Syrian Opposition on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Syrians () are the majority inhabitants of
 Those who retained the Aramaic language are divided among two groups:
* The Eastern Aramaic Syriac-speaking group, followers of the West Syriac Rite of the Syriac Orthodox Church and the Syrian Catholic Church; kept the pre-Islamic Syrian (Syriac) identity throughout the ages, asserting their culture in face of the Arab dominance. Linguists, such as
Those who retained the Aramaic language are divided among two groups:
* The Eastern Aramaic Syriac-speaking group, followers of the West Syriac Rite of the Syriac Orthodox Church and the Syrian Catholic Church; kept the pre-Islamic Syrian (Syriac) identity throughout the ages, asserting their culture in face of the Arab dominance. Linguists, such as
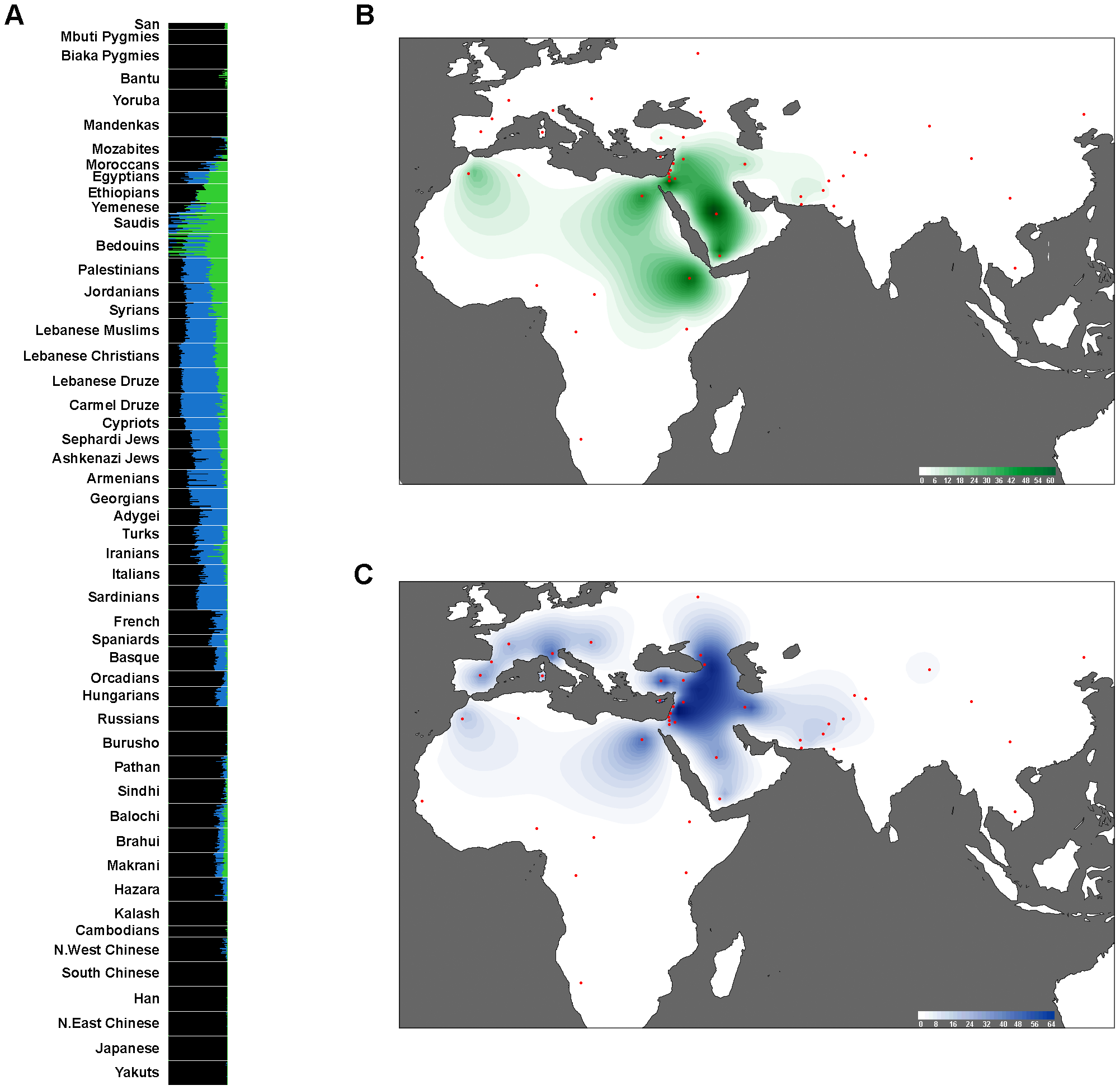 Genetic tests on Syrians were included in many genetic studies. The genetic marker which identifies descendants of the ancient
Genetic tests on Syrians were included in many genetic studies. The genetic marker which identifies descendants of the ancient
 Syrian cuisine is dominated by ingredients native to the region.
Syrian cuisine is dominated by ingredients native to the region.
Syrian people, Every Culture
Photos and images of Syrian people, Syrian History – Online
Collections of images of Eastern Mediterranean people, including Syrian people, Mideast Image
Syrian people, Encyclopædia Britannica
{{Authority control Syrian diaspora Semitic-speaking peoples Articles containing video clips Ethnic groups in the Middle East Arab ethnic groups
Syria
Syria, officially the Syrian Arab Republic, is a country in West Asia located in the Eastern Mediterranean and the Levant. It borders the Mediterranean Sea to the west, Turkey to Syria–Turkey border, the north, Iraq to Iraq–Syria border, t ...
, indigenous to the Levant
The Levant ( ) is the subregion that borders the Eastern Mediterranean, Eastern Mediterranean sea to the west, and forms the core of West Asia and the political term, Middle East, ''Middle East''. In its narrowest sense, which is in use toda ...
, most of whom have Arabic
Arabic (, , or , ) is a Central Semitic languages, Central Semitic language of the Afroasiatic languages, Afroasiatic language family spoken primarily in the Arab world. The International Organization for Standardization (ISO) assigns lang ...
, especially its Levantine and Mesopotamian dialects, as a mother tongue. The cultural
Culture ( ) is a concept that encompasses the social behavior, institutions, and Social norm, norms found in human societies, as well as the knowledge, beliefs, arts, laws, Social norm, customs, capabilities, Attitude (psychology), attitudes ...
and linguistic heritage of the Syrian people is a blend of both indigenous elements and the foreign cultures that have come to rule the land and its people over the course of thousands of years. By the seventh century, most of the inhabitants of the Levant spoke Aramaic
Aramaic (; ) is a Northwest Semitic language that originated in the ancient region of Syria and quickly spread to Mesopotamia, the southern Levant, Sinai, southeastern Anatolia, and Eastern Arabia, where it has been continually written a ...
. In the centuries after the Muslim conquest of the Levant
The Muslim conquest of the Levant (; ), or Arab conquest of Syria, was a 634–638 CE invasion of Byzantine Syria by the Rashidun Caliphate. A part of the wider Arab–Byzantine wars, the Levant was brought under Arab Muslim rule and develope ...
in 634, Arabic gradually became the dominant language, but a minority of Syrians (particularly the Assyrians and Syriac-Arameans
The Arameans, or Aramaeans (; ; , ), were a tribal Semitic people in the ancient Near East, first documented in historical sources from the late 12th century BCE. Their homeland, often referred to as the land of Aram, originally covered c ...
retained Aramaic (Syriac), which is still spoken in its Eastern and Western dialects.
The national name "Syrian" was originally an Indo-European corruption of Assyrian and applied to Assyria in northern Mesopotamia
Mesopotamia is a historical region of West Asia situated within the Tigris–Euphrates river system, in the northern part of the Fertile Crescent. Today, Mesopotamia is known as present-day Iraq and forms the eastern geographic boundary of ...
, however by antiquity it was used to denote the inhabitants of the Levant. Following the Muslim conquest of the Levant, Arab identity gradually became dominant among many Syrians, and the ethnonym "Syrian" was used mainly by Christians
A Christian () is a person who follows or adheres to Christianity, a monotheistic Abrahamic religion based on the life and teachings of Jesus Christ. Christians form the largest religious community in the world. The words '' Christ'' and ''C ...
in Levant, Mesopotamia and Anatolia who spoke Syriac. In the 19th century, the name "Syrian" was revived amongst the Arabic speakers of the Levant. Following the establishment of the Arab Kingdom of Syria in 1920, the name "Syrian" began to spread amongst its Arabic speaking inhabitants. The term gained more importance during the Mandate for Syria and the Lebanon, becoming the accepted national name for the Arabic speakers of the Syrian Republic.
Most Arabic-speaking Syrians identify as Arabs and are described as such by virtue of their modern-day language and bonds to Arab culture and history. But they are, in fact, genetically a blend of the various Semitic-speaking groups indigenous to the region. There is no contradiction between being an Arab and a Syrian since the Syrian Arab identity is multi-layered and being Syrian complements being Arab. In addition to denoting Syrian Arabs, the term "Syrian" also refer to all Syrian citizens, regardless of their ethnic background. In 2018, Syria had an estimated population of 19.5 million, which includes, aside from the aforementioned majority, Kurds
Kurds (), or the Kurdish people, are an Iranian peoples, Iranic ethnic group from West Asia. They are indigenous to Kurdistan, which is a geographic region spanning southeastern Turkey, northwestern Iran, northern Iraq, and northeastern Syri ...
, Assyrians, Turkmen, Armenians
Armenians (, ) are an ethnic group indigenous to the Armenian highlands of West Asia.Robert Hewsen, Hewsen, Robert H. "The Geography of Armenia" in ''The Armenian People From Ancient to Modern Times Volume I: The Dynastic Periods: From Antiq ...
and others.
Even before the Syrian Civil War, there was a large Syrian diaspora that had emigrated to North America (United States
The United States of America (USA), also known as the United States (U.S.) or America, is a country primarily located in North America. It is a federal republic of 50 U.S. state, states and a federal capital district, Washington, D.C. The 48 ...
and Canada
Canada is a country in North America. Its Provinces and territories of Canada, ten provinces and three territories extend from the Atlantic Ocean to the Pacific Ocean and northward into the Arctic Ocean, making it the world's List of coun ...
), European Union member states (including Sweden, France, and Germany), South America (mainly in Brazil
Brazil, officially the Federative Republic of Brazil, is the largest country in South America. It is the world's List of countries and dependencies by area, fifth-largest country by area and the List of countries and dependencies by population ...
, Argentina
Argentina, officially the Argentine Republic, is a country in the southern half of South America. It covers an area of , making it the List of South American countries by area, second-largest country in South America after Brazil, the fourt ...
, Venezuela
Venezuela, officially the Bolivarian Republic of Venezuela, is a country on the northern coast of South America, consisting of a continental landmass and many Federal Dependencies of Venezuela, islands and islets in the Caribbean Sea. It com ...
, and Chile
Chile, officially the Republic of Chile, is a country in western South America. It is the southernmost country in the world and the closest to Antarctica, stretching along a narrow strip of land between the Andes, Andes Mountains and the Paci ...
), the West Indies
The West Indies is an island subregion of the Americas, surrounded by the Atlantic Ocean, North Atlantic Ocean and the Caribbean Sea, which comprises 13 independent island country, island countries and 19 dependent territory, dependencies in thr ...
, Africa, Australia, and New Zealand. Six million refugees of the Syrian Civil War also live outside Syria now, mostly in Turkey
Turkey, officially the Republic of Türkiye, is a country mainly located in Anatolia in West Asia, with a relatively small part called East Thrace in Southeast Europe. It borders the Black Sea to the north; Georgia (country), Georgia, Armen ...
, Egypt
Egypt ( , ), officially the Arab Republic of Egypt, is a country spanning the Northeast Africa, northeast corner of Africa and Western Asia, southwest corner of Asia via the Sinai Peninsula. It is bordered by the Mediterranean Sea to northe ...
, Jordan
Jordan, officially the Hashemite Kingdom of Jordan, is a country in the Southern Levant region of West Asia. Jordan is bordered by Syria to the north, Iraq to the east, Saudi Arabia to the south, and Israel and the occupied Palestinian ter ...
, Lebanon
Lebanon, officially the Republic of Lebanon, is a country in the Levant region of West Asia. Situated at the crossroads of the Mediterranean Basin and the Arabian Peninsula, it is bordered by Syria to the north and east, Israel to the south ...
, Germany
Germany, officially the Federal Republic of Germany, is a country in Central Europe. It lies between the Baltic Sea and the North Sea to the north and the Alps to the south. Its sixteen States of Germany, constituent states have a total popu ...
as well as Sweden
Sweden, formally the Kingdom of Sweden, is a Nordic countries, Nordic country located on the Scandinavian Peninsula in Northern Europe. It borders Norway to the west and north, and Finland to the east. At , Sweden is the largest Nordic count ...
.
Etymology
Various sources indicate that the name ''Syria'' itself is derived from Luwian term "Sura/i", and the derivativeancient Greek
Ancient Greek (, ; ) includes the forms of the Greek language used in ancient Greece and the classical antiquity, ancient world from around 1500 BC to 300 BC. It is often roughly divided into the following periods: Mycenaean Greek (), Greek ...
name: , ', or , ', both of which originally derived from the Akkadian word Aššūrāyu (Assyria
Assyria (Neo-Assyrian cuneiform: , ''māt Aššur'') was a major ancient Mesopotamian civilization that existed as a city-state from the 21st century BC to the 14th century BC and eventually expanded into an empire from the 14th century BC t ...
) in northern Mesopotamia
Mesopotamia is a historical region of West Asia situated within the Tigris–Euphrates river system, in the northern part of the Fertile Crescent. Today, Mesopotamia is known as present-day Iraq and forms the eastern geographic boundary of ...
, modern-day Iraq. However, during the Seleucid Empire, this term was also applied to The Levant, and henceforth the Greeks applied the term without distinction between the Assyrians of north Mesopotamia and Arameans
The Arameans, or Aramaeans (; ; , ), were a tribal Semitic people in the ancient Near East, first documented in historical sources from the late 12th century BCE. Their homeland, often referred to as the land of Aram, originally covered c ...
of the Levant.
Applications of the name in antiquity
The Greeks used the terms "Syrian" and "Assyrian" interchangeably to indicate the indigenousArameans
The Arameans, or Aramaeans (; ; , ), were a tribal Semitic people in the ancient Near East, first documented in historical sources from the late 12th century BCE. Their homeland, often referred to as the land of Aram, originally covered c ...
, Assyrians and other inhabitants of the Levant
The Levant ( ) is the subregion that borders the Eastern Mediterranean, Eastern Mediterranean sea to the west, and forms the core of West Asia and the political term, Middle East, ''Middle East''. In its narrowest sense, which is in use toda ...
and Mesopotamia
Mesopotamia is a historical region of West Asia situated within the Tigris–Euphrates river system, in the northern part of the Fertile Crescent. Today, Mesopotamia is known as present-day Iraq and forms the eastern geographic boundary of ...
, Herodotus
Herodotus (; BC) was a Greek historian and geographer from the Greek city of Halicarnassus (now Bodrum, Turkey), under Persian control in the 5th century BC, and a later citizen of Thurii in modern Calabria, Italy. He wrote the '' Histori ...
considered "Syria" west of the Euphrates
The Euphrates ( ; see #Etymology, below) is the longest and one of the most historically important rivers of West Asia. Tigris–Euphrates river system, Together with the Tigris, it is one of the two defining rivers of Mesopotamia (). Originati ...
. Starting from the 2nd century BC onwards, ancient writers referred to the ruler of the Seleucid Empire as the King of Syria or King of the Syrians. The Seleucids designated the districts of Seleucis and Coele-Syria explicitly as Syria and ruled the Syrians as indigenous populations residing west of the Euphrates ( Aramea) in contrast to Assyrians who had their native homeland in Mesopotamia
Mesopotamia is a historical region of West Asia situated within the Tigris–Euphrates river system, in the northern part of the Fertile Crescent. Today, Mesopotamia is known as present-day Iraq and forms the eastern geographic boundary of ...
east of the Euphrates. However, the interchangeability between Assyrians and Syrians persisted during the Hellenistic period
In classical antiquity, the Hellenistic period covers the time in Greek history after Classical Greece, between the death of Alexander the Great in 323 BC and the death of Cleopatra VII in 30 BC, which was followed by the ascendancy of the R ...
.
In one instance, the Ptolemaic dynasty of the Hellenistic kingdom of Egypt
Egypt ( , ), officially the Arab Republic of Egypt, is a country spanning the Northeast Africa, northeast corner of Africa and Western Asia, southwest corner of Asia via the Sinai Peninsula. It is bordered by the Mediterranean Sea to northe ...
applied the term "Syrian Village" as the name of a settlement in Fayoum. The Ptolemies referred to all peoples originating from Modern Syria and Palestine
Palestine, officially the State of Palestine, is a country in West Asia. Recognized by International recognition of Palestine, 147 of the UN's 193 member states, it encompasses the Israeli-occupied West Bank, including East Jerusalem, and th ...
as Syrian.
The term ''Syrian'' was imposed upon Arameans of modern Levant
The Levant ( ) is the subregion that borders the Eastern Mediterranean, Eastern Mediterranean sea to the west, and forms the core of West Asia and the political term, Middle East, ''Middle East''. In its narrowest sense, which is in use toda ...
by the Romans. Pompey
Gnaeus Pompeius Magnus (; 29 September 106 BC – 28 September 48 BC), known in English as Pompey ( ) or Pompey the Great, was a Roman general and statesman who was prominent in the last decades of the Roman Republic. ...
created the province of Syria
Syria, officially the Syrian Arab Republic, is a country in West Asia located in the Eastern Mediterranean and the Levant. It borders the Mediterranean Sea to the west, Turkey to Syria–Turkey border, the north, Iraq to Iraq–Syria border, t ...
, which included modern-day Lebanon and Syria west of the Euphrates, framing the province as a regional social category with civic implications. Plutarch
Plutarch (; , ''Ploútarchos'', ; – 120s) was a Greek Middle Platonist philosopher, historian, biographer, essayist, and priest at the Temple of Apollo (Delphi), Temple of Apollo in Delphi. He is known primarily for his ''Parallel Lives'', ...
described the indigenous people of this newly created Roman province as "Syrians", so did Strabo
Strabo''Strabo'' (meaning "squinty", as in strabismus) was a term employed by the Romans for anyone whose eyes were distorted or deformed. The father of Pompey was called "Gnaeus Pompeius Strabo, Pompeius Strabo". A native of Sicily so clear-si ...
, who observed that Syrians resided west of the Euphrates in Roman Syria, and he explicitly mentions that those Syrians are the Arameans, whom he calls ''Aramaei'', indicating an extant ethnicity. Posidonius noted that the people called Syrians by the Greeks refer to themselves as Arameans.
In his book ''The Great Roman-Jewish War'', Josephus, a Hebrew
Hebrew (; ''ʿÎbrit'') is a Northwest Semitic languages, Northwest Semitic language within the Afroasiatic languages, Afroasiatic language family. A regional dialect of the Canaanite languages, it was natively spoken by the Israelites and ...
native to the Levant, mentioned the Syrians as the non-Hebrew, non-Greek indigenous inhabitants of Syria.
History
Syrians are mainly descended from the various ancient Semitic-speaking peoples of theancient Near East
The ancient Near East was home to many cradles of civilization, spanning Mesopotamia, Egypt, Iran (or Persia), Anatolia and the Armenian highlands, the Levant, and the Arabian Peninsula. As such, the fields of ancient Near East studies and Nea ...
. The Seleucids ruled the indigenous peoples of the Levant, whom they named "Syrians", as a conquered nation; Syrians were not assimilated into Greek communities, and many local peasants were exploited financially as they had to pay rent for Greek landlords. Outside Greek colonies, the Syrians lived in districts governed by local temples that did not use the Greek civic system of '' poleis'' and colonies. The situation changed after the Roman conquest in 64 BC; Semitic-speaking Syrians obtained the citizenship of Greek ''poleis'', and the line separating the Greeks and the natives blurred. The idioms Syrian and Greek were used by Rome to denote civic societies instead of separate ethnic groups.
Ancient Syria of the first millennium BC was dominated by the Aramaeans; they originated in the Northern Levant as a continuum of the Bronze Age
The Bronze Age () was a historical period characterised principally by the use of bronze tools and the development of complex urban societies, as well as the adoption of writing in some areas. The Bronze Age is the middle principal period of ...
populations of Syria. The Aramaeans assimilated most of the earlier Levantine populations through their language. With the adoption of a common religion, Christianity
Christianity is an Abrahamic monotheistic religion, which states that Jesus in Christianity, Jesus is the Son of God (Christianity), Son of God and Resurrection of Jesus, rose from the dead after his Crucifixion of Jesus, crucifixion, whose ...
, most of the inhabitants turned into Syrians (Aramaeans). Islam and the Arabic language had a similar effect where the Aramaeans themselves became Arabs regardless of their ethnic origin following the Muslim conquest of the Levant
The Muslim conquest of the Levant (; ), or Arab conquest of Syria, was a 634–638 CE invasion of Byzantine Syria by the Rashidun Caliphate. A part of the wider Arab–Byzantine wars, the Levant was brought under Arab Muslim rule and develope ...
. The presence of Arabs in Syria is recorded since the 9th century BC, and Roman period historians, such as Strabo
Strabo''Strabo'' (meaning "squinty", as in strabismus) was a term employed by the Romans for anyone whose eyes were distorted or deformed. The father of Pompey was called "Gnaeus Pompeius Strabo, Pompeius Strabo". A native of Sicily so clear-si ...
, Pliny the Elder
Gaius Plinius Secundus (AD 23/24 79), known in English as Pliny the Elder ( ), was a Roman Empire, Roman author, Natural history, naturalist, and naval and army commander of the early Roman Empire, and a friend of the Roman emperor, emperor Vesp ...
, and Ptolemy
Claudius Ptolemy (; , ; ; – 160s/170s AD) was a Greco-Roman mathematician, astronomer, astrologer, geographer, and music theorist who wrote about a dozen scientific treatises, three of which were important to later Byzantine science, Byzant ...
, reported that Arabs inhabited many parts of Syria, which according to modern historians indicate either an ethnic group or a nomadic way of life. The '' urheimat'' of the Arab ethnos is unclear; the traditional 19th century theory locates this in the Arabian Peninsula, while some modern scholars, such as David Frank Graf, note that the epigraphic and archaeological evidence render the traditional theory inadequate to explain the Arabs' appearance in Syria. The Arabs mentioned in Syria by Greco-Roman writers were assimilated into the newly formed "Greco–Aramaean culture" that dominated the region, and the texts they produced were written in Greek and Aramaic. Old Arabic, the precursor of Classical Arabic
Classical Arabic or Quranic Arabic () is the standardized literary form of Arabic used from the 7th century and throughout the Middle Ages, most notably in Umayyad Caliphate, Umayyad and Abbasid Caliphate, Abbasid literary texts such as poetry, e ...
, was not a literary language; its speakers used Aramaic for writing purposes.
Linguistic Arabization
On the eve of theRashidun Caliphate
The Rashidun Caliphate () is a title given for the reigns of first caliphs (lit. "successors") — Abu Bakr, Umar, Uthman, and Ali collectively — believed to Political aspects of Islam, represent the perfect Islam and governance who led the ...
conquest of the Levant, 634 AD, Syria's population mainly spoke Aramaic as the Lingua franca
A lingua franca (; ; for plurals see ), also known as a bridge language, common language, trade language, auxiliary language, link language or language of wider communication (LWC), is a Natural language, language systematically used to make co ...
, while Greek was the language of administration. Arabization
Arabization or Arabicization () is a sociology, sociological process of cultural change in which a non-Arab society becomes Arabs, Arab, meaning it either directly adopts or becomes strongly influenced by the Arabic, Arabic language, Arab cultu ...
and Islamization of Syria began in the 7th century, and it took several centuries for Islam, the Arab identity, and language to spread; the Arabs of the caliphate did not attempt to spread their language or religion in the early periods of the conquest, and formed an isolated aristocracy. The Arabs of the caliphate accommodated many new tribes in isolated areas to avoid conflict with the locals; caliph Uthman ordered his governor, Muawiyah I, to settle the new tribes away from the original population. Syrians who belonged to Monophysitic denominations welcomed the Muslim Arabs as liberators.
The Abbasids in the eighth and ninth centuries sought to integrate the peoples under their authority, and the Arabization of the administration was one of their methods. Arabization gained momentum with the increasing numbers of Muslim converts from Christianity
Christianity is an Abrahamic monotheistic religion, which states that Jesus in Christianity, Jesus is the Son of God (Christianity), Son of God and Resurrection of Jesus, rose from the dead after his Crucifixion of Jesus, crucifixion, whose ...
; the ascendancy of Arabic as the formal language of the state prompted the cultural and linguistic assimilation of Syrian converts. Some of those who remained Christian also became Arabized, while others stayed Aramean, it was probably during the Abbasid period in the ninth century that Christians adopted Arabic as their first language; the first translation of the gospels into Arabic took place in this century. Many historians, such as Claude Cahen and Bernard Hamilton, proposed that the Arabization of Christians was completed before the First Crusade
The First Crusade (1096–1099) was the first of a series of religious wars, or Crusades, initiated, supported and at times directed by the Latin Church in the Middle Ages. The objective was the recovery of the Holy Land from Muslim conquest ...
. By the thirteenth century, the Arabic language achieved complete dominance in the region, with many of its speakers having become Arabs. Those who retained the Aramaic language are divided among two groups:
* The Eastern Aramaic Syriac-speaking group, followers of the West Syriac Rite of the Syriac Orthodox Church and the Syrian Catholic Church; kept the pre-Islamic Syrian (Syriac) identity throughout the ages, asserting their culture in face of the Arab dominance. Linguists, such as
Those who retained the Aramaic language are divided among two groups:
* The Eastern Aramaic Syriac-speaking group, followers of the West Syriac Rite of the Syriac Orthodox Church and the Syrian Catholic Church; kept the pre-Islamic Syrian (Syriac) identity throughout the ages, asserting their culture in face of the Arab dominance. Linguists, such as Carl Brockelmann
Carl Brockelmann (17 September 1868 – 6 May 1956) German Semitic studies, Semiticist, was the foremost Orientalism, orientalist of his generation. He was a professor at the universities in University of Wrocław, Breslau, Berlin and, from 1903, ...
and François Lenormant, suggested that the rise of the Garshuni writing (using the Syriac alphabet
The Syriac alphabet ( ) is a writing system primarily used to write the Syriac language since the 1st century. It is one of the Semitic languages, Semitic abjads descending from the Aramaic alphabet through the Palmyrene alphabet, and shares sim ...
to write Arabic) was an attempt by the Syriac Orthodox to assert their identity. Syriac is still the liturgical language for most of the different Syriac churches in Syria. The Syriac Orthodox Church was known as the Syrian Orthodox Church until 2000, when the holy synod decided to rename it to avoid any nationalistic connotations; the Catholic Church still has "Syrian" in its official name.
* The Western Neo-Aramaic-speaking group, that is, the inhabitants of Bakh'a, Jubb'adin and Ma'loula. The residents of Bakh'a and Jubb'adin converted to Islam in the eighteenth century (retaining their Aramean identity), while in Ma'loula, the majority are Christians, mainly belonging to the Melkite Greek Catholic Church, but also to the Greek Orthodox Church of Antioch
The Greek Orthodox Patriarchate of Antioch (), also known as the Antiochian Orthodox Church and legally as the Rum (endonym), Rūm Orthodox Patriarchate of Antioch and All the East (), is an autocephalous Greek Orthodox church within the wider ...
, in addition to a Muslim minority, who speaks the same Aramaic dialect of the Christian residents. The people of those villages use Arabic intensively to communicate with each other and the rest of the country; this led to a noticeable Arabic influence on their Aramaic dialect where around 20% of its vocabulary is of Arabic roots. Bakh'a is steadily losing its dialect; by 1971, people aged younger than 40 could no longer use the Aramaic language properly, although they could understand it. The situation of Bakh'a might eventually lead to the extinction of its Aramaic dialect.
Revival of the designation "Syrian"
The Arabs in Arabia called the region of Syria region ''al-Sham
Syria, ( or ''Shaam'') also known as Greater Syria or Syria-Palestine, is a historical region located east of the Mediterranean Sea in West Asia, broadly synonymous with the Levant. The region boundaries have changed throughout history. Howe ...
'' () which became the dominant name of the Levant under the Rashidun Caliphate
The Rashidun Caliphate () is a title given for the reigns of first caliphs (lit. "successors") — Abu Bakr, Umar, Uthman, and Ali collectively — believed to Political aspects of Islam, represent the perfect Islam and governance who led the ...
and its successors. The geographic designation "Syria" returned in 1864 when Ottoman Syria was reorganized and the name was used for a vilayet encompassing generally the southern Levant. The use of the national designation "Syrian" however has its origin in the tense relationship between the Arabic-speaking Muslims and Christians of the Levant, where Christians wanted to distance themselves from the Muslims. Already in the 1830s, the Lebanese traveler As’ad Khayyat identified with the term Syria, but it took till the 1880s for the name to begin to be widely used by the inhabitants to refer to themselves. Both Muslims and Christians agreed that the Muslims were not Syrians because they belonged to the Arabs while the Christians retained the Syrianism of antiquity. The spread of the Syrian "idea" amongst the Muslims can be traced to the efforts of Rashid Rida who contributed to the formulation of the Syrian Union Party's manifesto in 1918, demanding that Syria, in the aftermath of World War I and the Ottoman withdrawal from the region, become an independent state and not part of larger Arab one ruled by the Hashemites of the Kingdom of Hejaz
The Hashemite Kingdom of Hejaz (, ''Al-Mamlakah al-Ḥijāziyyah Al-Hāshimiyyah'') was a state in the Hejaz region of Western Asia that included the western portion of the Arabian Peninsula that was ruled by the Hashemite dynasty. It was self ...
. Rida did not reject the Arab identity but recognized a Syrian uniqueness and advocated the idea of a Syrian state. In the end, Syria did become a separate state but under the Hashemite king Faisal. He entered Damascus in 1918 in the aftermath of the Ottomans' evacuation of the Levant at the end of World War I. His entry ignited the Syrian national consciousness after he declared an Arab government in the Levant centred in Damascus with him as prince. In June 1919, the Syrian National Congress, which included representatives from Palestine and Lebanon, demanded the full independence of Syria, within borders that encompass more or less the Levant; this helped to further strengthen the development of the Syrian national consciousness. Initially, most inhabitants were against the establishment of Syria as they considered this a step against Arab unity, but gradually, Faisal's Syria, which was declared an independent kingdom in 1920, prompted the Syrians to begin exploring the notion of Syrianism instead of pan-Arabism. Faisal was deposed by the French who established a mandate in 1920, but the formation of a Syrian consciousness amongst the members of the Syrian Arab national movement solidified and spread amongst the Muslims as well as the Christians.
Genetics
 Genetic tests on Syrians were included in many genetic studies. The genetic marker which identifies descendants of the ancient
Genetic tests on Syrians were included in many genetic studies. The genetic marker which identifies descendants of the ancient Levant
The Levant ( ) is the subregion that borders the Eastern Mediterranean, Eastern Mediterranean sea to the west, and forms the core of West Asia and the political term, Middle East, ''Middle East''. In its narrowest sense, which is in use toda ...
ines is found in Syrians in high proportion. Modern Syrians exhibit "high affinity to the Levant" based on studies comparing modern and ancient DNA samples. Syrians cluster closely with ancient Levantine populations of the Neolithic and Bronze Ages. A Levantine ancestral genetic component was identified; it is estimated that the Levantine, the Arabian and East African ancestral components diverged 23,700–15,500 years ago, while the divergence between the Levantine and European components happened 15,900–9,100 years ago. The Levantine ancestral component is the most recurrent in Levantines (42–68%); the Peninsular Arabian and East African ancestral components represent around 25% of Syrian genetic make-up.
The paternal Y-DNA haplogroup J1, which reaches its highest frequencies in Yemen 72.6% and Qatar 58.3%, accounted for 33.6% of Syrians. The J2 group accounted for 20.8% of Syrians; other Y-DNA haplogroups include the E1B1B 12.0%, I 5.0%, R1a 10.0% and R1b 15.0%. The Syrians are closest to other Levantine populations: the Lebanese, the Palestinians
Palestinians () are an Arab ethnonational group native to the Levantine region of Palestine.
*: "Palestine was part of the first wave of conquest following Muhammad's death in 632 CE; Jerusalem fell to the Caliph Umar in 638. The indigenou ...
and Jordanians; this closeness can be explained by the common Canaanite ancestry and geographical unity which was broken only in the twentieth century with the advent of British and French mandates. Regarding the genetic relation between the Syrians and the Lebanese based on Y-DNA, Muslims from Lebanon show closer relations to Syrians than their Christian compatriots. The people of Western Syria show close relations with the people of Northern Lebanon.
Mitochondrial DNA
Mitochondrial DNA (mtDNA and mDNA) is the DNA located in the mitochondrion, mitochondria organelles in a eukaryotic cell that converts chemical energy from food into adenosine triphosphate (ATP). Mitochondrial DNA is a small portion of the D ...
shows the Syrians to have an affinity with Europe; main haplogroups are H and R. Based on Mitochondrial DNA, the Syrians, Palestinians, Lebanese and Jordanians form a close cluster. Compared to the Lebanese, Bedouins and Palestinians, the Syrians have noticeably more Northern European component, estimated at 7%. Regarding the HLA alleles, Syrians, and other Levantine populations, exhibit "key differences" from other Arab
Arabs (, , ; , , ) are an ethnic group mainly inhabiting the Arab world in West Asia and North Africa. A significant Arab diaspora is present in various parts of the world.
Arabs have been in the Fertile Crescent for thousands of years ...
populations; based on HLA-DRB1 alleles, Syrians were close to eastern Mediterranean populations, such as the Cretans and Lebanese Armenians. Studying the genetic relation between Jews
Jews (, , ), or the Jewish people, are an ethnoreligious group and nation, originating from the Israelites of History of ancient Israel and Judah, ancient Israel and Judah. They also traditionally adhere to Judaism. Jewish ethnicity, rel ...
and Syrians showed that the two populations share a close affinity. Apparently, the cultural influence of Arabian expansion in the Eastern Mediterranean
The Eastern Mediterranean is a loosely delimited region comprising the easternmost portion of the Mediterranean Sea, and well as the adjoining land—often defined as the countries around the Levantine Sea. It includes the southern half of Turkey ...
in the seventh century was more prominent than the genetic influx. However, the expansion of Islam did leave an impact on Levantine genes; religion drove Levantine Muslims to mix with other Muslim populations, who were close culturally despite the geographic distance, and this produced genetic similarities between Levantine Muslims and Moroccan and Yemeni populations. Christians and Druze
The Druze ( ; , ' or ', , '), who Endonym and exonym, call themselves al-Muwaḥḥidūn (), are an Arabs, Arab Eastern esotericism, esoteric Religious denomination, religious group from West Asia who adhere to the Druze faith, an Abrahamic ...
became a genetic isolate in the predominantly Islamic world.
Language
Arabic
Arabic (, , or , ) is a Central Semitic languages, Central Semitic language of the Afroasiatic languages, Afroasiatic language family spoken primarily in the Arab world. The International Organization for Standardization (ISO) assigns lang ...
is the mother tongue of the majority of Syrians as well as the official state language. The Syrian variety of Levantine Arabic
Levantine Arabic, also called Shami (Endonym and exonym, autonym: or ), is an Varieties of Arabic, Arabic variety spoken in the Levant, namely in Syria, Jordan, Lebanon, Palestine, Israel and southern Turkey (historically only in Adana Prov ...
differs from Modern Standard Arabic
Modern Standard Arabic (MSA) or Modern Written Arabic (MWA) is the variety of Standard language, standardized, Literary language, literary Arabic that developed in the Arab world in the late 19th and early 20th centuries, and in some usages al ...
. Western Neo-Aramaic, the only surviving Western Aramaic dialect, is still spoken in three villages ( Maaloula, Bakh'a and Jubb'adin) in the Anti-Lebanon Mountains by both Muslim and Christian Arameans (Syriacs). Syriacs in the northeast of the country are mainly Turoyo-Aramaic speakers but there are also some speakers of Suret-Aramaic, especially in the Khabour Valley. Classical Syriac is also used as a liturgical language by Syriac Christians
Syriac Christianity (, ''Mšiḥoyuṯo Suryoyto'' or ''Mšiḥāyūṯā Suryāytā'') is a branch of Eastern Christianity of which formative theological writings and traditional liturgies are expressed in the Classical Syriac language, a var ...
. English, and to a lesser extent French, is widely understood and used in interactions with tourists and other foreigners.
Religion and minority groups
Religious differences in Syria have historically been tolerated, and religious minorities tend to retain distinct cultural, and religious identities.Sunni Islam
Sunni Islam is the largest Islamic schools and branches, branch of Islam and the largest religious denomination in the world. It holds that Muhammad did not appoint any Succession to Muhammad, successor and that his closest companion Abu Bakr ...
is the religion of 74% of Syrians. The Alawites
Alawites () are an Arab ethnoreligious group who live primarily in the Levant region in West Asia and follow Alawism, a sect of Islam that splintered from early Shia as a ''ghulat'' branch during the ninth century. Alawites venerate Ali ...
, a variety of Shia Islam
Shia Islam is the second-largest Islamic schools and branches, branch of Islam. It holds that Muhammad in Islam, Muhammad designated Ali ibn Abi Talib () as both his political Succession to Muhammad, successor (caliph) and as the spiritual le ...
, make up 12% of the population and mostly live in and around Tartus
Tartus ( / ALA-LC: ''Ṭarṭūs''; known in the County of Tripoli as Tortosa and also transliterated from French language, French Tartous) is a major port city on the Mediterranean coast of Syria. It is the second largest port city in Syria (af ...
and Latakia. Christians
A Christian () is a person who follows or adheres to Christianity, a monotheistic Abrahamic religion based on the life and teachings of Jesus Christ. Christians form the largest religious community in the world. The words '' Christ'' and ''C ...
make up 10% of the country. Most Syrian Christians adhere to the Byzantine Rite; the two largest are the Antiochian Orthodox Church and the Melkite Greek Catholic Church. The Druze
The Druze ( ; , ' or ', , '), who Endonym and exonym, call themselves al-Muwaḥḥidūn (), are an Arabs, Arab Eastern esotericism, esoteric Religious denomination, religious group from West Asia who adhere to the Druze faith, an Abrahamic ...
are a mountainous people who reside in Jabal al-Druze who helped spark the Great Syrian Revolt. The Ismailis are an even smaller sect that originated in Asia. Many Armenian and Assyrian Christians fled Turkey
Turkey, officially the Republic of Türkiye, is a country mainly located in Anatolia in West Asia, with a relatively small part called East Thrace in Southeast Europe. It borders the Black Sea to the north; Georgia (country), Georgia, Armen ...
during the Armenian genocide
The Armenian genocide was the systematic destruction of the Armenians, Armenian people and identity in the Ottoman Empire during World War I. Spearheaded by the ruling Committee of Union and Progress (CUP), it was implemented primarily t ...
and the Assyrian genocide and settled in Syria. There are also roughly 500,000 Palestinians
Palestinians () are an Arab ethnonational group native to the Levantine region of Palestine.
*: "Palestine was part of the first wave of conquest following Muhammad's death in 632 CE; Jerusalem fell to the Caliph Umar in 638. The indigenou ...
, who are mostly descendants of refugees from the 1948 Israeli-Arab War. The community of Syrian Jews inside Syria once numbered 30,000 in 1947, but has only 200 today.
The Syrian people's beliefs and outlooks, similar to those of most Arabs and people of the wider Middle-East, are a mosaic of West and East. Conservative and liberally minded people will live right next to each other. Like the other countries in the region, religion permeates life; the government registers every Syrian's religious affiliation. However, the number of non-believers in Syria is increasing but there is no credible source or statistics to support this information.
Cuisine
 Syrian cuisine is dominated by ingredients native to the region.
Syrian cuisine is dominated by ingredients native to the region. Olive oil
Olive oil is a vegetable oil obtained by pressing whole olives (the fruit of ''Olea europaea'', a traditional Tree fruit, tree crop of the Mediterranean Basin) and extracting the oil.
It is commonly used in cooking for frying foods, as a cond ...
, garlic, olive
The olive, botanical name ''Olea europaea'' ("European olive"), is a species of Subtropics, subtropical evergreen tree in the Family (biology), family Oleaceae. Originating in Anatolia, Asia Minor, it is abundant throughout the Mediterranean ...
s, spearmint, and sesame oil are some of the ingredients that are used in many traditional meals. Traditional Syrian dishes enjoyed by Syrians include, tabbouleh, labaneh
Strained yogurt, Greek or Greek-style yogurt, yogurt cheese, sack yogurt, kerned yogurt or labneh is yogurt that has been strained to remove most of its whey, resulting in a thicker consistency than normal unstrained yogurt, while still preser ...
, shanklish, wara' 'enab, makdous, kebab, Kibbeh, sfiha, moutabal, hummus, mana'eesh, bameh, and fattoush.
A typical Syrian breakfast is a meze. It is an assortment platter of foods with cheeses, meats, pickles, olives, and spreads. Meze is usually served with Arab-style tea – highly concentrated black tea, which is often highly sweetened and served in small glass cups. Another popular drink, especially with Christians and non-practicing Muslims, is the arak, a liquor produced from grapes or dates and flavored with anise that can have an alcohol content of over 90% ABV (however, most commercial Syrian arak brands are about 40–60% ABV).
Notable people
See also
* History of Syria * Ottoman Syria * Dobrujan Arabs *Arameans
The Arameans, or Aramaeans (; ; , ), were a tribal Semitic people in the ancient Near East, first documented in historical sources from the late 12th century BCE. Their homeland, often referred to as the land of Aram, originally covered c ...
* Armenians
Armenians (, ) are an ethnic group indigenous to the Armenian highlands of West Asia.Robert Hewsen, Hewsen, Robert H. "The Geography of Armenia" in ''The Armenian People From Ancient to Modern Times Volume I: The Dynastic Periods: From Antiq ...
* Arabs
Arabs (, , ; , , ) are an ethnic group mainly inhabiting the Arab world in West Asia and North Africa. A significant Arab diaspora is present in various parts of the world.
Arabs have been in the Fertile Crescent for thousands of yea ...
* Al-Shaitat
* Assyrians
* Greeks
Greeks or Hellenes (; , ) are an ethnic group and nation native to Greece, Greek Cypriots, Cyprus, Greeks in Albania, southern Albania, Greeks in Turkey#History, Anatolia, parts of Greeks in Italy, Italy and Egyptian Greeks, Egypt, and to a l ...
Notes
References
Citations
Sources
* * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * *External links
Syrian people, Every Culture
Photos and images of Syrian people, Syrian History – Online
Collections of images of Eastern Mediterranean people, including Syrian people, Mideast Image
Syrian people, Encyclopædia Britannica
{{Authority control Syrian diaspora Semitic-speaking peoples Articles containing video clips Ethnic groups in the Middle East Arab ethnic groups