Tooth Scaling 9301 on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 A tooth ( : teeth) is a hard,
A tooth ( : teeth) is a hard,
/ref> Living amphibians typically have small teeth, or none at all, since they commonly feed only on soft foods. In reptiles, teeth are generally simple and conical in shape, although there is some variation between species, most notably the venom-injecting

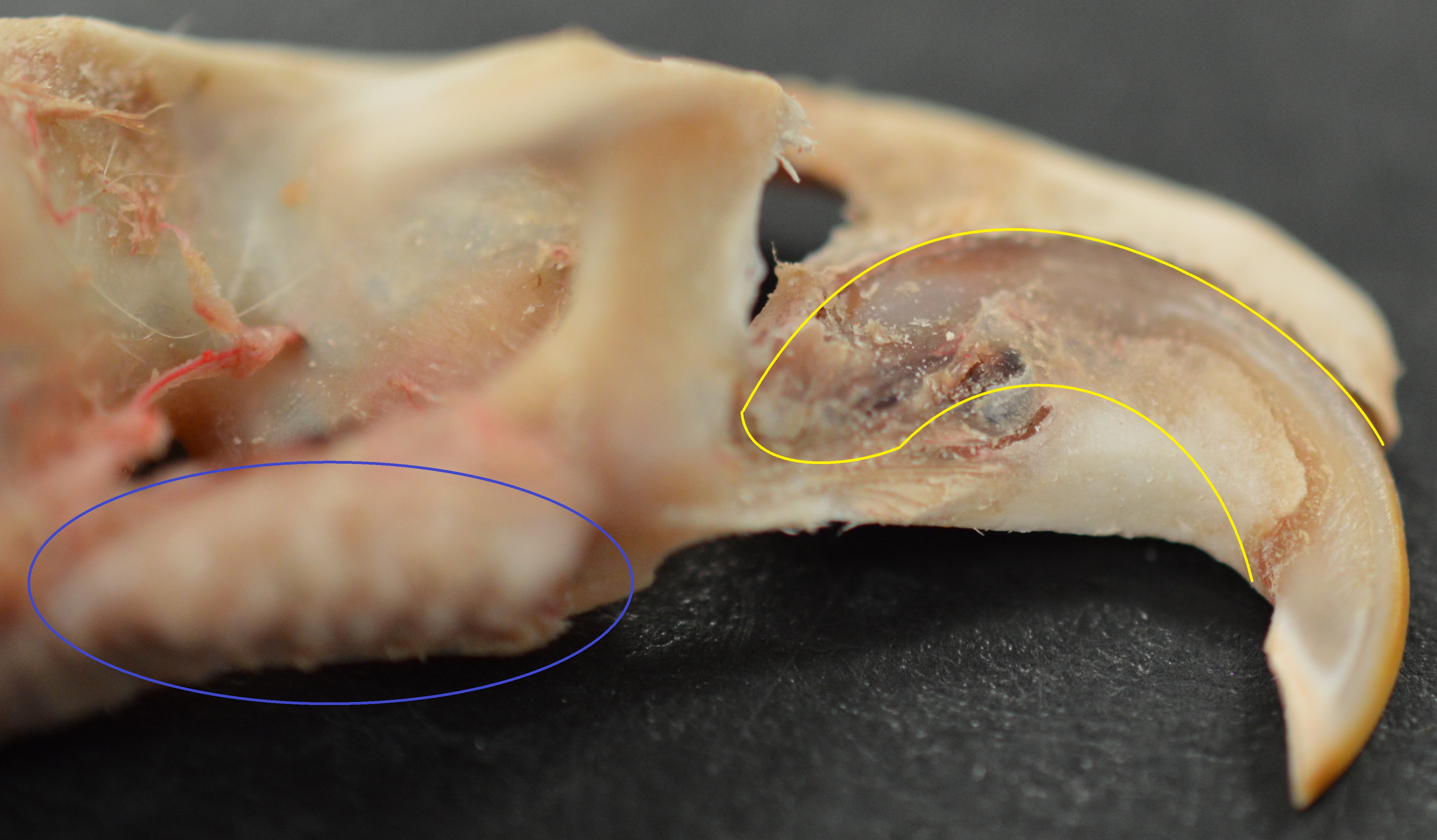



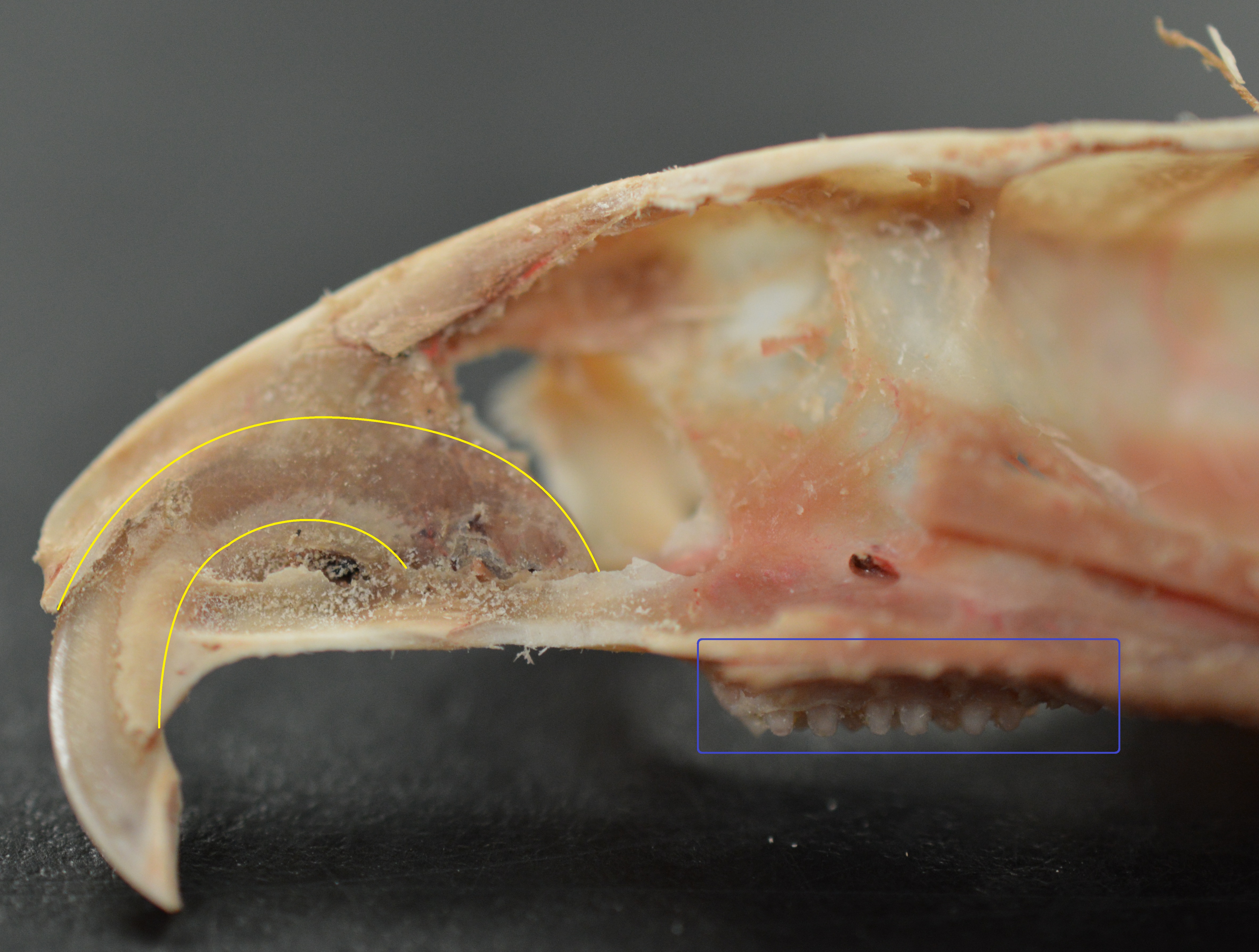 The teeth have enamel on the outside and exposed
The teeth have enamel on the outside and exposed

 True teeth are unique to vertebrates, although many invertebrates have analogous structures often referred to as teeth. The
True teeth are unique to vertebrates, although many invertebrates have analogous structures often referred to as teeth. The 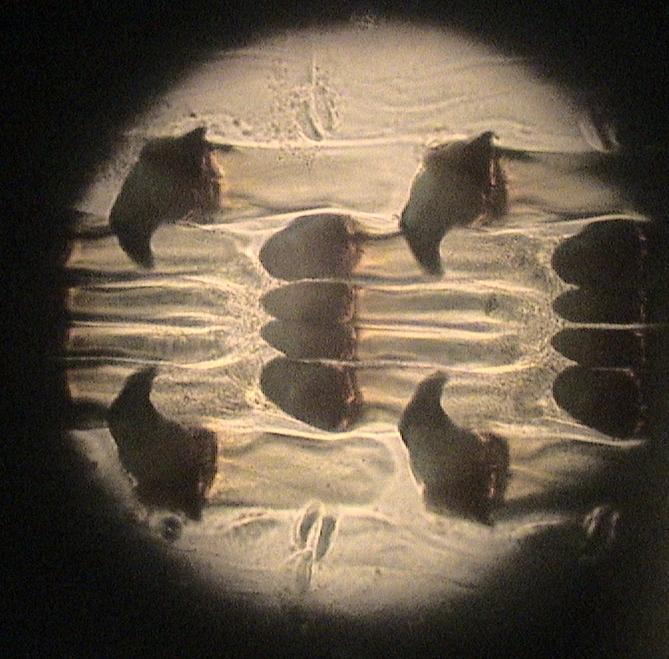 Molluscs have a structure called a
Molluscs have a structure called a
 A tooth ( : teeth) is a hard,
A tooth ( : teeth) is a hard, calcified
Calcification is the accumulation of calcium salts in a body tissue. It normally occurs in the formation of bone, but calcium can be deposited abnormally in soft tissue,Miller, J. D. Cardiovascular calcification: Orbicular origins. ''Nature Ma ...
structure found in the jaws (or mouth
In animal anatomy, the mouth, also known as the oral cavity, or in Latin cavum oris, is the opening through which many animals take in food and issue vocal sounds. It is also the cavity lying at the upper end of the alimentary canal, bounded on t ...
s) of many vertebrate
Vertebrates () comprise all animal taxon, taxa within the subphylum Vertebrata () (chordates with vertebral column, backbones), including all mammals, birds, reptiles, amphibians, and fish. Vertebrates represent the overwhelming majority of the ...
s and used to break down food
Food is any substance consumed by an organism for nutritional support. Food is usually of plant, animal, or fungal origin, and contains essential nutrients, such as carbohydrates, fats, proteins, vitamins, or minerals. The substance is ...
. Some animals, particularly carnivore
A carnivore , or meat-eater (Latin, ''caro'', genitive ''carnis'', meaning meat or "flesh" and ''vorare'' meaning "to devour"), is an animal or plant whose food and energy requirements derive from animal tissues (mainly muscle, fat and other ...
s and omnivore
An omnivore () is an animal that has the ability to eat and survive on both plant and animal matter. Obtaining energy and nutrients from plant and animal matter, omnivores digest carbohydrates, protein, fat, and fiber, and metabolize the nut ...
s, also use teeth to help with capturing or wounding prey, tearing food, for defensive purposes, to intimidate other animals often including their own, or to carry prey or their young. The roots of teeth are covered by gums
The gums or gingiva (plural: ''gingivae'') consist of the mucosal tissue that lies over the mandible and maxilla inside the mouth. Gum health and disease can have an effect on general health.
Structure
The gums are part of the soft tissue l ...
. Teeth are not made of bone, but rather of multiple tissues of varying density and hardness that originate from the embryonic germ layer
A germ layer is a primary layer of cells that forms during embryonic development. The three germ layers in vertebrates are particularly pronounced; however, all eumetazoans (animals that are sister taxa to the sponges) produce two or three pr ...
, the ectoderm
The ectoderm is one of the three primary germ layers formed in early embryonic development. It is the outermost layer, and is superficial to the mesoderm (the middle layer) and endoderm (the innermost layer). It emerges and originates from the o ...
.
The general structure of teeth is similar across the vertebrates, although there is considerable variation in their form and position. The teeth of mammals have deep roots, and this pattern is also found in some fish, and in crocodilian
Crocodilia (or Crocodylia, both ) is an order of mostly large, predatory, semiaquatic reptiles, known as crocodilians. They first appeared 95 million years ago in the Late Cretaceous period ( Cenomanian stage) and are the closest living ...
s. In most teleost
Teleostei (; Greek ''teleios'' "complete" + ''osteon'' "bone"), members of which are known as teleosts ), is, by far, the largest infraclass in the class Actinopterygii, the ray-finned fishes, containing 96% of all extant species of fish. Tel ...
fish, however, the teeth are attached to the outer surface of the bone, while in lizard
Lizards are a widespread group of squamate reptiles, with over 7,000 species, ranging across all continents except Antarctica, as well as most oceanic island chains. The group is paraphyletic since it excludes the snakes and Amphisbaenia al ...
s they are attached to the inner surface of the jaw by one side. In cartilaginous fish
Chondrichthyes (; ) is a class that contains the cartilaginous fishes that have skeletons primarily composed of cartilage. They can be contrasted with the Osteichthyes or ''bony fishes'', which have skeletons primarily composed of bone tissue. ...
, such as sharks, the teeth are attached by tough ligaments to the hoops of cartilage that form the jaw.
Some animals develop only one set of teeth (monophyodonts) while others are diphyodont A diphyodont is any animal with two ss of teeth, initially the ''deciduous'' set and consecutively the ''permanent'' set. Most mammals are diphyodonts—as to chew their food they need a strong, durable and complete set of teeth.
Diphyodonts contra ...
s, i.e. they have an early set of deciduous teeth and a later set of permanent or "adult" teeth. Still others develop many sets (polyphyodont
A polyphyodont is any animal whose teeth are continually replaced. In contrast, diphyodonts are characterized by having only two successive sets of teeth.
Polyphyodonts include most toothed fishes, many reptiles such as crocodiles and geckos, a ...
s). Shark
Sharks are a group of elasmobranch fish characterized by a cartilaginous skeleton, five to seven gill slits on the sides of the head, and pectoral fins that are not fused to the head. Modern sharks are classified within the clade Selachi ...
s, for example, grow a new set of teeth every two weeks to replace worn teeth. Most extant mammals including humans are diphyodonts, but there are exceptions including elephants, kangaroos, and manatees, all of which are polyphyodonts.
Rodent
Rodents (from Latin , 'to gnaw') are mammals of the Order (biology), order Rodentia (), which are characterized by a single pair of continuously growing incisors in each of the upper and lower jaws. About 40% of all mammal species are roden ...
incisors grow and wear away continually through gnawing, which helps maintain relatively constant length. The industry of the beaver
Beavers are large, semiaquatic rodents in the genus ''Castor'' native to the temperate Northern Hemisphere. There are two extant species: the North American beaver (''Castor canadensis'') and the Eurasian beaver (''C. fiber''). Beavers a ...
is due in part to this qualification. Many rodents such as vole
Voles are small rodents that are relatives of lemmings and hamsters, but with a stouter body; a longer, hairy tail; a slightly rounder head; smaller eyes and ears; and differently formed molars (high-crowned with angular cusps instead of lo ...
s and guinea pig
The guinea pig or domestic guinea pig (''Cavia porcellus''), also known as the cavy or domestic cavy (), is a species of rodent belonging to the genus '' Cavia'' in the family Caviidae. Breeders tend to use the word ''cavy'' to describe the ...
s, but not mice
A mouse ( : mice) is a small rodent. Characteristically, mice are known to have a pointed snout, small rounded ears, a body-length scaly tail, and a high breeding rate. The best known mouse species is the common house mouse (''Mus musculus' ...
, as well as leporidae
Leporidae is the family of rabbits and hares, containing over 60 species of extant mammals in all. The Latin word ''Leporidae'' means "those that resemble ''lepus''" (hare). Together with the pikas, the Leporidae constitute the mammalian ord ...
like rabbit
Rabbits, also known as bunnies or bunny rabbits, are small mammals in the family Leporidae (which also contains the hares) of the order Lagomorpha (which also contains the pikas). ''Oryctolagus cuniculus'' includes the European rabbit s ...
s, have continuously growing molars in addition to incisors. Also, tusk
Tusks are elongated, continuously growing front teeth that protrude well beyond the mouth of certain mammal species. They are most commonly canine teeth, as with pigs and walruses, or, in the case of elephants, elongated incisors. Tusks share ...
s (in tusked mammals) grow almost throughout life.
Teeth are not always attached to the jaw, as they are in mammals. In many reptiles and fish, teeth are attached to the palate
The palate () is the roof of the mouth in humans and other mammals. It separates the oral cavity from the nasal cavity.
A similar structure is found in crocodilians, but in most other tetrapods, the oral and nasal cavities are not truly s ...
or to the floor of the mouth, forming additional rows inside those on the jaws proper. Some teleost
Teleostei (; Greek ''teleios'' "complete" + ''osteon'' "bone"), members of which are known as teleosts ), is, by far, the largest infraclass in the class Actinopterygii, the ray-finned fishes, containing 96% of all extant species of fish. Tel ...
s even have teeth in the pharynx
The pharynx (plural: pharynges) is the part of the throat behind the mouth and nasal cavity, and above the oesophagus and trachea (the tubes going down to the stomach and the lungs). It is found in vertebrates and invertebrates, though its ...
. While not true teeth in the usual sense, the dermal denticle
A fish scale is a small rigid plate that grows out of the skin of a fish. The skin of most jawed fishes is covered with these protective scales, which can also provide effective camouflage through the use of reflection and colouration, as w ...
s of sharks are almost identical in structure and are likely to have the same evolutionary origin. Indeed, teeth appear to have first evolved in sharks, and are not found in the more primitive jawless fish
Agnatha (, Ancient Greek 'without jaws') is an infraphylum of jawless fish in the phylum Chordata, subphylum Vertebrata, consisting of both present (Cyclostomata, cyclostomes) and extinct (conodonts and ostracoderms) species. Among recent animal ...
– while lamprey
Lampreys (sometimes inaccurately called lamprey eels) are an ancient extant lineage of jawless fish of the order Petromyzontiformes , placed in the superclass Cyclostomata. The adult lamprey may be characterized by a toothed, funnel-like s ...
s do have tooth-like structures on the tongue, these are in fact, composed of keratin
Keratin () is one of a family of structural fibrous proteins also known as ''scleroproteins''. Alpha-keratin (α-keratin) is a type of keratin found in vertebrates. It is the key structural material making up scales, hair, nails, feathers, ...
, not of dentine or enamel, and bear no relationship to true teeth. Though "modern" teeth-like structures with dentine
Dentin () (American English) or dentine ( or ) (British English) ( la, substantia eburnea) is a calcified tissue of the body and, along with enamel, cementum, and pulp, is one of the four major components of teeth. It is usually covered by e ...
and enamel have been found in late conodont
Conodonts ( Greek ''kōnos'', " cone", + ''odont'', " tooth") are an extinct group of agnathan (jawless) vertebrates resembling eels, classified in the class Conodonta. For many years, they were known only from their tooth-like oral elements, w ...
s, they are now supposed to have evolved independently of later vertebrates' teeth.nature.com, ''Fossil scans reveal origins of teeth'', 16 October 2013/ref> Living amphibians typically have small teeth, or none at all, since they commonly feed only on soft foods. In reptiles, teeth are generally simple and conical in shape, although there is some variation between species, most notably the venom-injecting
fang
A fang is a long, pointed tooth. In mammals, a fang is a modified maxillary tooth, used for biting and tearing flesh. In snakes, it is a specialized tooth that is associated with a venom gland (see snake venom). Spiders also have external fan ...
s of snake
Snakes are elongated, limbless, carnivorous reptiles of the suborder Serpentes . Like all other squamates, snakes are ectothermic, amniote vertebrates covered in overlapping scales. Many species of snakes have skulls with several more j ...
s. The pattern of incisors, canines, premolars and molars is found only in mammals, and to varying extents, in their evolutionary ancestors. The numbers of these types of teeth vary greatly between species; zoologists use a standardised dental formula
Dentition pertains to the development of teeth and their arrangement in the mouth. In particular, it is the characteristic arrangement, kind, and number of teeth in a given species at a given age. That is, the number, type, and morpho-physiolog ...
to describe the precise pattern in any given group.
Etymology
The word ''tooth'' comes fromProto-Germanic
Proto-Germanic (abbreviated PGmc; also called Common Germanic) is the reconstructed proto-language of the Germanic branch of the Indo-European languages.
Proto-Germanic eventually developed from pre-Proto-Germanic into three Germanic bran ...
*''tanthu''- which in turn comes from Proto-Indo-European
Proto-Indo-European (PIE) is the reconstructed common ancestor of the Indo-European language family. Its proposed features have been derived by linguistic reconstruction from documented Indo-European languages. No direct record of Proto-Indo- ...
*''h₁dent''-, which was composed of the root *''h₁ed''- ("to eat") plus the active participle suffix -''nt'', therefore it literally meant "that which eats". Cognate with Latin
Latin (, or , ) is a classical language belonging to the Italic branch of the Indo-European languages. Latin was originally a dialect spoken in the lower Tiber area (then known as Latium) around present-day Rome, but through the power ...
''dēns'', Greek
Greek may refer to:
Greece
Anything of, from, or related to Greece, a country in Southern Europe:
*Greeks, an ethnic group.
*Greek language, a branch of the Indo-European language family.
**Proto-Greek language, the assumed last common ancestor ...
ὀδούς ''odous'', and Sanskrit
Sanskrit (; attributively , ; nominalization, nominally , , ) is a classical language belonging to the Indo-Aryan languages, Indo-Aryan branch of the Indo-European languages. It arose in South Asia after its predecessor languages had Trans-cul ...
''dát''.
Origin
Teeth are assumed to have evolved either fromectoderm
The ectoderm is one of the three primary germ layers formed in early embryonic development. It is the outermost layer, and is superficial to the mesoderm (the middle layer) and endoderm (the innermost layer). It emerges and originates from the o ...
denticles (scales, much like those on the skin of sharks) that folded and integrated into the mouth (called the "outside–in" theory), or from endoderm
Endoderm is the innermost of the three primary germ layers in the very early embryo. The other two layers are the ectoderm (outside layer) and mesoderm (middle layer). Cells migrating inward along the archenteron form the inner layer of the gast ...
pharyngeal teeth (primarily formed in the pharynx
The pharynx (plural: pharynges) is the part of the throat behind the mouth and nasal cavity, and above the oesophagus and trachea (the tubes going down to the stomach and the lungs). It is found in vertebrates and invertebrates, though its ...
of jawless vertebrates) (the "inside–out" theory). In addition, there is another theory stating that neural crest
Neural crest cells are a temporary group of cells unique to vertebrates that arise from the embryonic ectoderm germ layer, and in turn give rise to a diverse cell lineage—including melanocytes, craniofacial cartilage and bone, smooth muscle, ...
gene regulatory network
A gene (or genetic) regulatory network (GRN) is a collection of molecular regulators that interact with each other and with other substances in the cell to govern the gene expression levels of mRNA and proteins which, in turn, determine the fun ...
, and neural crest-derived ectomesenchyme are the key to generate teeth (with any epithelium, either ectoderm or endoderm).
The genes governing tooth development in mammals are homologous
Homology may refer to:
Sciences
Biology
*Homology (biology), any characteristic of biological organisms that is derived from a common ancestor
*Sequence homology, biological homology between DNA, RNA, or protein sequences
* Homologous chrom ...
to those involved in the development of fish scales. Study of a tooth plate of a fossil of the extinct fish '' Romundina stellina'' showed that the teeth and scales were made of the same tissues, also found in mammal teeth, lending support to the theory that teeth evolved as a modification of scales.
Mammals
Teeth are among the most distinctive (and long-lasting) features of mammal species.Paleontologists
Paleontology (), also spelled palaeontology or palæontology, is the scientific study of life that existed prior to, and sometimes including, the start of the Holocene epoch (roughly 11,700 years before present). It includes the study of fossi ...
use teeth to identify fossil
A fossil (from Classical Latin , ) is any preserved remains, impression, or trace of any once-living thing from a past geological age. Examples include bones, shells, exoskeletons, stone imprints of animals or microbes, objects preserved ...
species and determine their relationships. The shape of the animal
Animals are multicellular, eukaryotic organisms in the Kingdom (biology), biological kingdom Animalia. With few exceptions, animals Heterotroph, consume organic material, Cellular respiration#Aerobic respiration, breathe oxygen, are Motilit ...
's teeth are related to its diet. For example, plant matter is hard to digest, so herbivore
A herbivore is an animal anatomically and physiologically adapted to eating plant material, for example foliage or marine algae, for the main component of its diet. As a result of their plant diet, herbivorous animals typically have mouthp ...
s have many molars
The molars or molar teeth are large, flat teeth at the back of the mouth. They are more developed in mammals. They are used primarily to grind food during chewing. The name ''molar'' derives from Latin, ''molaris dens'', meaning "millstone to ...
for chewing
Chewing or mastication is the process by which food is crushed and ground by teeth. It is the first step of digestion, and it increases the surface area of foods to allow a more efficient break down by enzymes. During the mastication process, ...
and grinding. Carnivore
A carnivore , or meat-eater (Latin, ''caro'', genitive ''carnis'', meaning meat or "flesh" and ''vorare'' meaning "to devour"), is an animal or plant whose food and energy requirements derive from animal tissues (mainly muscle, fat and other ...
s, on the other hand, have canine teeth
In mammalian oral anatomy, the canine teeth, also called cuspids, dog teeth, or (in the context of the upper jaw) fangs, eye teeth, vampire teeth, or vampire fangs, are the relatively long, pointed teeth. They can appear more flattened however ...
to kill prey and to tear meat.
Mammals
Mammals () are a group of vertebrate animals constituting the class Mammalia (), characterized by the presence of mammary glands which in females produce milk for feeding (nursing) their young, a neocortex (a region of the brain), fu ...
, in general, are diphyodont A diphyodont is any animal with two ss of teeth, initially the ''deciduous'' set and consecutively the ''permanent'' set. Most mammals are diphyodonts—as to chew their food they need a strong, durable and complete set of teeth.
Diphyodonts contra ...
, meaning that they develop two sets of teeth. In humans
Humans (''Homo sapiens'') are the most abundant and widespread species of primate, characterized by bipedalism and exceptional cognitive skills due to a large and complex brain. This has enabled the development of advanced tools, culture, ...
, the first set (the "baby," "milk," "primary" or "deciduous
In the fields of horticulture and Botany, the term ''deciduous'' () means "falling off at maturity" and "tending to fall off", in reference to trees and shrubs that seasonally shed leaves, usually in the autumn; to the shedding of petals, a ...
" set) normally starts to appear at about six months of age, although some babies are born with one or more visible teeth, known as neonatal teeth. Normal tooth eruption
Tooth eruption is a process in tooth development in which the teeth enter the mouth and become visible. It is currently believed that the periodontal ligament plays an important role in tooth eruption. The first human teeth to appear, the decidu ...
at about six months is known as teething and can be painful. Kangaroos
Kangaroos are four marsupials from the family Macropodidae (macropods, meaning "large foot"). In common use the term is used to describe the largest species from this family, the red kangaroo, as well as the antilopine kangaroo, eastern ...
, elephant
Elephants are the largest existing land animals. Three living species are currently recognised: the African bush elephant, the African forest elephant, and the Asian elephant. They are the only surviving members of the family Elephantidae ...
s, and manatees
Manatees (family Trichechidae, genus ''Trichechus'') are large, fully aquatic, mostly herbivorous marine mammals sometimes known as sea cows. There are three accepted living species of Trichechidae, representing three of the four living species ...
are unusual among mammals because they are polyphyodont
A polyphyodont is any animal whose teeth are continually replaced. In contrast, diphyodonts are characterized by having only two successive sets of teeth.
Polyphyodonts include most toothed fishes, many reptiles such as crocodiles and geckos, a ...
s.
Aardvark
Inaardvark
The aardvark ( ; ''Orycteropus afer'') is a medium-sized, burrowing, nocturnal mammal native to Africa. It is the only living species of the order Tubulidentata, although other prehistoric species and genera of Tubulidentata are known. Unlike ...
s, teeth lack enamel and have many pulp tubules, hence the name of the order Tubulidentata
Orycteropodidae is a family of afrotherian mammals. Although there are many fossil species, the only species surviving today is the aardvark, ''Orycteropus afer''. Orycteropodidae is recognized as the only family within the order Tubulidentata ...
.
Canines
In dogs, the teeth are less likely than humans to formdental cavities
Dental may refer to:
* Dental consonant, in phonetics
* Dental Records, an independent UK record label
* Dentistry, oral medicine
* Teeth
See also
*
* Dental care (disambiguation)
* Dentist (disambiguation)
A dentist is a practitioner of denti ...
because of the very high pH of dog saliva, which prevents enamel from demineralizing. Sometimes called cuspids, these teeth are shaped like points (cusps) and are used for tearing and grasping food.
Cetaceans
Like human teeth,whale
Whales are a widely distributed and diverse group of fully aquatic placental marine mammals. As an informal and colloquial grouping, they correspond to large members of the infraorder Cetacea, i.e. all cetaceans apart from dolphins and ...
teeth have polyp-like protrusions located on the root surface of the tooth. These polyps are made of cementum in both species, but in human teeth, the protrusions are located on the outside of the root, while in whales the nodule is located on the inside of the pulp chamber. While the roots of human teeth are made of cementum on the outer surface, whales have cementum on the entire surface of the tooth with a very small layer of enamel at the tip. This small enamel layer is only seen in older whales where the cementum has been worn away to show the underlying enamel.
The toothed whale is a suborder
Order ( la, ordo) is one of the eight major hierarchical taxonomic ranks in Linnaean taxonomy. It is classified between family and class. In biological classification, the order is a taxonomic rank used in the classification of organisms and ...
of the cetacean
Cetacea (; , ) is an infraorder of aquatic mammals that includes whales, dolphins, and porpoises. Key characteristics are their fully aquatic lifestyle, streamlined body shape, often large size and exclusively carnivorous diet. They propel them ...
s characterized by having teeth. The teeth differ considerably among the species. They may be numerous, with some dolphin
A dolphin is an aquatic mammal within the infraorder Cetacea. Dolphin species belong to the families Delphinidae (the oceanic dolphins), Platanistidae (the Indian river dolphins), Iniidae (the New World river dolphins), Pontoporiidae (t ...
s bearing over 100 teeth in their jaws. On the other hand, the narwhals have a giant unicorn-like tusk, which is a tooth containing millions of sensory pathways and used for sensing during feeding, navigation, and mating. It is the most neurologically complex tooth known. Beaked whales are almost toothless, with only bizarre teeth found in males. These teeth may be used for feeding but also for demonstrating aggression and showmanship.
Primates
Inhuman
Humans (''Homo sapiens'') are the most abundant and widespread species of primate, characterized by bipedalism and exceptional cognitive skills due to a large and complex brain. This has enabled the development of advanced tools, culture, ...
s (and most other primates) there are usually 20 primary (also "baby" or "milk") teeth, and later up to 32 permanent teeth. Four of these 32 may be third molars or wisdom teeth, although these are not present in all adults, and may be removed surgically later in life.
Among primary teeth, 10 of them are usually found in the maxilla
The maxilla (plural: ''maxillae'' ) in vertebrates is the upper fixed (not fixed in Neopterygii) bone of the jaw formed from the fusion of two maxillary bones. In humans, the upper jaw includes the hard palate in the front of the mouth. The ...
(i.e. upper jaw) and the other 10 in the mandible
In anatomy, the mandible, lower jaw or jawbone is the largest, strongest and lowest bone in the human facial skeleton. It forms the lower jaw and holds the lower teeth in place. The mandible sits beneath the maxilla. It is the only movable bon ...
(i.e. lower jaw). Among permanent teeth, 16 are found in the maxilla and the other 16 in the mandible. Most of the teeth have uniquely distinguishing features.
Horse
An adulthorse
The horse (''Equus ferus caballus'') is a domesticated, one-toed, hoofed mammal. It belongs to the taxonomic family Equidae and is one of two extant subspecies of ''Equus ferus''. The horse has evolved over the past 45 to 55 million ...
has between 36 and 44 teeth. The enamel and dentin layers of horse teeth are intertwined. All horses have 12 premolars, 12 molars, and 12 incisors. Generally, all male equines also have four canine teeth
In mammalian oral anatomy, the canine teeth, also called cuspids, dog teeth, or (in the context of the upper jaw) fangs, eye teeth, vampire teeth, or vampire fangs, are the relatively long, pointed teeth. They can appear more flattened however ...
(called tushes) between the molars and incisors. However, few female horses (less than 28%) have canines, and those that do usually have only one or two, which many times are only partially erupted. A few horses have one to four wolf teeth
Wolf teeth are small, peg-like horse teeth, which sit just in front of (or rostral to) the first cheek teeth of horses and other equids. They are vestigial first premolars, and the first cheek tooth is referred to as the second premolar even whe ...
, which are vestigial
Vestigiality is the retention, during the process of evolution, of genetically determined structures or attributes that have lost some or all of the ancestral function in a given species. Assessment of the vestigiality must generally rely on co ...
premolars, with most of those having only one or two. They are equally common in male and female horses and much more likely to be on the upper jaw. If present these can cause problems as they can interfere with the horse's bit
The bit is the most basic unit of information in computing and digital communications. The name is a portmanteau of binary digit. The bit represents a logical state with one of two possible values. These values are most commonly represented a ...
contact. Therefore, wolf teeth are commonly removed.
Horse teeth
Horse teeth refers to the dentition of equine species, including horses and donkeys. Equines are both heterodontous and diphyodontous, which means that they have teeth in more than one shape (there are up to five shapes of tooth in a horse's mo ...
can be used to estimate the animal's age. Between birth and five years, age can be closely estimated by observing the eruption pattern on milk teeth and then permanent teeth. By age five, all permanent teeth have usually erupted. The horse is then said to have a "full" mouth. After the age of five, age can only be conjectured by studying the wear patterns on the incisors, shape, the angle at which the incisors meet, and other factors. The wear of teeth may also be affected by diet, natural abnormalities, and cribbing. Two horses of the same age may have different wear patterns.
A horse's incisors, premolars, and molars, once fully developed, continue to erupt as the grinding surface is worn down through chewing. A young adult horse will have teeth which are long, with the majority of the crown remaining below the gumline in the dental socket. The rest of the tooth will slowly emerge from the jaw, erupting about each year, as the horse ages. When the animal reaches old age, the crowns of the teeth are very short and the teeth are often lost altogether. Very old horses, if lacking molars, may need to have their fodder
Fodder (), also called provender (), is any agricultural foodstuff used specifically to feed domesticated livestock, such as cattle, rabbits, sheep, horses, chickens and pigs. "Fodder" refers particularly to food given to the animals (including ...
ground up and soaked in water to create a soft mush for them to eat in order to obtain adequate nutrition.
Proboscideans

Elephant
Elephants are the largest existing land animals. Three living species are currently recognised: the African bush elephant, the African forest elephant, and the Asian elephant. They are the only surviving members of the family Elephantidae ...
s' tusk
Tusks are elongated, continuously growing front teeth that protrude well beyond the mouth of certain mammal species. They are most commonly canine teeth, as with pigs and walruses, or, in the case of elephants, elongated incisors. Tusks share ...
s are specialized incisors for digging food up and fighting. Some elephant teeth are similar to those in manatee
Manatees (family Trichechidae, genus ''Trichechus'') are large, fully aquatic, mostly herbivorous marine mammals sometimes known as sea cows. There are three accepted living species of Trichechidae, representing three of the four living speci ...
s, and it is notable that elephants are believed to have undergone an aquatic phase in their evolution.
At birth, elephants have a total of 28 molar plate-like grinding teeth not including the tusks. These are organized into four sets of seven successively larger teeth which the elephant will slowly wear through during its lifetime of chewing rough plant material. Only four teeth are used for chewing at a given time, and as each tooth wears out, another tooth moves forward to take its place in a process similar to a conveyor belt. The last and largest of these teeth usually becomes exposed when the animal is around 40 years of age, and will often last for an additional 20 years. When the last of these teeth has fallen out, regardless of the elephant's age, the animal will no longer be able to chew food and will die of starvation.
Rabbit
Rabbit
Rabbits, also known as bunnies or bunny rabbits, are small mammals in the family Leporidae (which also contains the hares) of the order Lagomorpha (which also contains the pikas). ''Oryctolagus cuniculus'' includes the European rabbit s ...
s and other lagomorph
The lagomorphs are the members of the taxonomic order Lagomorpha, of which there are two living families: the Leporidae (hares and rabbits) and the Ochotonidae (pikas). The name of the order is derived from the Ancient Greek ''lagos'' (λαγ� ...
s usually shed their deciduous teeth before (or very shortly after) their birth, and are usually born with their permanent teeth. The teeth of rabbits complement their diet, which consists of a wide range of vegetation. Since many of the foods are abrasive enough to cause attrition, rabbit teeth grow continuously throughout life. Rabbits have a total of 6 incisors, three upper premolars, three upper molars, two lower premolars, and two lower molars on each side. There are no canines. Three to four millimeters of the tooth is worn away by incisors every week, whereas the posterior teeth require a month to wear away the same amount.
The incisors and cheek teeth of rabbits are called aradicular hypsodont teeth. This is sometimes referred to as an elodent dentition. These teeth grow or erupt continuously. The growth or eruption is held in balance by dental abrasion from chewing a diet high in fiber.



Rodents
Rodent
Rodents (from Latin , 'to gnaw') are mammals of the Order (biology), order Rodentia (), which are characterized by a single pair of continuously growing incisors in each of the upper and lower jaws. About 40% of all mammal species are roden ...
s have upper and lower hypselodont incisors that can continuously grow enamel throughout its life without having properly formed roots. These teeth are also known as aradicular teeth, and unlike humans whose ameloblasts
Ameloblasts are cells present only during tooth development that deposit tooth enamel, which is the hard outermost layer of the tooth forming the surface of the crown.
Structure
Each ameloblast is a columnar cell approximately 4 micrometers in ...
die after tooth development
Tooth development or odontogenesis is the complex process by which teeth form from embryonic cells, grow, and erupt into the mouth. For human teeth to have a healthy oral environment, all parts of the tooth must develop during appropriate stag ...
, rodents continually produce enamel, they must wear down their teeth by gnawing on various materials. Enamel and dentin
Dentin () (American English) or dentine ( or ) (British English) ( la, substantia eburnea) is a calcified tissue of the body and, along with enamel, cementum, and pulp, is one of the four major components of teeth. It is usually covered by e ...
are produced by the enamel organ
The enamel organ, also known as the dental organ, is a cellular aggregation seen in a developing tooth and it lies above the dental papilla. The enamel organ which is differentiated from the primitive oral epithelium lining the stomodeum.The enam ...
, and growth is dependent on the presence of stem cells
In multicellular organisms, stem cells are undifferentiated or partially differentiated cells that can differentiate into various types of cells and proliferate indefinitely to produce more of the same stem cell. They are the earliest type of ...
, cellular amplification, and cellular maturation structures in the odontogenic region. Rodent incisors are used for cutting wood, biting through the skin of fruit, or for defense. This allows for the rate of wear and tooth growth to be at equilibrium. The microstructure of rodent incisor enamel has shown to be useful in studying the phylogeny and systematics of rodents because of its independent evolution from the other dental traits. The enamel on rodent incisors are composed of two layers: the inner portio interna (PI) with Hunter-Schreger bands (HSB) and an outer portio externa (PE) with radial enamel (RE). It usually involves the differential regulation of the epithelial
Epithelium or epithelial tissue is one of the four basic types of animal tissue, along with connective tissue, muscle tissue and nervous tissue. It is a thin, continuous, protective layer of compactly packed cells with a little intercellu ...
stem cell
In multicellular organisms, stem cells are undifferentiated or partially differentiated cells that can differentiate into various types of cells and proliferate indefinitely to produce more of the same stem cell. They are the earliest type of ...
niche in the tooth of two rodent species, such as guinea pigs
The guinea pig or domestic guinea pig (''Cavia porcellus''), also known as the cavy or domestic cavy (), is a species of rodent belonging to the genus '' Cavia'' in the family Caviidae. Breeders tend to use the word ''cavy'' to describe the ...
.Tummers M and Thesleff I. Root or crown: a developmental choice orchestrated by the differential regulation of the epithelial stem cell niche in the tooth of two rodent species. Development (2003). 130(6):1049-57.AM Hunt. A description of the molar teeth and investing tissues of normal guinea pigs. J Dent Res. (1959) 38(2):216-31.
 The teeth have enamel on the outside and exposed
The teeth have enamel on the outside and exposed dentin
Dentin () (American English) or dentine ( or ) (British English) ( la, substantia eburnea) is a calcified tissue of the body and, along with enamel, cementum, and pulp, is one of the four major components of teeth. It is usually covered by e ...
on the inside, so they self-sharpen during gnawing. On the other hand, continually growing molars
The molars or molar teeth are large, flat teeth at the back of the mouth. They are more developed in mammals. They are used primarily to grind food during chewing. The name ''molar'' derives from Latin, ''molaris dens'', meaning "millstone to ...
are found in some rodent species, such as the sibling vole and the guinea pig
The guinea pig or domestic guinea pig (''Cavia porcellus''), also known as the cavy or domestic cavy (), is a species of rodent belonging to the genus '' Cavia'' in the family Caviidae. Breeders tend to use the word ''cavy'' to describe the ...
. There is variation in the dentition of the rodents, but generally, rodents lack canines and premolars
The premolars, also called premolar teeth, or bicuspids, are transitional teeth located between the canine and molar teeth. In humans, there are two premolars per quadrant in the permanent set of teeth, making eight premolars total in the mouth ...
, and have a space between their incisors
Incisors (from Latin ''incidere'', "to cut") are the front teeth present in most mammals. They are located in the premaxilla above and on the mandible below. Humans have a total of eight (two on each side, top and bottom). Opossums have 18, wh ...
and molars
The molars or molar teeth are large, flat teeth at the back of the mouth. They are more developed in mammals. They are used primarily to grind food during chewing. The name ''molar'' derives from Latin, ''molaris dens'', meaning "millstone to ...
, called the diastema
A diastema (plural diastemata, from Greek διάστημα, space) is a space or gap between two teeth. Many species of mammals have diastemata as a normal feature, most commonly between the incisors and molars. More colloquially, the condition ...
region.
Manatee
Manatees
Manatees (family Trichechidae, genus ''Trichechus'') are large, fully aquatic, mostly herbivorous marine mammals sometimes known as sea cows. There are three accepted living species of Trichechidae, representing three of the four living species ...
are polyphyodont with mandibular molars developing separately from the jaw and are encased in a bony shell separated by soft tissue.
Walrus
Walrus
The walrus (''Odobenus rosmarus'') is a large flippered marine mammal with a discontinuous distribution about the North Pole in the Arctic Ocean and subarctic seas of the Northern Hemisphere. The walrus is the only living species in the f ...
tusks are canine teeth that grow continuously throughout life.
Fish

Fish
Fish are aquatic, craniate, gill-bearing animals that lack limbs with digits. Included in this definition are the living hagfish, lampreys, and cartilaginous and bony fish as well as various extinct related groups. Approximately 95% ...
, such as shark
Sharks are a group of elasmobranch fish characterized by a cartilaginous skeleton, five to seven gill slits on the sides of the head, and pectoral fins that are not fused to the head. Modern sharks are classified within the clade Selachi ...
s, may go through many teeth in their lifetime. The replacement of multiple teeth is known as polyphyodont
A polyphyodont is any animal whose teeth are continually replaced. In contrast, diphyodonts are characterized by having only two successive sets of teeth.
Polyphyodonts include most toothed fishes, many reptiles such as crocodiles and geckos, a ...
ia.
A class of prehistoric shark are called cladodonts for their strange forked teeth.
Unlike the continuous shedding of functional teeth seen in modern sharks, the majority of stem
Stem or STEM may refer to:
Plant structures
* Plant stem, a plant's aboveground axis, made of vascular tissue, off which leaves and flowers hang
* Stipe (botany), a stalk to support some other structure
* Stipe (mycology), the stem of a mushr ...
chondrichthyan
Chondrichthyes (; ) is a class that contains the cartilaginous fishes that have skeletons primarily composed of cartilage. They can be contrasted with the Osteichthyes or ''bony fishes'', which have skeletons primarily composed of bone tissue. C ...
lineages retained all tooth generations developed throughout the life of the animal. This replacement mechanism is exemplified by the tooth whorl-based dentitions of acanthodians
Acanthodii or acanthodians is an extinct class of gnathostomes (jawed fishes), typically considered a paraphyletic group. They are currently considered to represent a grade of various fish lineages leading up to the extant Chondrichthyes, which ...
, which include the oldest known toothed vertebrate, ''Qianodus'' ''duplicis'.''
Amphibians
All amphibians havepedicellate teeth Pedicellate teeth are a tooth morphology today unique to modern amphibians
Amphibians are four-limbed and ectothermic vertebrates of the class Amphibia. All living amphibians belong to the group Lissamphibia. They inhabit a wide variety ...
which are modified to be flexible due to connective tissue and uncalcified dentin
Dentin () (American English) or dentine ( or ) (British English) ( la, substantia eburnea) is a calcified tissue of the body and, along with enamel, cementum, and pulp, is one of the four major components of teeth. It is usually covered by e ...
e that separates the crown from the base of the tooth.
Most amphibians exhibit teeth that have a slight attachment to the jaw or acrodont teeth. Acrodont teeth exhibit limited connection to the dentary
In anatomy, the mandible, lower jaw or jawbone is the largest, strongest and lowest bone in the human facial skeleton. It forms the lower jaw and holds the lower teeth in place. The mandible sits beneath the maxilla. It is the only movable bone ...
and have little enervation. This is ideal for organisms who mostly use their teeth for grasping, but not for crushing and allows for rapid regeneration of teeth at a low energy cost. Teeth are usually lost in the course of feeding if the prey is struggling. Additionally, amphibians that undergo a metamorphosis develop bicuspid shaped teeth.
Reptiles
The teeth ofreptiles
Reptiles, as most commonly defined are the animals in the class Reptilia ( ), a paraphyletic grouping comprising all sauropsids except birds. Living reptiles comprise turtles, crocodilians, squamates (lizards and snakes) and rhynchocephali ...
are replaced constantly throughout their lives. Crocodilian
Crocodilia (or Crocodylia, both ) is an order of mostly large, predatory, semiaquatic reptiles, known as crocodilians. They first appeared 95 million years ago in the Late Cretaceous period ( Cenomanian stage) and are the closest living ...
juveniles replace teeth with larger ones at a rate as high as one new tooth per socket every month. Once mature, tooth replacement rates can slow to two years and even longer. Overall, crocodilians may use 3,000 teeth from birth to death. New teeth are created within old teeth.
Birds
A skull ofIchthyornis
''Ichthyornis'' (meaning "fish bird", after its fish-like vertebrae) is an extinct genus of toothy seabird-like ornithuran from the late Cretaceous period of North America. Its fossil remains are known from the chalks of Alberta, Alabama, Kan ...
discovered in 2014 suggests that the beak of birds may have evolved from teeth to allow chicks to escape their shells earlier, and thus avoid predators and also to penetrate protective covers such as hard earth to access underlying food.
Invertebrates
organism
In biology, an organism () is any life, living system that functions as an individual entity. All organisms are composed of cells (cell theory). Organisms are classified by taxonomy (biology), taxonomy into groups such as Multicellular o ...
s with the simplest genome
In the fields of molecular biology and genetics, a genome is all the genetic information of an organism. It consists of nucleotide sequences of DNA (or RNA in RNA viruses). The nuclear genome includes protein-coding genes and non-coding ...
bearing such tooth-like structures are perhaps the parasitic worm
Worms are many different distantly related bilateral animals that typically have a long cylindrical tube-like body, no limbs, and no eyes (though not always).
Worms vary in size from microscopic to over in length for marine polychaete worm ...
s of the family Ancylostomatidae
The Ancylostomatidae are a family of worms that includes the hookworms.
Genera of Ancylostomatidae
* '' Agriostomum''
* ''Ancylostoma''
* ''Bunostomum
''Bunostomum'' is a genus of nematodes of the small intestine of ruminants and camelids. ...
. For example, the hookworm ''Necator americanus
''Necator americanus'' is a species of hookworm (a type of helminth) commonly known as the New World hookworm. Like other hookworms, it is a member of the phylum Nematoda. It is an obligatory parasitic nematode that lives in the small intestin ...
'' has two dorsal
Dorsal (from Latin ''dorsum'' ‘back’) may refer to:
* Dorsal (anatomy), an anatomical term of location referring to the back or upper side of an organism or parts of an organism
* Dorsal, positioned on top of an aircraft's fuselage
* Dorsal co ...
and two ventral
Standard anatomical terms of location are used to unambiguously describe the anatomy of animals, including humans. The terms, typically derived from Latin or Greek roots, describe something in its standard anatomical position. This position prov ...
cutting plates or teeth around the anterior margin of the buccal capsule. It also has a pair of subdorsal and a pair of subventral teeth located close to the rear.
Historically the European medicinal leech, another invertebrate parasite, has been used in medicine to remove blood from patients. They have three jaws (tripartite) that resemble saws in both appearance and function, and on them are about 100 sharp teeth used to incise the host. The incision leaves a mark that is an inverted Y inside of a circle. After piercing the skin and injecting anticoagulant
Anticoagulants, commonly known as blood thinners, are chemical substances that prevent or reduce coagulation of blood, prolonging the clotting time. Some of them occur naturally in blood-eating animals such as leeches and mosquitoes, where t ...
s (hirudin
Hirudin is a naturally occurring peptide in the salivary glands of blood-sucking leeches (such as '' Hirudo medicinalis'') that has a blood anticoagulant property. This is fundamental for the leeches’ habit of feeding on blood, since it keeps a ...
) and anaesthetic
An anesthetic (American English) or anaesthetic (British English; see spelling differences) is a drug used to induce anesthesia — in other words, to result in a temporary loss of sensation or awareness. They may be divided into ...
s, they suck out blood, consuming up to ten times their body weight in a single meal.
In some species of Bryozoa
Bryozoa (also known as the Polyzoa, Ectoprocta or commonly as moss animals) are a phylum of simple, aquatic invertebrate animals, nearly all living in sedentary colonies. Typically about long, they have a special feeding structure called a ...
, the first part of the stomach forms a muscular gizzard
The gizzard, also referred to as the ventriculus, gastric mill, and gigerium, is an organ found in the digestive tract of some animals, including archosaurs (pterosaurs, crocodiles, alligators, dinosaurs, birds), earthworms, some gastropods, som ...
lined with chitin
Chitin ( C8 H13 O5 N)n ( ) is a long-chain polymer of ''N''-acetylglucosamine, an amide derivative of glucose. Chitin is probably the second most abundant polysaccharide in nature (behind only cellulose); an estimated 1 billion tons of chit ...
ous teeth that crush armoured prey such as diatoms. Wave-like peristaltic contractions then move the food through the stomach for digestion.
radula
The radula (, ; plural radulae or radulas) is an anatomical structure used by molluscs for feeding, sometimes compared to a tongue. It is a minutely toothed, chitinous ribbon, which is typically used for scraping or cutting food before the food ...
which bears a ribbon of chitin
Chitin ( C8 H13 O5 N)n ( ) is a long-chain polymer of ''N''-acetylglucosamine, an amide derivative of glucose. Chitin is probably the second most abundant polysaccharide in nature (behind only cellulose); an estimated 1 billion tons of chit ...
ous teeth. However, these teeth are histologically and developmentally different from vertebrate teeth and are unlikely to be homologous
Homology may refer to:
Sciences
Biology
*Homology (biology), any characteristic of biological organisms that is derived from a common ancestor
*Sequence homology, biological homology between DNA, RNA, or protein sequences
* Homologous chrom ...
. For example, vertebrate teeth develop from a neural crest
Neural crest cells are a temporary group of cells unique to vertebrates that arise from the embryonic ectoderm germ layer, and in turn give rise to a diverse cell lineage—including melanocytes, craniofacial cartilage and bone, smooth muscle, ...
mesenchyme
Mesenchyme () is a type of loosely organized animal embryonic connective tissue of undifferentiated cells that give rise to most tissues, such as skin, blood or bone. The interactions between mesenchyme and epithelium help to form nearly every ...
-derived dental papilla, and the neural crest is specific to vertebrates, as are tissues such as enamel.
The radula
The radula (, ; plural radulae or radulas) is an anatomical structure used by molluscs for feeding, sometimes compared to a tongue. It is a minutely toothed, chitinous ribbon, which is typically used for scraping or cutting food before the food ...
is used by molluscs for feeding and is sometimes compared rather inaccurately to a tongue
The tongue is a muscular organ in the mouth of a typical tetrapod. It manipulates food for mastication and swallowing as part of the digestive process, and is the primary organ of taste. The tongue's upper surface (dorsum) is covered by taste bu ...
. It is a minutely toothed, chitin
Chitin ( C8 H13 O5 N)n ( ) is a long-chain polymer of ''N''-acetylglucosamine, an amide derivative of glucose. Chitin is probably the second most abundant polysaccharide in nature (behind only cellulose); an estimated 1 billion tons of chit ...
ous ribbon, typically used for scraping or cutting food before the food enters the oesophagus
The esophagus (American English) or oesophagus (British English; both ), non-technically known also as the food pipe or gullet, is an Organ (anatomy), organ in vertebrates through which food passes, aided by Peristalsis, peristaltic contracti ...
. The radula is unique to molluscs, and is found in every class of mollusc apart from bivalves
Bivalvia (), in previous centuries referred to as the Lamellibranchiata and Pelecypoda, is a class of marine and freshwater molluscs that have laterally compressed bodies enclosed by a shell consisting of two hinged parts. As a group, biv ...
.
Within the gastropods
The gastropods (), commonly known as snails and slugs, belong to a large taxonomic class of invertebrates within the phylum Mollusca called Gastropoda ().
This class comprises snails and slugs from saltwater, from freshwater, and from land. ...
, the radula
The radula (, ; plural radulae or radulas) is an anatomical structure used by molluscs for feeding, sometimes compared to a tongue. It is a minutely toothed, chitinous ribbon, which is typically used for scraping or cutting food before the food ...
is used in feeding by both herbivorous
A herbivore is an animal anatomically and physiologically adapted to eating plant material, for example foliage or marine algae, for the main component of its diet. As a result of their plant diet, herbivorous animals typically have mouthpart ...
and carnivorous
A carnivore , or meat-eater (Latin, ''caro'', genitive ''carnis'', meaning meat or "flesh" and ''vorare'' meaning "to devour"), is an animal or plant whose food and energy requirements derive from animal tissues (mainly muscle, fat and other ...
snail
A snail is, in loose terms, a shelled gastropod. The name is most often applied to land snails, terrestrial pulmonate gastropod molluscs. However, the common name ''snail'' is also used for most of the members of the molluscan class G ...
s and slugs. The arrangement of teeth (also known as denticles) on the radula ribbon varies considerably from one group to another as shown in the diagram on the left.
Predatory marine snails such as the Naticidae use the radula plus an acidic secretion to bore through the shell of other molluscs. Other predatory marine snails
A snail is, in loose terms, a shelled gastropod. The name is most often applied to land snails, terrestrial pulmonate gastropod molluscs. However, the common name ''snail'' is also used for most of the members of the molluscan class Ga ...
, such as the Conidae
Conidae, with the current common name of " cone snails", is a taxonomic family (previously subfamily) of predatory sea snails, marine gastropod molluscs in the superfamily Conoidea.
The 2014 classification of the superfamily Conoidea, group ...
, use a specialized radula tooth as a poisoned harpoon. Predatory pulmonate land slugs, such as the ghost slug
''Selenochlamys ysbryda'', the ghost slug, is a species of predatory air-breathing land slug. It is a shell-less pulmonate gastropod mollusc in the family Trigonochlamydidae.
The species was first recognised from various sites in Wales and was ...
, use elongated razor-sharp teeth on the radula to seize and devour earthworms
An earthworm is a terrestrial invertebrate that belongs to the phylum Annelida. They exhibit a tube-within-a-tube body plan; they are externally segmented with corresponding internal segmentation; and they usually have setae on all segments. T ...
. Predatory cephalopods, such as squid
True squid are molluscs with an elongated soft body, large eyes, eight arms, and two tentacles in the superorder Decapodiformes, though many other molluscs within the broader Neocoleoidea are also called squid despite not strictly fitting ...
, use the radula for cutting prey.
In most of the more ancient lineages of gastropods, the radula is used to graze by scraping diatoms and other microscopic alga
Algae ( , ; : alga ) are any of a large and diverse group of photosynthetic, eukaryotic organisms. The name is an informal term for a polyphyletic grouping that includes species from multiple distinct clades. Included organisms range from u ...
e off rock surfaces and other substrates. Limpet
Limpets are a group of aquatic snails that exhibit a conical gastropod shell, shell shape (patelliform) and a strong, muscular foot. Limpets are members of the class Gastropoda, but are polyphyletic, meaning the various groups called "limpets" ...
s scrape algae
Algae ( , ; : alga ) are any of a large and diverse group of photosynthetic, eukaryotic organisms. The name is an informal term for a polyphyletic grouping that includes species from multiple distinct clades. Included organisms range from ...
from rocks using radula equipped with exceptionally hard rasping teeth. These teeth have the strongest known tensile strength
Ultimate tensile strength (UTS), often shortened to tensile strength (TS), ultimate strength, or F_\text within equations, is the maximum stress that a material can withstand while being stretched or pulled before breaking. In brittle materials ...
of any biological material, outperforming spider silk
Spider silk is a protein fibre spun by spiders. Spiders use their silk to make webs or other structures, which function as sticky nets to catch other animals, or as nests or cocoons to protect their offspring, or to wrap up prey. They can a ...
. The mineral protein of the limpet teeth can withstand a tensile stress
In continuum mechanics, stress is a physical quantity. It is a quantity that describes the magnitude of forces that cause deformation. Stress is defined as ''force per unit area''. When an object is pulled apart by a force it will cause elonga ...
of 4.9 GPa, compared to 4 GPa of spider silk and 0.5 GPa of human teeth
The human teeth function to mechanically break down items of food by cutting and crushing them in preparation for swallowing and digesting. As such, they are considered part of the human digestive system. Humans have four types of teeth: incis ...
.
Fossilization and taphonomy
Because teeth are very resistant, often preserved when bones are not, and reflect the diet of the host organism, they are very valuable to archaeologists and palaeontologists. Early fish such as the thelodonts had scales composed of dentine and an enamel-like compound, suggesting that the origin of teeth was from scales which were retained in the mouth. Fish as early as the lateCambrian
The Cambrian Period ( ; sometimes symbolized Ꞓ) was the first geological period of the Paleozoic Era, and of the Phanerozoic Eon. The Cambrian lasted 53.4 million years from the end of the preceding Ediacaran Period 538.8 million years ag ...
had dentine in their exoskeletons, which may have functioned in defense or for sensing their environments.Teaford, Mark F and Smith, Moya Meredith, 2007. ''Development, Function and Evolution of Teeth'', Cambridge University Press. , Chapter 5. Dentine can be as hard as the rest of teeth and is composed of collagen fibres, reinforced with hydroxyapatite
Hydroxyapatite, also called hydroxylapatite (HA), is a naturally occurring mineral form of calcium apatite with the formula Ca5(PO4)3(OH), but it is usually written Ca10(PO4)6(OH)2 to denote that the crystal unit cell comprises two entities ...
.
Though teeth are very resistant, they also can be brittle and highly susceptible to cracking. However, cracking of the tooth can be used as a diagnostic tool for predicting bite force. Additionally, enamel fractures can also give valuable insight into the diet and behaviour of archaeological and fossil samples.
Decalcification removes the enamel from teeth and leaves only the organic interior intact, which comprises dentine and cementine. Enamel is quickly decalcified in acids, perhaps by dissolution by plant acids or via diagenetic solutions, or in the stomachs of vertebrate predators. Enamel can be lost by abrasion or spalling, and is lost before dentine or bone are destroyed by the fossilisation process. In such a case, the 'skeleton' of the teeth would consist of the dentine, with a hollow pulp cavity.
The organic part of dentine, conversely, is destroyed by alkalis.
See also
*Animal tooth development
Tooth development or odontogenesis is the process in which teeth develop and grow into the mouth. Tooth development varies among species.
Tooth development in vertebrates
Fish
In fish, Hox gene expression regulates mechanisms for tooth initiati ...
* Dragon's teeth (mythology)
In Greek myth, dragon's teeth (, ''odontes (tou) drakontos'') feature prominently in the legends of the Phoenician prince Cadmus and in Jason's quest for the Golden Fleece. In each case, the dragons are present and breathe fire. Their teeth, on ...
References
Sources
*External links
* {{Authority control Animal anatomy Speech organs