telecentric on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 A telecentric lens is a special optical lens (often an objective lens or a
A telecentric lens is a special optical lens (often an objective lens or a
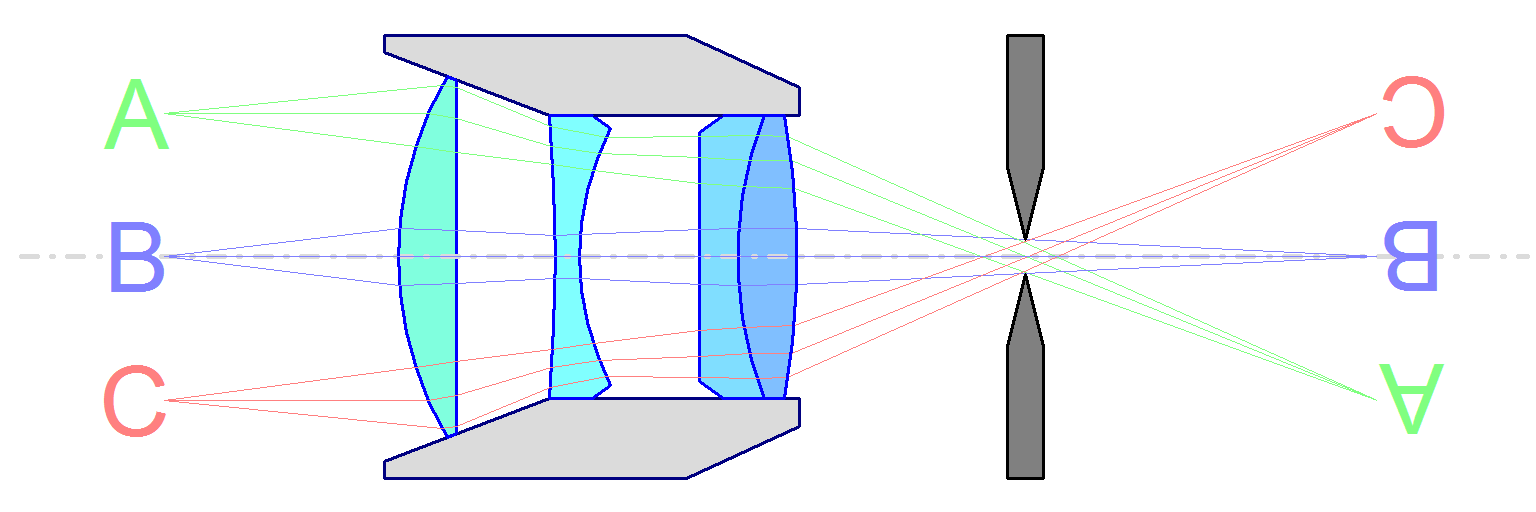 An object-space telecentric lens has the entrance pupil at infinity and provides an
An object-space telecentric lens has the entrance pupil at infinity and provides an
 An image-space telecentric lens has the exit pupil at infinity and produces images of the same size regardless of the distance between the lens and the
An image-space telecentric lens has the exit pupil at infinity and produces images of the same size regardless of the distance between the lens and the
 In a bi-telecentric (or double-telecentric) lens, both entrance and exit pupil are at infinity. The magnification is constant despite variations of both the distance of the object and the image sensor from the lens, allowing for more precise measurements than with a mono-telecentric lens.
A bi-telecentric lens is afocal as the image of an object at infinity formed by the first part of the lens is collimated by the second part.
Commercial bi-telecentric lenses are often optimized for very low image distortion and field curvature for accurate measurements across the entire field of view at great resolution. These lenses often comprise more than 10 elements.
Large and heavy bi-telecentric lenses with many elements are commonly used in
In a bi-telecentric (or double-telecentric) lens, both entrance and exit pupil are at infinity. The magnification is constant despite variations of both the distance of the object and the image sensor from the lens, allowing for more precise measurements than with a mono-telecentric lens.
A bi-telecentric lens is afocal as the image of an object at infinity formed by the first part of the lens is collimated by the second part.
Commercial bi-telecentric lenses are often optimized for very low image distortion and field curvature for accurate measurements across the entire field of view at great resolution. These lenses often comprise more than 10 elements.
Large and heavy bi-telecentric lenses with many elements are commonly used in
 A telecentric lens is a special optical lens (often an objective lens or a
A telecentric lens is a special optical lens (often an objective lens or a camera lens
A camera lens (also known as photographic lens or photographic objective) is an optical lens or assembly of lenses used in conjunction with a camera body and mechanism to make images of objects either on photographic film or on other media capab ...
) that has its entrance or exit pupil, or both, at infinity. Telecentric lenses are often used for precision optical two-dimensional measurements or reproduction and other applications that are sensitive to the image magnification or the angle of incidence
Angle of incidence is a measure of deviation of something from "straight on" and may refer to:
* Angle of incidence (aerodynamics), angle between a wing chord and the longitudinal axis, as distinct from angle of attack
In fluid dynamics, ang ...
of light.
The simplest way to make a lens telecentric is to put the aperture stop at one of the lens's focal point
Focal point may refer to:
* Focus (optics)
* Focus (geometry)
* Conjugate points, also called focal points
* Focal point (game theory)
* Unicom Focal Point, a portfolio management software tool
* Focal point review, a human resources process for ...
s. This makes the chief ray
In optics a ray is an idealized geometrical model of light, obtained by choosing a curve that is perpendicular to the ''wavefronts'' of the actual light, and that points in the direction of energy flow. Rays are used to model the propagation o ...
s (light rays that pass through the center of the aperture) on the other side of the lens parallel to the optical axis for any point in the field of view. Commercially available telecentric lenses are often ''compound lenses'' that include multiple lens elements, for improved optical performance. Telecentricity is not a property of the lenses inside the compound lens but is established by the location of the aperture stop in the lens. The aperture stop selects the rays that are passed through the lens and the specific selection is what makes a lens telecentric.
If a lens is not telecentric, it is either entocentric or hypercentric. Common lenses are usually entocentric. In particular, a single lens without a separate aperture stop is entocentric. For such a lens the chief ray originating at any point off of the optical axis is never parallel to the optical axis, neither in front of nor behind the lens.
A non-telecentric lens exhibits varying magnification
Magnification is the process of enlarging the apparent size, not physical size, of something. This enlargement is quantified by a calculated number also called "magnification". When this number is less than one, it refers to a reduction in siz ...
for objects at different distances from the lens. An entocentric lens has a smaller magnification for objects farther away; objects of the same size appear smaller the farther they are away. A hypercentric lens produces larger images the farther the object is away.
A telecentric lens can be ''object-space telecentric'', ''image-space telecentric'', or ''bi-telecentric'' (also ''double-telecentric''). In an object-space telecentric lens the image size does not change with the object distance, and in an image-space telecentric lens the image size does not change with the image-side distance from the lens.
Object-space telecentric lenses
 An object-space telecentric lens has the entrance pupil at infinity and provides an
An object-space telecentric lens has the entrance pupil at infinity and provides an orthographic projection
Orthographic projection (also orthogonal projection and analemma) is a means of representing Three-dimensional space, three-dimensional objects in Two-dimensional space, two dimensions. Orthographic projection is a form of parallel projection in ...
instead of the perspective projection
Linear or point-projection perspective (from la, perspicere 'to see through') is one of two types of graphical projection perspective in the graphic arts; the other is parallel projection. Linear perspective is an approximate representation, ...
in an entocentric lens.
Object-space telecentric lenses have a ''working distance''. Objects at this distance are ''in focus'' and imaged sharply onto the image sensor at flange focal distance
For an interchangeable lens camera, the flange focal distance (FFD) (also known as the flange-to-film distance, flange focal depth, flange back distance (FBD), flange focal length (FFL), back focus or register, depending on the usage and sourc ...
in the camera.
An object that is closer or farther is out of focus
In optics, defocus is the aberration in which an image is simply out of focus. This aberration is familiar to anyone who has used a camera, videocamera, microscope, telescope, or binoculars. Optically, defocus refers to a translation of the ...
and may be blurry, but will be the same size regardless of distance.
Telecentric lenses tend to be larger, heavier, and more expensive than normal lenses of similar focal length
The focal length of an optical system is a measure of how strongly the system converges or diverges light; it is the inverse of the system's optical power. A positive focal length indicates that a system converges light, while a negative foca ...
and f-number. This is partly due to the extra components needed to achieve telecentricity, and partly because the first element in an object-space telecentric lens must be at least as large as the largest object to be imaged. The front element in an object-space telecentric lens is often much larger than the camera mount. In contrast to entocentric lenses where lenses are made larger to increase the aperture for increased collection of light or shallower depth of field
The depth of field (DOF) is the distance between the nearest and the furthest objects that are in acceptably sharp focus in an image captured with a camera.
Factors affecting depth of field
For cameras that can only focus on one object dist ...
, a larger diameter (but otherwise similar) object-space telecentric lens is not faster than a smaller lens. Because of their intended applications, telecentric lenses often have higher resolution and transmit more light than normal photographic lenses.
Commercial object-space telecentric lenses are often characterized by their magnification, working distance and maximum image circle or image sensor size. A truly telecentric lens has no focus ring to adjust the position of the focal plane. Some commercial telecentric lenses, however, do feature a focus ring. This can be used to slightly adjust the working distance and magnification while losing a little bit of telecentricity. Sometimes, manufacturers specify a sensor resolution or pixel size to describe the optical quality of the lens and the maximum optical resolution
Optical resolution describes the ability of an imaging system to resolve detail, in the object that is being imaged.
An imaging system may have many individual components, including one or more lenses, and/or recording and display components. ...
it can achieve due to the lens's aberrations.
Because their images have constant magnification and constant viewing angle across the field of view, object-space telecentric lenses are used for metrology
Metrology is the scientific study of measurement. It establishes a common understanding of units, crucial in linking human activities. Modern metrology has its roots in the French Revolution's political motivation to standardise units in Fran ...
applications, where a machine vision system must determine the precise size and shape of objects independently from their exact distance and position within the field of view.
In order to optimize the telecentric effect when objects are illuminated from behind, an additional image-space telecentric lens can be used as a ''telecentric (or collimated) illuminator'', which produces a parallel light flow, often from LED
A light-emitting diode (LED) is a semiconductor Electronics, device that Light#Light sources, emits light when Electric current, current flows through it. Electrons in the semiconductor recombine with electron holes, releasing energy i ...
sources.
Image-space telecentric lenses
 An image-space telecentric lens has the exit pupil at infinity and produces images of the same size regardless of the distance between the lens and the
An image-space telecentric lens has the exit pupil at infinity and produces images of the same size regardless of the distance between the lens and the film
A film also called a movie, motion picture, moving picture, picture, photoplay or (slang) flick is a work of visual art that simulates experiences and otherwise communicates ideas, stories, perceptions, feelings, beauty, or atmosphere ...
or image sensor. This allows the lens to be focused to different distances without changing the size of the image. An image-space telecentric lens is a reversed object-space telecentric lens, and vice versa.
Since the chief rays after an image-space telecentric lens are always parallel to the optical axis, these lenses are often used in applications that are sensitive to the angle of incidence. Interference-based color-selective beam splitter
A beam splitter or ''beamsplitter'' is an optical device that splits a beam of light into a transmitted and a reflected beam. It is a crucial part of many optical experimental and measurement systems, such as interferometers, also finding wide ...
s or filters but also Fabry–Pérot interferometer
In optics, a Fabry–Pérot interferometer (FPI) or etalon is an optical cavity made from two parallel reflecting surfaces (i.e.: thin mirrors). Optical waves can pass through the optical cavity only when they are in resonance with it. It is ...
s are two examples where image-space telecentricity is used. Another example is minimizing crosstalk
In electronics, crosstalk is any phenomenon by which a signal transmitted on one circuit or channel of a transmission system creates an undesired effect in another circuit or channel. Crosstalk is usually caused by undesired capacitive, induc ...
between pixels in image sensors and maximizing the quantum efficiency
The term quantum efficiency (QE) may apply to incident photon to converted electron (IPCE) ratio of a photosensitive device, or it may refer to the TMR effect of a Magnetic Tunnel Junction.
This article deals with the term as a measurement of ...
of a sensor. The Four Thirds System initially required image-space telecentric lenses, but with the improvement of sensors, the angle of incidence requirement has been relaxed.
Since every pixel is illuminated at the same angle by an image-space telecentric lens, they are also used for radiometric and color measurement
Colorimetry is "the science and technology used to quantify and describe physically the human color perception".
It is similar to spectrophotometry, but is distinguished by its interest in reducing spectra to the physical correlates of color ...
applications, where one would need the irradiance In radiometry, irradiance is the radiant flux ''received'' by a ''surface'' per unit area. The SI unit of irradiance is the watt per square metre (W⋅m−2). The CGS unit erg per square centimetre per second (erg⋅cm−2⋅s−1) is often used ...
to be the same regardless of the field position.
Bi-telecentric lenses
 In a bi-telecentric (or double-telecentric) lens, both entrance and exit pupil are at infinity. The magnification is constant despite variations of both the distance of the object and the image sensor from the lens, allowing for more precise measurements than with a mono-telecentric lens.
A bi-telecentric lens is afocal as the image of an object at infinity formed by the first part of the lens is collimated by the second part.
Commercial bi-telecentric lenses are often optimized for very low image distortion and field curvature for accurate measurements across the entire field of view at great resolution. These lenses often comprise more than 10 elements.
Large and heavy bi-telecentric lenses with many elements are commonly used in
In a bi-telecentric (or double-telecentric) lens, both entrance and exit pupil are at infinity. The magnification is constant despite variations of both the distance of the object and the image sensor from the lens, allowing for more precise measurements than with a mono-telecentric lens.
A bi-telecentric lens is afocal as the image of an object at infinity formed by the first part of the lens is collimated by the second part.
Commercial bi-telecentric lenses are often optimized for very low image distortion and field curvature for accurate measurements across the entire field of view at great resolution. These lenses often comprise more than 10 elements.
Large and heavy bi-telecentric lenses with many elements are commonly used in optical lithography
In integrated circuit manufacturing, photolithography or optical lithography is a general term used for techniques that use light to produce minutely patterned thin films of suitable materials over a substrate, such as a silicon wafer, to protect ...
copying a template onto semiconductor wafers.
References
{{reflist Optical microscope components Photographic lenses Machine vision