thyroid scan on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Thyroid nodules are
 A thyroid scan using a radioactive iodine uptake test can be used in viewing the thyroid. A scan using
A thyroid scan using a radioactive iodine uptake test can be used in viewing the thyroid. A scan using
/ref> CT scans often incidentally find thyroid abnormalities, and thereby practically becomes the first investigation modality.
nodules
Nodule may refer to:
*Nodule (geology), a small rock or mineral cluster
*Manganese nodule, a metallic concretion found on the seafloor
*Nodule (medicine), a small aggregation of cells
*Root nodule
Root nodules are found on the roots of plants, p ...
(raised areas of tissue or fluid) which commonly arise within an otherwise normal thyroid gland
The thyroid, or thyroid gland, is an endocrine gland in vertebrates. In humans, it is a butterfly-shaped gland located in the neck below the Adam's apple. It consists of two connected lobes. The lower two thirds of the lobes are connected by ...
. They may be hyperplastic or tumorous, but only a small percentage of thyroid tumors are malignant
Malignancy () is the tendency of a medical condition to become progressively worse; the term is most familiar as a characterization of cancer.
A ''malignant'' tumor contrasts with a non-cancerous benign tumor, ''benign'' tumor in that a malig ...
. Small, asymptomatic
Asymptomatic (or clinically silent) is an adjective categorising the medical conditions (i.e., injuries or diseases) that patients carry but without experiencing their symptoms, despite an explicit diagnosis (e.g., a positive medical test).
P ...
nodules are common, and often go unnoticed. Nodules that grow larger or produce symptom
Signs and symptoms are diagnostic indications of an illness, injury, or condition.
Signs are objective and externally observable; symptoms are a person's reported subjective experiences.
A sign for example may be a higher or lower temperature ...
s may eventually need medical care. A goitre
A goitre (British English), or goiter (American English), is a swelling in the neck resulting from an enlarged thyroid gland. A goitre can be associated with a thyroid that is not functioning properly.
Worldwide, over 90% of goitre cases are ...
may have one nodule – uninodular, multiple nodules – multinodular, or be diffuse
Diffusion is the net movement of anything (for example, atoms, ions, molecules, energy) generally from a region of higher concentration to a region of lower concentration. Diffusion is driven by a gradient in Gibbs free energy or chemical p ...
.
Signs and symptoms
Often these abnormal growths of thyroid tissue are located at the edge of the thyroid gland and can befelt
Felt is a textile that is produced by matting, condensing, and pressing fibers together. Felt can be made of natural fibers such as wool or animal fur, or from synthetic fibers such as petroleum-based acrylic fiber, acrylic or acrylonitrile or ...
as a lump in the throat. When they are large, they can sometimes be seen as a lump in the front of the neck.
Sometimes a thyroid nodule presents as a fluid-filled cavity called a thyroid cyst. Often, solid components are mixed with the fluid. Thyroid cysts most commonly result from degenerating thyroid adenoma
A thyroid adenoma is a benign tumor of the thyroid gland, that may be inactive or active (functioning autonomously) as a toxic adenoma.
Signs and symptoms
A thyroid adenoma may be clinically silent ("cold" adenoma), or it may be a functional tumo ...
s, which are benign, but they occasionally contain malignant solid components.
Diagnosis
After anodule
Nodule may refer to:
* Nodule (geology), a small rock or mineral cluster
* Manganese nodule, a metallic concretion found on the seafloor
*Nodule (medicine), a small aggregation of cells
*Root nodule
Root nodules are found on the roots of plants, ...
is found during a physical examination, a referral to an endocrinologist
Endocrinology (from ''endocrine'' + '' -ology'') is a branch of biology and medicine dealing with the endocrine system, its diseases, and its specific secretions known as hormones. It is also concerned with the integration of developmental events ...
, a thyroidologist or otolaryngologist
Otorhinolaryngology ( , abbreviated ORL and also known as otolaryngology, otolaryngology–head and neck surgery (ORL–H&N or OHNS), or ear, nose, and throat (ENT)) is a surgical subspecialty within medicine that deals with the surgical an ...
may occur. Most commonly an ultrasound
Ultrasound is sound with frequency, frequencies greater than 20 Hertz, kilohertz. This frequency is the approximate upper audible hearing range, limit of human hearing in healthy young adults. The physical principles of acoustic waves apply ...
is performed to confirm the presence of a nodule, and assess the status of the whole gland. Measurement of thyroid stimulating hormone
The thyroid, or thyroid gland, is an endocrine gland in vertebrates. In humans, it is a butterfly-shaped gland located in the neck below the Adam's apple. It consists of two connected lobes. The lower two thirds of the lobes are connected by ...
and anti-thyroid antibodies will help decide if there is a functional thyroid disease such as Hashimoto's thyroiditis
Hashimoto's thyroiditis, also known as chronic lymphocytic thyroiditis, Hashimoto's disease and autoimmune thyroiditis, is an autoimmune disease in which the thyroid gland is gradually destroyed.
Early on, symptoms may not be noticed. Over ti ...
present, a known cause of a benign nodular goitre
A goitre (British English), or goiter (American English), is a swelling in the neck resulting from an enlarged thyroid gland. A goitre can be associated with a thyroid that is not functioning properly.
Worldwide, over 90% of goitre cases are ...
. Fine needle biopsy for cytopathology
Cytopathology (from Greek , ''kytos'', "a hollow"; , ''pathos'', "fate, harm"; and , ''-logia'') is a branch of pathology that studies and diagnoses diseases on the cellular level. The discipline was founded by George Nicolas Papanicolaou in ...
is also used.
Thyroid nodules are extremely common in young adults and children. Almost 50% of people have had one, but they are usually only detected by a physician during the course of a health examination or fortuitously discovered during the investigation of an unrelated condition.
Workup of incidental nodules
The American College of Radiology recommends the following workup for thyroid nodules as incidental imaging findings on CT,MRI
Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) is a medical imaging technique used in radiology to generate pictures of the anatomy and the physiological processes inside the body. MRI scanners use strong magnetic fields, magnetic field gradients, and rad ...
or PET-CT:
Ultrasound
Ultrasound
Ultrasound is sound with frequency, frequencies greater than 20 Hertz, kilohertz. This frequency is the approximate upper audible hearing range, limit of human hearing in healthy young adults. The physical principles of acoustic waves apply ...
imaging is useful as the first-line, non-invasive investigation in determining the size, texture, position, and vascularity of a nodule, accessing lymph nodes metastasis in the neck, and for guiding fine needle aspiration cytology (FNAC) or biopsy. Ultrasonographic findings will also guide the indication to biopsy and the long term follow-up. High frequency transducer (7–12 MHz) is used to scan the thyroid nodule, while taking cross-sectional and longitudinal sections during scan. Suspicious findings in a nodule are hypoechoic, ill-defined margins, absence of peripheral halo
HALO, halo, halos or haloes may refer to:
Most common meanings
* Halo (optical phenomenon)
* Halo (religious iconography), a ring of light around the image of a head
* ''Halo'' (franchise), a sci-fi video game series (2001–2021)
Arts and en ...
or irregular margin, fine, punctate microcalcification
Microcalcifications are tiny Calculus (medicine), deposits of calcium salts that are too small to be felt but can be detected by medical imaging, imaging.
They can be scattered throughout the mammary gland, or occur in clusters.
Microcalcificat ...
s, presence of solid nodule, high levels of irregular blood flow within the nodule or "taller-than-wide sign" (anterior-posterior diameter is greater than transverse diameter of a nodule). Features of benign lesion are: hyperechoic, having coarse, dysmorphic or curvilinear calcifications, comet tail artifact (reflection of a highly calcified object), absence of blood flow in the nodule, and presence of cystic (fluid-filled) nodule. However, the presence of solitary or multiple nodules is not a good predictor of malignancy. Malignancy is only diagnosed when ultrasound findings and FNAC report are suggestive of malignancy.
The TI-RADS (Thyroid Imaging Reporting and Data Systems) are sonographic classification systems which describe the suspicious findings of thyroid nodules. It was first proposed by Horvath et al., based on the BI-RADS (Breast Imaging Reporting and Data System) concept. Several systems were subsequently proposed and adopted by international scientific societies.
Their main aims are to characterize the risk of malignancy of nodules to better select nodules to submit to fine-needle aspiration cytology.
TI-RADS developed by the American College of Radiology
The American College of Radiology (ACR), founded in 1923, is a professional medical society representing nearly 40,000 diagnostic radiologists, radiation oncologists, interventional radiologists, nuclear medicine physicians and medical physicists ...
(ACR) guides clinicians in deciding which nodules require FNAC and in planning follow-up. Various online tools have been developed to assist in applying these criteria to clinical practice.
Another imaging modality, which is ultrasound elastography, is also useful in diagnosing thyroid malignancy especially for follicular thyroid cancer
Follicular thyroid cancer accounts for 15% of thyroid cancer and occurs more commonly in women over 50 years of age. Thyroglobulin (Tg) can be used as a tumor marker for well-differentiated follicular thyroid cancer. Thyroid follicular cells are ...
. However, it is limited by the presence of adequate amount of normal tissue around the lesion, calcified shell around a nodule, cystic nodules, coalescent
''Coalescent'' is a science-fiction novel by Stephen Baxter. It is part one of the '' Destiny's Children'' series. The story is set in two main time periods: modern Britain, when George Poole finds that he has a previously unknown sister and ...
nodules.
Fine needle biopsy
Fine Needle Aspiration Cytology (FNAC) is a cheap, simple, and safe method in obtaining cytological specimens for diagnosis by using a needle and a syringe. The indications to do FNAC are: nodules more than 1 cm with two ultrasound criteria suggestive of malignancy, nodules of any size with extracapsular extension or lymph nodes enlargement with unknown source, any sizes of nodules with history of head and neck radiation, family history of thyroid carcinoma in two or more first degree relatives, multiple endocrine neoplasia type II, and increased calcitonin levels. However, increased calcitonin levels can also be attributable to smoking, chronic alcohol consumption, usage of proton pump inhibitors, and renal failure. The ''Bethesda System for Reporting Thyroid Cytopathology'' is the system used to report whether the thyroid cytological specimen is benign or malignant. It can be divided into six categories:Blood tests
Blood test
A blood test is a medical laboratory, laboratory analysis performed on a blood sample that is usually extracted from a vein in the arm using a hypodermic needle, or via fingerprick. Multiple tests for specific blood components, such as a glucose ...
s may be done prior to or in lieu of a biopsy. The possibility of a nodule which secretes thyroid hormone (which is less likely to be cancer) or hypothyroidism is investigated by measuring thyroid stimulating hormone
The thyroid, or thyroid gland, is an endocrine gland in vertebrates. In humans, it is a butterfly-shaped gland located in the neck below the Adam's apple. It consists of two connected lobes. The lower two thirds of the lobes are connected by ...
(TSH), and the thyroid hormones thyroxine
Thyroxine, also known as T4, is a hormone produced by the thyroid gland. It is the primary form of thyroid hormone found in the blood and acts as a prohormone of the more active thyroid hormone, triiodothyronine (T3). Thyroxine and its acti ...
(T4) and triiodothyronine
Triiodothyronine, also known as T3, is a thyroid hormone. It affects almost every physiological process in the body, including growth and development, metabolism, body temperature, and heart rate.
Production of T3 and its prohormone thyroxi ...
(T3). Tests for serum thyroid autoantibodies
An autoantibody is an antibody (a type of protein) produced by the immune system that is directed against one or more of the individual's own proteins. Many autoimmune diseases (notably lupus erythematosus) are associated with such antibodies.
Pr ...
are sometimes done as these may indicate autoimmune
In immunology, autoimmunity is the system of immune responses of an organism against its own healthy cells, tissues and other normal body constituents. Any disease resulting from this type of immune response is termed an " autoimmune disease" ...
thyroid disease (which can mimic nodular disease).
Other imaging
 A thyroid scan using a radioactive iodine uptake test can be used in viewing the thyroid. A scan using
A thyroid scan using a radioactive iodine uptake test can be used in viewing the thyroid. A scan using iodine-123
Iodine-123 (123I) is a radioactive isotope of iodine used in nuclear medicine imaging, including single-photon emission computed tomography (SPECT) or SPECT/CT exams. The isotope's half-life is 13.2232 hours; the decay by electron capture to t ...
showing a hot nodule, accompanied by a lower than normal TSH, is strong evidence that the nodule is not cancerous, as most hot nodules are benign.
Computed tomography of the thyroid plays an important role in the evaluation of thyroid cancer.Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License/ref> CT scans often incidentally find thyroid abnormalities, and thereby practically becomes the first investigation modality.
Malignancy
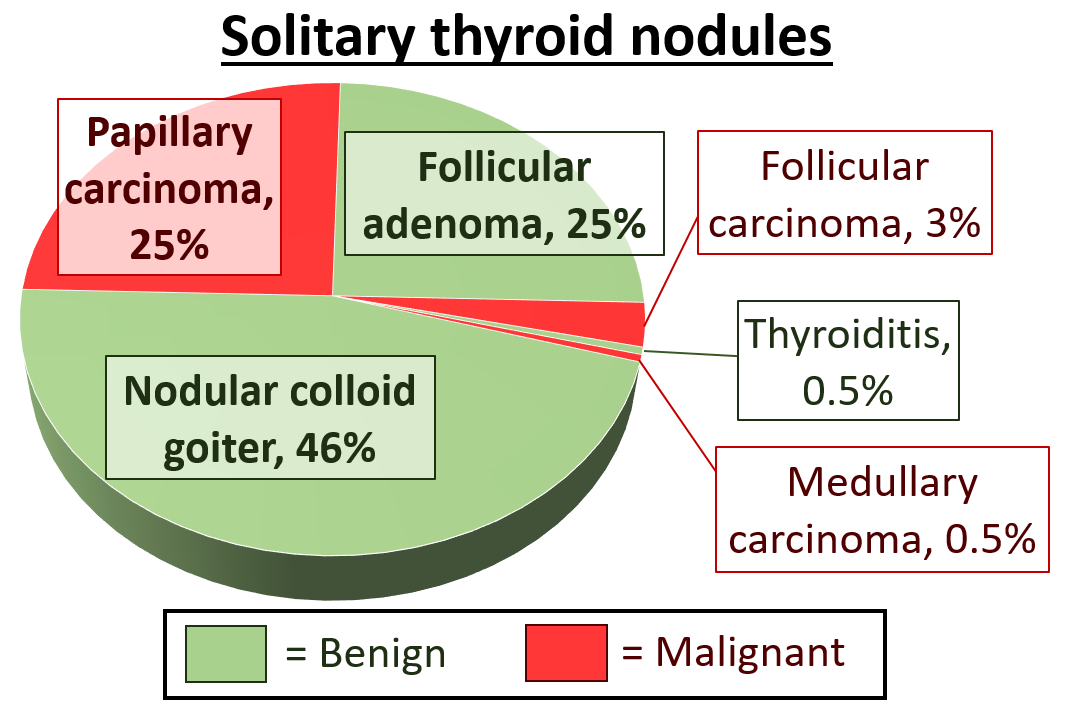
Only a small percentage of lumps in the neck are malignant (around 4 – 6.5%), and most thyroid nodules are benign colloid nodules. There are many factors to consider when diagnosing a malignant lump. Trouble swallowing or speaking, swollen cervical lymph nodes or a firm, immobile nodule are more indicative of malignancy, whereas a family history of autoimmune disease or goiter, thyroid hormonal dysfunction or a soft, painful nodule are more indicative of benignancy. The prevalence of cancer is higher in males, patients under 20 years old or over 70 years old, and patients with a history of head and neck irradiation or a family history of thyroid cancer.Solitary thyroid nodule

Risks for cancer
Solitarythyroid
The thyroid, or thyroid gland, is an endocrine gland in vertebrates. In humans, it is a butterfly-shaped gland located in the neck below the Adam's apple. It consists of two connected lobes. The lower two thirds of the lobes are connected by ...
nodules are more common in females yet more worrisome in males. Other associations with neoplastic nodules are family history of thyroid cancer
Thyroid cancer is cancer that develops from the tissues of the thyroid gland. It is a disease in which cells grow abnormally and have the potential to spread to other parts of the body. Symptoms can include swelling or a lump in the neck, ...
and prior radiation
In physics, radiation is the emission or transmission of energy in the form of waves or particles through space or a material medium. This includes:
* ''electromagnetic radiation'' consisting of photons, such as radio waves, microwaves, infr ...
to the head and neck.
Solitary thyroid nodules are mostly benign colloid nodules. The second most common type is follicular adenoma.
Radiation exposure to the head and neck may be for historic indications such as tonsillar and adenoid hypertrophy
Adenoid hypertrophy, also known as enlarged adenoids refers to an enlargement of the adenoid (pharyngeal tonsil) that is linked to nasopharyngeal mechanical blockage and/or chronic inflammation. Adenoid hypertrophy is a characterized by hearing ...
, "enlarged thymus", acne vulgaris
Acne ( ), also known as ''acne vulgaris'', is a long-term Cutaneous condition, skin condition that occurs when Keratinocyte, dead skin cells and Sebum, oil from the skin clog hair follicles. Typical features of the condition include comedo, ...
, or existent indications such as Hodgkin's lymphoma
Hodgkin lymphoma (HL) is a type of lymphoma in which cancer originates from a specific type of white blood cell called lymphocytes, where multinucleated Reed–Sternberg cells (RS cells) are present in the lymph nodes. The condition was named a ...
. Children living near the Chernobyl
Chernobyl, officially called Chornobyl, is a partially abandoned city in Vyshhorod Raion, Kyiv Oblast, Ukraine. It is located within the Chernobyl Exclusion Zone, to the north of Kyiv and to the southwest of Gomel in neighbouring Belarus. ...
nuclear power plant during the catastrophe of 1986 experienced a 60-fold increase in the incidence of thyroid cancer. Thyroid cancer arising in the background of radiation is often multifocal with a high incidence of lymph node metastasis and has a poor prognosis.
Signs and symptoms
Worrisome sign and symptoms include voice hoarseness, rapid increase in size, compressive symptoms (such asdyspnoea
Shortness of breath (SOB), known as dyspnea (in AmE) or dyspnoea (in BrE), is an uncomfortable feeling of not being able to breathe well enough. The American Thoracic Society defines it as "a subjective experience of breathing discomfort that c ...
or dysphagia
Dysphagia is difficulty in swallowing. Although classified under " symptoms and signs" in ICD-10, in some contexts it is classified as a condition in its own right.
It may be a sensation that suggests difficulty in the passage of solids or l ...
) and appearance of lymphadenopathy
Lymphadenopathy or adenopathy is a disease of the lymph nodes, in which they are abnormal in size or consistency. Lymphadenopathy of an inflammatory type (the most common type) is lymphadenitis, producing swollen or enlarged lymph nodes. In c ...
.
Investigations
* TSH – A thyroid-stimulating hormone level should be obtained first. If it is suppressed, then the nodule is likely a hyperfunctioning (or "hot") nodule. These are rarely malignant. * FNAC – fine needle aspiration cytology is the investigation of choice given a non-suppressed TSH. * Imaging –Ultrasound
Ultrasound is sound with frequency, frequencies greater than 20 Hertz, kilohertz. This frequency is the approximate upper audible hearing range, limit of human hearing in healthy young adults. The physical principles of acoustic waves apply ...
and radioiodine
There are 40 known isotopes of iodine (53I) from 108I to 147I; all undergo radioactive decay except 127I, which is stable. Iodine is thus a monoisotopic element.
Its longest-lived radioactive isotope, 129I, has a half-life of 16.14 million ye ...
scanning.
Thyroid scan
85% of nodules are cold nodules, and 5–8% of cold and warm nodules are malignant. 5% of nodules are hot. Malignancy is virtually non-existent in hot nodules.Surgery
Surgery (thyroidectomy
A thyroidectomy is an operation that involves the surgery, surgical removal of all or part of the thyroid gland. In general surgery, endocrine or head and neck surgeons often perform a thyroidectomy when a patient has thyroid cancer or some other ...
) may be indicated in some instances:
* Reaccumulation of the nodule despite 3–4 repeated FNACs
* Size in excess of 4 cm in some cases
* Compressive symptoms
* Signs of malignancy (vocal cord dysfunction, lymphadenopathy)
* Cytopathology that does not exclude thyroid
The thyroid, or thyroid gland, is an endocrine gland in vertebrates. In humans, it is a butterfly-shaped gland located in the neck below the Adam's apple. It consists of two connected lobes. The lower two thirds of the lobes are connected by ...
cancer
Minimally-invasive procedures
Non-surgical, minimally invasive ultrasound-guided techniques are used for the treatment of large, symptomatic nodules. They include percutaneous ethanol injection, laser thermal ablation,radiofrequency ablation
Radiofrequency ablation (RFA), also called fulguration, is a medical procedure in which part of the electrical conduction system of the heart, tumor, sensory nerves or a dysfunctional tissue is ablated using the heat generated from medium fre ...
, high intensity focused ultrasound
High-intensity focused ultrasound (HIFU), or MR-guided focused ultrasound surgery (MR-guided focused ultrasound ablation), is an incisionless therapeutic technique that uses non-ionizing ultrasonic waves to heat or ablate tissue. HIFU can be u ...
(HIFU), and percutaneous microwave ablation
Microwave ablation is a form of thermal ablation used in interventional radiology to treat cancer. MWA uses electromagnetic waves in the microwave energy spectrum (300 MHz to 300 GHz) to produce tissue-heating effects. The oscillation of ...
.
HIFU has recently proved its effectiveness in treating benign thyroid nodules. This method is noninvasive, without general anesthesia and is performed in an ambulatory setting. Ultrasound waves are focused and produce heat enabling them to destroy thyroid nodules.
Focused ultrasounds have been used to treat other benign tumors, such as breast fibroadenomas and fibroid disease in the uterus.
Treatment
Levothyroxine (T4) is aprohormone
A prohormone is a committed precursor of a hormone consisting of peptide hormones synthesized together that has a minimal hormonal effect by itself because of its expression-suppressing structure, often created by protein folding and binding addit ...
that peripheral tissues convert to the primary active thyroid hormone, triiodothyronine
Triiodothyronine, also known as T3, is a thyroid hormone. It affects almost every physiological process in the body, including growth and development, metabolism, body temperature, and heart rate.
Production of T3 and its prohormone thyroxi ...
(T3). Hypothyroid patients normally take it once per day.
Autonomous thyroid nodule
An autonomous thyroid nodule or "hot nodule" is one that has thyroid function independent of the homeostatic control of the HPT axis ( hypothalamic–pituitary–thyroid axis). According to a 1993 article, such nodules need to be treated only if they becometoxic
Toxicity is the degree to which a chemical substance or a particular mixture of substances can damage an organism. Toxicity can refer to the effect on a whole organism, such as an animal, bacterium, or plant, as well as the effect on a subst ...
; surgical excision (thyroidectomy
A thyroidectomy is an operation that involves the surgery, surgical removal of all or part of the thyroid gland. In general surgery, endocrine or head and neck surgeons often perform a thyroidectomy when a patient has thyroid cancer or some other ...
), radioiodine therapy
Iodine-131 (131I, I-131) is an important radioisotope of iodine discovered by Glenn Seaborg and John Livingood in 1938 at the University of California, Berkeley. It has a radioactive decay half-life of about eight days. It is associated with nu ...
, or both may be used.
See also
*Thyroid adenoma
A thyroid adenoma is a benign tumor of the thyroid gland, that may be inactive or active (functioning autonomously) as a toxic adenoma.
Signs and symptoms
A thyroid adenoma may be clinically silent ("cold" adenoma), or it may be a functional tumo ...
References
External links
{{DEFAULTSORT:Thyroid Nodule Thyroid disease