Topaz War Relocation Center on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The Topaz War Relocation Center, also known as the Central Utah Relocation Center (Topaz) and briefly as the Abraham Relocation Center, was an American concentration camp in which Americans of Japanese descent and immigrants who had come to the United States from Japan, called '' Nikkei'' were incarcerated. President
 In December 1941, the
In December 1941, the
 After Topaz was closed, the land was sold and most of the buildings were auctioned off, disassembled, and removed from the site. Even the water pipes and utility poles were sold. Numerous foundations, concrete-lined excavations and other ground-level features can be seen at the various sites, but few buildings remain, and natural vegetation has taken over most of the abandoned areas.
In 1976, the Japanese American Citizens League placed a monument on the northwestern corner of the central area. On March 29, 2007,
After Topaz was closed, the land was sold and most of the buildings were auctioned off, disassembled, and removed from the site. Even the water pipes and utility poles were sold. Numerous foundations, concrete-lined excavations and other ground-level features can be seen at the various sites, but few buildings remain, and natural vegetation has taken over most of the abandoned areas.
In 1976, the Japanese American Citizens League placed a monument on the northwestern corner of the central area. On March 29, 2007,
The Topaz Museum digital archive
with links to photographs of camp, ''The Topaz Times'', and the elementary school diary
Doren Benjamin Boyce papers
MSS 7980
Duane L. Bishop conversations
MSS 2222
Walton LeGrande Law papers
MSS 8293 *From the J. Willard Marriott Library,
Topaz Oral Histories
Topaz Internment Camp Documents, 1942–1943
MSS 170, Merrill-Cazier Library,
War Relocation Authority Photographs of Japanese-American Evacuation and Resettlement
Hisako Hibi pictorial collection concerning the Tanforan Assembly Center and the Central Utah Relocation Center
Japanese American National Museum
Photographs from the Yoshiaki Moriwaki family papers
The Bancroft Library
Topaz Times
at the
Franklin Roosevelt
Franklin Delano Roosevelt (January 30, 1882April 12, 1945), also known as FDR, was the 32nd president of the United States, serving from 1933 until his death in 1945. He is the longest-serving U.S. president, and the only one to have served ...
signed Executive Order 9066
Executive Order 9066 was a President of the United States, United States presidential executive order signed and issued during World War II by United States president Franklin D. Roosevelt on February 19, 1942. "This order authorized the fo ...
in February 1942, ordering people of Japanese ancestry to be incarcerated in what were euphemistically called "relocation centers" like Topaz during World War II. Most of the people incarcerated at Topaz came from the Tanforan Assembly Center and previously lived in the San Francisco Bay Area
The San Francisco Bay Area, commonly known as the Bay Area, is a List of regions of California, region of California surrounding and including San Francisco Bay, and anchored by the cities of Oakland, San Francisco, and San Jose, California, S ...
. The camp was opened in September 1942 and closed in October 1945.
The camp, approximately west of Delta, Utah
Delta is the largest city in Millard County, Utah, Millard County, Utah, United States. It is located in the northeastern area of Millard County along the Sevier River and is surrounded by farmland. The population was 3,622 at the 2020 United St ...
, consisted of , with a main living area. Most internees lived in the main living area, though some lived off-site as agricultural and industrial laborers. The approximately 9,000 internees and staff made Topaz into the fifth-largest city in Utah at the time. The extreme temperature fluctuations of the arid area combined with uninsulated barracks made conditions very uncomfortable, even after the belated installation of pot-bellied stoves. The camp housed two elementary schools and a high school, a library, and some recreational facilities. Camp life was documented in a newspaper, '' Topaz Times'', and in the literary publication ''Trek''. Internees worked inside and outside the camp, mostly in agricultural labor. Many internees became notable artists.
In the winter of 1942–1943, a loyalty questionnaire asked prisoners if they would declare their loyalty to the United States of America and if they would be willing to enlist. The questions were divisive, and prisoners who were considered "disloyal" because of their answers on the loyalty questionnaire were sent to the Tule Lake Segregation Camp. One internee, James Wakasa, was shot and killed for being too close to the camp's fence. Topaz prisoners held a large funeral and stopped working until administrators relaxed security.
In 1983, Jane Beckwith founded the Topaz Museum Board. Topaz became a U.S. National Historic Landmark
A National Historic Landmark (NHL) is a National Register of Historic Places property types, building, district, object, site, or structure that is officially recognized by the Federal government of the United States, United States government f ...
in 2007. After many years of organizing, fundraising, and collecting information and artifacts, the Topaz Museum was built in Delta and debuted with a display of the art created at Topaz. Permanent exhibits, installed in 2017, chronicle the people who were interned there and tell their stories.
Terminology
Since the end of World War II, there has been debate over the terminology used to refer to Topaz and the other camps in which Americans of Japanese ancestry and their immigrant parents were imprisoned by theUnited States government
The Federal Government of the United States of America (U.S. federal government or U.S. government) is the Federation#Federal governments, national government of the United States.
The U.S. federal government is composed of three distinct ...
during the war. Topaz has been referred to as a "relocation camp", "relocation center", "internment camp
Internment is the imprisonment of people, commonly in large groups, without Criminal charge, charges or Indictment, intent to file charges. The term is especially used for the confinement "of enemy citizens in wartime or of terrorism suspects ...
", and "concentration camp
A concentration camp is a prison or other facility used for the internment of political prisoners or politically targeted demographics, such as members of national or ethnic minority groups, on the grounds of national security, or for exploitati ...
", and the controversy over which term is the most appropriate continued throughout the late 1990s. In a preface to a 1997 book on Topaz written and published by the Topaz Museum, the Topaz Museum Board states that it is accurate to refer to the camps as a "detention camp" or "concentration camp" and its residents as "prisoners" or "internees".
History
 In December 1941, the
In December 1941, the Imperial Japan
The Empire of Japan, also known as the Japanese Empire or Imperial Japan, was the Japanese nation state that existed from the Meiji Restoration on January 3, 1868, until the Constitution of Japan took effect on May 3, 1947. From Japan–Kor ...
attacked Pearl Harbor in Hawaii. Shortly afterwards in February 1942, President Franklin Roosevelt
Franklin Delano Roosevelt (January 30, 1882April 12, 1945), also known as FDR, was the 32nd president of the United States, serving from 1933 until his death in 1945. He is the longest-serving U.S. president, and the only one to have served ...
signed Executive Order 9066
Executive Order 9066 was a President of the United States, United States presidential executive order signed and issued during World War II by United States president Franklin D. Roosevelt on February 19, 1942. "This order authorized the fo ...
. The order forced approximately 120,000 Americans of Japanese descent (''Nisei
is a Japanese language, Japanese-language term used in countries in North America and South America to specify the nikkeijin, ethnically Japanese children born in the new country to Japanese-born immigrants, or . The , or Second generation imm ...
'') and Japanese-born residents (''Issei
are Japanese immigrants to countries in North America and South America. The term is used mostly by ethnic Japanese. are born in Japan; their children born in the new country are (, "two", plus , "generation"); and their grandchildren are ...
'') in California
California () is a U.S. state, state in the Western United States that lies on the West Coast of the United States, Pacific Coast. It borders Oregon to the north, Nevada and Arizona to the east, and shares Mexico–United States border, an ...
, Oregon
Oregon ( , ) is a U.S. state, state in the Pacific Northwest region of the United States. It is a part of the Western U.S., with the Columbia River delineating much of Oregon's northern boundary with Washington (state), Washington, while t ...
, Washington, and Alaska
Alaska ( ) is a non-contiguous U.S. state on the northwest extremity of North America. Part of the Western United States region, it is one of the two non-contiguous U.S. states, alongside Hawaii. Alaska is also considered to be the north ...
on the West Coast of the United States
The West Coast of the United States, also known as the Pacific Coast and the Western Seaboard, is the coastline along which the Western United States meets the North Pacific Ocean. The term typically refers to the Contiguous United States, contig ...
to leave their homes. About 5,000 left the off-limits area during the "voluntary evacuation" period, and avoided internment
Internment is the imprisonment of people, commonly in large groups, without Criminal charge, charges or Indictment, intent to file charges. The term is especially used for the confinement "of enemy citizens in wartime or of terrorism suspects ...
. The remaining 110,000 were soon removed from their homes by Army and National Guard troops.
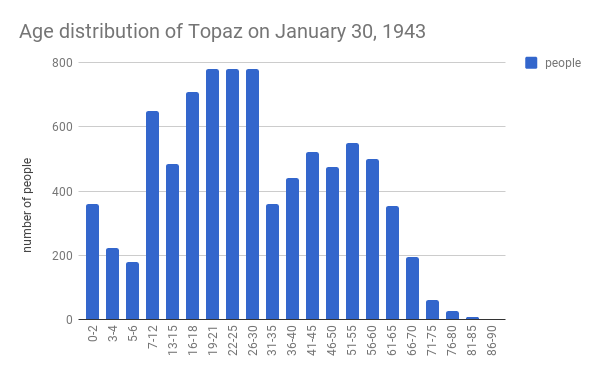
Topaz was opened September 11, 1942, and eventually became the fifth-largest city in Utah, with over 9,000 internees and staff, and covering approximately (mostly used for agriculture). A total of 11,212 people lived at Topaz at one time or another. Utah governor Herbert B. Maw opposed the relocation of any Japanese Americans into the state, stating that if they were such a danger to the West Coast, they would be a danger to Utah. Most internees arrived at Topaz from the Tanforan or Santa Anita Assembly Centers; the majority hailed from the San Francisco Bay Area. Sixty-five percent were ''Nisei'', American citizens born to Japanese immigrants. The camp was governed by Charles F. Ernst until June 1944, when the position was taken over by Luther T. Hoffman
Luther most commonly refers to:
* Martin Luther (1483–1546), German priest credited with initiating the Protestant Reformation
Luther may refer to:
People
* Luther (given name)
* Luther (surname)
Places
* Luther (crater), a lunar cra ...
following Ernst's resignation. It was closed on October 31, 1945.
Topaz was originally known as the Central Utah Relocation Authority, and then the Abraham Relocation Authority, but the names were too long for post office regulations. The final name, Topaz, came from Topaz Mountain which overlooks the camp from away.
Topaz was the primary internment site in the state of Utah
Utah is a landlocked state in the Mountain states, Mountain West subregion of the Western United States. It is one of the Four Corners states, sharing a border with Arizona, Colorado, and New Mexico. It also borders Wyoming to the northea ...
. A smaller camp existed briefly a few miles north of Moab
Moab () was an ancient Levant, Levantine kingdom whose territory is today located in southern Jordan. The land is mountainous and lies alongside much of the eastern shore of the Dead Sea. The existence of the Kingdom of Moab is attested to by ...
, which was used to isolate a few men considered to be troublemakers prior to their being sent to Leupp
Leupp () is a census-designated place (CDP) in Coconino County, Arizona, on the Navajo Nation, United States. The population was 951 at the 2010 United States Census, 2010 census.
In 1902 an Indian boarding school was constructed here, admi ...
, Arizona. A site at Antelope Springs, in the mountains west of Topaz, was used as a recreation area by the residents and staff of Topaz.
Life
Climate
Most internees came from the San Francisco Bay Area, which has awarm-summer Mediterranean climate
A Mediterranean climate ( ), also called a dry summer climate, described by Köppen and Trewartha as ''Cs'', is a temperate climate type that occurs in the lower mid-latitudes (normally 30 to 44 north and south latitude). Such climates typic ...
, with moist mild winters and dry summers. Topaz had an extreme climate, located at above sea level in the Sevier Desert. A "Midlatitude Desert" under the Köppen classification Köppen is a German surname. Notable people with the surname include:
* Bernd Köppen (1951–2014), German pianist and composer
* Carl Köppen (1833-1907), German military advisor in Meiji era Japan
* Edlef Köppen (1893–1939), German author ...
, temperatures could vary greatly throughout the day. The area experienced powerful winds and dust storms. One such storm caused structural damage to 75 buildings in 1944. Temperatures could reach below freezing from mid-September until the end of May. The average temperature in January was . Spring rains turned the clay soil to mud, which bred mosquitoes. Summers were hot, with occasional thunderstorms and temperatures that could exceed . In 1942, the first snowfall occurred on October 13, before camp construction was fully complete.
Architecture and living arrangements
Topaz contained a living complex known as the "city", about , as well as extensive agricultural lands. Within the city, 42 blocks were for internees, 34 of which were residential. Each residential block housed 200–300 people, housed in barracks that held five people within a single room. Families were generally housed together, while single adults would be housed with four other unrelated individuals. Residential blocks also contained a recreation hall, a mess hall, an office for the block manager, and a combined laundry/toilet/bathing facility. Each block contained only four bathtubs for all the women and four showers for all the men living there. These packed conditions often resulted in little privacy for residents. Barracks were built out of wood frame covered in tarpaper, with wooden floors. Many internees moved into the barracks before they were completed, exposing them to harsh weather. Eventually, they were lined with sheetrock, and the floors filled with masonite. While the construction began in July 1942, the first inmates moved in in September 1942, and the camp was not completed until early 1943. Camp construction was completed in part by 214 interned laborers who volunteered to arrive early and help build the camp. Rooms were heated by pot-bellied stoves. There was no furniture provided. Inmates used communal leftover scrap wood from construction to build beds, tables, and cabinets. Some families also modified their living quarters with fabric partitions. Water came from wells and was stored in a large wooden tank, and was "almost undrinkable" because of its alkalinity. Topaz also included a number of communal areas: a high school, two elementary schools, a 28-bed hospital, at least two churches, and a community garden. There was a cemetery as well, although it was never used. All 144 people who died in the camp were cremated and their ashes were held for burial until after the war. The camp was patrolled by 85–150 policemen, and was surrounded by a barbed wire fence. Manned watchtowers with searchlights were placed every surrounding the perimeter of the camp.Daily life
The camp was designed to be self-sufficient, and the majority of land within the camp was devoted to farming. Topaz inmates raised cattle, pigs, and chickens in addition to feed crops and vegetables. The vegetables were high-quality and won awards at the Millard County Fair. Due to harsh weather, poor soil, and short growing conditions, the camp was not able to supply all of its animal feed. Topaz contained two elementary schools: Desert View Elementary and Mountain View Elementary. Topaz High School educated students grades 7–12, and there was also an adult education program. The schools were taught by a combination of local teachers and internees. They were under-equipped and overcrowded, but enthusiastic teachers did their best. Topaz High School developed a devoted community, with frequent reunions after internment ended, and a final reunion in 2012. Sports were popular within the schools as well as within the adult population, with sports includingbaseball
Baseball is a bat-and-ball games, bat-and-ball sport played between two team sport, teams of nine players each, taking turns batting (baseball), batting and Fielding (baseball), fielding. The game occurs over the course of several Pitch ...
, basketball, and sumo
is a form of competitive full-contact wrestling where a ''rikishi'' (wrestler) attempts to force his opponent out of a circular ring (''dohyō'') or into touching the ground with any body part other than the soles of his feet (usually by th ...
wrestling. Cultural associations sprung up throughout the camp. Topaz had a newspaper called the ''Topaz Times'', a literary publication called ''Trek'', and two libraries which eventually contained almost 7,000 items in both English and Japanese. Artist Chiura Obata led the Tanforan Art School at Topaz, offering art instruction to over 600 students. Internment rules usurped parental authority, and teenagers often ate meals with their friends and only joined their families to sleep at night. This combined with a lack of privacy made it difficult for parents to discipline and bond with their children, which contributed to teenage delinquency in the camp.
Some internees were permitted to leave the camp to find employment. In 1942, internees were able to get permission to leave the camp for employment in nearby Delta, where they filled labor shortages caused by the draft, mostly in agricultural labor. In 1943, over 500 internees obtained seasonal agricultural work outside the camp, with another 130 working in domestic and industrial jobs. Polling showed that a majority of Utahns supported this policy. One teacher at the camp art school, Chiura Obata, was allowed to leave Topaz to run classes at nearby universities and churches.
Internees were also sometimes permitted to leave the camp for recreation. A former Civilian Conservation Corps
The Civilian Conservation Corps (CCC) was a voluntary government unemployment, work relief program that ran from 1933 to 1942 in the United States for unemployed, unmarried men ages 18–25 and eventually expanded to ages 17–28. The CCC was ...
camp at Antelope Springs, in mountains to the west, was taken over as a recreation area for internees and camp staff, and two buildings from Antelope Springs were brought to the central area to be used as Buddhist and Christian churches. During a rock hunting expedition in the Drum Mountains, west of Topaz, Akio Uhihera and Yoshio Nishimoto discovered and excavated a rare iron meteorite, which the Smithsonian Institution
The Smithsonian Institution ( ), or simply the Smithsonian, is a group of museums, Education center, education and Research institute, research centers, created by the Federal government of the United States, U.S. government "for the increase a ...
acquired.
Camp politics
In 1943, the War Relocation Authority (WRA) issued all adult internees a questionnaire assessing their level of Americanization. It was entitled "Application for Leave Clearance". Questions asked about what language they spoke most frequently, their religion, and recreational activities. Participating in judo and kendo were "Japanese" activities, while playing baseball or being Christian were considered "American". Two questions asked prisoners if they were willing to fight in the US Armed Forces and if they would swear allegiance to the United States and renounce loyalty to the Emperor of Japan. Many Japanese-bornIssei
are Japanese immigrants to countries in North America and South America. The term is used mostly by ethnic Japanese. are born in Japan; their children born in the new country are (, "two", plus , "generation"); and their grandchildren are ...
, who were barred from attaining American citizenship, resented the second question, feeling that an affirmative answer would leave them effectively stateless. Some Issei volunteered to join the army, even though there was no enlistment procedure for non-citizens. Others objected on other political grounds. In Topaz, nearly a fifth of male residents answered "no" to the question about allegiance. Inmates expressed their anger through a few scattered assaults against other inmates who they perceived as too close to the administration. Chiura Obata was among those attacked, resulting in his immediate release for fear of further assaults. A reworded version of the questionnaire for Issei did not require them to renounce their loyalty to the emperor of Japan. In response to the questionnaires, some Nisei formed the Resident Council for Japanese American Civil Rights, which encouraged other prisoners to register for the draft if their civil rights were restored.
A military sentry fatally shot 63-year-old chef James Hatsuaki Wakasa on April 11, 1943, while he was walking his dog inside the camp fence. Internees went on strike protesting the death and surrounding secrecy. They held a large funeral for Wakasa as a way to express their outrage. In response, the administration determined that fears of subversive activity at the camp were largely without basis, and significantly relaxed security. The military decided that officers who had been at war in the Pacific would not be assigned to guard duty at Topaz. The guard who shot Wakasa was reassigned after being found not guilty of violating military law; this information was not given to internees.
Topaz internees Fred Korematsu and Mitsuye Endo challenged their internment in court. Korematsu's case was heard and rejected at the US Supreme Court
The Supreme Court of the United States (SCOTUS) is the highest court in the federal judiciary of the United States. It has ultimate appellate jurisdiction over all Federal tribunals in the United States, U.S. federal court cases, and over Stat ...
('' Korematsu v. United States''), the largest case to challenge internment, while Endo's case was upheld. Chief Justice John Roberts
John Glover Roberts Jr. (born January 27, 1955) is an American jurist serving since 2005 as the 17th chief justice of the United States. He has been described as having a Moderate conservatism, moderate conservative judicial philosophy, thoug ...
repudiated and effectively overturned the ''Korematsu'' decision in his majority opinion in the 2018 case of ''Trump v. Hawaii
''Trump v. Hawaii'', No. 17-965, 585 U.S. 667 (2018), was a landmark United States Supreme Court case involving Presidential Proclamation 9645 signed by President Donald Trump, which restricted travel into the United States by people from seve ...
''. Korematsu would latter be awarded the Presidential Medal of Freedom
The Presidential Medal of Freedom is the highest civilian award of the United States, alongside the Congressional Gold Medal. It is an award bestowed by decision of the president of the United States to "any person recommended to the President ...
by Bill Clinton
William Jefferson Clinton (né Blythe III; born August 19, 1946) is an American politician and lawyer who was the 42nd president of the United States from 1993 to 2001. A member of the Democratic Party (United States), Democratic Party, ...
, and Endo would be awarded the Presidential Citizens Medal
The Presidential Citizens Medal is an award bestowed by the president of the United States. It is the second-highest civilian award in the United States and is second only to the Presidential Medal of Freedom. Established by executive order on N ...
by Joe Biden
Joseph Robinette Biden Jr. (born November 20, 1942) is an American politician who was the 46th president of the United States from 2021 to 2025. A member of the Democratic Party (United States), Democratic Party, he served as the 47th vice p ...
.
After closing
 After Topaz was closed, the land was sold and most of the buildings were auctioned off, disassembled, and removed from the site. Even the water pipes and utility poles were sold. Numerous foundations, concrete-lined excavations and other ground-level features can be seen at the various sites, but few buildings remain, and natural vegetation has taken over most of the abandoned areas.
In 1976, the Japanese American Citizens League placed a monument on the northwestern corner of the central area. On March 29, 2007,
After Topaz was closed, the land was sold and most of the buildings were auctioned off, disassembled, and removed from the site. Even the water pipes and utility poles were sold. Numerous foundations, concrete-lined excavations and other ground-level features can be seen at the various sites, but few buildings remain, and natural vegetation has taken over most of the abandoned areas.
In 1976, the Japanese American Citizens League placed a monument on the northwestern corner of the central area. On March 29, 2007, United States Secretary of the Interior
The United States secretary of the interior is the head of the United States Department of the Interior. The secretary and the Department of the Interior are responsible for the management and conservation of most federal land along with natura ...
Dirk Kempthorne designated "Central Utah Relocation Center Site" a National Historic Landmark
A National Historic Landmark (NHL) is a National Register of Historic Places property types, building, district, object, site, or structure that is officially recognized by the Federal government of the United States, United States government f ...
.
In 1982, Delta High School teacher Jane Beckwith and her journalism students began to study Topaz. She spearheaded the creation of the Topaz Museum Board in 1983, which oversaw the Topaz Museum, which initially shared space with the Great Basin Museum. Funding from the Japanese-American Confinement Sites organization enabled the Topaz Board to construct its own museum building in 2013. In 2015, the museum formally opened with an exhibition of art created at Topaz, entitled "When Words Weren't Enough: Works on Paper from Topaz, 1942–1945". The museum closed for remodeling in November 2016, and reopened in 2017 as a traditional museum focused on the history of Topaz. By 2017, the Topaz Museum and Board had purchased 634 of the 640 acres of the original internment site.
In media
In film
Using a smuggled camera, Dave Tatsuno shot film of Topaz. The documentary ''Topaz
Topaz is a silicate mineral made of aluminium, aluminum and fluorine with the chemical formula aluminium, Alsilicon, Sioxygen, O(fluorine, F, hydroxide, OH). It is used as a gemstone in jewelry and other adornments. Common topaz in its natural ...
'' uses film he shot from 1943 to 1945. This film was an inductee of the 1997 National Film Registry
The National Film Registry (NFR) is the United States National Film Preservation Board's (NFPB) collection of films selected for preservation (library and archival science), preservation, each selected for its cultural, historical, and aestheti ...
list, with the added distinction of being the second "home movie
A home movie is a short amateur film or video typically made just to preserve a visual record of family activities, a vacation, or a special event, and intended for viewing at home by family and friends. Originally, home movies were made on ph ...
" to be included on the Registry and the only color footage of camp life.
Topaz War Relocation Center is the setting for the 2007 film '' American Pastime'', a dramatization based on actual events, which tells the story of ''Nikkei'' baseball in the camps. A portion of the camp was duplicated for location shooting in Utah's Skull Valley, approximately west of Salt Lake City and north of the actual Topaz site. The film used some of Tatsuno's historical footage. In addition to Tatsuno's ''Topaz
Topaz is a silicate mineral made of aluminium, aluminum and fluorine with the chemical formula aluminium, Alsilicon, Sioxygen, O(fluorine, F, hydroxide, OH). It is used as a gemstone in jewelry and other adornments. Common topaz in its natural ...
'', Ken Verdoia made a 1987 documentary, also entitled ''Topaz''.
In literature
Yoshiko Uchida
Yoshiko Uchida (November 24, 1921 – June 21, 1992) was a Japanese American writer of children's books intended to share Japanese and Japanese-American history and culture with Japanese American children. She is most known for her series of bo ...
's young adult novel ''Journey to Topaz'' (published in 1971) recounts the story of Yuki, a young Japanese American girl, whose world is disrupted when, shortly after Pearl Harbor, she and her family must leave their comfortable home in the Berkeley, California
Berkeley ( ) is a city on the eastern shore of San Francisco Bay in northern Alameda County, California, United States. It is named after the 18th-century Anglo-Irish bishop and philosopher George Berkeley. It borders the cities of Oakland, Cali ...
suburbs for the dusty barracks of Topaz. The book is largely based on Uchida's personal experiences: she and her family were interned at Topaz for three years.
Julie Otsuka
Julie Otsuka (born May 15, 1962) is a Japanese-American author. She is known for drawing from her personal life to write autoethnographical historical novels about the life of Japanese Americans. In 2002 she published her first novel, ''When the ...
's novel '' When the Emperor was Divine'' (published in 2002) tells the story of a family forced to relocate from Berkeley to Topaz in September 1942. Each of the novel's five chapters is told from the point of view of a different character. Critics praised the book's "precise but poetic evocation of the ordinary" and "ability to empathize".
In his poetry collection ''Topaz'' (published in 2013), Brian Komei Dempster examines the experience of his mother and her family, tying the history of persecution and internment to subsequent generations’ search for a 21st-century identity.
In art
Much of the art made by detainees at the camp depicted life there, and survives. Drawings and woodcuts by Chiura Obata and Matsusaburō (George) Hibi are among the most prominent. Some of it is collected in ''The Art of Gaman: Arts and Crafts from the Japanese American Internment Camps, 1942–1946'' by Delphine Hirasuna, and has been exhibited in Topaz and at the Wight Art Gallery. In 2018, the Utah Museum of Fine Arts exhibited many Chiura Obata's works, including some made at Topaz.See also
*Japanese American Internment
During World War II, the United States forcibly relocated and incarcerated about 120,000 people of Japanese descent in ten concentration camps operated by the War Relocation Authority (WRA), mostly in the western interior of the country. Abou ...
* List of Japanese American Confinement Sites
* List of inmates of Topaz War Relocation Center
References
External links
The Topaz Museum digital archive
with links to photographs of camp, ''The Topaz Times'', and the elementary school diary
Archival links
*Papers from non-internee people at Topaz from the L. Tom Perry Special Collections, Harold B. Lee Library,Brigham Young University
Brigham Young University (BYU) is a Private education, private research university in Provo, Utah, United States. It was founded in 1875 by religious leader Brigham Young and is the flagship university of the Church Educational System sponsore ...
:
Doren Benjamin Boyce papers
MSS 7980
Duane L. Bishop conversations
MSS 2222
Walton LeGrande Law papers
MSS 8293 *From the J. Willard Marriott Library,
University of Utah
The University of Utah (the U, U of U, or simply Utah) is a public university, public research university in Salt Lake City, Utah, United States. It was established in 1850 as the University of Deseret (Book of Mormon), Deseret by the General A ...
Topaz Oral Histories
Topaz Internment Camp Documents, 1942–1943
MSS 170, Merrill-Cazier Library,
Utah State University
Utah State University (USU or Utah State) is a public university, public land grant colleges, land-grant research university with its main campus in Logan, Utah, United States. Founded in 1888 under the Morrill Land-Grant Acts as Utah's federal ...
*Collections from the University of California Calisphere:
War Relocation Authority Photographs of Japanese-American Evacuation and Resettlement
Bancroft Library
The Bancroft Library is the primary special-collections library of the University of California, Berkeley. It was acquired from its founder, Hubert Howe Bancroft, in 1905, with the proviso that it retain the name Bancroft Library in perpetuity. ...
Hisako Hibi pictorial collection concerning the Tanforan Assembly Center and the Central Utah Relocation Center
Japanese American National Museum
Photographs from the Yoshiaki Moriwaki family papers
The Bancroft Library
Topaz Times
at the
Library of Congress
The Library of Congress (LOC) is a research library in Washington, D.C., serving as the library and research service for the United States Congress and the ''de facto'' national library of the United States. It also administers Copyright law o ...
{{Authority control
1942 establishments in Utah
1945 disestablishments in Utah
Buildings and structures in Millard County, Utah
Great Basin National Heritage Area
Internment camps for Japanese Americans
National Historic Landmarks in Utah
Prisons in Utah
World War II on the National Register of Historic Places
Temporary populated places on the National Register of Historic Places
Buddhism in Utah