Thioester Bond on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
In
 This reaction is exploited in
This reaction is exploited in
organic chemistry
Organic chemistry is a subdiscipline within chemistry involving the science, scientific study of the structure, properties, and reactions of organic compounds and organic matter, organic materials, i.e., matter in its various forms that contain ...
, thioesters are organosulfur compounds
Organosulfur chemistry is the study of the properties and synthesis of organosulfur compounds, which are organic compounds that contain sulfur. They are often associated with foul odors, but many of the sweetest compounds known are organosulfur der ...
with the molecular structure . They are analogous to carboxylate esters () with the sulfur in the thioester replacing oxygen in the carboxylate ester, as implied by the thio-
The prefix thio-, when applied to a chemical, such as an ion, means that an oxygen atom in the compound has been replaced by a sulfur atom. This term is often used in organic chemistry. For example, from the word ''ether,'' referring to an oxy ...
prefix. They are the product of esterification
In chemistry, an ester is a compound derived from an acid (either organic or inorganic) in which the hydrogen atom (H) of at least one acidic hydroxyl group () of that acid is replaced by an organyl group (R). These compounds contain a distin ...
of a carboxylic acid
In organic chemistry, a carboxylic acid is an organic acid that contains a carboxyl group () attached to an Substituent, R-group. The general formula of a carboxylic acid is often written as or , sometimes as with R referring to an organyl ...
() with a thiol
In organic chemistry, a thiol (; ), or thiol derivative, is any organosulfur compound of the form , where R represents an alkyl or other organic substituent. The functional group itself is referred to as either a thiol group or a sulfhydryl grou ...
(). In biochemistry
Biochemistry, or biological chemistry, is the study of chemical processes within and relating to living organisms. A sub-discipline of both chemistry and biology, biochemistry may be divided into three fields: structural biology, enzymology, a ...
, the best-known thioesters are derivatives of coenzyme A
Coenzyme A (CoA, SHCoA, CoASH) is a coenzyme, notable for its role in the Fatty acid metabolism#Synthesis, synthesis and Fatty acid metabolism#.CE.B2-Oxidation, oxidation of fatty acids, and the oxidation of pyruvic acid, pyruvate in the citric ac ...
, e.g., acetyl-CoA
Acetyl-CoA (acetyl coenzyme A) is a molecule that participates in many biochemical reactions in protein, carbohydrate and lipid metabolism. Its main function is to deliver the acetyl group to the citric acid cycle (Krebs cycle) to be oxidation, o ...
.Matthys J. Janssen "Carboxylic Acids and Esters" in PATAI's Chemistry of Functional Groups: Carboxylic Acids and Esters, Saul Patai, Ed. John Wiley, 1969, New York: pp. 705–764. The R and R' represent organyl
In organic and organometallic chemistry, an organyl group (commonly denoted by the letter " R") is an organic substituent with one (sometimes more) free valence electron(s) at a carbon atom.. The term is often used in chemical patent literatur ...
groups, or H in the case of R.
Synthesis
One route to thioesters involves the reaction of anacid chloride
In organic chemistry, an acyl chloride (or acid chloride) is an organic compound with the functional group . Their formula is usually written , where R is a side chain. They are reactive derivatives of carboxylic acids (). A specific example o ...
with an alkali metal
The alkali metals consist of the chemical elements lithium (Li), sodium (Na), potassium (K),The symbols Na and K for sodium and potassium are derived from their Latin names, ''natrium'' and ''kalium''; these are still the origins of the names ...
salt of a thiol:
:
Another common route entails the displacement of halide
In chemistry, a halide (rarely halogenide) is a binary chemical compound, of which one part is a halogen atom and the other part is an element or radical that is less electronegative (or more electropositive) than the halogen, to make a fl ...
s by the alkali metal salt of a thiocarboxylic acid
In organic chemistry, thiocarboxylic acids or carbothioic acids are organosulfur compounds related to carboxylic acids by replacement of one of the oxygen atoms with a sulfur atom. Two tautomers are possible: a thione form () and a thiol form ( ...
. For example, thioacetate esters are commonly prepared by alkylation Alkylation is a chemical reaction that entails transfer of an alkyl group. The alkyl group may be transferred as an alkyl carbocation, a free radical, a carbanion, or a carbene (or their equivalents). Alkylating agents are reagents for effecting al ...
of potassium thioacetate
Potassium thioacetate is an organosulfur compound and a salt with the formula . This white, water-soluble solid is used as a reagent for preparing thioacetate esters and other derivatives.
Synthesis and reactions
Potassium thioacetate, which is ...
:
:
The analogous alkylation of an acetate salt is rarely practiced. The alkylation can be conducted using Mannich base A Mannich base is a beta- amino-ketone, which is formed in the reaction of an amine, formaldehyde (or an aldehyde) and a carbon acid. The Mannich base is an endproduct in the Mannich reaction, which is nucleophilic addition reaction of a non-en ...
s and the thiocarboxylic acid:
:
Thioesters can be prepared by condensation of thiols and carboxylic acids in the presence of dehydrating agents:
:
A typical dehydration agent is DCC DCC may refer to:
Biology
* Netrin receptor DCC, human receptor protein, and the gene encoding it
* Dosage compensation complex
Business
* Day Chocolate Company
* DCC plc, an Irish holding company
* Doppelmayr Cable Car, cable car company
* D ...
. Efforts to improve the sustainability of thioester synthesis have also been reported utilising safer coupling reagent T3P and greener solvent cyclopentanone
Cyclopentanone is the organic compound with the formula (CH2)4CO. This cyclic ketone is a colorless volatile liquid.
Preparation
Ketonic decarboxylation of adipic acid gives cyclopentanone. The reaction is conducted at elevated temperatures in t ...
. Acid anhydride
An acid anhydride is a type of chemical compound derived by the removal of water molecules from an acid.
In organic chemistry, organic acid anhydrides contain the functional group . Organic acid anhydrides often form when one equivalent of wa ...
s and some lactone
Lactones are cyclic carboxylic esters. They are derived from the corresponding hydroxycarboxylic acids by esterification. They can be saturated or unsaturated.
Lactones are formed by lactonization, the intramolecular esterification of the corresp ...
s also give thioesters upon treatment with thiols in the presence of a base.
Thioesters can be conveniently prepared from alcohols by the Mitsunobu reaction
The Mitsunobu reaction is an organic reaction that converts an alcohol into a variety of functional groups, such as an ester, using triphenylphosphine and an azodicarboxylate such as diethyl azodicarboxylate (DEAD) or diisopropyl azodicarboxy ...
, using thioacetic acid
Thioacetic acid is an organosulfur compound with the molecular formula . It is a thioic acid: the sulfur Structural analog, analogue of acetic acid (), as implied by the ''thio-'' prefix. It is a yellow liquid with a strong thiol-like odor. It is ...
.
They also arise via carbonylation
In chemistry, carbonylation refers to reactions that introduce carbon monoxide (CO) into organic and inorganic substrates. Carbon monoxide is abundantly available and conveniently reactive, so it is widely used as a reactant in industrial chemis ...
of alkyne
\ce
\ce
Acetylene
\ce
\ce
\ce
Propyne
\ce
\ce
\ce
\ce
1-Butyne
In organic chemistry, an alkyne is an unsaturated hydrocarbon containing at least one carbon—carbon triple bond. The simplest acyclic alkynes with only one triple bond and n ...
s and alkene
In organic chemistry, an alkene, or olefin, is a hydrocarbon containing a carbon–carbon double bond. The double bond may be internal or at the terminal position. Terminal alkenes are also known as Alpha-olefin, α-olefins.
The Internationa ...
s in the presence of thiols.
Reactions
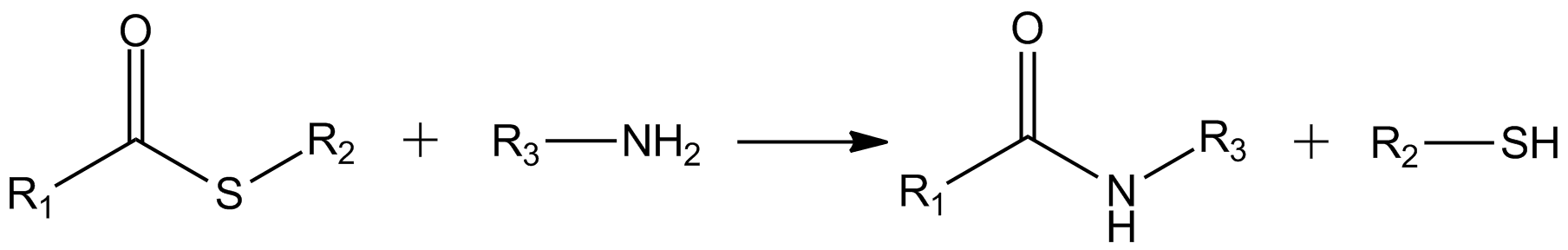
Thioesters hydrolyze to thiols and the carboxylic acid: : The carbonyl center in thioesters is more reactive toward amine than oxygen nucleophiles, givingamide
In organic chemistry, an amide, also known as an organic amide or a carboxamide, is a chemical compound, compound with the general formula , where R, R', and R″ represent any group, typically organyl functional group, groups or hydrogen at ...
s:
: This reaction is exploited in
This reaction is exploited in native chemical ligation Native Chemical Ligation (NCL) is an important extension of the chemical ligation concept for constructing a larger polypeptide chain by the covalent condensation of two or more unprotected peptides segments. Native chemical ligation is the most ...
, a protocol for peptide synthesis
In organic chemistry, peptide synthesis is the production of peptides, compounds where multiple amino acids are linked via amide bonds, also known as peptide bonds. Peptides are chemically synthesized by the condensation reaction of the carboxyl ...
.
In a related reaction, thioesters can be converted into esters. Thioacetate esters can also be cleaved with methanethiol in the presence of stoichiometric base, as illustrated in the preparation of pent-4-yne-1-thiol:
:
:
A reaction unique to thioesters is the Fukuyama coupling
The Fukuyama coupling is a coupling reaction taking place between a thioester and an organozinc halide in the presence of a palladium catalyst. The reaction product is a ketone. This reaction was discovered by Tohru Fukuyama et al. in 1998.
Adv ...
, in which the thioester is coupled with an organozinc halide
Organozinc chemistry is the study of the physical properties, synthesis, and reactions of organozinc compounds, which are organometallic compounds that contain carbon (C) to zinc (Zn) chemical bonds.The Chemistry of Organozinc Compounds' (Patai S ...
by a palladium catalyst to give a ketone.
:
Biochemistry
Thioesters are common intermediates in many biosynthetic reactions, including the formation and degradation offatty acid
In chemistry, in particular in biochemistry, a fatty acid is a carboxylic acid with an aliphatic chain, which is either saturated and unsaturated compounds#Organic chemistry, saturated or unsaturated. Most naturally occurring fatty acids have an ...
s and mevalonate
Mevalonic acid (MVA) is a key organic compound in biochemistry; the name is a contraction of dihydroxymethylvalerolactone. The carboxylate anion of mevalonic acid, which is the predominant form in biological environments, is known as ''mevalonate ...
, precursor to steroids. Examples include malonyl-CoA
Malonyl-CoA is a coenzyme A derivative of malonic acid.
Biosynthesis
Malonyl-CoA cannot cross membranes and there is no known malonyl-CoA import mechanism. The biosynthesis therefore takes place locally:
* cytosol: Malonyl-CoA is formed by c ...
, acetoacetyl-CoA
Acetoacetyl CoA is the precursor of HMG-CoA in the mevalonate pathway, which is essential for cholesterol biosynthesis. It also takes a similar role in the ketone bodies synthesis ( ketogenesis) pathway of the liver. In the ketone bodies digestion ...
, propionyl-CoA
Propionyl-CoA is a coenzyme A derivative of propionic acid. It is composed of a 24 total carbon chain (without the coenzyme, it is a 3 carbon structure) and its production and metabolic fate depend on which organism it is present in. Several diffe ...
, cinnamoyl-CoA
Cinnamoyl-coenzyme A is an intermediate in the Phenylpropanoids metabolism, phenylpropanoid metabolic pathway.
Enzymes using cinnamoyl-coenzyme A
* Cinnamoyl-CoA reductase, an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction cinnamaldehyde + CoA + N ...
, and acyl carrier protein
The acyl carrier protein (ACP) is a cofactor of both fatty acid and polyketide biosynthesis machinery. It is one of the most abundant proteins in cells of ''E. coli.'' In both cases, the growing chain is bound to the ACP via a thioester derived fr ...
(ACP) thioesters. Acetogenesis
Acetogenesis is a process through which acetyl-CoA or acetic acid is produced by anaerobic bacteria through the Redox, reduction of Carbon dioxide, via the Wood–Ljungdahl pathway. Other microbial processes that produce acetic acid (like certain ...
proceeds via the formation of acetyl-CoA
Acetyl-CoA (acetyl coenzyme A) is a molecule that participates in many biochemical reactions in protein, carbohydrate and lipid metabolism. Its main function is to deliver the acetyl group to the citric acid cycle (Krebs cycle) to be oxidation, o ...
. The biosynthesis of lignin
Lignin is a class of complex organic polymers that form key structural materials in the support tissues of most plants. Lignins are particularly important in the formation of cell walls, especially in wood and bark, because they lend rigidit ...
, which comprises a large fraction of the Earth's land biomass, proceeds via a thioester derivative of caffeic acid
Caffeic acid is an organic compound with the formula . It is a polyphenol with a key role in scavenging reactive oxygen species (ROS) generated in energy metabolism. Caffeic acid is also one major polyphenol responsible for maintaining normal le ...
. These thioesters arise analogously to those prepared synthetically, the difference being that the dehydration agent is ATP. In addition, thioesters play an important role in the tagging of proteins with ubiquitin
Ubiquitin is a small (8.6 kDa) regulatory protein found in most tissues of eukaryotic organisms, i.e., it is found ''ubiquitously''. It was discovered in 1975 by Gideon Goldstein and further characterized throughout the late 1970s and 19 ...
, which tags the protein for degradation.
Oxidation of the sulfur atom in thioesters (thiolactone
Thiolactones are a class of heterocyclic compounds in organic chemistry. They are analogs of the more common lactones in which an oxygen atom is replaced with a sulfur atom. The sulfur atom is within the ring system and adjacent to a carbonyl gro ...
s) is postulated in the bioactivation of the antithrombotic prodrugs ticlopidine
Ticlopidine, sold under the brand name Ticlid, is a medication used to reduce the risk of thrombotic strokes. It is an antiplatelet drug in the thienopyridine family which is an adenosine diphosphate (ADP) receptor inhibitor. Research initially ...
, clopidogrel
Clopidogrel, sold under the brand name Plavix among others, is an antiplatelet drug, antiplatelet medication used to reduce the risk of Cardiovascular disease, heart disease and stroke in those at high risk. It is also used together with aspi ...
, and prasugrel
Prasugrel, sold under the brand names Effient and Efient, is a medication used to prevent formation of blood clots. It is a platelet inhibitor and an irreversible antagonist of P2Y12 ADP receptors and is of the thienopyridine drug class. It ...
.
Thioesters and the origin of life
As posited in a "Thioester World", thioesters are possible precursors to life. AsChristian de Duve
Christian René Marie Joseph, Viscount de Duve (2 October 1917 – 4 May 2013) was a Nobel Prize-winning Belgian cytologist and biochemist. He made serendipitous discoveries of two cell organelles, peroxisomes and lysosomes, for which he sh ...
explains:
It is revealing that thioesters are obligatory intermediates in several key processes in which ATP is either used or regenerated. Thioesters are involved in the synthesis of allHowever, due to the high free energy change of thioester's hydrolysis and correspondingly their low equilibrium constants, it is unlikely that these compounds could have accumulated abiotically to any significant extent especially in hydrothermal vent conditions.esters In chemistry, an ester is a chemical compound, compound derived from an acid (either organic or inorganic) in which the hydrogen atom (H) of at least one acidic hydroxyl group () of that acid is replaced by an organyl group (R). These compounds c ..., including those found in complexlipid Lipids are a broad group of organic compounds which include fats, waxes, sterols, fat-soluble vitamins (such as vitamins A, D, E and K), monoglycerides, diglycerides, phospholipids, and others. The functions of lipids include storing ...s. They also participate in the synthesis of a number of other cellular components, includingpeptide Peptides are short chains of amino acids linked by peptide bonds. A polypeptide is a longer, continuous, unbranched peptide chain. Polypeptides that have a molecular mass of 10,000 Da or more are called proteins. Chains of fewer than twenty am ...s,fatty acid In chemistry, in particular in biochemistry, a fatty acid is a carboxylic acid with an aliphatic chain, which is either saturated and unsaturated compounds#Organic chemistry, saturated or unsaturated. Most naturally occurring fatty acids have an ...s,sterol A sterol is any organic compound with a Skeletal formula, skeleton closely related to Cholestanol, cholestan-3-ol. The simplest sterol is gonan-3-ol, which has a formula of , and is derived from that of gonane by replacement of a hydrogen atom on ...s,terpene Terpenes () are a class of natural products consisting of compounds with the formula (C5H8)n for n ≥ 2. Terpenes are major biosynthetic building blocks. Comprising more than 30,000 compounds, these unsaturated hydrocarbons are produced predomi ...s,porphyrin Porphyrins ( ) are heterocyclic, macrocyclic, organic compounds, composed of four modified pyrrole subunits interconnected at their α carbon atoms via methine bridges (). In vertebrates, an essential member of the porphyrin group is heme, w ...s, and others. In addition, thioesters are formed as key intermediates in several particularly ancient processes that result in the assembly of ATP. In both these instances, the thioester is closer than ATP to the process that uses or yields energy. In other words, thioesters could have actually played the role of ATP in a "thioester world" initially devoid of ATP. Eventually, hesethioesters could have served to usher in ATP through its ability to support the formation of bonds betweenphosphate group Phosphates are the naturally occurring form of the element phosphorus. In chemistry, a phosphate is an anion, salt, functional group or ester derived from a phosphoric acid. It most commonly means orthophosphate, a derivative of orthophosp ...s.
Thionoesters
Thionoesters are isomeric with thioesters. In a thionoester, sulfur replaces the carbonyl oxygen in an ester. Methyl thionobenzoate is C6H5C(S)OCH3. Such compounds are typically prepared by the reaction of thethioacyl chloride
In organic chemistry, a thioacyl chloride is an organic compound containing the functional group . Their formula is usually written , where R is a side chain. Thioacyl chlorides are analogous to acyl chlorides, but much rarer and less robust. Ind ...
with an alcohol.
They can also be made by the reaction of Lawesson's reagent
Lawesson's reagent (LR) is a chemical compound used in organic synthesis as a thiation agent. Lawesson's reagent was first made popular by Sven-Olov Lawesson, who did not, however, invent it. Lawesson's reagent was first made in 1956 during a sy ...
with esters or by treating pinner salts with hydrogen sulfide
Hydrogen sulfide is a chemical compound with the formula . It is a colorless chalcogen-hydride gas, and is toxic, corrosive, and flammable. Trace amounts in ambient atmosphere have a characteristic foul odor of rotten eggs. Swedish chemist ...
.
Various thionoesters may be prepared through the transesterification
Transesterification is the process of exchanging the organic functional group R″ of an ester with the organic group R' of an alcohol. These reactions are often catalyzed by the addition of an acid or base catalyst. Strong acids catalyze the r ...
of an existing methyl thionoester with an alcohol under base-catalyzed conditions.
Xanthate
A xanthate is a Salt (chemistry), salt or ester of a xanthic acid. The formula of the salt of xanthic acid is (where R is organyl group and M is usually Sodium, Na or Potassium, K). Xanthate also refers to the anion . The formula of a xanthic a ...
s and thioamide
A thioamide (rarely, thionamide, but also known as thiourylenes) is a functional group with the general structure , where are any groups (typically organyl groups or hydrogen). Analogous to amides, thioamides exhibit greater multiple bond charact ...
s can be transformed to thionoesters under metal-catalyzed cross-coupling conditions.
See also
*Thiocarboxylic acid
In organic chemistry, thiocarboxylic acids or carbothioic acids are organosulfur compounds related to carboxylic acids by replacement of one of the oxygen atoms with a sulfur atom. Two tautomers are possible: a thione form () and a thiol form ( ...
* Thiocarbonate Thiocarbonate describes a family of anions with the general chemical formula (''x'' = 0, 1, or 2):
*for ''x'' = 2 it is monothiocarbonate ion
*for ''x'' = 1 it is dithiocarbonate ion
*for ''x'' = 0 it is trithiocarbonate ion
Like the carbonate d ...
* Liebeskind–Srogl coupling
* Aldrithiol-2
References
{{Functional group Functional groups Origin of life