Tanum Tunnel on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Tanum Tunnel ( no, Tanumtunnelen) is double-track railway tunnel on the Asker Line, between Jong in Bærum and Åstad in Asker, Norway. It was built as part of the first stage of the Asker Line, between Asker and Sandvika; construction started in February 2002 and the tunnel opened on 27 August 2005. The tunnel was built by AF Gruppen for the Norwegian National Rail Administration. Most of the tunneling was conducted using the drilling and blasting method, although the easternmost were built using the cut-and-cover method. After the tunnel opened, there have been problems with leaks damaging the superstructure. The tunnel has
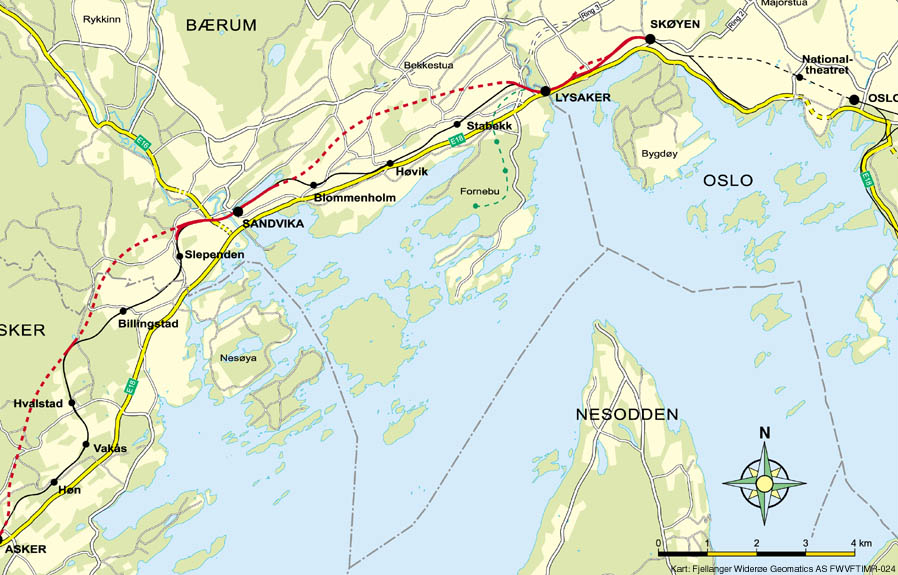 The Asker Line runs from Lysaker Station via Sandvika Station to Asker Station, in the municipalities of Bærum and Asker. The line was built to allow increased railway traffic though the main corridor west of Oslo. Previously, the only railway west of Oslo was the Drammen Line, which has limited capacity and is used by a mix of local, regional, intercity and freight trains. This caused many delays and poor utilization of tracks, as some trains make many stops and others only a few. The Asker Line allows regional and intercity trains to by-pass local stations east of Asker while local and freight trains remain on the Drammen Line. The Asker Line was built in two stages: the first, from Asker to Sandvika, was constructed between 2001 and 2005. The second stage, from Sandvika to Lysaker, was constructed between 2007 and 2011. The other two tunnels on the Asker Line are the Skaugm Tunnel and the
The Asker Line runs from Lysaker Station via Sandvika Station to Asker Station, in the municipalities of Bærum and Asker. The line was built to allow increased railway traffic though the main corridor west of Oslo. Previously, the only railway west of Oslo was the Drammen Line, which has limited capacity and is used by a mix of local, regional, intercity and freight trains. This caused many delays and poor utilization of tracks, as some trains make many stops and others only a few. The Asker Line allows regional and intercity trains to by-pass local stations east of Asker while local and freight trains remain on the Drammen Line. The Asker Line was built in two stages: the first, from Asker to Sandvika, was constructed between 2001 and 2005. The second stage, from Sandvika to Lysaker, was constructed between 2007 and 2011. The other two tunnels on the Asker Line are the Skaugm Tunnel and the
double track
A double-track railway usually involves running one track in each direction, compared to a single-track railway where trains in both directions share the same track.
Overview
In the earliest days of railways in the United Kingdom, most lin ...
, is electrified and allows for a maximum speed of . The cost to build the tunnel, excluding the superstructure, was 370 million Norwegian krone
The krone (, abbreviation: kr (also NKr for distinction); code: NOK), plural ''kroner'', is currency of the Kingdom of Norway (including Svalbard). Traditionally known as the Norwegian crown in English. It is nominally subdivided into 100 ''� ...
(NOK). The tunnel will accelerate intercity and regional traffic west of Oslo and free up capacity for the Oslo Commuter Rail on the Drammen Line.
Specifications
The Tanum Tunnel is long and has a cross section varying between . The tunnel consists of a blasted section and an , cut-and-cover section—the latter the easternmost part of the tunnel. It carries the double-tracked Asker Line between Jong and Åstad. The tunnel runs mostly throughCambrian
The Cambrian Period ( ; sometimes symbolized C with bar, Ꞓ) was the first geological period of the Paleozoic Era, and of the Phanerozoic Eon. The Cambrian lasted 53.4 million years from the end of the preceding Ediacaran Period 538.8 million ...
-Silurian
The Silurian ( ) is a geologic period and system spanning 24.6 million years from the end of the Ordovician Period, at million years ago ( Mya), to the beginning of the Devonian Period, Mya. The Silurian is the shortest period of the Paleozo ...
sedimentary slate
Slate is a fine-grained, foliated, homogeneous metamorphic rock derived from an original shale-type sedimentary rock composed of clay or volcanic ash through low-grade regional metamorphism. It is the finest grained foliated metamorphic rock. ...
, nodular limestone and shale
Shale is a fine-grained, clastic sedimentary rock formed from mud that is a mix of flakes of clay minerals (hydrous aluminium phyllosilicates, e.g. kaolin, Al2 Si2 O5( OH)4) and tiny fragments (silt-sized particles) of other minerals, especial ...
, with local occurrences of Permian igneous rock. There is also a section of less stable sedimentary rock in the Asker Group. The tunnel had a cover most of the way of between ; however at Billingstad
Billingstad is a village in Asker municipality, Akershus county, Norway. It is close to the border of Bærum and Vestmarka and is 18 km west of Oslo. It has 2,349 residents (2006).
The area is both residential and commercial. It is served b ...
there was a much lower margin, laying for the most at and at the least at . At Åstad, the line runs in the open before entering the Skaugum Tunnel. The line is electrified at and allows a maximum speed of . The tunnel has frost insulation into the tunnel form each end. The tunnel has frost fans which ensure that the air stays put in the middle of the tunnel, thus hindering cold air from flowing past the frost isolation.
History
 The Asker Line runs from Lysaker Station via Sandvika Station to Asker Station, in the municipalities of Bærum and Asker. The line was built to allow increased railway traffic though the main corridor west of Oslo. Previously, the only railway west of Oslo was the Drammen Line, which has limited capacity and is used by a mix of local, regional, intercity and freight trains. This caused many delays and poor utilization of tracks, as some trains make many stops and others only a few. The Asker Line allows regional and intercity trains to by-pass local stations east of Asker while local and freight trains remain on the Drammen Line. The Asker Line was built in two stages: the first, from Asker to Sandvika, was constructed between 2001 and 2005. The second stage, from Sandvika to Lysaker, was constructed between 2007 and 2011. The other two tunnels on the Asker Line are the Skaugm Tunnel and the
The Asker Line runs from Lysaker Station via Sandvika Station to Asker Station, in the municipalities of Bærum and Asker. The line was built to allow increased railway traffic though the main corridor west of Oslo. Previously, the only railway west of Oslo was the Drammen Line, which has limited capacity and is used by a mix of local, regional, intercity and freight trains. This caused many delays and poor utilization of tracks, as some trains make many stops and others only a few. The Asker Line allows regional and intercity trains to by-pass local stations east of Asker while local and freight trains remain on the Drammen Line. The Asker Line was built in two stages: the first, from Asker to Sandvika, was constructed between 2001 and 2005. The second stage, from Sandvika to Lysaker, was constructed between 2007 and 2011. The other two tunnels on the Asker Line are the Skaugm Tunnel and the Bærum Tunnel
The Bærum Tunnel ( no, Bærumstunnelen) is a long double track railway tunnel in Bærum, Norway. Running between Marstranderveien and Engervannet, it makes up most of the long section of the Asker Line between Lysaker Station and Sandvika S ...
.
The Norwegian National Rail Administration awarded the contract to build the Tanum Tunnel to AF Spesialprosjekt, part of AF Gruppen. The tunneling cost NOK 370 million, including the open section between Solstad and Åstad, but excluding superstructure. The main part of the tunnel was built using the drilling and blasting method, using two points of entry. Work on the tunneling started in 2002 and was concluded in February 2004. Construction included the removal of of earthwork and the laying of of ballast. Laying of tracks, signaling, power supply and other superstructures were done by Baneservice. The cost of superstructures for the entire section from Asker to Sandvika was NOK 70 million. The work was completed by November 2004. The opening of the tunnel and the rest of the section from Asker to Sandvika took place on 27 August 2005.
A concern from people living along the tunnel was that they would be subject to low-frequency noise. Originally the municipalities of Asker and Bærum had demanded that residents be subject to a maximum of 27 decibel
The decibel (symbol: dB) is a relative unit of measurement equal to one tenth of a bel (B). It expresses the ratio of two values of a power or root-power quantity on a logarithmic scale. Two signals whose levels differ by one decibel have a po ...
A-weighting
A-weighting is the most commonly used of a family of curves defined in the International standard IEC 61672:2003 and various national standards relating to the measurement of sound pressure level. A-weighting is applied to instrument-measured ...
(dBA), but the National Rail Administration appealed the requirements and was permitted to allow up to 32 dBA. In March 2004, a test was done in the tunnel to insure that the requirements would be met, as low-frequency sound is difficult to predict. Measurements after the opening of the tunnel showed background noise of 30 dBA, that no-one was subject to 32 dBA or higher, and that it was nearly impossible to measure the passing of trains.
Among the major concerns was leaks; during the construction on the Romerike Tunnel, there was a one-year delay and severe cost overruns due to improper leak handling methods. Therefore, one of the main focuses in the Skaugum Tunnel project was to avoid similar leaks. The contract specified a maximum leakage of per minute per . The contractor attempted to achieve this by extending the time used for pre-injection of concrete. However, there was still water dripping into the tunnel, which caused several types of damage. Some places the water dripped onto the track, causing rust; other places water dripped onto electrical equipment. There was also issues with water running down the walls and collecting in the cable conduit, and the water with limestone dripping on the ballast and mixing the ballast with limestone. By 2011, the emergency lighting system had to be replaced because of the high humidity. The National Rail Administration has stated that savings made to the specifications in the water and frost methods have caused higher maintenance costs because the small leaks which are present do a lot of harm. In addition, areas with leaks suffer from icing. This has been part of a national trend where older tunnels are nearly maintenance-free, while newer tunnels have incurred high maintenance costs.
References
{{good article Asker Railway tunnels in Viken Tunnels in Bærum 2005 establishments in Norway Tunnels completed in 2005 Tunnels on the Asker Line