Tirhut (region) on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
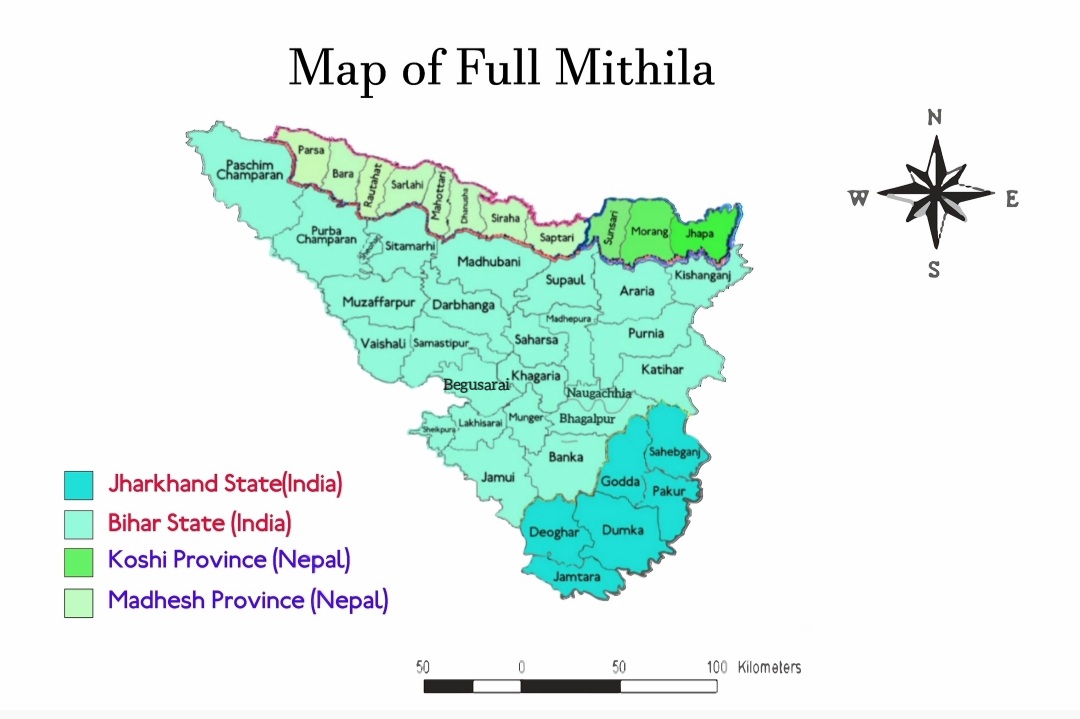
Mithila (), also known as Tirhut, Tirabhukti and Mithilanchal, is a geographical and cultural region of the

 Mithilā is one of the most significant pilgrimage sites in
Mithilā is one of the most significant pilgrimage sites in  The temples fell into disrepair, possibly due to a lack of Jaina population. The only remnant was the footprints of '' Mallinātha'' and '' Naminātha''. These footprints were later preserved in ''Bhāgalpur''. Based on historical evidence and research, initiatives to restore Mithilā’s lost Jaina heritage were launched. A two-storey temple along the Sitamarhi-Dumra road was constructed. In 2015, the foundation was laid by ''Ācārya'' ''Mahendrasāgarasūrī'' of
The temples fell into disrepair, possibly due to a lack of Jaina population. The only remnant was the footprints of '' Mallinātha'' and '' Naminātha''. These footprints were later preserved in ''Bhāgalpur''. Based on historical evidence and research, initiatives to restore Mithilā’s lost Jaina heritage were launched. A two-storey temple along the Sitamarhi-Dumra road was constructed. In 2015, the foundation was laid by ''Ācārya'' ''Mahendrasāgarasūrī'' of
 He built an Anglo-vernacular school at a cost of £1490, which he maintained, as well as nearly 30 vernacular schools of different grades; and subsidised a much larger number of educational institutions. He was also one of the founders of
He built an Anglo-vernacular school at a cost of £1490, which he maintained, as well as nearly 30 vernacular schools of different grades; and subsidised a much larger number of educational institutions. He was also one of the founders of
 Men and women in Mithila are very religious and dress for the festivals as well. The costumes of Mithila stem from the rich traditional culture of Mithila. Panjabi Kurta and
Men and women in Mithila are very religious and dress for the festivals as well. The costumes of Mithila stem from the rich traditional culture of Mithila. Panjabi Kurta and
 On 10 February 2017,
On 10 February 2017,
DNA, 8 April 2014 * Basanti Puja (Chaiti Durga Puja) * Til Sakraait * Aakhar Bochhor *
 *
*
Hello Mithila
on
The Maithil Brahmans - an online ethnography
{{Authority control . Regions of Bihar Regions of Nepal Historical Indian regions Cultural regions
Indian subcontinent
The Indian subcontinent is a physiographic region of Asia below the Himalayas which projects into the Indian Ocean between the Bay of Bengal to the east and the Arabian Sea to the west. It is now divided between Bangladesh, India, and Pakista ...
bounded by the Mahananda River
The Mahananda ( ) is a trans-boundary river that flows through the Indian states of Bihar and West Bengal before crossing into Bangladesh. It is an important tributary of the Ganges.
Course
The Mahananda river system consists of two streams- ...
in the east, the Ganges
The Ganges ( ; in India: Ganga, ; in Bangladesh: Padma, ). "The Ganges Basin, known in India as the Ganga and in Bangladesh as the Padma, is an international which goes through India, Bangladesh, Nepal and China." is a trans-boundary rive ...
in the south, the Gandaki River
The Gandaki River, also known as the Narayani and Gandak, is one of the major rivers in Nepal and a left-bank tributary of the Ganges in India. Its total catchment area is , most of it in Nepal. In the Nepal Himalayas, the Gandaki is notable f ...
in the west and by the foothills of the Himalayas
The Himalayas, or Himalaya ( ), is a mountain range in Asia, separating the plains of the Indian subcontinent from the Tibetan Plateau. The range has some of the Earth's highest peaks, including the highest, Mount Everest. More than list of h ...
in the north. It comprises certain parts of Bihar
Bihar ( ) is a states and union territories of India, state in Eastern India. It is the list of states and union territories of India by population, second largest state by population, the List of states and union territories of India by are ...
and Jharkhand
Jharkhand (; ) is a States and union territories of India, state in East India, eastern India. The state shares its border with the states of West Bengal to the east, Chhattisgarh to the west, Uttar Pradesh to the northwest, Bihar to the north ...
states of India and adjoining districts of the Koshi Province
Koshi Province () is an autonomous Provinces of Nepal, province of Nepal adopted by the Constitution of Nepal on 20 September 2015. It covers an area of , about 17.5% of the country's total area. With the industrial city of Biratnagar as its cap ...
, Bagmati Pradesh
Bagmati Province (, ''Bāgmatī pradēśa'') is one of the seven provinces of Nepal established by the constitution of Nepal. Bagmati is Nepal's second-most populous province and fifth largest province by area. It is bordered by Tibet Autonomous ...
and Madhesh Province
Madhesh Province () is a Provinces of Nepal, province of Nepal in the Terai region with an area of covering about 6.5% of the country's total area. It has a population of 6,126,288 as per the 2021 Nepal census, making it Nepal's most densely po ...
of Nepal
Nepal, officially the Federal Democratic Republic of Nepal, is a landlocked country in South Asia. It is mainly situated in the Himalayas, but also includes parts of the Indo-Gangetic Plain. It borders the Tibet Autonomous Region of China Ch ...
. The native language in Mithila is Maithili, and its speakers are referred to as Maithil
Maithils (Devanagari: मैथिल), also known as Maithili people, are an Indo-Aryan cultural and ethno-linguistic group from the Indian subcontinent, who speak the Maithili language as their native language. They inhabit the Mithila regio ...
s.
Mithila is commonly used to refer to the Videha
Videha ( Prākrit: ; Pāli: ; Sanskrit: ) was an ancient Indo-Aryan tribe of north-eastern Indian subcontinent whose existence is attested during the Iron Age. The population of Videha, the Vaidehas, were initially organised into a monarchy ...
Kingdom, as well as to the modern-day territories that fall within the ancient boundaries of Videha. Until the 20th century, Mithila was still ruled in part by the Raj Darbhanga
The Darbhanga Raj, also known as Raj Darbhanga and the Khandwala dynasty, was a chieftaincy located within the Mughal province of Bihar which controlled territories, not all contiguous, that were part of the Mithila region, now divided betwee ...
.
History
In Jainism

 Mithilā is one of the most significant pilgrimage sites in
Mithilā is one of the most significant pilgrimage sites in Jainism
Jainism ( ), also known as Jain Dharma, is an Indian religions, Indian religion whose three main pillars are nonviolence (), asceticism (), and a rejection of all simplistic and one-sided views of truth and reality (). Jainism traces its s ...
. Apart from its association with ''Mahavira
Mahavira (Devanagari: महावीर, ), also known as Vardhamana (Devanagari: वर्धमान, ), was the 24th ''Tirthankara'' (Supreme Preacher and Ford Maker) of Jainism. Although the dates and most historical details of his lif ...
'', the 24th Tirthankara
In Jainism, a ''Tirthankara'' (; ) is a saviour and supreme preacher of the ''Dharma (Jainism), dharma'' (righteous path). The word ''tirthankara'' signifies the founder of a ''Tirtha (Jainism), tirtha'', a fordable passage across ''Saṃsā ...
, it is also known for its association with ''Mallinatha
Mallinatha (Prakrit ''Mallinātha'', Devanagari: मल्लिनाथ, Sanskrit: मल्लिनाथः, 'Lord of jasmine or seat') was the 19th tīrthaṅkara "ford-maker" of the present ''avasarpiṇī'' age in Jainism.
In Jain his ...
'', the 19th Tirthankara, and ''Naminatha
Naminatha (Devanagari: नमिनाथ) (Sanskrit: नमिनाथः) was the twenty-first ''tirthankara'' of the present half time cycle, Avsarpini. He was born to the King Vijaya and Queen Vipra of the Ikshvaku dynasty. King Vijaya w ...
'', the 21st Tirthankara. As per the ''Śvetāmbara'' canon, the first four of the five significant events of the life of ''Mallinātha'' and ''Naminātha'' happened at Mithilā. The fifth one, which is the attainment of ''nirvana'', happened at ''Sammet Shikharji''.
''Mahavira
Mahavira (Devanagari: महावीर, ), also known as Vardhamana (Devanagari: वर्धमान, ), was the 24th ''Tirthankara'' (Supreme Preacher and Ford Maker) of Jainism. Although the dates and most historical details of his lif ...
'' spent 6 ''varshās'' (monsoon seasons) at Mithilā. ''Akampita Swāmi'', one of his 11 ganadharas, was born in Mithilā. Additionally, as per ancient ''Śvetāmbara
The Śvetāmbara (; also spelled Shwetambara, Shvetambara, Svetambara or Swetambara) is one of the two main branches of Jainism, the other being the Digambara. ''Śvetāmbara'' in Sanskrit means "white-clad", and refers to its ascetics' practi ...
'' texts, a branch of ancient Jaina ascetics was known as ''"Maithiliya"'' after Mithilā, signifying its historical importance as a center of Jaina scholarship.
''Vividha Tirtha Kalpa'', a 14th century CE Śvetāmbara
The Śvetāmbara (; also spelled Shwetambara, Shvetambara, Svetambara or Swetambara) is one of the two main branches of Jainism, the other being the Digambara. ''Śvetāmbara'' in Sanskrit means "white-clad", and refers to its ascetics' practi ...
Jaina text by ''Ācārya'' ''Jinaprabhasūrī'', describes Mithilā as a major Jaina pilgrimage center. The scripture locates Mithilā in the Tirhuta
The Tirhuta also known as Mithilakshar or Maithili script has historically been used for writing the Maithili, an Indo-Aryan language spoken by almost 35 million people of cultural Mithila. It was also used to write the Sanskrit language. The ...
region near the confluence of the ''Bāna Gangā'' and '' Gandaki'' rivers. It also mentions a village called ''"Jagai"'', where temples dedicated to '' Mallinātha'' and '' Naminātha'' existed. The site is also connected to Sita's marriage, ''"Sakulla Kunda"''. Some researchers suggest that ''"Jagai"'' may be an abbreviation of Jagadishpur, near present-day Sitamarhi
Sitamarhi is the headquarters of the Sitamarhi district in Tirhut Division, Bihar. The city was named in honour of Sītā, wife of Rāma, who was born in Sitamarhi according to Hindu legends.
In 1875, a subdivision for Sitamarhi was create ...
. In their pilgrimage parties of 17th century CE and 18th century CE respectively, ''Panyās Saubhāgyavijaya'' and ''Panyās Vijayasāgara'' mention the location of the Jaina pilgrimage of Mithilā near present-day Sitamarhi in Bihar
Bihar ( ) is a states and union territories of India, state in Eastern India. It is the list of states and union territories of India by population, second largest state by population, the List of states and union territories of India by are ...
.
 The temples fell into disrepair, possibly due to a lack of Jaina population. The only remnant was the footprints of '' Mallinātha'' and '' Naminātha''. These footprints were later preserved in ''Bhāgalpur''. Based on historical evidence and research, initiatives to restore Mithilā’s lost Jaina heritage were launched. A two-storey temple along the Sitamarhi-Dumra road was constructed. In 2015, the foundation was laid by ''Ācārya'' ''Mahendrasāgarasūrī'' of
The temples fell into disrepair, possibly due to a lack of Jaina population. The only remnant was the footprints of '' Mallinātha'' and '' Naminātha''. These footprints were later preserved in ''Bhāgalpur''. Based on historical evidence and research, initiatives to restore Mithilā’s lost Jaina heritage were launched. A two-storey temple along the Sitamarhi-Dumra road was constructed. In 2015, the foundation was laid by ''Ācārya'' ''Mahendrasāgarasūrī'' of Kharatara Gaccha
Kharatara Gaccha is one of Śvetāmbara Murtipujaka Gacchas. It is also called the Vidhisangha (the Assembly) or Vidhimarga (Path of Proper Conduct), as they regard their practices as scripturally correct.
History
Kharatara Gaccha was founde ...
. In 2020, the ritualistic installation of idols was conducted by ''Ācārya'' ''Piyushsāgarasūrī'' of Kharatara Gaccha and ''Ācārya'' ''Vinayasāgarasūrī'' of Tapa Gaccha
Tapa Gaccha is the largest Gaccha (monastic order) of Śvetāmbara Jainism. More than half of the existing Jain ascetics belong to the Tapa Gaccha. Several successful Sanskrit scholars belonged to Tapa Gaccha, including Hiravijaya, Meghavijaya, ...
.
Vedic period
Mithila first gained prominence after being settled by Indo-Aryan peoples who established theVideha
Videha ( Prākrit: ; Pāli: ; Sanskrit: ) was an ancient Indo-Aryan tribe of north-eastern Indian subcontinent whose existence is attested during the Iron Age. The population of Videha, the Vaidehas, were initially organised into a monarchy ...
kingdom. During the Later Vedic period
The Vedic period, or the Vedic age (), is the period in the late Bronze Age and early Iron Age of the history of India when the Vedic literature, including the Vedas (–900 BCE), was composed in the northern Indian subcontinent, between the e ...
(c. 1100–500 BCE), Videha became one of the major political and cultural centers of Ancient India, along with Kuru
Kuru may refer to:
Anthropology and history
* Kuru (disease), a type of transmissible spongiform encephalopathy associated with the cannibalistic funeral practices of the Fore people
* Kuru (mythology), part of Meitei mythology
* Kuru Kingdom, ...
and Panchala
Panchala () was an ancient kingdom of northern India, located in the Ganges-Yamuna Doab of the Upper Gangetic plain which is identified as Kanyakubja or region around Kannauj. During Late Vedic times (c. 1100–500 BCE), it was one of the ...
. The kings of the Videha Kingdom were called ''Janakas''. The Videha Kingdom was incorporated into the Vajjika League
The Vajjika (Pāli: ) or Vrijika () League, Confederacy, or Sangha, also called simply Vajji (Pāli: ) or Vriji (), was an ancient Indo-Aryan league which existed during the later Iron Age period in the north-eastern Indian subcontinent.
Na ...
, which had its capital in the city of Vaishali, and is also in Mithila.
Medieval period
From the 11th century to the 20th century, Mithila was ruled by various indigenous dynasties. The first of these was theKarnats of Mithila
The Karnats of Mithila or Karnata dynasty () was a dynasty established in 1097 CE by Nanyadeva. The dynasty controlled the areas we today know as Tirhut or Mithila (region), Mithila in India and adjoining parts of South Eastern Nepal. The main pow ...
, the Oiniwar Dynasty and the Khandwala Dynasty, also known as Raj Darbhanga
The Darbhanga Raj, also known as Raj Darbhanga and the Khandwala dynasty, was a chieftaincy located within the Mughal province of Bihar which controlled territories, not all contiguous, that were part of the Mithila region, now divided betwee ...
. The Malla dynasty and Licchavi dynasty of Nepal are also Maithil in origin. The rulers of the Oiniwar Dynasty and the Raj Darbhanga were Maithil Brahmin
Maithil Brahmins are the Indo-Aryan Hindu Brahmin community originating from the Mithila region and original inhabitants of Southern Nepal and bordering regions of India that comprises Madhesh Province & some areas of Koshi Province in Nepal ...
s. The Oiniwar Dynasty originated from the village Oini
Oini (Maithili language, Maithili: ओइनी) is a village in the Pusa block of the Samastipur district in Mithila (region), Mithila region of Bihar, India. It is an important village in the history of the Mithila region in the Indian subcontin ...
in the Samastipur district of the Mithila region. It was during the reign of the Raj Darbhanga family that the capital of Mithila was shifted to Darbhanga
Darbhanga is the fifth largest city and municipal corporation in the state of Bihar in India, and is considered an important city in North Bihar. It serves as the headquarters of the Darbhanga district and the Darbhanga division. Darbhanga ...
.
Tughlaq had attacked and taken control of Bihar, and from the end of the Tughlaq Dynasty
The Tughlaq dynasty (also known as the Tughluq or Tughluk dynasty; ) was the third dynasty to rule over the Delhi Sultanate in medieval India. Its reign started in 1320 in Delhi when Ghazi Malik assumed the throne under the title of Ghiyath ...
until the establishment of the Mughal Empire
The Mughal Empire was an Early modern period, early modern empire in South Asia. At its peak, the empire stretched from the outer fringes of the Indus River Basin in the west, northern Afghanistan in the northwest, and Kashmir in the north, to ...
in 1526, there was anarchy and chaos in the region. Akbar
Akbar (Jalal-ud-din Muhammad Akbar, – ), popularly known as Akbar the Great, was the third Mughal emperor, who reigned from 1556 to 1605. Akbar succeeded his father, Humayun, under a regent, Bairam Khan, who helped the young emperor expa ...
(reigned from 1556 to 1605) realised that taxes from Mithila could only be collected if there was a king who could ensure peace there. The Maithil Brahmins were dominant in the Mithila region and Mithila had Maithil Brahmin kings in the past.
Akbar summoned Rajpandit Chandrapati Thakur to Delhi
Delhi, officially the National Capital Territory (NCT) of Delhi, is a city and a union territory of India containing New Delhi, the capital of India. Straddling the Yamuna river, but spread chiefly to the west, or beyond its Bank (geography ...
and asked him to name one of his sons who could be made caretaker and tax collector for his lands in Mithila. Chandrapati Thakur named his middle son, Mahesh Thakur
Mahesh Thakur is an Indian actor who has played roles in many films, TV serials and web series. He has authored a book titled I-Quotes which was published in early 2021 by Popular Prakashan. Filmography
Films
Television
Bibliography ...
, and Akbar declared Mahesh Thakur
Mahesh Thakur is an Indian actor who has played roles in many films, TV serials and web series. He has authored a book titled I-Quotes which was published in early 2021 by Popular Prakashan. Filmography
Films
Television
Bibliography ...
as the caretaker of Mithila on the day of Ram Navami
Rama Navami () is a Hindus, Hindu festival that celebrates the birth of Lord Ram, Rama, one of the most popularly revered deities in Hinduism, also known as the seventh avatar of Vishnu. He is often held as an emblem within Hinduism for being a ...
in 1557 AD.
Lakshmeshwar Singh (reigned from 1860 to 1898) was the eldest son of Maharaja Maheshwar Singh of Darbhanga. He, along with his younger brother, Rameshwar Singh received a western education from Government appointed tutors as well as a traditional Indian education from a Sanskrit
Sanskrit (; stem form ; nominal singular , ,) is a classical language belonging to the Indo-Aryan languages, Indo-Aryan branch of the Indo-European languages. It arose in northwest South Asia after its predecessor languages had Trans-cultural ...
Pandit
A pandit (; ; also spelled pundit, pronounced ; abbreviated Pt. or Pdt.) is an individual with specialised knowledge or a teacher of any field of knowledge in Hinduism, particularly the Vedic scriptures, dharma, or Hindu philosophy; in colonial-e ...
. He spent approximately £300,000 on relief work during the famine of 1873–74. He constructed hundreds of miles of roads in various parts of the Raj, planting them with tens of thousands of trees for the comfort of travellers, as part of generating employment for people effected by famine. He constructed iron bridges over all the navigable rivers
He built, and entirely supported, a first-class Dispensary at Darbhanga, which cost £3400; a similar one at Kharakpur, which cost £3500; and largely contributed to many others.
Indian National Congress
The Indian National Congress (INC), colloquially the Congress Party, or simply the Congress, is a political parties in India, political party in India with deep roots in most regions of India. Founded on 28 December 1885, it was the first mo ...
as well as one of the main financial contributors thereto. Maharaja Lakshmeshwar Singh is known for purchasing Lowhter Castle for the venue of the 1888 Allahabad Congress session when the British denied permission to use any public place. The British Governor who?''] commissioned Edward Onslow Ford
Edward Onslow Ford (27 July 1852 – 23 December 1901) was an English sculptor. Much of Ford's early success came with portrait heads or busts. These were considered extremely refined, showing his subjects at their best and led to him receivin ...
to make a statue of Lakshmeshwar Singh. This is installed at Dalhousie Square
Binoy-Badal-Dinesh Bagh, shortened as B. B. D. Bagh, formerly called Tank Square and then Dalhousie Square (1847 to 1856), is the administrative, financial and commercial region and one of the central business districts of Kolkata (Calcutta), c ...
in Kolkata
Kolkata, also known as Calcutta ( its official name until 2001), is the capital and largest city of the Indian state of West Bengal. It lies on the eastern bank of the Hooghly River, west of the border with Bangladesh. It is the primary ...
.
On the occasion of the Jubilee of the reign of Queen Victoria, Lakshmeshwar Singh was declared as a Knight Commander of the Most Eminent Order of the Indian Empire
The Most Eminent Order of the Indian Empire is an order of chivalry founded by Queen Victoria on 1 January 1878. The Order includes members of three classes:
#Knight Grand Commander (:Knights Grand Commander of the Order of the Indian Empire, ...
, and was promoted to Knight Grand Commander in 1897.
He was also a member of the Royal Commission on Opium
The Royal Commission on Opium was a British Royal Commission that investigated the opium trade in British India in 1893–1895, particularly focusing on the medical effects of opium consumption within India. Set up by Prime Minister William Gl ...
of 1895, formed by British Government along with Haridas Viharidas Desai
Haridas Viharidas Desai (1840–1895) was Diwan of Junagadh state from 1883 onwards. He was a pious man and a brilliant administrator who in a decade made the most important reforms in every department of the Junagadh state. He built the 12,00 ...
who was the Diwan of Junagadh
Junagadh () is the city and headquarters of Junagadh district in the Indian state of Gujarat. Located at the foot of the Girnar hills, southwest of Ahmedabad and Gandhinagar (the state capital), it is the seventh largest city in the state. It i ...
. The Royal Opium Commission consisted of a 9-member team of which 7 were British and 2 were Indians and its chairman was Earl Brassey
Earl Brassey was a title in the Peerage of the United Kingdom. It was created in 1911 for the Liberal politician and former Governor of Victoria, Australia, Thomas Brassey, 1st Baron Brassey, eldest son of the railway magnate Thomas Brassey (18 ...
.
Geography
Mithila is a distinct geographical region with natural boundaries like rivers and hills. It is largely a flat and fertilealluvial
Alluvium (, ) is loose clay, silt, sand, or gravel that has been deposited by running water in a stream bed, on a floodplain, in an alluvial fan or beach, or in similar settings. Alluvium is also sometimes called alluvial deposit. Alluvium is ...
plain criss-crossed by numerous rivers which originate from the Himalayas
The Himalayas, or Himalaya ( ), is a mountain range in Asia, separating the plains of the Indian subcontinent from the Tibetan Plateau. The range has some of the Earth's highest peaks, including the highest, Mount Everest. More than list of h ...
. Due to the flat plains and fertile land Mithila has a rich variety of biotic resources; however, because of frequent floods people could not take full advantage of these resources.
Seven major rivers flow through Mithila: Gandak, Kosi
KOSI (101.1 FM) is a commercial radio station in Denver, Colorado. KOSI is owned by Salt Lake City–based Bonneville International and airs an adult contemporary music format, switching to Christmas music for much of November and December. ...
, Mahananda, Bagmati
The Bagmati River flows through the Kathmandu valley of Nepal, separating the cities of Kathmandu and Patan, before flowing through Madesh Province of southern Nepal and joining the Kamla River in the Indian state of Bihar. It is considered ...
, Kamala
Kamala may refer to:
People and fictional characters
* Kamala (name) — lists people and characters with the surname or given name
** Kamala Harris, 49th Vice President of the United States and 2024 Democratic Party presidential nominee
* Kamala ...
, Balan, and the Budhi Gandak
The Burhi Gandak River is a tributary of the Ganges. It is also known as the Sikrahna river. The Burhi (“Old”) Gandak flows parallel to and east of the Gandak River in an old channel.
Course
The Burhi Gandak originates from Chautarwa Chaur n ...
. They flow from the Himalayas in the north to the Ganges
The Ganges ( ; in India: Ganga, ; in Bangladesh: Padma, ). "The Ganges Basin, known in India as the Ganga and in Bangladesh as the Padma, is an international which goes through India, Bangladesh, Nepal and China." is a trans-boundary rive ...
river in the south. These rivers regularly flood, depositing silt onto the farmlands and sometimes causing death or hardship.
Culture
 Men and women in Mithila are very religious and dress for the festivals as well. The costumes of Mithila stem from the rich traditional culture of Mithila. Panjabi Kurta and
Men and women in Mithila are very religious and dress for the festivals as well. The costumes of Mithila stem from the rich traditional culture of Mithila. Panjabi Kurta and Dhoti
The dhoti is an ankle-length breechcloth, wrapped around the waist and the legs, in resemblance to the shape of trousers. The dhoti is a garment of ethnic wear for men in the Indian subcontinent. The dhoti is fashioned out of a rectangular p ...
with a Mithila Painting
Madhubani art (also known as Mithila art) is a style of painting practiced in the Mithila region of India and Nepal. It is named after the Madhubani district of Bihar, India, which is where it originated. Jitwarpur, Ranti and Rasidpur are the ...
bordered Maroon coloured Gamchha which is the Symbol of Passion, Love, Bravery and Courage are common clothing items for men. Men wear Gold ring in their nose which symbolizes prosperity, happiness and wealth inspired by Lord Vishnu
Vishnu (; , , ), also known as Narayana and Hari, is one of the principal deities of Hinduism. He is the supreme being within Vaishnavism, one of the major traditions within contemporary Hinduism, and the god of preservation (sattva).
Vish ...
. Also wear Balla on their wrist and Mithila Paag on their Head. In ancient times there was no colour option in Mithila, so the Maithil women wore white or yellow Saree with red Border but now they have a lot of variety and colour options and wear ''Laal-Paara'' (the traditional red-boarded white or yellow Saree
A sari (also called sharee, saree or sadi)The name of the garment in various regional languages include:
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
* is a drape (cloth) and a women's garment in the Indian subcontinent. It consists of an un-stit ...
) on some special occasions, and also wear ''Shakha-Pola'' with lahthi in their hand. In Mithila culture
Mithila culture or Maithil culture refers to the culture which originated in the Mithila region of the Indian subcontinent. Mithila comprises Tirhut, Darbhanga, Kosi, Purnia, Munger, Bhagalpur and Santhal Pargana divisions of India and adjoining ...
, this represents new beginnings, passion and prosperity. Red also represents the Hindu goddess Durga
Durga (, ) is a major Hindu goddess, worshipped as a principal aspect of the mother goddess Mahadevi. She is associated with protection, strength, motherhood, destruction, and wars.
Durga's legend centres around combating evils and demonic ...
, a symbol of new beginnings and feminine power. During Chhaith, the women of Mithila wear pure cotton dhoti without stitching which reflects the pure, traditional Culture of Mithila. Usually crafted from pure cotton for daily use and from pure silk for more glamorous occasions, traditional attire for the women of Mithila includes Jamdani, Banarisi and Bhagalpuri and many more.
Jhijhiya
Jhijhiya (also called Jhijhari) is a cultural folk dance of Mithila (region), Mithila region of India and Nepal. It is performed during the Vijayadashami, Dusshera festival, in the Hindu month of Ashvin (month), Ashwin (September/October). The da ...
and Dhuno-Naach are the Cultural Dance of Mithila. Jhijhiya is performed in Darbhanga, Muzaffarpur, Madhubani and their Neighbour Districts on the other hand Dhuno-Naach is performed in Begusarai, Khagaria, Katihar, Naugachia during Durga Puja and Kalipuja with Shankha-Dhaak Sound.
Many festivals are celebrated throughout the year in Mithila. Chhaith, Durga Puja
Durga Puja (ISO 15919, ISO: , ), also known as Durgotsava or Shaaradotsava, is an annual festival originating in the Indian subcontinent which pays homage to the Hinduism, Hindu goddess Durga, and is also celebrated because of Durga's victo ...
and Kali puja
Kali Puja (ISO: ), also known as Shyama Puja or Mahanisha Puja, is a festival originating from the Indian subcontinent, dedicated to the Hindu goddess Kali. It is celebrated on the new moon day (Dipannita Amavasya) of the Hindu calendar month o ...
is celebrated as perhaps the most important of all the celebrations of Mithila.
Mithila Paag
The Paag is a headdress in theMithila region
Mithila (), also known as Tirhut, Tirabhukti and Mithilanchal, is a geographical and cultural region of the Indian subcontinent bounded by the Mahananda River in the east, the Ganges in the south, the Gandaki River in the west and by the foothil ...
of India
India, officially the Republic of India, is a country in South Asia. It is the List of countries and dependencies by area, seventh-largest country by area; the List of countries by population (United Nations), most populous country since ...
and Nepal
Nepal, officially the Federal Democratic Republic of Nepal, is a landlocked country in South Asia. It is mainly situated in the Himalayas, but also includes parts of the Indo-Gangetic Plain. It borders the Tibet Autonomous Region of China Ch ...
worn by Maithil
Maithils (Devanagari: मैथिल), also known as Maithili people, are an Indo-Aryan cultural and ethno-linguistic group from the Indian subcontinent, who speak the Maithili language as their native language. They inhabit the Mithila regio ...
people. It is a symbol of honour and respect and a significant part of Maithil culture.
The Paag dates back to pre-historic times when it was made of plant leaves. It exists today in a modified form. The Paag is wore by the whole Maithil community. The colour of the Paag also carries a lot of significance. The red Paag is worn by the bridegroom
A bridegroom (often shortened to groom) is a man who is about to be married or who is newlywed.
When marrying, the bridegroom's future spouse is usually referred to as the bride. A bridegroom is typically attended by a best man and grooms ...
and by those who are undergoing the sacred thread rituals. Paag of mustard colour is donned by those attending wedding ceremonies and the elders wear a white Paag.
This Paag now features place in the popular Macmillan Dictionary. For now, Macmillan Dictionary explains Paag as “a kind of headwear worn by people in the Mithila belt of India.” On 10 February 2017,
On 10 February 2017, India Posts
The Department of Posts, d/b/a India Post, is an Indian public sector postal system statutory body headquartered in New Delhi, India. It is an organisation under the Ministry of Communications. It is the most widely distributed postal system in ...
released a set of 16 commemorative postage stamps
A commemorative stamp is a postage stamp, often issued on a significant date such as an anniversary, to honor or commemorate a place, event, person, or object. The ''subject'' of the commemorative stamp is usually spelled out in print, unlike defi ...
on "Headgears of India". The Mithila Paag was featured on one of those postage stamps.
The Mithilalok Foundation
The Mithilalok Foundation is an India-based social service organization that works to promote socio-cultural and economic development of the Mithila region
Mithila (), also known as Tirhut, Tirabhukti and Mithilanchal, is a geographical and ...
was (in 2017) a social service organization whose flagship programme was Paag Bachau Abhiyan (Save the Paag Campaign). NOTE - it is not clear (as at April 2024) whether this campaign or the Foundation still exist.
Languages and dialects
People of Mithila primarily speak in Maithili and its various dialects includingThēthi
Thēthi, also known as ''Thēth'', ''Thethiya'', ''Thenthi'', or ''Thati'', is a Maithili dialect, mainly spoken in the Mithila region of India and Nepal. It is spoken mainly in Kosi, Purnia and Munger divisions of Bihar, India and in Koshi Pr ...
and its perceived dialects Bajjika
Bajjika is an Indo-Aryan language variety spoken in parts of Bihar, India and in Nepal. It is also classified as a dialect of Maithili language and is known as Western Maithili.
Territory and speakers
Bajjika language is spoken in the north-w ...
, and Angika
Angika (also known as ''Anga'', ''Angikar'' or ''Chhika-Chhiki'') is an Eastern Indo-Aryan language spoken in some parts of the Indian states of Bihar and Jharkhand, as well as in parts of Nepal.
Angika is closely related to neighbouring Indi ...
while also being well versed in other languages like English
English usually refers to:
* English language
* English people
English may also refer to:
Culture, language and peoples
* ''English'', an adjective for something of, from, or related to England
* ''English'', an Amish ter ...
, Hindi
Modern Standard Hindi (, ), commonly referred to as Hindi, is the Standard language, standardised variety of the Hindustani language written in the Devanagari script. It is an official language of India, official language of the Government ...
and Nepali for official or administrative purposes.
This language is an Indo-Aryan language
The Indo-Aryan languages, or sometimes Indic languages, are a branch of the Indo-Iranian languages in the Indo-European language family. As of 2024, there are more than 1.5 billion speakers, primarily concentrated east of the Indus river in Ba ...
native to the Indian subcontinent
The Indian subcontinent is a physiographic region of Asia below the Himalayas which projects into the Indian Ocean between the Bay of Bengal to the east and the Arabian Sea to the west. It is now divided between Bangladesh, India, and Pakista ...
, mainly spoken in India
India, officially the Republic of India, is a country in South Asia. It is the List of countries and dependencies by area, seventh-largest country by area; the List of countries by population (United Nations), most populous country since ...
and Nepal
Nepal, officially the Federal Democratic Republic of Nepal, is a landlocked country in South Asia. It is mainly situated in the Himalayas, but also includes parts of the Indo-Gangetic Plain. It borders the Tibet Autonomous Region of China Ch ...
and is one of the 22 recognised Indian languages. In Nepal, it is spoken in the eastern Terai
The Terai or Tarai is a lowland region in parts of southern Nepal and northern India that lies to the south of the outer foothills of the Himalayas, the Sivalik Hills and north of the Indo-Gangetic Plain.
This lowland belt is characterised by ...
and is the second most prevalent language of Nepal. Tirhuta
The Tirhuta also known as Mithilakshar or Maithili script has historically been used for writing the Maithili, an Indo-Aryan language spoken by almost 35 million people of cultural Mithila. It was also used to write the Sanskrit language. The ...
is formerly the primary script for written Maithili. Less commonly, it was also written in the local variant of Kaithi
Kaithi (), also called Kayathi (), Kayasthi (), or Kayastani, is a Brahmic script historically used across parts of Northern and Eastern India. It was prevalent in regions corresponding to modern-day Uttar Pradesh, Bihar, and Jharkhand. The s ...
. Today it is written in the Devanagari
Devanagari ( ; in script: , , ) is an Indic script used in the Indian subcontinent. It is a left-to-right abugida (a type of segmental Writing systems#Segmental systems: alphabets, writing system), based on the ancient ''Brāhmī script, Brā ...
adopted script.
Maithil Cuisine
Maithil cuisine is a part ofIndian cuisine
Indian cuisine consists of a variety of regional and traditional cuisines native to the Indian subcontinent. Given the diversity in soil, climate, culture, ethnic groups, and occupations, these cuisines vary substantially and use locally av ...
and Nepalese cuisine
Nepali cuisine comprises a variety of cuisines based upon ethnicity, alluvial soil and Geography of Nepal#Climate, climate relating to cultural diversity and Geography of Nepal, geography of Nepal and neighboring regions of Sikkim and Gorkha ...
. It is a culinary style which originated in Mithila. Some traditional Maithil dishes are:
* Dahi- Chura
* Mithila Makhana
Mithila Makhana (botanical name: ''Euryale ferox'') is a special variety of aquatic fox nut cultivated in Mithila (region), Mithila region of Bihar state in India and in Nepal.
In Mithila, Makhana is also termed as Makhan. It is one of the th ...
* Vegetable of Arikanchan
* Ghooghni
* Traditional Pickles, made of fruits and vegetables which are generally mixed with ingredients like salt, spices, and vegetable oils and are set to mature in a moistureless medium.
* Tarua of Tilkor
* Bada
* Dahi Badee
* Yogurt
Yogurt (; , from , ; also spelled yoghurt, yogourt or yoghourt) is a food produced by bacterial Fermentation (food), fermentation of milk. Fermentation of sugars in the milk by these bacteria produces lactic acid, which acts on milk protein to ...
* Maachh
* Mutton
Lamb and mutton, collectively sheep meat (or sheepmeat) is one of the most common meats around the world, taken from the domestic sheep, ''Ovis aries'', and generally divided into lamb, from sheep in their first year, hogget, from sheep in thei ...
* Irhar
* Pudukiya (Purukiya) which is basically dumplings.
* Makhan Payas
* Anarasa
* Bagiya
Bagiya (also called Pithha) is a delicacy of the Maithils, Tharu and Dhimal communities of India and Nepal. It is a steamed dumpling that consists of an external covering of rice flour and an inner content of sweet substances such like chaku, v ...
Madhubani/Mithila Painting
Madhubani art or Mithila painting is practiced in the Mithila region of India and Nepal. It was traditionally created by the women of different communities of the Mithila region. It is named afterMadhubani district
Madhubani district is one of the thirty-eight districts of Bihar, India, and is a part of Darbhanga division. Its administrative headquarters are located in Madhubani. The district has an area of and has a population of 4,487,379 (as of 20 ...
of India which is where it originated.
This painting as a form of wall art was practiced widely throughout the region; the more recent development of painting on paper and canvas originated among the villages around Madhubani, and it is these latter developments that may correctly be referred to as Mithila Painting''.''
Yatra in Mithila
*Mithila Madhya Parikrama
Mithila Madhya Parikrama (मिथिला मध्य परिक्रमा) is an annual periodic journey of the central part of the ancient Mithila (region), Mithila in Nepal and Bihar (India). It is held every year between the months of ...
- It is a circular journey of the central part of the ancient Mithila.
* Sitamarhi Dham Parikrama
Sitamarhi Dham Parikrama ( Maithili: सीतामढ़ी धाम परिक्रमा) is a Hindu religious circumambulation of the sacred religious destinations around the region of ''Sitamarhi Dham'' in the Mithila region of Bihar. It ...
- It is a Hindu religious circumambulation of the sacred religious destinations around the region of Sitamarhi Dham in Mithila. It is associated with the birth anniversary known as Janaki Navami of Goddess Sita in Mithila.
Main festivals
* Indra Puja - Indra Puja is a festival celebrated in Mithila and only place where indra is worshipped , festival that honors Lord Indra and his wife Shachi. It is celebrated to ensure a good harvest season. * Saama-Chakeba: includes folk theater and song, celebrates the love between brothers and sisters and is based on a legend recounted in the s. *Jur Sital
Jur Sital or Maithil New Year is the celebration of the first day of the Maithil new year also called Aakhar Bochhor.
Maithils eat Bari with Bhaat (steamed rice) and Sondesh on the day. This day which usually falls on 14th or 15 April on Gregori ...
- Jur Sital or Maithil New Year is the celebration of the first day of the Maithil new year
* Chaurchan: Along with Lord Ganesha
Ganesha or Ganesh (, , ), also known as Ganapati, Vinayaka and Pillaiyar, is one of the best-known and most worshipped deities in the Hindu pantheon and is the Supreme God in the Ganapatya sect. His depictions are found throughout India. Hi ...
, Lord Vishnu
Vishnu (; , , ), also known as Narayana and Hari, is one of the principal deities of Hinduism. He is the supreme being within Vaishnavism, one of the major traditions within contemporary Hinduism, and the god of preservation (sattva).
Vish ...
, Goddess Parvati
Parvati (, , IPA: / pɑɾʋət̪iː/), also known as Uma (, , IPA: /ʊmɑː/) and Gauri (, , IPA: / gə͡ʊɾiː/), is one of the principal goddesses in Hinduism, revered as the goddess of power, energy, nourishment, harmony, love, beauty, d ...
and the moon god is worshipped. The story of Chorchan Puja is also heard on this day after that arghya
''Tarpana'' or (, , , ) is a term in the Vedic practice that refers to an offering made to divine entities. It refers to the act of offering as well as the substance used in the offering. ''Tilatarpana'' (, , , ) is a specific form of ''tarpana ...
is offered to the moon
The Moon is Earth's only natural satellite. It Orbit of the Moon, orbits around Earth at Lunar distance, an average distance of (; about 30 times Earth diameter, Earth's diameter). The Moon rotation, rotates, with a rotation period (lunar ...
god ( Chandra Deva).
*
* Madhushravani
Madhushravani ( Maithili: मधुश्रावणी) is a Hindu festival celebrated in the Mithila region by newly married Maithil Brahmin women. It is famous for popular faith and longevity of husbands and happy married life in Maithil Brahm ...
- It is a Hindu festival celebrated in Mithila by newly married Maithil Brahmin
Maithil Brahmins are the Indo-Aryan Hindu Brahmin community originating from the Mithila region and original inhabitants of Southern Nepal and bordering regions of India that comprises Madhesh Province & some areas of Koshi Province in Nepal ...
women
*
* Vivaha Panchami
Vivaha Panchami () is a Hindu festival celebrating the wedding of Rama and Sita in Janakpurdham which was the capital city of Mithila (region), Mithila. It is observed on the fifth day of the Paksha, Shukla paksha or waxing phase of moon in the ...
: Hindu festival celebrating the wedding of Rama and Sita. It is observed on the fifth day of the Shukla paksha or waxing phase of moon in the Agrahayana month (November – December) as per Maithili calendar and in the month of Margashirsha in the Hindu calendar.
* Sita Navami
Sita Navami () is a Hindu festival that celebrates the birth of the goddess Sita. It is celebrated on the ''navami'' (ninth day) of the ''Shukla Paksha'' (first lunar fortnight) of the Hindu month of ''Vaishakha''.
Legend
According to the ''Ra ...
- festival that celebrates the birth of Goddess Sita
Sita (; ), also known as Siya, Jānaki and Maithili, is a Hindu goddess and the female protagonist of the Hindu epic ''Ramayana''. Sita is the consort of Rama, the avatar of god Vishnu, and is regarded as an avatar of goddess Lakshmi. She is t ...
the daughter of mithila in Janakpur dham
Janakpurdham or Janakpur (), is the capital city of Madhesh Province. This sub-metropolitan city is a central hub for the Maithili language, as well as for religious and cultural tourism in Nepal.
The city was founded in the early 18th centur ...
* Ganga Dussehra
Ganga Dussehra, also known as Gangavataran, is a Hindu festival celebrating the ''avatarana'' (descent) of the Ganges. It is believed by Hindus that the holy river Ganges descended from heaven to earth on this day. Ganga Dussehra takes place o ...
: Ganga Dussehra, also known as Gangavataran, is a Hindu
Hindus (; ; also known as Sanātanīs) are people who religiously adhere to Hinduism, also known by its endonym Sanātana Dharma. Jeffery D. Long (2007), A Vision for Hinduism, IB Tauris, , pp. 35–37 Historically, the term has also be ...
festival celebrated by Maithils in Mokshdhaam Simaria Dhaam (The Welcome Gate of Mithila). ''avatarana'' (descent) of the Ganges. It is believed by Hindus that the holy river
Sacred waters are sacred natural sites characterized by tangible topographical land formations such as rivers, lakes, springs, reservoirs, and oceans, as opposed to holy water which is water elevated with the sacramental blessing of a cleri ...
Ganges
The Ganges ( ; in India: Ganga, ; in Bangladesh: Padma, ). "The Ganges Basin, known in India as the Ganga and in Bangladesh as the Padma, is an international which goes through India, Bangladesh, Nepal and China." is a trans-boundary rive ...
descended from heaven to earth on this day.
* Kalpwas: Celebrated every in the Kartik month at Simaria Ghat
Simaria Ghat ( Maithili: सिमरिया घाट) is a holy place in Hinduism for the sacred bath known as ''Ganga Snaana'' in the Mithila region of Indian subcontinent. It is located at the bank of Ganga river near Simaria village of ...
in Simaria
Simaria is an Indian village on the Ganges river. It is in the Begusarai District and near BTPS, Barauni
Barauni is an industrial town situated on the bank of the river Ganges in the Begusarai district in the state of Bihar, India. It ...
Dhaam, Begusarai
Begusarai is the industrial and financial capital of Bihar and the administrative headquarters of the Begusarai district, which is one of the 38 districts of the Indian state of Bihar. The district lies on the northern bank of the river Gan ...
.
* Kojagra
Kojagra ( Maithili: कोजगरा) is a special festival of the Mithila region in the Indian subcontinent. It is a sanskar ritual for the newly married couples among the communities of the Maithil Brahmins and Kayasthas. It is celebrated on ...
(Lachhmi Puja): harvest festival marking the end of monsoon season
* Paata Puja (Durga Maay Aagmon)
* Khutti Puja (Ritual of Durga Puja)
* Mohalaya
* Durga Puja
Durga Puja (ISO 15919, ISO: , ), also known as Durgotsava or Shaaradotsava, is an annual festival originating in the Indian subcontinent which pays homage to the Hinduism, Hindu goddess Durga, and is also celebrated because of Durga's victo ...
: a ten-day festival, of which the last five are of the most significance. is an important festival in the Shaktism
Shaktism () is a major Hindu denomination in which the God in Hinduism, deity or metaphysics, metaphysical reality is considered metaphorically to be a woman.
Shaktism involves a galaxy of goddesses, all regarded as different aspects, mani ...
tradition of Hinduism. It marks the victory of goddess Durga in her battle against the shape-shifting asura
Asuras () are a class of beings in Indian religions, and later Persian and Turkic mythology. They are described as power-seeking beings related to the more benevolent Devas (also known as Suras) in Hinduism. In its Buddhist context, the wor ...
, Mahishasura
Mahishasura (, ) is a bovine asura in Hinduism. He is depicted in Hindu texts, Hindu literature as a deceitful demon who pursued his evil ways by shape-shifting. Mahishasura was the son of the asura Rambha (asura), Rambha and the brother of buf ...
. Thus, the festival epitomizes the victory of good over evil, though it is also in part a harvest festival celebrating the goddess as the motherly power behind all of life and creation.
* Kali Puja
Kali Puja (ISO: ), also known as Shyama Puja or Mahanisha Puja, is a festival originating from the Indian subcontinent, dedicated to the Hindu goddess Kali. It is celebrated on the new moon day (Dipannita Amavasya) of the Hindu calendar month o ...
: dedicated to the Hindu goddess Kali, celebrated on the new moon day Dipannita Amavasya of the Hindu month Kartik
* Saraswati Puja
Vasant Panchami , also rendered Vasanta Panchami and Saraswati Puja in honour of the Hindu goddess Saraswati, is a festival that marks the preparation for the arrival of spring. The festival is celebrated in Indian religions in different ways ...
: marks the preparation for the arrival of spring
Spring(s) may refer to:
Common uses
* Spring (season), a season of the year
* Spring (device), a mechanical device that stores energy
* Spring (hydrology), a natural source of water
* Spring (mathematics), a geometric surface in the shape of a he ...
. The festival is celebrated by people of Dharmic religions
Indian religions, sometimes also termed Dharmic religions or Indic religions, are the religions that originated in the Indian subcontinent. These religions, which include Buddhism, Hinduism, Jainism, and Sikhism,Adams, C. J."Classification o ...
in the South Asia
South Asia is the southern Subregion#Asia, subregion of Asia that is defined in both geographical and Ethnicity, ethnic-Culture, cultural terms. South Asia, with a population of 2.04 billion, contains a quarter (25%) of the world's populatio ...
n countries in different ways depending on the region. Vasant Panchami also marks the start of preparation for Holika
Holika (, ), also known as Simhika, is an asuri in Hinduism. She is the sister of the asura-kings Hiranyakashipu and Hiranyaksha, and the paternal aunt of Prahlada.
The legend of '' Holika Dahan'' (Holika's burning) signifies the triumph o ...
and Holi
Holi () is a major Hindu festival celebrated as the Festival of Colours, Love and Spring.The New Oxford Dictionary of English (1998) p. 874 "Holi /'həʊli:/ noun a Hindu spring festival ...".Yudit Greenberg, Encyclopedia of Love in World ...
, which take place forty days later.Christian Roy (2005). Traditional Festivals: A Multicultural Encyclopedia. ABC-CLIO. pp. 192–193. .
* Rama Navami
Rama Navami () is a Hindu festival that celebrates the birth of Rama, one of the most popularly revered deities in Hinduism, also known as the seventh avatar of Vishnu. He is often held as an emblem within Hinduism for being an ideal king and h ...
: celebrates the descent of Vishnu as the Rama avatar, through his birth to King Dasharatha
Dasharatha (, IAST: Daśaratha; born Nemi) was the king of Kosala, with its capital at Ayodhya, in the Hindu epic ''Ramayana''. Dasharatha married Kausalya, Sumitra and Kaikeyi. He was the father of Rama, the protagonist of the epic Ramayana ...
and Queen Kausalya
Kausalya (, ) is a queen of Kosala in the Hindu epic ''Ramayana''. She is the first senior queen consort of Dasharatha, who ruled Kosala from its capital Ayodhya. She is the mother of Rama, the male protagonist of the epic. She is a secondar ...
in Ayodhya
Ayodhya () is a city situated on the banks of the Sarayu river in the Indian state of Uttar Pradesh. It is the administrative headquarters of the Ayodhya district as well as the Ayodhya division of Uttar Pradesh, India. Ayodhya became th ...
, Kosala
Kosala, sometimes referred to as Uttara Kosala () was one of the Mahajanapadas of ancient India. It emerged as a small state during the Late Vedic period and became (along with Magadha) one of the earliest states to transition from a lineage ...
.Hindus around the world celebrate Ram Navami todayDNA, 8 April 2014 * Basanti Puja (Chaiti Durga Puja) * Til Sakraait * Aakhar Bochhor *
Naag Panchami
Naga Panchami (Sanskrit: नागपञ्चमी, IAST: ''Nāgapañcamī'') is a day of traditional worship of ''naga''s (or najas or nags) or snakes (which are associated with the mythical Nāga beings) observed by Hindus, Jains, and Budd ...
* Barsaait
* Vishwakarma Puja
Vishvakarma Puja (), also rendered Vishvakarma Jayanti, is a Hindu observance dedicated to Vishvakarma, the architect of the gods.
It falls on the date of Kanya Sankranti of the Hindu calendar. It is generally celebrated every year between 16 ...
* Holi
Holi () is a major Hindu festival celebrated as the Festival of Colours, Love and Spring.The New Oxford Dictionary of English (1998) p. 874 "Holi /'həʊli:/ noun a Hindu spring festival ...".Yudit Greenberg, Encyclopedia of Love in World ...
People
Maithili language speakers are referred to as Maithils and they are an Indo-Aryanethno-linguistic
Ethnolinguistics (sometimes called cultural linguistics) is an area of anthropological linguistics that studies the relationship between a language or group of languages and the cultural practices of the people who speak those languages.
It exam ...
group. There are an estimated 75 million Maithils in India alone. The vast majority of them are Hindu
Hindus (; ; also known as Sanātanīs) are people who religiously adhere to Hinduism, also known by its endonym Sanātana Dharma. Jeffery D. Long (2007), A Vision for Hinduism, IB Tauris, , pp. 35–37 Historically, the term has also be ...
.
The people of Mithila can be split into various caste
A caste is a Essentialism, fixed social group into which an individual is born within a particular system of social stratification: a caste system. Within such a system, individuals are expected to marry exclusively within the same caste (en ...
/clan
A clan is a group of people united by actual or perceived kinship
and descent. Even if lineage details are unknown, a clan may claim descent from a founding member or apical ancestor who serves as a symbol of the clan's unity. Many societie ...
affiliations such as Maithil Brahmins, Kayastha
Kayastha (or Kayasth) denotes a cluster of disparate Indian communities broadly categorised by the regions of the Indian subcontinent in which they were traditionally locatedthe Chitraguptavanshi Kayasthas of North India, the Chandraseniya Ka ...
s, Kanu, Kewat
The Kewat, also spelled Kevat, is a Hindu caste, found in the states of Assam, Bihar, Tripura, Uttar Pradesh and West Bengal in India. They are the traditional boatmen of northern India, and also in neighbouring country Nepal.
Origin
The na ...
s, Rajput
Rājpūt (, from Sanskrit ''rājaputra'' meaning "son of a king"), also called Thākur (), is a large multi-component cluster of castes, kin bodies, and local groups, sharing social status and ideology of genealogical descent originating fro ...
s, Kushwaha
Kushwaha (sometimes Kushvaha), is a community of the Indo-Gangetic Plain that has traditionally been involved in agriculture, including beekeeping. The term has been used to represent different sub-castes of the Kachhis, Kachhvahas, Koeris ...
s, Baniya Baniya or Bania may refer to:
* Bania (caste)
Bania (also spelled Baniya, Banija, Banya, Vaniya, Vani, Vania, and Vanya) is a mercantile caste primarily from the Indian states of Rajasthan and Gujarat, with significant diasporic communities i ...
s, Kamatas, Ahir
Ahir or Aheer (derived from the Sanskrit word: abhira) is a community of traditionally non-elite pastoralists in India, most of whom now use the Yadav surname, as they consider the two terms synonymous. The Ahirs are variously described as a ...
s, Kurmi
Kurmi is traditionally a non-elite tiller caste in the lower Gangetic plain of India, especially southern regions of Awadh, eastern Uttar Pradesh and parts of Bihar and Jharkhand. The Kurmis came to be known for their exceptional work ethic, ...
s, Dushads, Kujras, Manush and many more.
Demands for administrative units
Proposed Indian state
There is an ongoing movement in the Maithili speaking region of India for a separateIndian state
India is a federal union comprising 28 states and 8 union territories, for a total of 36 subnational entities. The states and union territories are further subdivided into 800 districts and smaller administrative divisions by the respe ...
of Mithila.
Proposed Nepalese province
There was a movement in the Maithili speaking areas of Nepal for a separate province.Province No. 2
Madhesh Province () is a province of Nepal in the Terai region with an area of covering about 6.5% of the country's total area. It has a population of 6,126,288 as per the 2021 Nepal census, making it Nepal's most densely populated province and ...
was established under the 2015 Constitution, which transformed Nepal into a Federal Democratic Republic, with a total of seven provinces. Province No. 2 has a substantial Maithili speaking population and consists most of the Maithili speaking areas of Nepal. It was demanded by some Mithila activists that Province No. 2 be named 'Mithila Province'.
On 23 December 2021, four different names for the Province No. 2 were presented by the various parties of the Provincial Assembly of Madhesh Province
The Madhesh Provincial Assembly ( Nepali/ Maithili/ Bhojpuri: मधेश प्रदेश सभा) is a unicameral governing and law making body of Madhesh Province, one of the seven Provinces in Nepal, The assembly is seated in the provin ...
. The four names were ‘Madhesh Pradesh’, ‘Janaki Pradesh’, ‘Madhya Madhesh Pradesh’ and ‘Mithila Bhojpura’.
Among the four names, Madhesh Pradesh (Madhesh Province) was chosen and finalized on 17 January 2022. The name was finalized with 80 percent majority in the Provincial Assembly. Janakpur
Janakpurdham or Janakpur (), is the capital city of Madhesh Province. This sub-metropolitan city is a central hub for the Maithili language, as well as for religious and cultural tourism in Nepal.
The city was founded in the early 18th centur ...
was named as the capital of the province.
Notable people
The following are notable residents (past and present) of Mithila region.Ancient

 *
* Janaka
Janaka (, IAST: ''Janaka'') is the King of Videha who ruled from Mithila (region), Mithila, in the Hindu epic ''Ramayana''. Janaka was married to Sunayana (Ramayana), Sunayana. He is the father of Sita and Urmila in the epic. The term Janaka ...
, King of Mithila and Father in Law of King Rama
Rama (; , , ) is a major deity in Hinduism. He is worshipped as the seventh and one of the most popular avatars of Vishnu. In Rama-centric Hindu traditions, he is considered the Supreme Being. Also considered as the ideal man (''maryāda' ...
* Sita
Sita (; ), also known as Siya, Jānaki and Maithili, is a Hindu goddess and the female protagonist of the Hindu epic ''Ramayana''. Sita is the consort of Rama, the avatar of god Vishnu, and is regarded as an avatar of goddess Lakshmi. She is t ...
, Princess of Mithila Kingdom
Videha ( Prākrit: ; Pāli: ; Sanskrit: ) was an ancient Indo-Aryan tribe of north-eastern Indian subcontinent whose existence is attested during the Iron Age. The population of Videha, the Vaidehas, were initially organised into a monarchy ...
and wife of King Rama
Rama (; , , ) is a major deity in Hinduism. He is worshipped as the seventh and one of the most popular avatars of Vishnu. In Rama-centric Hindu traditions, he is considered the Supreme Being. Also considered as the ideal man (''maryāda' ...
* Shrutadeva
Shrutadeva (Sanskrit: श्रुतदेव) was a famous devotee of Lord Krishna in the Kingdom of Mithila. He was contemporary to the king Bahulashva Janaka in Mithila.
Etymology
According to the Bhagavata Purana, the literal meaning of t ...
, a notable devotee of Lord Krishna
Krishna (; Sanskrit: कृष्ण, ) is a major deity in Hinduism. He is worshipped as the eighth avatar of Vishnu and also as the Supreme God in his own right. He is the god of protection, compassion, tenderness, and love; and is wi ...
during the regime of Bahulashva Janaka
Bahulashva Janaka (Sanskrit: बहुलाश्व जनक) was the King of Videha (also known as the Mithila Kingdom) in the ancient Indian Subcontinent. He was a descendant from the lineage of Janaka Dynasty in Mithila.
Description
Acco ...
* Sulabha
Sulabha ( Sanskrit: सुलभ ) was a female scholar who lived during the Mithila Kingdom. She was a Vedic scholar knownas Brahmavadini. In ''Rigaveda'', a ''Samhita'' attributed to her was called ''Saulabha Samhita'', later lost. ''Sulabha ...
, female scholar during the period of Dharmadhwaja Janaka
Dharmadhwaja Janaka ( Sanskrit: धर्मध्वज जनक ) was the king of the ancient Mithila or Videha Kingdom in the Indian Subcontinent. Dharmadhwaja Janaka, also known as King Janaka, was a significant figure in ancient Indian hist ...
.
* Yajnavalkya
Yajnavalkya or Yagyavalkya (, International Alphabet of Sanskrit Transliteration, IAST:) is a Hindu Vedic sage prominently mentioned in the Brihadaranyaka Upanishad (c. 700 BCE) and Taittiriya Upanishad, ''Tattiriya Upanishad''., Quote: "Yajnav ...
, founder of Shukla Yajurveda
The ''Yajurveda'' (, , from यजुस्, "worship", and वेद, "knowledge") is the Veda primarily of prose mantras for worship rituals.Michael Witzel (2003), "Vedas and Upaniṣads", in ''The Blackwell Companion to Hinduism'' (Edito ...
and Shatapatha Brahmana
The Shatapatha Brahmana (, , abbreviated to 'SB') is a commentary on the Yajurveda, Śukla Yajurveda. It is attributed to the Vedic sage Yajnavalkya. Described as the most complete, systematic, and important of the Brahmanas (commentaries on the ...
* Akshapada Gautama, founder of Nyaya
Nyāya (Sanskrit: न्यायः, IAST: nyāyaḥ), literally meaning "justice", "rules", "method" or "judgment", is one of the six orthodox (Āstika) schools of Hindu philosophy. Nyāya's most significant contributions to Indian philosophy ...
school of Indian Philosophy
Indian philosophy consists of philosophical traditions of the Indian subcontinent. The philosophies are often called darśana meaning, "to see" or "looking at." Ānvīkṣikī means “critical inquiry” or “investigation." Unlike darśan ...
* Gargi Vachaknavi, female scholar of Vedas
FIle:Atharva-Veda samhita page 471 illustration.png, upright=1.2, The Vedas are ancient Sanskrit texts of Hinduism. Above: A page from the ''Atharvaveda''.
The Vedas ( or ; ), sometimes collectively called the Veda, are a large body of relig ...
* Kapila
Kapila () (7th-6th-century BCE), also referred to as Cakradhanus, is a Vedic sage in Hindu tradition, regarded the founder of the Samkhya school of Hindu philosophy., Quote:"Kapila (fl. 550 BC), Vedic sage and founder of the system of Samkhya, ...
, founder of Samkhya Philosophy
Samkhya or Sankhya (; ) is a dualistic orthodox school of Hindu philosophy. It views reality as composed of two independent principles, '' Puruṣa'' ('consciousness' or spirit) and ''Prakṛti'' (nature or matter, including the human mind an ...
Historical
*Udayana
Udayana, (Devanagari: उदयन) also known as Udayanācārya (Udyanacharya, or Master Udayana), (circa 975 - 1050 CE) was an Indian philosopher and logician of the tenth century of the Nyaya school who attempted to devise a rational theolog ...
charya, 10th/11th-century philosopher and logician
Logic is the study of correct reasoning. It includes both formal and informal logic. Formal logic is the study of deductively valid inferences or logical truths. It examines how conclusions follow from premises based on the structure of arg ...
of the Nyaya
Nyāya (Sanskrit: न्यायः, IAST: nyāyaḥ), literally meaning "justice", "rules", "method" or "judgment", is one of the six orthodox (Āstika) schools of Hindu philosophy. Nyāya's most significant contributions to Indian philosophy ...
school.
* Mandana Mishra
Mandana may refer to
* Mandana (given name)
* Mandane of Media, 6th century BCE princess of Media
* Mandana Paintings in Rajasthan and Madhya Pradesh, India
See also
* Mandhana (disambiguation)
{{Disambiguation ...
, scholar of Mimansa
* Ayachi Mishra, scholar Nyaya Shastra
* Vidyapati
Vidyapati ( – 1448), also known by the sobriquet ''Maithil Kavi Kokil'' (the poet cuckoo of Maithili), was a Maithili and Sanskrit polymath-poet-saint, playwright, composer, biographer, philosopher, law-theorist, writer, courtier and ...
, 14th/15th century Maithili and Sanskrit poet-saint
* Shivasimha - popular king of Oiniwar Dynasty in Mithila
* Lakhimadevi
Lakhimadevi (Maithili language, Maithili: लखीमादेवी) was the queen of the Videha, Mithila Kingdom in Oiniwar dynasty, Oiniwar Dynasty during the period of the Shiva Simha Singh, King Shivasimha in the kingdom. She was contemporar ...
- queen of Shivasimha and woman ruler of Mithila, scholar and poetess
* Vishwasa Devi
Vishwasa Devi (Maithili: विश्वास देवी, Romanised: ''Viśvasadevi'') was the queen of the Mithila Kingdom in the Oiniwar Dynasty during the 15th-century. She ascended the throne of the Mithila Kingdom after the death of the ' ...
- woman ruler of Oiniwar Dynasty in Mithila and scholar of Sanskrit literature
*Bhanudatta Misra
Bhanudatta Misra was a Sanskrit poet from the Mithila (region), Mithila region of India who has been dated to some time in the late 15th and early 16th century.
Bhanudatta's works started to gain popularity, particularly in the early modern perio ...
, 15th/16th-century Sanskrit
Sanskrit (; stem form ; nominal singular , ,) is a classical language belonging to the Indo-Aryan languages, Indo-Aryan branch of the Indo-European languages. It arose in northwest South Asia after its predecessor languages had Trans-cultural ...
poet from Mithila
*Harisimhadeva
Harisimhadeva (also called Hari Singh Deva) was a King of the Karnat dynasty who ruled the Mithila (region), Mithila region of modern-day parts of North Bihar in India and South Nepal.
He reigned from 1304 to 1325. He was the last king of the Karn ...
, King of Mithila during the Karnat dynasty
The Karnats of Mithila or Karnata dynasty () was a dynasty established in 1097 CE by Nanyadeva. The dynasty controlled the areas we today know as Tirhut or Mithila in India and adjoining parts of South Eastern Nepal. The main power centre of the K ...
from 1304 - 1324 CE
*Gangadeva
Gangadeva (also known as Gangeyadeva) was the second ruler of the Karnat dynasty of Mithila. He succeeded his father Nanyadeva as king in 1147 and ruled until 1187.
Rule
There is controversy surrounding the succession of the throne of Mithila ...
, King of Mithila during the Karnat dynasty
The Karnats of Mithila or Karnata dynasty () was a dynasty established in 1097 CE by Nanyadeva. The dynasty controlled the areas we today know as Tirhut or Mithila in India and adjoining parts of South Eastern Nepal. The main power centre of the K ...
from 1147-1187 CE
*Narsimhadeva
Narasimhadeva was the third King of the Karnat dynasty of Mithila. Most scholars agree that he came into power around 1174 CE and succeeded his predecessor, Gangadeva.
Rule
The Maithili poet, Vidyapati, referred to Narasimhadeva as "Satyavira" ...
, King of Mithila during the Karnat dynasty
The Karnats of Mithila or Karnata dynasty () was a dynasty established in 1097 CE by Nanyadeva. The dynasty controlled the areas we today know as Tirhut or Mithila in India and adjoining parts of South Eastern Nepal. The main power centre of the K ...
from 1174-1227 CE
*Ramasimhadeva
Ramasimhadeva was the fourth King of the Karnat dynasty of Mithila. He came into power around 1227 CE and succeeded his father, Narasimhadeva.
Rule
Ramasimhadeva has been described as a "pious devotee and was a firm patron of sacred literature" ...
, King of Mithila during the Karnat dynasty
The Karnats of Mithila or Karnata dynasty () was a dynasty established in 1097 CE by Nanyadeva. The dynasty controlled the areas we today know as Tirhut or Mithila in India and adjoining parts of South Eastern Nepal. The main power centre of the K ...
from 1227-1285 CE
*Jyotirishwar Thakur
Jyotirishwar Thakur or (1260–1340) was a Maithili poet, playwright, musician and an early Maithili and Sanskrit writer, known for the '' Varṇa Ratnākara'', his encyclopedic work in Maithili.
Life
Jyotirishwar was son of Rāmeśvara and ...
, 14th-century poet
A poet is a person who studies and creates poetry. Poets may describe themselves as such or be described as such by others. A poet may simply be the creator (thought, thinker, songwriter, writer, or author) who creates (composes) poems (oral t ...
, playwright
A playwright or dramatist is a person who writes play (theatre), plays, which are a form of drama that primarily consists of dialogue between Character (arts), characters and is intended for Theatre, theatrical performance rather than just
Readin ...
and musician
A musician is someone who Composer, composes, Conducting, conducts, or Performing arts#Performers, performs music. According to the United States Employment Service, "musician" is a general Terminology, term used to designate a person who fol ...
who composed the earliest prose work in the Maithili language
Maithili ( , ) is an Indo-Aryan language spoken in parts of India and Nepal. It is native to the Mithila region, which encompasses parts of the eastern Indian states of Bihar and Jharkhand as well as Nepal's Koshi Province, Koshi and Madhesh P ...
, the Varna Ratnakara
The ''Varna Ratnakara'', , (IAST: Varṇa Ratnākara), literally "Ocean of description", is the oldest prose work of Maithili language, written in 1324 CE by the Maithil scholar, priest and poet Jyotirishwar Thakur. The author was a part of the ...
*Caṇḍeśvara Ṭhakkura
Caṇḍeśvara Thakkura was a Maithili-language political theorist and general during the 14th century. He served as minister for peace and war and chief judge in the court of Harisimhadeva who was the last King of the Karnat dynasty of Mithila ...
, political theorist and general from the 14th century
*Gaṅgeśa
Gaṅgeśa ( ''/ Gaṅgeśa'' ) (first half of the 14th century) was an Indian philosopher, logician and mathematician from the kingdom of Mithila. He established the Navya-Nyāya ("New Logic") school. His '' Tattvachintāmaṇi'' (The Jewel ...
, 13th/14th century philosopher
Philosophy ('love of wisdom' in Ancient Greek) is a systematic study of general and fundamental questions concerning topics like existence, reason, knowledge, Value (ethics and social sciences), value, mind, and language. It is a rational an ...
, logic
Logic is the study of correct reasoning. It includes both formal and informal logic. Formal logic is the study of deductively valid inferences or logical truths. It examines how conclusions follow from premises based on the structure o ...
ian and mathematician
A mathematician is someone who uses an extensive knowledge of mathematics in their work, typically to solve mathematical problems. Mathematicians are concerned with numbers, data, quantity, mathematical structure, structure, space, Mathematica ...
and author of Tattavachintamani
*Pakshadhara Mishra
Pakshadhara Mishra (also known by the alias Jayadeva) was a 15th-century Indian philosopher from the Mithila region and the founder of the Nyaya Shastra sampradaya in the tradition of Gaṅgeśa. He was a practitioner of the Nyaya Shashtra during ...
, 15th-century philosopher
*Vāchaspati Misra
Vachaspati Mishra (IAST: Vācaspati Miśra), was a ninth or tenth century Indian Hindu philosopher of the Advaita Vedanta tradition, who wrote bhashya (commentaries) on key texts of almost every 9th-century school of Hindu philosophy. and h ...
, 9th/10th-century philosopher of the Advaita Vedanta tradition
*Lakshmeshwar Singh
Maharaja Sir Lakshmeshwar Singh, Maharaja of Darbhanga (25 September 1858 – 16 November 1898) was the Zamindar and principal landowner of Darbhanga in the Mithila region, presently in the state of Bihar, India. His philanthropic works, admin ...
, zamindar and principal landowner of Raj Darbhanga
The Darbhanga Raj, also known as Raj Darbhanga and the Khandwala dynasty, was a chieftaincy located within the Mughal province of Bihar which controlled territories, not all contiguous, that were part of the Mithila region, now divided betwee ...
, 1860–1898
*Rameshwar Singh
Rameshwar Singh Thakur (16 January 1860 – 3 July 1929) was the maharaja of Darbhanga in the Mithila region from 1898 to his death. He became maharaja on the death of his elder brother Lakshmeshwar Singh, who died without issue. He was appo ...
, zamindar and principal landowner of Raj Darbhanga
The Darbhanga Raj, also known as Raj Darbhanga and the Khandwala dynasty, was a chieftaincy located within the Mughal province of Bihar which controlled territories, not all contiguous, that were part of the Mithila region, now divided betwee ...
, 1898–1929
Modern
*Amitabh Singh
Amitabh Singh is an Indian Space Scientist. He was Project Manager for Chandrayaan-1 Mission and Deputy Project Director & Operations Director for Chandrayaan-2 & 3 Mission at Indian Space Research Organization. He handled the optical payloa ...
, Indian Space Scientist at ISRO
The Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO ) is India's national space agency, headquartered in Bengaluru, Karnataka. It serves as the principal research and development arm of the Department of Space (DoS), overseen by the Prime Minister o ...
* Y P Viyogi, Indian Nuclear Physicist and associated with ALICE Experiment
A Large Ion Collider Experiment (ALICE) is one of nine Particle detector, detector experiments at the Large Hadron Collider (LHC) at CERN. It is designed to study the conditions thought to have existed immediately after the Big Bang by measu ...
at CERN
The European Organization for Nuclear Research, known as CERN (; ; ), is an intergovernmental organization that operates the largest particle physics laboratory in the world. Established in 1954, it is based in Meyrin, western suburb of Gene ...
* Maghfoor Ahmad Ajazi
Maghfoor Ahmad Ajazi (3 March 1900 – 26 September 1966) was a political activist from Bihar, prominent in the Indian independence movement.
Early life
Ajazi was born on 3 March 1900 in village Dihuli, Block Sakra of District Muzaf ...
, Indian Freedom fighter
A freedom fighter is a person engaged in a struggle to achieve political freedom, particularly against an established government. The term is typically reserved for those who are actively involved in armed or otherwise violent rebellion.
Termi ...
, political activist, social worker, poet and writer, born in Muzaffarpur
Muzaffarpur () is a city located in Muzaffarpur district on the banks of Burhi Gandak River, Burhi Gandak river in the Tirhut division of the Indian state of Bihar. It serves as the headquarters of the Tirhut division, the Muzaffarpur distri ...
* H C Verma, Indian physicist
A physicist is a scientist who specializes in the field of physics, which encompasses the interactions of matter and energy at all length and time scales in the physical universe. Physicists generally are interested in the root or ultimate cau ...
and author of the popular book ''Concept of Physics''
* Ram Narayan Mishra
Ram Narayan Mishra was the Minister for Industry and Commerce in the BP Koirala cabinet of 1959. He took his office of the Ministry on 27 May 1959. He was also a democratic fighter of Nepal and a founder member of Nepali Congress. He was the fou ...
, The Plenipotentiary
A ''plenipotentiary'' (from the Latin ''plenus'' "full" and ''potens'' "powerful") is a diplomat who has full powers—authorization to sign a treaty or convention on behalf of a sovereign. When used as a noun more generally, the word can als ...
for Treaty of trade and transit between the Government of India and His Majesty's Government of Nepal in 1960, Nepalese political leader, democratic freedom fighter in Nepal, a founder member of Nepali Congress Party
The Nepali Congress ( ; abbr. NC), colloquially the Congress Party, or simply the Congress, is a social democratic political party in Nepal and the largest party in the country. The party has 870,106 members as of the party's 14th general con ...
.
* Bimalendra Nidhi
Bimalendra Nidhi (Maithili language, Maithili/Nepali language, Nepali/Devanagari: बिमलेन्द्र निधि ) is a Nepali politician who serves as a member of the House of Representatives (Nepal), House of Representatives and ...
, Member of Nepalese parliament, Vice president of ruling party Nepali Congress
The Nepali Congress ( ; Abbreviation, abbr. NC), colloquially the Congress Party, or simply the Congress, is a Social democracy, social democratic List of political parties in Nepal, political party in Nepal and the largest party in the country ...
and former Deputy Prime Minister of Nepal
The deputy prime minister of Nepal () is the deputy head of government of Nepal. The deputy prime minister is second in seniority in the Council of Ministers of Nepal. The deputy prime minister is the senior-most member of cabinet after prime min ...
.
*Ramdhari Singh 'Dinkar'
Ramdhari Singh (23 September 1908 – 24 April 1974), known by his pen name Dinkar, was an Indian Hindi language poet, essayist, freedom fighter, patriot and academic. He emerged as a poet of rebellion as a consequence of his nationalist ...
was an Indian
Indian or Indians may refer to:
Associated with India
* of or related to India
** Indian people
** Indian diaspora
** Languages of India
** Indian English, a dialect of the English language
** Indian cuisine
Associated with indigenous peoples o ...
Hindi
Modern Standard Hindi (, ), commonly referred to as Hindi, is the Standard language, standardised variety of the Hindustani language written in the Devanagari script. It is an official language of India, official language of the Government ...
poet, essayist, patriot and academic.
* Bindheshwari Prasad Mandal was an Indian parliamentarian and social reformer who served as the chairman of the Second Backward Classes Commission (popularly known as the Mandal Commission
The Mandal Commission or the Socially and Educationally Backward Classes Commission (SEBC), was established in India in 1979 by the Janata Party government under Prime Minister Morarji Desai with a mandate to "identify the socially or educatio ...
).
* C. K. Raut, formerly US-based computer scientist, author and political leader of Nepal.
* C. K. Lal, Nepalese journalist and writer from Mahottari District
Mahottari District (, ), a part of Madhesh Province, is one of the List of districts of Nepal, seventy-seven districts of Nepal. The district, with Jaleshwar as its district headquarters, covers an area of and had a population of 553,481 in 2001 ...
of Nepal.
* Phanishwar Nath 'Renu'
Phanishwar Nath Mandal 'Renu' (4 March 1921 – 11 April 1977) was one of the most successful and influential writers of modern Hindi literature in the post-Premchand era. He is the author of ''Maila Anchal'', which after Premchand's ''Godaan'' ...
, influential writer of modern Hindi
Modern Standard Hindi (, ), commonly referred to as Hindi, is the Standard language, standardised variety of the Hindustani language written in the Devanagari script. It is an official language of India, official language of the Government ...
literature in the post-Premchand
Dhanpat Rai Srivastava (31 July 1880 – 8 October 1936), better known as Munshi Premchand based on his pen name Premchand (), was an Indian writer famous for his modern Hindustani language, Hindustani literature.
Premchand was a pioneer ...
era.
* Gopal Jee Thakur
Gopal Jee Thakur (born 15 October 1969) is an Indian Politician from the Bharatiya Janata Party, and a Member of Parliament representing 14 - Darbhanga (Lok Sabha constituency) in India.
He is a Member of Standing Committee on Railways, Memb ...
, Indian Politician and Member of Parliament from Darbhanga Lok Sabha Constituency
Darbhanga Lok Sabha constituency is one of the 40 Lok Sabha (parliamentary) constituencies in Bihar state in eastern India. Currently Gopal Jee Thakur of Bhartiya Janta Party is the Member of Parliament from Darbhanga Loksabha. In 2024 Indian ...
.
* Syed Shahnawaz Hussain
Syed Shahnawaz Hussain is an Indian politician and a member of the Central Election Committee of Bharatiya Janata Party. He is one of the national spokespersons of Bharatiya Janata Party ( BJP). Hussain was the Minister of Textiles and the ...
, Indian politician, born in Supaul
Supaul is a town and municipality that is headquarters of Supaul district in the States and territories of India, Indian state of Bihar.
There are 11 blocks under the Supaul district: Supaul, Kishanpur, Saraigarh-Bhaptiyahi, Pipra, Triveniganj, ...
* Bhagwat Jha Azad
Bhagwat Jha Azad was an Indian freedom fighter and politician. He served as Chief Minister of Bihar from 14 February 1988 to 10 March 1989. He was at various times a member of parliament and a member of the Bihar state legislature.
Political c ...
was the Chief Minister of Bihar
Bihar ( ) is a states and union territories of India, state in Eastern India. It is the list of states and union territories of India by population, second largest state by population, the List of states and union territories of India by are ...
and a member of Lok Sabha
The Lok Sabha, also known as the House of the People, is the lower house of Parliament of India which is Bicameralism, bicameral, where the upper house is Rajya Sabha. Member of Parliament, Lok Sabha, Members of the Lok Sabha are elected by a ...
.
* Maithili Thakur
Maithili Thakur (born 25 July 2000) is an Indian playback singer trained in Indian classical music and folk music. She has sung original songs, covers, and traditional folk music prominently in Hindi, Bengali language, Bengali, Maithili music, M ...
, Indian singer
* Ram Baran Yadav
Ram Baran Yadav (; Nepali: डा. राम वरण यादव; born 4 February 1948) is a Nepali politician and physician who served as the first president of Nepal from 23 July 2008 to 29 October 2015, following the declaration of repub ...
, First president of Nepal
*Ramdev Mahato
Ramdev Mahato is an Indian politician and a former member of the Bihar Legislative Assembly from the Madhubani Assembly constituency. He had been elected from the Madhubani constituency to the Bihar Legislative Assembly four times between 2000 ...
, three time Member of Bihar Legislative Assembly from Madhubani Assembly constituency
Madhubani is an assembly constituency in Madhubani district in the Indian state of Bihar. In 2015 Bihar Legislative Assembly election, Madhubani will be one of the 36 seats to have VVPAT enabled electronic voting machines.
Overview
As per Del ...
of Mithila region.
* Sharda Sinha
Sharda Sinha (1 October 1952 – 5 November 2024) was an Indian folk and classical singer. Hailing from Bihar, she predominantly sang in Maithili and Bhojpuri language and is called ''Bihar Kokila'', the cuckoo of Bihar. Sinha has sung many f ...
, Indian folk singer
* Udit Narayan
Udit Narayan Jha (born 1 December 1955) is an Nepali and Indian playback singer whose songs have been featured mainly in Hindi cinema, Hindi films. He has also sung in various other languages including Telugu language, Telugu, Kannada, Tamil ...
, Bollywood playback singer
* Narendra Jha
Narendra Jha (21 January 1964 14 March 2018) was an Indian actor. He was known for his work in Bollywood productions; his most noted films being '' Haider'', '' Raees'', '' Ghayal Once Again'', ''Hamari Adhuri Kahani'', ''Mohenjodaro'', '' Sh ...
, Bollywood actor
* Sriti Jha
Sriti Jha (born 26 February 1986) is an Indian actress who primarily works in Hindi television. Jha earned wider recognition with her portrayal of Pragya Arora Mehra in '' Kumkum Bhagya''. She is a recipient of several accolades including two ...
, Indian television actress
* Kirti Azad
Kirtivardhan Bhagwat Jha Azad (; born 2 January 1959) is an Indian politician and former cricketer, who played seven Test matches and 25 One Day International for the India national cricket team between 1980 and 1986. Azad was a member of the ...
, former Indian cricketer and politician
* Sanjay Mishra, Bollywood actor
* Bhawana Kanth, one of the first female fighter pilots of India
* Vikas Kumar Jha
* George Orwell
Eric Arthur Blair (25 June 1903 – 21 January 1950) was an English novelist, poet, essayist, journalist, and critic who wrote under the pen name of George Orwell. His work is characterised by lucid prose, social criticism, opposition to a ...
, novelist and essayist, journalist and critic
* Rambriksh Benipuri
Ramavriksha Benipuri (, 23 December 1899 – 9 September 1968) was an independence activist, socialist leader, editor and Hindi writer. He was born in a small village named Benipur in Muzaffarpur district in a Bhumihar family in the Indian sta ...
, Indian freedom fighter, Socialist Leader
The ''Labour Leader'' was a British socialist newspaper published for almost one hundred years. It was later renamed ''New Leader'' and ''Socialist Leader'', before finally taking the name ''Labour Leader'' again.
19th century
The origins of th ...
, editor
Editing is the process of selecting and preparing written, visual, audible, or cinematic material used by a person or an entity to convey a message or information. The editing process can involve correction, condensation, organization, a ...
and Hindi
Modern Standard Hindi (, ), commonly referred to as Hindi, is the Standard language, standardised variety of the Hindustani language written in the Devanagari script. It is an official language of India, official language of the Government ...
writer
* Devaki Nandan Khatri
Devaki Nandan Khatri (18 June 1861– 1 August 1913) was an Indian writer who lived in Varanasi and wrote the historic fiction fantasy novel '' Chandrakanta''.
Biography
He was born on 18 June 1861 in a Punjabi family in Pusa village of Sa ...
, Indian writer
* Ganganath Jha
Mahamahopadhyaya Sir Gaṅgānāth Jhā (25 December 1872 – 9 November 1941) was a scholar of Sanskrit, Indian philosophy and Buddhist philosophy.
He is considered to have probably translated more Sanskrit philosophical texts than any o ...
, Indian scholar
* Ramjee Singh, former Member of Indian parliament and vice-chancellor of Jain Vishva Bharati University
* Acharya Ramlochan Saran
Acharya Ramlochan Saran (11 February 1889, Muzaffarpur–14 May 1971, Darbhanga) was a Hindi littérateur, grammarian and publisher. He founded Pustak Bhandar, a publishing enterprise, in Laheriasarai in 1915 and moved his publishing office ...
, Hindi literature, grammarian and publisher
* Ramesh Chandra Jha
Ramesh Chandra Jha(8 May 1928 – 7 April 1994) was an Indian poet, novelist and freedom fighter. Son of a senior Gandhian and freedom fighter Lakshmi Narayan Jha, who also contributed in Indian Freedom Struggle from Bihar. His maternal grand ...
, Indian poet, novelist and freedom fighter
* Acharya Rameshwar Jha
Acharya Rameshwar Jha (20th century) was an Indian traditional Sanskrit scholar and considered an authority on Nyaya, Vyakarana and Vedanta. He later became an exponent of non dualistic shaivisim and is often credited with establishing and prop ...
, scholar
* Phanishwar Nath 'Renu'
Phanishwar Nath Mandal 'Renu' (4 March 1921 – 11 April 1977) was one of the most successful and influential writers of modern Hindi literature in the post-Premchand era. He is the author of ''Maila Anchal'', which after Premchand's ''Godaan'' ...
, Indian author
* Ravindra Prabhat
Ravindra Prabhat (born 5 April 1969) is a Hindi-language novelist, journalist, poet, and short story writer from India.
Early life and education
Prabhat was born on 5 April 1969 in the village of Mahindwara, Sitamarhi, in Bihar, India. He was r ...
a Hindi novelist, journalist, poet, and short story writer
* Gajendra Thakur
Gajendra Thakur (born 1971) is an Indian author. He writes in the Maithili language, a language spoken in Northern Bihar (of India) and South-Eastern Nepal. He is an author, lexicographer, historian (of Mithila- ancient Videha and of ''Maithili ...
, Literary critic, historian, novelist, dramatist, poet, and a lexicographer
* Anerood Jugnauth
Sir Anerood Jugnauth, GCSK, (29 March 1930 – 3 June 2021) was a Mauritian statesman, politician and barrister who served both as President and Prime Minister of Mauritius. He was Member of Parliament for Piton & Riviere Du Rempart. The c ...
, former President of Mauritius
Mauritius, officially the Republic of Mauritius, is an island country in the Indian Ocean, about off the southeastern coast of East Africa, east of Madagascar. It includes the main island (also called Mauritius), as well as Rodrigues, Ag ...
* Parmanand Jha
Parmanand Jha (; born 1946) is a Nepali politician who served as the first vice president of Nepal from 23 July 2008 to 31 October 2015 following his term as a Supreme Court judge.
Jha was born to Nepali parents and brought Bihar in Darbhang ...
, first vice-president of Nepal
Nepal, officially the Federal Democratic Republic of Nepal, is a landlocked country in South Asia. It is mainly situated in the Himalayas, but also includes parts of the Indo-Gangetic Plain. It borders the Tibet Autonomous Region of China Ch ...
* Dhirendra Premarshi, presenter oHello Mithila
on
Radio Kantipur
Radio Kantipur () or Kantipur FM () is a Nepalese FM radio station, established in October 1998. It currently operates in the eastern, central, western, mid-western and far-western development regions. It is most popular in eastern region and i ...
* Godawari Dutta, madhubani artist, social activist
* Tarkishore Prasad
Tarkishore Prasad (born 5 February 1956) is an Indian politician belonging to the Bharatiya Janata Party who served as the 5th Deputy Chief Minister of Bihar from 16 November to 9 August 2022.He held the portfolios of Finance & Commercial Taxes a ...
, Deputy Chief Minister of Bihar
The deputy chief minister of Bihar is the seniormost cabinet member of the state government who serves as the de facto second head of the state. He is the second highest ranking executive authority of the state's council of ministers. The curr ...
, born in Saharsa district
Saharsa is one of the thirty-eight districts of Bihar, India. Saharsa city is the administrative headquarters of this district. Saharsa district is a part of the Kosi Division and it became a district on 1 April 1954 and has subsequently become ...
* Ramnath Goenka
Ramnath Goenka (22 April 1904 – 5 October 1991) was an Indian newspaper publisher. He bought the majority stake of ''The Indian Express'' in 1930s. He created the Indian Express Group with various English and regional language publications.'' ...
, Indian journalist, born in Darbhanga
Darbhanga is the fifth largest city and municipal corporation in the state of Bihar in India, and is considered an important city in North Bihar. It serves as the headquarters of the Darbhanga district and the Darbhanga division. Darbhanga ...
* Ashish Jha
Ashish Kumar Jha (born December 31, 1970) is an Indian-American general internist physician and academic who served as the White House COVID-19 response coordinator from 2022–2023. He has been Dean of the Brown University School of Public Hea ...
, general internist physician and academic serving the White House Coronavirus Response Coordinator
* Vartika Jha
Vartika Jha (born 8 April 2000) is an Indian choreographer, dancer, and actress. She was a contestant and runner-up in Star Plus's dance reality show '' Dance Plus (season 4)'' in 2018. She has since established herself as one of India's most po ...
(born 2000), Indian dancer, choreographer and actress
* Lalit Narayan Mishra
Lalit Narayan Mishra (2 February 1923 – 3 January 1975) was an Indian politician who served as Minister of Railways in the government of India from 1973 to 1975. His political career started when he was made parliamentary secretary to the ...
, Leader of Congress
A congress is a formal meeting of the representatives of different countries, constituent states, organizations, trade unions, political parties, or other groups. The term originated in Late Middle English to denote an encounter (meeting of ...
* Jagannath Mishra
Jagannath Mishra (24 June 1937 – 19 August 2019) was an Indian politician who served as Chief Minister of Bihar and as Union Council of Ministers, Minister in the Union Cabinet. He was also Member of Parliament, Rajya Sabha between 1988 - 1990 ...
, Leader of Congress
A congress is a formal meeting of the representatives of different countries, constituent states, organizations, trade unions, political parties, or other groups. The term originated in Late Middle English to denote an encounter (meeting of ...
* Pushpam Priya Choudhary
The Plurals Party (often known by the abbreviated name Plurals, TPP, दप्पा) is an Indian political party founded in the state of Bihar by Pushpam Priya Choudhary, alumna of the London School of Economics and Institute of Development St ...
, Founder of The Plurals Party
* Nitish Mishra
Nitish Mishra (born 9 July 1973) is an Indian politician hailing from eastern Indian state of Bihar, India. He represented Jhanjharpur assembly constituency in Madhubani district in 13th, 14th and 15th Bihar Legislative Assembly. Presently, h ...
, Leader of BJP
The Bharatiya Janata Party (BJP; , ) is a political party in India and one of the two major Indian political parties alongside the Indian National Congress. BJP emerged out from Syama Prasad Mukherjee's Bharatiya Jana Sangh. Since 2014, ...
* Sanjay Kumar Jha
Sanjay Kumar Jha (commonly known as Sanjay Jha; born 1 December 1967) is an Politics of India, Indian politician from Janata Dal (United). He currently serves as a Member of Parliament, Rajya Sabha, Member of Parliament in the Rajya Sabha, rep ...
, Leader of JD(U)
Janata Dal (United) ("People's Party (United)"), abbreviated as JD(U), is a social-democratic and secular Indian political party, rooted mainly in eastern and north-eastern India, whose stated goals are promoting social justice and lifting ...
* Vaibhav Suryavanshi
Vaibhav Sooryavanshi (born 27 March 2011) is an Indian cricketer who plays for Bihar in domestic cricket and Rajasthan Royals in the Indian Premier League. As a left-handed batsman, he made his first-class debut in January 2024. He is the young ...
, Indian Cricket Player
See also
*Mithila (proposed Indian state)
Mithila is a proposed state in India, comprising the Maithili speaking region of Bihar and Jharkhand. The Maithili language has own traditional script, known as Mithilakshar. It is part of the historical Mithila region.
The proposed state wi ...
*Mithila Painting
Madhubani art (also known as Mithila art) is a style of painting practiced in the Mithila region of India and Nepal. It is named after the Madhubani district of Bihar, India, which is where it originated. Jitwarpur, Ranti and Rasidpur are the ...
*Mithila Makhana
Mithila Makhana (botanical name: ''Euryale ferox'') is a special variety of aquatic fox nut cultivated in Mithila (region), Mithila region of Bihar state in India and in Nepal.
In Mithila, Makhana is also termed as Makhan. It is one of the th ...
*Mithilā (ancient city)
Mithila was the capital city of the Kingdom of the Videhas. The location of Mithila is disputed among Janakpur in present-day Nepal, Baliraajgadh in present-day Madhubani district, Bihar, India, Sitamarhi in present-day Bihar, India, and Mukhiya ...
*Jhijhiya
Jhijhiya (also called Jhijhari) is a cultural folk dance of Mithila (region), Mithila region of India and Nepal. It is performed during the Vijayadashami, Dusshera festival, in the Hindu month of Ashvin (month), Ashwin (September/October). The da ...
* Mithila Student Union
* Maithili duck
*King Mithi
Mithi ( Sanskrit: मिथि ) was the king of Videha Kingdom in the ancient Indian Subcontinent. He was the son of the King Nimi. He was the first King Janaka in the Janaka Dynasty of Mithila. Mention
According to ''Vishnu'' ''Purana'' an ...
*Gosaunik Ghar
Gosaunik Ghar (Maithili language, Maithili: गोसाउनिक घर) is special worship room of the Kuladevata, Kuldevata or ''Kuldevi'' also called as ''Gosaun'' or ''Gosauni'' in the houses of Maithils, Maithil people in the Mithila (reg ...
* Industrial ruins in Mithila region
*Maithili Cinema
Maithili cinema is the film industry of the Maithili language mainly active in the Mithila (region), Mithila region of Bihar and Nepal. It is a small scale film industry based in the Mithila region. In recent years the Maithili film industry is gr ...
*Tourism in Mithila
The region of Mithila in the Indian subcontinent is believed to be the ancient inhabitat place of the Videha, Videha Kingdom in the text Ramayana. The Mithila (region), Mithila region is widely known for its rich culture, tradition and historical h ...
*Rajarshi Janak Mandir
Rajarshi Janak Mandir (Maithili language, Maithili: राजर्षी जनक मंदिर) is a Hindu temple in the city of Janakpur in the Mithila (region), Mithila region of Nepal. It is dedicated to the Vedic Janaka, King Janaka of ...
*Maharani Sthan
Maharani Sthan ( Maithili: महारानी स्थान) also called as Bhagawati Sthan is a common Hindu temple dedicated to Goddess '' Bhagawati'' in the villages of the Mithila region in the Indian subcontinent. The Goddess Bhagawati i ...
*Gautam Kund
Gautam Kund ( Maithili: गौतम कुण्ड ) is a legendary lake in the Mithila region attributed to the Vedic sage Maharshi Gautama. It is located at ''Brahmpur West Panchayat'' of the ''Jale block'' in the Darbhanga district of Bihar ...
Notes
References
Bibliography
* *External links
The Maithil Brahmans - an online ethnography
{{Authority control . Regions of Bihar Regions of Nepal Historical Indian regions Cultural regions
.01
Crossbreed is an American industrial metal band from Clearwater, Florida, formed in 1996. They were signed with Artemis Records before being dropped from the label in 2003. The band released two EPs and three full-length albums before disbandi ...
.01
Crossbreed is an American industrial metal band from Clearwater, Florida, formed in 1996. They were signed with Artemis Records before being dropped from the label in 2003. The band released two EPs and three full-length albums before disbandi ...
.01
Crossbreed is an American industrial metal band from Clearwater, Florida, formed in 1996. They were signed with Artemis Records before being dropped from the label in 2003. The band released two EPs and three full-length albums before disbandi ...