Thaumasia Quadrangle on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 The Thaumasia quadrangle is one of a series of 30 quadrangle maps of Mars used by the
The Thaumasia quadrangle is one of a series of 30 quadrangle maps of Mars used by the
 The ice-rich mantle may be the result of climate changes. Changes in Mars's orbit and tilt cause significant changes in the distribution of water ice from polar regions down to latitudes equivalent to Texas. During certain climate periods water vapor leaves polar ice and enters the atmosphere. The water comes back to ground at lower latitudes as deposits of frost or snow mixed generously with dust. The atmosphere of Mars contains a great deal of fine dust particles. Water vapor will condense on the particles, then fall down to the ground due to the additional weight of the water coating. When Mars is at its greatest tilt or obliquity, up to 2 cm of ice could be removed from the summer ice cap and deposited at midlatitudes. This movement of water could last for several thousand years and create a snow layer of up to around 10 meters thick. When ice at the top of the mantling layer goes back into the atmosphere, it leaves behind dust, which insulating the remaining ice. Measurements of altitudes and slopes of gullies support the idea that snowpacks or glaciers are associated with gullies. Steeper slopes have more shade which would preserve snow.
Higher elevations have far fewer gullies because ice would tend to sublimate more in the thin air of the higher altitude. Very few gullies are found in the Thaumasia region; however, a few are present in the lower elevations like the one pictured below in Ross Crater.
The third theory might be possible since climate changes may be enough to simply allow ice in the ground to melt and thus form the gullies. During a warmer climate, the first few meters of ground could thaw and produce a "debris flow" similar to those on the dry and cold Greenland east coast. Since the gullies occur on steep slopes only a small decrease of the shear strength of the soil particles is needed to begin the flow. Small amounts of liquid water from melted ground ice could be enough. Calculations show that a third of a mm of runoff can be produced each day for 50 days of each Martian year, even under current conditions.
The ice-rich mantle may be the result of climate changes. Changes in Mars's orbit and tilt cause significant changes in the distribution of water ice from polar regions down to latitudes equivalent to Texas. During certain climate periods water vapor leaves polar ice and enters the atmosphere. The water comes back to ground at lower latitudes as deposits of frost or snow mixed generously with dust. The atmosphere of Mars contains a great deal of fine dust particles. Water vapor will condense on the particles, then fall down to the ground due to the additional weight of the water coating. When Mars is at its greatest tilt or obliquity, up to 2 cm of ice could be removed from the summer ice cap and deposited at midlatitudes. This movement of water could last for several thousand years and create a snow layer of up to around 10 meters thick. When ice at the top of the mantling layer goes back into the atmosphere, it leaves behind dust, which insulating the remaining ice. Measurements of altitudes and slopes of gullies support the idea that snowpacks or glaciers are associated with gullies. Steeper slopes have more shade which would preserve snow.
Higher elevations have far fewer gullies because ice would tend to sublimate more in the thin air of the higher altitude. Very few gullies are found in the Thaumasia region; however, a few are present in the lower elevations like the one pictured below in Ross Crater.
The third theory might be possible since climate changes may be enough to simply allow ice in the ground to melt and thus form the gullies. During a warmer climate, the first few meters of ground could thaw and produce a "debris flow" similar to those on the dry and cold Greenland east coast. Since the gullies occur on steep slopes only a small decrease of the shear strength of the soil particles is needed to begin the flow. Small amounts of liquid water from melted ground ice could be enough. Calculations show that a third of a mm of runoff can be produced each day for 50 days of each Martian year, even under current conditions.
 Many places on Mars have sand dunes. Some craters in Thaumasia show dark blotches in them. High resolution photos show that the dark markings are dark sand dunes. Dark sand dunes probably contain the igneous rock basalt. Brashear Crater, pictured below, is one crater with dark dunes.
Many places on Mars have sand dunes. Some craters in Thaumasia show dark blotches in them. High resolution photos show that the dark markings are dark sand dunes. Dark sand dunes probably contain the igneous rock basalt. Brashear Crater, pictured below, is one crater with dark dunes.
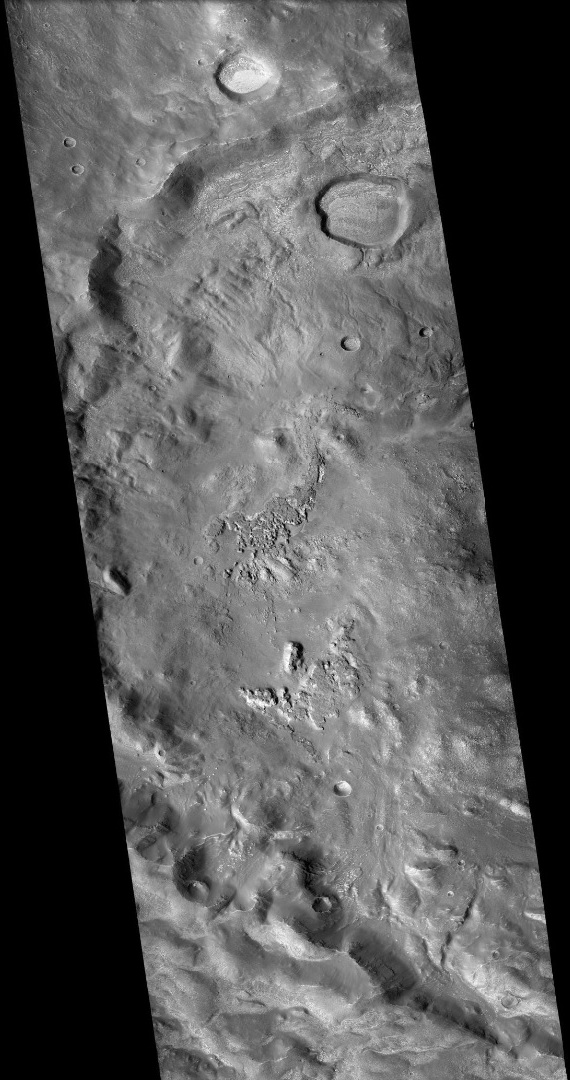 The density of impact craters is used to determine the surface ages of Mars and other solar system bodies. The older the surface, the more craters present. Crater shapes can reveal the presence of ground ice.
The area around craters may be rich in minerals. On Mars, heat from the impact melts ice in the ground. Water from the melting ice dissolves minerals, and then deposits them in cracks or faults that were produced with the impact. This process, called hydrothermal alteration, is a major way in which ore deposits are produced. The area around Martian craters may be rich in useful ores for the future colonization of Mars.
Studies on the earth have documented that cracks are produced and that secondary minerals veins are deposited in the cracks. Images from satellites orbiting Mars have detected cracks near impact craters. Great amounts of heat are produced during impacts. The area around a large impact may take hundreds of thousands of years to cool.
Many craters once contained lakes. Because some crater floors show deltas, we know that water had to be present for some time. Dozens of deltas have been spotted on Mars. Deltas form when sediment is washed in from a stream entering a quiet body of water. It takes a bit of time to form a delta, so the presence of a delta is exciting; it means water was there for a time, maybe for many years. Primitive organisms may have developed in such lakes; hence, some craters may be prime targets for the search for evidence of life on the Red Planet.
The density of impact craters is used to determine the surface ages of Mars and other solar system bodies. The older the surface, the more craters present. Crater shapes can reveal the presence of ground ice.
The area around craters may be rich in minerals. On Mars, heat from the impact melts ice in the ground. Water from the melting ice dissolves minerals, and then deposits them in cracks or faults that were produced with the impact. This process, called hydrothermal alteration, is a major way in which ore deposits are produced. The area around Martian craters may be rich in useful ores for the future colonization of Mars.
Studies on the earth have documented that cracks are produced and that secondary minerals veins are deposited in the cracks. Images from satellites orbiting Mars have detected cracks near impact craters. Great amounts of heat are produced during impacts. The area around a large impact may take hundreds of thousands of years to cool.
Many craters once contained lakes. Because some crater floors show deltas, we know that water had to be present for some time. Dozens of deltas have been spotted on Mars. Deltas form when sediment is washed in from a stream entering a quiet body of water. It takes a bit of time to form a delta, so the presence of a delta is exciting; it means water was there for a time, maybe for many years. Primitive organisms may have developed in such lakes; hence, some craters may be prime targets for the search for evidence of life on the Red Planet.
 There is enormous evidence that water once flowed in river valleys on Mars. Images of curved channels have been seen in images from Mars spacecraft dating back to the early 1970s with the
There is enormous evidence that water once flowed in river valleys on Mars. Images of curved channels have been seen in images from Mars spacecraft dating back to the early 1970s with the
 The Thaumasia quadrangle is one of a series of 30 quadrangle maps of Mars used by the
The Thaumasia quadrangle is one of a series of 30 quadrangle maps of Mars used by the United States Geological Survey
The United States Geological Survey (USGS), founded as the Geological Survey, is an agency of the U.S. Department of the Interior whose work spans the disciplines of biology, geography, geology, and hydrology. The agency was founded on Mar ...
(USGS) Astrogeology Research Program
The Astrogeology Science Center is the entity within the United States Geological Survey concerned with the study of planetary geology and planetary cartography. It is housed in the Shoemaker Building in Flagstaff, Arizona. The Center was esta ...
. The Thaumasia quadrangle is also referred to as MC-25 (Mars Chart-25).
The name comes from Thaumas
In Greek mythology, Thaumas or Thaumant (; ; ) was a sea god, son of Pontus and Gaia, and the full brother of Nereus, Phorcys, Ceto and Eurybia.
Mythology
According to Hesiod, Thaumas's wife was Electra (one of the Oceanids, the many daughter ...
, Greek god of the clouds and celestial apparitions.
The Thaumasia quadrangle covers the area from 60° to 120° west longitude and 30° to 65° south latitude on Mars
Mars is the fourth planet from the Sun. It is also known as the "Red Planet", because of its orange-red appearance. Mars is a desert-like rocky planet with a tenuous carbon dioxide () atmosphere. At the average surface level the atmosph ...
. The Thaumasia quadrangle contains many different regions or parts of many regions: Solis Planum, Icaria Planum, Aonia Terra, Aonia Planum, Bosporus Planum, and Thaumasia Planum. One of the first major networks of stream channels, called Warrego Valles, were discovered here by early orbiters. Another sign of water is the presence of gullies carved into steep slopes.
Martian gullies
Gullies are common in some parts of Mars. Gullies occur on steep slopes, especially on the walls of craters. Martian gullies are believed to be relatively young because they have few, if any craters. Moreover, they lie on top of sand dunes which themselves are considered to be quite young. Usually, each gully has an alcove, channel, and apron. Some studies have found that gullies occur on slopes that face all directions, others have found that the greater number of gullies are found on poleward facing slopes, especially from 30-44 S. Many ideas have been put forward to explain them; the most popular involve liquid water coming from anaquifer
An aquifer is an underground layer of water-bearing material, consisting of permeability (Earth sciences), permeable or fractured rock, or of unconsolidated materials (gravel, sand, or silt). Aquifers vary greatly in their characteristics. The s ...
, from melting at the base of old glaciers
A glacier (; or ) is a persistent body of dense ice, a form of rock, that is constantly moving downhill under its own weight. A glacier forms where the accumulation of snow exceeds its ablation over many years, often centuries. It acquires ...
, or from the melting of ice in the ground when the climate was warmer.
There is evidence for all three theories. Most of the gully alcove heads occur at the same level, just as one would expect of an aquifer
An aquifer is an underground layer of water-bearing material, consisting of permeability (Earth sciences), permeable or fractured rock, or of unconsolidated materials (gravel, sand, or silt). Aquifers vary greatly in their characteristics. The s ...
. Various measurements and calculations show that liquid water could exist in aquifers at the usual depths where gullies begin. One variation of this model is that rising hot magma
Magma () is the molten or semi-molten natural material from which all igneous rocks are formed. Magma (sometimes colloquially but incorrectly referred to as ''lava'') is found beneath the surface of the Earth, and evidence of magmatism has also ...
could have melted ice in the ground and caused water to flow in aquifers. Aquifers are layer that allow water to flow. They may consist of porous sandstone. The aquifer layer would be perched on top of another layer that prevents water from going down (in geological terms it would be called impermeable). Because water in an aquifer is prevented from going down, the only direction the trapped water can flow is horizontally. Eventually, water could flow out onto the surface when the aquifer reaches a break—like a crater wall. The resulting flow of water could erode the wall to create gullies. Aquifers are quite common on Earth. A good example is "Weeping Rock" in Zion National Park, Utah
Utah is a landlocked state in the Mountain states, Mountain West subregion of the Western United States. It is one of the Four Corners states, sharing a border with Arizona, Colorado, and New Mexico. It also borders Wyoming to the northea ...
.
As for the next theory, much of the surface of Mars is covered by a thick smooth mantle that is thought to be a mixture of ice and dust. This ice-rich mantle, a few yards thick, smooths the land, but in places it has a bumpy texture, resembling the surface of a basketball. The mantle may be like a glacier and under certain conditions the ice that is mixed in the mantle could melt and flow down the slopes and make gullies. Because there are few craters on this mantle, the mantle is relatively young. An excellent view of this mantle is shown below in the picture of the Ptolemaeus Crater Rim, as seen by HiRISE
High Resolution Imaging Science Experiment is a camera on board the '' Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter'' which has been orbiting and studying Mars since 2006. The 65 kg (143 lb), US$40 million instrument was built under the direction ...
.
 The ice-rich mantle may be the result of climate changes. Changes in Mars's orbit and tilt cause significant changes in the distribution of water ice from polar regions down to latitudes equivalent to Texas. During certain climate periods water vapor leaves polar ice and enters the atmosphere. The water comes back to ground at lower latitudes as deposits of frost or snow mixed generously with dust. The atmosphere of Mars contains a great deal of fine dust particles. Water vapor will condense on the particles, then fall down to the ground due to the additional weight of the water coating. When Mars is at its greatest tilt or obliquity, up to 2 cm of ice could be removed from the summer ice cap and deposited at midlatitudes. This movement of water could last for several thousand years and create a snow layer of up to around 10 meters thick. When ice at the top of the mantling layer goes back into the atmosphere, it leaves behind dust, which insulating the remaining ice. Measurements of altitudes and slopes of gullies support the idea that snowpacks or glaciers are associated with gullies. Steeper slopes have more shade which would preserve snow.
Higher elevations have far fewer gullies because ice would tend to sublimate more in the thin air of the higher altitude. Very few gullies are found in the Thaumasia region; however, a few are present in the lower elevations like the one pictured below in Ross Crater.
The third theory might be possible since climate changes may be enough to simply allow ice in the ground to melt and thus form the gullies. During a warmer climate, the first few meters of ground could thaw and produce a "debris flow" similar to those on the dry and cold Greenland east coast. Since the gullies occur on steep slopes only a small decrease of the shear strength of the soil particles is needed to begin the flow. Small amounts of liquid water from melted ground ice could be enough. Calculations show that a third of a mm of runoff can be produced each day for 50 days of each Martian year, even under current conditions.
The ice-rich mantle may be the result of climate changes. Changes in Mars's orbit and tilt cause significant changes in the distribution of water ice from polar regions down to latitudes equivalent to Texas. During certain climate periods water vapor leaves polar ice and enters the atmosphere. The water comes back to ground at lower latitudes as deposits of frost or snow mixed generously with dust. The atmosphere of Mars contains a great deal of fine dust particles. Water vapor will condense on the particles, then fall down to the ground due to the additional weight of the water coating. When Mars is at its greatest tilt or obliquity, up to 2 cm of ice could be removed from the summer ice cap and deposited at midlatitudes. This movement of water could last for several thousand years and create a snow layer of up to around 10 meters thick. When ice at the top of the mantling layer goes back into the atmosphere, it leaves behind dust, which insulating the remaining ice. Measurements of altitudes and slopes of gullies support the idea that snowpacks or glaciers are associated with gullies. Steeper slopes have more shade which would preserve snow.
Higher elevations have far fewer gullies because ice would tend to sublimate more in the thin air of the higher altitude. Very few gullies are found in the Thaumasia region; however, a few are present in the lower elevations like the one pictured below in Ross Crater.
The third theory might be possible since climate changes may be enough to simply allow ice in the ground to melt and thus form the gullies. During a warmer climate, the first few meters of ground could thaw and produce a "debris flow" similar to those on the dry and cold Greenland east coast. Since the gullies occur on steep slopes only a small decrease of the shear strength of the soil particles is needed to begin the flow. Small amounts of liquid water from melted ground ice could be enough. Calculations show that a third of a mm of runoff can be produced each day for 50 days of each Martian year, even under current conditions.
Sand dunes
 Many places on Mars have sand dunes. Some craters in Thaumasia show dark blotches in them. High resolution photos show that the dark markings are dark sand dunes. Dark sand dunes probably contain the igneous rock basalt. Brashear Crater, pictured below, is one crater with dark dunes.
Many places on Mars have sand dunes. Some craters in Thaumasia show dark blotches in them. High resolution photos show that the dark markings are dark sand dunes. Dark sand dunes probably contain the igneous rock basalt. Brashear Crater, pictured below, is one crater with dark dunes.
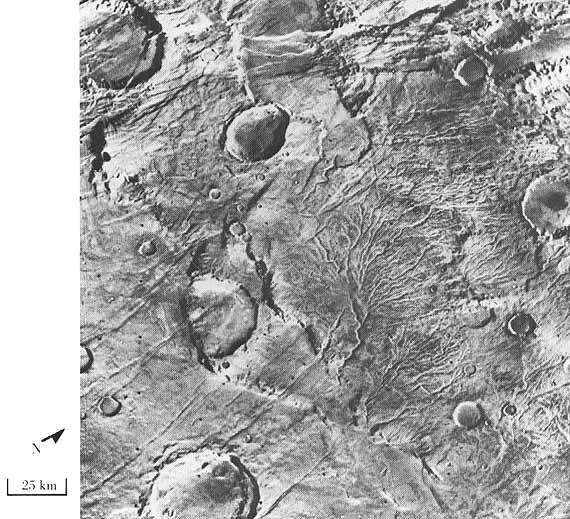
Warrego Valles
Mariner 9
Mariner 9 (Mariner Mars '71 / Mariner-I) was a robotic spacecraft that contributed greatly to the exploration of Mars and was part of the NASA Mariner program. Mariner 9 was launched toward Mars on May 30, 1971, from Spaceport Florida Launch Comp ...
and Viking Orbiter images, showed a network of branching valleys in Thaumasia called Warrego Valles. These networks are evidence that Mars may have once been warmer, wetter, and perhaps had precipitation in the form of rain or snow. A study with the Mars Orbiter Laser Altimeter
image:PIA02040 Martian hemispheres by MOLA.jpg, 260px, MOLA topographic images of the two hemispheres of Mars. This image appeared on the cover of ''Science'' magazine in May 1999.
The Mars Orbiter Laser Altimeter (MOLA) was one of five instruments ...
, Thermal Emission Imaging System
The Thermal Emission Imaging System (THEMIS) is a camera on board the 2001 Mars Odyssey orbiter. It images Mars in the visible and infrared parts of the electromagnetic spectrum in order to determine the thermal properties of the surface and to ...
(THEMIS) and the Mars Orbiter Camera (MOC) support the idea that Warrego Valles was formed from precipitation. At first glance they resemble river valleys on Earth. But sharper images from more advanced cameras reveal that the valleys are not continuous. They are very old and may have suffered from the effects of erosion. A picture below shows some of these branching valleys.
Craters
 The density of impact craters is used to determine the surface ages of Mars and other solar system bodies. The older the surface, the more craters present. Crater shapes can reveal the presence of ground ice.
The area around craters may be rich in minerals. On Mars, heat from the impact melts ice in the ground. Water from the melting ice dissolves minerals, and then deposits them in cracks or faults that were produced with the impact. This process, called hydrothermal alteration, is a major way in which ore deposits are produced. The area around Martian craters may be rich in useful ores for the future colonization of Mars.
Studies on the earth have documented that cracks are produced and that secondary minerals veins are deposited in the cracks. Images from satellites orbiting Mars have detected cracks near impact craters. Great amounts of heat are produced during impacts. The area around a large impact may take hundreds of thousands of years to cool.
Many craters once contained lakes. Because some crater floors show deltas, we know that water had to be present for some time. Dozens of deltas have been spotted on Mars. Deltas form when sediment is washed in from a stream entering a quiet body of water. It takes a bit of time to form a delta, so the presence of a delta is exciting; it means water was there for a time, maybe for many years. Primitive organisms may have developed in such lakes; hence, some craters may be prime targets for the search for evidence of life on the Red Planet.
The density of impact craters is used to determine the surface ages of Mars and other solar system bodies. The older the surface, the more craters present. Crater shapes can reveal the presence of ground ice.
The area around craters may be rich in minerals. On Mars, heat from the impact melts ice in the ground. Water from the melting ice dissolves minerals, and then deposits them in cracks or faults that were produced with the impact. This process, called hydrothermal alteration, is a major way in which ore deposits are produced. The area around Martian craters may be rich in useful ores for the future colonization of Mars.
Studies on the earth have documented that cracks are produced and that secondary minerals veins are deposited in the cracks. Images from satellites orbiting Mars have detected cracks near impact craters. Great amounts of heat are produced during impacts. The area around a large impact may take hundreds of thousands of years to cool.
Many craters once contained lakes. Because some crater floors show deltas, we know that water had to be present for some time. Dozens of deltas have been spotted on Mars. Deltas form when sediment is washed in from a stream entering a quiet body of water. It takes a bit of time to form a delta, so the presence of a delta is exciting; it means water was there for a time, maybe for many years. Primitive organisms may have developed in such lakes; hence, some craters may be prime targets for the search for evidence of life on the Red Planet.
Channels
 There is enormous evidence that water once flowed in river valleys on Mars. Images of curved channels have been seen in images from Mars spacecraft dating back to the early 1970s with the
There is enormous evidence that water once flowed in river valleys on Mars. Images of curved channels have been seen in images from Mars spacecraft dating back to the early 1970s with the Mariner 9
Mariner 9 (Mariner Mars '71 / Mariner-I) was a robotic spacecraft that contributed greatly to the exploration of Mars and was part of the NASA Mariner program. Mariner 9 was launched toward Mars on May 30, 1971, from Spaceport Florida Launch Comp ...
orbiter. Indeed, a study published in June 2017, calculated that the volume of water needed to carve all the channels on Mars was even larger than the proposed ocean that the planet may have had. Water was probably recycled many times from the ocean to rainfall around Mars.Luo, W., et al. 2017. New Martian valley network volume estimate consistent with ancient ocean and warm and wet climate. Nature Communications 8. Article number: 15766 (2017).
See also
* Climate of Mars *Dunes
A dune is a landform composed of wind- or water-driven sand. It typically takes the form of a mound, ridge, or hill. An area with dunes is called a dune system or a dune complex. A large dune complex is called a dune field, while broad, flat ...
* HiRISE
High Resolution Imaging Science Experiment is a camera on board the '' Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter'' which has been orbiting and studying Mars since 2006. The 65 kg (143 lb), US$40 million instrument was built under the direction ...
* HiWish program
HiWish is a program created by NASA so that anyone can suggest a place for the HiRISE camera on the Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter to photograph. It was started in January 2010. In the first few months of the program 3000 people signed up to use HiR ...
* Impact crater
An impact crater is a depression (geology), depression in the surface of a solid astronomical body formed by the hypervelocity impact event, impact of a smaller object. In contrast to volcanic craters, which result from explosion or internal c ...
* list of quadrangles on Mars
* Martian Gullies
* Valley network (Mars)
Valley networks are branching networks of valleys on Mars that superficially resemble terrestrial river drainage basins.Carr, M.H. (2006), The Surface of Mars. Cambridge Planetary Science Series, Cambridge University Press. They are found mainly ...
* Vallis
* Water on Mars
Although very small amounts of liquid water may occur transiently on the surface of Mars, limited to traces of dissolved moisture from the atmosphere and thin films, large quantities of ice are present on and under the surface. Small amounts of ...
References
Further reading
* Lorenz, R. 2014. The Dune Whisperers. The Planetary Report: 34, 1, 8-14 * Lorenz, R., J. Zimbelman. 2014. Dune Worlds: How Windblown Sand Shapes Planetary Landscapes. Springer Praxis Books / Geophysical Sciences.External links
{{DEFAULTSORT:Thaumasia Quadrangle Mars