Tehran Metro on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Tehran Metro () is a  The line uses standard gauge and is mostly underground. Ticket price is 5,300 Iranian Toman for each journey (about US$0.05), regardless of the distance traveled, but using prepaid tickets costs much less. Seniors may travel for free on the metro. On all Tehran metro trains the first and half of the second carriages from each end are reserved for women. Women can still ride other cars freely.
The line uses standard gauge and is mostly underground. Ticket price is 5,300 Iranian Toman for each journey (about US$0.05), regardless of the distance traveled, but using prepaid tickets costs much less. Seniors may travel for free on the metro. On all Tehran metro trains the first and half of the second carriages from each end are reserved for women. Women can still ride other cars freely.

 Line 1, coloured red on system maps, is long, of which are underground (from Tajrish station to Shoush-Khayyam crossing) and the rest runs at surface level. There are 5
2 stations along this line of which 23 stations are located underground and 8 above ground. , the total capacity of line 1 is 650,000 passenger per day, with trains stopping at each station for 20 seconds. The trains are each made up of seven wagons, with a nominal capacity of 1,300 seated and standing passengers. The maximum speed of the trains is which is tempered to an average of due to stoppages at stations along the route.
Line 1 runs mostly north–south. A , three station extension of the line from Mirdamad station to Qolhak station opened on May 20, 2009. The , four stations second phase of this extension from Qolhak station to Tajrish Square was completed in 2011. Construction was to be completed by March 2007 but faced major issues due to large boulders and rock bed in part of the tunnels as well as water drainage issues. It has also faced major financing issues as the government has refused to release funds earmarked for the project to the municipality.
Since August 2017, one of Line 1's stations, Darvazeh Dowlat is open 24 hours a day, in order to accommodate passengers traveling to and from Imam Khomeini Airport via Line 1.
Line 1 connects Tehran to Imam Khomeini International Airport. Its first phase, to Shahr-e-Aftab station, opened in 2016, and the airport station opened in August 2017. It is the only metro line in Tehran that is completely open 24 hours a day (even if the frequency is only 80 minutes...), in order to accommodate passengers from late night and early morning flights (Line 1's Darvazeh Dowlat station is the only other metro station outside of Line 1 with that classification). A third phase, which is currently operational, will extend Line 1 to the
Line 1, coloured red on system maps, is long, of which are underground (from Tajrish station to Shoush-Khayyam crossing) and the rest runs at surface level. There are 5
2 stations along this line of which 23 stations are located underground and 8 above ground. , the total capacity of line 1 is 650,000 passenger per day, with trains stopping at each station for 20 seconds. The trains are each made up of seven wagons, with a nominal capacity of 1,300 seated and standing passengers. The maximum speed of the trains is which is tempered to an average of due to stoppages at stations along the route.
Line 1 runs mostly north–south. A , three station extension of the line from Mirdamad station to Qolhak station opened on May 20, 2009. The , four stations second phase of this extension from Qolhak station to Tajrish Square was completed in 2011. Construction was to be completed by March 2007 but faced major issues due to large boulders and rock bed in part of the tunnels as well as water drainage issues. It has also faced major financing issues as the government has refused to release funds earmarked for the project to the municipality.
Since August 2017, one of Line 1's stations, Darvazeh Dowlat is open 24 hours a day, in order to accommodate passengers traveling to and from Imam Khomeini Airport via Line 1.
Line 1 connects Tehran to Imam Khomeini International Airport. Its first phase, to Shahr-e-Aftab station, opened in 2016, and the airport station opened in August 2017. It is the only metro line in Tehran that is completely open 24 hours a day (even if the frequency is only 80 minutes...), in order to accommodate passengers from late night and early morning flights (Line 1's Darvazeh Dowlat station is the only other metro station outside of Line 1 with that classification). A third phase, which is currently operational, will extend Line 1 to the
 This line opened between Sadeghieh and
This line opened between Sadeghieh and
 Line 3 travels from northeast to southwest. Line 3 is one of the most important lines as it connects southwest Tehran to northeast, crosses busy parts of the capital city, and can help to alleviate traffic problems. About of Line 3 became operational in December 2012, followed by in April 2014, and finally, the last section of the line which is opened on September 22, 2015, increasing the length of the line to a total of , and serving 25 stations .
Line 3 travels from northeast to southwest. Line 3 is one of the most important lines as it connects southwest Tehran to northeast, crosses busy parts of the capital city, and can help to alleviate traffic problems. About of Line 3 became operational in December 2012, followed by in April 2014, and finally, the last section of the line which is opened on September 22, 2015, increasing the length of the line to a total of , and serving 25 stations .
 The line is long with 23 stations. which connects the western part of Tehran to eastern part. This line initially runs through Ekbatan (western Tehran) to Kolahdooz (eastern Tehran). The construction of a western extension to line 4 has been started in 2012 connecting Ekbatan to Chaharbagh Sq. This extension will include 3 stations. A sub-line of this line connects Bimeh station to Mehrabad Airport. This sub-line has 3 stations at Bimeh, Terminal 1&2 and Terminal 4&6.
Section 1, from Ferdowsi Square to Darvazeh Shemiran, opened in April 2008. Section 2 from Darvazeh shemiran to Shohada Square opened in February 2009. On May 24, 2009, Section 3 from Ferdowsi Square to Enghelab Square opened. On July 23, 2012, two more stations were inaugurated, connecting line 4 with line 5.
Currently there are 23 stations in operation on Line 4, coloured yellow on the system maps.
The line is long with 23 stations. which connects the western part of Tehran to eastern part. This line initially runs through Ekbatan (western Tehran) to Kolahdooz (eastern Tehran). The construction of a western extension to line 4 has been started in 2012 connecting Ekbatan to Chaharbagh Sq. This extension will include 3 stations. A sub-line of this line connects Bimeh station to Mehrabad Airport. This sub-line has 3 stations at Bimeh, Terminal 1&2 and Terminal 4&6.
Section 1, from Ferdowsi Square to Darvazeh Shemiran, opened in April 2008. Section 2 from Darvazeh shemiran to Shohada Square opened in February 2009. On May 24, 2009, Section 3 from Ferdowsi Square to Enghelab Square opened. On July 23, 2012, two more stations were inaugurated, connecting line 4 with line 5.
Currently there are 23 stations in operation on Line 4, coloured yellow on the system maps.
 Line 5 is coloured green on system maps; it is a commuter rail line and has 13 stations. Entering the area of
Line 5 is coloured green on system maps; it is a commuter rail line and has 13 stations. Entering the area of
 Line 6 is pink coloured on system maps. An initial section between Shohada Square to Dowlat Abad opened on April 7, 2019. This line is long with 13 stations right now. When completed, this line will be long with 31 stations, connecting southeast Tehran to northwest. A tunnel boring machine (TBM) is used to construct the tunnel. TBM is using earth pressure balanced method to pass safely through urban areas without considerable settlement.
Line 6 is pink coloured on system maps. An initial section between Shohada Square to Dowlat Abad opened on April 7, 2019. This line is long with 13 stations right now. When completed, this line will be long with 31 stations, connecting southeast Tehran to northwest. A tunnel boring machine (TBM) is used to construct the tunnel. TBM is using earth pressure balanced method to pass safely through urban areas without considerable settlement.
 This line, similar to line 6, and in contrast with line 3, goes from northwest to southeast and was constructed with modern TBM machines. Its first phase, compromising of of line and 7 stations were opened in June 2017. This line has with 20 stations right now.
This line, similar to line 6, and in contrast with line 3, goes from northwest to southeast and was constructed with modern TBM machines. Its first phase, compromising of of line and 7 stations were opened in June 2017. This line has with 20 stations right now.

File:تهران-مترو-ایستگاه حقانی3.jpg, Escalators at Haghani Metro Station
File:Last Metro - panoramio.jpg, Tehran Metro in 2012
File:Tehran Metro Z1 2018.jpg, Passengers wait to board a train in 2018
File:February 2019 in Tehran Metro.jpg,
Tehran Metro (official site)
The Unofficial Homepage of Iranian RailwaysVideo Clip of one of the Tehran Metro stationsTehran Metro Application for AndroidTehran Metro Application for badaOSTehran Metro Map PDF
(in Persian)
''UrbanRail.Net''
– descriptions of all metro systems in the world, each with a schematic map showing all stations. {{Rapid transit in Asia Underground rapid transit in Iran 1999 establishments in Iran Standard-gauge railways in Iran Articles containing video clips Railway lines opened in 1999
rapid transit
Rapid transit or mass rapid transit (MRT) or heavy rail, commonly referred to as metro, is a type of high-capacity public transport that is generally built in urban areas. A grade separation, grade separated rapid transit line below ground su ...
system serving Tehran
Tehran (; , ''Tehrân'') is the capital and largest city of Iran. It is the capital of Tehran province, and the administrative center for Tehran County and its Central District (Tehran County), Central District. With a population of around 9. ...
, the capital of Iran
Iran, officially the Islamic Republic of Iran (IRI) and also known as Persia, is a country in West Asia. It borders Iraq to the west, Turkey, Azerbaijan, and Armenia to the northwest, the Caspian Sea to the north, Turkmenistan to the nort ...
. It is the largest metro system in the Middle East
The Middle East (term originally coined in English language) is a geopolitical region encompassing the Arabian Peninsula, the Levant, Turkey, Egypt, Iran, and Iraq.
The term came into widespread usage by the United Kingdom and western Eur ...
. The system is owned and operated by Tehran Urban and Suburban Railway. It consists of six operational metro lines (and an additional commuter rail
Commuter rail or suburban rail is a Passenger train, passenger rail service that primarily operates within a metropolitan area, connecting Commuting, commuters to a Central business district, central city from adjacent suburbs or commuter town ...
line), with construction under way on seven lines including northwestern extension of line 4, south extension line 6, northwestern and east extension line 7, east extension line 2 and Line 10, Line 8 and 9.
The Tehran Metro carries more than 3 million passengers a day. In 2018, 820 million trips were made on Tehran Metro. , the total system is long, of which is metro-grade rail. It is planned to have a length of with eleven lines once all construction is complete by 2040.
On all days of the week, the Metro service runs from 04:30 to 22:00.
 The line uses standard gauge and is mostly underground. Ticket price is 5,300 Iranian Toman for each journey (about US$0.05), regardless of the distance traveled, but using prepaid tickets costs much less. Seniors may travel for free on the metro. On all Tehran metro trains the first and half of the second carriages from each end are reserved for women. Women can still ride other cars freely.
The line uses standard gauge and is mostly underground. Ticket price is 5,300 Iranian Toman for each journey (about US$0.05), regardless of the distance traveled, but using prepaid tickets costs much less. Seniors may travel for free on the metro. On all Tehran metro trains the first and half of the second carriages from each end are reserved for women. Women can still ride other cars freely.
History
Initial plans for the metro system were laid in late 1960s but could not be executed until 1982 because of socio-political issues such as theIranian Revolution
The Iranian Revolution (, ), also known as the 1979 Revolution, or the Islamic Revolution of 1979 (, ) was a series of events that culminated in the overthrow of the Pahlavi dynasty in 1979. The revolution led to the replacement of the Impe ...
and the Iran-Iraq War. In 1970, the Plan and Budget Organization and the Municipality of Tehran
Tehran (; , ''Tehrân'') is the capital and largest city of Iran. It is the capital of Tehran province, and the administrative center for Tehran County and its Central District (Tehran County), Central District. With a population of around 9. ...
announced an international tender for construction of a metro in Tehran. The French company SOFRETU, affiliated with the state-owned Paris transportation authority RATP, won the tender and in the same year began to conduct preliminary studies on the project. In 1974, a final report with a so-called "street-metro" proposal was tendered. The street-metro system recommended a road network with a loop express way in the central area and two highways for new urban areas and an 8-line metro network which were complemented by bus network and taxi services. Geological surveys commenced in 1976. In 1978, construction on the line was started in northern Tehran by the French company, however this development was short-lived with the advent of the Iranian Revolution
The Iranian Revolution (, ), also known as the 1979 Revolution, or the Islamic Revolution of 1979 (, ) was a series of events that culminated in the overthrow of the Pahlavi dynasty in 1979. The revolution led to the replacement of the Impe ...
and Iran–Iraq War
The Iran–Iraq War, also known as the First Gulf War, was an armed conflict between Iran and Iraq that lasted from September 1980 to August 1988. Active hostilities began with the Iraqi invasion of Iran and lasted for nearly eight years, unti ...
in 1979 and 1980 respectively. SOFRETU ceased operations in Iran in December 1980. On March 3, 1982, the Iranian Cabinet ministers formally announced the stop of Tehran Metro operations by the French company.
In 1985, the "Tehran Metro Execution Plan" was re-approved by the '' Majiles'', the Iranian Parliament, on the basis of legal project of "Amendment of Law of Establishment of Tehran Urban and suburban Railway Company" which had been founded on Farvardin
Farvardin (, ) is the Iranian Persian name for the first month of the Solar Hijri calendar, the official calendar of Iran, and corresponds with Aries on the Zodiac. Farvardin has thirty-one days. It is the first month of the spring season (''B ...
1364 (April 1985). This was a literal continuation of exactly the same project that had been laid out before the revolution. Work proceeded slowly because of the continuing Iran–Iraq War and often ground to a halt. By the summer of 1985, urban pressure from the rapidly urbanising population, and lack of developed public transport system prompted the work to be resumed in earnest. "Line 1" (From Blvd. Shahid Ayatollah Haghani to City of Rey) and its extension to Behesht-e-Zahra Cemetery was made a priority. "Line 2" (From Dardasht in Tehran Pars district to Sadeghiyeh Second Square) and an extending towards the City of Karaj and Mehrshahr district was also made a secondary priority. Studies were also made to establish the previously designed Lines 3 & 4. It was decided that an organisation by the name of the Metro Company should be established in order to handle the future development of the system.
The Metro Company then became managed by Asghar Ebrahimi Asl for eleven years. During that time, hundreds of millions of dollars were spent on the system and the Metro Company was given government concessions for the exploitation of iron ore mines in Bandar Abbas (Hormuzgan Province), exploitation and sale of Moghan Diotomite mine in the Iranian region of Azarbaijan, export of refinery residues from Isfahan oil refinery as well as tar from Isfahan steel mill. The year after Asghar Ebrahimi Asl left the management of the Metro Company and Mohsen Hashemi succeeded him, the first line of the Tehran Metro was launched between Tehran and Karaj
Karaj (; ) is a List of cities in Iran by province, city in the Central District (Karaj County), Central District of Karaj County, Alborz province, Alborz province, Iran, serving as capital of the province, the county, and the district. Earl ...
.
On 7 March 1999, an overland Tehran-Karaj express electric train started a limited service of between Azadi Square (Tehran) and Malard (Karaj) that called at one intermediate station at Vardavard.
Line 5 of the Tehran
Tehran (; , ''Tehrân'') is the capital and largest city of Iran. It is the capital of Tehran province, and the administrative center for Tehran County and its Central District (Tehran County), Central District. With a population of around 9. ...
metro began operating in 1999. Iran
Iran, officially the Islamic Republic of Iran (IRI) and also known as Persia, is a country in West Asia. It borders Iraq to the west, Turkey, Azerbaijan, and Armenia to the northwest, the Caspian Sea to the north, Turkmenistan to the nort ...
's first metro system, the line was constructed by the Chinese company NORINCO
China North Industries Group Corporation Limited, doing business internationally as Norinco Group (an abbreviation of "North Industries Corporation"), and known within China as China Ordnance Industries Group Corporation Limited (), is a Chinese ...
.
From 2000 onwards, commercial operation began on Lines 1 and 2. The wagons on these lines are provided by CRV via CNTIC. The railway tracks and points on these lines are provided by the Austria
Austria, formally the Republic of Austria, is a landlocked country in Central Europe, lying in the Eastern Alps. It is a federation of nine Federal states of Austria, states, of which the capital Vienna is the List of largest cities in Aust ...
n company Voestalpine
Voestalpine AG – stylized as voestalpine – is an Austrian steel-based technology and capital goods group based in Linz, Austria. The company is active in steel, automotive, railway systems, profilform and tool steel industries. As of 201 ...
.
The Metro uses equipment manufactured by a wide range of international companies: double-deck passenger cars for the Tehran-Karaj regional line are supplied by CRV some trains are from SEGC via CNTIC and assembled by the Wagon Pars factory in Arak.
, approximately $2 billion has been spent on the Metro project. The Tehran Metro transports about 2.5 million passengers daily through its 7 operational lines (Lines 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 7, and 8). It also has additional one line under construction (Line 6), and an additional two lines in engineering phase. New 80 wagons have been added to the system in September 2012 to ease transportation and reduce rush-hour congestion. Iran is able to produce its need in wagons and trains independently.
A branch line of Line 4 began running to Mehrabad International Airport
Mehrabad Interglobal Airport is an airport serving Tehran, the capital of Iran. Prior to the construction of the larger Imam Khomeini International Airport in 2007, Mehrabad was Tehran's primary airport for both international and domestic tr ...
on 15 March 2016. A express
Express, The Expresss or EXPRESS may refer to:
Arts, entertainment and media Film
* ''Express: Aisle to Glory'', a 1998 comedy short film featuring Kal Penn
* ''The Express: The Ernie Davis Story'', a 2008 film starring Dennis Quaid
* The Expre ...
line to Imam Khomeini International Airport was opened in August 2017.
Amidst the COVID-19 cases increasing in Iran, Tehran Metro made wearing masks a requirement to enter the metro network at any station. Law enforcement located in every station were ordered to prevent passengers from entering without masks and such passengers would be led to purchase masks from mask selling desks located at every metro station.
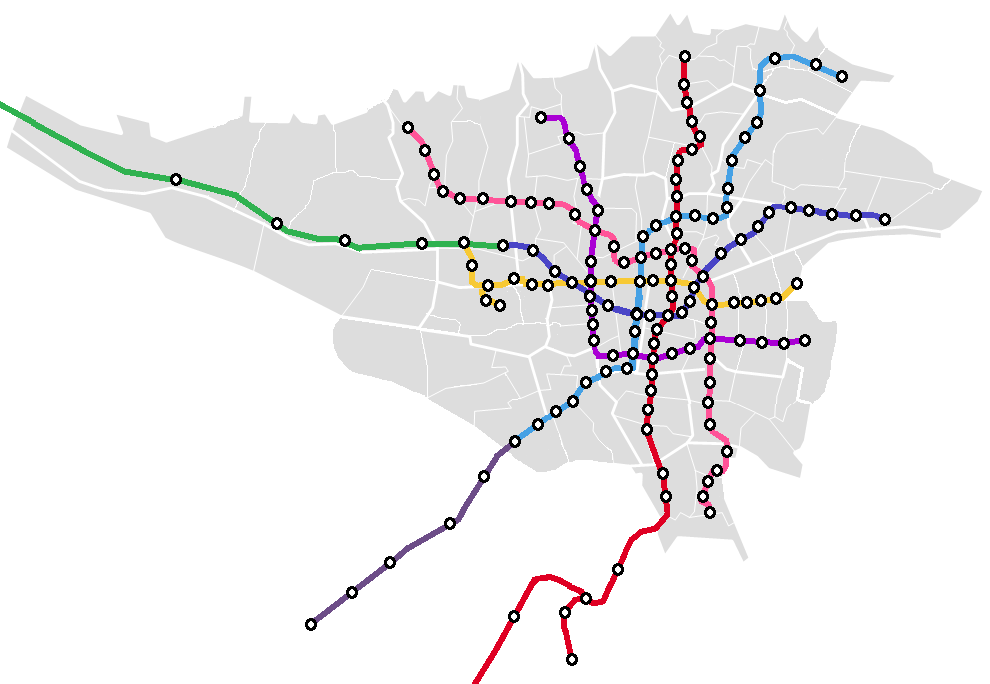
Lines

List
Line 1
 Line 1, coloured red on system maps, is long, of which are underground (from Tajrish station to Shoush-Khayyam crossing) and the rest runs at surface level. There are 5
2 stations along this line of which 23 stations are located underground and 8 above ground. , the total capacity of line 1 is 650,000 passenger per day, with trains stopping at each station for 20 seconds. The trains are each made up of seven wagons, with a nominal capacity of 1,300 seated and standing passengers. The maximum speed of the trains is which is tempered to an average of due to stoppages at stations along the route.
Line 1 runs mostly north–south. A , three station extension of the line from Mirdamad station to Qolhak station opened on May 20, 2009. The , four stations second phase of this extension from Qolhak station to Tajrish Square was completed in 2011. Construction was to be completed by March 2007 but faced major issues due to large boulders and rock bed in part of the tunnels as well as water drainage issues. It has also faced major financing issues as the government has refused to release funds earmarked for the project to the municipality.
Since August 2017, one of Line 1's stations, Darvazeh Dowlat is open 24 hours a day, in order to accommodate passengers traveling to and from Imam Khomeini Airport via Line 1.
Line 1 connects Tehran to Imam Khomeini International Airport. Its first phase, to Shahr-e-Aftab station, opened in 2016, and the airport station opened in August 2017. It is the only metro line in Tehran that is completely open 24 hours a day (even if the frequency is only 80 minutes...), in order to accommodate passengers from late night and early morning flights (Line 1's Darvazeh Dowlat station is the only other metro station outside of Line 1 with that classification). A third phase, which is currently operational, will extend Line 1 to the
Line 1, coloured red on system maps, is long, of which are underground (from Tajrish station to Shoush-Khayyam crossing) and the rest runs at surface level. There are 5
2 stations along this line of which 23 stations are located underground and 8 above ground. , the total capacity of line 1 is 650,000 passenger per day, with trains stopping at each station for 20 seconds. The trains are each made up of seven wagons, with a nominal capacity of 1,300 seated and standing passengers. The maximum speed of the trains is which is tempered to an average of due to stoppages at stations along the route.
Line 1 runs mostly north–south. A , three station extension of the line from Mirdamad station to Qolhak station opened on May 20, 2009. The , four stations second phase of this extension from Qolhak station to Tajrish Square was completed in 2011. Construction was to be completed by March 2007 but faced major issues due to large boulders and rock bed in part of the tunnels as well as water drainage issues. It has also faced major financing issues as the government has refused to release funds earmarked for the project to the municipality.
Since August 2017, one of Line 1's stations, Darvazeh Dowlat is open 24 hours a day, in order to accommodate passengers traveling to and from Imam Khomeini Airport via Line 1.
Line 1 connects Tehran to Imam Khomeini International Airport. Its first phase, to Shahr-e-Aftab station, opened in 2016, and the airport station opened in August 2017. It is the only metro line in Tehran that is completely open 24 hours a day (even if the frequency is only 80 minutes...), in order to accommodate passengers from late night and early morning flights (Line 1's Darvazeh Dowlat station is the only other metro station outside of Line 1 with that classification). A third phase, which is currently operational, will extend Line 1 to the satellite city
A satellite city or satellite town is a smaller municipality or settlement that is part of (or on the edge of) a larger metropolitan area and serves as a regional population and employment center. It differs from mere suburbs, Subdivision (la ...
of Parand and bring the total length of the line to . Its per hour speeds classify it as an express
Express, The Expresss or EXPRESS may refer to:
Arts, entertainment and media Film
* ''Express: Aisle to Glory'', a 1998 comedy short film featuring Kal Penn
* ''The Express: The Ernie Davis Story'', a 2008 film starring Dennis Quaid
* The Expre ...
subway line, the first of its kind on the Tehran Metro.
Line 2
 This line opened between Sadeghieh and
This line opened between Sadeghieh and Imam Khomeini
Ruhollah Musavi Khomeini (17 May 1900 or 24 September 19023 June 1989) was an Iranian revolutionary, politician, political theorist, and religious leader. He was the founder of the Islamic Republic of Iran and the main leader of the Iranian ...
in February 2000. Line 2 is long, with underground and elevated. There are 22 stations along the line, of which Imam Khomeini Station was shared by Line 1. Line 2 is coloured blue on system maps and runs mostly east–west through the city.
The line was extended from Imam-Khomeini to Baharestan Metro Station in 2004, and to Shahid Madani, Sarsabz and Elm-o-Sanat University in March 2006 with the intermediate stations, Darvazeh Shemiran and Sabalan, opening in July 2006. It was extended further from Elm-o-Sanat University to Tehran Pars in February 2009, and to Farhangsara in June 2010. The extension phase to new east terminal is under construction.
Line 3
 Line 3 travels from northeast to southwest. Line 3 is one of the most important lines as it connects southwest Tehran to northeast, crosses busy parts of the capital city, and can help to alleviate traffic problems. About of Line 3 became operational in December 2012, followed by in April 2014, and finally, the last section of the line which is opened on September 22, 2015, increasing the length of the line to a total of , and serving 25 stations .
Line 3 travels from northeast to southwest. Line 3 is one of the most important lines as it connects southwest Tehran to northeast, crosses busy parts of the capital city, and can help to alleviate traffic problems. About of Line 3 became operational in December 2012, followed by in April 2014, and finally, the last section of the line which is opened on September 22, 2015, increasing the length of the line to a total of , and serving 25 stations .
Line 4
Line 5
Karaj
Karaj (; ) is a List of cities in Iran by province, city in the Central District (Karaj County), Central District of Karaj County, Alborz province, Alborz province, Iran, serving as capital of the province, the county, and the district. Earl ...
with main stations at Karaj and Golshahr and Hashtgerd. It connects with the western end of Line 2 at Tehran (Sadeghiyeh) station, and with the western end of Line 4 at Eram-e Sabz Metro Station.
Line 6
Line 7
Future plans
There are several plans to expand Tehran's metro network to over in total. Some plans only concern additional inserted stations, like ''Vavan'' on line 1 in the South or ''Aghdasiyeh'' on line 3 in the North. Some extensions and completely new lines are under construction, some extensions or new lines are proposals in the moment.Under construction

Line 3 (formerly named ''Eslamshahr line'')
In the south, line 3 will continue for from the terminus ''Azadegan'' with five new stations to ''Eslamshahr''. Originally, the plan was to build a commuter rail-link like line 5 with a new interchange platform at ''Azadegan'' under the name "Eslamshahr Line". But until construction began in 2016, the plans were changed into a transfer-free extension of the existing route. The opening is scheduled for 2025.Line 6
Line 6 extension is on the way in the Northwest, where three new stations are built, and at the East end, where one additional station is under construction.Line 7
There is an extension of one station each from each recent terminus in the North and in the Southeast under construction.Line 10
The completely rebuilt line 10, coloured dark blue in the system map, stretching with 35 stations will run along a west–east corridor from Vardavard metro station of line 5 in the west of Tehran towards the area of Kosar aqueduct in the east with an interchange to the extended line 4. Construction started in September 2020.Further plans

Line 8
Line 8 of Tehran's Metro, coloured brown in the system map, is a planned circular line, surrounding the city center from ''Fadak station'' (line 2) in the North, over the West, and ending in the southeastern borough of ''Shahrak-e-Valfajr''. It might have 34 stations, 21 of them newly built, while the others will be expanded existing ones becoming interchange stations to other lines.Line 9
The planned line 9 of the metro network, coloured golden in the system map, is another circular line, starting further west at line 5 station ''Chitgar'', passing the city center in the North, turning south and ending at line 6 station ''Dowlat Abad''. It might have 39 stations all together, 27 of them new constructed, while the others will be expansions of existing stations to become interchanges to other lines.Line 11
Line 11, coloured light green in the system map, is another planned tangent line, starting from ''Chitgar'' station at line 5, connecting the southern parts of Tehran, and ending in the Southeast in the borough of ''Eslam Abad''. It might have 18 stations, most of them newly built, just five to be expanded existing stations to become interchanges with other lines.LRT Lines
3 LRT (Tram) lines are proposed along with the Metro lines.Express Commuter Railway
3 other commuter Rail lines are planned along with Line 5 (Tehran-Karaj-Hashtgerd Commuter Rail) bringing the total Metro Commuter Rails to 4 Lines .Interchange stations
* 1- Darvazeh Shemiran; Lines 2 & 4 * 2- Shahid Beheshti; Lines 1 & 3 * 3- Darvazeh Dowlat; Lines 1 & 4 * 4- Imam Khomeini; Lines 1 & 2 * 5- Theatr-e Shahr; Lines 3 & 4 * 6- Shademan; Lines 2 & 4 * 7- (Tehran) Sadeghiyeh; Lines 2 & 5 * 8- Eram-e Sabz; Lines 4 & 5 * 9- Shahid Navvab-e Safavi; Lines 2 & 7 * 10- Mahdiyeh; Lines 3 & 7 * 11- Meydan-e Shohada; Lines 4 & 6 * 12- Meydan-e Mohammadiyeh; Lines 1 & 7 * 13- Imam Hossein; Lines 2 & 6 * 14- Daneshgah-e Tarbiat Modares; Lines 6 & 7 * 15- Towhid; Lines 4 & 7 * 16- Shohada-ye Haftom-e Tir; Lines 1 & 6 * 17- Meydan-e Vali Asr; Lines 3 & 6 * 18- Shohada-ye Hefdah-e Shahrivar; Lines 6 & 7 (under construction on line 6, operational on line 7) * 19- Ayatollah Kashani; Lines 4 & 6 (under construction on line 4, operational on line 6) * 20- Shahr-e-Rey; Lines 1 & 6 (operational on line 1, under construction on line 6)Network map
Safety
All routes have been equipped withautomatic train protection
Automatic train protection (ATP) is the generic term for train protection systems that continually check that the speed of a train is compatible with the permitted speed allowed by signalling, including automatic stop at certain signal aspects ...
(ATP), automatic train stop (ATS), centralized traffic control (CTC), and SCADA
SCADA (an acronym for supervisory control and data acquisition) is a control system architecture comprising computers, networked data communications and graphical user interfaces for high-level supervision of machines and processes. It also cove ...
. More and more residents use the metro due to the improvement in the peak-hour headways, the opening of more stations and overall improvement with new escalators, elevators, and air-conditioning in the trains.
On 18 July 2007, a twenty square metres area immediately adjacent to the entrance of the Toupkhaneh metro station caved in. There were no casualties, but the station had to undergo numerous repairs.
On 15 April 2012, safety walls of Mianrood River broke due to heavy rain in Tehran, and consequently, 300,000 cubic meters of water entered metro tunnel of Line 4. The two nearest stations were still under construction, so Metro operators had enough time to evacuate other stations from passengers. Nobody was killed, but water depth in the Habib-o-llah station, the deepest station on Line 4, was estimated to be near 18 meters. It took nearly two weeks to reopen the flooded stations which were previously in operation.
Complaints
The Cultural Heritage Organization of Iran has complained that the vibrations caused by the Metro were having a significant and highly adverse effect on the Masoudieh Palace in the Baharestan neighbourhood of central Tehran. The Cultural Heritage Organisation has also complained about vibrations near other historic sites such as theGolestan Palace
The Golestan Palace (, ''Kākh-e Golestān''), also transliterated as the Gulistan Palace and sometimes translated as the Rose Garden Palace from Persian language, was built in the 16th century, renovated in the 18th century and finally rebuilt ...
and the National Museum of Iran.
Tickets
Regular single table tickets You can only use the subway once with this ticket. This ticket costs 12,000 Rials. If you plan to take a round trip, you need to get two single tickets. Suburban single table tickets This is the ticket from the 5th metro line that reaches Sadeghieh station fromKaraj
Karaj (; ) is a List of cities in Iran by province, city in the Central District (Karaj County), Central District of Karaj County, Alborz province, Alborz province, Iran, serving as capital of the province, the county, and the district. Earl ...
station. This ticket costs 12,000 Rials.
International Airport Single Ticket
This ticket is used for the subway line of Imam Khomeini Airport. This ticket costs 90,000 Rials.
Electronic ticket
You can use the subway as many times as you want by charging it. The cost of each of these e-cards is 30,000 Rials or 50,000 Rials and you can charge up to 500,000 Rials after purchase. You can charge your e-card using various booths and wall-mounted electronic charging devices at the bus and subway stations, either by cash or by bank credit card and with non-attendance methods such as my Tehran app
Tehran Metro Snapshot
Gallery
Samsung
Samsung Group (; stylised as SΛMSUNG) is a South Korean Multinational corporation, multinational manufacturing Conglomerate (company), conglomerate headquartered in the Samsung Town office complex in Seoul. The group consists of numerous a ...
advertising in Tehran Metro
File:Tehran Metro Workers 2019 21.jpg, Tehran Metro Line 6
File:L7 Tehran Metro 2019 01.jpg, Tehran Metro Line 7
File:Tehran Metro Workers 2019 23.jpg, Tehran Metro Line 7
File:Ashrafi Esfahani Metro Station 1.jpg, Ashrafi Esfahani Metro Station at Tehran Metro Line 6
File:Tehran Metro Depot.jpg, Tehran Metro Depot
File:Tehran metro station.ogv, thumbtime=00:34, Tehran Subway arriving at the Vali-e-asr station.
File:2 Tehran Metro 2019.jpg, Meydan-e San'at Metro Station ( Line 7)
File:FM Zarif departures to his office by Metro 01.jpg, Former foreign Minister Mohammad Javad Zarif, using metro to his office.
File:TM1 (SIK 04-E1424-272).jpg, Tehran Suburban Railway train
See also
References
External links
Tehran Metro (official site)
The Unofficial Homepage of Iranian Railways
(in Persian)
''UrbanRail.Net''
– descriptions of all metro systems in the world, each with a schematic map showing all stations. {{Rapid transit in Asia Underground rapid transit in Iran 1999 establishments in Iran Standard-gauge railways in Iran Articles containing video clips Railway lines opened in 1999