Sichuan is a
province
A province is an administrative division within a country or sovereign state, state. The term derives from the ancient Roman , which was the major territorial and administrative unit of the Roman Empire, Roman Empire's territorial possessions ou ...
in
Southwestern China
Southwestern China () is a region in the People's Republic of China. It consists of five provincial administrative regions, namely Chongqing, Sichuan, Guizhou, Yunnan, and Xizang.
Geography
Southwestern China is a rugged and mountainous region, ...
, occupying the
Sichuan Basin
The Sichuan Basin (), formerly transliterated as the Szechwan Basin, sometimes called the Red Basin, is a lowland region in southwestern China. It is surrounded by mountains on all sides and is drained by the upper Yangtze River and its tributar ...
and
Tibetan Plateau
The Tibetan Plateau, also known as the Qinghai–Tibet Plateau or Qingzang Plateau, is a vast elevated plateau located at the intersection of Central Asia, Central, South Asia, South, and East Asia. Geographically, it is located to the north of H ...
—between the
Jinsha River
The Jinsha River (, Classical Tibetan, Tibetan: Dri Chu, འབྲི་ཆུ, ) or Lu river, is the Chinese name for the upper stretches of the Yangtze River. It flows through the provinces of the PRC, provinces of Qinghai, Sichuan, and Yu ...
to the west, the
Daba Mountains
The Daba Mountains, also known by their Chinese name as the Dabashan, are a mountain range in Central China between the watersheds of the Yellow and Yangtze Rivers. Part of the larger Qinling mountain range, it cuts through four provinces: S ...
to the north, and the
Yunnan–Guizhou Plateau
The Yunnan–Guizhou Plateau or Yungui Plateau () is a highland region located in southwest China. The region is primarily spread over the provinces of Yunnan and Guizhou. In the southwest, the Yungui is a true plateau with relatively flatt ...
to the south. Its capital city is
Chengdu
Chengdu; Sichuanese dialects, Sichuanese pronunciation: , Standard Chinese pronunciation: ; Chinese postal romanization, previously Romanization of Chinese, romanized as Chengtu. is the capital city of the Chinese province of Sichuan. With a ...
, and its population stands at 83 million. Sichuan neighbors
Qinghai
Qinghai is an inland Provinces of China, province in Northwestern China. It is the largest provinces of China, province of China (excluding autonomous regions) by area and has the third smallest population. Its capital and largest city is Xin ...
and
Gansu
Gansu is a provinces of China, province in Northwestern China. Its capital and largest city is Lanzhou, in the southeastern part of the province. The seventh-largest administrative district by area at , Gansu lies between the Tibetan Plateau, Ti ...
to the north,
Shaanxi
Shaanxi is a Provinces of China, province in north Northwestern China. It borders the province-level divisions of Inner Mongolia to the north; Shanxi and Henan to the east; Hubei, Chongqing, and Sichuan to the south; and Gansu and Ningxia to t ...
and
Chongqing
ChongqingPostal Romanization, Previously romanized as Chungking ();. is a direct-administered municipality in Southwestern China. Chongqing is one of the four direct-administered municipalities under the State Council of the People's Republi ...
to the east,
Guizhou
)
, image_skyline =
, image_caption =
, image_map = Guizhou in China (+all claims hatched).svg
, mapsize = 275px
, map_alt = Map showing the location of Guizhou Province
, map_caption = Map s ...
and
Yunnan
Yunnan; is an inland Provinces of China, province in Southwestern China. The province spans approximately and has a population of 47.2 million (as of 2020). The capital of the province is Kunming. The province borders the Chinese provinces ...
to the south, and
Tibet
Tibet (; ''Böd''; ), or Greater Tibet, is a region in the western part of East Asia, covering much of the Tibetan Plateau and spanning about . It is the homeland of the Tibetan people. Also resident on the plateau are other ethnic groups s ...
to the west.
During antiquity, Sichuan was home to the kingdoms of
Ba and
Shu until their incorporation by the
Qin. During the
Three Kingdoms
The Three Kingdoms of Cao Wei, Shu Han, and Eastern Wu dominated China from AD 220 to 280 following the end of the Han dynasty. This period was preceded by the Eastern Han dynasty and followed by the Jin dynasty (266–420), Western Jin dyna ...
era (220–280),
Liu Bei
Liu Bei (, ; ; 161 – 10 June 223), courtesy name Xuande (), was a China, Chinese warlord in the late Han dynasty#Eastern Han, Eastern Han dynasty who later became the founding Emperor of China, emperor of Shu Han, one of the Three Kingdoms of ...
's state of
Shu was based in Sichuan. The area was devastated in the 17th century by
Zhang Xianzhong
Zhang Xianzhong (張獻忠 or Chang Hsien-chung; 18 September 1606 – 2 January 1647), courtesy name Bingwu (秉吾), art name Jingxuan (敬軒), was a Chinese peasant leader who led a peasant rebellion from Yan'an wei, Shaanxi (today Yulin, ...
's rebellion and the area's subsequent
Manchu
The Manchus (; ) are a Tungusic peoples, Tungusic East Asian people, East Asian ethnic group native to Manchuria in Northeast Asia. They are an officially recognized Ethnic minorities in China, ethnic minority in China and the people from wh ...
conquest, but recovered to become one of China's most productive areas by the 19th century. During
World War II
World War II or the Second World War (1 September 1939 – 2 September 1945) was a World war, global conflict between two coalitions: the Allies of World War II, Allies and the Axis powers. World War II by country, Nearly all of the wo ...
, Chongqing served as the temporary capital of the
Republic of China
Taiwan, officially the Republic of China (ROC), is a country in East Asia. The main geography of Taiwan, island of Taiwan, also known as ''Formosa'', lies between the East China Sea, East and South China Seas in the northwestern Pacific Ocea ...
, and was
heavily bombed. It was one of the last
mainland
Mainland is defined as "relating to or forming the main part of a country or continent, not including the islands around it egardless of status under territorial jurisdiction by an entity" The term is often politically, economically and/or demogr ...
areas captured by the
People's Liberation Army
The People's Liberation Army (PLA) is the military of the Chinese Communist Party (CCP) and the People's Republic of China (PRC). It consists of four Military branch, services—People's Liberation Army Ground Force, Ground Force, People's ...
during the
Chinese Civil War
The Chinese Civil War was fought between the Kuomintang-led Nationalist government, government of the Republic of China (1912–1949), Republic of China and the forces of the Chinese Communist Party (CCP). Armed conflict continued intermitt ...
, and was divided into four parts from 1949 to 1952, with Chongqing restored two years later. It suffered gravely during the
Great Chinese Famine (1959–1961) but remained China's
most-populous province until Chongqing was again separated from it in 1997.
The
Sichuanese people
The Sichuanese people or zh, c=川渝人, p=Chuānyú rén, labels=no, sometimes shortened to zh, c=川人, labels=no; Sichuanese Pinyin: ''Sicuanren''; former romanization: Szechwanese people are a Han Chinese subgroup comprising most of the ...
speak distinctive
dialects
A dialect is a variety of language spoken by a particular group of people. This may include dominant and standardized varieties as well as vernacular, unwritten, or non-standardized varieties, such as those used in developing countries or iso ...
of
Mandarin Chinese
Mandarin ( ; zh, s=, t=, p=Guānhuà, l=Mandarin (bureaucrat), officials' speech) is the largest branch of the Sinitic languages. Mandarin varieties are spoken by 70 percent of all Chinese speakers over a large geographical area that stretch ...
. The
Sichuan pepper
Sichuan pepper (, also known as Sichuanese pepper, Szechuan pepper, Chinese prickly ash, Chinese pepper, Mountain pepper, and ''mala'' pepper, is a spice commonly used in Sichuan cuisine in China, Bhutan and in northeast India. It is called mej ...
, with its distinctive flavor and numbing effect, is prominent in modern
Sichuan cuisine
Sichuan cuisine or Sichuanese cuisine, alternatively romanized as Szechwan cuisine or Szechuan cuisine (, Standard Mandarin pronunciation: ) is a style of Chinese cuisine originating from Sichuan province and the neighboring Chongqing munic ...
, featuring dishes, including
Kung Pao chicken
Kung Pao chicken (), also transcribed Gong Bao or Kung Po, is a spicy, stir-fried Chinese dish made with cubes of cooked chicken, peanuts, vegetables and chili peppers, and Sichuan peppercorns. From its origins in Sichuan cuisine, the dish' ...
and
mapo tofu, that have become staples of Chinese cuisine around the world.
There are many
panda
The giant panda (''Ailuropoda melanoleuca''), also known as the panda bear or simply panda, is a bear species endemic to China. It is characterised by its white coat with black patches around the eyes, ears, legs and shoulders. Its body is ...
stations in the province and large reserves for these creatures, such as the
Chengdu Research Base of Giant Panda Breeding.
Sichuan is the
6th-largest provincial economy of China, the largest in
Western China
Western China ( zh, s=中国西部, l=, labels=no or zh, s=华西, l=, labels=no) is the west of China. It consists of Southwestern China and Northwestern China. In the definition of the Chinese government, Western China covers six provinces ...
, and the second-largest among inland provinces after
Henan
Henan; alternatively Honan is a province in Central China. Henan is home to many heritage sites, including Yinxu, the ruins of the final capital of the Shang dynasty () and the Shaolin Temple. Four of the historical capitals of China, Lu ...
. As of 2021, its nominal GDP was (US$847.68 billion), ahead of that of Turkey ($815 billion).
If it were its own country, Sichuan would be the
18th-largest economy and
19th-most populous as of 2021.
Names
It is commonly assumed that the name ''Sichuan'' means 'four
rivers
A river is a natural stream of fresh water that flows on land or inside caves towards another body of water at a lower elevation, such as an ocean, lake, or another river. A river may run dry before reaching the end of its course if it ru ...
'; in
folk etymology
Folk etymology – also known as (generative) popular etymology, analogical reformation, (morphological) reanalysis and etymological reinterpretation – is a change in a word or phrase resulting from the replacement of an unfamiliar form by a mo ...
, this is usually taken to mean four of the province's major rivers: the
Jialing,
Jinsha (or
Wu),
Min, and
Tuo.
According to historical geographer
Tan Qixiang, 'four rivers' is an erroneous interpretation of the name.
The name of the province is a contraction of the phrases 'Four Plain
Circuits' () and 'Four Circuits of Chuanxia' (), referring to the division of the existing
imperial administrative circuit in the area into four during the
Northern Song dynasty
The Song dynasty ( ) was an imperial dynasty of China that ruled from 960 to 1279. The dynasty was founded by Emperor Taizu of Song, who usurped the throne of the Later Zhou dynasty and went on to conquer the rest of the Ten Kingdoms, endin ...
, which were
Yizhou,
Lizhou,
Zizhou, and
Kuizhou. The word ''chuan'' () here means 'plain', not its typical meaning of 'river' as popularly assumed. In addition to its
postal map and
Wade–Giles
Wade–Giles ( ) is a romanization system for Mandarin Chinese. It developed from the system produced by Thomas Francis Wade during the mid-19th century, and was given completed form with Herbert Giles's '' A Chinese–English Dictionary'' ...
forms, the name has also been irregularly romanized as ''Szű-chuan'' and ''Szechuen''.
In antiquity, the area of modern Sichuan including the now-separated Chongqing Municipality was known to the Chinese as ''Ba–Shu'', in reference to the
ancient state of
Ba and the
ancient kingdom of Shu that once occupied the
Sichuan Basin
The Sichuan Basin (), formerly transliterated as the Szechwan Basin, sometimes called the Red Basin, is a lowland region in southwestern China. It is surrounded by mountains on all sides and is drained by the upper Yangtze River and its tributar ...
. ''Shu'' continued to be used to refer to the region to the present day; several states formed in the area used the same name, for example, the
Shu of the
Three Kingdoms
The Three Kingdoms of Cao Wei, Shu Han, and Eastern Wu dominated China from AD 220 to 280 following the end of the Han dynasty. This period was preceded by the Eastern Han dynasty and followed by the Jin dynasty (266–420), Western Jin dyna ...
period (220–280), and
Former Shu
Great Shu ( zh, c=大蜀, p=Dàshǔ), known in historiography as the Former Shu ( zh, c=前蜀, p=Qiánshǔ, links=no) or occasionally Wang Shu (王蜀), was a dynastic state of China and one of the Ten Kingdoms during the Five Dynasties and ...
and
Later Shu
Shu, referred to as Later Shu ( zh, t=後蜀, s=后蜀, first=t, p=Hòu Shǔ) and Meng Shu ( zh, c=孟蜀) in historiography, was a dynastic state of China and one of the Ten Kingdoms during the Five Dynasties and Ten Kingdoms period. It was ...
of the
Ten Kingdoms period (907–979). Currently, both characters for ''Shu'' and ''Chuan'' are common abbreviations for Sichuan.
The region was formerly referred to as "West China" or "Western China" by
Protestant missions.
History
Prehistory
The
Sichuan Basin
The Sichuan Basin (), formerly transliterated as the Szechwan Basin, sometimes called the Red Basin, is a lowland region in southwestern China. It is surrounded by mountains on all sides and is drained by the upper Yangtze River and its tributar ...
and adjacent areas of the
Yangtze
The Yangtze or Yangzi ( or ) is the longest river in Eurasia and the third-longest in the world. It rises at Jari Hill in the Tanggula Mountains of the Tibetan Plateau and flows including Dam Qu River the longest source of the Yangtze, i ...
watershed were a cradle of indigenous civilizations dating back to at least the 15th century BC, coinciding with the
Shang
The Shang dynasty (), also known as the Yin dynasty (), was a Chinese royal dynasty that ruled in the Yellow River valley during the second millennium BC, traditionally succeeding the Xia dynasty and followed by the Western Zhou dyn ...
in northern China. The region had its own distinct religious beliefs and worldview. The earliest excavated culture found therein is the
Baodun culture (2700–1750 BC) excavated in the
Chengdu Plain
The Chengdu Plain ( zh, t=成都平原, s=成都平原, p=Chéngdū Píngyuán), referred to in Sichuanese as the Western Sichuan Plain ( zh, s=川西坝子, first=t; Sichuanese Pinyin: ''Cuanxi Bazi''), is an alluvial plain located in the wes ...
.
Ba and Shu Kingdoms
The most important native states were those of Ba and Shu.
Ba stretched into Sichuan from the
Han Valley in
Shaanxi
Shaanxi is a Provinces of China, province in north Northwestern China. It borders the province-level divisions of Inner Mongolia to the north; Shanxi and Henan to the east; Hubei, Chongqing, and Sichuan to the south; and Gansu and Ningxia to t ...
and
Hubei
Hubei is a province of China, province in Central China. It has the List of Chinese provincial-level divisions by GDP, seventh-largest economy among Chinese provinces, the second-largest within Central China, and the third-largest among inland ...
down the
Jialing River
The Jialing River, formerly known by numerous other names, is a major tributary of the Yangtze River in the Sichuan Basin. It is named after the Jialing Valley in Feng County, Shaanxi through which it flows.
The Jialing River's most notable c ...
as far as its confluence with the
Yangtze
The Yangtze or Yangzi ( or ) is the longest river in Eurasia and the third-longest in the world. It rises at Jari Hill in the Tanggula Mountains of the Tibetan Plateau and flows including Dam Qu River the longest source of the Yangtze, i ...
at
Chongqing
ChongqingPostal Romanization, Previously romanized as Chungking ();. is a direct-administered municipality in Southwestern China. Chongqing is one of the four direct-administered municipalities under the State Council of the People's Republi ...
.
occupied the valley of the
Min, including
Chengdu
Chengdu; Sichuanese dialects, Sichuanese pronunciation: , Standard Chinese pronunciation: ; Chinese postal romanization, previously Romanization of Chinese, romanized as Chengtu. is the capital city of the Chinese province of Sichuan. With a ...
and other areas of western Sichuan.
[ The existence of the early state of Shu was poorly recorded in the main historical records of China. It was, however, referred to in the '']Book of Documents
The ''Book of Documents'' ( zh, p=Shūjīng, c=書經, w=Shu King) or the ''Classic of History'', is one of the Five Classics of ancient Chinese literature. It is a collection of rhetorical prose attributed to figures of ancient China, a ...
'' as an ally of the Zhou. Accounts of Shu exist mainly as a mixture of mythological stories and historical legends recorded in local annals such as the ''Chronicles of Huayang
The ''Chronicles of Huayang'' or ''Huayang Guo Zhi'' ( zh, t=華陽國志, s=华阳国志, first=t, l=Records of the Lands South of Mt. Hua) is the oldest extant gazetteer of a region of China. It was compiled by Chang Qu during the Jin dynast ...
'' compiled in the Jin dynasty (266–420)
The Jin dynasty or Jin Empire, sometimes distinguished as the or the , was an Dynasties of China, imperial dynasty in China that existed from 266 to 420. It was founded by Emperor Wu of Jin, Sima Yan, eldest son of Sima Zhao, who had previou ...
,Sanxingdui
Sanxingdui () is an archaeological site and a major Bronze Age culture in modern Guanghan, Sichuan, China. Largely discovered in 1986, following a preliminary finding in 1927, archaeologists excavated artifacts that radiocarbon dating placed ...
in Guanghan
Guanghan ( zh, s=广汉, t=廣漢, p=Guǎnghàn; formerly known as Hanchow) is a county-level city under the administration of Deyang in Sichuan province, southwest China, and only from Chengdu. The predominant industries are tourism, pharmaceut ...
, Sichuan.Yellow River
The Yellow River, also known as Huanghe, is the second-longest river in China and the List of rivers by length, sixth-longest river system on Earth, with an estimated length of and a Drainage basin, watershed of . Beginning in the Bayan H ...
valley of north-central China.
Qin dynasty
The rulers of the expansionist state of Qin, based in present-day Gansu
Gansu is a provinces of China, province in Northwestern China. Its capital and largest city is Lanzhou, in the southeastern part of the province. The seventh-largest administrative district by area at , Gansu lies between the Tibetan Plateau, Ti ...
and Shaanxi
Shaanxi is a Provinces of China, province in north Northwestern China. It borders the province-level divisions of Inner Mongolia to the north; Shanxi and Henan to the east; Hubei, Chongqing, and Sichuan to the south; and Gansu and Ningxia to t ...
, were the first strategists to realize that the area's military importance matched its commercial and agricultural significance. The Sichuan basin is surrounded by the Hengduan Mountains
The Hengduan Mountains () are a group of mountain ranges in southwest China, southwest China that connect the southeast portions of the Tibetan Plateau with the Yunnan–Guizhou Plateau. The Hengduan Mountains are primarily large north-south ...
to the west, the Qin Mountains
The Qinling () or Qin Mountains, formerly known as the Nanshan ("Southern Mountains"), are a major east–west mountain range in southern Shaanxi Province, China. The mountains mark the divide between the drainage basins of the Yangtze and Ye ...
to the north, and Yungui Plateau to the south. Since the Yangtze flows through the basin and then through the perilous Three Gorges to eastern and southern China, Sichuan was a staging area for amphibious military forces and a haven for political refugees.
Qin armies finished their conquest of the kingdoms of Shu and Ba by 316 BC. Any written records and civil achievements of earlier kingdoms were destroyed. Qin administrators introduced improved agricultural technology. Li Bing, engineered the Dujiangyan irrigation system
The Dujiangyan () is an ancient irrigation system in Dujiangyan City, Sichuan, China. Originally constructed around 256 BC by the State of Qin as an irrigation and flood control project, it is still in use today. The system's infrastructure dev ...
to control the Min River, a major tributary
A tributary, or an ''affluent'', is a stream or river that flows into a larger stream (''main stem'' or ''"parent"''), river, or a lake. A tributary does not flow directly into a sea or ocean. Tributaries, and the main stem river into which they ...
of the Yangtze. This innovative hydraulic system was composed of movable weirs which could be adjusted for high or low water flow according to the season, to either provide irrigation or prevent floods. The increased agricultural output and taxes made the area a source of provisions and men for Qin's unification of China.
Han dynasty
 Sichuan was subjected to the autonomous control of kings named by the imperial family of the Han dynasty. During the 11 years hiatus between 25 and 36 AD, Sichuan was controlled by the
Sichuan was subjected to the autonomous control of kings named by the imperial family of the Han dynasty. During the 11 years hiatus between 25 and 36 AD, Sichuan was controlled by the Chengjia
Chengjia (; 25–36 AD), also called the Cheng dynasty or Great Cheng, was a self-proclaimed empire established by Gongsun Shu in 25 AD after the collapse of the Xin dynasty of Chinese history, rivalling the Eastern Han dynasty founded by ...
Kingdom. Following the declining central government of the Han dynasty
The Han dynasty was an Dynasties of China, imperial dynasty of China (202 BC9 AD, 25–220 AD) established by Liu Bang and ruled by the House of Liu. The dynasty was preceded by the short-lived Qin dynasty (221–206 BC ...
in the second century, the Sichuan basin, surrounded by mountains and easily defensible, became a popular place for upstart generals to found kingdoms that challenged the authority of Yangtze Valley emperors over China.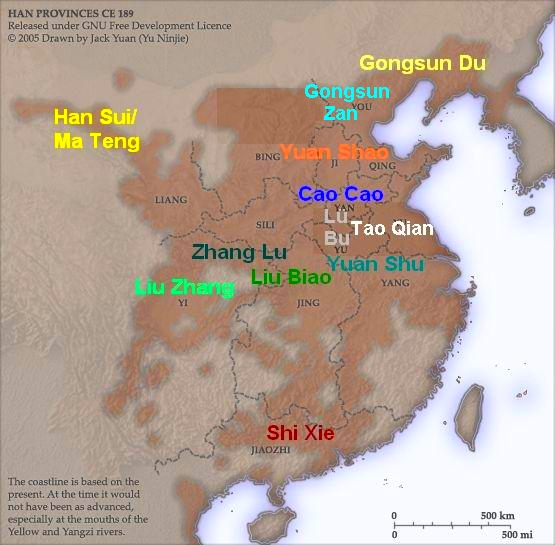
Three Kingdoms
In 221, during the partition following the fall of the Eastern Han
The Han dynasty was an Dynasties of China, imperial dynasty of China (202 BC9 AD, 25–220 AD) established by Liu Bang and ruled by the House of Liu. The dynasty was preceded by the short-lived Qin dynasty (221–206 BC ...
– the era of the Three Kingdoms
The Three Kingdoms of Cao Wei, Shu Han, and Eastern Wu dominated China from AD 220 to 280 following the end of the Han dynasty. This period was preceded by the Eastern Han dynasty and followed by the Jin dynasty (266–420), Western Jin dyna ...
– Liu Bei
Liu Bei (, ; ; 161 – 10 June 223), courtesy name Xuande (), was a China, Chinese warlord in the late Han dynasty#Eastern Han, Eastern Han dynasty who later became the founding Emperor of China, emperor of Shu Han, one of the Three Kingdoms of ...
founded the southwest kingdom of Shu Han
Han (; 221–263), known in historiography as Shu Han ( ) or Ji Han ( "Junior Han"), or often shortened to Shu ( zh, t=蜀, p=Shǔ; Sichuanese Pinyin: ''Su'' < Middle Chinese: *''źjowk'' < Eastern Han Chinese: *''dźok''), was a Dynasties in ...
(; 221–263) in parts of Sichuan, Guizhou, and Yunnan, with Chengdu
Chengdu; Sichuanese dialects, Sichuanese pronunciation: , Standard Chinese pronunciation: ; Chinese postal romanization, previously Romanization of Chinese, romanized as Chengtu. is the capital city of the Chinese province of Sichuan. With a ...
as its capital. Shu-Han claimed to be the successor to the Han dynasty.Cao Wei
Wei () was one of the major Dynasties in Chinese history, dynastic states in China during the Three Kingdoms period. The state was established in 220 by Cao Pi based upon the foundations laid by his father Cao Cao during the end of the Han dy ...
of North China conquered
Conquest involves the annexation or control of another entity's territory through war or coercion. Historically, conquests occurred frequently in the international system, and there were limited normative or legal prohibitions against conquest ...
the Kingdom of Shu-Han as a step on the path to reuniting China. Salt production
In common usage, salt is a mineral composed primarily of sodium chloride (NaCl). When used in food, especially in granulated form, it is more formally called table salt. In the form of a natural crystalline mineral, salt is also known as ro ...
becomes a major business in Ziliujing District. During the Six Dynasties
Six Dynasties (; 220–589 or 222–589) is a collective term for six Han-ruled Chinese dynasties that existed from the early 3rd century AD to the late 6th century AD, between the end of the Eastern Han dynasty and the beginning of the Sui ...
period of Chinese disunity, Sichuan began to be populated by non- Han ethnic minority peoples, owing to the migration of Gelao people from the Yunnan–Guizhou Plateau
The Yunnan–Guizhou Plateau or Yungui Plateau () is a highland region located in southwest China. The region is primarily spread over the provinces of Yunnan and Guizhou. In the southwest, the Yungui is a true plateau with relatively flatt ...
to the Sichuan basin.
Tang dynasty
Sichuan came under the firm control of a Chinese central government during the Sui dynasty
The Sui dynasty ( ) was a short-lived Dynasties of China, Chinese imperial dynasty that ruled from 581 to 618. The re-unification of China proper under the Sui brought the Northern and Southern dynasties era to a close, ending a prolonged peri ...
, but it was during the subsequent Tang dynasty
The Tang dynasty (, ; zh, c=唐朝), or the Tang Empire, was an Dynasties of China, imperial dynasty of China that ruled from 618 to 907, with an Wu Zhou, interregnum between 690 and 705. It was preceded by the Sui dynasty and followed ...
that Sichuan regained its previous political and cultural prominence for which it was known during the Han. Chengdu became nationally known as a supplier of armies and the home of Du Fu
Du Fu (; 712–770) was a Chinese poet and politician during the Tang dynasty. Together with his elder contemporary and friend Li Bai, Du is often considered one of the greatest Chinese poets of his time. His greatest ambition was to serve ...
, who is sometimes called China's greatest poet. During the An Lushan Rebellion
The An Lushan rebellion was a civil war in China that lasted from 755 to 763, at the approximate midpoint of the Tang dynasty (618–907). It began as a commandery rebellion attempting to overthrow and replace the Tang government with the rogue ...
(755–763), Emperor Xuanzong of Tang
Emperor Xuanzong of Tang (; 8 September 685 – 3 May 762), personal name Li Longji, was an Emperor of China, emperor of the Tang dynasty of China, reigning from 712 to 756. His reign of 44 years was the longest during the Tang dynasty. Throu ...
fled from Chang'an
Chang'an (; zh, t=長安, s=长安, p=Cháng'ān, first=t) is the traditional name of the city now named Xi'an and was the capital of several Chinese dynasties, ranging from 202 BCE to 907 CE. The site has been inhabited since Neolithic time ...
to Sichuan which became his refuge. The region was torn by constant warfare and economic distress as it was besieged by the Tibetan Empire
The Tibetan Empire (,) was an empire centered on the Tibetan Plateau, formed as a result of expansion under the Yarlung dynasty heralded by its 33rd king, Songtsen Gampo, in the 7th century. It expanded further under the 38th king, Trisong De ...
.
Five Dynasties and Ten Kingdoms
In the Five Dynasties and Ten Kingdoms period, Sichuan became the heart of the Shu kingdom with its capital in Chengdu
Chengdu; Sichuanese dialects, Sichuanese pronunciation: , Standard Chinese pronunciation: ; Chinese postal romanization, previously Romanization of Chinese, romanized as Chengtu. is the capital city of the Chinese province of Sichuan. With a ...
. In 925, the kingdom was absorbed into Later Tang
Tang, known in historiography as the Later Tang, was a short-lived imperial dynasty of China and the second of the Five Dynasties during the Five Dynasties and Ten Kingdoms period in Chinese history.
The first three of the Later Tang's four ...
but would regain independence under Meng Zhixiang who founded Later Shu
Shu, referred to as Later Shu ( zh, t=後蜀, s=后蜀, first=t, p=Hòu Shǔ) and Meng Shu ( zh, c=孟蜀) in historiography, was a dynastic state of China and one of the Ten Kingdoms during the Five Dynasties and Ten Kingdoms period. It was ...
in 934. Later Shu would continue until 965 when it was absorbed by the Song
A song is a musical composition performed by the human voice. The voice often carries the melody (a series of distinct and fixed pitches) using patterns of sound and silence. Songs have a structure, such as the common ABA form, and are usu ...
.
Song and Yuan dynasties
During the Song dynasty
The Song dynasty ( ) was an Dynasties of China, imperial dynasty of China that ruled from 960 to 1279. The dynasty was founded by Emperor Taizu of Song, who usurped the throne of the Later Zhou dynasty and went on to conquer the rest of the Fiv ...
(960–1279), Sichuanese was able to protect themselves from Tibetan attacks with the help of the central government. There were rebellions against the Song by Li Shun in 994 and Wang Jun in 1000. Sichuan also saw cultural revivals like the great poets Su Xun
Su Xun (; 22 May 1009 – 21 May 1066) was a scholar, essayist and philosopher during the Song dynasty, listed as one of the Eight Masters of the Tang and Song, along with his sons Su Shi and Su Zhe.
Life and career
Early life and educati ...
(), Su Shi
Su Shi ( zh, t=, s=苏轼, p=Sū Shì; 8 January 1037 – 24 August 1101), courtesy name Zizhan (), art name Dongpo (), was a Chinese poet, essayist, calligrapher, painter, scholar-official, literatus, artist, pharmacologist, and gastronome wh ...
, and Su Zhe
Su Zhe (; 1039–1112), or Su Che, courtesy names Ziyou and Tongshu , was a Chinese essayist, historian, poet, and politician from Meishan, located in modern-day Sichuan Province, China.
Su was highly honored as a politician and essayist in th ...
.paper money
Paper money, often referred to as a note or a bill (North American English), is a type of negotiable promissory note that is payable to the bearer on demand, making it a form of currency. The main types of paper money are government notes, which ...
in human history () was issued in Chengdu
Chengdu; Sichuanese dialects, Sichuanese pronunciation: , Standard Chinese pronunciation: ; Chinese postal romanization, previously Romanization of Chinese, romanized as Chengtu. is the capital city of the Chinese province of Sichuan. With a ...
.
It was also during the Song dynasty that the bulk of the native Ba people of eastern Sichuan assimilated into the Han Chinese ethnicity.
In the 12th and 13th centuries, the Southern Song dynasty established coordinated defenses against the Mongolian Yuan dynasty
The Yuan dynasty ( ; zh, c=元朝, p=Yuáncháo), officially the Great Yuan (; Mongolian language, Mongolian: , , literally 'Great Yuan State'), was a Mongol-led imperial dynasty of China and a successor state to the Mongol Empire after Div ...
, in Sichuan and Xiangyang
Xiangyang is the second-largest prefecture-level city by population in northwestern Hubei province, China. It was known as Xiangfan from 1950 to 2010. The Han River (Hanshui), Han River runs through Xiangyang's centre and divides the city n ...
. The Southern Song state monopolized the Sichuan tea industry to pay for warhorses, but this state intervention eventually brought devastation to the local economy. The line of defense was finally broken through after the first use of firearm
A firearm is any type of gun that uses an explosive charge and is designed to be readily carried and operated by an individual. The term is legally defined further in different countries (see legal definitions).
The first firearms originate ...
s in history during the six-year Battle of Xiangyang
The Battle of Xiangyang () was a protracted series of battles between the Yuan dynasty and the Southern Song dynasty from 1267 to 1273. The battle was a significant victory for the Yuan dynasty and ended a 30-year defensive campaign waged by t ...
, which ended in 1273. Allegedly there were a million pieces of unspecified types of skeleton bones belonging to war animals and both Song and Yuan soldiers who perished in the fighting over the city, although the figure may have been grossly exaggerated. The recorded number of families in Sichuan dropped from 2,640,000 families, as recorded from the census taken in 1162 AD, to 120,000 families in 1282 AD. Possible causes include forced population transfer to nearby areas, evacuation to nearby provinces, census under-reporting or inaccuracy, and war-related deaths.
One instance of the deportation of Sichuanese civilians to Mongolia occurred in the aftermath of a battle in 1259 when more than 80,000 people were taken captive from one city in Sichuan and moved to Mongolia.
Ming dynasty
The Ming dynasty defeated Ming Yuzhen
Ming Yuzhen (; 2 October 1328 – 17 March 1366) was a peasant rebel leader who established the dynasty of Ming Xia during the late Yuan dynasty in China.
Ming was born in Suizhou (today Sui County, Hubei) in a farmer family. He changed the ...
's Xia polity which ruled Sichuan.Ming dynasty
The Ming dynasty, officially the Great Ming, was an Dynasties of China, imperial dynasty of China that ruled from 1368 to 1644, following the collapse of the Mongol Empire, Mongol-led Yuan dynasty. The Ming was the last imperial dynasty of ...
, major architectural works were created in Sichuan. Buddhism remained influential in the region. Bao'en Temple is a well-preserved 15th-century monastery complex built between 1440 and 1446 during the Zhengtong Emperor
, succession = Emperor of the Ming dynasty
, reign-type = First reign
, reign = 31 January 1435 – 22 September 1449
, coronation = 7 February 1435
, cor-type = Enthronement
, regent =
, reg-type = Regents
, ...
's reign (1427–64). Dabei Hall enshrines a thousand-armed wooden image of Guanyin
Guanyin () is a common Chinese name of the bodhisattva associated with Karuṇā, compassion known as Avalokiteśvara (). Guanyin is short for Guanshiyin, which means " he One WhoPerceives the Sounds of the World". Originally regarded as m ...
and Huayan Hall is a repository with a revolving sutra
''Sutra'' ()Monier Williams, ''Sanskrit English Dictionary'', Oxford University Press, Entry fo''sutra'' page 1241 in Indian literary traditions refers to an aphorism or a collection of aphorisms in the form of a manual or, more broadly, a ...
cabinet. The wall paintings, sculptures, and other ornamental details are masterpieces of the Ming period.Zhang Xianzhong
Zhang Xianzhong (張獻忠 or Chang Hsien-chung; 18 September 1606 – 2 January 1647), courtesy name Bingwu (秉吾), art name Jingxuan (敬軒), was a Chinese peasant leader who led a peasant rebellion from Yan'an wei, Shaanxi (today Yulin, ...
(1606–1646) from Yan'an
Yan'an; ; Chinese postal romanization, alternatively spelled as Yenan is a prefecture-level city in the Shaanbei region of Shaanxi Province of China, province, China, bordering Shanxi to the east and Gansu to the west. It administers several c ...
, Shaanxi
Shaanxi is a Provinces of China, province in north Northwestern China. It borders the province-level divisions of Inner Mongolia to the north; Shanxi and Henan to the east; Hubei, Chongqing, and Sichuan to the south; and Gansu and Ningxia to t ...
Province, nicknamed ''Yellow Tiger'', led his peasant troop from north China to the south and conquered Sichuan. Upon capturing it, he declared himself emperor of the Daxi dynasty (). In response to the resistance from local elites, he massacred a large number of people in Sichuan, killing around one in three people. As a result of the massacre as well as years of turmoil during the Ming-Qing transition
The transition from Ming to Qing (or simply the Ming-Qing transition) or the Manchu conquest of China from 1618 to 1683 saw the transition between two major dynasties in Chinese history. It was a decades-long conflict between the emerging Qin ...
, the population of Sichuan fell sharply, requiring massive resettlement of people from the neighboring Huguang Province (modern Hubei and Hunan) and other provinces during the Qing dynasty.
Qing dynasty
Sichuan was originally the origin of the Deng lineage until one of them was hired as an official in Guangdong during the Ming dynasty but during the Qing plan to increase the population in 1671 they came to Sichuan again. In 1904 Deng Xiaoping
Deng Xiaoping also Romanization of Chinese, romanised as Teng Hsiao-p'ing; born Xiansheng (). (22 August 190419 February 1997) was a Chinese statesman, revolutionary, and political theorist who served as the paramount leader of the People's R ...
was born in Sichuan.Qing dynasty
The Qing dynasty ( ), officially the Great Qing, was a Manchu-led Dynasties of China, imperial dynasty of China and an early modern empire in East Asia. The last imperial dynasty in Chinese history, the Qing dynasty was preceded by the ...
, Sichuan was merged with Shaanxi
Shaanxi is a Provinces of China, province in north Northwestern China. It borders the province-level divisions of Inner Mongolia to the north; Shanxi and Henan to the east; Hubei, Chongqing, and Sichuan to the south; and Gansu and Ningxia to t ...
and Shanxi
Shanxi; Chinese postal romanization, formerly romanised as Shansi is a Provinces of China, province in North China. Its capital and largest city of the province is Taiyuan, while its next most populated prefecture-level cities are Changzhi a ...
to create "Shenzhuan" during 1680–1731 and 1735–1748.Chongqing
ChongqingPostal Romanization, Previously romanized as Chungking ();. is a direct-administered municipality in Southwestern China. Chongqing is one of the four direct-administered municipalities under the State Council of the People's Republi ...
) were established in the early 18th century. In the aftermath of the Sino-Nepalese War
The Sino-Nepalese War (), also known as the Sino-Gorkha War and in Chinese as the campaign of Gorkha (), was a war fought between the Qing dynasty of China and the Kingdom of Nepal in the late 18th century following an invasion of Tibet by th ...
on China's southwestern border, the Qing gave Sichuan's provincial government direct control over the minority-inhabited areas of Sichuan west of Kangding, which had previously been handled by an amban
Amban (Manchu language, Manchu and Mongolian language, Mongol: ''Amban'', Standard Tibetan, Tibetan: ་''am ben'', zh, t=昂邦, Uyghur language, Uighur:''am ben'') is a Manchu language term meaning "high official" ( zh, t=大臣, p=dàchén ...
.landslide dam
A landslide dam or barrier lake is the natural damming of a river by some kind of landslide, such as a debris flow, rock avalanche or volcanic eruption. If the damming landslide is caused by an earthquake, it may also be called a quake lake. Some ...
on the Dadu River
The Dadu River (, ), known in Tibetan as the Gyelmo Ngul Chu (), is a major river located primarily in Sichuan province, southwestern China. The Dadu flows from the eastern Tibetan Plateau into the Sichuan Basin where it joins with the Min Rive ...
caused by an earthquake gave way on 10 June 1786. The resulting flood killed 100,000 people.
Republic of China
 In the early 20th century, the newly founded
In the early 20th century, the newly founded Republic of China
Taiwan, officially the Republic of China (ROC), is a country in East Asia. The main geography of Taiwan, island of Taiwan, also known as ''Formosa'', lies between the East China Sea, East and South China Seas in the northwestern Pacific Ocea ...
established the Chuanbian Special Administrative District () on the province's territories to the west of the Sichuan Basin
The Sichuan Basin (), formerly transliterated as the Szechwan Basin, sometimes called the Red Basin, is a lowland region in southwestern China. It is surrounded by mountains on all sides and is drained by the upper Yangtze River and its tributar ...
. The Special District later became the province of Xikang
Xikang (formerly romanized as Sikang or Hsikang, or 'Kham to the west f Sichuan) was a nominal province
formed by the Republic of China (1912–1949)">Republic of China in 1939 on the initiative of prominent Sichuan warlord Liu Wenhui and re ...
, incorporating the areas inhabited by Yi, Tibetan, and Qiang ethnic minorities to its west, and eastern part of today's Tibet Autonomous Region
The Tibet Autonomous Region (TAR), often shortened to Tibet in English or Xizang in Pinyin, Hanyu Pinyin, is an Autonomous regions of China, autonomous region of the China, People's Republic of China. It was established in 1965 to replace the ...
.
In the 20th century, as Beijing
Beijing, Chinese postal romanization, previously romanized as Peking, is the capital city of China. With more than 22 million residents, it is the world's List of national capitals by population, most populous national capital city as well as ...
, Shanghai
Shanghai, Shanghainese: , Standard Chinese pronunciation: is a direct-administered municipality and the most populous urban area in China. The city is located on the Chinese shoreline on the southern estuary of the Yangtze River, with the ...
, Nanjing
Nanjing or Nanking is the capital of Jiangsu, a province in East China. The city, which is located in the southwestern corner of the province, has 11 districts, an administrative area of , and a population of 9,423,400.
Situated in the Yang ...
, and Wuhan
Wuhan; is the capital of Hubei, China. With a population of over eleven million, it is the most populous city in Hubei and the List of cities in China by population, eighth-most-populous city in China. It is also one of the nine National cent ...
had all been occupied by the Japanese during the Second Sino-Japanese War
The Second Sino-Japanese War was fought between the Republic of China (1912–1949), Republic of China and the Empire of Japan between 1937 and 1945, following a period of war localized to Manchuria that started in 1931. It is considered part ...
, the capital of the Republic of China had been temporarily relocated to Chongqing
ChongqingPostal Romanization, Previously romanized as Chungking ();. is a direct-administered municipality in Southwestern China. Chongqing is one of the four direct-administered municipalities under the State Council of the People's Republi ...
, then a major city in Sichuan. An enduring legacy of this move is those nearby inland provinces, such as Shaanxi
Shaanxi is a Provinces of China, province in north Northwestern China. It borders the province-level divisions of Inner Mongolia to the north; Shanxi and Henan to the east; Hubei, Chongqing, and Sichuan to the south; and Gansu and Ningxia to t ...
, Gansu
Gansu is a provinces of China, province in Northwestern China. Its capital and largest city is Lanzhou, in the southeastern part of the province. The seventh-largest administrative district by area at , Gansu lies between the Tibetan Plateau, Ti ...
, and Guizhou
)
, image_skyline =
, image_caption =
, image_map = Guizhou in China (+all claims hatched).svg
, mapsize = 275px
, map_alt = Map showing the location of Guizhou Province
, map_caption = Map s ...
, which previously never had modern Western-style universities, began to be developed in this regard. The difficulty of accessing the region overland from the eastern part of China and the foggy climate hindering the accuracy of the Japanese bombing of the Sichuan Basin made the region the stronghold of Chiang Kai-shek's Kuomintang
The Kuomintang (KMT) is a major political party in the Republic of China (Taiwan). It was the one party state, sole ruling party of the country Republic of China (1912-1949), during its rule from 1927 to 1949 in Mainland China until Retreat ...
government during 1938–45 and led to the Bombing of Chongqing
The bombing of Chongqing (, ), from 18 February 1938 to 19 December 1944, was a series of massive terror bombing operations authorized by the Empire of Japan's Imperial General Headquarters and conducted by the Imperial Japanese Army Air Servic ...
.
The Second Sino-Japanese War
The Second Sino-Japanese War was fought between the Republic of China (1912–1949), Republic of China and the Empire of Japan between 1937 and 1945, following a period of war localized to Manchuria that started in 1931. It is considered part ...
was soon followed by the resumed Chinese Civil War
The Chinese Civil War was fought between the Kuomintang-led Nationalist government, government of the Republic of China (1912–1949), Republic of China and the forces of the Chinese Communist Party (CCP). Armed conflict continued intermitt ...
, and the cities of East China are obtained by the Communists one after another, the Kuomintang government again tried to make Sichuan its stronghold on the mainland, although it already saw some Communist activity since it was one area on the road of the Long March
The Long March ( zh, s=长征, p=Chángzhēng, l=Long Expedition) was a military retreat by the Chinese Red Army and Chinese Communist Party (CCP) from advancing Kuomintang forces during the Chinese Civil War, occurring between October 1934 and ...
. Chiang Kai-shek himself flew to Chongqing from Taiwan
Taiwan, officially the Republic of China (ROC), is a country in East Asia. The main geography of Taiwan, island of Taiwan, also known as ''Formosa'', lies between the East China Sea, East and South China Seas in the northwestern Pacific Ocea ...
in November 1949 to lead the defense. But the same month Chongqing switched to the Communists, followed by Chengdu on 10 December. The Kuomintang general Wang Sheng wanted to stay behind with his troops to continue the anticommunist guerilla war in Sichuan, but was recalled to Taiwan. Many of his soldiers made their way there as well, via Burma
Myanmar, officially the Republic of the Union of Myanmar; and also referred to as Burma (the official English name until 1989), is a country in northwest Southeast Asia. It is the largest country by area in Mainland Southeast Asia and ha ...
.
People's Republic of China
The People's Republic of China was founded in 1949, and it split Sichuan into four areas and separated Chongqing municipality. Sichuan was reconstituted in 1952, with Chongqing added in 1954, while the former Xikang
Xikang (formerly romanized as Sikang or Hsikang, or 'Kham to the west f Sichuan) was a nominal province
formed by the Republic of China (1912–1949)">Republic of China in 1939 on the initiative of prominent Sichuan warlord Liu Wenhui and re ...
province was split between Tibet
Tibet (; ''Böd''; ), or Greater Tibet, is a region in the western part of East Asia, covering much of the Tibetan Plateau and spanning about . It is the homeland of the Tibetan people. Also resident on the plateau are other ethnic groups s ...
in the west and Sichuan in the east.Deng Xiaoping
Deng Xiaoping also Romanization of Chinese, romanised as Teng Hsiao-p'ing; born Xiansheng (). (22 August 190419 February 1997) was a Chinese statesman, revolutionary, and political theorist who served as the paramount leader of the People's R ...
took power, Sichuan was one of the first provinces to experiment with the market economic enterprise.
From 1955 until 1997, Sichuan had been China's most populous province; the population hit the 100 million mark shortly after the 1982 census figure of 99,730,000. This changed in 1997 when the Sub-provincial city
Strictly speaking, China's legal system neither recognizes the concept of "sub-provincial administrative divisions" () or "sub-provincial cities" () nor provides specific legislation for such designations, and these categories are absent from off ...
of Chongqing as well as the three surrounding prefectures of Fuling
Fuling District ( zh, s=涪陵区 , t=涪陵區 , p=Fúlíng Qū) is a district in central Chongqing, China. As the second largest city in Chongqing, the area is known for '' zha cai'', a hot pickled mustard tuber, as well as serving as the locat ...
, Wanxian
Wanzhou District ( zh, s=万州区 , t=萬州區 , p=Wànzhōu Qū) is Chongqing's second most populated urban core area on the upper reaches of the Three Gorges of the Yangtze River in China. It is currently governed as a district of Chongqing M ...
, and Qianjiang were split off into the new Chongqing Municipality
Chongqing Previously romanized as Chungking ();. is a direct-administered municipality in Southwestern China. Chongqing is one of the four direct-administered municipalities under the Central People's Government, along with Beijing, Shanghai ...
. The new municipality was formed to spearhead China's effort to economically develop its western provinces, as well as to coordinate the resettlement of residents from the reservoir areas of the Three Gorges Dam
The Three Gorges Dam (), officially known as Yangtze River Three Gorges Water Conservancy Project () is a hydroelectric gravity dam that spans the Yangtze River near Sandouping in Yiling District, Yichang, Hubei province, central China, downs ...
project.
In 1997, when Sichuan split, the sum of the two parts was recorded to be 114,720,000 people. As of 2010, Sichuan ranks as both the 3rd largest (the largest among Chinese provinces with a population greater than 50 million) and 4th most populous province in China.[, and ]
Administrative divisions
Sichuan consists of twenty-one prefecture-level division
zh, p=Dì Jí Xíngzhèngqū, labels=no
, alt_name =
, map =
, category = Second level administrative division of a unitary state
, territory = China
, start_date =
, current_number ...
s: eighteen prefecture-level cities
A prefecture-level city () or prefectural city is an administrative division of the China, People's Republic of China (PRC), ranking below a province of China, province and above a Counties of the People's Republic of China, county in China's ...
(including a sub-provincial city
Strictly speaking, China's legal system neither recognizes the concept of "sub-provincial administrative divisions" () or "sub-provincial cities" () nor provides specific legislation for such designations, and these categories are absent from off ...
) and three autonomous prefecture
Autonomous prefectures ( zh, c=自治州, p=zìzhìzhōu) are one type of autonomous administrative divisions of China, autonomous administrative division in China, existing at the Prefecture-level divisions of China, prefectural level, with eith ...
s:
The twenty prefectures
A prefecture (from the Latin word, "''praefectura"'') is an administrative jurisdiction traditionally governed by an appointed prefect. This can be a regional or local government subdivision in various countries, or a subdivision in certain inter ...
of Sichuan are subdivided into 183 county-level division
The administrative divisions of China have consisted of several levels since 1412, due to mainland China's large population and geographical area. In the People's Republic of China, the constitution provides for three levels of government. Ho ...
s (53 district
A district is a type of administrative division that in some countries is managed by the local government. Across the world, areas known as "districts" vary greatly in size, spanning regions or county, counties, several municipality, municip ...
s, 17 county-level cities
, map =
, category = Third level administrative division of a unitary state
, territory = People's Republic of China
, upper_unit = Prefectures, Provinces
, start_date =
, current_number = 411 (408 controlled, 3 claimed)
, number_da ...
, 109 counties
A county () is a geographic region of a country used for administrative or other purposesL. Brookes (ed.) '' Chambers Dictionary''. Edinburgh: Chambers Harrap Publishers Ltd, 2005. in some nations. The term is derived from the Old French denoti ...
, and 4 autonomous counties
Autonomous counties () and autonomous banners () are county-level autonomous administrative divisions of China. Autonomous counties tend to have a large number of ethnic minority citizens compared to ordinary counties (if not an outright major ...
). At the end of the year 2017, the total population is 83.02 million.
Urban areas
Geography and biodiversity
Sichuan consists of two geographically very distinct parts. The eastern part of the province is mostly within the fertile Sichuan basin
The Sichuan Basin (), formerly transliterated as the Szechwan Basin, sometimes called the Red Basin, is a lowland region in southwestern China. It is surrounded by mountains on all sides and is drained by the upper Yangtze River and its tributar ...
(which is shared by Sichuan with Chongqing Municipality). The western Sichuan consists of numerous mountain ranges forming the easternmost part of the Tibetan Plateau
The Tibetan Plateau, also known as the Qinghai–Tibet Plateau or Qingzang Plateau, is a vast elevated plateau located at the intersection of Central Asia, Central, South Asia, South, and East Asia. Geographically, it is located to the north of H ...
, which are known generically as the Hengduan Mountains
The Hengduan Mountains () are a group of mountain ranges in southwest China, southwest China that connect the southeast portions of the Tibetan Plateau with the Yunnan–Guizhou Plateau. The Hengduan Mountains are primarily large north-south ...
. One of these ranges, the Daxue Mountains
The Daxue Range or Daxue Mountains () are a great mountain range in the western part of Sichuan province in Southwest China. It is part of the Hengduan Mountains, a complicated system of mountain ranges of western Sichuan, which itself is adjacen ...
, contains the highest point of the province Gongga Shan, at above sea level. The mountains are formed by the collision of the Tibetan Plateau with the Yangtze Plate
The Yangtze plate, also called the South China block or the South China subplate, comprises the bulk of southern China. It is separated on the east from the Okinawa plate by a rift that forms the Okinawa Trough which is a back-arc basin, on the ...
. Faults here include the Longmenshan Fault
The Longmenshan Fault () is a thrust fault which runs along the base of the Longmen Mountains in Sichuan province in southwestern China. The strike of the fault plane is approximately NE.
Motion on this fault is responsible for the uplift of t ...
which ruptured during the 2008 Sichuan earthquake. Other mountain ranges surround the Sichuan Basin from north, east, and south. Among them are the Daba Mountains
The Daba Mountains, also known by their Chinese name as the Dabashan, are a mountain range in Central China between the watersheds of the Yellow and Yangtze Rivers. Part of the larger Qinling mountain range, it cuts through four provinces: S ...
, in the province's northeast.
The Yangtze River
The Yangtze or Yangzi ( or ) is the longest river in Eurasia and the third-longest in the world. It rises at Jari Hill in the Tanggula Mountains of the Tibetan Plateau and flows including Dam Qu River the longest source of the Yangtze, i ...
and its tributaries flow through the mountains of western Sichuan and the Sichuan Basin; thus, the province is upstream of the great cities that stand along the Yangtze River further to the east, such as Chongqing
ChongqingPostal Romanization, Previously romanized as Chungking ();. is a direct-administered municipality in Southwestern China. Chongqing is one of the four direct-administered municipalities under the State Council of the People's Republi ...
, Wuhan
Wuhan; is the capital of Hubei, China. With a population of over eleven million, it is the most populous city in Hubei and the List of cities in China by population, eighth-most-populous city in China. It is also one of the nine National cent ...
, Nanjing
Nanjing or Nanking is the capital of Jiangsu, a province in East China. The city, which is located in the southwestern corner of the province, has 11 districts, an administrative area of , and a population of 9,423,400.
Situated in the Yang ...
, and Shanghai
Shanghai, Shanghainese: , Standard Chinese pronunciation: is a direct-administered municipality and the most populous urban area in China. The city is located on the Chinese shoreline on the southern estuary of the Yangtze River, with the ...
. One of the major tributaries of the Yangtze within the province is the Min River of central Sichuan, which joins the Yangtze at Yibin
Yibin ( zh, s=宜宾 , t=宜賓 , p=Yíbīn , w=I-pin, region=CN-SC-15; Sichuanese Pinyin: ȵi2bin1; Sichuanese pronunciation: ) is a prefecture-level city in the southeastern part of Sichuan province, China, located at the junction of the Min ...
. There are also a number of other rivers, such as the Jialing River
The Jialing River, formerly known by numerous other names, is a major tributary of the Yangtze River in the Sichuan Basin. It is named after the Jialing Valley in Feng County, Shaanxi through which it flows.
The Jialing River's most notable c ...
, Tuo River
The Tuo River () is -long river in Sichuan province of southern China.
The Tuo River is one of the major tributaries of the upper Yangtze River (''Chang Jiang'').
Geography
The river originates at the northwest edge of Sichuan basin. It flows ...
, Yalong River
The Yalong River ( zh, 雅砻江, Pinyin, p ''Yǎlóngjiāng'', Wade–Giles, w ''Ya-lung Chiang'', Help:IPA/Mandarin, IPA ), or Nyag Chu (Standard Tibetan, Tibetan: , Tibetan pinyin, z ''Nyag Qu''), is a major tributary ...
, Wu River, and Jinsha River
The Jinsha River (, Classical Tibetan, Tibetan: Dri Chu, འབྲི་ཆུ, ) or Lu river, is the Chinese name for the upper stretches of the Yangtze River. It flows through the provinces of the PRC, provinces of Qinghai, Sichuan, and Yu ...
, and any four of the various rivers are often grouped as the "four rivers" that the name of Sichuan is commonly and mistakenly believed to mean.Qinghai
Qinghai is an inland Provinces of China, province in Northwestern China. It is the largest provinces of China, province of China (excluding autonomous regions) by area and has the third smallest population. Its capital and largest city is Xin ...
to the northwest, Gansu
Gansu is a provinces of China, province in Northwestern China. Its capital and largest city is Lanzhou, in the southeastern part of the province. The seventh-largest administrative district by area at , Gansu lies between the Tibetan Plateau, Ti ...
to the north, Shaanxi
Shaanxi is a Provinces of China, province in north Northwestern China. It borders the province-level divisions of Inner Mongolia to the north; Shanxi and Henan to the east; Hubei, Chongqing, and Sichuan to the south; and Gansu and Ningxia to t ...
to the northeast, Chongqing
ChongqingPostal Romanization, Previously romanized as Chungking ();. is a direct-administered municipality in Southwestern China. Chongqing is one of the four direct-administered municipalities under the State Council of the People's Republi ...
to the east, Guizhou
)
, image_skyline =
, image_caption =
, image_map = Guizhou in China (+all claims hatched).svg
, mapsize = 275px
, map_alt = Map showing the location of Guizhou Province
, map_caption = Map s ...
to the southeast, Yunnan
Yunnan; is an inland Provinces of China, province in Southwestern China. The province spans approximately and has a population of 47.2 million (as of 2020). The capital of the province is Kunming. The province borders the Chinese provinces ...
to the south, and the Tibet Autonomous Region
The Tibet Autonomous Region (TAR), often shortened to Tibet in English or Xizang in Pinyin, Hanyu Pinyin, is an Autonomous regions of China, autonomous region of the China, People's Republic of China. It was established in 1965 to replace the ...
to the west.
File:Larix potaninii trees Huluhai.jpg, '' Larix potaninii'' in fall.
File:1 Seda facing south.jpg, Garzê Prefecture
File:Zitong-sichuan-china.jpg, Zitong County
File:A Typical Linpan unit in Pi County.jpg, Linpan in Chengdu Plain is a well-known landmark in Chengdu Plain
The Chengdu Plain ( zh, t=成都平原, s=成都平原, p=Chéngdū Píngyuán), referred to in Sichuanese as the Western Sichuan Plain ( zh, s=川西坝子, first=t; Sichuanese Pinyin: ''Cuanxi Bazi''), is an alluvial plain located in the wes ...
, Sichuan.
Giant panda

Giant panda
The giant panda (''Ailuropoda melanoleuca''), also known as the panda bear or simply panda, is a bear species endemic to China. It is characterised by its white animal coat, coat with black patches around the eyes, ears, legs and shoulders. ...
s live in bamboo forests and low mountainous areas such as the Minshan Mountains in Sichuan. The majority of the panda population lives in Sichuan, with their range spreading into Shaanxi
Shaanxi is a Provinces of China, province in north Northwestern China. It borders the province-level divisions of Inner Mongolia to the north; Shanxi and Henan to the east; Hubei, Chongqing, and Sichuan to the south; and Gansu and Ningxia to t ...
and Gansu
Gansu is a provinces of China, province in Northwestern China. Its capital and largest city is Lanzhou, in the southeastern part of the province. The seventh-largest administrative district by area at , Gansu lies between the Tibetan Plateau, Ti ...
. As it is abundant where they live, pandas' diet consists of 99% bamboo, with small other plants, or small animals consisting of the other 1%. As the panda is native to China, they have become a national symbol of China.
Climate
Due to great differences in terrain, the climate of the province is highly variable. In general, it has strong monsoon
A monsoon () is traditionally a seasonal reversing wind accompanied by corresponding changes in precipitation but is now used to describe seasonal changes in Atmosphere of Earth, atmospheric circulation and precipitation associated with annu ...
al influences, with rainfall heavily concentrated in the summer. Under the Köppen climate classification
The Köppen climate classification divides Earth climates into five main climate groups, with each group being divided based on patterns of seasonal precipitation and temperature. The five main groups are ''A'' (tropical), ''B'' (arid), ''C'' (te ...
, the Sichuan Basin
The Sichuan Basin (), formerly transliterated as the Szechwan Basin, sometimes called the Red Basin, is a lowland region in southwestern China. It is surrounded by mountains on all sides and is drained by the upper Yangtze River and its tributar ...
(including Chengdu
Chengdu; Sichuanese dialects, Sichuanese pronunciation: , Standard Chinese pronunciation: ; Chinese postal romanization, previously Romanization of Chinese, romanized as Chengtu. is the capital city of the Chinese province of Sichuan. With a ...
) in the eastern half of the province experiences a humid subtropical climate
A humid subtropical climate is a subtropical -temperate climate type, characterized by long and hot summers, and cool to mild winters. These climates normally lie on the southeast side of all continents (except Antarctica), generally between ...
(Köppen Köppen is a German surname. Notable people with the surname include:
* Bernd Köppen (1951–2014), German pianist and composer
* Carl Köppen (1833-1907), German military advisor in Meiji era Japan
* Edlef Köppen (1893–1939), German author ...
''Cwa'' or ''Cfa''), with long, hot, wet summers and short, mild to cool, dry, and cloudy winters. Consequently, it has China's lowest sunshine totals.
The western region has mountainous areas producing a cooler but sunnier climate. Having cool to very cold winters and mild summers, temperatures generally decrease with greater elevation. Due to high altitude and inland location, the far northwestern areas like Garzê County
Garzê County or Kardze County (), called Ganzi County in Chinese ( zh, s=甘孜县, p=Gānzī xiàn), is one of the 18 subdivisions of the Garzê Tibetan Autonomous Prefecture, in northwestern Sichuan province, China. The Yalong River passes ju ...
and Zoigê County exhibit a subalpine climate
The subarctic climate (also called subpolar climate, or boreal climate) is a continental climate with long, cold (often very cold) winters, and short, warm to cool summers. It is found on large landmasses, often away from the moderating effects of ...
(Köppen ''Dwc'') or even an alpine climate
Alpine climate is the typical climate for elevations above the tree line, where trees fail to grow due to cold. This climate is also referred to as a mountain climate or highland climate.
Definition
There are multiple definitions of alpine cli ...
(''ETH''), featuring frigid winters down to and even cold summer nights. The region is geologically active with landslides and earthquakes. Average elevation ranges from ; average temperatures range from .
Politics
The politics of Sichuan is structured in a dual party-government system like all other governing institutions in mainland China
"Mainland China", also referred to as "the Chinese mainland", is a Geopolitics, geopolitical term defined as the territory under direct administration of the People's Republic of China (PRC) in the aftermath of the Chinese Civil War. In addit ...
.
The governor of Sichuan
The governor of Sichuan, officially the Governor of the Sichuan Provincial People's Government, is the head of Sichuan, Sichuan Province and leader of the Sichuan Provincial People's Government.
The governor is elected by the Sichuan Provincial P ...
is the highest-ranking official in the People's Government of Sichuan. However, in the province's dual party-government governing system, the Governor has less power than the Sichuan Communist Party of China's Party Committee Secretary
A Party Committee Secretary () is the leader of the Chinese Communist Party (CCP) organization in a province, city, village, or other administrative unit. In most cases, it is the ''de facto'' highest political office of its area of jurisdictio ...
, colloquially termed the "Sichuan CCP Party Chief".
Governance
The Sichuan Provincial Prison Administrative Bureau is the main corrections agency in Sichuan.
The is the primary law enforcement agency in Sichuan. It has a SWAT unit, a forestry unit, an anti-drug unit, an economic crime unit, a food safety unit and an investigation unit.[2021 年度四川省公安厅(本级)单位决算](_blank)
021 Sichuan Provincial Public Security Department Budget retrieved 12/3/2025 In 2021, the agency had a budget of 45.8 million Renminbi
The renminbi ( ; currency symbol, symbol: Yen and yuan sign, ¥; ISO 4217, ISO code: CNY; abbreviation: RMB), also known as the Chinese yuan, is the official currency of the China, People's Republic of China. The renminbi is issued by the Peop ...
.Highway patrol
A highway patrol is a police unit, detail, or law enforcement agency created primarily for the purpose of overseeing and enforcing traffic safety compliance on roads and highways within a jurisdiction. They are also referred to in many countri ...
agency.
 The provides paramilitary law enforcement and disaster relief services within Sichuan province. The Yibin Detachment was deployed for disaster relief during the of February 8, 2025 in Junlian County,
The provides paramilitary law enforcement and disaster relief services within Sichuan province. The Yibin Detachment was deployed for disaster relief during the of February 8, 2025 in Junlian County, Yibin
Yibin ( zh, s=宜宾 , t=宜賓 , p=Yíbīn , w=I-pin, region=CN-SC-15; Sichuanese Pinyin: ȵi2bin1; Sichuanese pronunciation: ) is a prefecture-level city in the southeastern part of Sichuan province, China, located at the junction of the Min ...
.
The Sichuan Provincial Fire and Rescue Department () is in charge of firefighting and rescue duties within the province.
Economy

 Sichuan is the 6th-largest provincial economy of China, the largest in
Sichuan is the 6th-largest provincial economy of China, the largest in Western China
Western China ( zh, s=中国西部, l=, labels=no or zh, s=华西, l=, labels=no) is the west of China. It consists of Southwestern China and Northwestern China. In the definition of the Chinese government, Western China covers six provinces ...
and the second largest among inland provinces after Henan
Henan; alternatively Honan is a province in Central China. Henan is home to many heritage sites, including Yinxu, the ruins of the final capital of the Shang dynasty () and the Shaolin Temple. Four of the historical capitals of China, Lu ...
. As of 2021, its nominal GDP was 5,385 billion yuan (US$847.68 billion), ahead of the GDP of Turkey of 815 billion.disposable income
Disposable income is total personal income minus current taxes on income. In national accounting, personal income minus personal current taxes equals disposable personal income or household disposable income. Subtracting personal outlays ( ...
of the urbanites averaged 41,444 yuan (US$6510).
Sichuan has been historically known as the "Province of Abundance". It is one of the major agricultural production bases of China. Grain, including rice and wheat, is the major product with output that ranked first in China in 1999. Commercial crops include citrus fruits, sugar cane, sweet potatoes, peaches, and grapes. Sichuan also had the largest output of pork among all the provinces and the second largest output of silkworm cocoons in 1999. Sichuan is rich in mineral resources. It has more than 132 kinds of proven underground mineral resources including vanadium, titanium, and lithium is the largest in China. The Panxi region alone possesses 13.3% of the reserves of iron, 93% of titanium, 69% of vanadium, and 83% of cobalt in the whole country. Sichuan also possesses China's largest proven natural gas reserves (such as the Dazhou
Dazhou ( zh, s= 达州 , t= 達州 , p=Dázhōu , w=Ta-chou) is a prefecture-level city in the northeast corner of Sichuan province, China, bordering Shaanxi to the north and Chongqing to the east and south. As of 2020 census, Dazhou was home t ...
and Yuanba gas fields), the majority of which are transported to more developed eastern regions.Chengdu
Chengdu; Sichuanese dialects, Sichuanese pronunciation: , Standard Chinese pronunciation: ; Chinese postal romanization, previously Romanization of Chinese, romanized as Chengtu. is the capital city of the Chinese province of Sichuan. With a ...
and Mianyang
Mianyang ( zh, s=绵阳, t=綿陽, w=Mien2-yang2, p=Miányáng; Sichuanese Pinyin, Sichuanese romanization: ''Mien-iang''; formerly known as Mienchow, zh, t=綿州, p=Mianzhou, links=no; Sichuanese romanization: ''Miencheo''; ) is the second lar ...
are the production centers for textiles and electronics products. Deyang
Deyang ( zh, s=德阳 , t=德陽 , p=Déyáng) is a prefecture-level city of Sichuan province, China. Deyang is a largely industrial city, with companies such as China National Erzhong Group and Dongfang Electric having major operations there. The ...
, Panzhihua
Panzhihua ( zh, c=攀枝花, p=Pānzhīhuā), formerly Dukou ( zh, labels=no, c=渡口), is a prefecture-level city located in the far south of Sichuan province, China, at the confluence of the Jinsha and Yalong Rivers. It has an administrative ...
, and Yibin
Yibin ( zh, s=宜宾 , t=宜賓 , p=Yíbīn , w=I-pin, region=CN-SC-15; Sichuanese Pinyin: ȵi2bin1; Sichuanese pronunciation: ) is a prefecture-level city in the southeastern part of Sichuan province, China, located at the junction of the Min ...
are the production centers for machinery, metallurgical industries, and wine, respectively. Sichuan's wine production accounted for 21.9% of the country's total production in 2000.
Great strides have been made in developing Sichuan into a modern hi-tech industrial base, by encouraging both domestic and foreign investments in electronics and information technology (such as software), machinery and metallurgy (including automobiles), hydropower, pharmaceutical, food and beverage industries.
The auto industry is an important and key sector of the machinery industry in Sichuan. Most of the auto manufacturing companies are located in Chengdu, Mianyang, Nanchong
Nanchong ( zh, c=南充 , p=Nánchōng , w=Nan-ch'ung; Sichuanese: lan2cong1) is a prefecture-level city in the northeast of Sichuan province, China, with an area of . At the 2020 census it was home to 5,607,565 people, of whom 1,936,534 liv ...
, and Luzhou
Luzhou ( zh, s=泸州, p=Lúzhōu; Sichuanese Pinyin: Nu2zou1; Minjiang dialect, Luzhou dialect: ) is a prefecture-level city located in the southeast of Sichuan Province, China. It is also known as the "Liquor City" (). It was named Jiangyang () ...
.
Other important industries in Sichuan include aerospace
Aerospace is a term used to collectively refer to the atmosphere and outer space. Aerospace activity is very diverse, with a multitude of commercial, industrial, and military applications. Aerospace engineering consists of aeronautics and astron ...
and defense (military) industries. A number of China's rockets (Long March rocket
The Long March rockets are a family of expendable launch system rockets operated by the China Aerospace Science and Technology Corporation. The rockets are named after the Chinese Red Army's 1934–35 Long March military retreat during the Chi ...
s) and satellite
A satellite or an artificial satellite is an object, typically a spacecraft, placed into orbit around a celestial body. They have a variety of uses, including communication relay, weather forecasting, navigation ( GPS), broadcasting, scient ...
s were launched from the Xichang Satellite Launch Center
The Xichang Satellite Launch Center (XSLC), also known as the Xichang Space Center, is a spaceport in China. It is located in (), Mianning county, approximately northwest of Xichang, Liangshan Yi Autonomous Prefecture in Sichuan.
It is op ...
, located in the city of Xichang
Xichang ( Northern Yi: /o̝˨˩dʐo̝˧/) is a city in and the seat of the Liangshan Yi Autonomous Prefecture in the south of Sichuan, China.
History
The Qiongdu were the local people at the time of contact with China. The county of Qiongdu is ...
.
Sichuan's landscapes and rich historical relics have also made the province a center for tourism.
The Three Gorges Dam
The Three Gorges Dam (), officially known as Yangtze River Three Gorges Water Conservancy Project () is a hydroelectric gravity dam that spans the Yangtze River near Sandouping in Yiling District, Yichang, Hubei province, central China, downs ...
, the largest dam
A dam is a barrier that stops or restricts the flow of surface water or underground streams. Reservoirs created by dams not only suppress floods but also provide water for activities such as irrigation, human consumption, industrial use, aqua ...
ever constructed, was built on the Yangtze River
The Yangtze or Yangzi ( or ) is the longest river in Eurasia and the third-longest in the world. It rises at Jari Hill in the Tanggula Mountains of the Tibetan Plateau and flows including Dam Qu River the longest source of the Yangtze, i ...
in nearby Hubei
Hubei is a province of China, province in Central China. It has the List of Chinese provincial-level divisions by GDP, seventh-largest economy among Chinese provinces, the second-largest within Central China, and the third-largest among inland ...
province to control flooding in the Sichuan Basin, neighboring Yunnan
Yunnan; is an inland Provinces of China, province in Southwestern China. The province spans approximately and has a population of 47.2 million (as of 2020). The capital of the province is Kunming. The province borders the Chinese provinces ...
province, and downstream. The plan is hailed by some as China's efforts to shift towards alternative energy sources and to further develop its industrial and commercial bases, but has been denounced for mass resettlement, loss of archeological sites, and ecological damage.
Economic development zones
Chengdu Hi-tech Comprehensive Free Trade Zone
Chengdu Hi-tech Comprehensive Free Trade Zone was established with the approval of the State Council on October 18, 2010, and passed the national acceptance on February 25, 2011. It was officially operated in May 2011. Chengdu High-tech Comprehensive Free Trade Zone is integrated and expanded from the former Chengdu Export Processing Zone and Chengdu Bonded Logistics Center. it is located in the Chengdu West High-tech Industrial Development Zone, with an area of 4.68 square kilometers and divided into three areas A, B, and C. The industries focus on notebook computer manufacturing, tablet computer manufacturing, wafer manufacturing, chip packaging testing, electronic components, precision machining, and the biopharmaceutical industry. Chengdu Hi-Tech Comprehensive Free Trade Zone has attracted the top 500 multinational enterprises such as Intel, Foxconn, Texas Instruments, Dell, Morse, and so on.
In 2020, the Chengdu Hi-Tech Comprehensive Free Trade Zone achieved a total import and export volume of 549.1 billion yuan (including the Shuangliu Sub-zone), accounting for 68% of the province's total foreign trade import and export volume, ranking first in the national comprehensive insurance zone import and export volume for three consecutive years.
Chengdu Economic and Technological Development Zone
Chengdu Economic and Technological Development Zone () was approved as state-level development zone in February 2000. The zone now has a developed area of and a planned area of . Chengdu Economic and Technological Development Zone (CETDZ) lies east of Chengdu, the capital city of Sichuan Province and the hub of transportation and communication in southwest China. The zone has attracted investors and developers from more than 20 countries to carry out their projects there. Industries encouraged in the zone include mechanical, electronic, new building materials, medicine, and food processing.
Chengdu Export Processing Zone
Chengdu Export Processing Zone ()) was ratified by the State Council as one of the first 15 export processing zones in the country in April 2000. In 2002, the state ratified the establishment of the Sichuan Chengdu Export Processing West Zone with a planned area of , located inside the west region of the Chengdu Hi-tech Zone.
Chengdu Hi-Tech Industrial Development Zone
 Established in 1988, Chengdu Hi-tech Industrial Development Zone () was approved as one of the first national hi-tech development zones in 1991. In 2000, it was open to APEC and has been recognized as a national advanced hi-tech development zone in successive assessment activities held by China's Ministry of Science and Technology. It ranks 5th among the 53 national hi-tech development zones in China in terms of comprehensive strength.
Chengdu Hi-tech Development Zone covers an area of , consisting of South Park and West Park. By relying on the city sub-center, which is under construction, South Park is focusing on creating a modernized industrial park of science and technology with scientific and technological innovation, incubation R&D, modern service industry, and Headquarters economy playing leading roles. Priority has been given to the development of the software industry. Located on both sides of the "Chengdu-Dujiangyan-Jiuzhaigou" golden tourism channel, the West Park aims at building a comprehensive industrial park targeting industrial clustering with complete supportive functions. West Park gives priority to three major industries i.e. electronic information, biomedicine, and precision machinery.
Established in 1988, Chengdu Hi-tech Industrial Development Zone () was approved as one of the first national hi-tech development zones in 1991. In 2000, it was open to APEC and has been recognized as a national advanced hi-tech development zone in successive assessment activities held by China's Ministry of Science and Technology. It ranks 5th among the 53 national hi-tech development zones in China in terms of comprehensive strength.
Chengdu Hi-tech Development Zone covers an area of , consisting of South Park and West Park. By relying on the city sub-center, which is under construction, South Park is focusing on creating a modernized industrial park of science and technology with scientific and technological innovation, incubation R&D, modern service industry, and Headquarters economy playing leading roles. Priority has been given to the development of the software industry. Located on both sides of the "Chengdu-Dujiangyan-Jiuzhaigou" golden tourism channel, the West Park aims at building a comprehensive industrial park targeting industrial clustering with complete supportive functions. West Park gives priority to three major industries i.e. electronic information, biomedicine, and precision machinery.
Mianyang Hi-Tech Industrial Development Zone
Mianyang Hi-Tech Industrial Development Zone was established in 1992, with a planned area of . The zone is situated 96 kilometers away from Chengdu and is away from Mianyang Airport. Since its establishment, the zone accumulated 177.4 billion yuan of industrial output, 46.2 billion yuan of gross domestic product, and fiscal revenue of 6.768 billion yuan. There are more than 136 high-tech enterprises in the zone and they accounted for more than 90% of the total industrial output.
The zone is a leader in the electronic information industry, biological medicine, new materials, and the production of motor vehicles and parts.
Transportation
For millennia, Sichuan's rugged and riverine landscape presented enormous challenges to the development of transportation infrastructure, and the lack of roads out of the Sichuan Basin contributed to the region's isolation. Since the 1950s, numerous highways and railways have been built through the Qinling in the north and the Bashan in the east. Dozens of bridges across the Yangtze and its tributaries to the south and west have brought greater connectivity with Yunnan and Tibet.
Airports
Chengdu Shuangliu International Airport
Chengdu Shuangliu International Airport (; traditionally as Chengdu Airport) is one of two international airports serving Chengdu, the capital of Sichuan province in Southwestern China, with the other being Chengdu Tianfu International Airpo ...
is the 4th-busiest airport in mainland China. It was among the world's top 30 busiest airports in 2015, and the busiest in western and central China. It was also the fifth-busiest airport in terms of cargo traffic in China in 2013. Chengdu airport is the hub of Sichuan Airlines, Chengdu Airlines, Shenzhen Airlines, Tibet Airlines, China Southern Airlines
China Southern Airlines (branded as China Southern) is a major airline in China, headquartered in Guangzhou, Guangdong. It is one of the three major airlines in the country, along with Air China and China Eastern Airlines.
Established on 1 ...
, China Eastern Airlines
China Eastern Airlines (branded as China Eastern) is a major airline in China, headquartered in Changning, Shanghai, Changning, Shanghai. It is one of the three major airlines in the country, along with Air China and China Southern Airlines.
...
, Lucky Air
Lucky Air () is a Chinese low-cost airline based in Kunming, Yunnan, China. The airline started with flights connecting Kunming with Dali and Xishuangbanna, and later expanded to other domestic and international destinations. Its main base i ...
, and Air China
Air China, officially Air China Limited, ( zh, s=中国国际航空公司, labels=no, ''Zhōngguó guójì hángkōng gōngsī'') is a major Chinese airline and the flag carrier of the People's Republic of China. It is headquartered in Shunyi ...
. Alongside Shuangliu Airport, Chengdu Tianfu International Airport
Chengdu Tianfu International Airport (; also known as Tianfu Airport) is one of two international airports serving Chengdu, the capital of Sichuan province in Southwestern China. It was planned in 2013 and opened in 2021 as Chengdu Shuangliu I ...
has opened in 2021.
Chengdu airports are also 144-hour transit visa-free airports for foreigners from 53 countries.
Expressways
On 3 November 2007, the Sichuan Transportation Bureau announced that the Suining-Chongqing Expressway was completed after three years of construction. After the completion of the Chongqing section of the road, the expressway connected Chengdu-Nanchong Expressway and formed the shortest expressway from Chengdu
Chengdu; Sichuanese dialects, Sichuanese pronunciation: , Standard Chinese pronunciation: ; Chinese postal romanization, previously Romanization of Chinese, romanized as Chengtu. is the capital city of the Chinese province of Sichuan. With a ...
to Chongqing
ChongqingPostal Romanization, Previously romanized as Chungking ();. is a direct-administered municipality in Southwestern China. Chongqing is one of the four direct-administered municipalities under the State Council of the People's Republi ...
. The new expressway is shorter than the pre-existing road between Chengdu and Chongqing; thus journey time between the two cities was reduced by an hour, now taking two and a half hours. The Sui-Yu Expressway is a four-lane overpass with a speed limit of . The total investment was 1.045 billion yuan.
Rail
China Railway Chengdu Group is headquartered in Chengdu, the capital of Sichuan Province, managing railway systems in Sichuan, Chongqing, and Guizhou. Sichuan's major railways in Sichuan include the Baoji–Chengdu, Chengdu–Chongqing, Chengdu–Kunming, Neijiang–Kunming, Suining–Chongqing, and Chengdu–Dazhou railways. High-speed rail
High-speed rail (HSR) is a type of rail transport network utilising trains that run significantly faster than those of traditional rail, using an integrated system of specialised rolling stock and dedicated railway track, tracks. While there is ...
ways in Sichuan include the Chengdu–Chongqing high-speed railway, Xi'an-Chengdu high-speed railway, Chengdu-Guiyang high-speed railway, and Chengdu–Kunming high-speed railway. A suburban railway connects Chengdu and Dujiangyan.
Demographics
 The majority of the province's population is
The majority of the province's population is Han Chinese
The Han Chinese, alternatively the Han people, are an East Asian people, East Asian ethnic group native to Greater China. With a global population of over 1.4 billion, the Han Chinese are the list of contemporary ethnic groups, world's la ...
(95% of the provincial population), who are found scattered throughout the region except for the far western areas. Thus, significant minorities of Tibetan, Yi, Qiang, and Nakhi people
The Nakhi, Nashi, or Naxi (; Naxi: ) are a people inhabiting the Hengduan Mountains abutting the Eastern Himalayas in the northwestern part of Yunnan Province, as well as the southwestern part of Sichuan Province in China.
The Nakhi are tho ...
reside in the western portion that is impacted by inclement weather and natural disasters, environmentally fragile, and impoverished. Sichuan's capital of Chengdu
Chengdu; Sichuanese dialects, Sichuanese pronunciation: , Standard Chinese pronunciation: ; Chinese postal romanization, previously Romanization of Chinese, romanized as Chengtu. is the capital city of the Chinese province of Sichuan. With a ...
is home to a large community of Tibetans, with 30,000 permanent Tibetan residents and up to 200,000 Tibetan floating population. The Eastern Lipo, included with either the Yi or the Lisu people, as well as the A-Hmao, also are among the ethnic groups of the provinces.
Sichuan was China's List of Chinese administrative divisions by population, most populous province before Chongqing
ChongqingPostal Romanization, Previously romanized as Chungking ();. is a direct-administered municipality in Southwestern China. Chongqing is one of the four direct-administered municipalities under the State Council of the People's Republi ...
became a directly controlled municipality; it is currently the fourth most populous, after Guangdong, Shandong, and Henan. As of 1832, Sichuan was the most populous of the 18 provinces in China, with an estimated population at that time of 21 million.
Religion
The predominant religions in Sichuan are Chinese folk religions, Taoism, Taoist traditions, and Chinese Buddhism. According to surveys conducted in 2007 and 2009, 10.6% of the population believes and is involved in Chinese ancestral religion, cults of ancestors, while 0.68% of the population identifies as Christianity in Sichuan, Christian.[
The reports did not give figures for other types of religion; the vast majority may be either irreligious or involved in Chinese folk religion, Buddhism, etc. Tibetan Buddhism is widespread, especially in areas inhabited by ethnic Tibetans. Sichuan is one of the cradles of the early Zhengyi Taoism, Heavenly Masters' Taoist religious movements.
According to "Vestiges of Zoroastrianism in Medieval Sichuan" by Yao Chongxin, professor at Sun Yat-sen University, Zoroastrianism flourished during the period of Tang dynasty, Tang (618–907), ]Former Shu
Great Shu ( zh, c=大蜀, p=Dàshǔ), known in historiography as the Former Shu ( zh, c=前蜀, p=Qiánshǔ, links=no) or occasionally Wang Shu (王蜀), was a dynastic state of China and one of the Ten Kingdoms during the Five Dynasties and ...
(907–925), Later Shu
Shu, referred to as Later Shu ( zh, t=後蜀, s=后蜀, first=t, p=Hòu Shǔ) and Meng Shu ( zh, c=孟蜀) in historiography, was a dynastic state of China and one of the Ten Kingdoms during the Five Dynasties and Ten Kingdoms period. It was ...
(934–965), and Song
A song is a musical composition performed by the human voice. The voice often carries the melody (a series of distinct and fixed pitches) using patterns of sound and silence. Songs have a structure, such as the common ABA form, and are usu ...
(960–1279).
A Chabad house, Chabad Jewish Center was established in Chengdu
Chengdu; Sichuanese dialects, Sichuanese pronunciation: , Standard Chinese pronunciation: ; Chinese postal romanization, previously Romanization of Chinese, romanized as Chengtu. is the capital city of the Chinese province of Sichuan. With a ...
in 2012, after moving five times, a permanent location was secured at Wuhou District.
File:Huanglong Sichuan China Multicolored-ponds-04.jpg, View of the Temple of the Yellow Dragon (Chinese Buddhism) in Huanglong Scenic and Historic Interest Area, Huanglong.
File:Litang8.jpg, Statues of buddhas at Litang Monastery of the Tibetan tradition.
File:Main altar before Shangqing Temple on Qingchengshan, in Chengdu, Sichuan.jpg, A pavilion of the Shangqing Temple (Taoist) in Qingchengshan, Chengdu
Chengdu; Sichuanese dialects, Sichuanese pronunciation: , Standard Chinese pronunciation: ; Chinese postal romanization, previously Romanization of Chinese, romanized as Chengtu. is the capital city of the Chinese province of Sichuan. With a ...
.
File:China - Mount Emei - EmeiShan - Sichuan 11.jpg, Golden Temple of Mount Emei (Chinese Buddhism).
File:巴巴寺.JPG, , a Menhuan, Chinese Sufism, Sufi mosque in Langzhong.
File:Cathedral of the Immaculate Conception, Chengdu.png, Immaculate Conception Cathedral, Chengdu (Catholic Church in Sichuan, Catholic)
File:St John's Cathedral, Paoning.jpg, St John's Cathedral, Langzhong (History of Anglicanism in Sichuan, Anglican)
File:成都恩光堂.jpg, Sï-Shen-Tsï Methodist Church (History of Methodism in Sichuan, Methodist)
Culture
The ''Sichuanese people'' (Sichuanese Mandarin, Sichuanese: Ba1su2ren2; International Phonetic Alphabet, IPA: ; alternatively , , or ) are a subgroup of Han Chinese living in mostly Sichuan province and the neighboring Chongqing
ChongqingPostal Romanization, Previously romanized as Chungking ();. is a direct-administered municipality in Southwestern China. Chongqing is one of the four direct-administered municipalities under the State Council of the People's Republi ...
municipality. Beginning from the 9th century BC, Shu (on the Chengdu Plain
The Chengdu Plain ( zh, t=成都平原, s=成都平原, p=Chéngdū Píngyuán), referred to in Sichuanese as the Western Sichuan Plain ( zh, s=川西坝子, first=t; Sichuanese Pinyin: ''Cuanxi Bazi''), is an alluvial plain located in the wes ...
) and Ba (which had its first capital at Enshi City in Hubei
Hubei is a province of China, province in Central China. It has the List of Chinese provincial-level divisions by GDP, seventh-largest economy among Chinese provinces, the second-largest within Central China, and the third-largest among inland ...
and controlled part of the Han River (Shaanxi and Hubei), Han Valley) emerged as cultural and administrative centers where two rival kingdoms were established. Although eventually, the Qin dynasty destroyed the kingdoms of Shu and Ba, the Qin government accelerated the technological and agricultural advancements of Sichuan making it comparable to that of the Yellow River
The Yellow River, also known as Huanghe, is the second-longest river in China and the List of rivers by length, sixth-longest river system on Earth, with an estimated length of and a Drainage basin, watershed of . Beginning in the Bayan H ...
Valley. The now-extinct Ba–Shu Chinese, Ba–Shu language was derived from Qin-era settlers and represents the earliest documented division from what is now called Middle Chinese.
During the Yuan dynasty, Yuan and Ming dynasty, Ming dynasties, the population of the area was reduced through wars and the bubonic plague, and settlers arrived from the area of modern Hubei, replacing the earlier common Chinese with a new standard.
The Li Bai Memorial, located in Jiangyou, is a museum in memory of Li Bai, a Chinese poet of Tang dynasty, Tang China (618–907) built at the place where he grew up. The building was begun in 1962 on the occasion of the 1200th anniversary of his death, completed in 1981, and opened to the public in October 1982. The memorial is built in the style of the classic Tang garden.
In 2003, Sichuan had "88 art performing troupes, 185 culture centers, 133 libraries, and 52 museums". Companies based in Sichuan also produced 23 television series and one film.
Languages
 The Sichuanese once spoke their variety of Spoken Chinese called Ba-Shu Chinese, or Old Sichuanese before it became extinct during the Ming dynasty. Now most of them speak Sichuanese Mandarin. The Minjiang dialects are thought by some linguists to be a bona fide descendant of Old Sichuanese, but there is no conclusive evidence whether Minjiang dialects are derived from Old Sichuanese or Southwestern Mandarin.
The languages of Sichuan are primarily members of three subfamilies of the Sino-Tibetan languages.
The most widely used variety of Chinese spoken in Sichuan is Sichuanese dialects, Sichuanese, which is the lingua franca in Sichuan,
The Sichuanese once spoke their variety of Spoken Chinese called Ba-Shu Chinese, or Old Sichuanese before it became extinct during the Ming dynasty. Now most of them speak Sichuanese Mandarin. The Minjiang dialects are thought by some linguists to be a bona fide descendant of Old Sichuanese, but there is no conclusive evidence whether Minjiang dialects are derived from Old Sichuanese or Southwestern Mandarin.
The languages of Sichuan are primarily members of three subfamilies of the Sino-Tibetan languages.
The most widely used variety of Chinese spoken in Sichuan is Sichuanese dialects, Sichuanese, which is the lingua franca in Sichuan, Chongqing
ChongqingPostal Romanization, Previously romanized as Chungking ();. is a direct-administered municipality in Southwestern China. Chongqing is one of the four direct-administered municipalities under the State Council of the People's Republi ...
, and parts of the Tibet Autonomous Region
The Tibet Autonomous Region (TAR), often shortened to Tibet in English or Xizang in Pinyin, Hanyu Pinyin, is an Autonomous regions of China, autonomous region of the China, People's Republic of China. It was established in 1965 to replace the ...
. Although Sichuanese is generally classified as a dialect of Mandarin Chinese
Mandarin ( ; zh, s=, t=, p=Guānhuà, l=Mandarin (bureaucrat), officials' speech) is the largest branch of the Sinitic languages. Mandarin varieties are spoken by 70 percent of all Chinese speakers over a large geographical area that stretch ...
, it is highly divergent in phonology, vocabulary, and even grammar from Standard Chinese.
Sichuan brocade
Commonly known as "Shu brocade" () in Chinese, Sichuan brocade is referred to as the "mother of brocade in China" given its age. This technique of embroidery originates in the capital city of Chengdu
Chengdu; Sichuanese dialects, Sichuanese pronunciation: , Standard Chinese pronunciation: ; Chinese postal romanization, previously Romanization of Chinese, romanized as Chengtu. is the capital city of the Chinese province of Sichuan. With a ...
during the time of the Shu (kingdom), Ancient Kingdom of Shu. It enjoyed high popularity throughout the regions along the Silk Road, which stimulated an "Exoticism, exoticization" of the embroidery designs during the 1st millennium, with most of the patterns imported from Sogdia and other parts of Central Asia. According to the ''Book of Sui'', in the year 605 AD, the head of the Sichuan ateliers producing silks in the "western style" was a certain He Chou, a name which betrays his Sogdian origins. Most of the silk products unearthed in Xinjiang (History of Xinjiang, Chinese Turkestan) and Qinghai
Qinghai is an inland Provinces of China, province in Northwestern China. It is the largest provinces of China, province of China (excluding autonomous regions) by area and has the third smallest population. Its capital and largest city is Xin ...
(Tuyuhun, Tuyuhun Kingdom) confirmed to be manufactured in Sichuan.
Cuisine
Sichuan is well known for its spicy cuisine and use of Sichuan pepper
Sichuan pepper (, also known as Sichuanese pepper, Szechuan pepper, Chinese prickly ash, Chinese pepper, Mountain pepper, and ''mala'' pepper, is a spice commonly used in Sichuan cuisine in China, Bhutan and in northeast India. It is called mej ...
s due to its humid climate.
The Sichuanese are proud of their cuisine, known as one of the Four Great Traditions of Chinese cuisine. The cuisine here is of "one dish, one shape, hundreds of dishes, hundreds of tastes", as the saying goes, to describe its acclaimed diversity. The most prominent traits of Sichuanese cuisine are described by four words: spicy, hot, fresh, and fragrant. Sichuan cuisine is popular in the whole nation of China, and so are Sichuan chefs.
Another famous Sichuan delicacy is hot pot. Hot pot is a Chinese soup containing a variety of East Asian foodstuffs and ingredients, prepared with a simmering pot of soup stock at the dining table. While the hot pot is kept simmering, ingredients are placed into the pot and cooked at the table. Typical hot pot dishes include thinly sliced meat, leaf vegetables, mushrooms, wontons, egg dumplings, tofu, and seafood. The cooked food is usually eaten with a dipping sauce.
File:Kung-pao-shanghai.jpg, Kung Pao chicken
Kung Pao chicken (), also transcribed Gong Bao or Kung Po, is a spicy, stir-fried Chinese dish made with cubes of cooked chicken, peanuts, vegetables and chili peppers, and Sichuan peppercorns. From its origins in Sichuan cuisine, the dish' ...
, one of the best known dishes of Sichuan cuisine
File:Mapodoufu.jpg, Mapo doufu
File:担担面 Dandan noodles.jpg, Dandan noodles
File:Mixed sauce noodles.JPG, Zajiangmian ()
Education
Colleges and universities
As of 2022, Sichuan hosts 134 institutions of higher education, ranking first in the Western China
Western China ( zh, s=中国西部, l=, labels=no or zh, s=华西, l=, labels=no) is the west of China. It consists of Southwestern China and Northwestern China. In the definition of the Chinese government, Western China covers six provinces ...
region and fifth among all Chinese provinces after Jiangsu, Guangdong, Henan
Henan; alternatively Honan is a province in Central China. Henan is home to many heritage sites, including Yinxu, the ruins of the final capital of the Shang dynasty () and the Shaolin Temple. Four of the historical capitals of China, Lu ...
and Shandong.Chengdu
Chengdu; Sichuanese dialects, Sichuanese pronunciation: , Standard Chinese pronunciation: ; Chinese postal romanization, previously Romanization of Chinese, romanized as Chengtu. is the capital city of the Chinese province of Sichuan. With a ...
)
*Southwest Jiaotong University (Chengdu)
*University of Electronic Science and Technology of China (Chengdu)
*Southwestern University of Finance and Economics (Chengdu)
*Chengdu University of Technology (Chengdu)
*Chengdu University of Information Technology (Chengdu)
*Chengdu University of Traditional Chinese Medicine (Chengdu)
*Civil Aviation Flight University of China (Guanghan
Guanghan ( zh, s=广汉, t=廣漢, p=Guǎnghàn; formerly known as Hanchow) is a county-level city under the administration of Deyang in Sichuan province, southwest China, and only from Chengdu. The predominant industries are tourism, pharmaceut ...
)
*Southwest University for Nationalities (Chengdu)
*Sichuan Normal University (Chengdu)
*Sichuan Agricultural University (Ya'an, Chengdu, Dujiangyan)
*Southwest Petroleum University (Nanchong
Nanchong ( zh, c=南充 , p=Nánchōng , w=Nan-ch'ung; Sichuanese: lan2cong1) is a prefecture-level city in the northeast of Sichuan province, China, with an area of . At the 2020 census it was home to 5,607,565 people, of whom 1,936,534 liv ...
and Chengdu)
*Xihua University (Chengdu)
*Southwest University of Science and Technology (Mianyang
Mianyang ( zh, s=绵阳, t=綿陽, w=Mien2-yang2, p=Miányáng; Sichuanese Pinyin, Sichuanese romanization: ''Mien-iang''; formerly known as Mienchow, zh, t=綿州, p=Mianzhou, links=no; Sichuanese romanization: ''Miencheo''; ) is the second lar ...
)
*China West Normal University (Nanchong
Nanchong ( zh, c=南充 , p=Nánchōng , w=Nan-ch'ung; Sichuanese: lan2cong1) is a prefecture-level city in the northeast of Sichuan province, China, with an area of . At the 2020 census it was home to 5,607,565 people, of whom 1,936,534 liv ...
)
*North Sichuan Medical College (Nanchong)
*Panzhihua University (Panzhihua)
*Sichuan Police College (Luzhou
Luzhou ( zh, s=泸州, p=Lúzhōu; Sichuanese Pinyin: Nu2zou1; Minjiang dialect, Luzhou dialect: ) is a prefecture-level city located in the southeast of Sichuan Province, China. It is also known as the "Liquor City" (). It was named Jiangyang () ...
)
*Sichuan University of Science and Engineering (Zigong and Yibin
Yibin ( zh, s=宜宾 , t=宜賓 , p=Yíbīn , w=I-pin, region=CN-SC-15; Sichuanese Pinyin: ȵi2bin1; Sichuanese pronunciation: ) is a prefecture-level city in the southeastern part of Sichuan province, China, located at the junction of the Min ...
)
*Chengdu University (Chengdu)
*Xichang University (Xichang
Xichang ( Northern Yi: /o̝˨˩dʐo̝˧/) is a city in and the seat of the Liangshan Yi Autonomous Prefecture in the south of Sichuan, China.
History
The Qiongdu were the local people at the time of contact with China. The county of Qiongdu is ...
)
*Aba Teachers University (Ngawa Tibetan and Qiang Autonomous Prefecture)
*Yibin University (Yibin
Yibin ( zh, s=宜宾 , t=宜賓 , p=Yíbīn , w=I-pin, region=CN-SC-15; Sichuanese Pinyin: ȵi2bin1; Sichuanese pronunciation: ) is a prefecture-level city in the southeastern part of Sichuan province, China, located at the junction of the Min ...
)
Tourism
File:Beauty of Jiuzhaigou National Park - Apr 2017.png, Jiuzhaigou
File:Yading - panoramio (1).jpg, Yading
File:1 huanglong pools aerial 2011.jpg, Huanglong Scenic and Historic Interest Area
File:Jiuzhaigou, Aba, Sichuan, China - panoramio - dayu490301.jpg, Waterfalls at Jiuzhaigou
File:毕棚沟.jpg, Bipenggou Valley
File:四姑娘山景区 Mount Siguniang Scenic Area 45.jpg, Mount Siguniang Scenic Area
File:大冰瀑布-Q30023595.jpg, Hailuogou Glacier Forest Park
File:Mount Emei - Sunrise above the clouds.jpg, alt=, Mount Emei
UNESCO World Heritage Sites in Sichuan province and Chongqing municipality include:
*Dazu Rock Carvings and Wulong Karst (Chongqing
ChongqingPostal Romanization, Previously romanized as Chungking ();. is a direct-administered municipality in Southwestern China. Chongqing is one of the four direct-administered municipalities under the State Council of the People's Republi ...
municipality)
*Huanglong Scenic and Historic Interest Area
*Jiuzhaigou Valley Scenic and Historic Interest Area
*Mount Emei Scenic Area, including Leshan Giant Buddha Scenic Area
*Mount Qincheng and the Dujiangyan Irrigation System
*Sichuan Giant Panda Sanctuaries
As of July 2013, the world's largest building, the New Century Global Center is located in Chengdu. At high, long, and wide, the Center houses retail outlets, movie theaters, offices, hotels, the Paradise Island waterpark, an artificial beach, a -long Light-emitting diode, LED screen, skating rink, pirate ship, fake Mediterranean village, 24-hour artificial sun, and 15,000-spot parking area.
Notable individuals
*Ba Jin (25 November 1904 – 17 October 2005), novelist and writer
*Bai Ling, actress
*Bao Sanniang, a possibly fictional woman warrior of the Three Kingdoms
The Three Kingdoms of Cao Wei, Shu Han, and Eastern Wu dominated China from AD 220 to 280 following the end of the Han dynasty. This period was preceded by the Eastern Han dynasty and followed by the Jin dynasty (266–420), Western Jin dyna ...
period.
*Zhang Qun, Chang Chün, premier of the Republic of China
*Chang Dai-chien, artist
*Che Yongli (28 January 1980), actress
*Chen Kenmin (27 June 1912 – 12 May 1990), chef who specialized in Sichuan cuisine
Sichuan cuisine or Sichuanese cuisine, alternatively romanized as Szechwan cuisine or Szechuan cuisine (, Standard Mandarin pronunciation: ) is a style of Chinese cuisine originating from Sichuan province and the neighboring Chongqing munic ...
. Father of well-known Iron Chef, Chen Kenichi.
*Chen Pokong (1963–), author, political commentator and democracy activist
*Chen Shou, official and writer
*Cheung Chung-kiu, business magnate
*Deng Xiaoping
Deng Xiaoping also Romanization of Chinese, romanised as Teng Hsiao-p'ing; born Xiansheng (). (22 August 190419 February 1997) was a Chinese statesman, revolutionary, and political theorist who served as the paramount leader of the People's R ...
, Chinese Paramount Leader during the 1980s, his Deng Xiaoping's Former Residence, former residence is now a museum.
*Guifeng Zongmi (780–841), Tang dynasty Buddhist scholar-monk, fifth patriarch of the Huayan school as well as a patriarch of the Heze lineage of Southern Chan
*Guo Moruo, renowned author
*Akio Hong, broadcaster
*Huang Jiguang, highly decorated soldier during the Korean War
*Jiang Zhuyun, revolutionary martyr
*Li Bai (701–762), poet of the Tang dynasty
*Li Bifeng, activist
*Li Ching-Yuen, Herbalism, herbalist, Martial arts, martial artist and tactical advisor, also known for extreme longevity claims
*Li Shou-min, better known as Huanzhulouzhu (1902–1961), novelist of the xianxia genre
*Li Shunxian (–926), Iranians in China#Former Shu, Persian-Sichuanese poet, concubine of Emperor Wang Zongyan of Former Shu
Great Shu ( zh, c=大蜀, p=Dàshǔ), known in historiography as the Former Shu ( zh, c=前蜀, p=Qiánshǔ, links=no) or occasionally Wang Shu (王蜀), was a dynastic state of China and one of the Ten Kingdoms during the Five Dynasties and ...
*Li Yifeng, actor and singer
*Li Yuchun, singer, songwriter, and actress
*Liao Yiwu, author, reporter, musician, and poet
*Liu Yonghao, businessman
*Luo Ruiqing, army officer and politician
*Meng Caicheng, (蒙裁成, 1859–1928), activist in the Railway Protection Movement
*Ouyang Xiu (1007–22 September 1072), Confucian historian, essayist, calligrapher, poet, and official bureaucrat of the Song dynasty
*Sanyu (painter)
*Song Cheng-tsi (1892–1955), Anglican bishop
*Song Yonghua, scholar
*Su Shi
Su Shi ( zh, t=, s=苏轼, p=Sū Shì; 8 January 1037 – 24 August 1101), courtesy name Zizhan (), art name Dongpo (), was a Chinese poet, essayist, calligrapher, painter, scholar-official, literatus, artist, pharmacologist, and gastronome wh ...
(8 January 1037 – 24 August 1101), Confucian bureaucrat official, poet, artist, calligrapher, pharmacologist, gastronome, and official bureaucrat of the Song dynasty
*Su Xun
Su Xun (; 22 May 1009 – 21 May 1066) was a scholar, essayist and philosopher during the Song dynasty, listed as one of the Eight Masters of the Tang and Song, along with his sons Su Shi and Su Zhe.
Life and career
Early life and educati ...
(1009–1066), poet and prose-writer of the Song dynasty
*Su Zhe
Su Zhe (; 1039–1112), or Su Che, courtesy names Ziyou and Tongshu , was a Chinese essayist, historian, poet, and politician from Meishan, located in modern-day Sichuan Province, China.
Su was highly honored as a politician and essayist in th ...
(1039–1112), poet and essayist, a Confucian bureaucratic official of the Song dynasty
*Tan Weiwei, singer and actress
*Tang Chun-i, philosopher and scholar
*Wang Jiujiang (1957–), painter
*Wang Jianlin, business magnate, investor, and philanthropist
*Wang Xiaoya, television host and media personality
*Wang Yi (pastor) (1973–)
*Wuzhun Shifan (1178–1249), Zen Buddhist monk
*Kep1er, Xiaoting(12 November 1999),singer member of Kep1er
*SM Rookies#Former members, Xu Yiyang (12 August 1997), singer
Sports
Professional sports teams in Sichuan include:
*Chinese Basketball Association
**Sichuan Blue Whales
*Chinese Super League
**Chengdu Rongcheng F.C.
*Chinese Volleyball League
**Sichuan Volleyball Team
*China Table Tennis Super League
**Sichuan Quan-Xing Table-Tennis Team
Sister states and regions
* Washington (state), Washington, United States (1982)
* Michigan, United States (1982)
* Hiroshima Prefecture, Japan (1984)
* Yamanashi Prefecture, Japan (1985)
* South P'yŏngan, North Korea (1985)
* Kedah, Malaysia (1985)
* Midi-Pyrénées, France (1987)
* North Rhine-Westphalia, Germany (1988)
* Leicestershire, United Kingdom (1988)
* Piedmont, Italy (1990)
* Pernambuco, Brazil (1992)
* Tolna (county), Tolna County, Hungary (1993)
* Valencian Community, Spain (1994)
* Brussels-Capital Region, Belgium (1995)
* Barinas State, Venezuela (2001)
* Friesland, Netherlands (2001)
* Almaty Province, Kazakhstan (2001)
* Mpumalanga, South Africa (2002)
* Suphan Buri, Thailand (2010)
* Victoria (Australia), Victoria, Australia (2015)
* Lavalleja, Uruguay (2020)
See also
*2008 Sichuan earthquake
*Bashu culture
*''Chronicles of Huayang
The ''Chronicles of Huayang'' or ''Huayang Guo Zhi'' ( zh, t=華陽國志, s=华阳国志, first=t, l=Records of the Lands South of Mt. Hua) is the oldest extant gazetteer of a region of China. It was compiled by Chang Qu during the Jin dynast ...
''
*Eight Immortals from Sichuan
*''The Good Person of Szechwan''
*List of prisons in Sichuan
*Major national historical and cultural sites (Sichuan)
*Qutang Gorge
* Sichuan Airlines
*Sichuan cuisine
Sichuan cuisine or Sichuanese cuisine, alternatively romanized as Szechwan cuisine or Szechuan cuisine (, Standard Mandarin pronunciation: ) is a style of Chinese cuisine originating from Sichuan province and the neighboring Chongqing munic ...
*Sichuan dialect
*Sichuan Giant Panda Sanctuaries
Notes
References
External links
*
Economic profile for Sichuan
at Hong Kong Trade Development Council, HKTDC
Ancient silver coins of Sichuan
*
{{Authority control
Sichuan,
Provinces of the People's Republic of China
Western China
 Sichuan was subjected to the autonomous control of kings named by the imperial family of the Han dynasty. During the 11 years hiatus between 25 and 36 AD, Sichuan was controlled by the
Sichuan was subjected to the autonomous control of kings named by the imperial family of the Han dynasty. During the 11 years hiatus between 25 and 36 AD, Sichuan was controlled by the 
 In the early 20th century, the newly founded
In the early 20th century, the newly founded 
 The provides paramilitary law enforcement and disaster relief services within Sichuan province. The Yibin Detachment was deployed for disaster relief during the of February 8, 2025 in Junlian County,
The provides paramilitary law enforcement and disaster relief services within Sichuan province. The Yibin Detachment was deployed for disaster relief during the of February 8, 2025 in Junlian County, 
 Sichuan is the 6th-largest provincial economy of China, the largest in
Sichuan is the 6th-largest provincial economy of China, the largest in  Established in 1988, Chengdu Hi-tech Industrial Development Zone () was approved as one of the first national hi-tech development zones in 1991. In 2000, it was open to APEC and has been recognized as a national advanced hi-tech development zone in successive assessment activities held by China's Ministry of Science and Technology. It ranks 5th among the 53 national hi-tech development zones in China in terms of comprehensive strength.
Chengdu Hi-tech Development Zone covers an area of , consisting of South Park and West Park. By relying on the city sub-center, which is under construction, South Park is focusing on creating a modernized industrial park of science and technology with scientific and technological innovation, incubation R&D, modern service industry, and Headquarters economy playing leading roles. Priority has been given to the development of the software industry. Located on both sides of the "Chengdu-Dujiangyan-Jiuzhaigou" golden tourism channel, the West Park aims at building a comprehensive industrial park targeting industrial clustering with complete supportive functions. West Park gives priority to three major industries i.e. electronic information, biomedicine, and precision machinery.
Established in 1988, Chengdu Hi-tech Industrial Development Zone () was approved as one of the first national hi-tech development zones in 1991. In 2000, it was open to APEC and has been recognized as a national advanced hi-tech development zone in successive assessment activities held by China's Ministry of Science and Technology. It ranks 5th among the 53 national hi-tech development zones in China in terms of comprehensive strength.
Chengdu Hi-tech Development Zone covers an area of , consisting of South Park and West Park. By relying on the city sub-center, which is under construction, South Park is focusing on creating a modernized industrial park of science and technology with scientific and technological innovation, incubation R&D, modern service industry, and Headquarters economy playing leading roles. Priority has been given to the development of the software industry. Located on both sides of the "Chengdu-Dujiangyan-Jiuzhaigou" golden tourism channel, the West Park aims at building a comprehensive industrial park targeting industrial clustering with complete supportive functions. West Park gives priority to three major industries i.e. electronic information, biomedicine, and precision machinery.
 The Sichuanese once spoke their variety of Spoken Chinese called Ba-Shu Chinese, or Old Sichuanese before it became extinct during the Ming dynasty. Now most of them speak Sichuanese Mandarin. The Minjiang dialects are thought by some linguists to be a bona fide descendant of Old Sichuanese, but there is no conclusive evidence whether Minjiang dialects are derived from Old Sichuanese or Southwestern Mandarin.
The languages of Sichuan are primarily members of three subfamilies of the Sino-Tibetan languages.
The most widely used variety of Chinese spoken in Sichuan is Sichuanese dialects, Sichuanese, which is the lingua franca in Sichuan,
The Sichuanese once spoke their variety of Spoken Chinese called Ba-Shu Chinese, or Old Sichuanese before it became extinct during the Ming dynasty. Now most of them speak Sichuanese Mandarin. The Minjiang dialects are thought by some linguists to be a bona fide descendant of Old Sichuanese, but there is no conclusive evidence whether Minjiang dialects are derived from Old Sichuanese or Southwestern Mandarin.
The languages of Sichuan are primarily members of three subfamilies of the Sino-Tibetan languages.
The most widely used variety of Chinese spoken in Sichuan is Sichuanese dialects, Sichuanese, which is the lingua franca in Sichuan,