Tobna on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
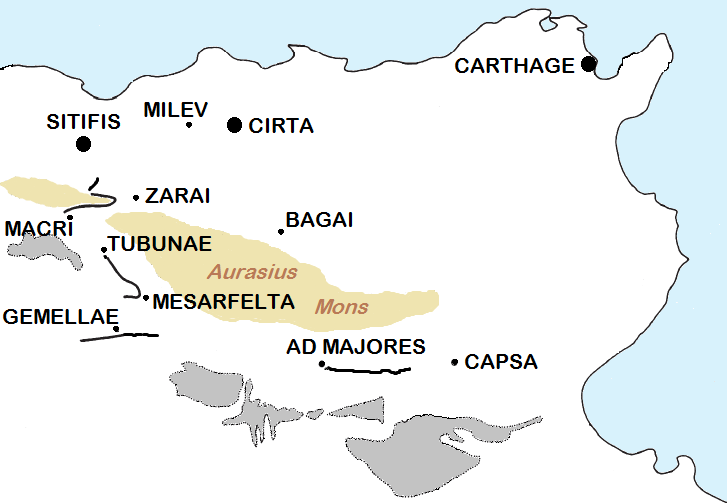 Tobna (), also known by the ancient names of Tubunae or Thubunae, is a ruined former city in
Tobna (), also known by the ancient names of Tubunae or Thubunae, is a ruined former city in
''Africa christiana''
Volume I, Brescia 1816, pp. 331–332 but the
''Augustine and the Arians''
(Association University Presse 1984 ), p. 86 In 479
in ''Catholic Encyclopedia'' (New York 1912)
Roman Tubunae
{{Authority control Archaeological sites in Algeria Roman towns and cities in Algeria Former populated places in Algeria Ancient Berber cities Catholic titular sees in Africa
 Tobna (), also known by the ancient names of Tubunae or Thubunae, is a ruined former city in
Tobna (), also known by the ancient names of Tubunae or Thubunae, is a ruined former city in Batna Province
Batna Province (, Latn, ar, Wilāyat Bātnah) is a provinces of Algeria, province of Algeria, in the region of Aurès. The capital is Batna (city), Batna. Localities in this province include N'Gaous, Merouana and Timgad. Belezma National Park i ...
of Algeria
Algeria, officially the People's Democratic Republic of Algeria, is a country in the Maghreb region of North Africa. It is bordered to Algeria–Tunisia border, the northeast by Tunisia; to Algeria–Libya border, the east by Libya; to Alger ...
, located just south of the modern city of Barika
Barika () is a city in Batna Province, in Eastern Algeria
Algeria, officially the People's Democratic Republic of Algeria, is a country in the Maghreb region of North Africa. It is bordered to Algeria–Tunisia border, the northeast by Tu ...
. From this position, it once controlled the eastern part of the Hodna
The Hodna () is a natural region of Algeria located between the Tell and Saharan Atlas ranges at the eastern end of the '' Hautes Plaines''. It is a vast depression lying in the northeastern section of M'Sila Province and the western end of Bat ...
region, while M'Sila
M'sila (also spelled Msila) (); is the capital of M'Sila Province, Algeria, and is co-extensive with M'sila District. It has a population of 132,975 as per the 2008 census. M'sila University is also located in this city.
History
The city was f ...
did the west. It flourished from the time of the Roman Empire
The Roman Empire ruled the Mediterranean and much of Europe, Western Asia and North Africa. The Roman people, Romans conquered most of this during the Roman Republic, Republic, and it was ruled by emperors following Octavian's assumption of ...
through the Islamic Middle Ages until it was sacked and destroyed by the Banu Hilal
The Banu Hilal () was a confederation of Arab tribes from the Najd region of the central Arabian Peninsula that emigrated to the Maghreb region of North Africa in the 11th century. They ruled the Najd, and campaigned in the borderlands between I ...
in the 11th century, after which it was finally abandoned.
Poorly documented by archaeologists today, Tobna's ruins occupy an extensive area and include the remains of a Byzantine
The Byzantine Empire, also known as the Eastern Roman Empire, was the continuation of the Roman Empire centred on Constantinople during late antiquity and the Middle Ages. Having survived the events that caused the fall of the Western Roman E ...
fortress as well as the traces of a wall covering a 950 m by 930 m area.
History
The site of Tobna is poorly studied by archaeologists as of 2019. The same is true of the surroundingHodna
The Hodna () is a natural region of Algeria located between the Tell and Saharan Atlas ranges at the eastern end of the '' Hautes Plaines''. It is a vast depression lying in the northeastern section of M'Sila Province and the western end of Bat ...
region in general. Jean Baradez's aerial surveys in Algeria, published in 1949, provided the first aerial images of the site. From this data, he worked on reconstructing the Roman road network surrounding the city. Only a single milestone appearing to mention Tobna by name has been found; it was located on the ancient road to Nicivibus ( Ngaous) and carries the inscription " Thuonis". Reconstruction of the surrounding road network has mostly been deduced from the distances recorded on other milestones in the area as well as their locations.
Roman Tubunae first became a municipium
In ancient Rome, the Latin term (: ) referred to a town or city. Etymologically, the was a social contract among ('duty holders'), or citizens of the town. The duties () were a communal obligation assumed by the in exchange for the privileges ...
under Septimius Severus
Lucius Septimius Severus (; ; 11 April 145 – 4 February 211) was Roman emperor from 193 to 211. He was born in Leptis Magna (present-day Al-Khums, Libya) in the Roman province of Africa. As a young man he advanced through cursus honorum, the ...
. In 427 CE, Count Boniface
Bonifatius (or Bonifacius; also known as Count Boniface or Comes Bonifacius; died 432) was a Roman general and governor of the diocese of Africa. He campaigned against the Visigoths in Gaul and the Vandals in North Africa. An ally of Galla Plac ...
met with Augustine of Hippo
Augustine of Hippo ( , ; ; 13 November 354 – 28 August 430) was a theologian and philosopher of Berber origin and the bishop of Hippo Regius in Numidia, Roman North Africa. His writings deeply influenced the development of Western philosop ...
during his stay in the city.
In Late Antiquity
Late antiquity marks the period that comes after the end of classical antiquity and stretches into the onset of the Early Middle Ages. Late antiquity as a period was popularized by Peter Brown (historian), Peter Brown in 1971, and this periodiza ...
, Tobna was the seat of a military district called the ''limes Tubuniensis'', which is listed in the Notitia Dignitatum
The (Latin for 'List of all dignities and administrations both civil and military') is a document of the Late Roman Empire that details the administrative organization of the Western and the Eastern Roman Empire. It is unique as one of very ...
as one of the sixteen ''praepositi limitis'' under the jurisdiction of the Comes
''Comes'' (plural ''comites''), translated as count, was a Roman title, generally linked to a comitatus or comital office.
The word ''comes'' originally meant "companion" or "follower", deriving from "''com-''" ("with") and "''ire''" ("go"). Th ...
of Africa and later a part of Byzantine North Africa
Byzantine rule in North Africa spanned around 175 years. It began in the years 533/534 with the reconquest of territory formerly belonging to the Western Roman Empire by the Byzantine Empire, Eastern Roman (Byzantine) Empire under Justinian I and ...
. A fortress was built here during the reign of Justinian
Justinian I (, ; 48214 November 565), also known as Justinian the Great, was Roman emperor from 527 to 565.
His reign was marked by the ambitious but only partly realized ''renovatio imperii'', or "restoration of the Empire". This ambition was ...
. This fortress has survived to the present day; it is moderately sized, located at a point somewhat higher than the surrounding plain. By the 680s, it had become a base for the Berber king Kasila
Kusaila ibn Malzam (), also known as Aksel, was a 7th-century Berber Christian ruler of the kingdom of Altava and leader of the Awraba tribe, a Christianised sedentary Berber tribe of the Aures and possibly Christian king of the Sanhaja. Under ...
, with the Byzantine officials acquiescing. Tobna had formerly been the seat of the Comes of Africa, but that office had fallen out of use by the mid-600s.
Byzantine Tobna lay at the border of the provinces of Numidia and Mauretania Caesariensis (aka Mauretania Sitifensis
Mauretania Sitifensis was a Roman province in Northwest Africa. The capital was Setifis.
History
In the later division of the Roman Empire under the Emperor Diocletian, the eastern part of Mauretania Caesariensis, from Saldae to the river Amps ...
). Later on, the Muslim historian Abu Bakr al-Maliki
Abū Bakr ʿAbdallāh ibn Muḥammad ibn ʿAbdallāh al-Qurashī al-Qayrawānī al-Mālikī ( 1036–1057) was an Ifrīqiyan historian, Mālikī jurist and Ashʿarī theologian and traditionist. He played a major role in spreading Mālikism and ...
considered Tobna to be on the western limit of Ifriqiya
Ifriqiya ( '), also known as al-Maghrib al-Adna (), was a medieval historical region comprising today's Tunisia, eastern Algeria, and Tripolitania (roughly western Libya). It included all of what had previously been the Byzantine province of ...
.
Tobna was an important city in the Islamic Middle Ages: the geographer al-Bakri
Abū ʿUbayd ʿAbd Allāh ibn ʿAbd al-ʿAzīz ibn Muḥammad ibn Ayyūb ibn ʿAmr al-Bakrī (), or simply al-Bakrī (c. 1040–1094) was an Arab Andalusian historian and a geographer of the Muslim West.
Life
Al-Bakri was born in Huelva, the ...
called it the most important city of the Maghreb between Kairouan
Kairouan (, ), also spelled El Qayrawān or Kairwan ( , ), is the capital of the Kairouan Governorate in Tunisia and a UNESCO World Heritage Site. The city was founded by the Umayyads around 670, in the period of Caliph Mu'awiya (reigned 661� ...
and Sijilmassa
Sijilmasa (; also transliterated Sijilmassa, Sidjilmasa, Sidjilmassa and Sigilmassa) was a medieval Moroccan city and trade entrepôt at the northern edge of the Sahara in Morocco. The ruins of the town extend for five miles along the River Ziz ...
. Al-Bakri described the city as being surrounded by a brick wall, with monumental gateways. Tobna had five gates: to the west, the Bāb Khakān; to the east, the Bāb Fatḥ (with vents); to the south, the Bāb Tāhūdha (made of iron) and the Bāb al-Jadīd; and to the north, the Bāb Kurāma. On the south side of the city was the fortress, which featured vaulted chambers, a cistern dating to the Byzantine period, a Jami mosque, and the governor's palace (''dār al-'imāra'').
Inside the walls, the main street of Tobna ran east–west (''"simaṭ"'', corresponding to the Roman Decumanus Maximus
In Roman urban planning, a ''decumanus'' was an east–west-oriented road in a Roman city or '' castrum'' (military camp). The main ''decumanus'' of a particular city was the ''decumanus maximus'', or most often simply "the ''decumanus''". In t ...
) and was lined with shops and markets. More markets lay outside the city walls in the extensive suburbs, of which the most important was to the west. There was also a hammam
A hammam (), also often called a Turkish bath by Westerners, is a type of steam bath or a place of public bathing associated with the Islamic world. It is a prominent feature in the culture of the Muslim world and was inherited from the model ...
. Tobna had an eclectic population including Arabs
Arabs (, , ; , , ) are an ethnic group mainly inhabiting the Arab world in West Asia and North Africa. A significant Arab diaspora is present in various parts of the world.
Arabs have been in the Fertile Crescent for thousands of yea ...
, Persians
Persians ( ), or the Persian people (), are an Iranian ethnic group from West Asia that came from an earlier group called the Proto-Iranians, which likely split from the Indo-Iranians in 1800 BCE from either Afghanistan or Central Asia. They ...
serving in the army, Berbers
Berbers, or the Berber peoples, also known as Amazigh or Imazighen, are a diverse grouping of distinct ethnic groups indigenous to North Africa who predate the arrival of Arab migrations to the Maghreb, Arabs in the Maghreb. Their main connec ...
, and Roman Africans
The Roman Africans or African Romans () were the ancient populations of Roman North Africa that had a Romanized culture, some of whom spoke their own variety of Latin as a result. They existed from the Roman conquest until their language gradua ...
who were mostly of Berber descent with some Roman ancestry. Ibn Hawqal
Muḥammad Abū’l-Qāsim Ibn Ḥawqal (), also known as Abū al-Qāsim b. ʻAlī Ibn Ḥawqal al-Naṣībī, born in Nisibis, Al-Jazira (caliphal province), Upper Mesopotamia; was a 10th-century Arab Muslim writer, geographer, and chronic ...
and al-Bakri both remarked on the bitter rivalry between the Arabs and the Roman Africans in the city, with the Arabs seeking allies in the Arabs of Tahudha and Sétif
Sétif () is the capital city of the Sétif Province and the 5th most populous city of Algeria, with an estimated population of 1.866.845 in 2017). It is one of the most important cities of eastern Algeria and the country as a whole, since it is c ...
and the Roman Africans seeking allies in the Biskra
Biskra () is the capital city of Biskra Province, Algeria. In 2007, its population was recorded as 307,987. Biskra is located in northeastern Algeria, about from Algiers, southwest of Batna, Algeria, Batna and north of Touggourt. It is nickna ...
region.
Beyond the walls were extensive suburbs, a cemetery (to the east), and irrigated gardens and farms. The city was irrigated by the waters of the Oued Bitham; according to al-Bakri, "Every time it overflows, it waters all the gardens and fields in the suburbs and provides the inhabitants with abundant harvests." Major crops included wheat
Wheat is a group of wild and crop domestication, domesticated Poaceae, grasses of the genus ''Triticum'' (). They are Agriculture, cultivated for their cereal grains, which are staple foods around the world. Well-known Taxonomy of wheat, whe ...
, barley
Barley (), a member of the grass family, is a major cereal grain grown in temperate climates globally. It was one of the first cultivated grains; it was domesticated in the Fertile Crescent around 9000 BC, giving it nonshattering spikele ...
, flax
Flax, also known as common flax or linseed, is a flowering plant, ''Linum usitatissimum'', in the family Linaceae. It is cultivated as a food and fiber crop in regions of the world with temperate climates. In 2022, France produced 75% of t ...
, and cotton
Cotton (), first recorded in ancient India, is a soft, fluffy staple fiber that grows in a boll, or protective case, around the seeds of the cotton plants of the genus '' Gossypium'' in the mallow family Malvaceae. The fiber is almost pure ...
. Orchards grew date
Date or dates may refer to:
* Date, the fruit of the date palm (''Phoenix dactylifera'')
* Jujube, also known as red date or Chinese date, the fruit of ''Ziziphus jujuba''
Social activity
*Dating, a form of courtship involving social activi ...
s, among other fruits, and there was cattle
Cattle (''Bos taurus'') are large, domesticated, bovid ungulates widely kept as livestock. They are prominent modern members of the subfamily Bovinae and the most widespread species of the genus '' Bos''. Mature female cattle are calle ...
and sheep
Sheep (: sheep) or domestic sheep (''Ovis aries'') are a domesticated, ruminant mammal typically kept as livestock. Although the term ''sheep'' can apply to other species in the genus '' Ovis'', in everyday usage it almost always refers to d ...
breeding until the 10th century.
For two centuries beginning c. 700 CE, Tobna was a major strategic center for Muslim rulers, serving as capital of the Zab region. It had a garrison ('' jund'') and newly built walls, and it served as the main ''point d'appui
A ''point d'appui'' (French fofulcrum, in military theory, is a location where troops are assembled prior to a battle. Often a monument is erected to commemorate the ''point d'appui'' for notable battles. In some battles there may be more than a s ...
'' for campaigns against rebellious Berbers, including members of the Khawarij
The Kharijites (, singular ) were an Islamic sect which emerged during the First Fitna (656–661). The first Kharijites were supporters of Ali who rebelled against his acceptance of arbitration talks to settle the conflict with his challenge ...
and, later, the Kutama
The Kutama (Berber: ''Ikutamen''; ) were a Berber tribe in northern Algeria classified among the Berber confederation of the Bavares. The Kutama are attested much earlier, in the form ''Koidamousii'' by the Greek geographer Ptolemy.
The Kutama p ...
tribe. One military governor of Tobna, Ibrahim I ibn al-Aghlab
Ibrahim I ibn al-Aghlab (; 756–812) was the first Emir of the Ifriqiya from Aghlabid family (800–812).
Origin and early career
He was the son of al-Aghlab, a Khurasani Arab who had been a companion of Abu Muslim during the Abbasid Revolu ...
, went on to found the Aghlabid dynasty
The Aghlabid dynasty () was an Arab dynasty centered in Ifriqiya (roughly present-day Tunisia) from 800 to 909 that conquered parts of Sicily, Southern Italy, and possibly Sardinia, nominally as vassals of the Abbasid Caliphate. The Aghlabids ...
, which would rule Ifriqiya for a century.
In 906 CE, during the final years of Aghlabid power, Tobna was besieged by the forces of Abu Abdallah al-Shi'i
Abu Abdallah al-Husayn ibn Ahmad ibn Muhammad ibn Zakariyya, better known as Abu Abdallah al-Shi'i (), was an Isma'ili missionary (''da'i, dāʿī'') active in Yemen and North Africa. He was successful in converting and unifying a large part of th ...
, an Isma'ili
Ismailism () is a branch of Shia Islam. The Isma'ili () get their name from their acceptance of Imam Isma'il ibn Jafar as the appointed spiritual successor (Imamate in Nizari doctrine, imām) to Ja'far al-Sadiq, wherein they differ from the ...
missionary who had gathered a large following among the Kutama tribe. Tobna was fortified with structures dating back to the Byzantine Empire
The Byzantine Empire, also known as the Eastern Roman Empire, was the continuation of the Roman Empire centred on Constantinople during late antiquity and the Middle Ages. Having survived History of the Roman Empire, the events that caused the ...
, as well as a large Aghlabid garrison which defended itself with mangonel
The mangonel, also called the traction trebuchet, was a type of trebuchet used in Ancient China starting from the Warring States period, and later across Eurasia by the 6th century AD. Unlike the later counterweight trebuchet, the mangonel was ...
s during the siege. Abu Abdallah's Kutama army sent sapper
A sapper, also called a combat engineer, is a combatant or soldier who performs a variety of military engineering duties, such as breaching fortifications, demolitions, bridge-building, laying or clearing minefields, preparing field defenses ...
s to the wall, protected by a ''dabbāba'' (literally "crawler") or battering ram
A battering ram is a siege engine that originated in ancient times and was designed to break open the masonry walls of fortifications or splinter their wooden gates. In its simplest form, a battering ram is just a large, heavy log carried ...
with a protective roof. The sappers succeeded in collapsing one of the towers along the city wall, and the Kutama were able to enter the city through the breach. The defenders soon surrendered; Ibn Idhari
Abū al-ʽAbbās Aḥmad ibn Muḥammad ibn ʽIḏārī al-Marrākushī () was a Maghrebi historian of the late-13th/early-14th century, and author of the famous '' Al-Bayan al-Mughrib'', an important medieval history of the Maghreb (Morocco, No ...
recorded this as taking place at the end of Dhu al-Hijjah
Dhu al-Hijjah (also Dhu al-Hijja ) is the twelfth and final month in the Islamic calendar. Being one of the four sacred months during which war is forbidden, it is the month in which the '' Ḥajj'' () takes place as well as Eid al-Adha ().
T ...
, 293 AH (~ mid-October 906 CE).
Tobna then became part of the Fatimid Caliphate
The Fatimid Caliphate (; ), also known as the Fatimid Empire, was a caliphate extant from the tenth to the twelfth centuries CE under the rule of the Fatimids, an Isma'ili Shi'a dynasty. Spanning a large area of North Africa and West Asia, i ...
. The Zenata
The Zenata (; ) are a group of Berber tribes, historically one of the largest Berber confederations along with the Sanhaja and Masmuda. Their lifestyle was either nomadic or semi-nomadic.
Society
The 14th-century historiographer Ibn Khaldun repo ...
tribe to the west were enemies of the Fatimids, and in 927, in order to contain them, the Fatimids established a new regional capital further west, at Msila. Tobna thus lost much of its civic and military importance. Many of its inhabitants relocated west to Msila, and economic activity declined. The wars with the Zenata also hindered agricultural development.
Under the Zirid dynasty
The Zirid dynasty (), Banu Ziri (), was a Sanhaja Berber dynasty from what is now Algeria which ruled the central Maghreb from 972 to 1014 and Ifriqiya (eastern Maghreb) from 972 to 1148.
Descendants of Ziri ibn Manad, a military leader of t ...
, Tobna had a Zenata governor named Fulful ibn Sa'id ibn Khazrun, who was appointed by al-Mansur ibn Buluggin
al-Mansûr ibn Buluggin () (died 26 March 996 ) was the second ruler of the Zirids in Ifriqiya (r. 984–995).
Life
Al-Mansur succeeded his father Buluggin ibn Ziri (r. 972–984) in Ifriqiya. Despite further campaigns by the Zirids against ...
in 992 and reconfirmed by his successor Badis ibn Mansur
Bādīs ibn al-Manṣūr (; 14 August 984 - 10 May 1016), known fully as ʾAbū Manād Bādīs Nāṣir al-Dawla (), was the third ruler of the Zirids in Ifriqiya from 996 to 1016.
Badis ibn Mansur succeeded his father al-Mansur ibn Buluggin () ...
in 996. However, in 999, Fulful rebelled, and in retaliation, Badis pillaged the city. In 1017, a peace treaty between Badis's successor, al-Mu'izz
Abu Tamim Ma'ad al-Mu'izz li-Din Allah (; 26 September 932 – 19 December 975) was the fourth Fatimid caliph and the 14th Ismaili imam, reigning from 953 to 975. It was during his caliphate that the center of power of the Fatimid dynasty was m ...
, and Hammad ibn Buluggin
Hammad ibn Buluggin () (died August 1029) was the first ruler of the Hammadid dynasty in what is now Algeria (1014–1029).
Life
After the death of his father Buluggin ibn Ziri, al-Mansur ibn Buluggin (984–995), Hammad's brother, became the ...
, al-Mansur's brother and founder of the Hammadid dynasty
The Hammadid dynasty (), also known as the Hammadid Emirate or the Kingdom of Bejaia, was a medieval Islamic kingdom in the central Maghreb, encompassing what is now Algeria. It was established at the beginning of the 11th century when Hammad ...
, gave control of Tobna to the Hammadids, and Hammad's son al-Qa'id was made its governor. Under Hammadid rule, Tobna briefly enjoyed a renewed prosperity.
That ended during the mid-11th century, when the Banu Hilal
The Banu Hilal () was a confederation of Arab tribes from the Najd region of the central Arabian Peninsula that emigrated to the Maghreb region of North Africa in the 11th century. They ruled the Najd, and campaigned in the borderlands between I ...
invaded the region. Ibn Khaldun
Ibn Khaldun (27 May 1332 – 17 March 1406, 732–808 Hijri year, AH) was an Arabs, Arab Islamic scholar, historian, philosopher and sociologist. He is widely acknowledged to be one of the greatest social scientists of the Middle Ages, and cons ...
described the devastation they brought: after sacking and destroying both Tobna and Msila, the Banu Hilal attacked the caravanserai
A caravanserai (or caravansary; ) was an inn that provided lodging for travelers, merchants, and Caravan (travellers), caravans. They were present throughout much of the Islamic world. Depending on the region and period, they were called by a ...
s, towns, villages, and farms, razing them completely to the ground.
Tobna never recovered. While it was repopulated, it lost its importance in favor of Biskra
Biskra () is the capital city of Biskra Province, Algeria. In 2007, its population was recorded as 307,987. Biskra is located in northeastern Algeria, about from Algiers, southwest of Batna, Algeria, Batna and north of Touggourt. It is nickna ...
, and soon after it was abandoned altogether.
List of known governors
* al-Aghlab (761) * al-Muhallab ibn Yazid (date not given) * al-Fadl ibn Rawh (until 791, when he was appointed governor of Ifriqiya) * al-'Ala ibn Sa'id (791-794) * Ibrahim ibn al-Aghlab (797-800, founder ofAghlabid dynasty
The Aghlabid dynasty () was an Arab dynasty centered in Ifriqiya (roughly present-day Tunisia) from 800 to 909 that conquered parts of Sicily, Southern Italy, and possibly Sardinia, nominally as vassals of the Abbasid Caliphate. The Aghlabids ...
)
* Salim ibn Jalbun (dismissed in 847)
* Yahya ibn Salim (appointed by Abu Abdallah al -Shi'i in 906)
* Fulful ibn Sa'id ibn Khazrun (992-999)
Christian diocese
There were two towns called ''Tubunae'' in the territory of what is nowAlgeria
Algeria, officially the People's Democratic Republic of Algeria, is a country in the Maghreb region of North Africa. It is bordered to Algeria–Tunisia border, the northeast by Tunisia; to Algeria–Libya border, the east by Libya; to Alger ...
, when it was part of the Roman Empire
The Roman Empire ruled the Mediterranean and much of Europe, Western Asia and North Africa. The Roman people, Romans conquered most of this during the Roman Republic, Republic, and it was ruled by emperors following Octavian's assumption of ...
. One is referred to as ''Tubunae in Mauretania'', because it was part of the Roman province
The Roman provinces (, pl. ) were the administrative regions of Ancient Rome outside Roman Italy that were controlled by the Romans under the Roman Republic and later the Roman Empire. Each province was ruled by a Roman appointed as Roman g ...
of Mauretania Caesariensis
Mauretania Caesariensis (Latin for "Caesarea, Numidia, Caesarean Mauretania") was a Roman province located in present-day Algeria. The full name refers to its capital Caesarea, Numidia, Caesarea Mauretaniae (modern Cherchell).
The province had ...
. The other (the modern town of Tobna) is called ''Tubunae in Numidia'', because it was situated in the Roman province of Numidia
Numidia was the ancient kingdom of the Numidians in northwest Africa, initially comprising the territory that now makes up Algeria, but later expanding across what is today known as Tunisia and Libya. The polity was originally divided between ...
. Writers such as Morcelli uses the spelling "Tubunae" for both of them,Stefano Antonio Morcelli''Africa christiana''
Volume I, Brescia 1816, pp. 331–332 but the
Catholic Church
The Catholic Church (), also known as the Roman Catholic Church, is the List of Christian denominations by number of members, largest Christian church, with 1.27 to 1.41 billion baptized Catholics Catholic Church by country, worldwid ...
's list of titular see
A titular see in various churches is an episcopal see of a former diocese that no longer functions, sometimes called a "dead diocese". The ordinary or hierarch of such a see may be styled a "titular metropolitan" (highest rank), "titular archbi ...
s refers to the second of them (corresponding to modern Tobna) as ''Thubunae in Numidia''.
There it is even the possibility that both names are for the same settlement.
Tubunae in Mauretania
The names of none of the bishops of this town, which is mentioned byPtolemy
Claudius Ptolemy (; , ; ; – 160s/170s AD) was a Greco-Roman mathematician, astronomer, astrologer, geographer, and music theorist who wrote about a dozen scientific treatises, three of which were important to later Byzantine science, Byzant ...
, have been preserved. The see was vacant when Huneric
Huneric, Hunneric or Honeric (died December 23, 484) was King of the (North African) Vandal Kingdom (477–484) and the oldest son of Gaiseric. He abandoned the imperial politics of his father and concentrated mainly on internal affairs. He was ma ...
summoned the North African bishops to Carthage
Carthage was an ancient city in Northern Africa, on the eastern side of the Lake of Tunis in what is now Tunisia. Carthage was one of the most important trading hubs of the Ancient Mediterranean and one of the most affluent cities of the classic ...
in 484.
Tubunae/Thubunae in Numidia
It was to this town "in the depths of Numidia" thatAugustine of Hippo
Augustine of Hippo ( , ; ; 13 November 354 – 28 August 430) was a theologian and philosopher of Berber origin and the bishop of Hippo Regius in Numidia, Roman North Africa. His writings deeply influenced the development of Western philosop ...
and Alypius went, probably in 421, to meet the Roman official Boniface and exhort him "to serve the Church by protecting the empire from the barbarians".William A. Sumruld''Augustine and the Arians''
(Association University Presse 1984 ), p. 86 In 479
Huneric
Huneric, Hunneric or Honeric (died December 23, 484) was King of the (North African) Vandal Kingdom (477–484) and the oldest son of Gaiseric. He abandoned the imperial politics of his father and concentrated mainly on internal affairs. He was ma ...
exiled a large number of Catholics there. Its ruins, known as Tobna, are in the Department of Constantine, Algeria
Algeria, officially the People's Democratic Republic of Algeria, is a country in the Maghreb region of North Africa. It is bordered to Algeria–Tunisia border, the northeast by Tunisia; to Algeria–Libya border, the east by Libya; to Alger ...
, at the gates of the Sahara, west of the Chott el Hodna, the "Salinae Tubunenses" of the Romans. They are very extensive, for three successive towns occupied different sites, under the Romans, the Byzantines, and the Arabs. Besides the remains of the fortress, the most remarkable monument is a church now used as a mosque.Sophrone Pétridès, "Tubunae"in ''Catholic Encyclopedia'' (New York 1912)
Bishops
Three bishops of Tubunae/Thubunae in Numidia are known. SaintNemesianus
Marcus Aurelius Nemesianus was a Roman poet thought to have been a native of Carthage and flourished about AD 283. He was a popular poet at the court of the Roman emperor Carus (Historia Augusta, ''Carus'', 11).
Bogus name "Olympius"
A bogu ...
assisted at the Council of Carthage (256)
The Councils of Carthage were church synods held during the 3rd, 4th, and 5th centuries in the city of Carthage in Africa. The most important of these are described below.
Synod of 251
In May 251 a synod, assembled under the presidency of Cyprian ...
. Saint Cyprian often speaks of him in his letters, and one letter survives which he wrote to Cyprian in his own name and in the name of those who were condemned with him to the mines. An inscription testifies to his cult at Tixter
Tixter is a town and commune in Bordj Bou Arréridj Province, Algeria
Algeria, officially the People's Democratic Republic of Algeria, is a country in the Maghreb region of North Africa. It is bordered to Algeria–Tunisia border, the nort ...
in 360, and the ''Roman Martyrology
The ''Roman Martyrology'' () is the official martyrology of the Catholic Church. Its use is obligatory in matters regarding the Roman Rite liturgy, but dioceses, countries and religious institutes may add duly approved appendices to it. It provid ...
'' mentions him on 10 September. Another bishop was Cresconius, who usurped the see after quitting that of Bulla Regia
Bulla Regia was a Berbers, Berber, Punics, Punic, and ancient Romans, Roman town near present-day Jendouba, Tunisia. Its surviving ruins and archaeological site are noted for their Emperor Hadrian, Hadrianic-era semi-subterranean housing, a prote ...
, and who assisted at the Council of Carthage (411)
The Councils of Carthage were church synods held during the 3rd, 4th, and 5th centuries in the city of Carthage in Africa. The most important of these are described below.
Synod of 251
In May 251 a synod, assembled under the presidency of Cyprian ...
, where his rival was the Donatist
Donatism was a schism from the Catholic Church in the Archdiocese of Carthage from the fourth to the sixth centuries. Donatists argued that Christian clergy must be faultless for their ministry to be effective and their prayers and sacraments to ...
Protasius. A third, Reparatus, was exiled by Huneric in 484.
See also
*Mauretania Caesariensis
Mauretania Caesariensis (Latin for "Caesarea, Numidia, Caesarean Mauretania") was a Roman province located in present-day Algeria. The full name refers to its capital Caesarea, Numidia, Caesarea Mauretaniae (modern Cherchell).
The province had ...
* Gemellae
Gemellae was a Roman fort and associated camp on the fringe of the Sahara Desert in what is today part of Algeria. It is now an archaeological site, 25 km south and 19 km west of Biskra, and 5 km southwest of the present-day village ...
* Sitifis
Sétifis (Arabic: سطيف; Berber: Sṭif), was a Roman town located in northeastern Algeria. It was the capital of the Roman province called ''Mauretania Sitifensis'', and it is today Setif in the Sétif Province (Algeria).
History
Sitifis wa ...
References
Bibliography
* Laffi, Umberto. ''Colonie e municipi nello Stato romano'' Ed. di Storia e Letteratura. Roma, 2007 * Mommsen, Theodore. ''The Provinces of the Roman Empire'' Section: Roman Africa. (Leipzig 1865; London 1866; London: Macmillan 1909; reprint New York 1996) Barnes & Noble. New York, 1996 * Smyth Vereker, Charles. ''Scenes in the Sunny South: Including the Atlas Mountains and the Oases of the Sahara in Algeria''. Volume 2. Publisher Longmans, Green, and Company. University of Wisconsin. Madison,1871Roman Tubunae
{{Authority control Archaeological sites in Algeria Roman towns and cities in Algeria Former populated places in Algeria Ancient Berber cities Catholic titular sees in Africa