Teutonic Order on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The Teutonic Order is a Catholic religious institution founded as a military society in

 The fraternity which preceded the formation of the Order was formed in the year 1191 in
The fraternity which preceded the formation of the Order was formed in the year 1191 in
 In 1143, Pope Celestine II ordered the
In 1143, Pope Celestine II ordered the
 The Order ruled Prussia under charters issued by the Pope and the Holy Roman Emperor as a
The Order ruled Prussia under charters issued by the Pope and the Holy Roman Emperor as a
 After suffering a devastating defeat in the
After suffering a devastating defeat in the
 A dispute over the claims to
A dispute over the claims to
 In 1337, Emperor Louis IV, Holy Roman Emperor, Louis IV allegedly granted the Order the imperial privilege to conquer all Lithuania and Russia. During the reign of Grand Master Winrich von Kniprode (1351–1382), the Order reached the peak of its international prestige and hosted numerous European crusaders and nobility.
King Albert of Sweden ceded Gotland to the Order as a pledge (similar to a fiefdom), with the understanding that they would eliminate the pirating Victual Brothers from this strategic island base in the
In 1337, Emperor Louis IV, Holy Roman Emperor, Louis IV allegedly granted the Order the imperial privilege to conquer all Lithuania and Russia. During the reign of Grand Master Winrich von Kniprode (1351–1382), the Order reached the peak of its international prestige and hosted numerous European crusaders and nobility.
King Albert of Sweden ceded Gotland to the Order as a pledge (similar to a fiefdom), with the understanding that they would eliminate the pirating Victual Brothers from this strategic island base in the
 In 1440, the Prussian Confederation was founded by gentry and burghers of the State of the Teutonic Order. In 1454, it rose up against the Order and asked Polish King Casimir IV Jagiellon to incorporate the region into the Crown of the Kingdom of Poland, Kingdom of Poland, to which the King agreed and signed an act of incorporation in Kraków. Mayors, burghers and representatives from the region pledged allegiance to the Polish King during the incorporation in March 1454 in Kraków. This marked the beginning of the Thirteen Years' War (1454–1466), Thirteen Years' War between the Teutonic Order and Poland. The main cities of the incorporated territory were authorized by Casimir IV to mint Polish coins. Much of Prussia was devastated in the war, during the course of which the Order returned Neumark to Brandenburg in 1455 to raise funds for war. Because Marienburg Castle was handed over to mercenaries in lieu of their pay, and eventually passed to Poland, the Order moved its base to
In 1440, the Prussian Confederation was founded by gentry and burghers of the State of the Teutonic Order. In 1454, it rose up against the Order and asked Polish King Casimir IV Jagiellon to incorporate the region into the Crown of the Kingdom of Poland, Kingdom of Poland, to which the King agreed and signed an act of incorporation in Kraków. Mayors, burghers and representatives from the region pledged allegiance to the Polish King during the incorporation in March 1454 in Kraków. This marked the beginning of the Thirteen Years' War (1454–1466), Thirteen Years' War between the Teutonic Order and Poland. The main cities of the incorporated territory were authorized by Casimir IV to mint Polish coins. Much of Prussia was devastated in the war, during the course of which the Order returned Neumark to Brandenburg in 1455 to raise funds for war. Because Marienburg Castle was handed over to mercenaries in lieu of their pay, and eventually passed to Poland, the Order moved its base to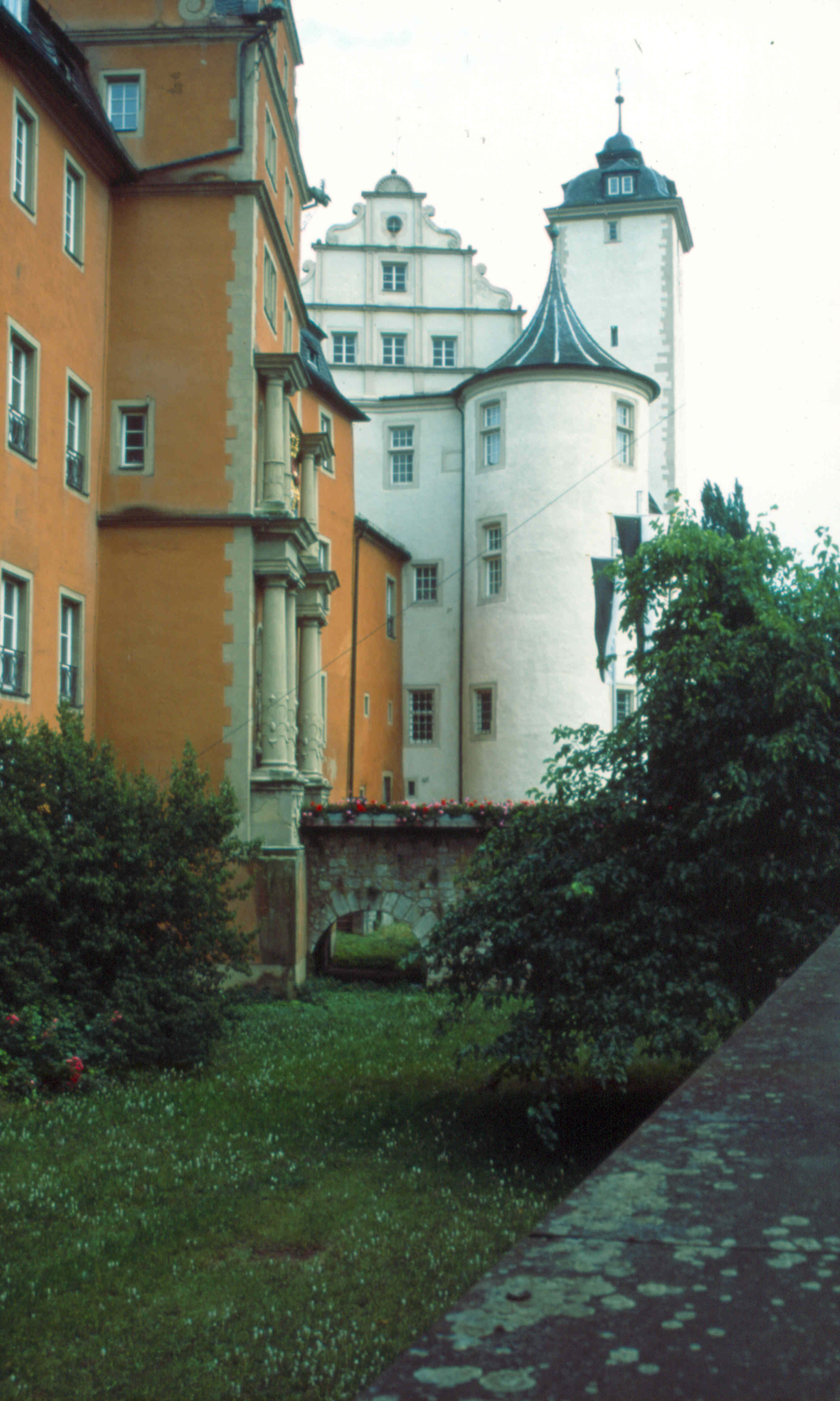  There were twelve German bailiwicks:
*
There were twelve German bailiwicks:
*
File:Stamp of the Teutonic Knights, 14th century.jpg, 14th-century brass stamp with the shield insignia.
File:Wappen 1594 BSB cod icon 326 030 crop.jpg, In the 16th century, officers of the order would quarter their family arms with the order's arms.
File:Deutschmeisterwappen mergentheim.jpg, Example of the ''Deutschmeisterwappen'' on the gate of the Bad Mergentheim residence
File:CoA - Bruntal Castle.jpg, Coat of arms of Prince Charles Alexander of Lorraine, Grand Master from 1761 to 1780.
File:Hermann Brommer Orden.jpg, Modern (20th century) medal
File:Grabesritter bei der Liboriprozession.jpg, Procession in honour of Saint Liborius of Le Mans with Knights of the Holy Sepulchre together with Teutonic Knights in Paderborn, Germany.
Biała leganda czarnego krzyża
". Accessed 6 June 2006. An organization predating the Nazi Party itself, as well as Bund Deutscher Osten, Nazi-supported preceding and Nazi propaganda, Nazi preceding and during World War II propaganda made use of the Teutonic Knights' imagery, with the common goal of instilling the importance of for the future of Germany and the German people. According to medieval historian Eric Christiansen, Erik Christiansen, "Heinrich Himmler, Himmler's plan to mould the Schutzstaffel, SS as a reincarnation of [The Teutonic Order] proved [...] the irresistible strength of bad history." Though gradually taking hold ever since with one of Prince Adalbert of Prussia (1811–1873), Prince Adalbert of Prussia's 1849 proposals, after a lull during the Weimar Republic, whereupon it reverted to a simple tricolor overlayed with an
The order's homepage in Germany
The order's homepage in Austria
Territorial extent of the Teutonic Knights in Europe
(map)
by William Urban
"The Early Years of the Teutonic Order"
by William Urban
Museum in the residential castle of the Teutonic Order in Bad Mergentheim
Zwaetzen and the German Order in Central Germany
"Massive Ceremonial Hall Discovered Under Crusader Castle in Northern Israel" – Haaretz, Nov. 22, 2018
* This contains a detailed chronological history of the Order, and is itself based on Heinrich von Treitschke ''Das deutsche Ordensland Preussens'', in ''Historische und politische Aufsätze'', vol. II. (Leipzig, 1871), and on Johann Loserth ''Geschichte des späteren Mittelalters'' (Munich and Berlin, 1903). {{Authority control Teutonic Order, 1190 establishments in Asia 1190 establishments in Europe Christian religious orders established in the 12th century Kingdom of Jerusalem
Acre
The acre ( ) is a Unit of measurement, unit of land area used in the Imperial units, British imperial and the United States customary units#Area, United States customary systems. It is traditionally defined as the area of one Chain (unit), ch ...
, Kingdom of Jerusalem
The Kingdom of Jerusalem, also known as the Crusader Kingdom, was one of the Crusader states established in the Levant immediately after the First Crusade. It lasted for almost two hundred years, from the accession of Godfrey of Bouillon in 1 ...
. The Order of Brothers of the German House of Saint Mary in Jerusalem was formed to aid Christians
A Christian () is a person who follows or adheres to Christianity, a monotheistic Abrahamic religion based on the life and teachings of Jesus Christ. Christians form the largest religious community in the world. The words '' Christ'' and ''C ...
on their pilgrimage
A pilgrimage is a travel, journey to a holy place, which can lead to a personal transformation, after which the pilgrim returns to their daily life. A pilgrim (from the Latin ''peregrinus'') is a traveler (literally one who has come from afar) w ...
s to the Holy Land
The term "Holy Land" is used to collectively denote areas of the Southern Levant that hold great significance in the Abrahamic religions, primarily because of their association with people and events featured in the Bible. It is traditionall ...
and to establish hospital
A hospital is a healthcare institution providing patient treatment with specialized Medical Science, health science and auxiliary healthcare staff and medical equipment. The best-known type of hospital is the general hospital, which typically ...
s. Its members have commonly been known as the Teutonic Knights, having historically served as a crusading military order for supporting Catholic rule in the Holy Land and the Northern Crusades
The Northern Crusades or Baltic Crusades were Christianization campaigns undertaken by Catholic Church, Catholic Christian Military order (society), military orders and kingdoms, primarily against the paganism, pagan Balts, Baltic, Baltic Finns, ...
during the Middle Ages
In the history of Europe, the Middle Ages or medieval period lasted approximately from the 5th to the late 15th centuries, similarly to the post-classical period of global history. It began with the fall of the Western Roman Empire and ...
, as well as supplying military protection for Catholics in Eastern Europe
Eastern Europe is a subregion of the Europe, European continent. As a largely ambiguous term, it has a wide range of geopolitical, geographical, ethnic, cultural and socio-economic connotations. Its eastern boundary is marked by the Ural Mountain ...
.
Purely religious since 1810, the Teutonic Order still confers limited honorary knighthoods. The Bailiwick of Utrecht of the Teutonic Order, a Protestant
Protestantism is a branch of Christianity that emphasizes Justification (theology), justification of sinners Sola fide, through faith alone, the teaching that Salvation in Christianity, salvation comes by unmerited Grace in Christianity, divin ...
chivalric order, is descended from the same medieval military order and also continues to award knighthoods and perform charitable work.
Name
The name of the Order of Brothers of the German House of Saint Mary in Jerusalem is in and inLatin
Latin ( or ) is a classical language belonging to the Italic languages, Italic branch of the Indo-European languages. Latin was originally spoken by the Latins (Italic tribe), Latins in Latium (now known as Lazio), the lower Tiber area aroun ...
. Thus the term "Teutonic" echoes the German origins of the order () in its Latin name. German-speakers commonly refer to the (official short name, literally "German Order"), historically also as ("German Order of Knights"), ("Order of the German Lords"), ("Order of the German Knights"), ("Knights of Mary"), ("The lords in white capes"), ''etc.''.
The Teutonic Knights have been known as in Polish ("Order of the Cross") and as in Lithuanian, in Latvian, or, simply, ("The Order") in Estonian.
History

 The fraternity which preceded the formation of the Order was formed in the year 1191 in
The fraternity which preceded the formation of the Order was formed in the year 1191 in Acre
The acre ( ) is a Unit of measurement, unit of land area used in the Imperial units, British imperial and the United States customary units#Area, United States customary systems. It is traditionally defined as the area of one Chain (unit), ch ...
by German merchants from Bremen
Bremen (Low German also: ''Breem'' or ''Bräm''), officially the City Municipality of Bremen (, ), is the capital of the States of Germany, German state of the Bremen (state), Free Hanseatic City of Bremen (), a two-city-state consisting of the c ...
and Lübeck
Lübeck (; or ; Latin: ), officially the Hanseatic League, Hanseatic City of Lübeck (), is a city in Northern Germany. With around 220,000 inhabitants, it is the second-largest city on the German Baltic Sea, Baltic coast and the second-larg ...
. After the capture of Acre they took over a hospital in the city in order to take care of the sick and began to describe themselves as the Hospital of St. Mary of the German House in Jerusalem. Pope Clement III approved it and the Order started to play an important role in Outremer
The Crusader states, or Outremer, were four Catholic polities established in the Levant region and southeastern Anatolia from 1098 to 1291. Following the principles of feudalism, the foundation for these polities was laid by the First Crusade ...
(the general name for the Crusader states
The Crusader states, or Outremer, were four Catholic polities established in the Levant region and southeastern Anatolia from 1098 to 1291. Following the principles of feudalism, the foundation for these polities was laid by the First Crusade ...
), controlling the port tolls of Acre. In 1211, during the second, much weaker Crusader kingdom in the Holy Land, but still long before its final demise in 1291, the Order was invited to the Burzenland (southeastern Transylvania
Transylvania ( or ; ; or ; Transylvanian Saxon dialect, Transylvanian Saxon: ''Siweberjen'') is a List of historical regions of Central Europe, historical and cultural region in Central Europe, encompassing central Romania. To the east and ...
) to help defend the southeastern borders of the Kingdom of Hungary
The Kingdom of Hungary was a monarchy in Central Europe that existed for nearly a millennium, from 1000 to 1946 and was a key part of the Habsburg monarchy from 1526-1918. The Principality of Hungary emerged as a Christian kingdom upon the Coro ...
against the Cumans
The Cumans or Kumans were a Turkic people, Turkic nomadic people from Central Asia comprising the western branch of the Cumania, Cuman–Kipchak confederation who spoke the Cuman language. They are referred to as Polovtsians (''Polovtsy'') in Ru ...
. The Order invited German planters to help build up settlements to provide support. As the Order pushed back the invaders, the settlements expanded. King Andrew II of Hungary
Andrew II (, , , ; 117721 September 1235), also known as Andrew of Jerusalem, was King of Hungary and King of Croatia, Croatia between 1205 and 1235. He ruled the Principality of Halych from 1188 until 1189/1190, and again between 1208/1209 and ...
became concerned he was losing influence. So, in 1225, after Pope Honorius III's papal bull claiming his authority over the Order's territory in Transylvania and its tax exemption toward the king, Andrew expelled the Order.
The Order's next assignment concerned Konrad I of Masovia, who was settling a frontier around Prussia
Prussia (; ; Old Prussian: ''Prūsija'') was a Germans, German state centred on the North European Plain that originated from the 1525 secularization of the Prussia (region), Prussian part of the State of the Teutonic Order. For centuries, ...
, a region named for the Prussians who lived there. Konrad was unable to stop the Prussian raids and the Dobrzyń knights he had gathered for this purpose were defeated, in 1228. So, in coordination with the Holy Roman Empire and Konrad, the Grand Master Hermann von Salza
Hermann von Salza (or Herman of Salza; – 20 March 1239) was the fourth Grand Master of the Teutonic Knights, serving from 1210 to 1239. A skilled diplomat with ties to the Frederick II and the Pope, Hermann oversaw the expansion of the ...
and his Teutonic Order arrived in the region, in 1230. Along with Konrad's forces, the Order pushed back the Prussians and began to push further to conquer and Christianize them.
Through the Golden Bull of Rimini and Treaty of Kruszwica, the Order asserted its claims to the territory that was now secure, the Chełmno Land (also: Ziemia Chełmińska or Kulmerland). From this, the Order created the independent State of the Teutonic Order, to which conquered territory was continuously added. Through the incorporation of the Livonian Brothers of the Sword
The Livonian Brothers of the Sword (; ) was a Catholic Church, Catholic Military order (monastic society), military order established in 1202 during the Livonian Crusade by Albert of Riga, Albert, the third bishop of Riga (or possibly by Theode ...
and further crusading, the added territory included Livonia
Livonia, known in earlier records as Livland, is a historical region on the eastern shores of the Baltic Sea. It is named after the Livonians, who lived on the shores of present-day Latvia.
By the end of the 13th century, the name was extende ...
. Over time, certain kings and dukes of Poland would challenge the Order's land claims, specifically Chełmno Land and, later, Pomerelia
Pomerelia, also known as Eastern Pomerania, Vistula Pomerania, and also before World War II as Polish Pomerania, is a historical sub-region of Pomerania on the southern shore of the Baltic Sea in northern Poland.
Gdańsk Pomerania is largely c ...
(also Pomorze Gdańskie or Vistula Pomerania), Kuyavia
Kuyavia (; ), also referred to as Cuyavia, is a historical region in north-central Poland, situated on the left bank of Vistula, as well as east from Noteć River and Lake Gopło. It is divided into three traditional parts: north-western (with th ...
, and Dobrzyń Land.
Following the Christianization of Lithuania
The Christianization of Lithuania () occurred in 1387, initiated by the Lithuanian royals Jogaila, King of Poland and Grand Duke of Lithuania, and his cousin Vytautas the Great. It signified the official adoption of Catholic Christianity by Li ...
, the Order State was no longer crusading. It was instead recruiting planters from the Holy Roman Empire and a fighting force to augment feudal levies. There were also wars against the Kingdom of Poland
The Kingdom of Poland (; Latin: ''Regnum Poloniae'') was a monarchy in Central Europe during the Middle Ages, medieval period from 1025 until 1385.
Background
The West Slavs, West Slavic tribe of Polans (western), Polans who lived in what i ...
, the Grand Duchy of Lithuania
The Grand Duchy of Lithuania was a sovereign state in northeastern Europe that existed from the 13th century, succeeding the Kingdom of Lithuania, to the late 18th century, when the territory was suppressed during the 1795 Partitions of Poland, ...
, and the Novgorod Republic. Through its control of port cities and trade, specifically with the Hanseatic League
The Hanseatic League was a Middle Ages, medieval commercial and defensive network of merchant guilds and market towns in Central Europe, Central and Northern Europe, Northern Europe. Growing from a few Northern Germany, North German towns in the ...
, the Order State built up its economic base. The Order State also built ships and had a naval presence in the Baltic Sea
The Baltic Sea is an arm of the Atlantic Ocean that is enclosed by the countries of Denmark, Estonia, Finland, Germany, Latvia, Lithuania, Poland, Russia, Sweden, and the North European Plain, North and Central European Plain regions. It is the ...
. In 1410, a Polish-Lithuanian army decisively defeated the Order State and broke its military power at the Battle of Grunwald
The Battle of Grunwald was fought on 15 July 1410 during the Polish–Lithuanian–Teutonic War. The alliance of the Crown of the Kingdom of Poland and the Grand Duchy of Lithuania, led respectively by King Władysław II Jagiełło (Jogaila), a ...
. However, the Order State successfully defended its capital in the following Siege of Marienburg (Malbork
Malbork (German: ''Marienburg'') is a town in the Pomeranian Voivodeship, Poland. It is the seat of Malbork County and has a population of 36,709 people as of 2024. The town is located on the Nogat river, in the historical region of Pomerelia.
Fo ...
) and was saved from collapse.
In 1515, Holy Roman Emperor
The Holy Roman Emperor, originally and officially the Emperor of the Romans (disambiguation), Emperor of the Romans (; ) during the Middle Ages, and also known as the Roman-German Emperor since the early modern period (; ), was the ruler and h ...
Maximilian I made a marriage alliance with Sigismund I of Poland-Lithuania. Thereafter, the empire did not support the Order against Poland. In 1525, Grand Master Albert of Brandenburg resigned and converted to Lutheranism
Lutheranism is a major branch of Protestantism that emerged under the work of Martin Luther, the 16th-century German friar and Protestant Reformers, reformer whose efforts to reform the theology and practices of the Catholic Church launched ...
, becoming Duke of Prussia as a vassal of Poland. Soon after, the Order lost Livonia and its holdings in the Protestant areas of Germany. The Order did keep its considerable holdings in Catholic areas of Germany until 1809, when Napoleon Bonaparte
Napoleon Bonaparte (born Napoleone di Buonaparte; 15 August 1769 – 5 May 1821), later known by his regnal name Napoleon I, was a French general and statesman who rose to prominence during the French Revolution and led Military career ...
ordered its dissolution and the Order lost its last secular holdings.
However, the Order continued to exist as a charitable and ceremonial body. It was outlawed by Nazi Germany
Nazi Germany, officially known as the German Reich and later the Greater German Reich, was the German Reich, German state between 1933 and 1945, when Adolf Hitler and the Nazi Party controlled the country, transforming it into a Totalit ...
in 1938, but re-established in 1945. Today it operates primarily with charitable aims in Central Europe
Central Europe is a geographical region of Europe between Eastern Europe, Eastern, Southern Europe, Southern, Western Europe, Western and Northern Europe, Northern Europe. Central Europe is known for its cultural diversity; however, countries in ...
.
The Knights wore white surcoat
A surcoat or surcote is an outer garment that was commonly worn in the Middle Ages by soldiers. It was worn over armor to show insignia and help identify what side the soldier was on. In the battlefield the surcoat was also helpful with keeping ...
s with a black cross. A cross pattée
A cross pattée or cross patty (, ), also known as a cross formée or cross formy, or even a Templar cross, is a type of Christian cross with arms that are narrow at the centre and often flared in a curve or straight line shape to be broader at th ...
was sometimes used as their coat of arms
A coat of arms is a heraldry, heraldic communication design, visual design on an escutcheon (heraldry), escutcheon (i.e., shield), surcoat, or tabard (the last two being outer garments), originating in Europe. The coat of arms on an escutcheon f ...
; this emblem was later used for military decoration and insignia by the Kingdom of Prussia
The Kingdom of Prussia (, ) was a German state that existed from 1701 to 1918.Marriott, J. A. R., and Charles Grant Robertson. ''The Evolution of Prussia, the Making of an Empire''. Rev. ed. Oxford: Clarendon Press, 1946. It played a signif ...
and Germany as the Iron Cross
The Iron Cross (, , abbreviated EK) was a military decoration in the Kingdom of Prussia, the German Empire (1871–1918), and Nazi Germany (1933–1945). The design, a black cross pattée with a white or silver outline, was derived from the in ...
. The motto of the Order was: "Helfen, Wehren, Heilen" ("Help, Defend, Heal").
Foundation
 In 1143, Pope Celestine II ordered the
In 1143, Pope Celestine II ordered the Knights Hospitaller
The Order of Knights of the Hospital of Saint John of Jerusalem, commonly known as the Knights Hospitaller (), is a Catholic military order. It was founded in the crusader Kingdom of Jerusalem in the 12th century and had headquarters there ...
to take over management of a German hospital in Jerusalem
Jerusalem is a city in the Southern Levant, on a plateau in the Judaean Mountains between the Mediterranean Sea, Mediterranean and the Dead Sea. It is one of the List of oldest continuously inhabited cities, oldest cities in the world, and ...
, which, according to the chronicler Jean d'Ypres, accommodated the countless German pilgrims and crusaders who could neither speak the local language nor Latin (''patriæ linguam ignorantibus atque Latinam''). Although formally an institution of the Hospitallers, the pope commanded that the prior and the brothers of the ''domus Theutonicorum'' (house of the Germans) should always be Germans themselves, so a tradition of a German-led religious institution could develop during the 12th century in the Kingdom of Jerusalem
The Kingdom of Jerusalem, also known as the Crusader Kingdom, was one of the Crusader states established in the Levant immediately after the First Crusade. It lasted for almost two hundred years, from the accession of Godfrey of Bouillon in 1 ...
.
After the loss of Jerusalem in 1187, some merchants from Lübeck
Lübeck (; or ; Latin: ), officially the Hanseatic League, Hanseatic City of Lübeck (), is a city in Northern Germany. With around 220,000 inhabitants, it is the second-largest city on the German Baltic Sea, Baltic coast and the second-larg ...
and Bremen
Bremen (Low German also: ''Breem'' or ''Bräm''), officially the City Municipality of Bremen (, ), is the capital of the States of Germany, German state of the Bremen (state), Free Hanseatic City of Bremen (), a two-city-state consisting of the c ...
took up the idea and founded a field hospital for the duration of the Siege of Acre in 1190, which became the nucleus of the order; Pope Celestine III recognized it in 1192 by granting the monks Augustinian Rule. However, based on the model of the Knights Templar
The Poor Fellow-Soldiers of Christ and of the Temple of Solomon, mainly known as the Knights Templar, was a Military order (religious society), military order of the Catholic Church, Catholic faith, and one of the most important military ord ...
, it was transformed into a military order in 1198 and the head of the order became known as the Grand Master (''magister hospitalis''). It received papal orders for crusades to take and hold Jerusalem for Christianity and defend the Holy Land against the Muslim Saracen
upright 1.5, Late 15th-century German woodcut depicting Saracens
''Saracen'' ( ) was a term used both in Greek and Latin writings between the 5th and 15th centuries to refer to the people who lived in and near what was designated by the Rom ...
s. During the rule of Grand Master Hermann von Salza
Hermann von Salza (or Herman of Salza; – 20 March 1239) was the fourth Grand Master of the Teutonic Knights, serving from 1210 to 1239. A skilled diplomat with ties to the Frederick II and the Pope, Hermann oversaw the expansion of the ...
(1209–1239) the Order changed from being a hospice
Hospice care is a type of health care that focuses on the palliation of a terminally ill patient's pain and symptoms and attending to their emotional and spiritual needs at the end of life. Hospice care prioritizes comfort and quality of life b ...
brotherhood for pilgrims to primarily a military order.
The Order was founded in Acre, and the Knights purchased Montfort Castle, northeast of Acre, in 1220. This castle, which defended the route between Jerusalem and the Mediterranean Sea
The Mediterranean Sea ( ) is a sea connected to the Atlantic Ocean, surrounded by the Mediterranean basin and almost completely enclosed by land: on the east by the Levant in West Asia, on the north by Anatolia in West Asia and Southern Eur ...
, was made the seat of the Grand Masters in 1229, although they returned to Acre after losing Montfort to Muslim control in 1271. The Order received donations of land in the Holy Roman Empire
The Holy Roman Empire, also known as the Holy Roman Empire of the German Nation after 1512, was a polity in Central and Western Europe, usually headed by the Holy Roman Emperor. It developed in the Early Middle Ages, and lasted for a millennium ...
(especially in present-day Germany and Italy
Italy, officially the Italian Republic, is a country in Southern Europe, Southern and Western Europe, Western Europe. It consists of Italian Peninsula, a peninsula that extends into the Mediterranean Sea, with the Alps on its northern land b ...
), Frankokratia
The Frankish Occupation (; anglicized as ), also known as the Latin Occupation () and, for the Venetian domains, Venetian Occupation (), was the period in Greek history after the Fourth Crusade (1204), when a number of primarily French ...
, and the Kingdom of Jerusalem.
Frederick II, Holy Roman Emperor
Frederick II (, , , ; 26 December 1194 – 13 December 1250) was King of Sicily from 1198, King of Germany from 1212, King of Italy and Holy Roman Emperor from 1220 and King of Jerusalem from 1225. He was the son of Emperor Henry VI, Holy Roman ...
, elevated his close friend Hermann von Salza to the status of '' Reichsfürst'', or "Prince of the Empire", enabling the Grand Master to negotiate with other senior princes as an equal. During Frederick's coronation as King of Jerusalem
The king or queen of Jerusalem was the supreme ruler of the Kingdom of Jerusalem, a Crusader state founded in Jerusalem by the Latin Church, Latin Catholic leaders of the First Crusade, when the city was Siege of Jerusalem (1099), conquered in ...
in 1225, Teutonic Knights served as his escort in the Church of the Holy Sepulchre
The Church of the Holy Sepulchre, also known as the Church of the Resurrection, is a fourth-century church in the Christian Quarter of the Old City of Jerusalem, Old City of Jerusalem. The church is the seat of the Greek Orthodox Patriarchat ...
; von Salza read the emperor's proclamation in both French and German. However, the Teutonic Knights were never as influential in Outremer
The Crusader states, or Outremer, were four Catholic polities established in the Levant region and southeastern Anatolia from 1098 to 1291. Following the principles of feudalism, the foundation for these polities was laid by the First Crusade ...
as the older Knights Templar
The Poor Fellow-Soldiers of Christ and of the Temple of Solomon, mainly known as the Knights Templar, was a Military order (religious society), military order of the Catholic Church, Catholic faith, and one of the most important military ord ...
and Knights Hospitaller
The Order of Knights of the Hospital of Saint John of Jerusalem, commonly known as the Knights Hospitaller (), is a Catholic military order. It was founded in the crusader Kingdom of Jerusalem in the 12th century and had headquarters there ...
.
Teutonic Order domains in the Levant:
* In the Kingdom of Jerusalem
The Kingdom of Jerusalem, also known as the Crusader Kingdom, was one of the Crusader states established in the Levant immediately after the First Crusade. It lasted for almost two hundred years, from the accession of Godfrey of Bouillon in 1 ...
:
** Montfort Castle (''Starkenberg''), 1220–1271; inland from Nahariya
Nahariya () is the northernmost coastal city in Israel. As of , the city had a population of .
The city was founded in 1935 by Jewish refugees fleeing Nazi Germany.
Etymology
Nahariya takes its name from the stream of Ga'aton River, Ga'aton (riv ...
in Northern Israel
** Mi'ilya
Mi'ilya (, ), also called Mi'elya, is an Arab local council in the western Galilee in the Northern District of Israel. Its name during the Kingdom of Jerusalem era in Galilee was Castellum Regis. In it had a population of , all of whom are M ...
(''Castellum Regis''), 1220–1271; near Montfort
** Khirbat Jiddin (''Judin''), 1220–1271; near Montfort
** Cafarlet, 1255–1291; south of Haifa
Haifa ( ; , ; ) is the List of cities in Israel, third-largest city in Israel—after Jerusalem and Tel Aviv—with a population of in . The city of Haifa forms part of the Haifa metropolitan area, the third-most populous metropolitan area i ...
** the Lordship of Toron and Lordship of Joscelin in Northern Israel and Southern Lebanon, both owned by the Teutonic Knights 1220–1229 but under Muslim rule during that period. The Knights retained Maron, a vassal of Toron, after 1229, and in 1261 acquired another Toron-Ahmud, another vassal lordship. They also leased (1256) and bought (1261) the stronghold of Achziv (''Casale Umberti'', Arabic ''Az-Zīb'') on the coast north of Nahariya
Nahariya () is the northernmost coastal city in Israel. As of , the city had a population of .
The city was founded in 1935 by Jewish refugees fleeing Nazi Germany.
Etymology
Nahariya takes its name from the stream of Ga'aton River, Ga'aton (riv ...
.
** the Lordship of the Schuf, an offshoot of the Lordship of Sidon, 1256–1268; inland from modern Saida in Lebanon
* In the Armenian Kingdom of Cilicia
The Armenian Kingdom of Cilicia, also known as Cilician Armenia, Lesser Armenia, Little Armenia or New Armenia, and formerly known as the Armenian Principality of Cilicia, was an Armenian state formed during the High Middle Ages by Armenian ...
:
** Amouda, 1212–1266; near modern Osmaniye, Turkey
** Düziçi (''Aronia''), 1236–1270s; near Amouda
Transylvania, Kingdom of Hungary
In 1211,Andrew II of Hungary
Andrew II (, , , ; 117721 September 1235), also known as Andrew of Jerusalem, was King of Hungary and King of Croatia, Croatia between 1205 and 1235. He ruled the Principality of Halych from 1188 until 1189/1190, and again between 1208/1209 and ...
accepted the services of the Teutonic Knights and granted them the district of Burzenland in Transylvania
Transylvania ( or ; ; or ; Transylvanian Saxon dialect, Transylvanian Saxon: ''Siweberjen'') is a List of historical regions of Central Europe, historical and cultural region in Central Europe, encompassing central Romania. To the east and ...
, where they would be exempt from fees and duties and could administer their own justice. Andrew had been involved in negotiations for the marriage of his daughter with the son of Hermann, Landgrave of Thuringia
Thuringia (; officially the Free State of Thuringia, ) is one of Germany, Germany's 16 States of Germany, states. With 2.1 million people, it is 12th-largest by population, and with 16,171 square kilometers, it is 11th-largest in area.
Er ...
, whose vassals included the family of Hermann von Salza. Led by a brother called Theoderich or Dietrich, the Order defended the south-eastern borders of the Kingdom of Hungary against the neighbouring Cumans
The Cumans or Kumans were a Turkic people, Turkic nomadic people from Central Asia comprising the western branch of the Cumania, Cuman–Kipchak confederation who spoke the Cuman language. They are referred to as Polovtsians (''Polovtsy'') in Ru ...
. Many forts of wood and mud were built for defence. They settled new German peasants among the existing Transylvanian Saxon inhabitants. The Cumans had no fixed settlements for resistance, and soon the Teutons
The Teutons (, ; ) were an ancient northern European tribe mentioned by Roman authors. The Teutons are best known for their participation, together with the Cimbri and other groups, in the Cimbrian War with the Roman Republic in the late seco ...
were expanding into their territory. By 1220, the Teutonics Knights had built five castles, some of them made of stone. Their rapid expansion made the Hungarian nobility and clergy, who were previously uninterested in those regions, jealous and suspicious. Some nobles claimed these lands, but the Order refused to share them, ignoring the demands of the local bishop.
After the Fifth Crusade, King Andrew returned to Hungary and found his kingdom full of resentment because of the expenses and losses of the failed military campaign. When the nobles demanded that he cancel the concessions made to the Knights, he concluded that they had exceeded their task and that the agreement should be revised, but did not revert the concessions. However, Prince Béla, heir to the throne, was allied with the nobility. In 1224, the Teutonic Knights, seeing that they would have problems when the Prince inherited the Kingdom, petitioned Pope Honorius III to be placed directly under the authority of the Papal See, rather than that of the King of Hungary. This was a grave mistake, as King Andrew, angered and alarmed at their growing power, responded in 1225 by expelling the Teutonic Knights, although he allowed the ethnically German commoners and peasants settled here by the Order to remain and these became part of the larger group of the Transylvanian Saxons. Lacking the military organization and experience of the Teutonic Knights, the Hungarians failed to replace them with adequate defence against the attacking Cumans. Soon, the steppe warriors would be a threat again.
Prussia
In 1226, Konrad I, Duke ofMasovia
Mazovia or Masovia ( ) is a historical region in mid-north-eastern Poland. It spans the North European Plain, roughly between Łódź and Białystok, with Warsaw being the largest city and Płock being the capital of the region . Throughout the ...
in north-eastern Poland, appealed to the Knights to defend his borders and subdue the pagan Baltic Old Prussians, allowing the Teutonic Knights use of Chełmno Land as a base for their campaign. This being a time of widespread crusading fervor throughout Western Europe, Hermann von Salza considered Prussia
Prussia (; ; Old Prussian: ''Prūsija'') was a Germans, German state centred on the North European Plain that originated from the 1525 secularization of the Prussia (region), Prussian part of the State of the Teutonic Order. For centuries, ...
a good training ground for his knights for the wars against the Muslim
Muslims () are people who adhere to Islam, a Monotheism, monotheistic religion belonging to the Abrahamic religions, Abrahamic tradition. They consider the Quran, the foundational religious text of Islam, to be the verbatim word of the God ...
s in Outremer
The Crusader states, or Outremer, were four Catholic polities established in the Levant region and southeastern Anatolia from 1098 to 1291. Following the principles of feudalism, the foundation for these polities was laid by the First Crusade ...
. With the Golden Bull of Rimini, Emperor Frederick II bestowed on the Order a special imperial privilege for the conquest and possession of Prussia, including Chełmno Land, with nominal papal sovereignty. In 1235 the Teutonic Knights assimilated the smaller Order of Dobrzyń, which had been established earlier by Christian
A Christian () is a person who follows or adheres to Christianity, a Monotheism, monotheistic Abrahamic religion based on the life and teachings of Jesus in Christianity, Jesus Christ. Christians form the largest religious community in the wo ...
, the first Bishop of Prussia.
The conquest of Prussia was accomplished with much bloodshed over more than fifty years, during which native Prussians who remained unbaptised were subjugated, killed, or exiled. Fighting between the Knights and the Prussians was ferocious; chronicles of the Order state the Prussians would "roast captured brethren alive in their armour, like chestnuts, before the shrine of a local god".
The native nobility who submitted to the crusaders had many of their privileges confirmed by the Treaty of Christburg. After the Prussian uprisings of 1260–83, however, much of the Prussian nobility emigrated or were resettled, and many free Prussians lost their rights. The Prussian nobles who remained were more closely allied with the German landowners and were gradually assimilated. Peasants in frontier regions, such as Samland, had more privileges than those in more populated lands, such as Pomesania. The crusading knights often accepted baptism
Baptism (from ) is a Christians, Christian sacrament of initiation almost invariably with the use of water. It may be performed by aspersion, sprinkling or affusion, pouring water on the head, or by immersion baptism, immersing in water eit ...
as a form of submission by the natives. Christianity along western lines slowly spread through Prussian culture. Bishops were reluctant to have pagan Prussian religious practices integrated into the new faith, while the ruling knights found it easier to govern the natives when they were semi-pagan and lawless. After fifty years of warfare and brutal conquest, the end result was that most of the Prussian natives were either killed or deported.
 The Order ruled Prussia under charters issued by the Pope and the Holy Roman Emperor as a
The Order ruled Prussia under charters issued by the Pope and the Holy Roman Emperor as a sovereign
''Sovereign'' is a title that can be applied to the highest leader in various categories. The word is borrowed from Old French , which is ultimately derived from the Latin">-4; we might wonder whether there's a point at which it's appropriate to ...
monastic state, comparable to the arrangement of the Knights Hospitallers in Rhodes
Rhodes (; ) is the largest of the Dodecanese islands of Greece and is their historical capital; it is the List of islands in the Mediterranean#By area, ninth largest island in the Mediterranean Sea. Administratively, the island forms a separ ...
and later in Malta
Malta, officially the Republic of Malta, is an island country in Southern Europe located in the Mediterranean Sea, between Sicily and North Africa. It consists of an archipelago south of Italy, east of Tunisia, and north of Libya. The two ...
.
To make up for losses from the plague and to replace the partially exterminated native population, the Order encouraged immigration
Immigration is the international movement of people to a destination country of which they are not usual residents or where they do not possess nationality in order to settle as Permanent residency, permanent residents. Commuting, Commuter ...
from the Holy Roman Empire (mostly Germans
Germans (, ) are the natives or inhabitants of Germany, or sometimes more broadly any people who are of German descent or native speakers of the German language. The Basic Law for the Federal Republic of Germany, constitution of Germany, imple ...
, Flemish, and Dutch) and from Masovia (Poles
Pole or poles may refer to:
People
*Poles (people), another term for Polish people, from the country of Poland
* Pole (surname), including a list of people with the name
* Pole (musician) (Stefan Betke, born 1967), German electronic music artist
...
), the later Masurians
The Masurians or Mazurs (; ; Masurian dialects, Masurian: ''Mazurÿ''), historically also known as Prussian Masurians (Polish language, Polish: ''Mazurzy pruscy''), are an ethnic group originating from the region of Masuria, within the Warmian- ...
. These included nobles, burghers, and peasants, and the surviving Old Prussians were gradually assimilated through Germanization
Germanisation, or Germanization, is the spread of the German language, German people, people, and German culture, culture. It was a central idea of German conservative thought in the 19th and the 20th centuries, when conservatism and ethnic nati ...
. The settlers founded numerous towns and cities on former Prussian settlements. The Order itself built a number of castles (''Ordensburg
''Ordensburg'' (plural ''Ordensburgen'') is a German language, German term meaning a "castle of a (military) order". It is used specifically for the fortified structures built by Crusades, crusading German Military order (religious society), m ...
en'') from which it could defeat uprisings of Old Prussians, as well as continue its attacks on the Grand Duchy of Lithuania and the Kingdom of Poland, with which the Order was often at war during the 14th and 15th centuries. Major towns founded by the Order included Thorn (Toruń), Kulm (Chełmno), Allenstein (Olsztyn), Elbing (Elbląg), Memel (Klaipėda), and Königsberg
Königsberg (; ; ; ; ; ; , ) is the historic Germany, German and Prussian name of the city now called Kaliningrad, Russia. The city was founded in 1255 on the site of the small Old Prussians, Old Prussian settlement ''Twangste'' by the Teuton ...
, founded in 1255 in honor of King Otakar II of Bohemia on the site of a destroyed Prussian settlement.
Livonia
Battle of Saule
The Battle of Saule (; ; ) was fought on 22 September 1236, between the Livonian Brothers of the Sword and pagan troops of Samogitians and Semigallians. Between 48 and 60 knights were killed, including the Livonian Master, Volkwin. It was the ea ...
, the Livonian Brothers of the Sword
The Livonian Brothers of the Sword (; ) was a Catholic Church, Catholic Military order (monastic society), military order established in 1202 during the Livonian Crusade by Albert of Riga, Albert, the third bishop of Riga (or possibly by Theode ...
were absorbed by the Teutonic Knights in 1237. The Livonian branch subsequently became known as the Livonian Order
The Livonian Order was an autonomous branch of the Teutonic Order,
formed in 1237. From 1435 to 1561 it was a member of the Livonian Confederation.
History
The order was formed from the remnants of the Livonian Brothers of the Sword after thei ...
.
Although the Northern Crusades
The Northern Crusades or Baltic Crusades were Christianization campaigns undertaken by Catholic Church, Catholic Christian Military order (society), military orders and kingdoms, primarily against the paganism, pagan Balts, Baltic, Baltic Finns, ...
were aimed at pagan Balts
The Balts or Baltic peoples (, ) are a group of peoples inhabiting the eastern coast of the Baltic Sea who speak Baltic languages. Among the Baltic peoples are modern-day Lithuanians (including Samogitians) and Latvians (including Latgalians ...
and Finns
Finns or Finnish people (, ) are a Baltic Finns, Baltic Finnic ethnic group native to Finland. Finns are traditionally divided into smaller regional groups that span several countries adjacent to Finland, both those who are native to these cou ...
, rather than Orthodox Russians, several unsuccessful attempts were made to persuade Novgorod to convert to Catholicism after the capture of Tartu
Tartu is the second largest city in Estonia after Tallinn. Tartu has a population of 97,759 (as of 2024). It is southeast of Tallinn and 245 kilometres (152 miles) northeast of Riga, Latvia. Tartu lies on the Emajõgi river, which connects the ...
. Livonian missionary and Crusade activity in Estonia caused conflicts with Novgorod
Veliky Novgorod ( ; , ; ), also known simply as Novgorod (), is the largest city and administrative centre of Novgorod Oblast, Russia. It is one of the oldest cities in Russia, being first mentioned in the 9th century. The city lies along the V ...
, which had also attempted to subjugate, raid and convert the pagan Estonians. Hoping to exploit Novgorod's weakness in the wake of the Mongol and Swedish invasions, the Teutonic Knights penetrated deep into Novgorodian territory; however, in 1242, they were defeated in the Battle of the Ice at the hands of Prince Alexander Nevsky
Alexander Yaroslavich Nevsky (; ; monastic name: ''Aleksiy''; 13 May 1221 – 14 November 1263) was Prince of Novgorod (1236–1240; 1241–1256; 1258–1259), Grand Prince of Kiev (1249–1263), and Grand Prince of Vladimir (1252–1263).
...
. The '' Livonian Rhymed Chronicle'' describes the events:
Over the next decades the Order focused on the subjugation of the Curonians
:''The Kursenieki are also sometimes known as Curonians.''
The Curonians or Kurs (; ) were a medieval Balts, Baltic tribe living on the shores of the Baltic Sea in the 5th–16th centuries, in what are now western parts of Latvia and Lithuania. ...
and Semigallians
Semigallians (; ; also ''Zemgalians'', ''Semigalls'' or ''Semigalians'') were the Balts, Baltic tribe that lived in the south central part of contemporary Latvia and northern Lithuania. They are noted for their long resistance (1219–1290) agai ...
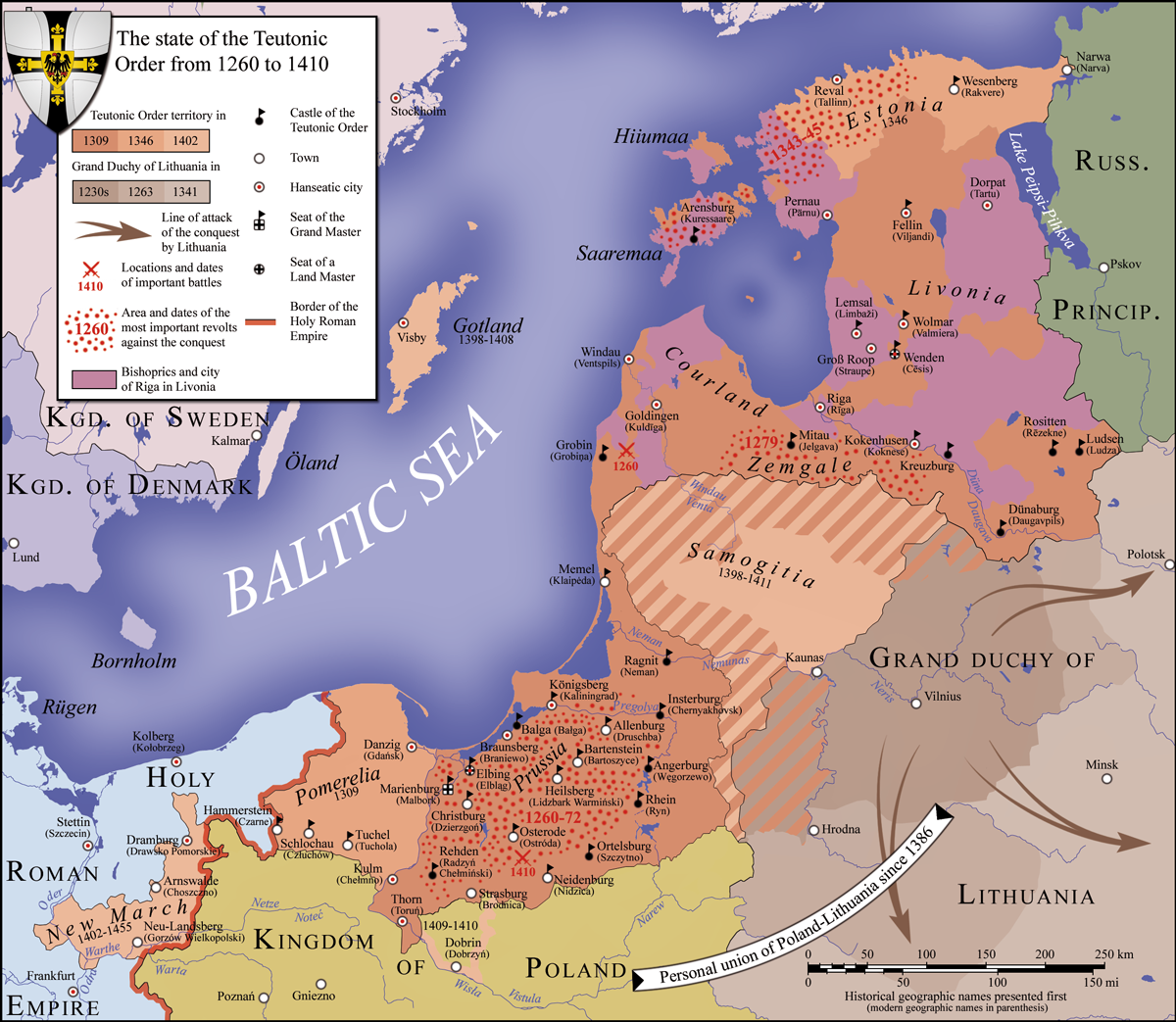
. In 1260 it suffered a disastrous defeat in the Battle of Durbe against Samogitians, and this inspired rebellions throughout Prussia and Livonia. After the Knights won a crucial victory in the Siege of Königsberg from 1262 to 1265, the war had reached a turning point. The Curonians were finally subjugated in 1267 and the Semigallians in 1290. The Order suppressed a St. George's Night Uprising, major Estonian rebellion in 1343–1345, and in 1346 purchased the Danish Estonia#Duchy of Estonia, Duchy of Estonia from Denmark.
Against Lithuania
The Teutonic Knights began to direct their campaigns against pagan Grand Duchy of Lithuania, Lithuania (see Lithuanian mythology), due to the long existing conflicts in the region (including constant incursions into the Holy Roman Empire's territory by pagan raiding parties) and the lack of a proper area of operation for the Knights, after the fall of the Kingdom of Jerusalem at Siege of Acre (1291), Acre in 1291 and their later expulsion from Hungary. At first the knights moved their headquarters to Venice, from which they planned the recovery of Outremer; this plan was, however, soon abandoned, and the Order later moved its headquarters to Marienburg, so it could better focus its efforts on the region of Prussia. Because "Lithuania proper, Lithuania Propria" remained non-Christian until the end of the 14th century, much later than the rest of eastern Europe, the conflicts were dragged out over a longer time, and many Knights from western European countries, such as England and France, journeyed to Prussia to participate in the seasonal campaigns (''reyse'') against the Grand Duchy of Lithuania. In 1348, the Order won a great victory over the Lithuanians in the Battle of Strėva, severely weakening them. In 1370 it won a decisive victory over Lithuania in the Battle of Rudau. Warfare between the Order and the Lithuanians was particularly brutal. It was common practice for Lithuanians to torture captured enemies and civilians. It is recorded by a Teutonic chronicler that they had the habit of tying captured knights to their horses and having both of them burned alive, while sometimes a stake would be driven into their bodies or the knight would be flayed. Lithuanian pagan customs included ritualistic human sacrifice, the hanging of widows, and the burying of a warrior's horses and servants with him after his death. The knights would also, on occasion, take captives from defeated Lithuanians, whose condition (as that of other war captives in the Middle Ages) was extensively researched by Jacques Heers. The conflict had much influence in the political situation of the region and was the source of many rivalries between Lithuanians or Poles and Germans; the degree to which it impacted the mentalities of the time can be seen in the lyrical works of men such as the contemporary Archduchy of Austria, Austrian poet Peter Suchenwirt. Overall, the conflict lasted over 200 years (although with varying degrees of active hostility during that time), its front line extending along both banks of the Neman River, with as many as twenty forts and castles between Seredžius and Jurbarkas alone.Against Poland
 A dispute over the claims to
A dispute over the claims to Pomerelia
Pomerelia, also known as Eastern Pomerania, Vistula Pomerania, and also before World War II as Polish Pomerania, is a historical sub-region of Pomerania on the southern shore of the Baltic Sea in northern Poland.
Gdańsk Pomerania is largely c ...
embroiled the Order in further conflict at the beginning of the 14th century. Duke Władysław I the Elbow-high of Poland wanted the region, citing inheritance from Przemysł II. He was opposed by some Pomeranian nobles, but also a Christopher II of Denmark, Danish prince, who supported the Margrave of Waldemar, Margrave of Brandenburg-Stendal, Brandenburg's claim that the region had been granted to Brandenburg as a fief by King Wenceslaus III of Bohemia, Wenceslaus. Forces from Denmark and Brandenburg had tried and failed to take the site in 1301 and 1306 but, in the summer of 1308, Brandenburg's forces tried again, targeting the present-day site of Gdańsk, where a rebellion had erupted in their favor. Władysław pressed the Teutonic Order for help and the Teutonic Knights, led by Grand Master Siegfried von Feuchtwangen, drove Brandenburg out. The Knights requested payment in exchange and Władysław refused.
By November, the Order forces under a Prussian Landmeister Heinrich von Plötzke took the site for themselves. According to some sources, they Teutonic takeover of Danzig (Gdańsk), massacred the town's inhabitants, although the exact extent of the violence is unknown and widely recognized by historians to be an unsolvable mystery. The estimates range from 60 rebellious leaders, reported by dignitaries of the region and Knight chroniclers, to 10,000 civilians, a number cited in a papal bull (of dubious provenance) that was used in a legal process installed to punish the Order for the event; the legal dispute went on for a time, but the Order was eventually absolved of the charges. In the Treaty of Soldin (1309), Treaty of Soldin, the Teutonic Order purchased the castles of Gdańsk, Świecie, and Tczew and their hinterlands from the margraves for 10,000 marks on 13 September 1309.
Control of Pomerelia allowed the Order to connect their monastic state with the borders of the Holy Roman Empire. Crusading reinforcements and supplies could travel from the Imperial territory of Hither Pomerania through Pomerelia to Prussia, while Poland's access to the Baltic Sea was blocked. While Poland had mostly been an ally of the knights against the pagan Prussians and Lithuanians, the capture of Pomerelia turned the kingdom into a determined enemy of the Order.
The capture of Gdańsk marked a new phase in the history of the Teutonic Knights. The persecution and abolition of the powerful Knights Templar, which began in 1307, worried the Teutonic Knights, but control of Pomerelia allowed them to move their headquarters in 1309 from Venice to Malbork, Marienburg (Malbork) on the Nogat River, outside the reach of secular powers. The position of Prussian Landmeister was merged with that of the Grand Master. The Pope began investigating misconduct by the knights, but no charges were found to have substance. Along with the campaigns against the Lithuanians, the knights faced a vengeful Poland and legal threats from the Papacy.
The Treaty of Kalisz (1343), Treaty of Kalisz of 1343 ended the open war between the Teutonic Knights and Poland. The Knights relinquished Kuyavia
Kuyavia (; ), also referred to as Cuyavia, is a historical region in north-central Poland, situated on the left bank of Vistula, as well as east from Noteć River and Lake Gopło. It is divided into three traditional parts: north-western (with th ...
and Dobrzyń Land to Poland, but retained Chełmno Land and Pomerelia with Gdańsk (Germanized as ''Danzig'').
Battle of Legnica
In 1236, the Knights of Saint Thomas, an English order, adopted the rules of the Teutonic Order. A contingent of Teutonic Knights of indeterminate number is traditionally believed to have participated at the Battle of Legnica in 1241 during the first Mongol invasion of Poland. The combined Polish-German army was crushed by the Mongol army and their superior tactics, with few survivors.Height of power
 In 1337, Emperor Louis IV, Holy Roman Emperor, Louis IV allegedly granted the Order the imperial privilege to conquer all Lithuania and Russia. During the reign of Grand Master Winrich von Kniprode (1351–1382), the Order reached the peak of its international prestige and hosted numerous European crusaders and nobility.
King Albert of Sweden ceded Gotland to the Order as a pledge (similar to a fiefdom), with the understanding that they would eliminate the pirating Victual Brothers from this strategic island base in the
In 1337, Emperor Louis IV, Holy Roman Emperor, Louis IV allegedly granted the Order the imperial privilege to conquer all Lithuania and Russia. During the reign of Grand Master Winrich von Kniprode (1351–1382), the Order reached the peak of its international prestige and hosted numerous European crusaders and nobility.
King Albert of Sweden ceded Gotland to the Order as a pledge (similar to a fiefdom), with the understanding that they would eliminate the pirating Victual Brothers from this strategic island base in the Baltic Sea
The Baltic Sea is an arm of the Atlantic Ocean that is enclosed by the countries of Denmark, Estonia, Finland, Germany, Latvia, Lithuania, Poland, Russia, Sweden, and the North European Plain, North and Central European Plain regions. It is the ...
. An invasion force under Grand Master Konrad von Jungingen conquered the island in 1398 and drove the Victual Brothers out of Gotland and the Baltic Sea.
In 1386, Grand Duke Jogaila of Lithuania was baptism, baptised into Christianity and married Queen Jadwiga of Poland, taking the name Władysław II Jagiełło and becoming King of Poland. This created a Polish–Lithuanian union, personal union between the two countries and a potentially formidable opponent for the Teutonic Knights. The Order initially managed to play Władysław II Jagiełło and his cousin Vytautas the Great, Vytautas against each other, but this strategy failed when Vytautas began to suspect that the Order was planning to annex parts of his territory.
The baptism of Jogaila began the official conversion of Lithuania to Christianity. Although the crusading rationale for the Order's state ended when Prussia and Lithuania had become officially Christian, the Order's feuds and wars with Lithuania and Poland continued. The Lizard Union (medieval), Lizard Union was created in 1397 by Prussian nobles in Chełmno Land to oppose the Order's policy.
In 1407, the Teutonic Order reached its greatest territorial extent and included the lands of Prussia
Prussia (; ; Old Prussian: ''Prūsija'') was a Germans, German state centred on the North European Plain that originated from the 1525 secularization of the Prussia (region), Prussian part of the State of the Teutonic Order. For centuries, ...
, Pomerelia
Pomerelia, also known as Eastern Pomerania, Vistula Pomerania, and also before World War II as Polish Pomerania, is a historical sub-region of Pomerania on the southern shore of the Baltic Sea in northern Poland.
Gdańsk Pomerania is largely c ...
, Samogitia, Courland, Livonia
Livonia, known in earlier records as Livland, is a historical region on the eastern shores of the Baltic Sea. It is named after the Livonians, who lived on the shores of present-day Latvia.
By the end of the 13th century, the name was extende ...
, Estonia, Gotland, Hiiumaa, Dagö, Saaremaa, Ösel, and the Neumark, pawned by Brandenburg in 1402.
Decline
In 1410, at theBattle of Grunwald
The Battle of Grunwald was fought on 15 July 1410 during the Polish–Lithuanian–Teutonic War. The alliance of the Crown of the Kingdom of Poland and the Grand Duchy of Lithuania, led respectively by King Władysław II Jagiełło (Jogaila), a ...
a combined Polish–Lithuanian army, led by Władysław II Jagiełło and Vytautas, decisively defeated the Order in the Polish–Lithuanian–Teutonic War. Grand Master Ulrich von Jungingen and most (50 out of 60) of the Order's higher dignitaries fell on the battlefield. The Polish–Lithuanian army then began the Siege of Marienburg (Malbork
Malbork (German: ''Marienburg'') is a town in the Pomeranian Voivodeship, Poland. It is the seat of Malbork County and has a population of 36,709 people as of 2024. The town is located on the Nogat river, in the historical region of Pomerelia.
Fo ...
), the capital of the Order, but was unable to take Malbork Castle, Marienburg owing to the resistance of Heinrich von Plauen. When the Peace of Thorn (1411), First Peace of Thorn was signed in 1411, the Order managed to retain essentially all of its territories, although the Knights' reputation as invincible warriors was irreparably damaged.
While Poland and Lithuania were growing in power, that of the Teutonic Knights dwindled through infighting. They were forced to impose high taxes to pay a substantial indemnity but did not give the cities sufficient requested representation in the administration of their state. The authoritarian and reforming Grand Master Heinrich von Plauen was forced from power and replaced by Michael Küchmeister von Sternberg, but the new Grand Master was unable to revive the Order's fortunes. After the Gollub War the Knights lost some small border regions and renounced all claims to Samogitia in the 1422 Treaty of Melno. Austrians, Austrian and Bavarians, Bavarian knights feuded with those from the Rhineland, who likewise bickered with Low German-speaking Saxons, from whose ranks the Grand Master was usually chosen. The western Prussian lands of the Vistula River Valley and the Brandenburg Neumark were ravaged by the Hussites during the Hussite Wars. Some Teutonic Knights were sent to battle the invaders but were defeated by the Bohemian infantry. The Knights also sustained a defeat in the Polish-Teutonic War (1431–1435).
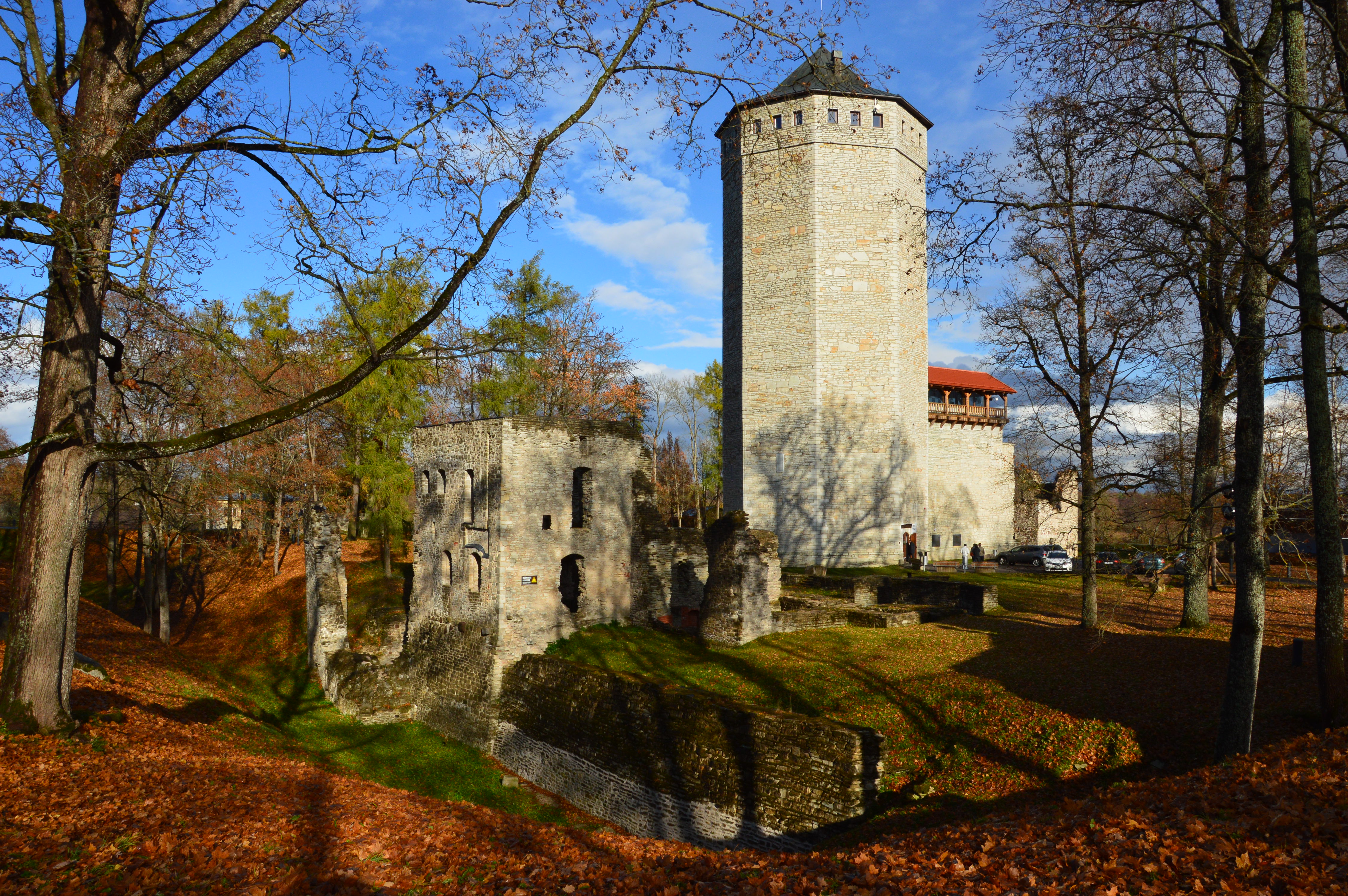
 In 1440, the Prussian Confederation was founded by gentry and burghers of the State of the Teutonic Order. In 1454, it rose up against the Order and asked Polish King Casimir IV Jagiellon to incorporate the region into the Crown of the Kingdom of Poland, Kingdom of Poland, to which the King agreed and signed an act of incorporation in Kraków. Mayors, burghers and representatives from the region pledged allegiance to the Polish King during the incorporation in March 1454 in Kraków. This marked the beginning of the Thirteen Years' War (1454–1466), Thirteen Years' War between the Teutonic Order and Poland. The main cities of the incorporated territory were authorized by Casimir IV to mint Polish coins. Much of Prussia was devastated in the war, during the course of which the Order returned Neumark to Brandenburg in 1455 to raise funds for war. Because Marienburg Castle was handed over to mercenaries in lieu of their pay, and eventually passed to Poland, the Order moved its base to
In 1440, the Prussian Confederation was founded by gentry and burghers of the State of the Teutonic Order. In 1454, it rose up against the Order and asked Polish King Casimir IV Jagiellon to incorporate the region into the Crown of the Kingdom of Poland, Kingdom of Poland, to which the King agreed and signed an act of incorporation in Kraków. Mayors, burghers and representatives from the region pledged allegiance to the Polish King during the incorporation in March 1454 in Kraków. This marked the beginning of the Thirteen Years' War (1454–1466), Thirteen Years' War between the Teutonic Order and Poland. The main cities of the incorporated territory were authorized by Casimir IV to mint Polish coins. Much of Prussia was devastated in the war, during the course of which the Order returned Neumark to Brandenburg in 1455 to raise funds for war. Because Marienburg Castle was handed over to mercenaries in lieu of their pay, and eventually passed to Poland, the Order moved its base to Königsberg
Königsberg (; ; ; ; ; ; , ) is the historic Germany, German and Prussian name of the city now called Kaliningrad, Russia. The city was founded in 1255 on the site of the small Old Prussians, Old Prussian settlement ''Twangste'' by the Teuton ...
in Sambia Peninsula, Sambia. In the Second Peace of Thorn (1466), the defeated Order renounced any claims to the territories of Gdańsk Pomerania, Gdańsk/Eastern Pomerania and Chełmno Land, which were reintegrated with Poland, and the region of Elbląg and Malbork, and the Prince-Bishopric of Warmia, which were also recognized as part of Poland, while retaining the eastern territories in historic Prussia, but as a fief and protectorate of Poland, also considered an integral part of "one and indivisible" Kingdom of Poland. From now on, every Grand Master of the Teutonic Order was obliged to swear an oath of allegiance to the reigning Polish king within six months of taking office. The Grand Master became a prince and counselor of the Polish king and the Kingdom of Poland.
After the Polish–Teutonic War (1519–1521), the Order was completely ousted from Prussia when Grand Master Albert I, Duke of Prussia, Albert of Brandenburg converted to Lutheranism
Lutheranism is a major branch of Protestantism that emerged under the work of Martin Luther, the 16th-century German friar and Protestant Reformers, reformer whose efforts to reform the theology and practices of the Catholic Church launched ...
in 1525. He secularized the Order's remaining Prussian territories and assumed from his uncle Sigismund I the Old, King of Poland, the hereditary rights to the Duchy of Prussia as a personal vassal of the Polish Crown, the Prussian Homage. Ducal Prussia retained its currency, laws and faith. The aristocracy was not present in the Sejm.
Although it had lost control of all of its Prussian lands, the Teutonic Order retained its territories within the Holy Roman Empire
The Holy Roman Empire, also known as the Holy Roman Empire of the German Nation after 1512, was a polity in Central and Western Europe, usually headed by the Holy Roman Emperor. It developed in the Early Middle Ages, and lasted for a millennium ...
and Livonia
Livonia, known in earlier records as Livland, is a historical region on the eastern shores of the Baltic Sea. It is named after the Livonians, who lived on the shores of present-day Latvia.
By the end of the 13th century, the name was extende ...
, although the Livonian branch retained considerable autonomy. Many of the Imperial possessions were ruined in the German Peasants' War from 1524 to 1525 and subsequently confiscated by Protestant territorial princes. The Livonian territory was then partitioned by neighboring powers during the Livonian War; in 1561 the Livonian Master Gotthard Kettler secularized the southern Livonian possessions of the Order to create the Duchy of Courland, also a vassal of Poland.
After the loss of Prussia in 1525, the Teutonic Knights concentrated on their possessions in the Holy Roman Empire. Since they held no contiguous territory, they developed a three-tiered administrative system: holdings were combined into commandry (feudalism), commanderies that were administered by a komtur, commander (''Komtur''). Several commanderies were combined to form a bailiwick headed by a ''Landkomtur''. All of the Teutonic Knights' possessions were subordinate to the Grand Master, whose seat was in Bad Mergentheim.
 There were twelve German bailiwicks:
*
There were twelve German bailiwicks:
* Thuringia
Thuringia (; officially the Free State of Thuringia, ) is one of Germany, Germany's 16 States of Germany, states. With 2.1 million people, it is 12th-largest by population, and with 16,171 square kilometers, it is 11th-largest in area.
Er ...
;
* Alden Biesen Castle, Alden Biesen (in present-day Belgium);
* Hesse;
* Saxony;
* Westphalia;
* Franconia;
* Koblenz;
* Alsace-Burgundy;
* An der Etsch, An der Etsch und im Gebirge (in County of Tyrol, Tyrol);
* Utrecht;
* Lorraine; and
* Austria.
Outside of German areas were the bailiwicks of
* Sicily;
* Apulia;
* Lombardy;
* Bohemia;
* "Romania" (in Greece); and
* Armenia-Cyprus.
The Order gradually lost control of these holdings until, by 1809, only the seat of the Grand Master at Mergentheim remained.
Following the abdication of Albert of Brandenburg, Walter von Cronberg became ''Deutschmeister'' in 1527, and later Administrator of Prussia and Grand Master in 1530. Emperor Charles V, Holy Roman Emperor, Charles V combined the two positions in 1531, creating the title ''Hoch- und Deutschmeister'', which also had the rank of Fürst, Prince of the Empire. A new Grand Magistery was established in Mergentheim in Württemberg, which was attacked during the German Peasants' War. The Order also helped Charles V against the Schmalkaldic League. After the Peace of Augsburg in 1555, membership in the Order was open to Protestants, although the majority of brothers remained Catholic. The Teutonic Knights became tri-denominational, with Catholic, Lutheran and Reformed bailiwicks.
The Grand Masters, often members of the great German families (and, after 1761, members of the House of Habsburg-Lorraine), continued to preside over the Order's considerable holdings in Germany. Teutonic Knights from Germany, Austria, and Bohemia were used as battlefield commanders leading mercenaries for the Habsburg monarchy during the Ottoman wars in Europe.
The military history of the Teutonic Knights was to end in 1805 by the Article XII of the Peace of Pressburg (1805), Peace of Pressburg, which ordered the German territories of the Knights converted into a hereditary domain and gave the Austrian Emperor responsibility for placing a Habsburg prince on its throne. These terms had not been fulfilled by the time of the Treaty of Schönbrunn in 1809, and therefore Napoleon Bonaparte
Napoleon Bonaparte (born Napoleone di Buonaparte; 15 August 1769 – 5 May 1821), later known by his regnal name Napoleon I, was a French general and statesman who rose to prominence during the French Revolution and led Military career ...
ordered the Knights' remaining territory to be disbursed to his German allies, which was completed in 1810.
Medieval organization
Administrative structure about 1350
Dieter Zimmerling: ''Der Deutsche Orden,'' S. 166 ff.Universal leadership
Generalkapitel
The ''Generalkapitel'' (general chapter) was the collection of all the priests, knights and half-brothers (). Because of the logistical problems in assembling the members, who were spread over large distances, only deputations of the bailiwicks and Commandry (feudalism), commandries gathered to form the General chapter. The General chapter was designed to meet annually, but the conventions were usually limited to the election of a new Grandmaster. The decisions of the ''Generalkapitel'' had a binding effect on the ''Großgebietigers'' of the order.Hochmeister
The ''Hochmeister'' (Grand master (order), Grand Master) was the highest officer of the order. Until 1525, he was elected by the ''Generalkapitel''. He had the rank of the ruler of an ecclesiastic imperial state and was sovereign prince of Prussia until 1466. Despite this high formal position, in practice, he was only a kind of Primus inter pares, first among equals.Großgebietige
The ''Großgebietige'' were high officers with competence on the whole order, appointed by the ''Hochmeister''. There were five offices. * The ''Großkomtur'' (''Magnus Commendator''), the deputy of the Grandmaster * The ''Treßler'', the treasurer * The ''Spitler'' (''Summus Hospitalarius''), responsible for all hospital affairs * The ''Trapier'', responsible for dressing and armament * The ''Marschall'' (''Summus Marescalcus''), the chief of military affairsNational leadership
Landmeister
The order was divided into three national chapters, Prussia,Livonia
Livonia, known in earlier records as Livland, is a historical region on the eastern shores of the Baltic Sea. It is named after the Livonians, who lived on the shores of present-day Latvia.
By the end of the 13th century, the name was extende ...
and the territory of the Holy Roman Empire of the German Nation. The highest officer of each chapter was the ''Landmeister'' (country master). They were elected by the regional chapters. In the beginning, they were only substitutes of the Grandmaster but were able to create a power of their own so that, within their territory, the Grandmaster could not decide against their will. At the end of their rule over Prussia, the Grandmaster was only ''Landmeister'' of Prussia. There were three Landmeisters:
*The ''Landmeister in Livland'', the successor of the ''Herrenmeister'' (lords master) of the former Livonian Brothers of the Sword
The Livonian Brothers of the Sword (; ) was a Catholic Church, Catholic Military order (monastic society), military order established in 1202 during the Livonian Crusade by Albert of Riga, Albert, the third bishop of Riga (or possibly by Theode ...
.
*The ''Landmeister of Prussia'', after 1309 united with the office of the Grandmaster, who was situated in Prussia from then.
*The ''Deutschmeister'', the ''Landsmeister'' of the Holy Roman Empire. When Prussia and Livland were lost, the ''Deutschmeister'' also became Grandmaster.
Regional leadership
Because the properties of the order within the rule of the ''Deutschmeister'' did not form a contiguous territory, but were spread over the whole empire and parts of Europe, there was an additional regional structure, the bailiwick. ''Kammerballeien'' ("Chamber Bailiwicks") were governed by the Grandmaster himself. Some of these bailiwicks had the rank of imperial states: * Teutonic Order Bailiwick ofThuringia
Thuringia (; officially the Free State of Thuringia, ) is one of Germany, Germany's 16 States of Germany, states. With 2.1 million people, it is 12th-largest by population, and with 16,171 square kilometers, it is 11th-largest in area.
Er ...
(Zwätzen)
* Teutonic Order Bailiwick of Hesse (Marburg)
* Teutonic Order Bailiwick of Saxony, Saxonia (Elmsburg from 1221 until 1260 moved to Lucklum)
* Brandenburg
* Teutonic Order Bailiwick of Westphalia (Deutschordenskommende Mülheim)
* Teutonic Order Bailiwick of Franconia (Ellingen)
* "Chamber Bailiwick" of Koblenz
* Teutonic Order Bailiwick of Swabia-Alsace-Burgundy (region), Burgundy (Rouffach)
* Teutonic Order Bailiwick at the Etsch and in the Mountains (South Tyrol) (Bolzano, Bozen)
* Utrecht
* Lotharingia, Lorraine (Trier)
* "Chamber Bailiwick" of Austria
* Teutonic Order Bailiwick of Alden Biesen
* Sicily
* Teutonic Order Bailiwick of Apulia (San Leonardo)
* Lombardy (also called Lamparten)
* "Chamber Bailiwick" of Bohemia
* Teutonic Order Bailiwick of Romania (Achaia, Greece)
* Armenia–Cyprus
Local leadership
Komtur
The smallest administrative unit of the order was the Kommende. It was ruled by a Komtur, who had all administrative rights and controlled the ''Vogteien'' (district of a reeve) and ''Zehnthöfe'' (tithe collectors) within his rule. In the commandry, all kinds of brothers lived together in a monastic way. Noblemen served as Knight-brothers or Priest-brothers. Other people could serve as Sariantbrothers, who were armed soldiers, and as Half-brothers, who were working in the economy and healthcare.Special offices
* The ''Kanzler'' (chancellor) of the Grandmaster and the Deutschmeister. The chancellor took care of the keys and seals and was also the recording clerk of the chapter. * The ''Münzmeister'' (master of the mint) of Thorn. In 1226, the order received the right to produce its own coins – the ''Moneta Dominorum Prussiae'' – Schillingen. Customary laws for coinage did not come about until the Kulm laws of 1233 were written. And the first coins were not minted until late 1234 or early 1235. * The ''Pfundmeister'' (customs master) of Danzig. The ''Pfund'' was a local customs duty. * The ''Generalprokurator'' the representative of the order at the Holy See. * The ''Großschäffer'', a trading representative with special authority.Modern organization
Evolution and reconfiguration as a Catholic religious order
The Catholic order continued to exist in the various territories ruled by the Austrian Empire, out of Napoleon's reach. From 1804 the Order was headed by members of the Habsburg dynasty. The collapse of the Habsburg monarchy and the Empire it governed in Austria, the Italian Tyrol, Bohemia and the Balkans brought a shattering crisis to the Order. While in the new Austrian Republic, the Order seemed to have some hope of survival, in the other former parts of the Habsburg territories, the tendency was to regard the Order as an honorary chivalric Order of the House of Habsburg. The consequence of this risked being the confiscation of the Order's property as belongings of the House of Habsburg. So as to make the distinction clearer, in 1923 the then High Master, Archduke Eugen of Austria, Field Marshal Eugen of Austria-Teschen, Archduke of Austria, a member of the House of Habsburg and an active army commander before and during the First World War, had one of the Order's priests, Norbert Klein, at the time Bishop of Brno (Brünn) elected his Coadjutor and then abdicated, leaving the Bishop as High Master of the Order. As a result of this move, by 1928 the now-independent former Habsburg territories all recognized the Order as a Catholic Church, Catholic religious order. The Order itself introduced a new Rule, approved by Pope Pius XI in 1929, according to which the government of the Order would in the future be in the hands of a priest of the Order, as would its constituent provinces, while the women religious of the Order would have women superiors. In 1936 the situation of the women religious was further clarified and the Congregation of the Sisters of the Order was given as their supreme moderator the High Master of the Order, the Sisters also having representation at the Order's general chapter. This completed the transformation of what remained in the Catholic Church of the Teutonic knights into a Catholic Church, Catholic religious order now renamed simply the ''Deutscher Orden'' ("German Order"). However, further difficulties were in store. The promising beginnings of this reorganization and spiritual transformation suffered a severe blow through the expansion of German might under the National Socialist regime. After Anschluss, Austria's annexation by Germany in 1938, and similarly the Czech lands in 1939 the Teutonic Order was suppressed throughout the ''Großdeutsches Reich'' until Germany's defeat. This did not prevent the National Socialists from using imagery of the medieval Teutonic knights for propagandistic purposes. The Fascist rule in Italy, which since the end of the First World War had absorbed the Southern Tyrol, was not a propitious setting, but following the end of hostilities, a now democratic Italy provided normalized conditions, In 1947 Austria legally abolished the measures taken against the Order and restored confiscated property. Despite being hampered by the Communist regimes in Yugoslavia and in Czechoslovakia, the Order was now broadly in a position to take up activities in accordance with elements of its tradition, including care for the sick, for the elderly, for children, including work in education, in parishes and in its own internal houses of study. In 1957 a residence was established in Rome for the Order's Procurator General to the Holy See, to serve also as a pilgrim hostel. Conditions in Czechoslovakia gradually improved and in the meanwhile, the forced exile of some members of the Order led to the Order's re-establishing itself with some modest, but historically significant, foundations in Germany. The Sisters, in particular, gained several footholds, including specialist schools and care of the poor and in 1953 the former house of Augustinian Canons, St. Nikola, in Passau became the Sisters' Motherhouse. Although the reconstruction represented by the reformed Rule of 1929 had set aside categories such as the knights, over time the spontaneous involvement of laypeople in the Order's apostolates has led to their revival in a modernized form, a development formalized by Pope Paul VI in 1965. With the official title of "Brethren of the German House of St Mary in Jerusalem", the Order today is unambiguously a Catholic Church, Catholic religious order, though sui generis. Various features of its life and activities recall those of monastic and mendicant orders. At its core are priests who make a solemn religious profession, along with lay brothers who make a perpetual simple profession. Also part of the Order are the Sisters, with internal self-government within their own structures but with representation in the Order's General Chapter. Their ultimate superior is the High Master of the Order. The approximately 100 Catholic priests and 200 nuns of the Order are divided into five provinces, namely, Austria-Italy, Slovenia, Germany, Czech Republic and Slovakia. While the priests predominantly provide spiritual guidance, the nuns primarily care for the ill and the aged. Many of the priests care for German-speaking communities outside of Germany and Austria, especially in Italy and Slovenia; in this sense, the Teutonic Order has returned to its 12th-century roots: the spiritual and physical care of Germans in foreign lands. There is an Institute of "Familiares", most of whom are laypeople, and who are attached by spiritual bonds to the Order but do not take vows. The "Familiares" are grouped especially into the bailiwicks of Germany, Austria, Southern Tyrol, Ad Tiberim (Rome), and the bailiwick of the Czech Republic and Slovakia, as also in the independent commandry of Alden Biesen in Belgium, though others are dispersed throughout the world. Overall, there are in recent years some 700. By the end of the 20th century, then, this religious Order had developed into a charitable organization and established numerous clinics, as well as sponsoring excavation and tourism projects in Israel. In 2000, the German chapter of the Teutonic Order declared bankruptcy, and its upper management was dismissed; an investigation by a special committee of the Landtag of Bavaria, Bavarian parliament in 2002 and 2003 to determine the cause was inconclusive. The current Abbot General of the Order, who also holds the title of High Master, is Father Frank Bayard. The current seat of the High Master is the ''Church of the Teutonic Order, Vienna, Church of the German Order'' ("Deutschordenskirche") in Vienna. Near the Stephansdom, St Stephen's Cathedral ("Stephansdom") in the Austrian capital is the Treasury of the Teutonic Order, which is open to the public, and the Order's central archive. Since 1996, there has also been a museum dedicated to the Teutonic Knights at Mergentheim Palace, their former castle in Bad Mergentheim in Germany, which was the seat of the High Master from 1525 to 1809.Honorary Knights
Honorary Knights of the Teutonic Order have included: * Konrad Adenauer * Udo Arnold * Franz Josef II * Rudolf Graber * Otto von Habsburg * Karl Habsburg-Lothringen * Joachim Meisner * Eduard Gaston Pöttickh von Pettenegg * Eduard Schick * Christoph Schönborn * Carl Herzog von WürttembergProtestant Bailiwick of Utrecht
A portion of the Order retains more of the character of the knights during the height of its power and prestige. Der ''Balije van Utrecht'' ("Bailiwick of Utrecht") of the ''Ridderlijke Duitsche Orde'' ("Chivalric German [i.e., 'Teutonic'] Order") became Protestantism, Protestant at the Protestant Reformation, Reformation, and it remained an aristocratic society. The relationship of the Bailiwick of Utrecht to the Catholic ''Deutscher Orden'' resembles that of the Protestant Order of Saint John (Bailiwick of Brandenburg), Bailiwick of Brandenburg to the Catholic Order of Malta: each is an authentic part of its original order, though differing from and smaller than the Catholic branch.Insignia
The Knights wore white surcoats with a black cross, granted by Pope Innocent III, Innocent III in 1205. Across pattée
A cross pattée or cross patty (, ), also known as a cross formée or cross formy, or even a Templar cross, is a type of Christian cross with arms that are narrow at the centre and often flared in a curve or straight line shape to be broader at th ...
was sometimes used. The coat of arms representing the grandmaster (''Hochmeisterwappen'') is shown with a golden cross fleury or cross potent superimposed on the black cross, with the Reichsadler, imperial eagle as a central inescutcheon. The golden cross fleury overlaid on the black cross became widely used in the 15th century. A legendary account attributes its introduction to Louis IX of France, who is said to have granted the master of the order this cross as a variation of the Jerusalem cross, with the fleur-de-lis symbol attached to each arm, Seventh Crusade, in 1250. While this legendary account cannot be traced back further than the early modern period (Christoph Hartknoch, 1684), there is some evidence that the design does indeed date to the mid 13th century.
The black cross pattée was later used for military decoration and insignia by the Kingdom of Prussia
The Kingdom of Prussia (, ) was a German state that existed from 1701 to 1918.Marriott, J. A. R., and Charles Grant Robertson. ''The Evolution of Prussia, the Making of an Empire''. Rev. ed. Oxford: Clarendon Press, 1946. It played a signif ...
and Germany as the Iron Cross
The Iron Cross (, , abbreviated EK) was a military decoration in the Kingdom of Prussia, the German Empire (1871–1918), and Nazi Germany (1933–1945). The design, a black cross pattée with a white or silver outline, was derived from the in ...
.
The motto of the Order is "Helfen, Wehren, Heilen" ("to help, to defend, to heal").
Influence on German and Polish nationalism and Soviet patriotism
The German historian Heinrich von Treitschke used imagery of the Teutonic Knights, a Germanic Myth, Germanic myth, to promote pro-German and Anti-Polish sentiment, anti-Polish rhetoric. Many middle-class German nationalists adopted this imagery and its symbols. During the Weimar Republic, associations and organisations of this nature contributed to laying the groundwork for the formation of Nazi Germany. ''Mówią wieki''.Biała leganda czarnego krzyża
". Accessed 6 June 2006. An organization predating the Nazi Party itself, as well as Bund Deutscher Osten, Nazi-supported preceding and Nazi propaganda, Nazi preceding and during World War II propaganda made use of the Teutonic Knights' imagery, with the common goal of instilling the importance of for the future of Germany and the German people. According to medieval historian Eric Christiansen, Erik Christiansen, "Heinrich Himmler, Himmler's plan to mould the Schutzstaffel, SS as a reincarnation of [The Teutonic Order] proved [...] the irresistible strength of bad history." Though gradually taking hold ever since with one of Prince Adalbert of Prussia (1811–1873), Prince Adalbert of Prussia's 1849 proposals, after a lull during the Weimar Republic, whereupon it reverted to a simple tricolor overlayed with an
Iron Cross
The Iron Cross (, , abbreviated EK) was a military decoration in the Kingdom of Prussia, the German Empire (1871–1918), and Nazi Germany (1933–1945). The design, a black cross pattée with a white or silver outline, was derived from the in ...
, (though itself also derivative,) a version of Germany's Reichskriegsflagge (war ensign) emerged with a more closely resembling The State of the Teutonic Order's cross's original shape with a circle-overlaid balkenkreuz. Hitler based his German Order (distinction), German Order on the Teutonic Order, while especially the Hochmeister's ceremonial regalia, also the Marian Cross of the Teutonic Order, the Knight's Cross of the Iron Cross and of the cross of the Knight of Justice of the Order of St. John (Bailiwick of Brandenburg).
After Hitler approved the ''Generalplan Ost'' (GPO), Germanisation, Germanization campaigns were extolled as the modern adaptation of what it portrayed as "civilizing missions" of the Teutonic Order.
Yet, despite these references to the Teutonic Order's history in Nazi propaganda, the Order itself was abolished in 1938 and its members were persecuted by the German authorities. This occurred mostly due to Hitler's and Himmler's belief that, throughout history, Catholic military-religious orders had been tools of the Holy See and as such constituted a threat to the Nazi regime.
The converse was true for Polish nationalism, for example ''The Knights of the Cross'' by Henryk Sienkiewicz, which used the Teutonic Knights as symbolic shorthand for Germans in general, conflating the two into an easily recognisable image of the hostile. After the Battle of Grunwald
The Battle of Grunwald was fought on 15 July 1410 during the Polish–Lithuanian–Teutonic War. The alliance of the Crown of the Kingdom of Poland and the Grand Duchy of Lithuania, led respectively by King Władysław II Jagiełło (Jogaila), a ...
, the Teutonic Order was portrayed as the medieval forerunners of Hitler's armies.
In the Soviet Union, the image of Alexander Nevsky
Alexander Yaroslavich Nevsky (; ; monastic name: ''Aleksiy''; 13 May 1221 – 14 November 1263) was Prince of Novgorod (1236–1240; 1241–1256; 1258–1259), Grand Prince of Kiev (1249–1263), and Grand Prince of Vladimir (1252–1263).
...
became a national symbol of the struggle against German occupation during World War II, and many Soviet historians portrayed him as a Russian bastion against both German and papal aggression. The government sought historical continuity by referring to the Soviet struggle as the Great Patriotic War. The Order of Alexander Nevsky was re-established in 1942 by the Soviet government during the war, which would be awarded to servicemen in the Soviet army. The 1938 film ''Alexander Nevsky (film), Alexander Nevsky'' by Sergei Eisenstein, which depicts the Battle on the Ice, was re-released in 1941 following the German invasion. Joseph Stalin used the film to mobilize feelings of Russian patriotism.
See also
* Prussian virtues * Teutonic Knights in popular cultureReferences
Bibliography
* * * * * * * * *External links
The order's homepage in Germany
The order's homepage in Austria
Territorial extent of the Teutonic Knights in Europe
(map)
by William Urban
"The Early Years of the Teutonic Order"
by William Urban
Museum in the residential castle of the Teutonic Order in Bad Mergentheim
Zwaetzen and the German Order in Central Germany
"Massive Ceremonial Hall Discovered Under Crusader Castle in Northern Israel" – Haaretz, Nov. 22, 2018
* This contains a detailed chronological history of the Order, and is itself based on Heinrich von Treitschke ''Das deutsche Ordensland Preussens'', in ''Historische und politische Aufsätze'', vol. II. (Leipzig, 1871), and on Johann Loserth ''Geschichte des späteren Mittelalters'' (Munich and Berlin, 1903). {{Authority control Teutonic Order, 1190 establishments in Asia 1190 establishments in Europe Christian religious orders established in the 12th century Kingdom of Jerusalem