|
Arab Kingdom Of Syria
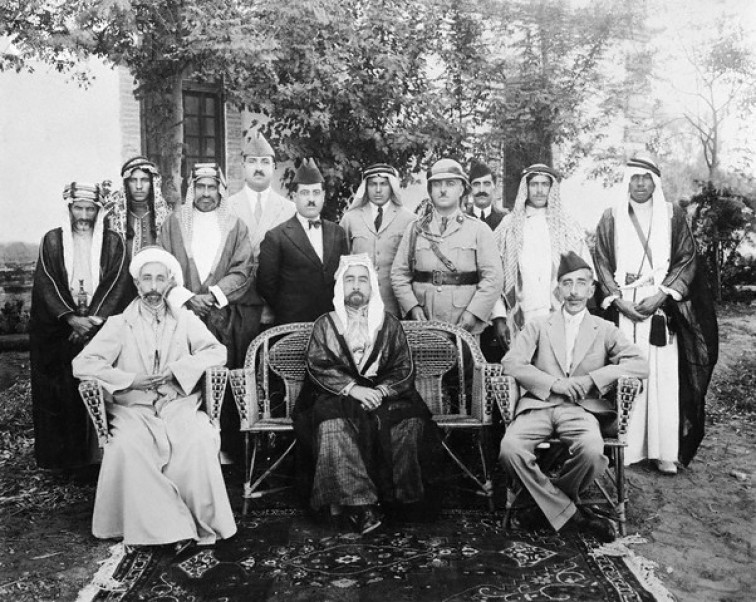
The Syrian Arab Kingdom (, ') was a self-proclaimed, unrecognized monarchy existing briefly in the territory of Bilad al-Sham, historical Syria. It was announced on 5 October 1918 as a fully independent Arab constitutional government with the permission of the British military. It gained independence as an emirate after the withdrawal of the British forces from Occupied Enemy Territory Administration, OETA East on 26 November 1919, and was proclaimed as a kingdom on 8 March 1920. As a kingdom the state existed a little over four months, from 8 March to 25 July 1920. During its brief existence, the kingdom was led by Sharif Hussein bin Ali, Sharif of Mecca, Hussein bin Ali's son Faisal bin Hussein. Despite its claims to the territory of the Syria (region), region of Syria, Faisal's government controlled a limited area and was dependent on Britain which, along with France, generally opposed the idea of a Greater Syria and refused to recognize the kingdom. After a Franco-Syrian War, f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Flag Of Syria
Since gaining full independence from France in 1946, Syria has used a number of different flags, all featuring the pan-Arab colours, pan-Arab colors of green, black, white, and red. Initially a green, white and black triband charged with three red five-pointed stars, known as the independence flag, was used. In Ba'athist Syria, this was replaced by the flag of the United Arab Republic with red, white and black tribands with either two or three green stars or charged with the national coat of arms. Following the fall of the Assad regime on 8 December 2024, the revolution flag, a modified version of the independence flag, began to be used within the country by the Syrian parliament and the Syrian caretaker government, and at Syrian embassies abroad. On 13 March 2025, an 2025 Interim Constitution of Syria, interim constitution made the independence flag the primary flag. However, the final text ultimately retained the revolution flag. Design Specifications Article 6 of the 2 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bilad Al-Sham
Bilad al-Sham (), often referred to as Islamic Syria or simply Syria in English-language sources, was a province of the Rashidun, Umayyad, Abbasid, and Fatimid caliphates. It roughly corresponded with the Byzantine Diocese of the East, conquered by the Muslims in 634–647. Under the Umayyads (661–750), Bilad al-Sham was the metropolitan province of the Caliphate and different localities throughout the province served as the seats of the Umayyad caliphs and princes. Bilad al-Sham was first organized into the four '' ajnad'' (military districts; singular ''jund'') of Dimashq (Damascus), Hims (Homs), al-Urdunn (Jordan), and Filastin (Palestine), between 637 and 640 by Caliph Umar following the Muslim conquest. The ''jund'' of Qinnasrin was created out of the northern part of Hims by caliphs Mu'awiya I () or Yazid I (). The Jazira (Upper Mesopotamia) was made an independent province from the Mesopotamian part of Qinnasrin by Caliph Abd al-Malik in 692. In 786, the ''j ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Desert Mounted Corps
The Desert Mounted Corps was an army corps of the British Army during the First World War, of three mounted divisions renamed in August 1917 by General Edmund Allenby, from Desert Column. These divisions which served in the Sinai and Palestine Campaign had been formed by Australian light horse, British yeomanry during the First World War, British yeomanry, and New Zealand Mounted Rifles Brigade, New Zealand mounted rifles brigades, supported by Royal Horse Artillery, horse artillery, infantry and support troops. They were later joined by Indian Army during the First World War, Indian cavalry and a small French cavalry detachment. The Desert Mounted Corps (DMC) comprised the ANZAC Mounted Division, the Australian Mounted Division and the Yeomanry Mounted Division, with infantry formations attached when required, as had Desert Column. In the first month of its existence, the corps continued training and patrolling no man's land preparing for manoeuvre warfare. Their first operatio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sharif Of Mecca
The Sharif of Mecca () was the title of the leader of the Sharifate of Mecca, traditional steward of the Holiest sites in Islam, Islamic holy cities of Mecca and Medina. The term ''sharif'' is Arabic for "noble", "highborn", and is used to describe the descendants of Hashim ibn Abd Manaf. The Sharif was charged with protecting the cities and their environs and ensuring the safety of pilgrims performing the Hajj. The title is sometimes spelled Sheriff or Sherif, with the latter variant used, for example, by T. E. Lawrence in ''Seven Pillars of Wisdom''. The office of the Sharif of Mecca dates back to the late Abbasid era. Until 1200, the Sharifate was held by a member of the Hashim ibn Abd Manaf, Hashim clan, not to be confused with the larger clan of Banu Hashim from which all Sharifs claim descent. Descendants of the Banu Hashim continued to hold the position until the 20th century on behalf of various Muslim powers including the Ayyubid dynasty, Ayyubids and the Mamluks. In 1 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kingdom Of Iraq
The Hashemite Kingdom of Iraq was the Iraqi state located in the Middle East from 1932 to 1958. It was founded on 23 August 1921 as the Kingdom of Iraq, following the defeat of the Ottoman Empire in the Mesopotamian campaign of the First World War. Although a League of Nations mandate was awarded to the United Kingdom in 1920, the 1920 Iraqi revolt resulted in the scrapping of the original mandate plan in favour of a formally sovereign Iraqi kingdom, but one that was under effective British administration. The plan was formally established by the Anglo-Iraqi Treaty. The role of the United Kingdom in the formal administration of the Kingdom of Iraq was ended in 1932, following the Anglo-Iraqi Treaty (1930). Now officially a fully independent kingdom, officially named the Hashemite Kingdom of Iraq, it underwent a period of turbulence under its Hashemite rulers throughout its entire existence. Establishment of Sunni religious domination in Iraq was followed by Assyrian, Yazidi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kingdom Of Hejaz
The Hashemite Kingdom of Hejaz (, ''Al-Mamlakah al-Ḥijāziyyah Al-Hāshimiyyah'') was a state in the Hejaz region of Western Asia that included the western portion of the Arabian Peninsula that was ruled by the Hashemite dynasty. It was self-proclaimed as a kingdom in June 1916 during the First World War, to be independent from the Ottoman Empire, on the basis of an alliance with the British Empire to drive the Ottoman Army from the Arabian Peninsula during the Arab Revolt. The British government had promised Hussein bin Ali, King of Hejaz, a single independent Arab state that would include, in addition to the Hejaz region, modern-day Jordan, Iraq, and most of Syria, with the fate of the Palestine region (today's Israel and Palestine) being mentioned in more ambiguous terms. However, at the end of the First World War, the Treaty of Versailles turned Syria into a French League of Nations mandate and Iraq, Mandate Palestine and Transjordan into British mandates. Hashemi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hashemite
The Hashemites (), also House of Hashim, are the Dynasty, royal family of Jordan, which they have ruled since 1921, and were the royal family of the kingdoms of Kingdom of Hejaz, Hejaz (1916–1925), Arab Kingdom of Syria, Syria (1920), and Kingdom of Iraq, Iraq (1921–1958). The family had ruled the city of Mecca continuously from the 10th century, primarily as vassals of outside powers, and ruled the thrones of the Hejaz, Syria, Iraq, and Jordan following their World War I alliance with the British Empire. The family belongs to the Dhawu Awn, one of the branches of the Hasanids, Ḥasanid Sharifs of Mecca, also referred to as Hashemites. Their eponymous ancestor is traditionally considered to be Hashim ibn Abd Manaf, great-grandfather of the Islamic prophet Muhammad. Another claimed ancestor is Ali ibn Abi Talib, the usurped successor of the prophet Muhammad according to Shia Islam. The Ḥasanid Sharifs of Mecca (from whom the Hashemite royal family is directly descended), inc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sykes–Picot Agreement
The Sykes–Picot Agreement () was a 1916 secret treaty between the United Kingdom and France, with assent from Russia and Italy, to define their mutually agreed spheres of influence and control in an eventual partition of the Ottoman Empire. The agreement was based on the premise that the Triple Entente would achieve success in defeating the Ottoman Empire during World War I and formed part of a series of secret agreements contemplating its partition. The primary negotiations leading to the agreement took place between 23 November 1915 and 3 January 1916, on which date the British and French diplomats, Mark Sykes and François Georges-Picot, initialled an agreed memorandum. The agreement was ratified by their respective governments on 9 and 16 May 1916. The agreement effectively divided the Ottoman provinces outside the Arabian Peninsula into areas of British and French control and influence. The British- and French-controlled countries were divided by the Sykes–Picot line ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
McMahon–Hussein Correspondence
The McMahon–Hussein correspondence is a series of letters that were exchanged during World War I, in which the government of the United Kingdom agreed to recognize Arab independence in a large region after the war Quid pro quo, in exchange for the Sharif of Mecca launching the Arab Revolt against the Ottoman Empire. The correspondence had a significant influence on Middle Eastern history during and after the war; a dispute over Palestine (region), Palestine continued thereafter. The correspondence is composed of ten letters that were exchanged from July 1915 to March 1916 between Hussein bin Ali, Sharif of Mecca and Lieutenant Colonel (British Army), Lieutenant Colonel Henry McMahon (diplomat), Sir Henry McMahon, List of ambassadors of the United Kingdom to Egypt, British High Commissioner to Egypt. Whilst there was some military value in the Arab manpower and local knowledge alongside the British Army, the primary reason for the arrangement was to counteract the 1914 Ottoma ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Franco-Syrian War
The Franco-Syrian War took place during 1920 between France and the Hashemite rulers of the newly established Arab Kingdom of Syria. During a series of engagements, which climaxed in the Battle of Maysalun, French forces defeated the forces of the Hashemite List of Syrian monarchs, monarch Faisal I of Iraq, King Faisal, and his supporters, entering Damascus on July 24, 1920. A new pro-French government was declared in Syria on July 25, headed by 'Alaa al-Din al-Darubi and the region of Syria (region), Syria was eventually divided into several client states under the Mandate for Syria and the Lebanon. The British government, concerned for their position in the new mandate in Mandatory Iraq, Iraq, agreed to declare the fugitive Faisal as the new king of Iraq. Background Near the end of World War I, the Egyptian Expeditionary forces of Edmund Allenby Capture of Damascus (1918), captured Damascus on September 30, 1918, and shortly thereafter on October 3, 1918, Hashemite ruler Faisal ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Itamar Rabinovich
Itamar Rabinovich (; born 8 October 1942) is the president of the Israel Institute (Washington and Jerusalem). He was Israel's Ambassador to the United States in the 1990s and former chief negotiator with Syria between 1993 and 1996, and the former president of Tel Aviv University (1999–2007). Currently he is professor emeritus of Middle Eastern History at Tel Aviv University, distinguished global professor at New York University and a distinguished fellow at the Brookings Institution. Biography Itamar Rabinovich received a B.A. degree from the Hebrew University of Jerusalem, an M.A. from Tel Aviv University, and a Ph.D. from the University of California, Los Angeles. Academic career Rabinovich has been a member of Tel Aviv University's faculty since 1971, and served as Ettinger Professor of the Contemporary History of the Middle East, chairman of the Department of Middle Eastern Studies, director of thMoshe Dayan Center for Middle Eastern and African Studies and Dean of Hu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Syria (region)
Syria, ( or ''Shaam'') also known as Greater Syria or Syria-Palestine, is a historical region located east of the Mediterranean Sea in West Asia, broadly synonymous with the Levant. The region boundaries have changed throughout history. However, in modern times, the term "Syria" alone is used to refer to the Syria, Syrian Arab Republic. The term is originally derived from Assyria, an Ancient Semitic-speaking peoples, ancient Semitic-speaking civilization centered in northern Mesopotamia, modern-day Iraq. During the Hellenistic period, the term Syria was applied to the entire Levant as Coele-Syria. Under Roman Empire, Roman rule, the term was used to refer to the Roman Syria, province of Syria, later divided into Phoenice (Roman province), Syria Phoenicia and Coele-Syria, Coele Syria, and to the province of Syria Palaestina. Under the Byzantine Empire, Byzantines, the provinces of Syria Prima and Syria Secunda emerged out of Coele Syria. After the Muslim conquest of the Levant ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |