IFN-gamma and TNF-alpha production are also increased when the ''Tox'' and ''Tox2'' genes are deleted. Upregulation of effector function in cells lacking TOX is not always seen and it has been proposed that inhibitory receptor function is separated from effector CD8+ cytotoxic T cell function. T-cell exhaustion does not occur when TOX is deleted from CD8+ T cells, but the cells instead adopt the KLRG1+ terminal effector state and undergo apoptosis
Apoptosis (from ) is a form of programmed cell death that occurs in multicellular organisms and in some eukaryotic, single-celled microorganisms such as yeast. Biochemistry, Biochemical events lead to characteristic cell changes (Morphology (biol ...
, or programmed cell death. It was therefore proposed that TOX prevents this terminal differentiation and instead promotes exhaustion so that the T-cell has a slightly more sustained response.
Cancer & chronic infection
Incancer
Cancer is a group of diseases involving Cell growth#Disorders, abnormal cell growth with the potential to Invasion (cancer), invade or Metastasis, spread to other parts of the body. These contrast with benign tumors, which do not spread. Po ...
or during chronic viral infection
A viral disease (or viral infection) occurs when an organism's body is invaded by pathogenic viruses, and infectious virus particles (virions) attach to and enter susceptible cells.
Examples include the common cold, gastroenteritis, COVID-19, t ...
, T-cell exhaustion occurs when cytotoxic T-cells are constantly stimulated. TOX is upregulated in CD8+ T cells from chronic infection when compared to acute infection. Patients with cancer typically have high levels of TOX in their tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes
Tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes (TIL) are white blood cells that have left the bloodstream and cell migration, migrated towards a tumor. They include T cells and B cells and are part of the larger category of ‘tumor-infiltrating immune cells’ wh ...
, and anti-tumor immunity is heightened when ''Tox'' and ''Tox2'' are deleted. TOX and TOX2-deficient tumor-specific CAR T cells
In biology, chimeric antigen receptors (CARs)—also known as chimeric immunoreceptors, chimeric T cell receptors or artificial T cell receptors—are receptor (biochemistry), receptor proteins that have been engineered to give T cells the new abil ...
additionally have increased antitumor effector cell function as well as decreased levels of inhibitory receptors.
Activation
NFAT
Nuclear factor of activated T-cells (NFAT) is a family of transcription factors shown to be important in immune response. One or more members of the NFAT family is expressed in most cells of the immune system. NFAT is also involved in the developme ...
transcription factors are essential for activating TOX in CD8+ T-cells, and it has been suggested that TOX is a downstream target of NFAT. The expression and function of NR4a (a target of NFAT) and TOX are strongly linked with reduced ''NR4a'' expression in ''Tox'' double knockout T cells and minimized ''Tox'' expression in ''NR4a'' triple knockout T cells.
T-cell development
TOX is necessary for positive selection in developingthymocyte
A thymocyte is an immune cell present in the thymus, before it undergoes transformation into a T cell. Thymocytes are produced as stem cells in the bone marrow and reach the thymus via the blood.
Thymopoiesis describes the process which turns thy ...
s. Knock out TOX mice shows a requirement of TOX for the CD4 T cell lineage, however CD8 single positive T-cells were still able to develop.
Innate lymphoid cells development
TOX is necessary for the development ofinnate lymphoid cell
Innate lymphoid cells (ILCs) are the most recently discovered family of Innate immune system, innate immune cells, derived from common lymphoid progenitors (CLPs). In response to pathogenic tissue damage, ILCs contribute to immunity via the secreti ...
s. Innate lymphoid cells include ILC1, ILC2, ILC3 and NK cells
Natural killer cells, also known as NK cells, are a type of cytotoxic lymphocyte critical to the innate immune system. They are a kind of large granular lymphocytes (LGL), and belong to the rapidly expanding family of known innate lymphoid cell ...
.
Notch signaling
The Notch signaling pathway is a highly conserved cell signaling system present in most animals. Mammals possess four different notch receptors, referred to as NOTCH1, NOTCH2, NOTCH3, and NOTCH4. The notch receptor is a single-pass transme ...
can aid in the development of all innate lymphoid cells, but in TOX-deficient cells, Notch target genes are expressed at low levels, so it is possible that TOX is required for downstream activation of these Notch target genes. TOX was also found to bind ''Hes1
Transcription factor HES1 (hairy and enhancer of split-1) is a protein that is encoded by the ''Hes1'' gene, and is the mammalian homolog of the hairy gene in ''Drosophila.'' HES1 is one of the seven members of the Hes gene family (HES1-7). Hes g ...
,'' a Notch target gene, in embryonic kidney cells.
Several ILC3 populations are reduced in the absence of TOX, implicating TOX’s role in their development. In the small intestine, major ILC3 populations are normal in TOX-deficient cells, suggesting that gut ILC3 development may occur independently of TOX. Some ILC3 populations in the gut expand in the absence of TOX.
It has been proposed that NFIL3 and TOX regulate the transition of common lymphoid progenitor to early innate lymphoid progenitor. In NFIL3-deficient mice, the expression of TOX is downregulated, indicating that NFIL3 is directly affecting the expression of TOX which is then acting downstream in ILC development. TOX-deficient mice and NFIL3-deficient mice both lack mature ILCs and ILC progenitors.
References
Further reading
* * * {{Transcription factors, g4 Transcription factors